A MADS-Box Gene-Based InDel Marker Discriminating Sex in Actinidia arguta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
2.2. Resequencing and Polymorphic InDel Detection
2.3. Detection of Candidate InDels Discriminating Sex
2.4. Development of a Sex-Discriminating InDel Marker
3. Results
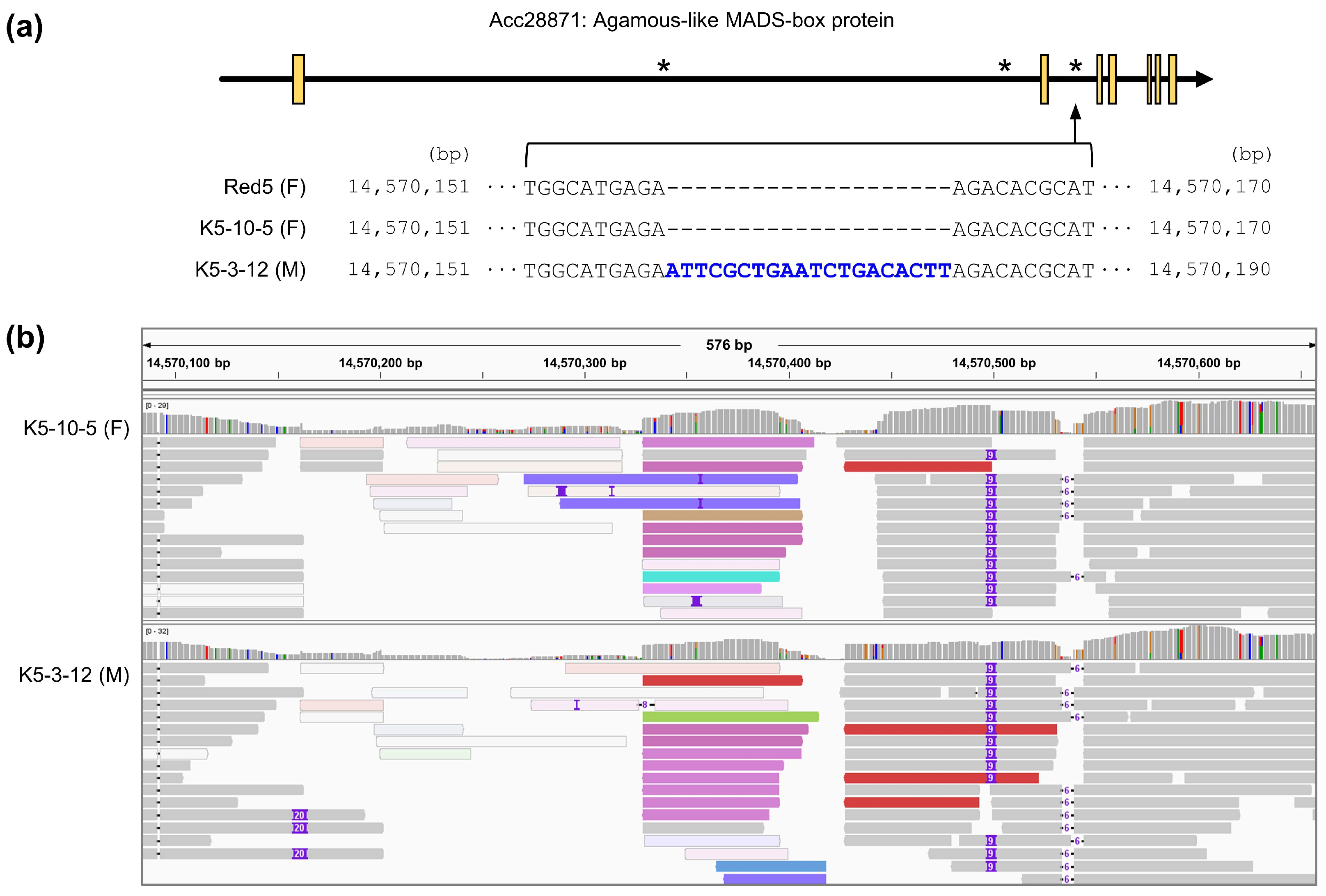
3.1. Resequencing and InDel Detection
3.2. Selection of Polymorphic InDels Occurring in Sex-Related Genes
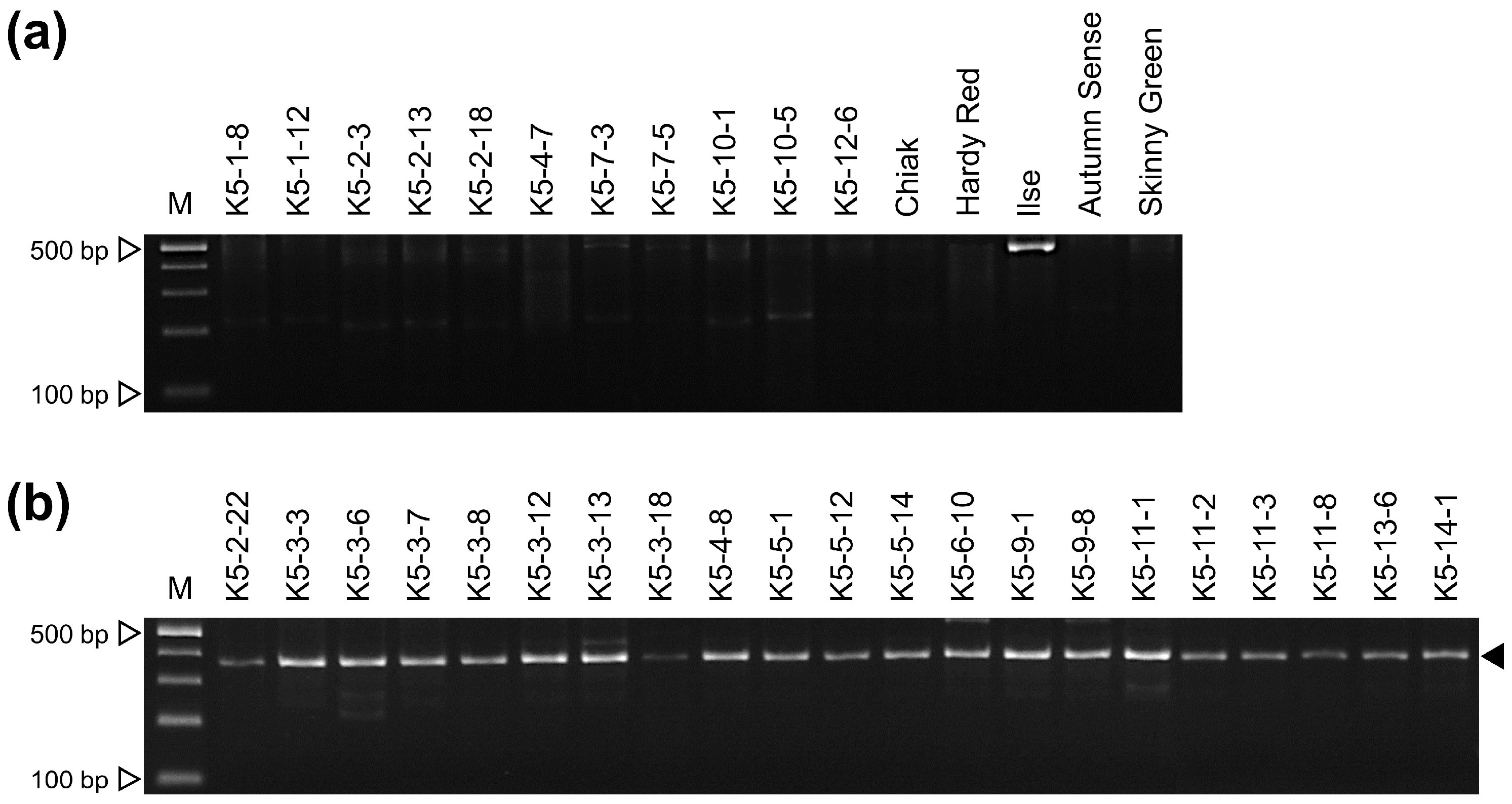
3.3. Development of a Sex-Discriminating InDel Marker
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wellmer, F.; Riechmann, J.L.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Genome-wide analysis of spatial gene expression in Arabidopsis flowers. Plant Cell 2004, 15, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Altman, N.; Ma, H. Genome-wide expression profiling and identification of gene activities during early flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, R.; Bendahmane, A.; Renner, S.S. Sex chromosomes in land plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 485–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazama, Y.; Ishii, K.; Aonuma, W.; Ikeda, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Koizumi, A.; Filatov, D.A.; Chibalina, M.; Bergero, R.; Charlesworth, D.; et al. A new physical mapping approach refines the sex-determining gene positions on the Silene latifolia Y-chromosome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkess, A.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C.; Bowers, J.E.; Ven der Hulst, R.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Mercati, F.; Riccardi, P.; McKain, M.R.; Kakrana, A.; et al. The asparagus genome sheds light on the origin and evolution of a young Y chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Henry, I.M.; Tao, R.; Comai, L. A Y-chromosome-encoded small RNA acts as a sex determinant in persimmons. Science 2014, 346, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Henry, I.M.; Kawai, T.; Comai, L.; Tao, R. Epigenetic regulation of the sex-determination gene MeGI in polyploid persimmon. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Du, R.; Gou, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Nguyen, J.K.; Ming, R.; Yin, T.; Huang, S.; Yan, J. The genomic architecture of the sex-determining region and sex-related metabolic variation in Ginkgobiloba. Plant J. 2020, 104, 1399–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.F.; Mathew, L.S.; Ahmed, I.; Al-Azwani, I.K.; Krueger, R.; Rivera-Nuñez, D.; Mohamoud, Y.A.; Clark, A.G.; Suhre, K.; Malek, J.A. Genus-wide sequencing supports a two-locus model for sex-determination in Phoenix. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Takahata, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Onodera, Y. Molecular evidence for recent divergence of X- and Y-linked gene pairs in Spinacia oleracea L. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Henry, I.M.; Ohtani, H.; Morimoto, T.; Beppu, K.; Kataoka, I.; Tao, R. A Y-encoded suppressor of feminization arose via lineage-specific duplication of a cytokinin response regulator in kiwifruit. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, T.; Pilkington, S.M.; Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Henry, I.M.; Sugano, S.S.; Sonoda, M.; Firl, A.; McNeilage, M.A.; Douglas, M.J.; Wang, T.; et al. Two Y-chromosome-encoded genes determine sex in kiwifruit. Nat. Plant 2019, 5, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, C.F.; Fraser, L.G.; Gill, G.P. Sex determination in Actinidia. Acta Hortic. 1997, 444, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, G.P.; Harvey, C.F.; Gardner, R.C.; Fraser, L.G. Development of sex-linked PCR markers for gender identification in Actinidia. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirkot, P.; Sharma, D.R.; Mohapatra, T. Molecular identification of sex in Actinidia deliciosa var. deliciosa by RAPD markers. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 94, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; VanBuren, R.; Yao, X.; Zhong, C.; Huang, H. High-density interspecific genetic maps of kiwifruit and the identification of sex-specific markers. DNA Res. 2015, 22, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, I.; Melo, A.T.O.; Gustafson, H. Sex-linked molecular markers for two cold-hardy kiwifruit species, Actinidia arguta and A. kolomikta. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 83, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Kwack, Y.B.; Kim, D. Development of a CAPS marker for discriminating sex in Actinidia arguta. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.X.; Luo, M.M.; Wang, Z.; Bai, F.X.; Luo, X.; Gao, L.; Peng, L.; Chen, Q.H.; Zhang, L. Genome-wide analysis of MADS-box gene family in kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis var. chinensis) and their potential role in floral sex differentiation. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1043178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, K.; Han, H.; Won, K.; Kwack, Y.B.; Shin, H.; Kim, D. Genetic diversity of kiwifruit (Actinidia spp.), including Korean native A. arguta, using single nucleotide polymorphisms derived from genotyping-by-sequencing. Hortic. Environ. Biotehcnol. 2019, 60, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.P.; Peterson, D.A.; Biggs, P.J. Solexa QA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington, S.M.; Crowhurst, R.; Hilario, E.; Nardozza, S.; Fraser, L.; Peng, Y.; Gunaseelan, K.; Simpson, R.; Tahir, J.; Deroles, S.C.; et al. A manually annotated Actinidia chinensis var. chinensis (kiwifruit) genome highlights the challenges associated with draft genomes and gene prediction in plants. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkess, A.; Huang, K.; ven der Hulst, R.; Tissen, B.; Caplan, J.L.; Kloppula, A.; Batish, M.; Meyers, B.C.; Leebens-Mack, J. Sex determination by two Y-linked genes in garden asparagus. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegan, R.; Marais, G.A.B.; Kubekova, H.; Blavet, N.; Widmer, A.; Vyskot, B.; Doležel, J.; Šafář, J.; Hobza, R. Structure and evolution of Apetala3, a sex-linked gene in Silene latifolia. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, D.S.; Charlesworth, D. An X-linked gene with a degenerate Y-linked homologue in a dioecious plant. Nature 1998, 393, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delichère, C.; Veuskens, J.; Hernould, M.; Barbacar, N.; Nouras, A.; Negrutiu, I.; Monéger, F. SlY1, the first active gene cloned from a plant Y chromosome, encodes a WD-repeat protein. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4169–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, I.; Delichère, C.; Filatov, D.A.; Charlesworth, D.; Negrutiu, I.; Monéger, F. Analysis and evolution of two functional Y-linked loci in a plant sex chromosome system. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moore, R.C.; Kozyreva, O.; Lebel-Hardenack, S.; Siroky, J.; Hobza, R.; Vyskot, B.; Grant, S.R. Genetic and functional analysis of DD44, a sex-linked gene from the dioecious plant Silene latifolia, provides clues to early events in sex chromosome evolution. Genetics 2003, 163, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Bergero, R.; Forrest, A.; Kaiser, V.B.; Charlesworth, D. Nucleotide diversity in Silene latifolia autosomal and sex-linked genes. Proc. R. Soc. B 2010, 227, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, G.; Bergero, R.; Charlesworth, D.; Filatov, D.A. Does local adaptation cause high population differentiation of Silene latifolia Y chromosomes? Evolution 2011, 62, 3368–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, L.A.; Delph, L.F. Neo-sex chromosome inheritance across species in Silene hybrids. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanderbali, A.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Zahn, L.M.; Brockington, S.F.; Wall, P.K.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Albert, V.A.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Altman, N.S.; Ma, H.; et al. Conservation and canalization of gene expression during angiosperm diversification accompany the origin and evolution of the flower. Biol. Sci. 2010, 107, 22570–22575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, Y.; Li, J.R.; Shen, H.L.; Yang, Y.M.; Fan, S.T.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.S.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.D.; Guo, X.W. VaAPRT3 gene is associated with sex determination in Vitis amurensis. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 727260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanum, P.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, I.A.; Chaffar, A.; Khan, Z. TPD1-like gene as a suitable marker for early sex determination in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Genes 2023, 14, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, F.; Geng, S.; Guan, J.; Tao, S.; Jia, M.; Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Ye, X.; et al. The wheat AGL6-like MADS-box gene is a master regulator for floral organ identity and a target for spikelet meristem development manipulation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 20, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, C.H.; Shen, C.Y.; Huang, K.S. Origination and selection of ABCDE and AGL6 subfamily MADS-box genes in gymnosperms and angiosperms. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkony-Gasic, E.; Moss, M.S.; Voogd, G.; Wu, R.; Lough, R.H.; Wnag, Y.Y.; Hellens, R.P. Identification and characterization of flowering genes in kiwifruit: Sequence conservation and role in kiwifruit flower development. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mori, G.; Testolin, R.; Cipriani, G. A molecular protocol for early sex discrimination (ESD) in Actinidia spp. J. Berry Res. 2022, 12, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex | Species | Accession | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Actinidia arguta | K5-1-8 | K5-1-12 | K5-2-3 | K5-2-13 |
| K5-2-18 | K5-4-7 | K5-7-3 | K5-7-5 | ||
| K5-10-1 | K5-10-5 | K5-12-6 | Chiak | ||
| Hardy Red | Ilse | Autumn Sense | |||
| (A. arguta × A. deliciosa) × A. arguta | Skinny Green | ||||
| Male | A. arguta | K5-2-22 | K5-3-3 | K5-3-6 | K5-3-7 |
| K5-3-8 | K5-3-12 | K5-3-13 | K5-3-18 | ||
| K5-4-8 | K5-5-1 | K5-5-12 | K5-5-14 | ||
| K5-6-10 | K5-9-1 | K5-9-8 | K5-11-1 | ||
| K5-11-2 | K5-11-3 | K5-11-8 | K5-13-6 | ||
| K5-14-1 | |||||
| Sex-Related Gene | Gene ID 1 | Description | Identity (%) | E-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GbMADS1 | Acc28871 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | 68.33 | 1.08 × 10−41 |
| GbMADS2 | ||||
| GbMADS4 | ||||
| GbMADS18 | ||||
| CYP703 | Acc28333 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12 like | 58.84 | 1.85 × 10−75 |
| TDF1 | Acc28900 | Hypothetical protein | 78.63 | 7.05 × 10−57 |
| Acc28821 | Transcription factor like | 73.85 | 1.77 × 10−49 | |
| Acc28639 | Transcription factor like | 68.64 | 2.73 × 10−39 | |
| Acc28638 | Transcription factor like | 68.64 | 2.73 × 10−39 | |
| Acc28429 | Myb-related protein | 73.26 | 1.98 × 10−30 | |
| GDSL esterase/lipase | Acc28776 | GDSL esterase/lipase, partial | 74.78 | 9.52 × 10−145 |
| AP3Y | Acc28719 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | 69.49 | 5.06 × 10−12 |
| Acc28717 | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | 62.22 | 2.03 × 10−22 |
| Variation | Position (bp) | InDel (Reference/Alternative) | Gene ID 1 | Region | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | |||||
| Insertion | 12,919,896 | -/AT | -/- | Acc28719 | Exon | Agamous-like MADS-box protein |
| 14,557,224 | -/AG | -/- | Acc28871 | Intron | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | |
| 14,559,075 | -/- | -/T | Acc28871 | Intron | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | |
| 14,570,161 | -/- | -/ATTCGGTGAATCTGACACTT | Acc28871 | Intron | Agamous-like MADS-box protein | |
| Deletion | 12,896,671 | TGAT/- | TGAT/TGAT | Acc28717 | Exon | Agamous-like MADS-box protein |
| 14,814,902 | A/A | A/- | Acc28900 | Intron | Hypothetical protein | |
| 14,815,837 | -/- | -/T | Acc28900 | Intron | Hypothetical protein | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, D. A MADS-Box Gene-Based InDel Marker Discriminating Sex in Actinidia arguta. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121310
Oh S, Kim J, Kim Y, Lee M, Kim D. A MADS-Box Gene-Based InDel Marker Discriminating Sex in Actinidia arguta. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(12):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121310
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Sewon, Jung Kim, Yumi Kim, Mockhee Lee, and Daeil Kim. 2023. "A MADS-Box Gene-Based InDel Marker Discriminating Sex in Actinidia arguta" Horticulturae 9, no. 12: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121310
APA StyleOh, S., Kim, J., Kim, Y., Lee, M., & Kim, D. (2023). A MADS-Box Gene-Based InDel Marker Discriminating Sex in Actinidia arguta. Horticulturae, 9(12), 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121310






