Biodegradation Rate of EDTA and IDS and Their Metal Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Biodegradation
2.3. Toxicity
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
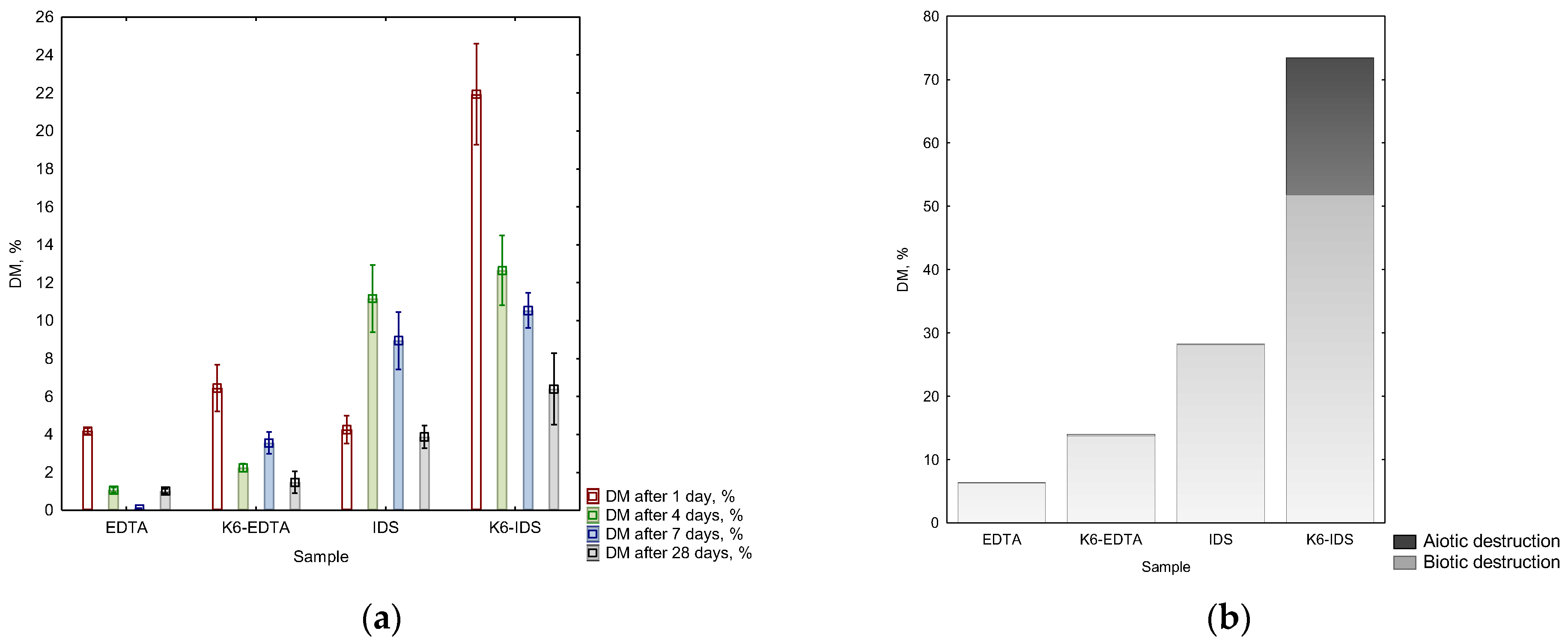
3.1. Degradation Ability of EDTA, IDS and Their Complexes with Metals
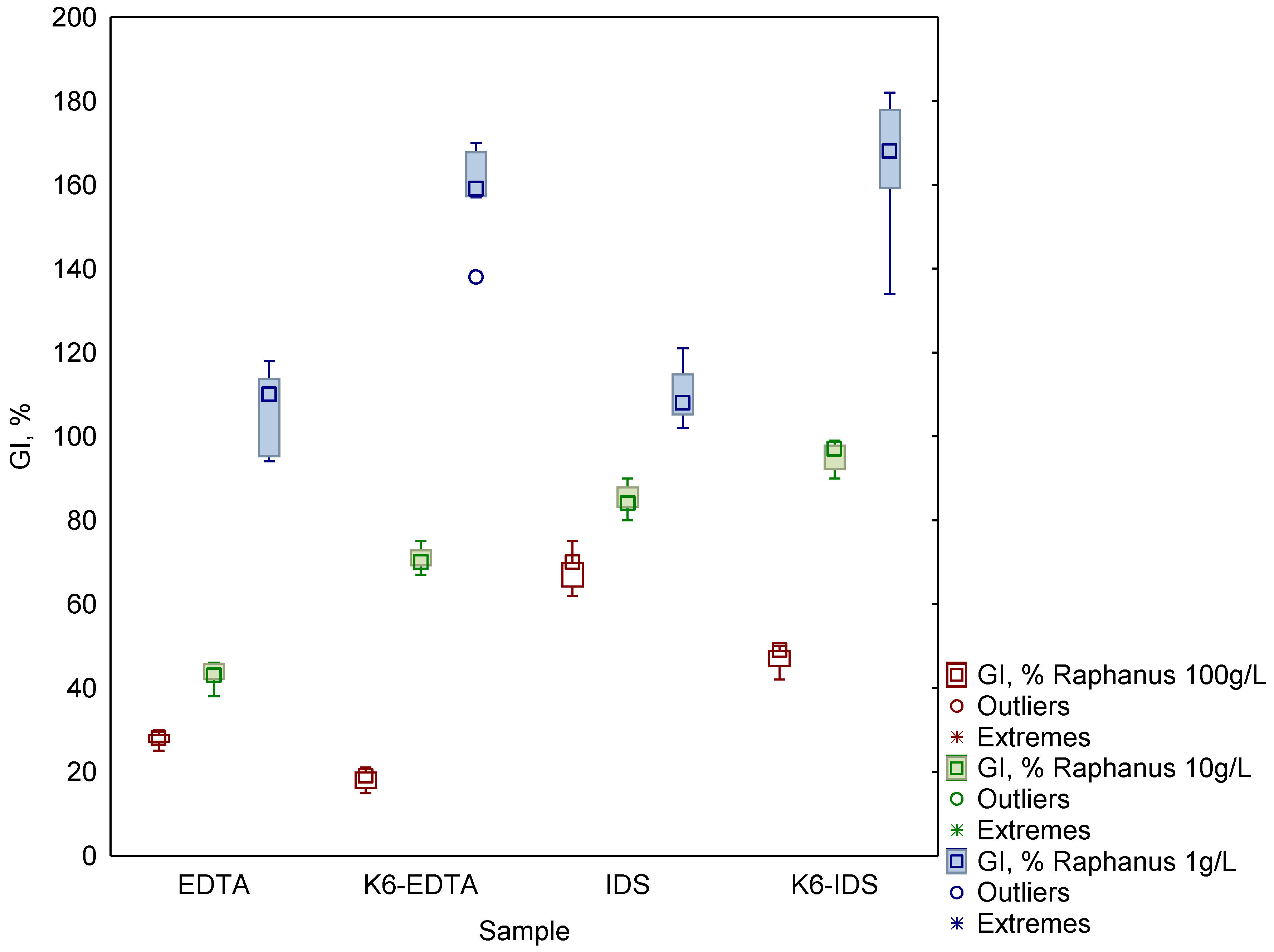
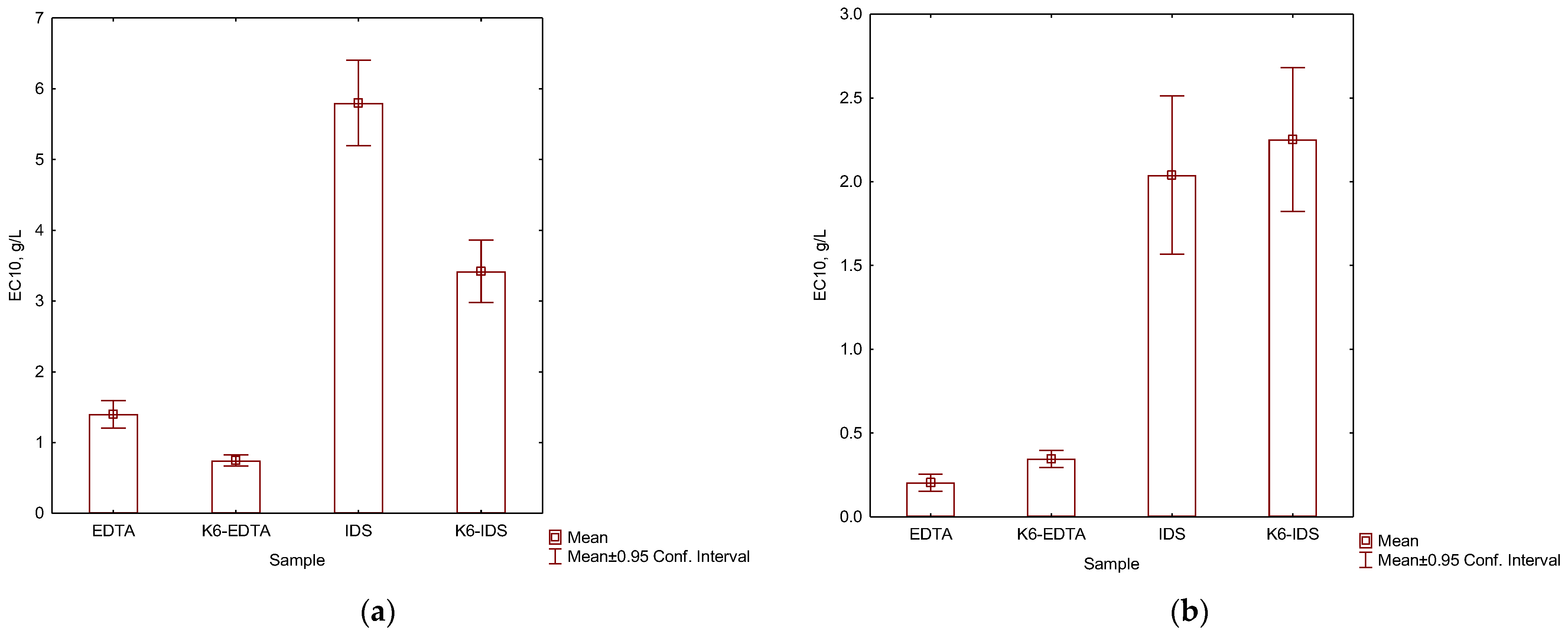
3.2. Ecotoxicity of EDTA, IDS and Their Complexes with Metals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Tian, G.; Naidu, R.; Kunhikrishnan, A. Role of organic amendment application on greenhouse gas emission from soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozik, E.; Wojciechowska, E.; Pacholska, M. A comparison of the effect of mineral and chelate forms of copper, zinc and manganese on yield and nutrient status of greenhouse lettuce. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2012, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Loginova, E.S.; Nikolsky, V.M.; Smirnova, T.I. Ecologically safe complexones as growth stimulators. Technosphere Saf. Technol. 2015, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sillanpää, M.E.T.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H. Degradation of chelating agents in aqueous solution using advanced oxidation process (AOP). Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rayo, S.; Nadal, P.; Lucena, J.J. Reactivity and effectiveness of traditional and novel ligands for multi-micronutrient fertilization in a calcareous soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.S.S.; Neto, I.F.F.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Biodegradable chelating agents for industrial, domestic, and agricultural applications—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11893–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, A.S.; Renberg, L.; Neilson, A.H. Absence of 14C02 evolution from 14C-labelled EDTA and DTPA and the sediment/water partition ratio. Chemosphere 1996, 33, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, F.G.; Giger, W. Modeling the Photochemical Degradation of Ethylenediaminetetraacetate in the River Glatt. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2814–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, M.W.H.; Ebel, M.; Schaeffer, A. Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, Z.A.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Sawai, H.; Mizutani, S.; Maki, T.; Hasegawa, H. Effect of extraction variables on the biodegradable chelant-assisted removal of toxic metals from artificially contaminated european reference soils. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, B.; Leštan, D. Influence of a biodegradable ([S,S]-EDDS) and nondegradable (EDTA) chelate and hydrogel modified soil water sorption capacity on Pb phytoextraction and leaching. Plant Soil 2003, 253, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, C.; Rodríguez, J. EDTA: The chelating agent under environmental scrutiny. Quim. Nova 2003, 26, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanigan, R.S.; Yamarik, T.A.; Andersen, F.A. Final report on the safety assessment of EDTA, calcium disodium EDTA, diammonium EDTA, dipotassium EDTA, disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, tetrasodium EDTA, tripotassium EDTA, trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and trisodium HEDTA. Int. J. Toxicol. 2002, 21 (Suppl. S2), 95–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/58 Edetic Acid (EDTA) in Drinking-Water; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Farberova, E.A.; Vinogradova, A.V.; Shults, E.V. Study of the effect of EDTA on the growth and development of a culture of microorganisms. Bull. PNRPU. Chem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Lauff, J.J.; Steele, D.B.; Coogan, L.A.; Breitfeller, J.M. Degradation of the Ferric Chelate of EDTA by a Pure Culture of an Agrobacterium sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 3346–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.A.P.; Lawlor, K.; Bailey, M.; Macaskie, L.E. Biodegradation of metal-EDTA complexes by an enriched microbial population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satroutdinov, A.D.; Dedyukhina, E.G.; Chistyakova, T.I.; Minkevich, I.G.; Eroshin, V.K.; Egli, T. Bacterial degradation of EDTA. Microbiology 2003, 72, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, C. Metal complexation and biodegradation of EDTA and S,S-EDDS: A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ginkel, C.G.; Kester, H.; Stroo, C.A.; Van Haperen, A.M. Biodegradation of EDTA in pulp and paper mill rffluents by activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucheli-Witschel, M.; Egli, T. Environmental fate and microbial degradation of aminopolycarboxylic acids. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 69–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, J.L.; Kucak, T.; Crerar, D.A. Relative degradation rates of NTA, EDTA and DTPA and environmental implications. Environ. Pollution. Ser. B Chem. Phys. 1980, 1, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongved, P.; Klaveness, J.; Dugstad, H. Aminopolycarboxylic acid chelating. agents. Patent WO1991015467A1, 17 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kołodyńska, D. Iminodisuccinic acid as a new complexing agent for removal of heavy metal ions from industrial effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, D.R.; Kihara, S.; Reinhardt, J.; Miskelly, G.M.; McGillivray, D.J.; Jeffs, A.G. Biodegradable chelating agent improves the survival of early larvae for shellfish aquaculture. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 228, 105645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolsky, A.M. Iminodisuccinic acid as a complexone. Patent RU No 629208, 11 September.
- Hawkes, C.; Ruel, M. The links between agriculture and health: An intersectoral opportunity to improve the health and livelihoods of the poor. Bull. World Health Organ. 2006, 84, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelate Fertilizer Market—Forecast (2023–2028). Available online: https://www.marketwatch.com/press-release/chelate-fertilizer-market-research-2023-2030-2023-05-23?tesla=y (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Wu, Q.; Duan, G.; Cui, Y.; Sun, J. Removal of heavy metal species from industrial sludge with the aid of biodegradable iminodisuccinic acid as the chelating ligand. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, P.G.; Ahmadpour, F.; Buczynski, M.A.; Burns, T.J.; Green, N.B.; Korwin, R.; Long, D.; Massad, S.K.; Manley, J.B.; Omidbakhsh, N.; et al. Opportunities for Greener Alternatives in Chemical Formulations. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2664–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koodynska, D. Chelating Agents of a New Generation as an Alternative to Conventional Chelators for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Different Waste Waters. In Expanding Issues in Desalination; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Groth, T.; Joentgen, K.; Wagner, P.; Dövert, F.; Wenderoth, E.; Roick, T. Preparation and Use of Iminodisuccinic Acid Salts. US6107518A, 22 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dyatlova, N.M.; Temkina, V.Y. Complexones; Cheemistry: Moskau, Russia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD 301—Ready Biodegradability (301 A, 301 B, 302 C, 301 D, 301 E, 301 F). OECD Guidel. Test. Chem. 1992, 301, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6341; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia Magna STRAUS (Cladocera, Crustacea)—Acute Toxicity Test. 2012. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/54614.html (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Alga, Growth Inhibition Test. 1984. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:22030:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- ISO 22030; Soil Quality—Biological Methods—Chronic Toxicity in Higher Plants. The International Organization: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 18.
- Zucconi, F.; Pera, A.; Forte, M.; De Bertoldi, M. Evaluating toxicity of immature compost [Phytotoxicity]. Biocycle 1981, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- EDTA, Disodium Salt, Dihydrate|CAS 6381-92-6|SCBT—Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Available online: https://www.scbt.com/p/edta-disodium-salt-dihydrate-6381-92-6 (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Dufková, V. EDTA in algal culture media. Algol. Stud. Für Hydrobiol. 1984, 67, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolsky, V.M.; Smirnova, T.I. Investigation of the possibility of biodegradation of iminodisuccinic acid and borate complex based on it. In Proceedings of the Agrarian Landscapes, Their Stability and Features of Development; 2020; pp. 265–267. [Google Scholar]
- Cokesa, Z.; Knackmuss, H.J.; Rieger, P.G. Biodegradation of all stereoisomers of the EDTA substitute iminodisuccinate by agrobacterium tumefaciens BY6 requires an epimerase and a stereoselective C-N lyase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3941–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, T.I.; Khizhnyak, S.; Nikolskii, V.M.; Khalyapina, Y.M.; Pakhomov, P.M. Degradation of complexons derived from succinic acid under UV radiation. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginkel, C.G.; Vandenbroucke, K.L.; Stroo, C.A. Biological removal of EDTA in conventional activated-sludge plants operated under alkaline conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 1997, 59, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedyukhina, E.G.; Chistyakova, T.I.; Minkevich, I.G. Biodegradation of EDTA. Bull. Biotechnol. Phys.-Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, T.I.; Marukhlenko, V.N.; Khalyapina, Y.M. Prediction and study of the biological activity of iminodisuccinic acid. Bull. Volgogr. Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2008, 3, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, T.I.; Khizhnyak, S.D.; Nikolsky, V.M.; Khalyapina, Y.M.; Pakhomov, P.M. Degradation of complexones, derivatives of succinic acid, under the action of UV radiation. Phys.-Chem. Stud. Syst. Process. 2017, 90, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Cokesa, Ž.; Lakner, S.; Knackmuss, H.J.; Rieger, P.G. A stereoselective carbon-nitrogen lyase from Ralstonia sp. SLRS7 cleaves two of three isomers of iminodisuccinate. Biodegradation 2004, 15, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, H.; Li, S.W.; Workman, D.J.; Girvin, D.C. Biodegradation of Synthetic Chelates in Subsurface Sediments from the Southeast Coastal Plain. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, F.G.; Giger, W. Speciation and fate of ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) in municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res. 1996, 30, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Stacey, S.P.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kirby, J.K. Biodegradation of rhamnolipid, EDTA and citric acid in cadmium and zinc contaminated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassil, A.D.; Kapulnik, Y.; Raskin, I.; Sait, D.E. The Role of EDTA in Lead Transport and Accumulation by Indian Mustard. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grčman, H.; Velikonja-Bolta, Š.; Vodnik, D.; Kos, B.; Leštan, D. EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: Metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant Soil 2001, 235, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Du, J.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, K.; Shen, S.; et al. Chelator Iminodisuccinic Acid Regulates Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation and Improves Maize (Zea mays L.) Seed Germination under Pb Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and the salts of EDTA: Science Assessment Document for Tolerance Reassessment. 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-04/documents/edta.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Sorvari, J.; Sillanpää, M. Influence of metal complex formation on heavy metal and free EDTA and DTPA acute toxicity determined by Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 1996, 33, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth GmbH, C. SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking 1.1 Product identifier. Safe Work Aust.—Code Pract. 2017, 0339, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Zhu, Z.; Song, H.; Wu, X. Iminodisuccinic Acid Relieved Cadmium Stress in Rapeseed Leaf by Affecting Cadmium Distribution and Cadmium Chelation with Pectin. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7747152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- rugFuture. Iminodisuccinic-Acid. Available online: https://www.drugfuture.com/chemdata/iminodisuccinic-acid.html (accessed on 22 May 2023).
| Sample | Na2EDTA | K6-EDTA | (NH4)3IDS | K6-IDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chelating agent | EDTA | EDTA | IDS | IDS |
| Fe | - | 0.054% | - | 0.054% |
| Mn | - | 0.042% | - | 0.042% |
| Zn | - | 0.014% | - | 0.014% |
| B | - | 0.02% (non chelated) | - | 0.02% (non chelated) |
| Cu | - | 0.01% | - | 0.01% |
| Mo | - | 0.004% (non chelated) | - | 0.004% (non chelated) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N2Na2O8•2H2O | (NH4)3C8H20N4O8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltyukova, M.; Kuryntseva, P.; Galitskaya, P.; Selivanovskaya, S.; Brusko, V.; Dimiev, A. Biodegradation Rate of EDTA and IDS and Their Metal Complexes. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060623
Beltyukova M, Kuryntseva P, Galitskaya P, Selivanovskaya S, Brusko V, Dimiev A. Biodegradation Rate of EDTA and IDS and Their Metal Complexes. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(6):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060623
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltyukova, Maria, Polina Kuryntseva, Polina Galitskaya, Svetlana Selivanovskaya, Vasiliy Brusko, and Ayrat Dimiev. 2023. "Biodegradation Rate of EDTA and IDS and Their Metal Complexes" Horticulturae 9, no. 6: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060623
APA StyleBeltyukova, M., Kuryntseva, P., Galitskaya, P., Selivanovskaya, S., Brusko, V., & Dimiev, A. (2023). Biodegradation Rate of EDTA and IDS and Their Metal Complexes. Horticulturae, 9(6), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060623





