Three Different Fertilizers Enhance Spinach Growth and Reduce Spinach Cd Concentration in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Cultivation Method
2.2. Plant Biomass and Nutrients Uptake
2.3. Soil Physiochemical Properties
2.4. The Cadmium Concentration in the Soil, Organic Fertilizers and Plant, as well as the Plant Cadmium Biological Concentration and Transportation
2.5. Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Plant Cadmium Absorption, Biomass Accumulation and Mineral Nutrient Uptake
3.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties, Mineral Nutrient and Cadmium Content
3.3. The Relation between the Plant Growth, Soil Nutrients and the Cd Migration in Soil-Plant System
4. Discussions
4.1. The Improvement of Peach Branch Fertilizer and Cow Manure Fertilizer on Plant Biomass, Plant Cd Concentration and Total Cd Accumulation
4.2. The Influence of Silicon Liquid Fertilizer on Plant Cadmium Concentration and Inner Plant Cd Transportation
4.3. The Influence of Fertilizers on Soil Physiochemical Properties and Cd Availability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Mahmood, Q.; Peng, D.; Fu, W.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, D. The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals and risk assessment of moso bamboo forest soil around lead–zinc mine in Southeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People′s Republic of China. Report on the National General Survey of Soil Contamination; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People′s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cai, K.; Huang, F.; Pan, B.; Wang, W. Cd accumulation, biomass and yield of rice are varied with silicon application at different growth phases under high concentration cadmium-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chen, A.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, C.; Luo, S.; Shao, J. Application of a newly recorded diazotrophic cyanobacterium in acidified and Cd contaminated paddy soil: Promotes rice yield and decreases Cd accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Islam, E.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Yan, W.; Peng, D.; Liu, D. Cadmium-induced oxidative stress, response of antioxidants and detection of intracellular cadmium in organs of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) seedlings. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, D.; Hua, L. Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd exhibited by different vegetables. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, P.D.; Alloway, B.J.; Dourado, A.M. Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn exhibited by six commonly grown vegetables. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, M. Low pe+pH induces inhibition of cadmium sulfide precipitation by methanogenesis in paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xiao, X.; Guo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, H.; Peng, C.; Liang, Y. Release of cadmium in contaminated paddy soil amended with NPK fertilizer and lime under water management. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahori, A.H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Mahar, A.; Li, R.; Awasthi, M.K.; Sial, T.A.; Kumbhar, F.; Wang, P.; Shen, F.; et al. Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2017, 145, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Takeda, H.; Oyanagi, W.; Nishihara, E.; Murakami, M. Reduction of cadmium uptake in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by soil amendment with animal waste compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Mao, W.; Lou, L.; Shen, C.; Lin, Q. Biofertilizer-induced response to cadmium accumulation in Oryza sativa L. grains involving exogenous organic matter and soil bacterial community structure. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 211, 111952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Ji, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, S.; Tian, F.; Liu, X. Influence of soil properties on cadmium accumulation in vegetables: Thresholds, prediction and pathway models based on big data. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X. The combined application of biochar and high phosphate fertilizer promoted the mobilization and redistribution of cadmium in rhizosphere soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Cheng, H.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Hill, P.; Chadwick, D.; Jones, D.L. Field aging declines the regulatory effects of biochar on cadmium uptake by pepper in the soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Qiao, J.; Liang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W. Impact of nanominerals on the migration and distribution of cadmium on soil aggregates. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 262, 121355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Shi, X.; Zhou, N.; Liu, K.; Ma, J.; Yu, F.; Li, Y. Mechanism underlying how a chitosan-based phosphorus adsorbent alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Bidens pilosa L. and its impact on soil microbial communities: A field study. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yu, Y.; Lin, J.; Hong, Z.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Alkaline lignin does not immobilize cadmium in soils but decreases cadmium accumulation in the edible part of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, P.; Li, X.; Ji, P. Possibility of using modified fly ash and organic fertilizers for remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated soils. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 284, 124713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Nie, Z.; Rngel, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, P. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Naeth, M.A. Lignite derived humic products and cattle manure biochar are effective soil amendments in cadmium contaminated and uncontaminated soils. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zia, U.R.M.; Saleem, M.H.; Adrees, M.; Rizwan, M.; Javed, A.; Rafique, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ali, S. Effect of phosphorus sources on growth and cadmium accumulation in wheat under different soil moisture levels. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, P.; Elbaum, R.; Weiss, I.M. Calcium and silicon mineralization in land plants: Transport, structure and function. Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišúthova, A.; Ludmila, S.; Kollarova, K.; Vaculík, M. Effect of silicon on root growth, ionomics and antioxidant performance of maize roots exposed to as toxicity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, H.; Luo, S.; Luo, L. Silicon-based additive on heavy metal remediation in soils: Toxicological effects, remediation techniques, and perspectives. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Awan, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Hassan, M.J.; Brestic, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L. Effects of silicon on heavy metal uptake at the soil-plant interphase: A review. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 222, 112510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Meunier, J.; Miche, H.; Keller, C. Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio, W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 62, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Xie, L.; Zhu, Z. Determination of Phosphorus Content in Foods by Vanadium Molybdate Yellow Colorimetric Method. China Rice 2012, 18, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.J.; Xu, C.U.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhu, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, F.Q.; Huang, D.Y. Effects of three organic materials on the availability of cadmium in soil and cadmium accumulation and translocation in rice plants. J. Agro Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 2143–2150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Fang, B.; Yue, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Su, N.; Jin, C. The research progress of vegetable Cd contamination and physiological blocking agents of Cd. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2020, 6, 988–997. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, J. Simultaneous determination of soil available potassium and exchangeable calcium and magnesium by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry with oscillating extraction. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2020, 8, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Volk, T.A.; Xu, J. Variability in growth and cadmium accumulation capacity among willow hybrids and their parents: Implications for yield-based selection of Cd-efficient cultivars. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, M.; He, W.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhug, Y. Effect of phosphorus supplementation on growth, nutrient uptake, physiological responses, and cadmium absorption by tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) exposed to cadmium. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 213, 112021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Ahmad, I. Involvement of phosphate supplies in different transcriptional regulation pathway of Oryza sativa L.’s antioxidative system in response to arsenite and cadmium stress. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, G.; Xia, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kumar, S.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Hou, H. Combined effects of temperature and nutrients on the toxicity of cadmium in duckweed (Lemna aequinoctialis). J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Ling, L.; Zeng, E.Y. Use of low-calcium cultivars to reduce cadmium uptake and accumulation in edible amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.). Chemosphere 2017, 171, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Su, N.; Cui, J. Mechanisms of calcium sulfate in alleviating cadmium toxicity and accumulation in pak choi seedlings. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Nazir, M.M.; Ali, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Ye, S.; Zeng, F. Calcium Plays a Double-Edged Role in Modulating Cadmium Uptake and Translocation in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, F.; Brix, H. Influence of low calcium availability on cadmium uptake and translocation in a fast-growing shrub and a metal- accumulating herb. Aob Plants 2015, 7, v143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Yang, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, C.; Liu, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, N.; et al. Silicon fertilizers, humic acid and their impact on physicochemical properties, availability and distribution of heavy metals in soil and soil aggregates. Sci. Total Envrion. 2022, 822, 153483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Cai, P.; Liang, W.; Li, M. Poultry Manure Compost Alleviates the Phytotoxicity of Soil Cadmium: Influence on Growth of Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Pedosphere 2010, 20, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, Y.K.; Barkat, A.; Cui, X.; Feng, Y.; Pan, F.; Tang, L.; Yang, X. Cow manure and cow manure-derived biochar application as a soil amendment for reducing cadmium availability and accumulation by Brassica chinensis L. in acidic red soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Effect of alkaline lignin on immobilization of cadmium and lead in soils and the associated mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmita, H.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Pan, X. Copper and cadmium sorption onto kraft and organosolv lignins. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6183–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Gao, B.; Lyu, X.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, Y. Insight into the mechanism of phosphate and cadmium co-transport in natural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

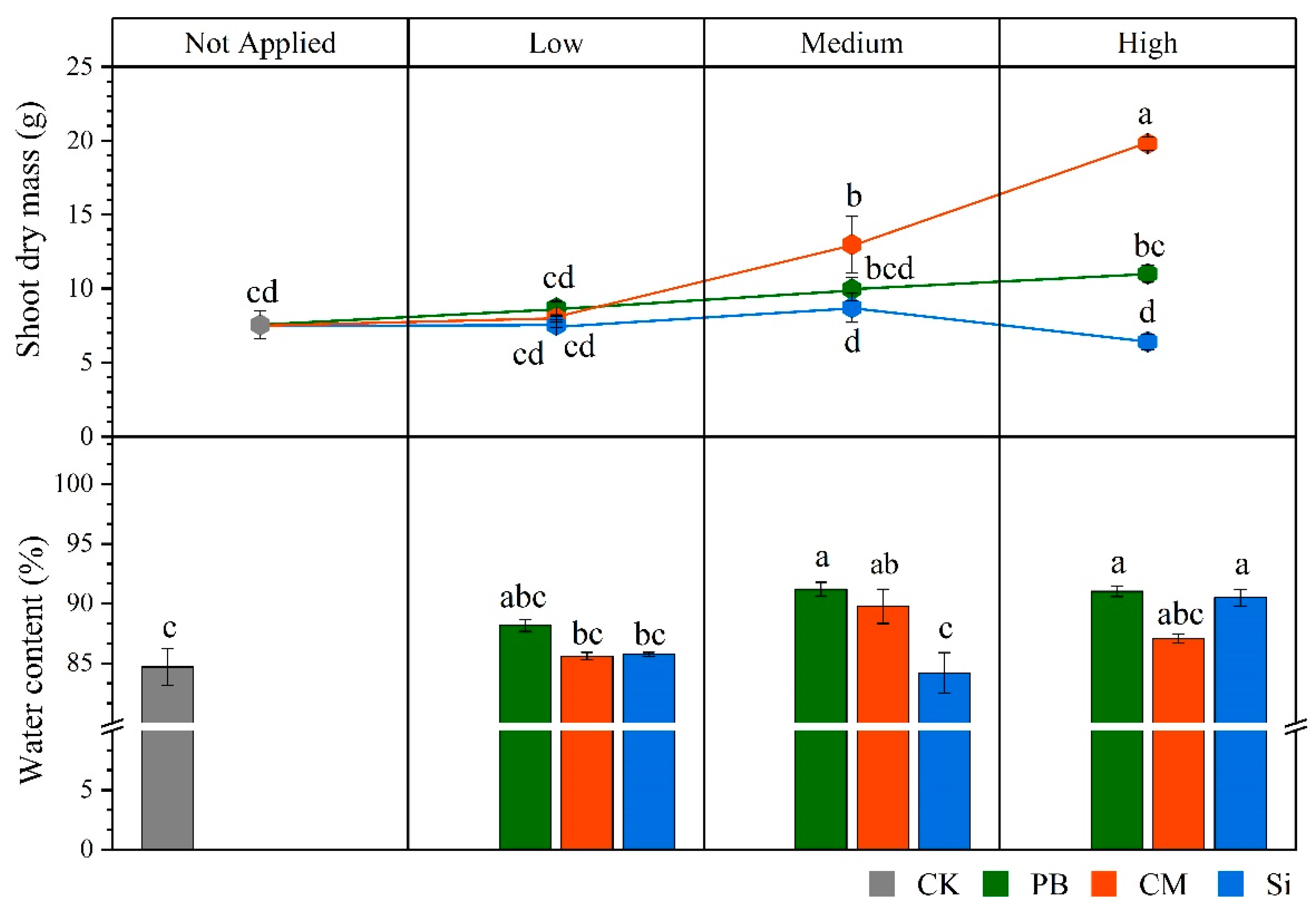
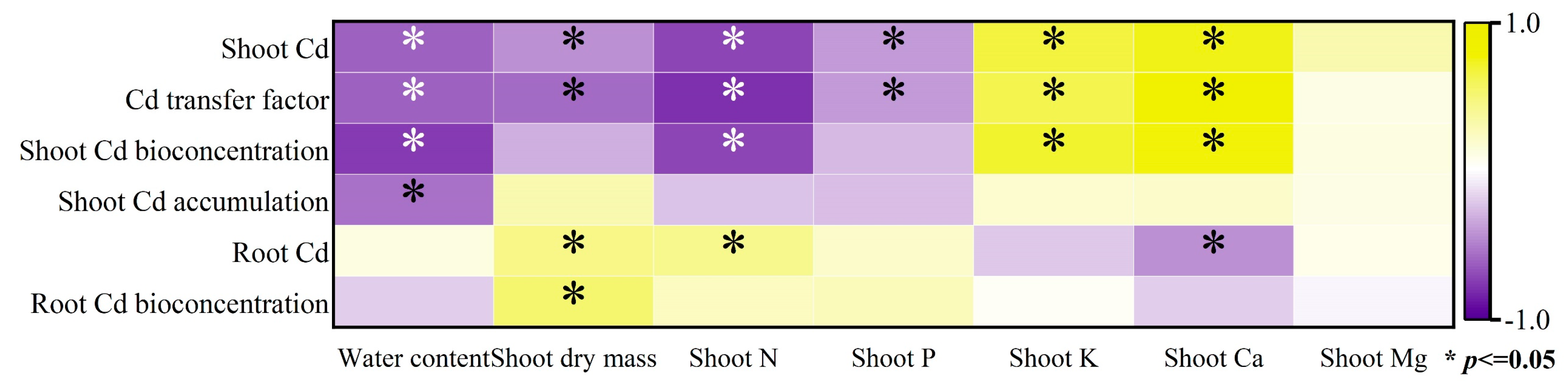
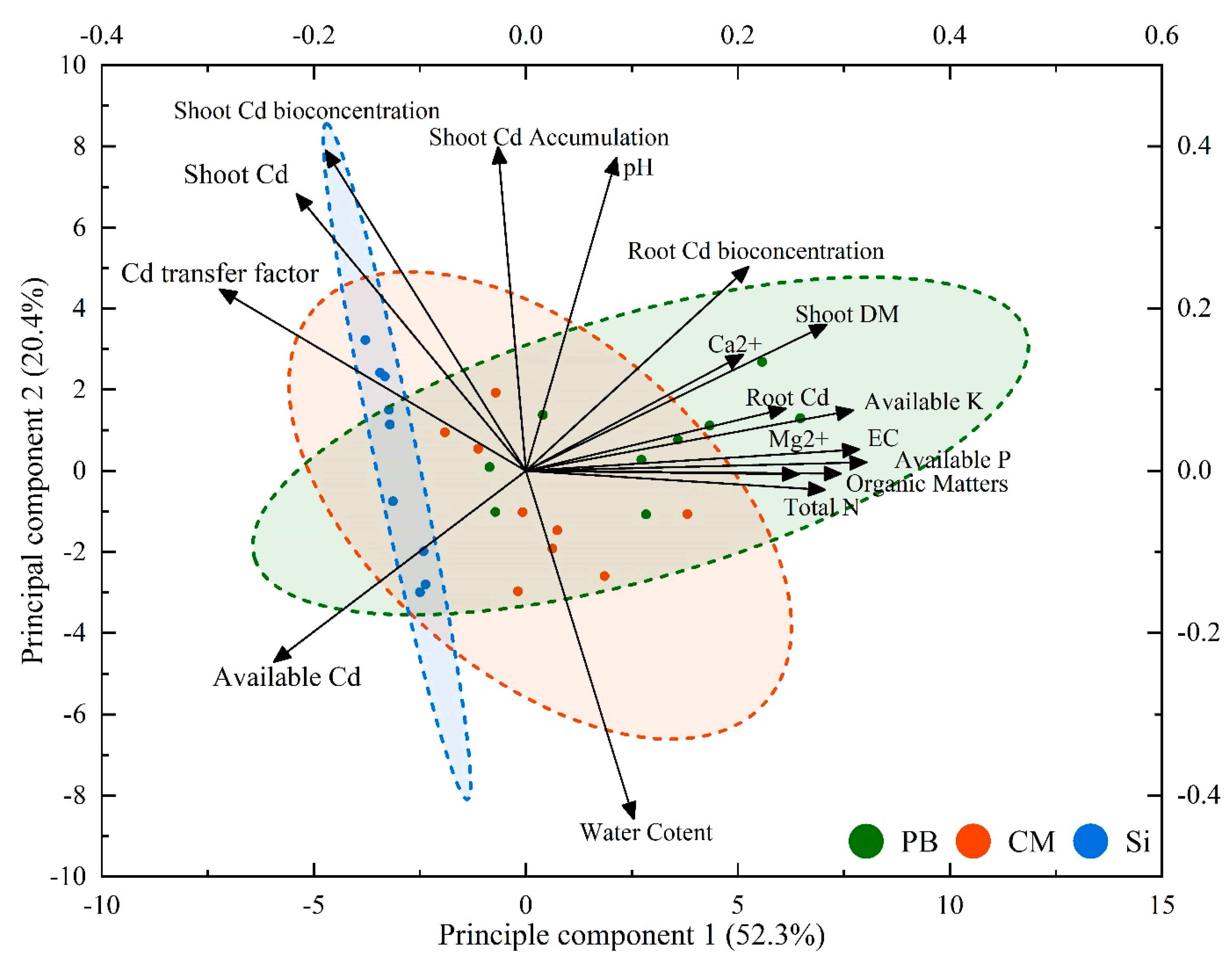
| Cd Transfer Factor | Shoot Cd Accumulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot Cd/Root Cd | mg | ||
| CK | 0 | 1.31 ± 0.11 ab | 29.47 ± 5.99 a |
| PB | L | 1.10 ± 0.09 abc | 27.06 ± 2.84 a |
| M | 0.80 ± 0.07 cd | 20.81 ± 3.11 a | |
| H | 0.63 ± 0.10 d | 18.88 ± 2.82 a | |
| CM | L | 0.89 ± 0.10 bcd | 19.01 ± 1.41 a |
| M | 0.58 ± 0.08 d | 25.69 ± 2.86 a | |
| H | 0.55 ± 0.06 d | 34.04 ± 3.31 a | |
| Si | L | 1.53 ± 0.08 a | 32.88 ± 1.56 a |
| M | 1.45 ± 0.11 a | 31.48 ± 3.67 a | |
| H | 0.95 ± 0.03 bcd | 26.82 ± 1.00 a |
| N | P | K | Ca | Mg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||
| CK | 0 | 13.03 ± 1.21 d | 23.90 ± 1.85 b | 2.95 ± 0.23 ab | 119.69 ± 10.19 a | 96.66 ± 12.44 a |
| PB | L | 14.38 ± 0.31 cd | 75.43 ± 3.95 ab | 3.03 ± 0.20 ab | 103.51 ± 15.10 abc | 31.09 ± 0.91 b |
| M | 27.58 ± 0.78 ab | 72.03 ± 16.30 ab | 1.99 ± 0.11 c | 65.56 ± 6.49 cd | 43.39 ± 2.28 b | |
| H | 26.31 ± 2.27 ab | 112.87 ± 13.43 a | 2.31 ± 0.04 bc | 71.57 ± 1.90 bcd | 30.80 ± 1.57 b | |
| CM | L | 13.40 ± 0.03 d | 85.50 ± 17.43 ab | 3.41 ± 0.09 a | 105.79 ± 8.67 ab | 20.85 ± 3.48 b |
| M | 30.19 ± 2.28 a | 99.27 ± 9.05 a | 1.94 ± 0.28 c | 46.46 ± 6.17 d | 32.84 ± 4.59 b | |
| H | 28.28 ± 0.17 ab | 64.33 ± 12.31 a | 1.98 ± 0.04 c | 35.23 ± 2.29 d | 52.76 ± 4.99 b | |
| Si | L | 13.2 ± 0.13 d | 57.7 ± 10.80 ab | 3.03 ± 0.15 ab | 127 ± 3.16 a | 34.7 ± 5.29 b |
| M | 13.1 ± 0.83 d | 69.3 ± 3.74 ab | 2.93 ± 0.24 ab | 127 ± 3.53 a | 31.6 ± 2.83 b | |
| H | 21.8 ± 3.48 bc | 56.3 ± 12.75 ab | 1.97 ± 0.19 c | 73.0 ± 9.34 bcd | 45.5 ± 12.71 b |
| pH | EC | Organic Matters | Total N | Soil TCd | AP | AK | ACd | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μs cm−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | |||
| CK | 0 | 8.31 ± 0.06 a | 243 ± 4 d | 18.23 ± 0.42 b | 1.12 ± 0.01 c | 1.91 ± 0.04 ab | 9.00 ± 0.12 f | 161 ± 3 e | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 6.49 ± 0.68 a | 1.03 ± 0.09 abc |
| PB | L | 7.99 ± 0.06 bc | 246 ± 3 cd | 19.92 ± 0.66 b | 1.21 ± 0.01 bc | 1.92 ± 0.06 ab | 15.10 ± 0.27 f | 172 ± 7 e | 0.92 ± 0.00 a | 5.96 ± 0.08 a | 1.03 ± 0.05 ab |
| M | 7.61 ± 0.05 de | 283 ± 3 bc | 21.98 ± 0.11 ab | 1.35 ± 0.03 abc | 1.98 ± 0.02 ab | 40.01 ± 2.60 d | 216 ± 7 de | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 5.65 ± 0.02 a | 1.15 ± 0.03 a | |
| H | 7.81 ± 0.02 bc | 287 ± 2 bc | 34.60 ± 8.71 a | 1.88 ± 0.41 a | 1.82 ± 0.05 b | 57.30 ± 2.12 c | 285 ± 33 bc | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 5.79 ± 0.26 a | 1.20 ± 0.09 a | |
| CM | L | 8.01 ± 0.04 c | 246 ± 38 cd | 21.47 ± 0.41 ab | 1.32 ± 0.03 abc | 1.93 ± 0.02 ab | 29.40 ± 0.91 e | 246 ± 15 cd | 0.92 ± 0.01 a | 5.50 ± 0.08 a | 1.08 ± 0.04 a |
| M | 7.83 ± 0.03 cd | 294 ± 5 b | 26.06 ± 0.85 ab | 1.61 ± 0.04 abc | 1.95 ± 0.09 ab | 68.00 ± 3.03 b | 337 ± 9 b | 0.87 ± 0.00 b | 5.89 ± 0.26 a | 1.35 ± 0.07 a | |
| H | 8.01 ± 0.04 c | 383 ± 18 a | 31.98 ± 0.20 ab | 1.81 ± 0.07 ab | 1.87 ± 0.02 ab | 97.60 ± 0.91 a | 448 ± 3 a | 0.86 ± 0.01 b | 6.72 ± 0.62 a | 1.42 ± 0.23 a | |
| L | 7.89 ± 0.04 bc | 200 ± 8 e | 18.90 ± 0.43 b | 1.07 ± 0.01 c | 2.03 ± 0.05 ab | 10.00 ± 1.29 f | 190 ± 15 de | 0.92 ± 0.00 a | 5.65 ± 0.47 a | 0.58 ± 0.01 d | |
| Si | M | 7.85 ± 0.02 bc | 188 ± 12 e | 18.80 ± 0.44 b | 1.07 ± 0.01 c | 1.95 ± 0.05 ab | 9.96 ± 0.87 f | 176 ± 6 e | 0.93 ± 0.03 a | 5.44 ± 0.06 a | 0.58 ± 0.01 cd |
| H | 7.51 ± 0.02 e | 215 ± 5 de | 18.10 ± 0.22 b | 1.10 ± 0.01 c | 2.08 ± 0.06 a | 11.50 ± 2.27 f | 184 ± 4 de | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 5.51 ± 0.10 a | 0.58 ± 0.00 bcd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Xu, X.; Lang, Q.; Liao, S.; Li, Y. Three Different Fertilizers Enhance Spinach Growth and Reduce Spinach Cd Concentration in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040445
Pan Y, Xu X, Lang Q, Liao S, Li Y. Three Different Fertilizers Enhance Spinach Growth and Reduce Spinach Cd Concentration in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(4):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040445
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yingjie, Xiangnan Xu, Qianqian Lang, Shangqiang Liao, and Yanmei Li. 2023. "Three Different Fertilizers Enhance Spinach Growth and Reduce Spinach Cd Concentration in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil" Horticulturae 9, no. 4: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040445
APA StylePan, Y., Xu, X., Lang, Q., Liao, S., & Li, Y. (2023). Three Different Fertilizers Enhance Spinach Growth and Reduce Spinach Cd Concentration in Cd Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae, 9(4), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040445







