Abstract
Panax ginseng Meyer is an important medicinal crop; however, most ginseng farmers cultivate native species that are not genetically fixed. Although several cultivars have been developed in Korea, distribution to farmers remains insufficient given their low propagation characteristics. This study compared the efficiency of seed production and micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis. Seeds were collected from cultivars, and zygotic embryo-derived explants were inoculated and cultured in a series of media for micropropagation. Seed production and characteristics of commercial cultivars were evaluated. The number of seeds from a 4-year-old individual cultivar was 23.1–58.8, and seed characteristics varied with cultivars. The genotype had a notable effect on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration. The number of somatic embryos and shoots obtained from a single seed of cultivars was 71.3–100.2 and 50.7–61.3, respectively. The number of in vitro grown roots (IGRs) per a single seed was 37.1–41.1 in one year. IGRs were successfully acclimatized and sprouted normally in the field. Flow cytometry analysis suggested that micropropagated plants had no ploidy variations. The results demonstrated the utility of somatic embryogenesis in the in vitro micropropagation of P. ginseng cultivars. Our findings can enhance the distribution of cultivars among farmers in the future.
1. Introduction
Panax ginseng Meyer is an important medicinal crop native to the Korean Peninsula and Manchuria [1]. The agronomic importance of this crop is primarily attributed to its root, which is a rich source of ginsenosides that possess a wide range of therapeutics [2]. In the Republic of Korea, the cultivation of ginseng began in earnest as a cash crop in the early 1900s, although the cultivation of ginseng has been around for thousands of years [3].
The high demand for ginseng roots coupled with climate change increases the need to develop new cultivars that are both resistant to abiotic stress and possess high-yield roots [4]. Several cultivars, including cv. Chunpoong, Yunpoong, Gumpoong, and Cheonryang, were developed in the Republic of Korea. Chunpoong was the first registered cultivar in Korea because of its good root shape [5]. Yunpoong is characterized by a high yield but has a poor root shape [6]. Gumpoong is a yellow-fruited cultivar with a good yield and root shape [7]. Cheonryang, a recently registered cultivar, exhibits a high yield and good root shape along with salt tolerance [8]. However, most ginseng farmers have cultivated native species that are not genetically fixed, leading to non-uniform quality and low productivity.
P. ginseng cannot be vegetatively reproduced; therefore, seeds are the only method of propagation. P. ginseng self-fertilizes and requires more than three years to produce dozens of seeds and, thus, has a low reproductive efficiency [9]. For this reason, although developed ginseng cultivars have many advantages over native species, they have not been widely distributed to farmers. Since the efficiency of P. ginseng seed production varies depending on the genotype [10], cultivars with low propagation efficiency take longer to reproduce, requiring new approaches. In vitro regeneration technology is an alternative approach for the large-scale propagation of many plant species over a short period [11]. Somatic embryogenesis is the process by which a somatic cell undergoes dedifferentiation to become a totipotent embryonic stem cell capable of developing an embryo in vitro [12]. Because of the high number of regenerants and low frequency of somaclonal variation, direct somatic embryogenesis is preferred over other in vitro techniques [13]. For example, micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) was reported by Zhou and Brown [14], who observed that approximately 310 plants could be produced from a single seed in about 31 weeks. In addition, somatic embryogenesis can be used as a model to study the early developments of zygotic embryos in higher plants, because its stages are comparable to those of zygotic embryogenesis [12]. Genotype is a major factor that considerably affects somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration [15]. Although somatic embryogenesis of P. ginseng has been reported in two cultivars, Chunpoong and Yunpoong [16], the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis and regeneration by cultivars has not been clarified.
This present study aims to improve the propagation efficiency of P. ginseng cultivars. First, each cultivar’s efficiency for conventional seed propagation was evaluated and compared. Furthermore, the efficiency of micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis of each cultivar was evaluated and compared with seed propagation. In vitro grown roots (IGRs) derived from somatic embryogenesis were successfully acclimated and transferred to the field. The ploidy level of the micropropagated plants was validated using flow cytometry. Our findings revealed that micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis is a more reliable and valuable method for the propagation of P. ginseng cultivars than traditional seed propagation.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
P. ginseng plants were grown under semi-shade conditions for 4 years in the fields of the National Institute of Horticultural and Herbal Science, Rural Development Administration, Eumseong, Republic of Korea, which is located at 36°94′17″ N, 127°74′85″ E. The fruits of four commercial cultivars, namely Chunpoong, Cheonryang, Gumpoong, and Yunpoong, were harvested simultaneously in late July when they were fully mature. Fruits were obtained from 10 individuals randomly selected for each cultivar; this process was repeated three times. Photographs were taken if necessary.
2.2. Seed Production and Characteristics
After harvesting the fruits, the mean number of fruits per individual plant and the mean weight of the individual fruits were recorded. Then, the sarcocarp was removed from the fruit, and the mean number of seeds per individual plant was recorded. The weight, thickness, diameter, and length of each seed was measured before and after warm stratification (dehiscence) for 90 d using the method described in previous studies [9,17].
2.3. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration
Seed disinfection was performed as previously described [18]. Zygotic embryos were isolated from the endosperm in a clean bench. The cotyledons from zygotic embryos were used as the explants. The top and bottom portions of the cotyledon were cut, yielding 4–6 explants per each single seed. All media and reagents used in this study were purchased from Duchefa Biochemie, Haarlem, The Netherlands. Cotyledon-derived explants were inoculated into an induction medium consisting of a Murashige and Skoog (MS) [19] medium, 5% sucrose, and 0.8% agar at a pH of 5.7 and maintained without a subculture. After 60 d of culturing, data on the somatic embryo induction rate and the number of somatic embryos were recorded. The induced somatic embryos were transferred to the maturation media containing 1/3 MS, 2% sucrose, and 0.8% agar at a pH of 5.7 for 30 d. Mature embryos were germinated as previously described by Kim et al. [20]. The number of shoots per a single seed and the shoot conversion rate (the mean number of shoots/the mean number of somatic embryos × 100) were investigated after 30 days of being transferred to the germination medium. Shoots separated from explants were placed in an elongation medium (1/2 Schenk and Hildebrandt medium [21], 2% sucrose, and 0.9% agar; pH 5.7) to induce root and plantlet development. After culturing for 4 months without a subculture, the leaves of the plantlets senesced, and the IGRs that were usable for acclimatization were formed. The number of IGRs and their conversion rates (mean number of IGRs/mean number of somatic embryos × 100) were recorded.
2.4. Acclimatization
One thousand and two hundred IGRs, derived from the micropropagation of cv. Cheonryang, were treated with 25 mg/L of gibberellic acid (GA3) and transferred to soil in a greenhouse maintained at approximately 25 °C. The sprouting rate (number of sprouted plants/number of transplanted IGRs × 100) was observed one month after transplantation. After several months of cultivation, the leaves became senescent, and the acclimated 2-year-old IGRs were harvested. The 2-year-old IGRs were stored for several months in a refrigerator maintained at 2 °C to break dormancy. In mid-April, when the average daily temperature was 15 °C, they were transplanted to a location (36°94′08″ N, 127°75′05″ E) next to the field where the fruits were harvested. The transplanted 2-year-old IGRs were maintained in semi-shade conditions in accordance with general ginseng cultivation.
2.5. Ploidy Level Analysis
Flow cytometry was used to determine sample ploidy. Briefly, 10 fully expanded fresh leaves from both regenerated and control plants (1-year-old ginseng plants derived from seed) of cv. Cheonryang were excised and cut into segments in 500 μL of CyStain UV precise P (Sysmex Partec, Görlitz, Germany). The liquid was caught on a nylon mesh (50 μm) to remove debris. The ploidy was determined by checking the fluorescence intensity of the regenerated plants compared to the control.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using the R program (R version 4.0.3, The R foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). When a difference among the treatments was found by performing an analysis of variance (ANOVA), a post hoc test was performed at the 5% significance level (p ≤ 0.05) with the Duncan Multiple Range Test (DMRT).
3. Results
3.1. Seed Production and Characteristics
The characteristics of the fruits were investigated (Figure 1 and Table 1). The maximum mean number of fruits was observed in Gumpoong (38.8) and Yunpoong (37.6), followed by Chunpoong (32.2) and Cheonryang (16.5) (Table 1). The maximum fruit weight was observed in Cheonryang and the minimum in Chunpoong. The maximum mean number of seeds was observed in Gumpoong (58.8) and Yunpoong (53.4), followed by Chunpoong (45.8) and Cheonryang (23.1).
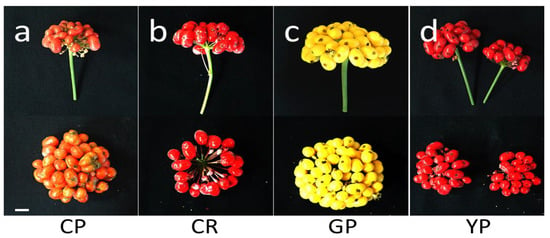
Figure 1.
Fruit characteristics of P. ginseng depending on the cultivar. The fruits of the cultivar were harvested from 4-year-old ginseng. Immediately after harvesting, the characteristics of each cultivar regarding the mean number and weight of fruits and indehiscent seeds were investigated. (a) Chunpoong, (b) Cheonryang, (c) Gumpoong, and (d) Yunpoong. Scale bars, 1 cm. CP, Chunpoong; CR, Cheonryang; GP, Gumpoong; YP, Yunpoong.

Table 1.
Fruit and seed production depending on the cultivar of P. ginseng.
After the sarcocarp was removed, the characteristics of the indehiscent seeds were evaluated (Table 2 and Figure 2). The weight of the indehiscent seeds was the highest in Cheonryang, followed by Yunpoong, Gumpoong, and Chunpoong. The indehiscent seeds were thicker in Cheonryang and Yunpoong than in the other cultivars. The length and width of the indehiscent seeds were the largest in Cheonryang.

Table 2.
Characteristics of indehiscent seeds depending on the cultivar of P. ginseng.
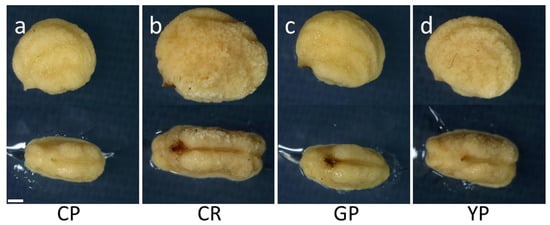
Figure 2.
Morphological characteristics of indehiscent seeds depending on P. ginseng cultivar. Indehiscent seeds were obtained by removing the sarcocarp from the fruit for each cultivar. The seeds were evaluated for main characteristics, including weight, length, and diameter. (a) Chunpoong, (b) Cheonryang, (c) Gumpoong, and (d) Yunpoong. Scale bars, 1 mm. CP, Chunpoong; CR, Cheonryang; GP, Gumpoong; YP, Yunpoong.
After the stratification treatment, the characteristics of the dehiscent seeds were monitored (Table 3 and Figure 3). Similar to before the stratification, the weight of the dehiscent seeds was the highest in Cheonryang. The diameters of the dehiscent seeds of Cheonryang and Yunpoong were thicker than those of the other cultivars. The greatest length and width of the dehiscent seeds were observed in Cheonryang.

Table 3.
Characteristics of dehiscent seeds depending on the cultivar of P. ginseng after stratification treatment for 90 days.
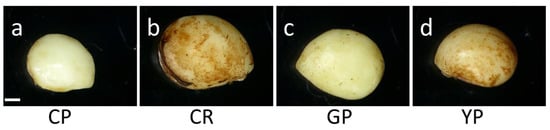
Figure 3.
Morphological characteristics of dehiscent seeds depending on the cultivar of P. ginseng. After the stratification treatment for 90 days, the dehiscent seeds removed the seed coat. The seeds were evaluated for main characteristics, including weight, length, and diameter. (a) Chunpoong, (b) Cheonryang, (c) Gumpoong, and (d) Yunpoong. Scale bars, 1 mm. CP, Chunpoong; CR, Cheonryang; GP, Gumpoong; YP, Yunpoong.
3.2. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration
The efficiency of somatic embryogenesis was evaluated in each cultivar. Successful somatic embryogenesis was observed in all four cultivars (Table 4 and Figure 4). There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in somatic embryo induction rate; however, the number of somatic embryos was different among cultivars. The maximum mean number of somatic embryos per explant was obtained in Cheonryang (14.4). The mean number of somatic embryos per a single seed was also the highest in Cheonryang (100.2), followed by Gumpoong (76.9), Chunpoong (76.4), and, finally, Yunpoong (71.3). No significant differences (p > 0.05) were observed among the cultivars, except for Cheonryang.

Table 4.
Influence of cultivars on somatic embryogenesis of P. ginseng.
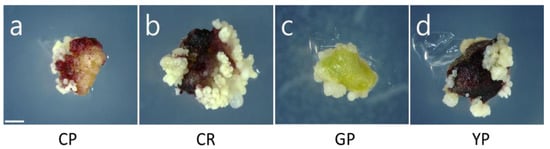
Figure 4.
Morphological characteristics of explants containing somatic embryos depending on the cultivar of P. ginseng. Photographs were taken 60 days after culturing in the induction media. (a) Chunpoong, (b) Cheonryang, (c) Gumpoong, and (d) Yunpoong. Scale bars, 1 mm. CP, Chunpoong CR, Cheonryang GP, Gumpoong YP, Yunpoong.
The mean number of regenerated shoots was examined 30 d after inoculation in the germination medium (Figure 5 and Table 5). Cheonryang (61.3) formed the most shoots, followed by Gumpoong (57.1), Yunpoong (52.0), and Chunpoong (50.7). However, no significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed in the shoot conversion rate for the cultivars.
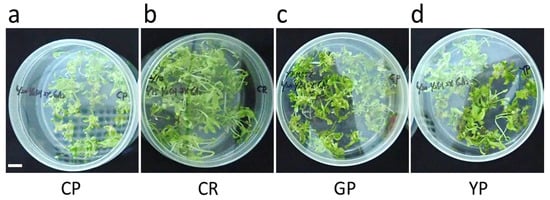
Figure 5.
Shoot regeneration in different P. ginseng cultivars. (a) Chunpoong, (b) Cheonryang, (c) Gumpoong, and (d) Yunpoong. Scale bars, 1 cm. CP, Chunpoong; CR, Cheonryang; GP, Gumpoong; YP, Yunpoong.

Table 5.
Influence of cultivars on shoot regeneration of P. ginseng.
3.3. Acclimatization and Ploidy Level Analysis
After culturing in the elongation media for 4 months, IGRs were formed, and their numbers were investigated. The maximum mean number of IGRs per a single seed was observed in Cheonryang (41.0) and Gumpoong (41.1), but no significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed from the other cultivars (Table 6). In addition, there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the IGR conversion rate.

Table 6.
Influence of cultivar on in vitro grown root (IGR) formation in P. ginseng.
The harvested IGRs were treated with GA3 and transferred to the soil (Figure 6a). Of the 1200 IGRs transplanted, 1055 of them sprouted one month after acclimatization, and the sprouting rate was 87.9% (Table 7 and Figure 6b). After 5 months of cultivation, 2-year-old IGRs were harvested (Figure 6c). However, the aerial and underground parts derived from IGRs are morphologically different from those obtained from conventional ginseng derived from seeds. With or without acclimatization, IGRs were composed of short, thickened taproots with several lateral roots (Figure 6a,c). In addition, the sprouted IGRs formed multiple leaflets (Figure 6b). After breaking dormancy by keeping 2-year-old IGRs in cold storage for several months, they were transplanted into the field. The transplanted 2-year-old IGRs sprouted successfully in the field (Figure 6d).
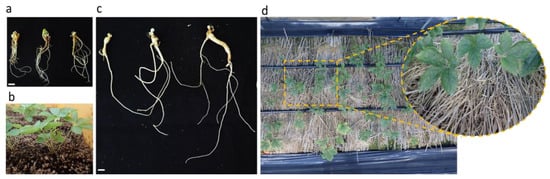
Figure 6.
Acclimatization of in vitro grown roots (IGRs) in P. ginseng cv. Cheonryang. (a) IGRs before soil transfer, (b) Sprouted IGRs in a greenhouse, (c) Harvested 2-year-old IGRs after acclimatization for several months, (d) Transplantation of 2-year-old IGRs into the field. Scale bars, 1 cm. IGR, in vitro grown root.

Table 7.
Sprouting rate after acclimatization of IGRs derived from micropropagation of P. ginseng cv. Cheonryang.
The ploidy stability of the regenerated plants derived from the IGRs were assessed using flow cytometry analysis. The histogram resulting from the flow cytometry analysis showed a similar peak at channel 400 between regenerated plants and controls (Figure 7a,b). The results revealed that the ploidy level of the regenerated plants was the same as that of the control.
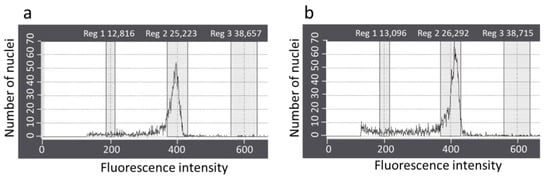
Figure 7.
Flow cytometry analysis of the regenerated plants derived from IRGs and control of P. ginseng cv. Cheonryang. Histogram fluorescence intensity documenting the relative DNA content of the nuclear suspension from young roots of (a) regenerated plant and (b) control derived from seed. IGR, in vitro grown root.
4. Discussion
Although many medicinal plants can be propagated by asexual reproduction [22], successful vegetative propagation has not yet been reported in P. ginseng. Therefore, P. ginseng is propagated by seeds through sexual reproduction. Ginseng seeds have been mainly studied for their germination [9,23], dormancy breaking [24], and dehiscence processes [25,26]. A previous study reported that the Gumpoong cultivar produces more seeds than other cultivars, such as Yunpoong and Chunpoong [10]. However, there have been no studies on the seed production of the cv. Cheonryang or on the seed characteristics of the cultivars of P. ginseng. In this present study, 4-year-old P. ginseng cultivars were able to produce 16.5–38.8 fruits and 23.1–58.8 seeds per individual plant (Table 1 and Figure 1). The difference between the number of fruits and the number of seeds depends on the number of seeds per fruit. Kim et al. [10] reported that one or two seeds are generally formed in the fruits of P. ginseng. Compared to that of other cultivars, the seed propagation of Cheonryang was relatively lower, whereas the seed size was significantly larger than that of the other cultivars (Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 2 and Figure 3). These results suggest that the distribution of Cheonryang to farmers takes longer than that of other cultivars, and alternative propagation methods, such as in vitro micropropagation, should be established.
Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis is a valuable means of propagating large-scale clones from many crops in a short time [14,27]. The tissue culture studied of P. ginseng so far has only been studied up to the production of the somatic embryos and regenerated plants [16,20,28,29], and it has not been demonstrated how many plants can be produced from a single seed.
A number of studies have indicated that the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis and regeneration is greatly influenced by genotype [15,30]. In the present study, the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis was evaluated for each cultivar. The results showed that successful somatic embryo induction was achieved in all cultivars, and there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in the induction rate by cultivars (Table 4). Cheonryang had the highest number of somatic embryos (100.2) from a single seed. Other cultivars also showed high somatic embryo formation (71.3–76.9), although not as high as Cheonryang. Given that Cheonryang has a low efficiency of seed production, our results suggest that somatic embryogenesis may be a viable alternative for the large-scale propagation of this cultivar. Research on the somatic embryogenesis of P. ginseng cultivars has been rarely conducted, and the only report so far published is that of Kim et al. [16], according to which somatic embryogenesis was induced in Chunpoong and Yunpoong. However, in this present study, we provided information on the somatic embryogenesis of Cheonryang and Gunpoong as well as these cultivars. A comparison of somatic embryogenesis among the Panax genus was performed by Kim et al. [31], who reported that interspecific hybrids resulting from crossing P. ginseng and P. quinquefolius have a higher efficiency of somatic embryogenesis than their parents.
In vitro shoot regeneration may be the most important factor for the success of micropropagation. The low conversion rate of somatic embryos to plants has become a limiting factor for the practical use of micropropagation in many crops [32]. Several studies have reported that genotype significantly influences shoot and plant regeneration [33,34]. In this study, 50.7–61.3 shoots per a single seed were regenerated from somatic embryos, and the highest mean number of shoots was observed in Cheonryang (Table 5). The conversion of somatic embryos to shoots was 61.4–75.4%, and there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) among cultivars. Failure to convert some embryos into shoots is closely related to the formation of abnormal somatic embryos [35]. Abnormalities in somatic embryos have previously been reported in P. ginseng [28]. Wetzstein and Baker [36] pointed out that the weak development of the shoot meristem is the cause of the low conversion rate. Future studies should focus on improving the conversion rate of somatic embryos into plants. Furthermore, research on the recycling of abnormal somatic embryos via secondary somatic embryogenesis is required.
Micropropagation through plant tissue culture is difficult to apply at a commercial level because of the low survival rate after acclimatization of regenerated plants [36]. IGRs are known as a new type of micropropagation for the successful acclimatization of P. ginseng [18,20]. In this study, the number and conversion rates of IGRs were investigated by cultivars. The cultivars formed 37.1–41.1 IGRs per a single seed, with a conversion rate range of 41.6–58.7% (Table 5). There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between cultivars. Some studies have indicated that root formation of the Panax genus under in vitro conditions is a recalcitrant process [14,28]. Similar to previous findings, in this study, regenerated plants did not form roots as desired. Supplementation with auxin hormones, such as indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), could improve in vitro rooting [14,29], and it seems necessary to apply them to future research.
A high sprouting rate (87.9%) was observed after IGRs were transferred to the soil (Figure 6 and Table 7). Similar results reported that the sprouting rate increased when transferred to soil with an IGR type than with whole plants [20]. However, the shoot and root derived from IGRs are morphologically different from those obtained from conventional ginseng (Figure 6). Lee et al. [18] revealed that such differences are only morphological changes caused by the in vitro environment, and there are no genetic differences. Similarly, the flow cytometry results revealed that there were no differences in the genome size of both regenerated plants and controls (Figure 7). Flow cytometry is a valuable instrument for polyploid determination because of its fast speed and accuracy [27]. Ploidy assessment of micropropagated plants was reported in other species, such as Allium sativum [37] and Zepheranthes spp [38]. Future studies should investigate whether the transplanted IGRs can produce seeds normally as well as the genetic stability of seeds produced from IGRs.
5. Conclusions
A general P. ginseng plant derived from seeds can produce between 23.1–58.8 seeds per individual plant in 4 years, whereas micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis can produce between 37.1–41.1 IGRs per a single seed in 1 year. Thus, the time period of more than 3 years to propagate the same clone was shortened. In particular, the improvement in propagation efficiency by in vitro plant regeneration was greater in cultivars with a small number of seeds, such as Cheonryang. The micropropagation method developed in this present study could produce approximately 40 IGRs from a single seed of Cheonryang in 1 year, with an expected yield of at least 800 seeds in 4 years. The results of flow cytometry indicated that no genetic abnormalities, such as aneuploidy and polyploidy, occurred during the somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration. This present study demonstrated that micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis is highly stable and valuable for commercial cultivar propagation of P. ginseng, especially for cultivars with low seed production. Our results revealed that micropropagation via somatic embryogenesis makes it possible to quickly mass-produce the cultivar, which could increase the spread of cultivars among farmers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-W.L. and Y.-D.P.; Data curation, J.-W.L.; Formal analysis, J.-W.L., N.K., I.-H.J. and K.-H.B.; Investigation, J.-W.L., N.K., S.M.J. and S.W.L.; Methodology, J.-W.L.; Resources, J.-W.L., D.-H.K., Y.-C.K. and J.-U.K.; Software, J.-W.L.; Validation, J.-W.L., J.-U.K. and K.-H.B.; Writing—original draft, J.-W.L.; Writing—review and editing, J.-W.L. and Y.-D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ01426502) of the Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L. Ancient herbal therapy: A brief history of Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, R.; Roy, A.; Pandit, S.; Prasad, R. Biotechnological methods for the production of ginsenosides. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 141, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Jeong, B.R. In vitro cultivation of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Indus. Crop. Prod. 2018, 122, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Abid, S.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Panax ginseng Cultivars in Korea and China. Molecules 2020, 25, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.G.; Choi, K.T. Red ginseng quality and characteristics of KG101 a promising line of Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 1998, 22, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, W.S.; Lee, M.G.; Choi, K.T. Breeding process and characteristics of Yunpoong, a new variety of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Ginseng Res. 2000, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kwon, W.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; In, J.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Seo, J.; Baeg, I.H.; Chang, I.M.; et al. Characteristics of Korean ginseng varieties of Gumpoong, Sunun, Sunpoong, Sunone, Cheongsun, and Sunhyang. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Bang, K.H.; Kim, J.U.; Hyun, D.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Kang, S.W.; Cha, S.W.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, J.K.; et al. A high yielding and salt resistance ginseng variety ‘Cheonryang’. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2013, 45, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Jo, I.H.; Kim, J.U.; Hong, C.E.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.D. Improvement of seed dehiscence and germination in ginseng by stratification, gibberellin, and/or kinetin treatments. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2018, 59, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Bang, K.H.; Kim, J.U.; Lee, J.W.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, K.H. Flowering and fruits formation characteristics in major varieties of Panax ginseng. Korean Soc. Med. Crop. Sci. 2016, 24, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufan, M.; Belkoura, I.; Mazri, M.A. In vitro propagation of caper (Capparis spinosa L.): A review. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, S.G.; Fan, X.F.; Su, Z.H. Application of somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, M.D. Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2001, 64, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Brown, D.C.W. High efficiency plant production of North American ginseng via somatic embryogenesis from cotyledon explants. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, G.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from commercial soybean cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.K.; Shim, J.S.; Pulla, R.K.; Yang, D.C. Somatic embryogenesis of two new Panax ginseng cultivars, Yun-Poong and Chun-Poong. Russ J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 57, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jo, I.; Hong, C.; Bang, K.; Kim, J. Effect of gamma-irradiation on seed dehiscence, development, survival, and growth in Panax ginseng. Korean J. Breed. Sci. 2020, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Do, G.R.; Jo, I.H.; Hong, C.E.; Bang, K.H.; Kim, J.U.; Park, Y.D. Zygotic embryo culture is an efficient way to optimize in vitro growth in Panax ginseng. Indus. Crop. Prod. 2021, 167, 1134971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, K.H.; Han, J.Y.; Choi, Y.E. In vitro grown thickened taproots, a new type of soil transplanting source in Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, R.U.; Hildebrandt, A.C. Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 1972, 50, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, N.; Manifestod, M.M.; Fortunato, R.H. Vegetative propagation and proposal for sustainable management of Valeriana carnosa Sm., a traditional medicinal plant from Patagonia. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants. 2019, 14, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Balaraju, K.; Mok, Y.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Jeon, Y. Enhancement of seed germination and microbial disinfection on ginseng by cold plasma treatment. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J.U.; Jo, I.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.H. Effects of gibberellic acid and alternating temperature on breaking seed dormancy of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Korean Soc. Med. Crop. Sci. 2016, 24, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.E.; Long, N.P.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Anh, N.H.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, S.J. The dehiscence process in Panax ginseng seeds and the stigmasterol biosynthesis pathway in terms of metabolomics. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Shim, C.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Hong, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Han, E.J.; Kim, S.C. Enhancement of Seed Dehiscence by Seed Treatment with Talaromyces flavus GG01 and GG04 in ginseng (Panax ginseng). Plant Pathol. J. 2017, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, D.; Mariz-Ponte, N.; Loureiro, J.; Castro, S.; Debiasi, C.; Domingues, J.; Santos, C.; Gonçalves, J.C. A protocol for micropropagation of the medicinal species Tuberaria lignosa provides ploidy true-to-type plants with high antioxidant capacity. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2022, 150, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.E.; Yang, D.C.; Park, J.C.; Soh, W.Y.; Choi, K.T. Regenerative ability of somatic single and multiple embryos from cotyledons of Korean ginseng on hormone-free medium. Plant Cell Rep. 1998, 17, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.E.; Yang, D.C.; Yoon, E.S.; Choi, K.T. Plant regeneration via adventitious bud formation from cotyledon explants of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Plant Cell Rep. 1998, 17, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.; Luis, Z.G.; Scherwinski-Pereira, J.E. Differential responses to somatic embryogenesis of different genotypes of Brazilian oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2012, 111, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Adhikari, P.B.; Ahn, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Chang Kim, Y.C.; Han, J.Y.; Kondeti, S.; Choi, Y.E. High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of interspecific ginseng hybrid between Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, T.; Corredoira, E.; Valladares, S.; Jorquera, L.; Vieitez, A.M. Germination and conversion of somatic embryos derived from mature Quercus robur trees: The effects of cold storage and thidiazuron. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2008, 95, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, G.D.; Ernst, S.G. In vitro shoot regeneration of Populus deltoides: Effect of cytokinin and genotype. Plant Cell Rep. 1989, 8, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, P.; Ashwath, N.; Midmore, D.J. Effects of genotype, explant orientation, and wounding on shoot regeneration in tomato. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol-Plant. 2005, 41, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griga, M. Direct somatic embryogenesis from shoot apical meristems of pea, and thidiazuron-induced high conversion rate of somatic embryos. Biol. Plant. 1998, 41, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzstein, H.Y.; Baker, C.M. The relationship between somatic embryo morphology and conversion in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Sci. 1993, 92, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.Q.; Mujib, A.; Gulzar, B.; Zafar, N.; Syeed, R.; Mamgain, J.; Ejaz, B. Genome size analysis of field grown and somatic embryo regenerated plants in Allium sativum L. J. Appl. Genet. 2020, 61, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeed, R.; Mujib, A.; Malik, M.Q.; Mamgain, J.; Ejaz, B.; Gulzar, B.; Zafar, N. Mass propagation through direct and indirect organogenesis in three species of genus Zephyranthes and ploidy assessment of regenerants through flow cytometry. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).