Transcriptomic Analysis of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Red and Yellow Fruits of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) during Ripening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Determination of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Content
2.3. Total RNA Extraction
2.4. Library Construction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.5. Sequencing Data Filtration and Transcripts Mapping
2.6. Functional Gene Annotation
2.7. Different Expression Gene (DEG) Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Content at Different Ripening Stages and Maturity Levels of Sweet Cherry
3.2. Transcriptome Profile of the RNA Libraries of Sweet Cherry
3.3. Functional Annotation and Classification
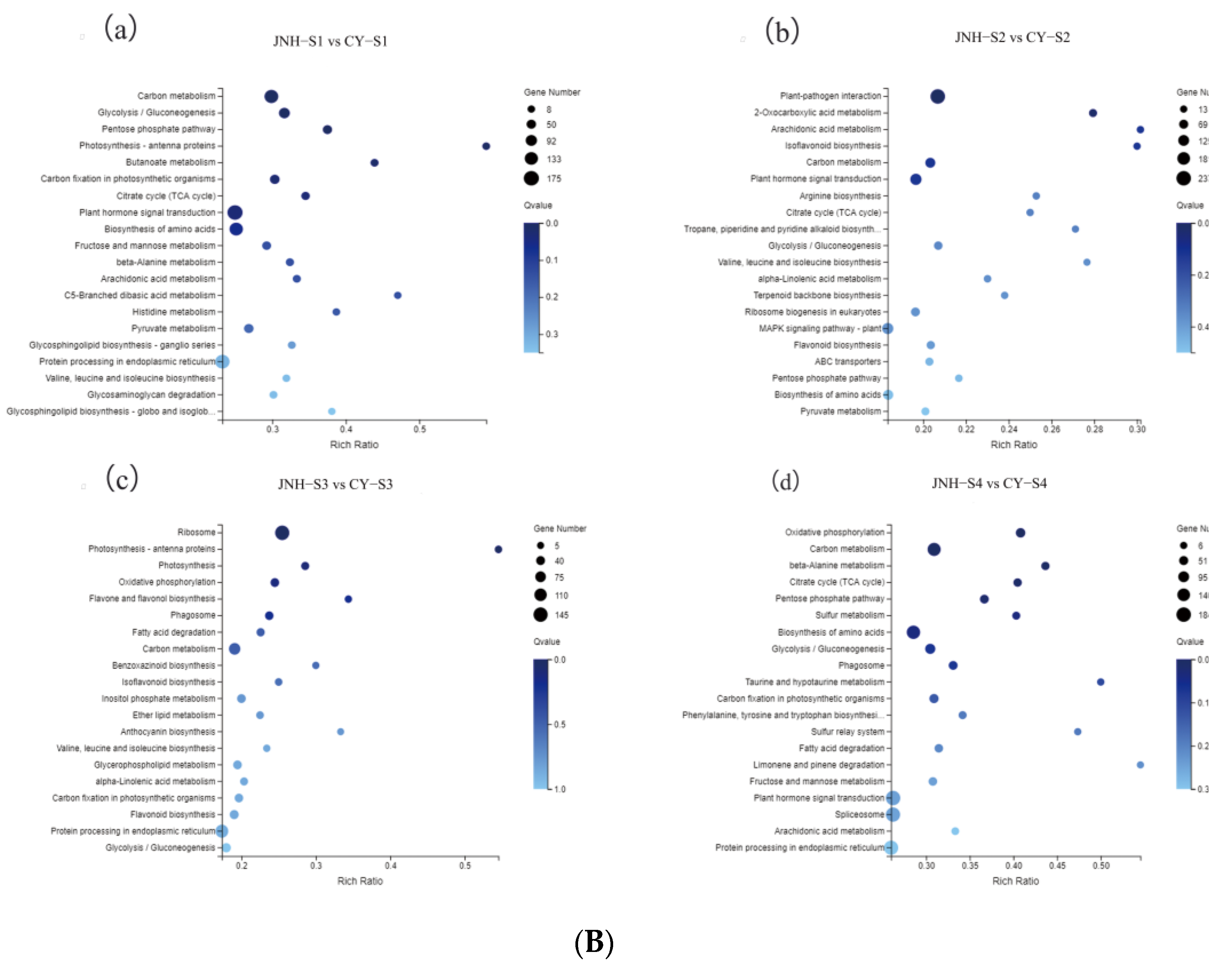
3.4. Differential Genes Expression
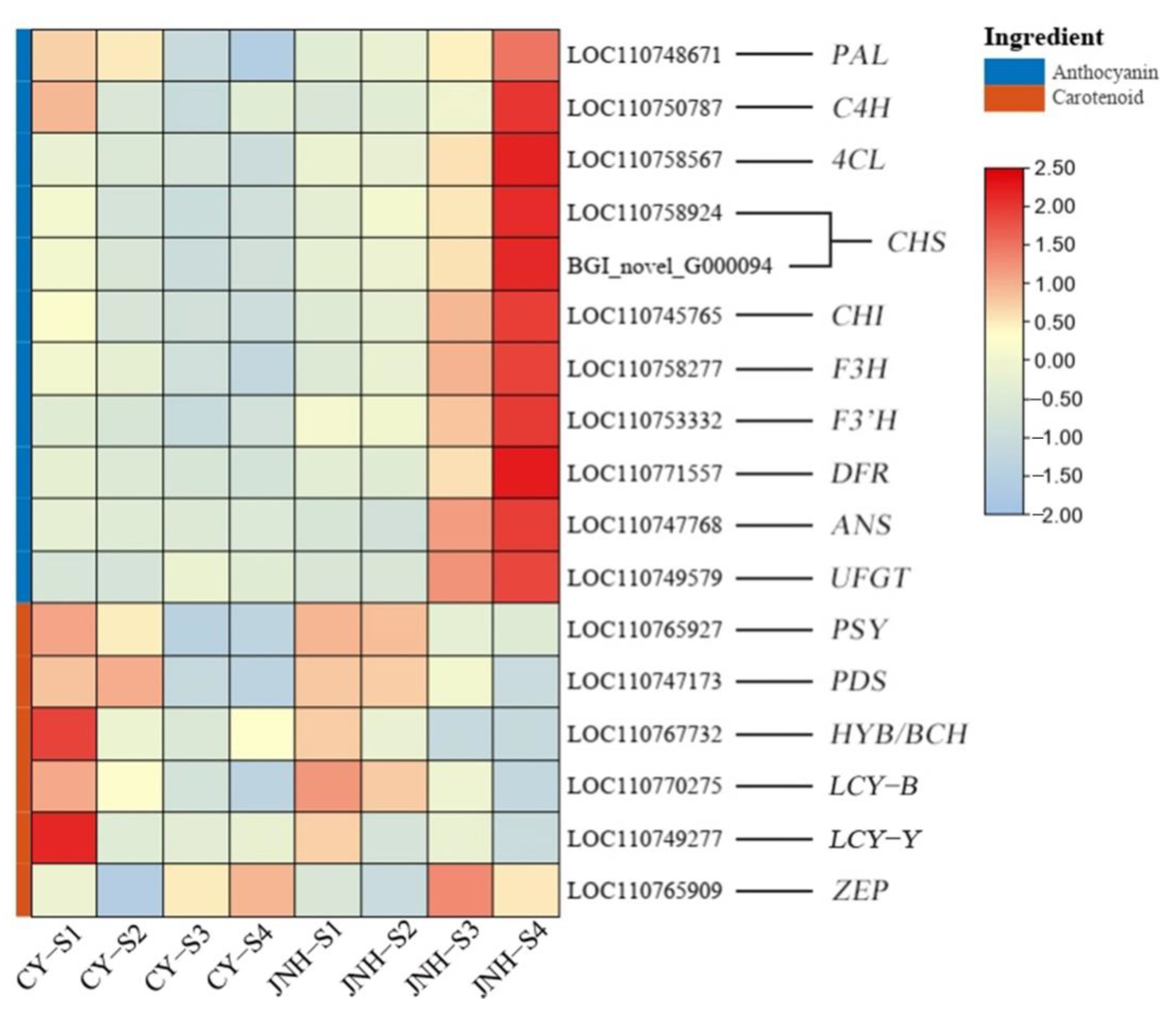
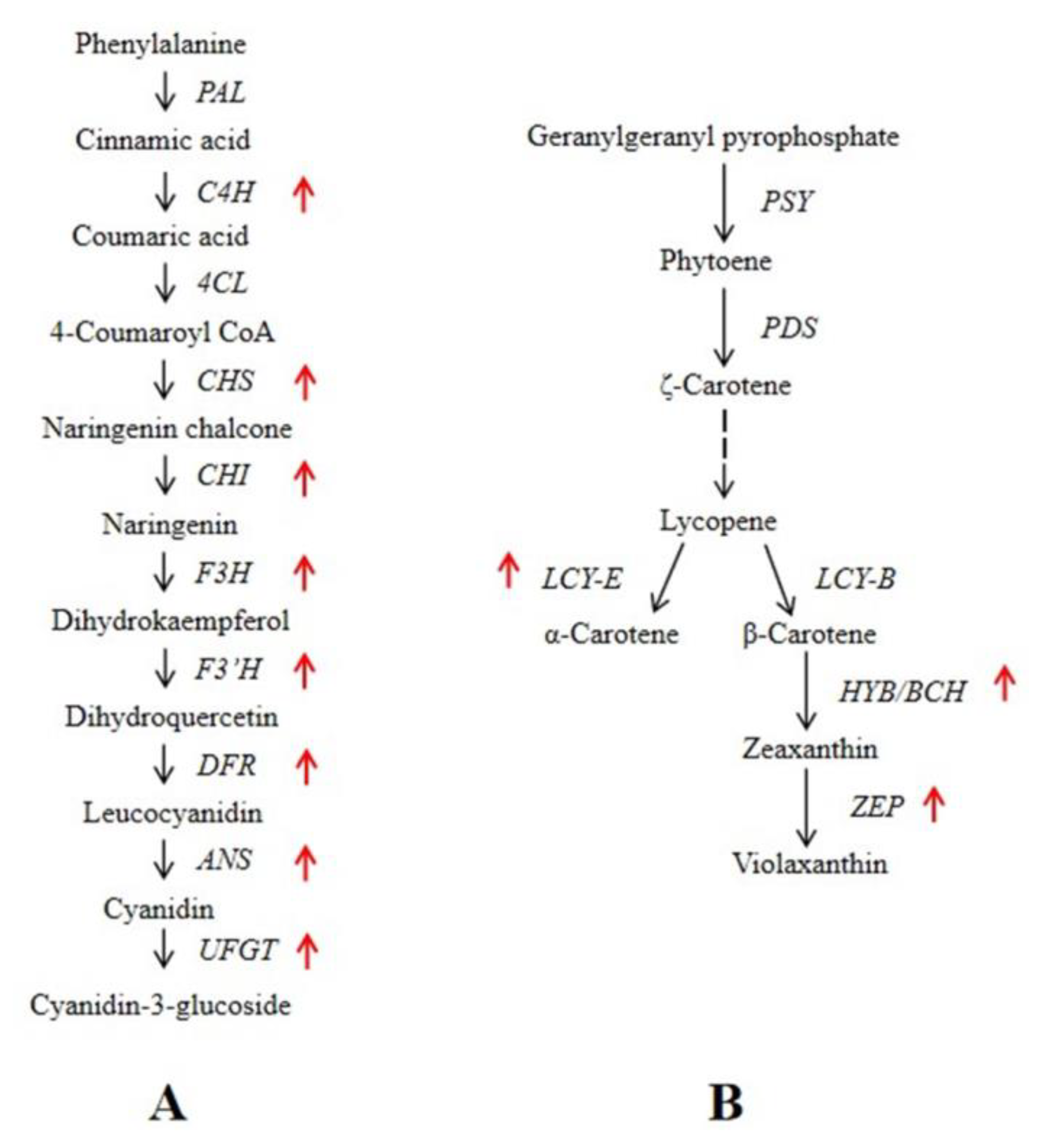
3.5. Identification of DEGs Involved in Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Metabolic Pathways
3.6. Correlation Analysis of the DEGs between Red and Yellow Sweet Cherries
3.7. Validation of RNA-seq Data Using qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nawirska-Olszańska, A.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Oziembłowski, M.; Ticha, A.; Hyšpler, R.; Zadak, Z.; Židová, P.; Paprstein, F. Comparison of old cherry cultivars grown in Czech Republic by chemical composition and bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, B.; Silva, A.P.; Moutinho-Pereia, J.; Bacelar, E.; Rosa, E.; Meyer, A.S. Effect of ripeness and postharvest storage on the evolution of color and anthocyanins in cherries (Prunus avium L.). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, D.; Lozano, M.; Fernández-León, M.F.; Bernalte, M.J.; Ayuso, M.C.; Rodríguez, A.B. Sweet cherry phytochemicals: Identification and characterization by HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS in six sweet-cherry cultivars grown in Valle del Jerte (Spain). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Meng, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z. Fruit coloration and anthocyanin biosynthesis after bag removal in non-red and red apples (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Molecules 2013, 18, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins: Natural colorants with health-promoting properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, R. Pigments. In Food Analysis by HPLC; Nollet, L.M.L., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: Monticello, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 845–880. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.M.; Chia, L.S.; Goh, N.K.; Chia, T.F.; Brouillard, R. Analysis and biological activities of anthocyanins. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F.; Ronald, K. Flavonoids: A colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Qu, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Z. Anthocyanin accumulation and related gene family expression in the skin of dark-grown red and non-red apples (Malus domestica Borkh.) in response to sunlight. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 189, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, G.; Tan, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y. Identification of candidate genes involved in anthocyanin accumulation using Illmuina-based RNA-seq in peach skin. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 250, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, X.; Zong, X.; Shu, H.; Gao, D.; Liu, Q. Comparative transcriptome analysis of genes Involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in the Red and yellow fruits of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, Y.; Ge, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. Functional characterization of SmMYB86, a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Sci. 2021, 302, 110696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Deng, L.; Du, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, T.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Li, C. A transcriptional network promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis in tomato flesh. Mol. Plant 2019, 13, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhao, K.; Ben, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, T. Expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in different colored sweet cherries (Prunus avium L.) during fruit development. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, H.; Qu, S. Accumulation of carotenoids and expression of carotenoid biosynthesis genes in fruit flesh during fruit development in two Cucurbita maxima inbred lines. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, R.; Failla, M.L. Recent advances in the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of carotenoids and effects of other dietary lipophiles. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 68, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Bi, X.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Transcriptome and carotenoid profiling of different varieties of Coffea arabica provides insights into fruit color formation. Plant Divers. 2022, 44, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.; Chen, Z.; Jackson, A. Development of fruit color in Rubus chingii Hu (Chinese raspberry): A story about novel offshoots of anthocyanin and carotenoid biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 110996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Chan, H.; Gong, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Feng, B.; et al. S1MYB72 regulates the metabolism of chlorophylls, carotenoids, and flavonoids in tomato fruit. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis of genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in the pink-white and red fruits of Chinese bayberry (Morella rubra). Sci. Hortic. 2019, 250, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dere, S.; Günes, T.; Sivaci, R. Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll-A, B and total carotenoid contents of some algae species using different solvents. Botany 1998, 22, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. Soap: Short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Hisat: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballistreri, G.; Continella, A.; Gentile, A.; Amenta, M.; Fabroni, S.; Rapisarda, P. Fruit quality and bioactive compounds relevant to human health of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars grown in Italy. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, F.; Tian, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, T. Comparative study of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in different species of cherries. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tian, C.; Li, X.; Gong, H.; Zhang, A. Transcriptome co-expression network analysis identifies key genes and regulators of sweet cherry anthocyanin biosynthesis. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, X.; Song, L.; Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Pan, F.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Guo, W.; et al. Large-fragment deletion encompasses the R2R3 MYB transcription factor, PavMYB10. 1, causes yellow fruits in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 309, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Huang, T.; Zhao, D.; Peng, X.; Feng, C.; Xiao, Y.; Li, T. Transcriptomic analysis of light-dependent anthocyanin accumulation in bicolored cherry fruits. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Bolitho, K.; Grafton, K.; Kortstee, A.; Karunairetnam, S.; Mcghie, T.K.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shi, B.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, K.; Qian, M.; Wu, H. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Expression Analysis of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) chalcone synthase (CHS) Genes in Response to Light. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M. The joint role of the late anthocyanin biosynthetic UFGT-encoding genes in the flowers and fruits coloration of horticultural plants. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 301, 111110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Nawa, N.; Lupsea, S.A. Anthocyaninless1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a UDP-glucose: Flavonoid-3-O-glucosyltransferase. J. Plant Res. 2007, 3, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, P.K.; Davies, C.; Robinson, S.P. Expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway genes in red and white grapes. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 32, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C. Relationship betweenanthocyanin biosynthesis and related enzymes activity in Pyrus pyrifolia Mantianhong and its bud sports Aoguan. Agric. Sci. China 2008, 7, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, C. The relationships between the enzyme activity of anthocyanin biosynthesis, ethylene release and anthocyanin accumulation in fruits of precocious apple cultivar. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2012, 7, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Z. Characterization and primary functional analysis of a bamboo ZEP gene from Phyllostachys edulis. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhu, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ye, J.; Deng, X. Citrus β-carotene hydroxylase 2 (BCH2) participates in xanthophyll synthesis by catalyzing the hydroxylation of β-carotene and compensates for BCH1 in citrus carotenoid metabolism. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, L.; Yungyuen, W.; Tsukamoto, I.; Iijima, N.; Oikawa, M.; Yamawaki, K.; Yahata, M.; Kato, M. Expression and functional analysis of citrus carotene hydroxylases: Unravelling the xanthophyll biosynthesis in citrus fruits. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquezar, B.; Rodrigo, M.J.; Zacarías, L. Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis during fruit maturation in the red-fleshed orange mutant Cara Cara. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cultivars | Scientific Name | Abbreviation | Ripening Stage a | Maturity Level b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Jiangnanhong’ | Prunus avium | JNH | S1, S2, S3, S4 | Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ |
| ‘Chaoyang’ | P. avium | CY | S1, S2, S3, S4 | Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ |
| Cultivars | Color a | a/b b | Weight (g) | Length (cm) | Width (cm) | TSS (°Brix) c | TA (%) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JNH | Red | 2.73 ± 0.43 a | 8.73 ± 0.69 a | 21.29 ± 0.88 a | 25.31 ± 1.25 a | 15.77 ± 0.49 a | 0.40 ± 0.02 a |
| CY | Yellow | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | 7.93 ± 0.46 a | 21.56 ± 0.29 a | 26.57 ± 0.37 a | 14.93 ± 1.06 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a |
| Sample | Cyanidin-3-O-Rutinoside (μg/g·FW) | Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (μg/g·FW) | Pelargonidin 3-Glucoside (μg/g·FW) | Total Carotenoid (μg/g·FW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ripening stages | JNH S1 | 0.23 ± 0.01 d | 4.35 ± 0.35 a | nd | 2.03 ± 0.05 f |
| JNH S2 | 2.62 ± 0.18 c | 1.46 ± 0.06 c | nd | 4.22 ± 0.34 e | |
| JNH S3 | 38.04 ± 2.31 b | 1.10 ± 0.05 d | nd | 11.78 ± 0.69 b | |
| JNH S4 | 719.31 ± 19.84 a | 1.93 ± 0.06 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 11.17 ± 0.86 c | |
| CY S1 | nd | 0.19 ± 0.03 e | nd | 2.48 ± 0.14 f | |
| CY S2 | nd | 0.17 ± 0.07 e | nd | 7.05 ± 0. 07 d | |
| CY S3 | 0.32 ± 0.01 e | 0.12 ± 0.02 e | nd | 11.79 ± 0.28 b | |
| CY S4 | 2.34 ± 0.21 c | 0.09 ± 0.02 e | nd | 12.86 ± 0.38 a | |
| Maturity level | JNH Ⅰ | 112.62 ± 5.59 d | 1.00 ± 0.06 d | nd | 10.63 ± 0.02 d |
| JNH Ⅱ | 111.07 ± 5.17 d | 1.13 ± 0.04 d | nd | 9.01 ± 0.10 c | |
| JNH Ⅲ | 837.70 ± 15.12 c | 1.71 ± 0.02 c | nd | 8.27 ± 0.07 b | |
| JNH Ⅳ | 1424.16 ± 7.56 b | 4.29 ± 0.05 b | nd | 6.53 ± 0.09 e | |
| JNH Ⅴ | 3909.32 ± 112.67 a | 13.54 ± 0.28 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 3.19 ± 0.21 f | |
| CY Ⅰ | 1.35 ± 0.23 e | 0.94 ± 0.03 de | nd | 13.49 ± 0.06 a | |
| CY Ⅱ | 1.44 ± 0.12 e | 1.07 ± 0.16 d | nd | 13.75 ± 0.08 a | |
| CY Ⅲ | 6.25 ± 0.44 e | 0.74 ± 0.11 e | nd | 13.80 ± 0.13 a |
| Sample | Clean Bases (Gb) | Clean Reads/Raw Reads (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | Total Mapping (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JNH S1 | 6.38 | 97.03% | 97.44 | 92.21 | 86.76 |
| JNH S2 | 6.44 | 97.95% | 97.32 | 91.79 | 88.95 |
| JNH S3 | 6.43 | 97.79% | 97.05 | 90.94 | 88.34 |
| JNH S4 | 6.41 | 97.49% | 97.43 | 92.01 | 87.60 |
| CY S1 | 6.40 | 93.88% | 97.87 | 93.68 | 91.12 |
| CY S2 | 6.38 | 93.60% | 97.91 | 93.83 | 91.71 |
| CY S3 | 6.35 | 93.20% | 97.96 | 93.93 | 90.75 |
| CY S4 | 6.39 | 93.73% | 97.92 | 93.82 | 90.50 |
| Items | Number of the Unigenes and Transcripts | Percentage of Annotated Unigenes and Transcripts (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Total genes | 26,247 | 100 |
| Known genes | 23,308 | 88.80 |
| Novel genes | 2939 | 11.20 |
| Total transcripts | 14,523 | 100 |
| Known transcript | 11,509 | 79.25 |
| Novel transcript | 3014 | 20.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Jing, L.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, W. Transcriptomic Analysis of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Red and Yellow Fruits of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) during Ripening. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040516
Wang Q, Jing L, Xu Y, Zheng W, Zhang W. Transcriptomic Analysis of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Red and Yellow Fruits of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) during Ripening. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(4):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040516
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qinghao, Luyang Jing, Yue Xu, Weiwei Zheng, and Wangshu Zhang. 2023. "Transcriptomic Analysis of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Red and Yellow Fruits of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) during Ripening" Horticulturae 9, no. 4: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040516
APA StyleWang, Q., Jing, L., Xu, Y., Zheng, W., & Zhang, W. (2023). Transcriptomic Analysis of Anthocyanin and Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Red and Yellow Fruits of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) during Ripening. Horticulturae, 9(4), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040516





