Abstract
Cold plasma and ozone sanitation of irrigation solutions can oxidize both microbes and non-target micronutrients because their high oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) is a non-selective mode of action. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of cold plasma and ozone treatment on oxidation of iron and manganese in nutrient solutions containing one of four iron chelates (iron-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Fe-EDTA), iron-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Fe-DTPA), iron-ethylenediamine-N,N′-bis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) (Fe-EDDHA), and hydroxybenzyl ethylenediamine (Fe-HBED)). Nutrient solutions were recirculated through the cold plasma or ozone system until the ORP reached 700 mV. The concentrations of total dissolved iron, manganese, and chelated iron were measured before and after passing through the treatment systems. Both cold plasma and ozone oxidized chelates and decreased the solubility of iron and manganese. Cold plasma and ozone had similar effects on micronutrients, pH, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen at a standardized target ORP of 700 mV. Fe-EDTA was the most resistant chelate to oxidation. With Fe-EDTA, ORP increased more quickly, and the concentration of chelated Fe decreased less with the increasing ORP over time compared with Fe-DTPA, Fe-EDDHA, and Fe-HBED. The concentration of chelated Fe decreased by up to 80% for EDDHA at 700 mV compared with a 20% decrease for EDTA. The concentration of Mn decreased by up to 85% at 700 mV. The design of water treatment with cold plasma or ozone therefore requires consideration of secondary effects on micronutrients. The treatment dosage, flow rate, and nutrient solution at a particular grower operation are likely to affect the quantity of micronutrient fertilizer that needs to be supplemented following treatment. Use of Fe-EDTA is one strategy to reduce the loss of iron and increase residual ORP that is available for sanitation.
1. Introduction
Cold plasma technology is an emerging water treatment option because of its ability to oxidize contaminants and disinfect water without residual agrichemicals [1]. Plasma is the fourth state of matter and is a fully or partially ionized gas that can be generated by electrical discharge and contains positive and negative ions, electrons, neutrons, photons, and electric fields [2]. Thermal plasma and non-thermal or cold plasma are the two main categories based on the thermodynamic temperature equilibrium of their constituents. Cold plasma can be produced in ambient air at standard temperature and pressure with gases including oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), and air [3]. A high voltage needs to be applied to gas samples for ionization, which results in the formation of reactive species with high oxidizing power, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), ozone (O3), and hydroxyl radicals (OH·) [4]. Cold plasma has received attention for practical application and research due to its lack of toxic residues, ease of use, low energy consumption, and ambient temperature operating conditions [5]. Several studies have demonstrated the potential of cold plasma technology in agriculture, including seed germination, microbial inactivation, pesticide removal, plant growth, and fruit ripening [6]. Although it is still a relatively new field, the use of cold plasma in the treatment of water has demonstrated promising potential. In one study, cold plasma generated by a coaxial electrode system with ambient air resulted in the inactivation of sulfate-reducing and acid-producing bacteria [7]. A dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric cold plasma was also effective at rapidly inactivating high concentrations of E. coli suspended in liquids within sealed packages, within seconds [8].
The presence of organic and inorganic compounds in water can affect the disinfection efficiency of cold plasma. Addition of organic compounds (peptone and beef extract powder) greatly reduced the disinfection efficiency of cold plasma against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus [9]. Similarly, the presence of iron (FeSO4) in wastewater had an inhibitory effect on the degradation of phenol via a dielectric barrier discharge plasma reactor [10]. After a 90 min treatment without iron, about 57.5% of the phenol was degraded, whereas 43% of the phenol was degraded during the removal process with iron.
Ozone is another technology that results in a high oxidation-reduction potential and is a more established option for irrigation than cold plasma. Ozone is similar to cold plasma for water treatment in that oxygen is the influent gas which is converted to a higher oxidation state (in this case O3), usually via corona discharge. Ozone has been shown to have numerous effects, including the removal of inorganic species, aid to the coagulation–flocculation process, oxidation of organic matter and micropollutants, and inactivation of microorganisms [11]. As a strong oxidizer, ozone is not selective, and it may oxidize both microbes and micronutrients such as manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) present in the nutrient solution [12]. The amount of organic load present in water during ozonation has a significant impact on the ORP. In one study, which illustrated the effect of contaminants on the oxidative demand, ozonation was used to treat either pure tap water, 30% stagnant water with 70% tap water, or 100% stagnant lake water [13]. Tap water most quickly increased the ORP and had the highest maximum ORP (840 mV), and the rate of increase in the ORP and the maximum ORP decreased as the concentration of stagnant water increased. The relationship between the amount of total organic carbon (TOC) present in the water samples and the ozone dose required for the inactivation of bacterial density has also been studied [14]. Water samples with a higher TOC concentration required a greater dose of applied ozone for bacterial inactivation, indicating that the organic loading inhibited the disinfection ability of ozone. The disinfection ability of ozone for microorganisms is also dependent on the species present. An ozone residual concentration of 0.1 mg·L−1 at an ozonation contact time of 4 min was enough to completely eradicate the coliforms present in water [15]. However, the same concentration of residual ozone was not effective in decreasing the heterotrophic bacteria count, suggesting the differing susceptibilities of bacterial species to ozone disinfection. In another study, it was reported that ozone at a concentration of 1.5 mg·L−1 was effective in reducing the colony-forming units of Phytophthora capsici; however, it also decreased the iron component of the nutrient solution containing Fe-EDTA as the iron form [16].
Chelating agents such as iron-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Fe-EDTA), iron-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Fe-DTPA), and iron-ethylenediamine-N,N′-bis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) (Fe-EDDHA) are used to increase the solubility of iron fertilizer and plant uptake over a wide range of pH levels [17]. Ozone, as a powerful oxidizing agent, has been used to oxidize iron and manganese from simulated groundwater in order to limit the concentration of these pollutants to a safe drinking water level [18]. It has been reported that the oxidation of iron with ozone occurs rapidly, but it tends to produce fine colloidal particles that are challenging to filter out with sand or an anthracite filter. Stoichiometric estimates of the ozone dose required for oxidation were reported to be 0.43 mg O3 per mg of iron and 0.88 mg O3 per mg of manganese, which are much lower compared to the dose required for other oxidants such as chlorine and chlorine dioxide [12]. Sanitizing agents including copper, hydrogen peroxide, and chlorine were also found to interact with micronutrients present in the nutrient solution, resulting in the reduced concentration of Fe-EDDHA and Fe-EDTA [19], although we are not aware of studies of fertilizer interactions with cold plasma.
It is important to determine the change in concentration of micronutrients after treating the nutrient solution with cold plasma or ozone systems, so that the required amounts of micronutrients can be resupplied after water treatment. It is also helpful to compare oxidation of different chelate types and their oxidation demand to help guide fertilizer selection. Based on the literature, we hypothesized that the oxidation demand of micronutrients is dependent on the type of chelate used and is likely to consume reactive oxygen species, thereby reducing the sanitizing ability of treated water to control pathogens, and potentially increasing the time to achieve a target ORP. We also hypothesized that ozone and cold plasma would have similar effects on micronutrient concentrations at a given ORP level because of their similar modes of action. Therefore, a study was conducted with the objective to evaluate the effects of cold plasma and ozone treatment on oxidation of iron and manganese in nutrient solutions. The experiment quantified and compared the effects of cold plasma and ozone treatment on soluble and chelated Fe and Mn concentrations as well as water quality, including the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, and EC of nutrient solutions containing one of the four iron chelates (EDTA, EDDHA, DTPA, and HBED). Nutrient solutions were recirculated through the treatment system until a target ORP was achieved, and the samples were tested for the above-mentioned parameters before and after treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Treatment Systems
The cold plasma technology unit tested (“Ion solutions”, Ingersoll Rand, Inc., Lenexa, KS, USA) consisted of a 60 L reservoir for the solution and a chamber with a plasma reactor. Ambient air was used as a feeding gas, which was drawn to the system using an air compressor. The air was then passed through an oxygen concentrator to remove atmospheric nitrogen, and the oxygen-concentrated air was then fed into the plasma chamber, where an electrical current was applied to the gas by a high-voltage transformer. Nutrient solution was added to the reservoir, which was then pumped into a specialized plasma chamber where patented hardware and software established a layer of cold plasma within an oxygen “cloud”. The cold plasma, in turn, created positively charged ions which were drawn via electromotive force to an electrode under the sheet of water within the chamber. Injection of stable and reactive species passing through the cold plasma field resulted in high levels of DO and ORP in the water. The nutrient solution was treated with oxygen-gas-fed cold plasma that directly contacted the water by flowing through the Ion Solutions machine, with a nutrient water flow rate of 18.9 L·min−1 and oxygen at 0.5 L·min−1.
The ozone system (“CD10”, ClearWater Tech, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA) consisted of an oxygen concentration unit (AEROUS) to supply oxygen to the CD10 ozone unit, with a flow rate of 7.6 L·min−1 into a 60 L reservoir. The ozone unit was kept at maximum (100%) operating power, producing 0.57 mg O3·L−1. Ozone was injected to the nutrient solution through a venturi into a pressurized contact vessel to increase ozone dissolution.
The equivalent of one reservoir volume was passed through the cold plasma unit every 3.2 min, and ozone every 7.9 min, because of differences in the flow rates. Power consumption of the cold plasma unit was 320 Watts per hour, equivalent to 282 Wh per cubic meter treated with a single treatment pass, compared with a higher 602 Watts per hour and 1320 Wh per cubic meter for ozone. Both units produced ozone, as shown in Table 1 below. Other oxidative components of the cold plasma were not quantified.

Table 1.
Dissolved ozone gas produced by the two treatment units, measured in deionized water using an AQUAfast IV® AQ4000 colorimeter (Thermo Scientific, Watham, MA, USA) and Ozone AccuVac® ampules (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA).
2.2. Nutrient Solution
A complete fertilizer solution was prepared in each 60 L reservoir and recirculated through either the cold plasma or the ozone system. The amount of nutrients added per 60 L of deionized water to prepare the nutrient solution was 70.6 g of custom blend 17-4-17 (N-P2O5-K2O) without micronutrients, 0.8 g of a micronutrient blend without Fe containing MnSO4, CuSO4, ZnSO4, boric acid, sodium molybdate, and citric acid (Greencare Fertilizers, Kankakee, IL, USA), and one of the four iron chelates (EDTA, EDDHA, DTPA, and hydroxybenzyl ethylenediamine (HBED)). The concentration of each nutrient, in mg·L−1, was 200 N, 21 P, 166 K, 47 Ca, 12 Mg, 1 Fe, 1 Mn, 1 Zn, 0.5 Cu, 0.18 Mo, 63 Na, and 61 Cl. All macronutrients, micronutrients, and iron were individually prepared to allow addition of Fe-EDTA, Fe-EDDHA, Fe-HBED, or Fe-DTPA as the iron forms.
The nutrient solution was recirculated through the ozone or cold plasma treatment systems until the ORP in the tank reached 700 mV. A standardized target ORP of 700 mV was selected based on reports that water should be oxidized to an ORP of 600 to 800 mV for disinfection and sterilization using ozone [13], 650 to 700 mV for killing pathogenic bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella using oxidizing technologies including ozone [20], and 748 to 790 mV for disinfestation of Pythium species using hypochlorous acid [21]. Control samples were taken before the samples were recirculated through the treatment systems. Sample pairs of pretreatment (reservoir) and post-treatment (immediately after cold plasma unit or the ozone contact vessel) were collected, and the ORP, DO, temperature, pH, and EC of these samples were recorded every 5 min until the target ORP of 700 mV was reached in the reservoir. The ORP was recorded using a laboratory-grade ORP sensor (Env-20, Atlas Scientific, Long Island City, NY, USA). The DO and temperature were recorded using an Orion 083010MD probe (Thermo Scientific, Watham, MA, USA). Solution pH and EC were recorded using a HI 9813-51 portable meter (Hanna Instruments, Smithfield, RI, USA). Collected samples were analyzed for soluble iron and manganese using an AQUAfast IV® AQ4000 colorimeter (Thermo Scientific, Watham, MA, USA) and Hach reagents. Total chelated iron was determined by UV-visible spectrophotometry (SpectraMax® Plus 384 Microplate Reader, Molecular Devices, LLC., San Jose, CA, USA) at 296 nm for Fe-EDTA, 480 nm for Fe-EDDHA, 260 nm for Fe-DTPA, and 215 nm for HBED [19,22].
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
The experiment was conducted in a climatically controlled growth chamber, with the air temperature set at 21 °C and 60% average relative humidity. The study was conducted with a randomized complete block design with two factors and three replications. Factors were water treatment (cold plasma or ozone) and iron chelate type (EDTA, EDDHA, DTPA, or HBED). The three blocks were experimental runs, where treatment combinations of water treatment and iron chelate were randomly ordered within each run. Treatment effects were analyzed by ANOVA using R 3.6.3 [23] and the agricolae package [24] Pairwise comparisons were performed using least-square means and Tukey’s honestly significant difference at the 0.05, 0.001, and 0.0001 levels. In order to relate the post-ORP (mV) to different parameters (percent of initial chelated iron, percent of initial soluble manganese, pH, and percent saturation of DO), linear regression was used, with the exception of Fe-EDDHA, which showed a plateau in these parameters with the increasing ORP. For Fe-EDDHA, therefore, non-linear regression with SAS (version 9.4) PROC NLIN was used to fit a monomolecular function, as shown in Equation (1), to provide an empirical fit to the data, which were then graphed:
where Y was the measured variable, a represented the initial value of Y (set to 1 for 100% of iron chelate and 100% of measured Mn, and estimated for pH and % DO), b was the final asymptote value, k was a rate parameter (how quickly the variable reached an equilibrium or asymptote), and ORPInitial was an offset for the initial untreated ORP measurement.
Y = b + (a − b) × EXP(−k × (ORPMeasured − ORPInitial))
3. Results
3.1. Effects on Micronutrients
Both cold plasma and ozone treatments resulted in a high level of ORP, and the time to reach a target ORP of 700 mV was significantly affected by the sampling location (reservoir (“Pre”) or immediately after the injector (“Post”), p < 0.01), the water treatment type (cold plasma or ozone, p < 0.01), the iron chelate type (EDTA, DTPA, EDDHA, or HBED, p < 0.0001), and the interaction of the water treatment and the chelate (p < 0.001). Pretreatment samples from the reservoir took longer (overall least-square mean ± 95% confidence intervals of 43.7 ± 4.2 min) to increase to a target ORP of 700 mV than post-treatment samples immediately after the injector (35.5 ± 4.2 min). This occurred because the pretreatment sample represented the entire reservoir solution, which diluted the ozone or cold plasma dosage compared with the post-treatment samples collected immediately after the injector or contact tank. The significant interaction of water treatment × chelate type is represented in Figure 1. Nutrient solutions containing Fe-EDTA reached the target ORP of 700 mV most quickly with both water treatments. With cold plasma, the time required was greater with Fe-EDDHA and Fe-HBED than with FeEDTA or FeDTPA. With ozone, FeEDDHA and FeHBED required more time than FeEDTA, but FeDTPA was intermediate. The difference between chelate types presumably occurred because Fe-EDDHA and Fe-HBED were oxidized more quickly, creating a high oxidative demand, whereas Fe-EDTA and Fe-DTPA were more resistant to oxidation.
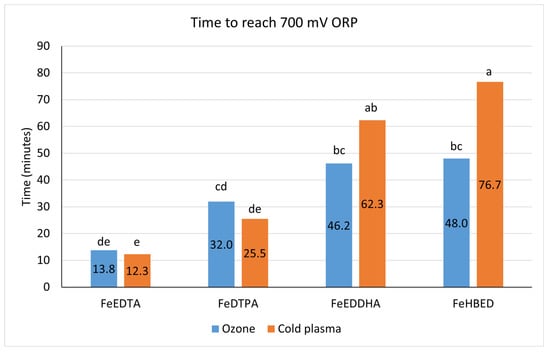
Figure 1.
Time in minutes to reach 700 mV ORP. Bars represent least-square means of six replicates from both the reservoir (“Pre”) and immediately after the injector (“Post”). Letters indicate mean comparisons using Tukey’s honestly significant different test at p = 0.05.
Figure 2 shows the decrease in chelated Fe over time with cold plasma and ozone treatments. There was a significant main effect of the iron chelate type on the percent change in chelated Fe from the initial concentration of 1 mg·L−1 at 700 mV ORP (Table 2). The concentration of chelated Fe decreased the least with EDTA as the iron form, whereby the iron chelate concentration was 79% of the original 1 mg·L−1 Fe at 700 mV for EDTA, followed by 52% for DTPA, 30% for HBED, and 18% for EDDHA.
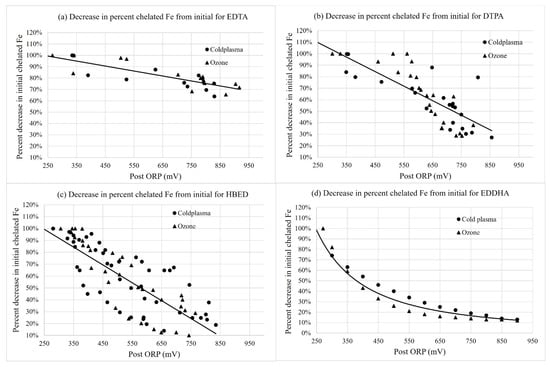
Figure 2.
Percent change in initial chelated iron (1 mg·L−1 Fe) with the change in ORP (mV) over time for (a) Fe-EDTA, (b) Fe-DTPA, (c) Fe-HBED, and (d) Fe-EDDHA for cold plasma- and ozone-treated samples collected immediately after the injector (“Post”). Curves were fit with linear regressions for Fe-EDTA, Fe-DTPA, and Fe-HBED, and Equation (1) was fit with non-linear regression for Fe-EDDHA. Regressions were significant at p < 0.0001.

Table 2.
Effects of the iron chelate type on the percent of remaining soluble Mn, chelated Fe, and soluble Fe of the samples collected post-injector ‘Post’ and the pH of samples collected in reservoir ‘Pre’ and post-injector ‘Post’ at 700 mV ORP.
There was no significant main or interaction effect of the water treatment type for the percent change in chelated Fe, or other micronutrient or pH variables in Table 2. This indicates that there was a consistent oxidation effect of cold plasma and ozone on Fe and Mn at the same ORP level between treatment technologies. For Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, therefore, a single regression line was used to show trends between ORP and the measured variables.
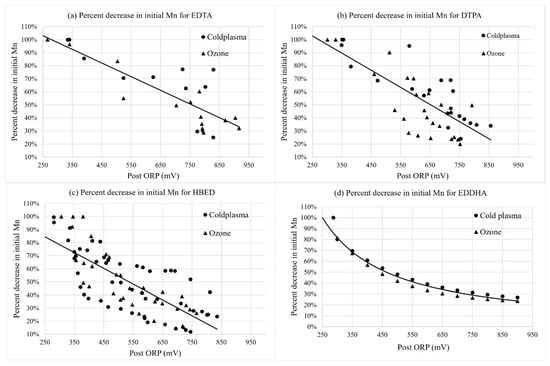
Figure 3.
Percent change in initial Mn (1 mg·L−1 Mn) with the change in ORP (mV) over time for nutrient solutions containing (a) Fe-EDTA, (b) Fe-DTPA (c) Fe-HBED, and (d) Fe-EDDHA for cold plasma- and ozone-treated samples collected immediately after the injector (“Post”). Curves were fit with linear regressions for Fe-EDTA, Fe-DTPA, and Fe-HBED, and Equation (1) was fit with non-linear regression for Fe-EDDHA. Regressions were significant at p < 0.0001.
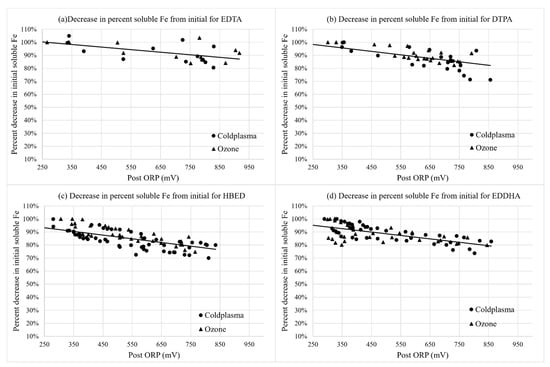
Figure 4.
Percent change in soluble Fe with the change in ORP (mV) over time from the initial nutrient solutions containing (a) Fe-EDTA, (b) Fe-DTPA, (c) Fe-HBED, and (d) Fe-EDDHA for cold plasma- and ozone-treated samples collected immediately after the injector (“Post”). Curves were fit with linear regressions for Fe-EDTA, Fe-DTPA, and Fe-HBED, and Equation (1) was fit with non-linear regression for Fe-EDDHA. Regressions were significant at p < 0.0001.
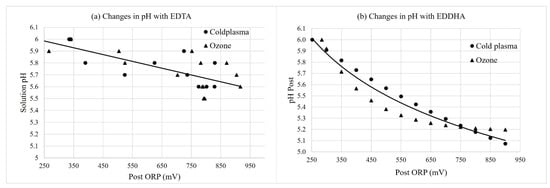
Figure 5.
Change in pH of nutrient solutions containing (a) Fe-EDTA and (b) Fe-EDDHA of samples collected immediately after the injector (“Post”) with the change in ORP (mV) over time. Curves were fit with linear regressions for Fe-EDTA, and Equation (1) was fit with non-linear regression for Fe-EDDHA. Regressions were significant at p < 0.0001.
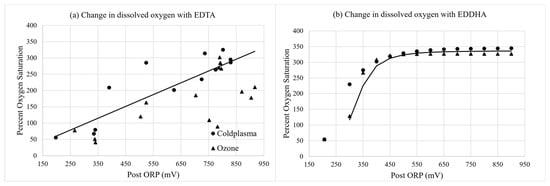
Figure 6.
Change in percent of dissolved oxygen saturation of nutrient solutions containing (a) Fe-EDTA and (b) Fe-EDDHA of samples collected immediately after the injector (“Post”) with the change in ORP (mV) over time. Curves were fit with linear regressions for Fe-EDTA, and Equation (1) was fit with non-linear regression for Fe-EDDHA. Regressions were significant at p < 0.0001.
Figure 3 shows the decrease in the Mn concentration with the increasing ORP over time. Both ozone and cold plasma treatments greatly decreased the Mn concentration at 700 mV ORP. However, there was no significant main or interaction effect of the water treatment type on the final Mn concentration (Table 2). The percent of Mn being oxidized at a given ORP was significantly less in the nutrient solution containing Fe-EDTA compared to solutions containing Fe-HBED (Table 2). This trend in Mn loss at a given ORP probably occurred because Fe-EDTA required less treatment time (Figure 1) to reach 700 mV. A greater treatment time through ozone or cold plasma with Fe-HBED led to greater oxidation of manganese than with Fe-EDTA at 700 mV.
There was also a slight decrease in the total soluble iron content with the increasing ORP over time (Figure 4). The decrease in the soluble iron content at 700 mV ORP was less in the solution containing EDTA compared with the solution containing HBED as the iron form (Table 2). Soluble iron content could include both inorganic and chelated iron, whereby oxidation of a chelate would lead to conversion of iron to an inorganic, non-chelated form that would be sensitive to the pH of the solution.
3.2. Effects on Physicochemical Properties of Nutrient Solutions
The pH of nutrient solutions decreased from an initial pH of 6.0 ± 0.1 with the increasing ORP over time (Figure 5). The solution EC also slightly decreased by 0 to 0.1 mS/cm. There were no significant main or interaction effects of the water treatment type on the final pH (Table 2). However, the iron chelate type had a highly significant effect on the pH of samples collected from reservoir and post-injector at 700 mV ORP. The change in pH was greater with EDDHA and HBED compared with EDTA and DTPA. This may have resulted from fewer passes through the cold plasma and ozone systems for EDTA and DTPA than EDDHA and HBED, resulting in less physicochemical changes of the nutrient solutions.
The dissolved oxygen level (mg·L−1) increased as the ORP (mV) increased over time with both cold plasma and ozone treatments (Figure 6a,b). At 700 mV ORP, both the cold plasma and the ozone treatment increased the DO of the nutrient solution to a super-saturation level.
4. Discussion
The ORP of the solution can be used to assess the ability of the sample to oxidize or reduce a compound (such as a micronutrient chelate) and is related to species strength, reactivity, and the presence of an oxidizer [25]. Similar to the results of this study, many authors have reported a high value of ORP in solutions after cold plasma or ozone treatment. The ORP value of distilled water increased from an initial 250 mV to 540 mV after cold plasma treatment of water for 20 min [26]. In another study, distilled water with an initial ORP value of 250 mV reached 485 mV in 5 min and increased up to 650 mV after 30 min with cold plasma treatment [27]. Differences between studies, including ours, in the duration to reach a high ORP depend on the demand from components in the water source and the power and design of the water treatment unit. Cold plasma generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as H2O2, OH radicals, and ozone that can react and form stable and active molecules, contributing to high levels of the ORP [28]. Ozone, being one of the most powerful oxidants, with a redox potential near 2.06 V, has the capacity to breakdown recalcitrant compounds into smaller molecules and reacts either through direct reactions with target chelating agents or through OH radicals [29]. The degradation of chelating agents by ROS is dependent on various factors, such as the chemical structure of the chelates, the solution pH, and the dose of oxidant. Chelating agents are composed of several carboxylate groups connected to a number of tertiary amino groups, and the nature of their structure affects the reactivity with ozone. Chelating agents with aromatic rings, such as DTPA and EDDHA, are more susceptible to OH radical attacks that can cause their aromatic rings to rupture and produce aliphatic acids [29,30]. This explains why there was a difference in the oxidative demand for each iron chelate, and the difference in the final iron chelate concentrations following treatment.
Several studies have reported the ability of ozone to breakdown chelating agents. Ozone treatment of river water containing Fe(III)DTPA complex resulted in 80% degradation of the compound at pH 7 and 60% degradation at pH 6 [31]. The dose of dissolved oxygen used was 1 mg·L−1, compared to the 0.57 mg·L−1 ozone dose recorded in our study, which could be one of the possible reasons for the greater amount of degradation of Fe(III)DTPA complex compared to our study. In another study, ozone was used as a disinfestation treatment against Corynebacterium michiganese and Fusarium oxysporum in pure water and nutrient solution containing either EDDHA, EDTA, or DTPA as iron forms [32]. Promising results were obtained in pure water against the pathogens, whereby the number of living conidia greatly decreased, and no more fungal growth was found. In contrast, in the solution with EDDHA, only a slight decrease in living conidia was observed. In line with our results, the nutrient solution with EDDHA had a higher oxidative demand compared to the solutions containing DTPA or EDTA. The authors concluded that a component of ozone was interacting with the chelate, which resulted in more than a 50% decrease in the soluble Fe concentration and a slow build-up of ozone in the nutrient solution containing EDDHA compared to the solutions with DTPA or EDTA. These studies highlight the ability of ozone to oxidize chelates by disrupting the chelate bonds, and the interaction between sanitation and fertilization for horticulture nutrient solutions.
Other studies have shown similar trends with oxidation of soluble metals by ozone and cold plasma. A study on the removal of Fe and Mn from simulated contaminated groundwater at various pH levels found that a 3 mg·L−1 ozone dose removed soluble ferrous sulphate heptahydrate and manganese sulphate monohydrate by more than 96% and 83%, respectively, with maximum removal observed at a high pH of 9 to 11 [18]. In another study with cold plasma, groundwater samples were supplemented with ferrous irons at concentrations of 3.76 mg·L−1 and 9.09 mg·L−1 [33]. Cold plasma removed 98.9% of Fe at a low Fe concentration (3.76 mg·L−1), and 97.8% of Fe at a 9.09 mg·L−1 concentration. One experiment [34] studied the change in physical, chemical, and biological parameters of groundwater by means of direct dielectric discharge barrier plasma activation. There was a significant reduction in the concentration of heavy metals such as chromium, manganese, cadmium, iron, lead, and zinc after cold plasma treatment. A considerable decrease in iron content was also observed, whereby the concentration of iron changed from the initial 2 mg·L−1 to approximately 0 mg·L−1 after 15 min of plasma treatment. The reaction of iron with ozone and hydroxides to form iron oxides and hydroxides, which precipitate and settle at the bottom of the water, accounts for the decreasing trend in the iron concentration [18]. These results support our findings that the ozone or cold plasma treatment resulted in oxidation of soluble metals such as iron and manganese present in the solution. However, numerous factors, such as pH, oxidant dose, quantity, and the form (species) of oxidants present in a reactor, can affect how quickly the chelating agents and other elements present in the nutrient solution are degraded by ROS [35].
Both cold plasma and ozone treatment affected the physicochemical properties of water, including pH, EC, and DO. The presence of reactive oxygen species in water following cold plasma or ozone treatment can lead to a change in the chemical composition of nutrients, which can change the physicochemical properties of water, including pH, EC, and redox potential [25]. The interactions taking place between water and chemical species formed in the plasma result in the generation of hydrogen peroxides, nitric acid, and peroxynitrous acid, which attributes to the decrease in the pH of the solution [36]. Consistent with our study, several studies have reported a decrease in the pH of solutions after cold plasma treatment. A gradual declination in the pH of a groundwater sample was reported over time when treated with a dielectric barrier discharge plasma system [34]. Similarly, a decrease in the pH of plasma-treated water with air as the influent gas was attributed to the effects of nitric and nitrate acids produced as a result of the reaction between H2O molecules and NOx species [37]. However, changes in the physicochemical parameters of water can be dependent on the electric voltage, flow rate, the method of plasma generation, and the gas source [38,39,40]. A study using oxygen and air as working gases for plasma generation resulted in a significant decrease in pH, whereas using argon as the working gas did not result in an observable change [40]. The relationship between the change in pH and the treatment time was reported in a study that used ambient air and dielectric barrier discharge to produce plasma-activated water [41]. Initially, the pH of water samples slightly decreased, whereas a rapid decrease in pH was observed as the treatment time exceeded 15 min. A dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma system was used for direct treatment of water collected from various sources [42]. Contrary to our results, the pH value of water collected from a river increased from an initial range of 8.5 to 9.3 to the range of 9.1 to 9.3 after 12–24 s of contact time of the water with the discharge zone in the reactor, whereas the water samples collected from wells did not show any effects on the pH. A cold plasma system with ambient air as the source gas was used to generate ozone and active species in water for the inactivation of E. coli [33] and resulted in a 10% increase in electrical conductivity and a slight decrease of the pH of water [33].
The dissolved oxygen level (mg·L−1) increased as the ORP (mV) increased over time with both cold plasma and ozone treatments, probably through both direct dissolution of non-converted oxygen and decomposition of ozone molecules and ROS into oxygen. Another study reported increased DO when using a dielectric barrier discharge to produce ozone for treating wastewater, whereby DO increased from 0.72 and 4.36 mg·L−1 for untreated samples to 9.41 and 9.55 mg·L−1, respectively, after ozone treatment [43]. Similar results were found in [13], whereby the DO level of surface water increased from 2.6 to 5.3 mg·L−1 after cold plasma treatment.
5. Conclusions
In this study, both cold plasma and ozone treatments resulted in a high level of ORP and oxidation of chelates and a reduced solubility of iron and manganese in nutrient solutions. The nutrient solution containing EDTA as the iron form reached a target ORP of 700 mV most rapidly and had the least change in the concentration of micronutrients, compared with nutrient solutions containing DTPA, HBED, or EDDHA as the iron forms. Besides the change in micronutrients, water treatment with cold plasma and ozone technology decreased the pH by up to 1 unit, caused a slight decrease in EC, and greatly increased DO by over three times saturation. Although this study showed that using Fe-EDTA as the iron form could help reduce the loss in micronutrients and increase the residual ORP for sanitation, further research could be performed to investigate the effects of cold plasma and ozone technology on oxidation of other micronutrients, such as manganese salts or chelates, when applied at different concentrations and pH levels. Cold plasma and ozone had very similar impacts on micronutrients at the same ORP level, and it would be useful to compare the dose responses of the two technologies with other target microorganisms and molecules.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R.F. and D.T.; methodology, P.R.F. and D.T.; formal analysis, D.T. and P.R.F.; investigation, D.T.; resources, P.R.F.; data curation, D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, D.T.; writing—review and editing, P.R.F.; funding acquisition, P.R.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Service under the Floriculture and Nursery Research Initiative #58-3607-8-725, USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture projects multi-state NC1186 and Hatch FLA-ENH-005918. Industry funding was provided by Ingersoll Rand and partners in the Floriculture Research Alliance at the University of Florida (floriculturealliance.org).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Greencare Fertilizers, ADOB, and ICL for providing fertilizers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gururani, P.; Bhatnagar, P.; Bisht, B.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, N.C.; Tomar, M.S.; Pathak, B. Cold plasma technology: Advanced and sustainable approach for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65062–65082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barjasteh, A.; Dehghani, Z.; Lamichhane, P.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H. Recent progress in applications of non-thermal plasma for water purification, bio-sterilization, and decontamination. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma, a novel promising anti-cancer treatment modality. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15977–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, S.; Habib, M.R.; Moore, J.M. Effect of high-voltage atmospheric cold plasma treatment on germination and heavy metal uptake by soybeans (Glycine max). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niveditha, A.; Pandiselvam, R.; Prasath, V.A.; Singh, S.K.; Khalid, G.; Kothakota, A. Application of cold plasma and ozone technology for decontamination of Escherichia coli in foods- a review. Food Con. 2021, 130, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-activated water: Generation, origin of reactive species and biological applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Wright, K.; Piccioni, J.; Cho, D.J.; Cho, Y.I. Inactivation of bacteria by the application of spark plasma in produced water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Patil, S.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K.M.; Bourke, P. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of Escherichia coli in liquid media inside a sealed package. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Kang, C.; Zhao, D.; Niu, L.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y. Influence of organic matters on the inactivation efficacy of plasma-activated water against E. coli O157:H7 and S. aureus. Food Control. 2019, 99, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyani, R.A.; Permata, Y.E.; Karamah, E.F.; Bismoa, S. Removal of organic and inorganic (phenolic and iron compound) pollutants from wastewater using DBD cold plasma reactor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2175, 020005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camel, V.; Bermond, A. The use of ozone and associated oxidation processes in drinking water treatment. Water Res. 1988, 32, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rosal, R.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Mezcua, M.; Agüera, A.; Hernando, M.D.; Letón, P.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Calvo, E. Ozone-based technologies in water and wastewater treatment. Emerging contaminants from industrial and municipal waste. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Barceló, D., Petrovic, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Cuong, L.C.; Dieu, T.V.; Ngu, T.; Oanh, D.T.Y. Ozonation process and water disinfection. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2018, 56, 717–720. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, K.; Chrostowski, P.; Wright, R.L.; Suffet, I.H. Ozonation and oxidation competition values: Relationship to disinfection and microorganisms regrowth. Water Res. 1984, 18, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirsardari, Y.; Yu, Q.; Williams, P. Effect of Ozonation and UV irradiation with direct filtration on disinfection and disinfection by-product precursors in drinking water treatment. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, G.V. Ozone (O3) Efficacy on Reduction of Phytopththora capsici in Recirculated Horticultural Irrigation Water. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2007. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/handle/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-1328 (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Shaddox, T.W.; Fu, H.; Gardner, V.R.; Goss, M.; Guertal, V.W.; Kreuser, C.; Miller, G.L.; Stewart, B.R.; Tang, K.; Unruh, J.B. Solubility of ten iron fertilizers in eleven north American soils. Agron J. 2019, 111, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araby, R.E.; Hawash, S.; Diwani, G.E. Treatment of iron and manganese in simulated groundwater via ozone technology. Desalination 2009, 249, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.R.; Mohammad-Pour, G. Interactions of fertilizer and chemical sanitizing agents in water. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1335, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslow, T.V. Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) for water disinfection monitoring, control, and documentation. ANR Pub. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.M.; Rebits, B.; Newman, S.E.; Tisserat, N. Monitoring mortality of Pythium zoospores in chlorinated water using oxidation reduction potential. Plant Health Prog. 2008, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, J.P.; Miller, W.B. Ferric ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Fe-EDTA) photodegradation in commercially produced soluble fertilizers. Hort. Tech. 2001, 11, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2020. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Mendiburu, F.D.; Yasee, M. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. R Package version 1.4.0. 2020. Available online: https://myaseen208.github.io/agricolae (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Gao, Y.; Francis, K.; Zhang, X. Review on formation of cold plasma activated water (PAW) and the applications in food and agriculture. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Bactericidal effects against S. aureus and physicochemical properties of plasma activated water stored at different temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Naidis, G.V.; Laroussi, M.; Reuter, S.; Graves, D.B.; Ostrikov, K. Reactive species in non-equilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasmas: Generation, transport, and biological effects. Phys. Rep. 2016, 630, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.E.T.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W. Degradation of chelating agents in aqueous solution using advanced oxidation process (AOP). Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sein, M.M.; Zedda, M.; Tuerk, J.; Schmidt, T.C.; Golloch, A.; Sonntag, C.V. Oxidation of diclofenac with ozone in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6656–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemmler, K.; Glod, G.; Gunten, U.V. Oxidation of metal–diethylenetriamine-pentaacetate (DTPA)—Complexes during drinking water ozonation. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanachter, A.; Thys, L.; Wambeke, E.V.; Assche, C.V. Possible use of ozone for disinfestation of plant nutrient solutions. Acta Hortic. 1988, 221, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Ho, N.M.; Hoang, K.D.; Le, T.V.; Le, V.H. An investigation on treatment of groundwater with cold plasma for domestic water supply. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Pradhan, S.; Guragain, R.; Subedi, D.; Pandey, B. Investigating the Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Air DBD Plasma on Physio-Chemical and Microbial Parameters of Groundwater. Open Access Libr. J. 2020, 7, 99162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legube, B.; Leitner, N.K.V. Catalytic ozonation: A promising advanced oxidation technology for water treatment. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Kothakota, A.; Annapure, U.; Siliveru, K.; Blundell, R.; Gatt, R.; Valdramidis, V.P. Plasma activated water (PAW): Chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, T. Properties of plasma-activated water with different activation time and its effects on the quality of button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus). LWT 2021, 147, 111633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Ho, P.Q.; Pham, T.V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Kim, L. Treatment of surface water using cold plasma for domestic water supply. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 24, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Assessment of the physicochemical properties and biological effects of water activated by non-thermal plasma above and beneath the water surface. Plasma Process Polym. 2015, 12, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shainsky, N.; Dobrynin, D.; Ercan, U.; Joshi, S.; Ji, H.; Brooks, A.; Fridman, G.; Cho, Y.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G. Plasma Acid: Water treated by dielectric barrier discharge. Plasma Process Polym. 2012, 9, 555–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Lai, Y.T.; Duh, J.G. Improving the growth rate of Lettuce sativa young plants via plasma-activated water generated by multitubular dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma system. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2022, 50, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, D.P.; Tyata, R.; Khadgi, A.; Wong, C. Treatment of Water by Dielectric Barrier Discharge. J. Sci. Technol. Trop. 2009, 5, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, R.; Kayastha, R.; Subedi, D.P.; Joshi, R. Treatment of wastewater by ozone produced in dielectric barrier discharge. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 648162 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).