Significance of Soil Siderophore-Producing Bacteria in Evaluation and Elevation of Crop Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Date Sources
2.2. Date Analysis
2.3. Model Diagnostic and Influencing Factor Analysis
3. Results
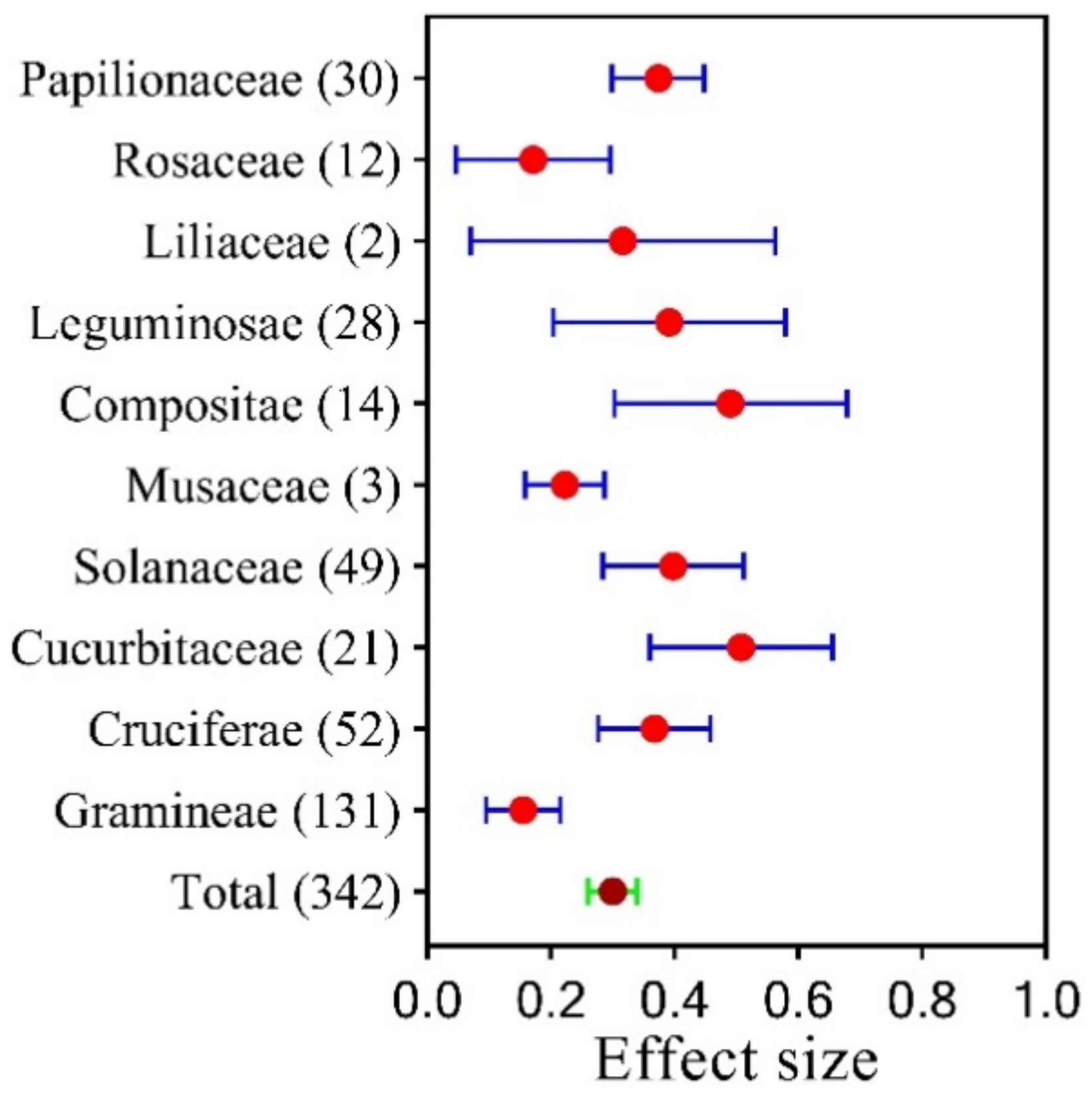
3.1. Variation in Plant Family Growth under SPB
3.2. Growth Changes under SPB for Various Measurement Modes
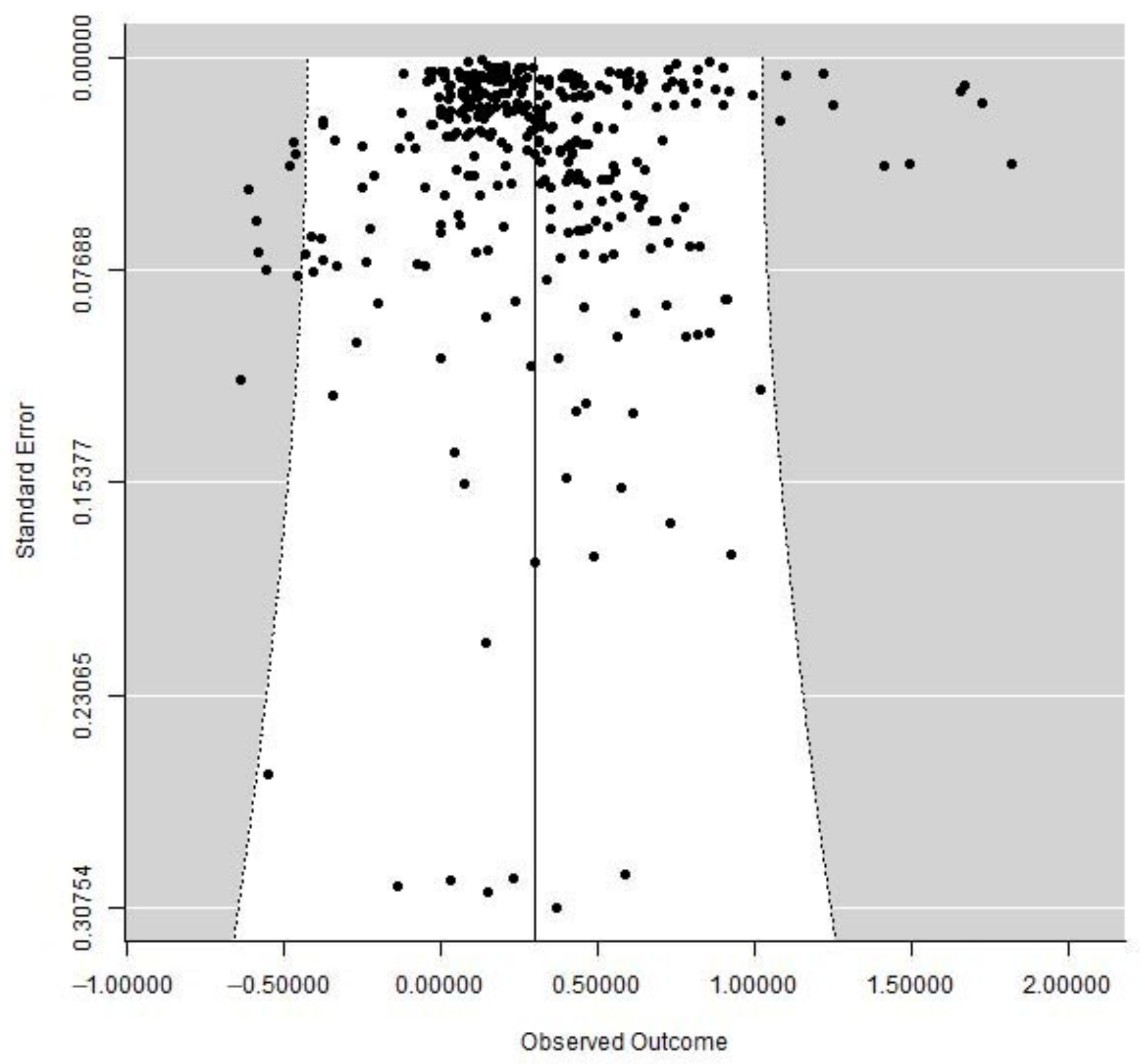
3.3. Potential Bias in Publications
4. Discussion
4.1. The Inhibitory Effect of SPB on Plant Pathogens
4.2. The Effect of SPB on Other Metal Ions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguado-Santacruz, G.A.; Moreno-Gomez, B.; Jimenez-Francisco, B.; Garcia-Moya, E.; Preciado-Ortiz, R.E. Impact of the microbial siderophores and phytosiderophores on the iron assimilation by plants: A synthesis. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2012, 35, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fardeau, S.; Demailly-Mullie, C.; Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Audic, N.; Sonnet, P. Bacterial iron’s uptake: A promising solution against multidrug resistant bacteria. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technological Advances; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, España, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schalk, I.J. Metal trafficking via siderophores in Gram-negative bacteria: Specificities and characteristics of the pyoverdine pathway. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.F.; Zhu, H.Y.; Lan, P. Research Progress of Iron Homeostasis Regulation in Strategy I Plants. Soil 2021, 53, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Hu, B.L. Regulation of microbial siderophore transport and its application in environmental remediation. Chin. J. biotechnol. 2019, 35, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.H.; Zhao, C.G.; Yang, S.P. Influence of iron on siderophore and photosynthetic pigments biosynthesis by siderophore-producing Rhodopesudomonnas palustris. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2014, 54, 408–416. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.T.; Yao, F.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Huang, L.Y. Advances on the Mechanism of Iron Absorption in Plants. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2022, 42, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.L. Iron oxide solubilization by organic matter and its effect on iron availability. Plant Soil 1991, 130, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.M.; Zheng, F.C. The Development and Utilization of Siderophore on Plant Growth Promotion and Plant Disease Control. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2007, 23, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, A.; Nangia, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Carbon-Bound Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prevent Calcium-Induced Iron Deficiency in Oryza sativa L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ellermann, M.; Arthur, J.C. Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition and modulation of host-bacterial interactions. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 2017, 105, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Josts, I.; Veith, K.; Normant, V.; Schalk, I.J.; Tidow, H. Structural insights into a novel family of integral membrane siderophore reductases. PNAS 2021, 118, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Boukhalfa, H.; Crumbliss, A.L. Chemical aspects of siderophore mediated iron transport. Biometals 2002, 15, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Lin, Q.Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, S.Z.; Qiu, R.L. Application potential of siderophore-producing rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metals-contaminated soils: A review. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdappa, S.; Jagannath, S.; Konappa, N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Jogaiah, S. Detection and Characterization of Antibacterial Siderophores Secreted by Endophytic Fungi from Cymbidium aloifolium. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Li, M.G.; Xu, S.T.; Chen, S.Q.; Yang, P.W. Screening and Identification of Secretory Siderophore from Plant Pathogen. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2020, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sarode, P.D.; Rane, M.R.; Chaudhari, B.L.; Chincholkar, S.B. Siderophoregenic Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Isolated from Wheat Rhizosphere with Strong PGPR Activity. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2009, 5, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Helmann, J.D. Functional specialization within the Fur family of metalloregulators. Biometals 2007, 20, 485–499. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, H.; Helmann, J.D. Sequential induction of Fur-regulated genes in response to iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. PNAS 2017, 114, 12785–12790. [Google Scholar]
- Sasirekha, B.; Srividya, S. Siderophore production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa FP6, a biocontrol strain for Rhizoctonia solani and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides causing diseases in chilli. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2016, 50, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Merten, D.; Svatoš, A.; Büchel, G.; Kothe, E. Metal-induced oxidative stress impacting plant growth in contaminated soil is alleviated by microbial siderophores. Soil Boil Biochem. 2009, 41, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Braud, A.; Geoffroy, V.; Hoegy, F.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Schalk, I.J. Presence of the siderophores pyoverdine and pyochelin in the extracellular medium reduces toxic metal accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and increases bacterial metal tolerance. Env. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, K.A.; Joo, J.H. Zinc Ions Affect Siderophore Production by Fungi Isolated from the Panax ginseng Rhizosphere. J. Microbiol. Biotechn. 2019, 29, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M.; Heine, T.; Malik, L.; Hofmann, S.; Joffroy, K.; Senges, C.H.R.; Bandow, J.E.; Tischler, D. Screening for Microbial Metal-Chelating Siderophores for the Removal of Metal Ions from Solutions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.L.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.F.; Liao, B.H.; Peng, P.Q.; Li, J.; Mei, J.X. Isolation, culture condition optimization, and preliminary application of siderophore-producing strains. Microbiology 2022, 49, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.M.; Zhou, G.F.; Xin, L. Conditions for siderophore production by Bacillus subtilis Bs-15 and its effect on disease prevention and growth promotion of sweet pepper. Chin. J. Pesticide Sci. 2010, 12, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lastochkina, O. Effect of endophytic Bacillus subtilis on drought stress tolerance of Triticum aestivum plants of steppe volga and forest-steppe west siberian agroecological groups. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific Conference “Plants and Microbes: The Future of Biotechnology”, Saratov, Russia, 5–9 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vivas, A.; Marulanda, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M.; Barea, J.; Azcón, R. Influence of a Bacillus sp. on physiological activities of two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and on plant responses to PEG-induced drought stress. Mycorrhiza 2023, 13, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulron, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.B.; Chai, X.F.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, X.N.; Han, Z.H.; Xu, X.F.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, Y. Siderophore production in pseudomonas SP. strain SP3 enhances iron acquisition in apple rootstock. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 720–732. [Google Scholar]
- Boiteau, R.M.; Markillie, L.M.; Hoyt, D.W.; Hu, D.H. Metabolic Interactions between Brachypodiumand Pseudomonas fluorescens under Controlled Iron-Limited Condition. mSystems 2021, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Min, L.J.; Guo, L.; Ye, J.R. Mechanism of Burkholderia pyrrocinia JK-SH007 growth-promoting to plant via siderophore-mediation. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2019, 43, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Radzki, W.; Gutierrez Mañero, F.J.; Algar, E.; Lucas García, J.A.; García-Villaraco, A.; Ramos Solano, B. Bacterial siderophores efficiently provide iron to iron-starved tomato plants in hydroponics culture. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, L.; Guo, J.S.; Xiao, X.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, J.F. Bacillus subtilis STU6 Ameliorates Iron Deficiency in Tomato by Enhancement of Polyamine-Mediated Iron Remobilization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Karablieh, N.; Al-Shomali, I.; Al-Elaumi, L.; Hasan, K. Pseudomonas fluorescens NK4 siderophore promotes plant growth and biocontrol in cucumber. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.Y.; Doxey, S.; McLean, J.E.; Britt, D.; Watson, A.; Al Qassy, D.; Jacobson, A.; Anderson, A.J. Remodeling of root morphology by CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: Effects on drought tolerance for plants colonized by a beneficial pseudomonad. Botany 2018, 96, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Hao, Y.W.; Wang, C.C.; Zhang, Z.F.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.Z.; Liu, Y.C.; Li, L.L.; Sun, Z.K. Bacillus sp. WR12 alleviates iron deficiency in wheat via enhancing siderophore- and phenol-mediated iron acquisition in roots. Plant Soil 2022, 471, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Yue, Z.H.; Chen, C.; Li, C.Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.K. Enhancing Iron uptake and Alleviating Iron Toxicity in Wheat by Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria: Theories and Practices. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2020, 23, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Svatos, A.; Dabrowska, P.; Schmidt, A.; Boland, W.; Kothe, E. Involvement of siderophores in the reduction of metal-induced inhibition of auxin synthesis in Streptomyces spp. Chemosphere 2008, 74, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Etesami, H.; Maheshwari, D.K. Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.M.; Ai, C.X.; Xin, L.; Zhou, G.F. The siderophore-producing bacterium, Bacillus subtilis CAS15, has a biocontrol effect on Fusarium wilt and promotes the growth of pepper. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Karuppiah, V.; Natarajan, S.; Gangatharan, M.; Aldayel, M.F.; Alsowayeh, N.; Thangavel, K. Development of siderophore-based rhizobacterial consortium for the mitigation of biotic and abiotic environmental stresses in tomatoes: An in vitro and in planta approach. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 3276–3287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.J.; Zhan, Y.J.; Lei, P.; Sun, T.; Qian, J.Y.; Xu, H. Characteristics of siderophores production bu Penicilium astuiianum XK-12 and its effect on antibacterial activity. Jiangsu J. Agr. Sci. 2022, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.L.; Zhou, M.; Wu, X.Q. Characteristics of siderophores production by Rahnella aquatilis JZ-GX1 and its antagonism against forest pathogens. Microbiology 2019, 46, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Braud, A.; Hoegy, F.; Jezequel, K.; Lebeau, T.; Schalk, I.J. New insights into the metal specificity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine-iron uptake pathway. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyed, R.Z.; Chincholkar, S.B. Growth and siderophores production in Alcaligenes faecalis is regulated by metal ions. Indian J. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Braud, A.; Jezequel, K.; Bazot, S.; Lebeau, T. Enhanced phytoextraction of an agricultural Cr- and Pb-contaminated soil by bioaugmentation with siderophore-producing bacteria. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Virpiranta, H.; Banasik, M.; Taskila, S.; Leiviska, T.; Halttu, M.; Sotaniemi, V.H.; Tanskanen, J. Isolation of Efficient Metal-Binding Bacteria from Boreal Peat Soils and Development of Microbial Biosorbents for Improved Nickel Scavenging. Water 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Fu, J.W.; Da Silva, E.; Shi, X.X.; Cao, Y.; Rathinasabapathi, B.; Chen, Y.S.; Ma, L.Q. Microbial siderophores and root exudates enhanced goethite dissolution and Fe/As uptake by As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.W.; Xue, L.G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.M.; Chang, S.J.; Li, M.C.; Liu, Y.T.; He, Y.Y. Isolation of a siderophore-producing and cadmium-resistant bacteria and its effect on seed germination of ryegrass. Microbiology 2021, 48, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Huang, W.; Ali, S.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Yu, F.B.; Deng, H.H. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of an Efficient Siderophore Producing Bacterium From Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. Cur. Microbio. 2022, 79, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Feng, J.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Yu, F.B. Studies on growth-promoting properties of an efficient siderophore producing bacterium, Burkholderia vietnamiensis YQ9, and its effects on seed germination under heavy metal stress. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2022, 42, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Mukherjee, S.K. Cadmium-induced siderophore production by a high cd-resistant bacterial strain relieved cd toxicity in plants through root colonization. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamariz-Angeles, C.; Huaman, G.D.; Palacios-Robles, E.; Olivera-Gonzales, P.; Castaneda-Barreto, A. Characterization of siderophore-producing microorganisms associated to plants from high-Andean heavy metal polluted soil from Callejon de Huaylas (Ancash, Peru). Microbiol. Res. 2021, 250, 126811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Merten, D.; Svatos, A.; Buechel, G.; Kothe, E. Siderophores mediate reduced and increased uptake of cadmium by Streptomyces tendae F4 and sunflower (Helianthus annuus), respectively. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.M.; Yu, F.B.; Ye, Z.Q.; Fang, X.B.; Lin, H.P. Isolation and identification of a cadmium-resistant and siderophores-producing strain. Environ. Poll. Control 2017, 39, 999–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.H.; Wei, Z.; Shao, Z.Y.; Friman, V.P.; Cao, K.H.; Yang, T.J.; Kramer, J.; Wang, X.F.; Li, M.; Mei, X.L.; et al. Competition for iron drives phytopathogen control by natural rhizosphere microbiomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Deng, Z.; Borham, A.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Bohu, T. Significance of Soil Siderophore-Producing Bacteria in Evaluation and Elevation of Crop Yield. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030370
Zhang S, Deng Z, Borham A, Ma Y, Wang Y, Hu J, Wang J, Bohu T. Significance of Soil Siderophore-Producing Bacteria in Evaluation and Elevation of Crop Yield. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(3):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030370
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Siwen, Zishi Deng, Ali Borham, Yao Ma, Yi Wang, Jiawei Hu, Juanjuan Wang, and Tsing Bohu. 2023. "Significance of Soil Siderophore-Producing Bacteria in Evaluation and Elevation of Crop Yield" Horticulturae 9, no. 3: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030370
APA StyleZhang, S., Deng, Z., Borham, A., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, J., Wang, J., & Bohu, T. (2023). Significance of Soil Siderophore-Producing Bacteria in Evaluation and Elevation of Crop Yield. Horticulturae, 9(3), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9030370






