UPLC–MS/MS and Gene Expression Research to Distinguish the Colour Differences of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Experimental Method
2.2.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.2.2. UPLC Conditions
2.2.3. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
2.2.4. Data Quality Control and Statistics Analysis
3. Results
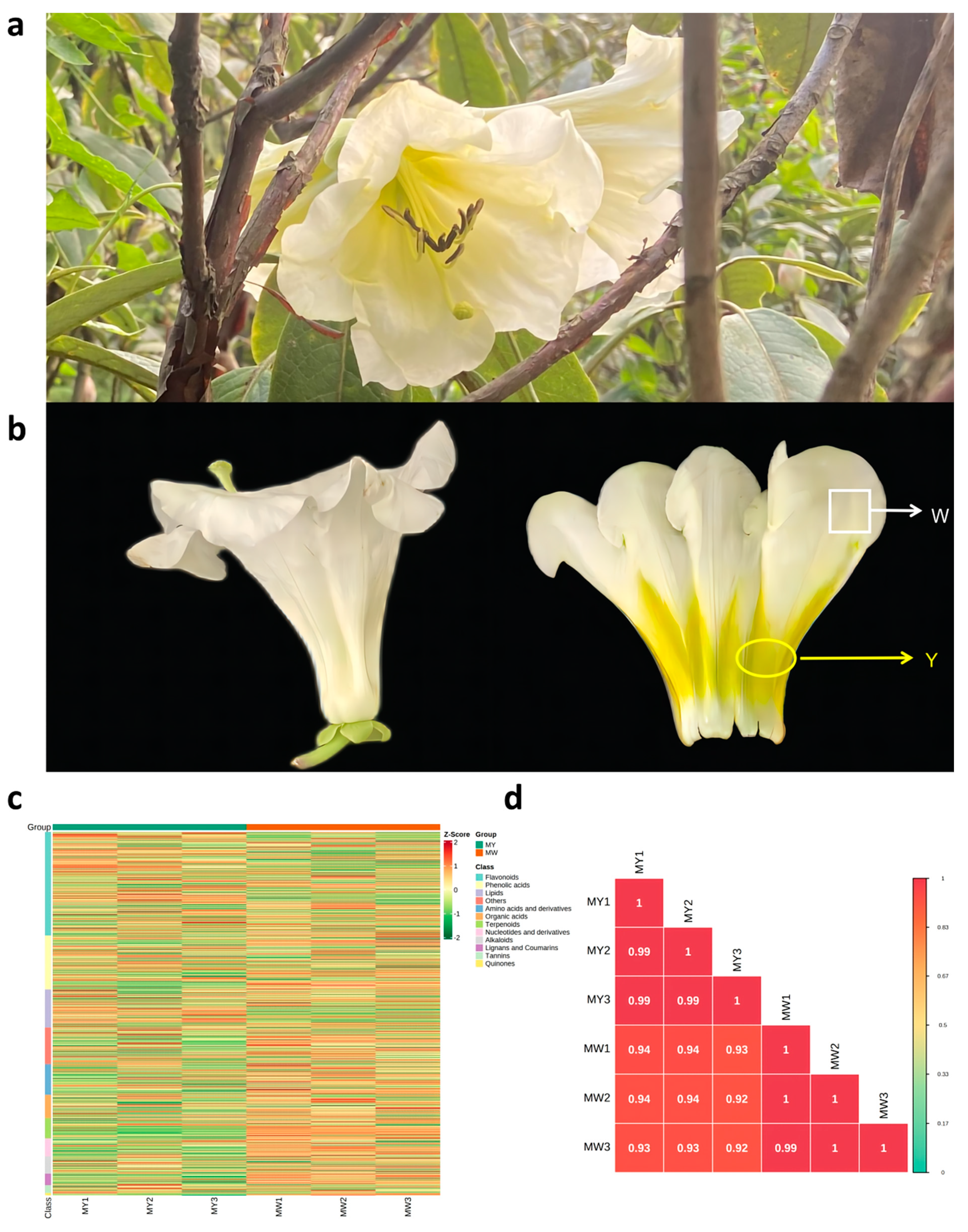
3.1. Morphological Characteristics and Overall Characteristics of Metabolites
3.2. Identification and Comparison of Metabolites and Differentiated Metabolites
3.3. Flavonoid Differential Metabolites
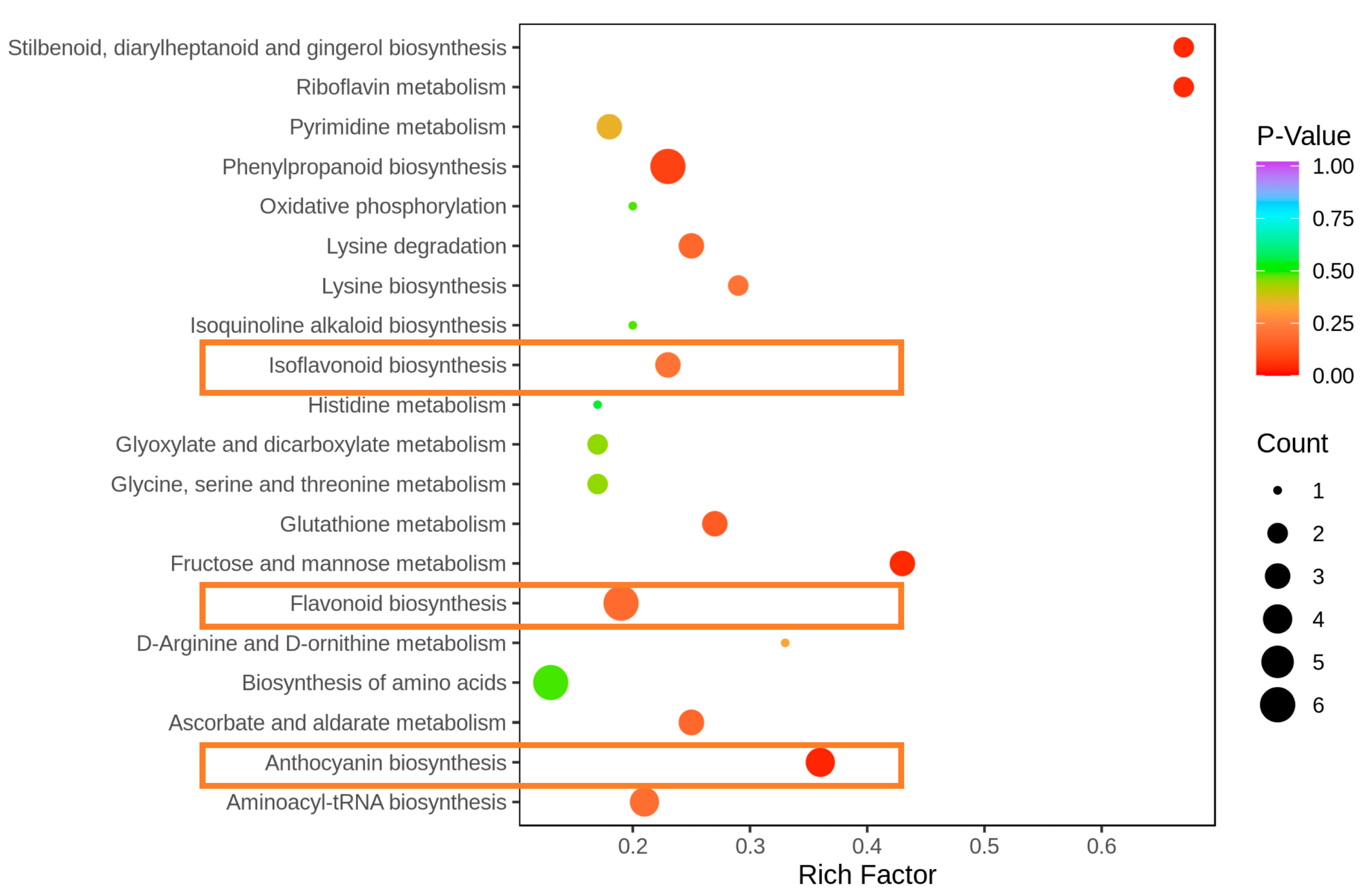
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Metabolites
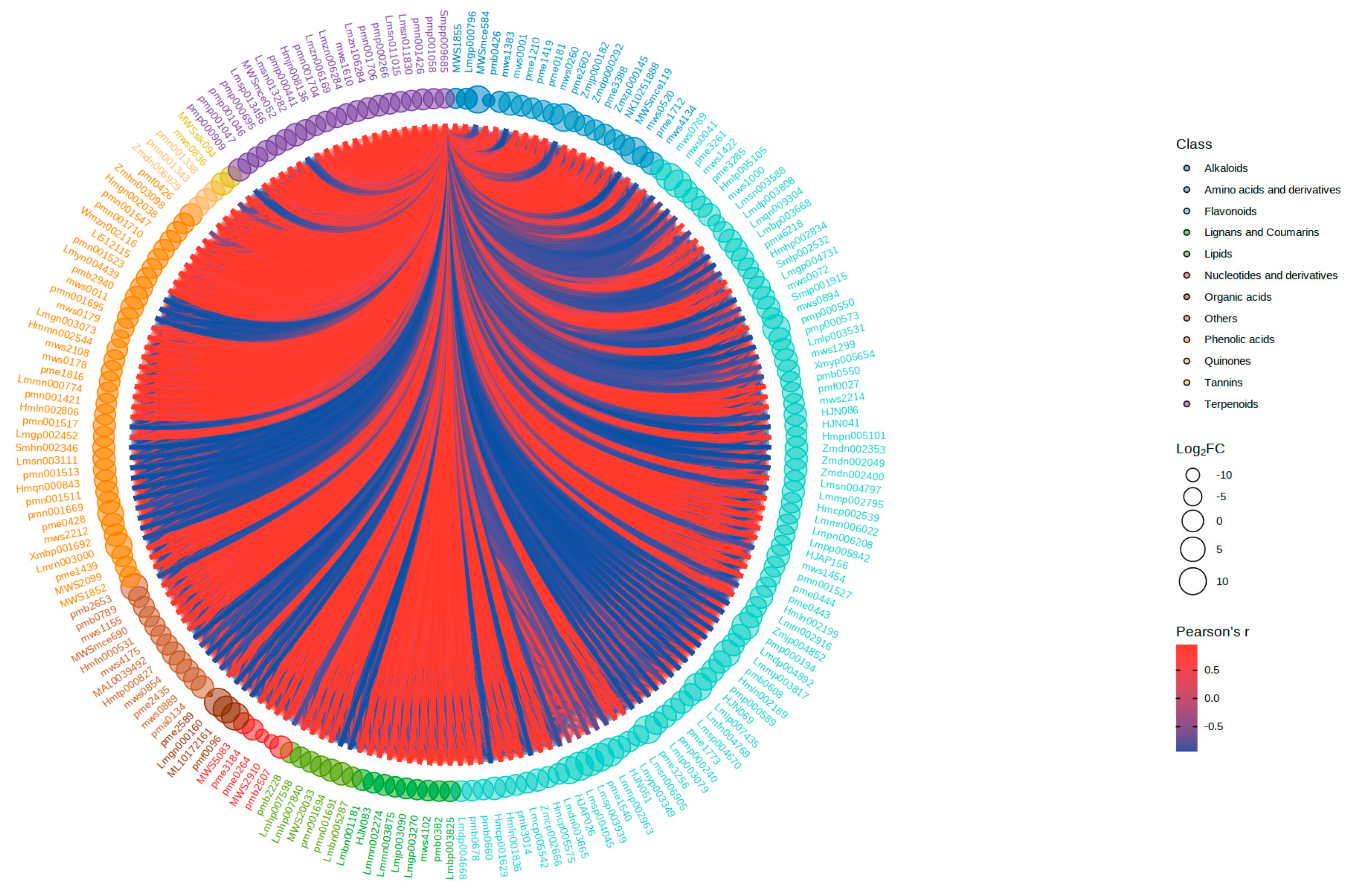
3.5. Flavonoid, Isoflavone, Anthocyanin Biosynthesis-Related, and Metabolite-Related Networks and Metabolite and Gene Correlation Networks
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Metabolites and Related Enzymes Enriched in Flavonoid Biosynthesis
4.2. Analysis of Metabolites and Related Enzymes Enriched in Isoflavonoid Biosynthesis
4.3. Analysis of Metabolites and Related Enzymes Enriched in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, X.-M.; Yang, M.-Q.; Li, C.-L.; Huang, S.-X.; Jin, W.-T.; Shen, T.-T.; Wang, F.; Li, X.-H.; Yoichi, W.; Zhang, L.-H.; et al. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Global Species Diversity of Rhododendron. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 39, msab314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.-G.; Hong, K.; Tang, M.; Tang, J.; Liu, L.-X.; Gao, G.-F.; Shen, Z.-J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Yi, Y. Untargeted metabolite profiling of petal blight in field-grown Rhododendron agastum using GC-TOF-MS and UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Phytochemistry 2021, 184, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keyser, E.; Lootens, P.; Van Bockstaele, E.; De Riek, J. Image analysis for QTL mapping of flower colour and leaf characteristics in pot azalea (Rhododendron simsii hybrids). Euphytica 2013, 189, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Yeo, H.; Kim, N.; Park, Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Metabolomic Profiling of the White, Violet, and Red Flowers of Rhododendron schlippenbachii Maxim. Molecules 2018, 23, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhiliang, L.; Qiaofeng, Y.; Xue, D.; Yu, Z.; Shuang, Z.; Wenying, Z.; Shuzhen, W. Transcriptome analysis of flower color variation in five Rhododendron species (Ericaceae). Rev. Bras. Bot. 2021, 44, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Lai, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y. Characterisation of flower colouration in 30 Rhododendron species via anthocyanin and flavonol identification and quantitative traits. Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxton, G.D.; Schaefer, H.M. Floral colour change as a potential signal to pollinators. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 32, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, L.; Rubio-Moraga, Á.; López-Jiménez, A.J.; Argandoña, J.; Niza, E.; Ahrazem, O.; Gómez-Gómez, L. A carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4 from Paulownia tomentosa determines visual and aroma signals in flowers. Plant Sci. 2023, 329, 111609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumi, Y.; Yuki, T.-K.; Kiyoshi, K.; Tadao, K. Sepal color variation of Hydrangea macrophylla and vacuolar pH measured with a proton-selective microelectrode. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikazu, T.; Nobuhiro, S.; Akemi, O. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-y.; Li, Q.; Bi, K.-s. Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: Structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, W.; Li, Y.; Shu, X.; Pu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. The Classification, Molecular Structure and Biological Biosynthesis of Flavonoids, and Their Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Molecules 2023, 28, 3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lv, S.; Zhao, L.; Gao, T.; Yu, C.; Hu, J.; Ma, F. Advances in the study of the function and mechanism of the action of flavonoids in plants under environmental stresses. Planta 2023, 257, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.; Zheng, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Q. Determination of flavonoids and carotenoids and their contributions to various colors of rose cultivars (Rosa spp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chang, C.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D. Metabolome Analysis Reveals Flavonoid Changes During Leaf Colour Transition in Populus × euramericana ‘Zhonghuahongye’. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Vainstein, A.; Chen, S.; Ma, H. Regulation of fig (Ficus carica L.) fruit color: Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, S.; Tian, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y. Transcriptome sequencing and metabolite analysis reveals the role of delphinidin metabolism in flower colour in grape hyacinth. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendri, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, B.; Purohit, R.; Bhandari, P. Effect of co-pigments on anthocyanins of Rhododendron arboreum and insights into interaction mechanism. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, P. Systematic qualitative and quantitative assessment of anthocyanins, flavones and flavonols in the petals of 108 lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) cultivars. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Ning, G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Bao, M. Disequilibrium of Flavonol Synthase and Dihydroflavonol-4-Reductase Expression Associated Tightly to White vs. Red Color Flower Formation in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Tang, J.; Gong, J.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév. Flower Colour Differences. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, D.; Ban, T.; Miyajima, I.; Nakatsuka, A.; Kobayashi, N. Comparison of flower color with anthocyanin composition patterns in evergreen azalea. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, L.; Kammerer, D.R.; Stintzing, F.C.; Spring, O.; Roessner, U. Comparative Metabolite Profiling of Triterpenoid Saponins and Flavonoids in Flower Color Mutations of Primula veris L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; He, L.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Su, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Gao, H. Comparative transcriptome analyses reveal genes related to pigmentation in the petals of a flower color variation cultivar of Rhododendron obtusum. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L. Anthocyanin Metabolite and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveals White Flowers in Rhododendron dauricum var. albiflorum. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, Y.; Ali, A.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, D.; Guo, Q.; Riaz, A.; Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Liao, Y.; et al. Transcriptome and Proteome Profiling of Different Colored Rice Reveals Physiological Dynamics Involved in the Flavonoid Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Xu, G.; Li, J. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in blueberry (Vaccinium spp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1082245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ai, Y.; Zhuang, W. Metabolic profiling and transcriptome analysis provide insights into the accumulation of flavonoids in chayote fruit during storage. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1029745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Zheng, Q.-D.; Wang, M.-J.; Xiong, L.-W.; Li, P.; Guo, L.-T.; Wang, M.-Y.; Peng, D.-H.; Lan, S.-R.; Liu, Z.-J. Molecular mechanism of different flower color formation of Cymbidium ensifolium. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 113, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Mu, Y.; Sun, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, N.; Ji, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Flower Color Differentiation Mechanisms in Various Sophora japonica L. Petal Types. Biology 2023, 12, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, H.; Ma, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Kong, L. Metabolomics and gene expression analysis reveal the accumulation patterns of phenylpropanoids and flavonoids in different colored-grain wheats (Triticum aestivum L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, M.; Wen, C.; Xie, X.; Tian, W.; Wen, S.; Lu, R.; Liu, L. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the anthocyanin regulatory networks in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. flowers. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, M.I.; Falcone-Ferreyra, M.L.; Jiang, N.; Mejía-Guerra, M.K.; Rodríguez, E.; Wilson, T.; Engelmeier, J.; Casati, P.; Grotewold, E. Identification and Characterization of Maize salmon silks Genes Involved in Insecticidal Maysin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, Y.; Witte, S.; Forkmann, G.; Lukačin, R.; Matern, U.; Martens, S. Molecular evolution of flavonoid dioxygenases in the family Apiaceae. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhenhua, P. Advances in study on formation mechanism and genetic engineering of yellow flowers. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2009, 45, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Deng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Cui, F.; Zhou, W. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomic analysis of the flavonoid regulatory networks in Sorghum bicolor seeds. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondo, K.; Sukhumpinij, P.; Kakihara, F. Flower color and pigments in yellow-flowered hybrid progeny raised from the interspecific cross Pelargonium quinquelobatum × white-flowered geraniums. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 195, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, D.; Fan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M. Molecular characterization of flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene and flavonoid accumulation in two chemotyped safflower lines in response to methyl jasmonate stimulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Hill, L.; Weng, J.-K.; Chen, X.-Y.; Xue, H.; Martin, C. A specialized flavone biosynthetic pathway has evolved in the medicinal plant, Scutellaria baicalensis. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Bashandy, H.; Ainasoja, M.; Kontturi, J.; Pietiäinen, M.; Laitinen, R.A.E.; Albert, V.A.; Valkonen, J.P.T.; Elomaa, P.; Teeri, T.H. Functional diversification of duplicated chalcone synthase genes in anthocyanin biosynthesis of Gerbera hybrida. New Phytol. 2013, 201, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Abrahan, C.; Colquhoun, T.A.; Liu, C.-J. A Proteolytic Regulator Controlling Chalcone Synthase Stability and Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schijlen, E.G.W.M.; de Vos, C.H.R.; Martens, S.; Jonker, H.H.; Rosin, F.M.; Molthoff, J.W.; Tikunov, Y.M.; Angenent, G.C.; van Tunen, A.J.; Bovy, A.G. RNA interference silencing of chalcone synthase, the first step in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, leads to parthenocarpic tomato fruits. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, H.; Sun, N.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y. Isolation, characterization, and function analysis of a flavonol synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 39, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkmann, G.; Martens, S. Metabolic engineering and applications of flavonoids. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yin, H. The Flavonoid Biosynthesis Network in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walliser, B.; Lucaciu, C.R.; Molitor, C.; Marinovic, S.; Nitarska, D.A.; Aktaş, D.; Rattei, T.; Kampatsikas, I.; Stich, K.; Haselmair-Gosch, C.; et al. Dahlia variabilis cultivar ‘Seattle’ as a model plant for anthochlor biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Lu, W.; Yang, L.; Karim, A.; Luo, K. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding leucoanthocyanidin reductase and anthocyanidin reductase from Populus trichocarpa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfanelli, C.; Poggi, A.; Loreti, E.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Sucrose-specific induction of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 140, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ren, C.; Dong, S.; Chen, C.; Xian, B.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Pei, J.; Chen, J. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptome analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) with different colors. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 712038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Kumaran Anguraj, V.; Tim, M.; Justin, B.R.; Sangeeta, D. A combinatorial action of GmMYB176 and GmbZIP5 controls isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean (Glycine max). Commun. Biol. 2021, 19, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Functional properties of anthocyanins and betalains in plants, food, and in human nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.S.; Wang, H.; Tu, H.X.; Zhou, J.T.; Luo, X.R.; Chen, Q.; He, W.; et al. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide Insights into the Coloring Mechanism of Dark-red and Yellow Fruits in Chinese Cherry [Cerasus pseudocerasus (Lindl.) G. Don]. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, W.P.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhao, G.H. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor PaMYB10 is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in apricots and determines red blushed skin. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, J.; Kanno, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Tsugawa, H.; Suzuki, M. Plant biochemistry: Anthocyanin biosynthesis in roses. Nature 2005, 435, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offen, W.; Martinez-Fleites, C.; Yang, M.; Kiat-Lim, E.; Davis, B.G.; Tarling, C.A.; Ford, C.M.; Bowles, D.J.; Davies, G.J. Structure of a flavonoid glucosyltransferase reveals the basis for plant natural product modification. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Secondary Classification of Flavonoids | Quantity | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Chalcone | 20 | 5.8% |
| Flavanones | 44 | 12.9% |
| Flavanonols | 13 | 3.8% |
| Flavones | 54 | 15.9% |
| Flavonols | 122 | 35.9% |
| Flavonoid carbonoside | 16 | 4.7% |
| Flavanols | 23 | 6.7% |
| Anthocyanidins | 27 | 7.9% |
| Isoflavones | 18 | 5.3% |
| Dihydroisoflavones | 2 | 0.5% |
| Formula | Compounds | Class II | Type | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C15H12O4 | Pinocembrin (Dihydrochrysin) | Flavanones | down | 480-39-7 |
| C15H10O5 | 6-Hydroxydaidzein | Isoflavones | up | 17817-31-1 |
| C15H14O5 | Epiafzelechin | Flavanols | up | 24808-04-6 |
| C15H14O5 | Afzelechin (3,5,7,4′-Tetrahydroxyflavan) | Flavanols | up | 2545-00-8 |
| C15H12O6 | Fustin | Flavanonols | up | 20725-03-5 |
| C22H22O10 | Glycitin (Glycitein 7-O-Glucoside) | Isoflavones | down | 40246-10-4 |
| C21H21O11+ | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (Kuromanin) | Anthocyanidins | down | 47705-70-4 |
| C23H25O12+ | Malvidin-3-O-glucoside (Oenin) | Anthocyanidins | down | 18470-06-9 |
| C24H22O13 | 6″-O-Malonylgenistin | Isoflavones | up | 51011-05-3 |
| C27H31O15+ | Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside (Keracyanin) | Anthocyanidins | up | 28338-59-2 |
| C27H31O16+ | Delphinidin-3-O-rutinoside | Anthocyanidins | up | 15674-58-5 |
| C16H16O8 | 5-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid | Phenolic acids | down | 180981-12-8 |
| C16H18O9 | Chlorogenic acid (3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid) | Phenolic acids | down | 327-97-9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yi, Y.; Liu, L.; Shen, T. UPLC–MS/MS and Gene Expression Research to Distinguish the Colour Differences of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121351
Dai J, Wang X, Meng X, Zhang X, Zhou Q, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Yi Y, Liu L, Shen T. UPLC–MS/MS and Gene Expression Research to Distinguish the Colour Differences of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(12):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121351
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Jin, Xinglin Wang, Xingpan Meng, Xu Zhang, Qihang Zhou, Zhengdong Zhang, Ximin Zhang, Yin Yi, Lunxian Liu, and Tie Shen. 2023. "UPLC–MS/MS and Gene Expression Research to Distinguish the Colour Differences of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév" Horticulturae 9, no. 12: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121351
APA StyleDai, J., Wang, X., Meng, X., Zhang, X., Zhou, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Yi, Y., Liu, L., & Shen, T. (2023). UPLC–MS/MS and Gene Expression Research to Distinguish the Colour Differences of Rhododendron liliiflorum H. Lév. Horticulturae, 9(12), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121351






