Effects of Tactile Stimulation Using an Assortment of Natural Elements on the Psychophysiological Responses of Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Participants
2.2. Experimental Condition
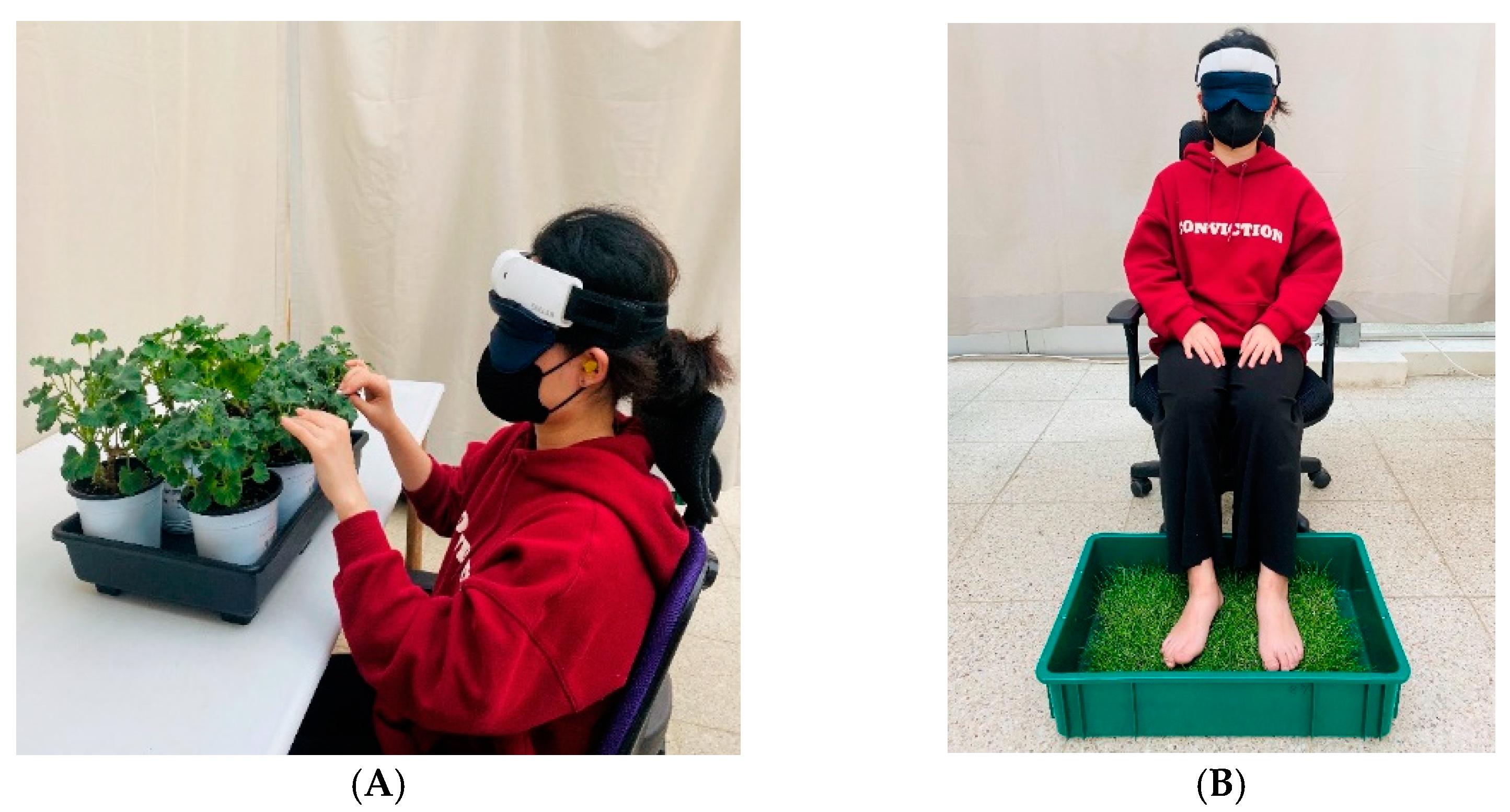
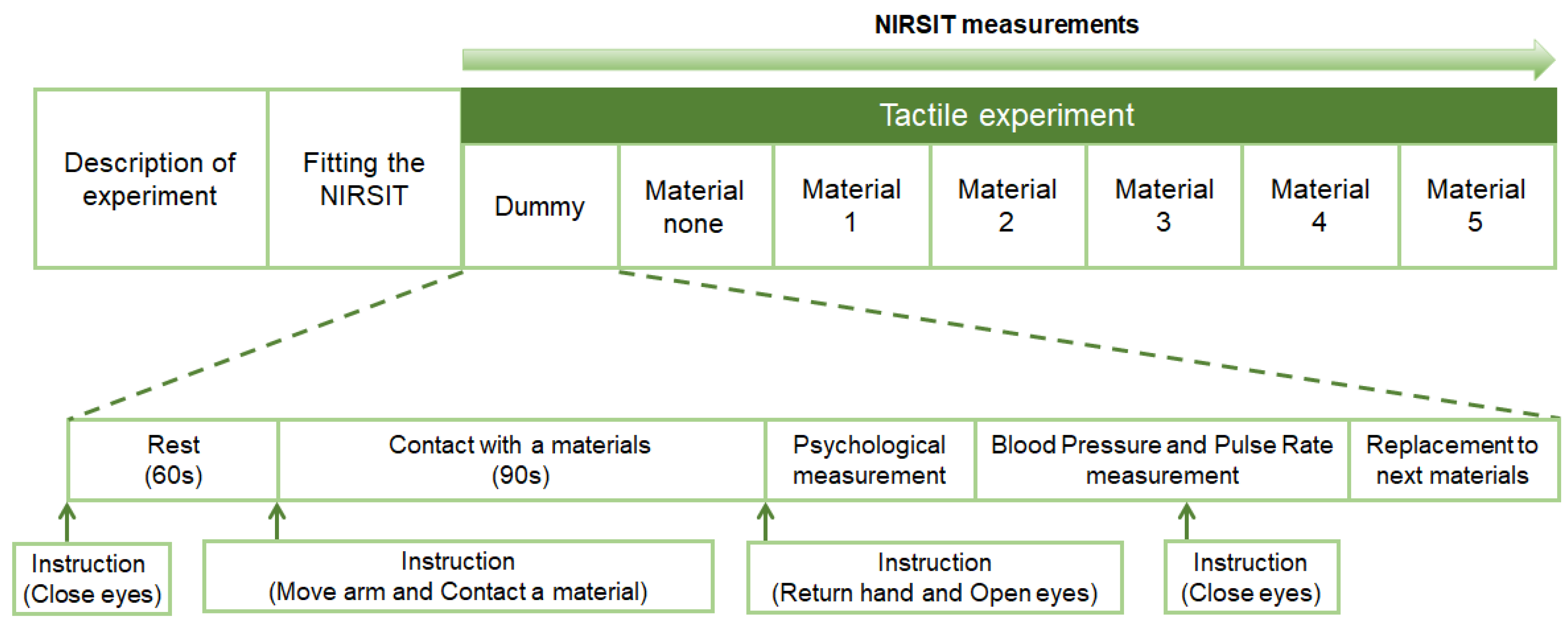
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Tactile Stimulation Element
2.4.1. Hand
2.4.2. Foot
2.5. Measurement Items
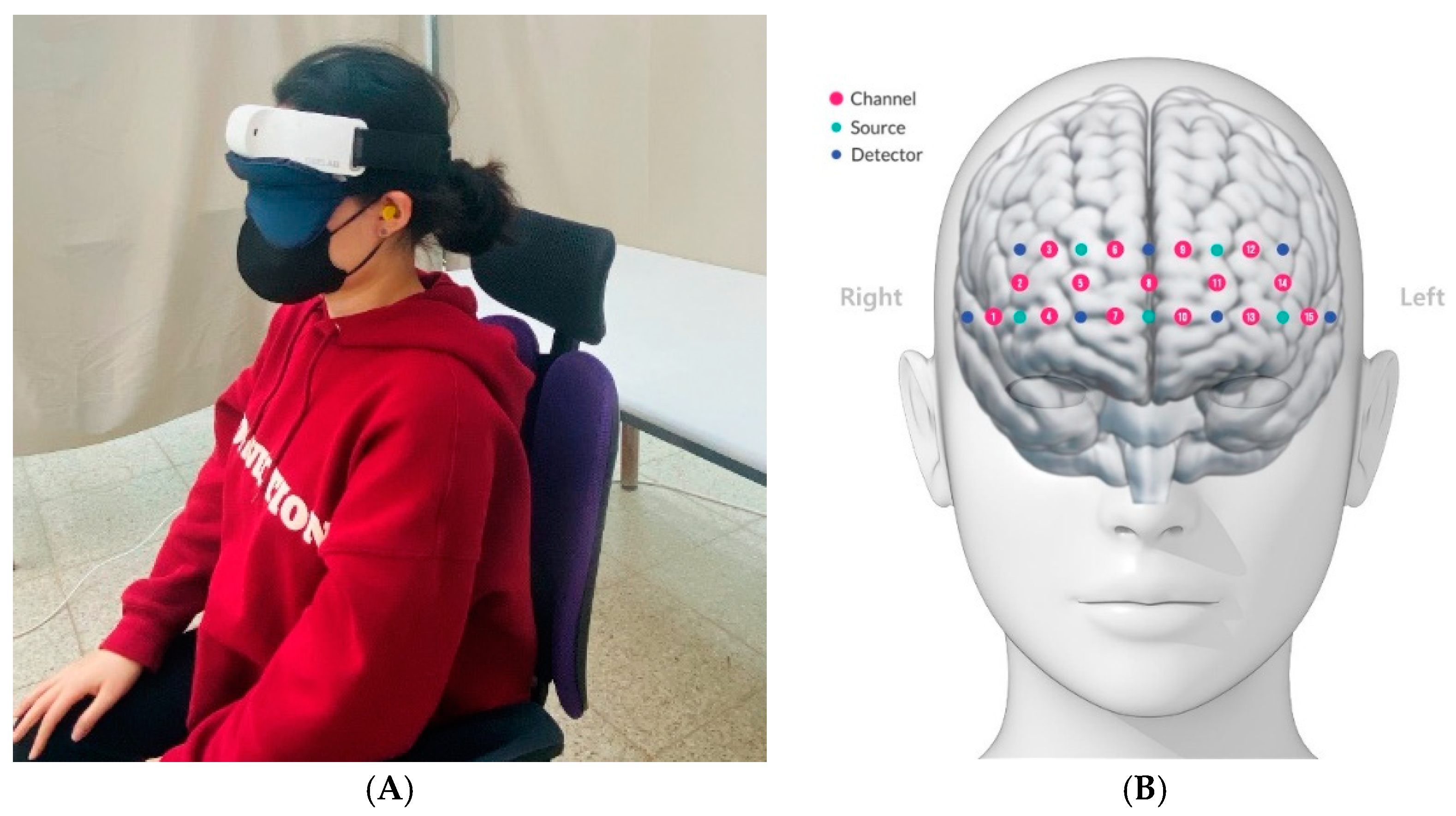
2.5.1. Near-Infrared Time-Resolved Spectroscopy
2.5.2. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate
2.5.3. Psychological Measurement
2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Tactile Stimulation (Hand)
3.2.1. Near-Infrared Time-Resolved Spectroscopy
3.2.2. Pulse Rate and Blood Pressure
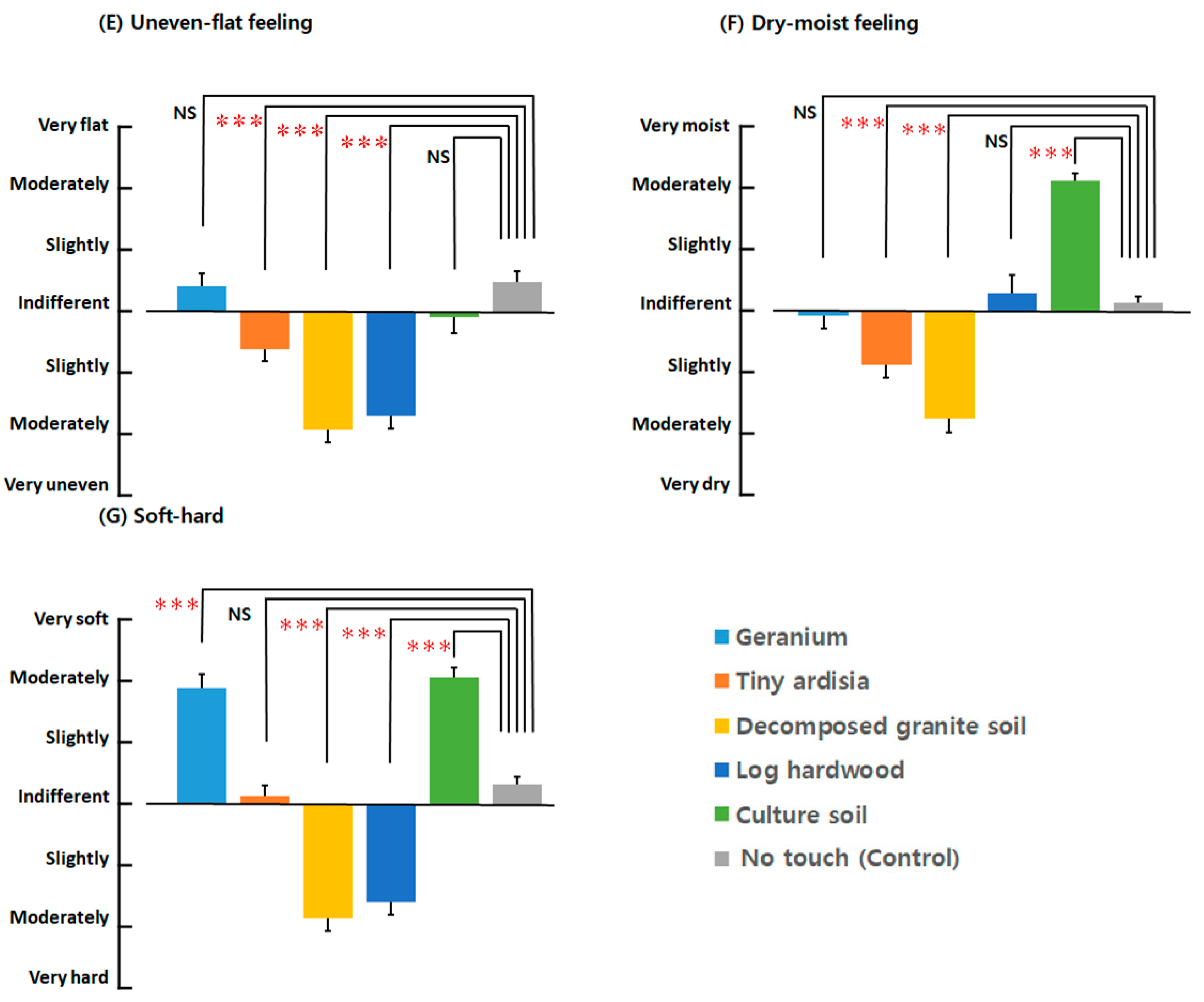
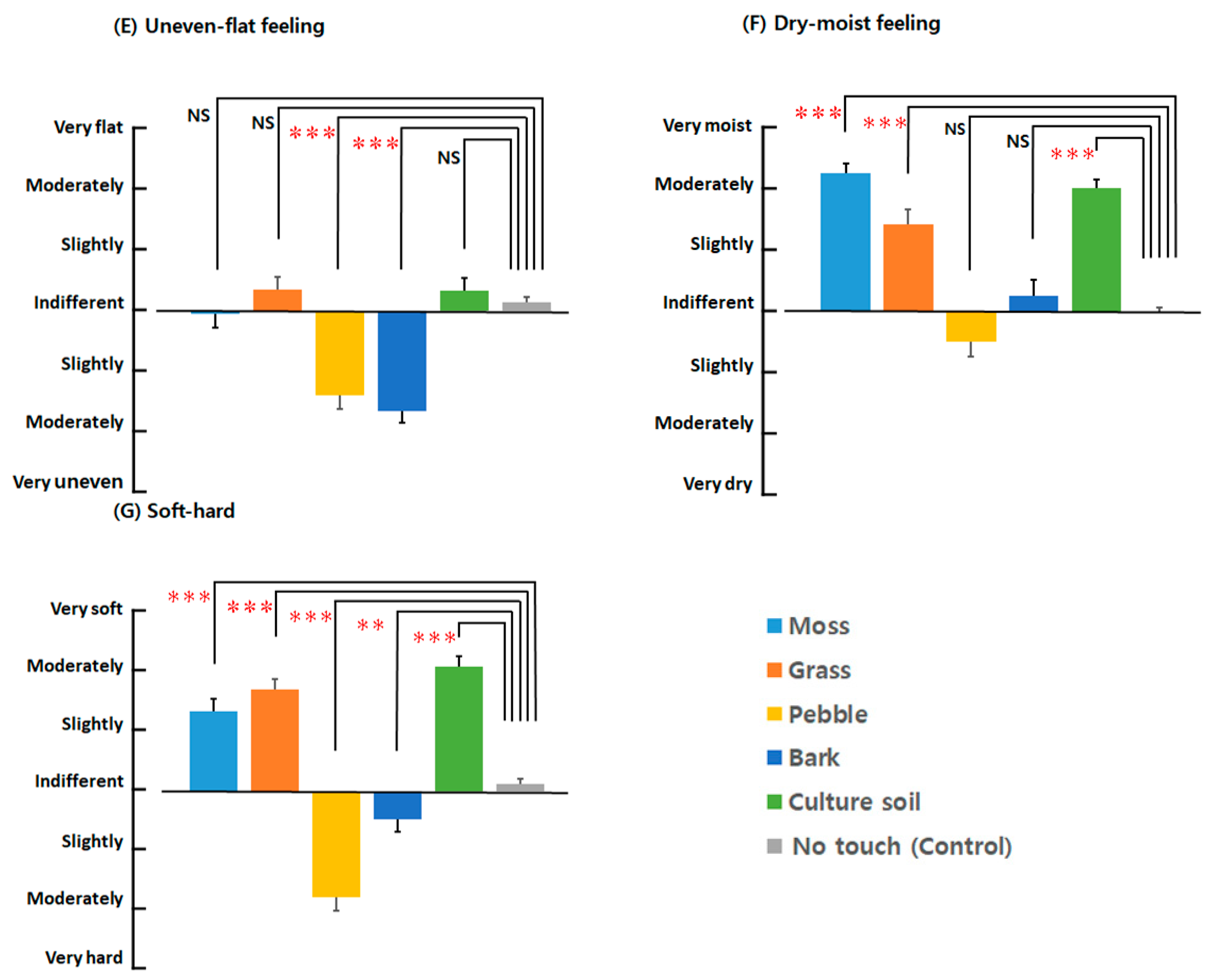
3.2.3. Semantic Differential Method (SDM)
3.3. Tactile Stimulation (Foot)
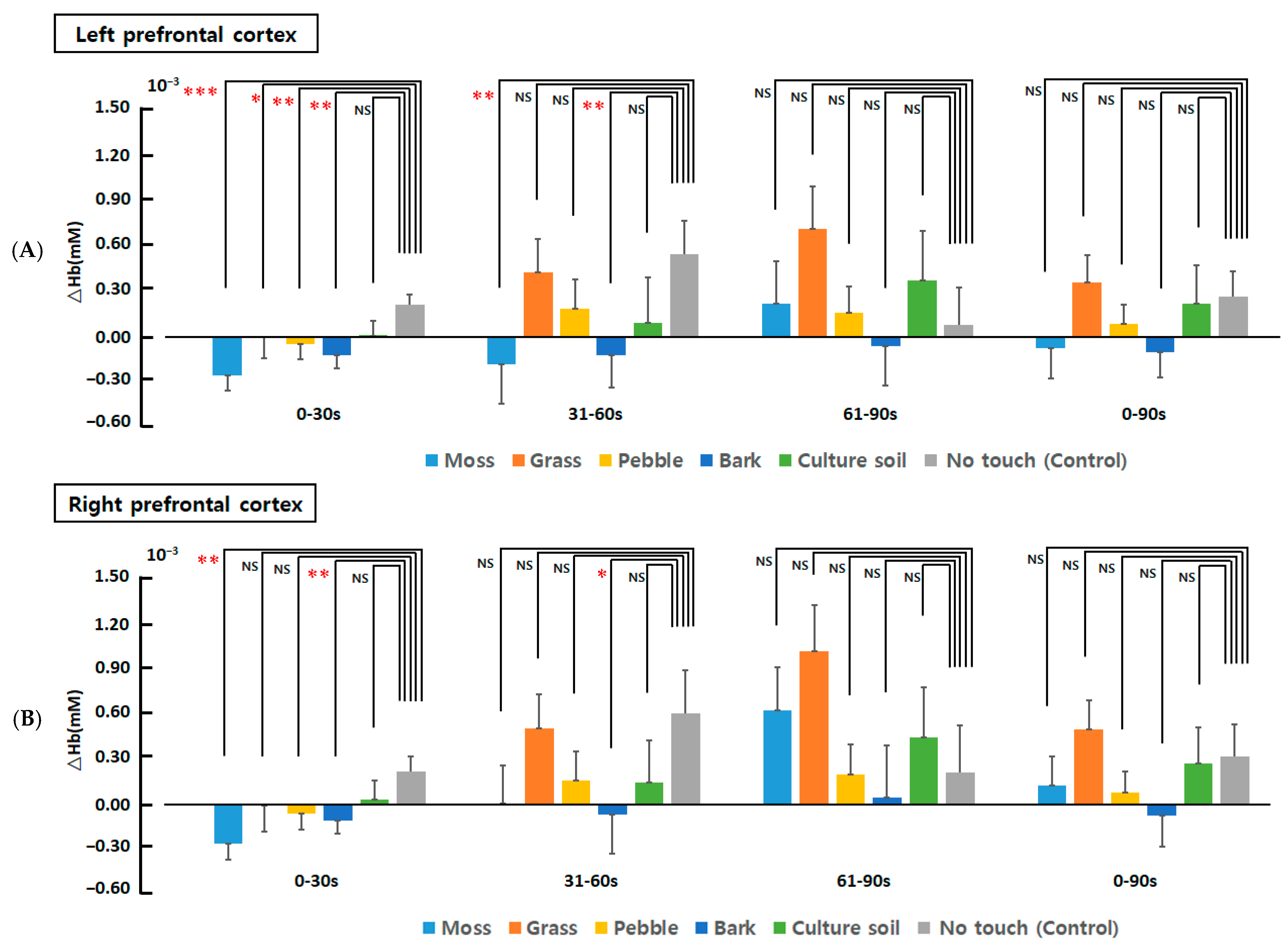
3.3.1. Near-Infrared Time-Resolved Spectroscopy
3.3.2. Pulse Rate and Blood Pressure
3.3.3. SDM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bae, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.S. Priority analysis of activation policies for agro-healing services. J. Korea Soc. Rural Plan. 2019, 25, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoisington, A.J.; Stearns-Yoder, K.A.; Schuldt, S.J.; Beemer, C.J.; Maestre, J.P.; Kinney, K.A.; Postolache, T.T.; Lowry, C.A.; Brenner, L.A. Ten questions concerning the built environment and mental health. Build Environ. 2019, 155, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, M.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Environmental exposures and depression: Biological mechanisms and epidemiological evidence. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2019, 40, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.S.; Simons, R.F.; Losito, B.D.; Fiorito, E.; Miles, M.A.; Zelson, M. Stress recovery during exposure to natural and urban environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 1991, 11, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O. Biophilia and the conservation ethic. In Evolutionary Perspectives on Environmental Problems; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017; pp. 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A.; Lee, A.Y.; Park, H.G.; Lee, W.L. Benefits of gardening activities for cognitive function according to measurement of brain nerve growth factor levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.J.; Kim, D.S.; Park, S.A. Horticultural Therapy for Improving the Work Performance and Interpersonal Relationships of Persons with Intellectual Disabilities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.A.; Park, S.A.; Ahn, B.E. Assessment of the psychopathological effects of a horticultural therapy program in patients with schizophrenia. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 36, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, A.M.; Kam, M.; Mok, I. Horticultural therapy program for people with mental illness: A mixed-method evaluation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.E.; Park, S.A. Physiological and Psychological Effects of Visual Stimulation with Green Plant Types. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Park, S.A. Effects of olfactory stimulation with aroma oils on psychophysiological responses of female adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Effects of forest-derived visual, auditory, and combined stimuli. Urban For. Urban Green 2021, 64, 127253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, F. The unity of haptic touch. Philos. Psychol. 2011, 24, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Psychological and physiological effect in humans of touching plant foliage-using the semantic differential method and cerebral activity as indicators. J. Physiol. Anthropo. L 2013, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of touching wood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Positive physiological effects of touching sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) with the sole of the feet. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, P.; Tachtsidis, I.; Hamilton, A.; Hirsch, J.; Aichelburg, C.; Gilbert, S.; Burgess, P.W. The present and future use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) for cognitive neuroscience. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sc. 2020, 1464, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osgood, C.E.; Suci, G.J.; Tannenbaum, P.H. The Measurement of Meaning; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1957; Available online: https://books.google.co.kr/books?id=Qj8GeUrKZdAC&printsec=frontcover&hl=ko&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 30 January 1997).
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of touching coated wood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological effects of touching hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa). J Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayer, C.; Freedman, M. Frontal lobe functions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2001, 1, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, B.; Mychasiuk, R.; Muhammad, A.; Li, Y.; Frost, D.O.; Gibb, R. Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex. PNAS 2012, 109 (Suppl. 2), 17186–17193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöbsis, F.F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 1977, 198, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S. NIRS for measuring cerebral hemodynamic responses during exercise. In Functional Neuroimaging in Exercise and Sport Sciences; Boecker, H., Hillman, C.H., Scheef, L., Strüder, H.K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrey, S. Non-invasive NIR spectoroscopy of human brain function during exercise. Methods 2008, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.T.; Raichle, M.E. Focal physiological uncoupling of cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism during somatosensory stimulation in human subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Tamura, M. Interpretation of near-infrared spectroscopy signals: A study with a newly developed perfused rat brain model. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Effects of olfactory stimulation with perilla essential oil on prefrontal cortex activity. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2014, 20, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M.; Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Miyazaki, Y. Effect of Stimulation by Foliage Plant Display Images on Prefrontal Cortex Activity: A Comparison with Stimulation using Actual Foliage Plants. J. Neuroimaging 2015, 25, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homae, F. A brain of two halves: Insights into interhemispheric organization provided by near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasio, A.R. The Feeling of What Happens. Body and Emotion in Making of Consciousness; Heinemann: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Waxenbaum, J.A.; Reddy, V.; Varacallo, M. Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System; Stat Pearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019; Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk539845 (accessed on 30 April 2019).
- Schwartz, G.E.; Weinberger, D.A.; Singer, J.A. Cardiovascular differentiation of happiness, sadness, anger, and fear following imagery and exercise. Psychosom. Med. 1981, 43, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.S. View through a window may influence recovery from surgery. Science 1984, 224, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunetsugu, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, B.J.; Tyrväinen, L.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological and Psychological Effects of Viewing Urban Forest Landscapes Assessed by Multiple Measurements. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 113, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Tao, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, M.; Ai, L.; Zhihui, J.; Zongfang, L.; Qibing, C. Effects of walking in bamboo forest and city environments on brainwave activity in young adults. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 9653857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Lu, L.; Gao, J.; He, X. Horticultural activities can achieve the same affect improvement effect of green exercise: A randomized field controlled trial. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 989919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.A.; Lee, A.Y.; Park, H.G.; Son, K.C.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, W.R. Gardening intervention as a low-to moderate-intensity physical activity for improving blood lipid profiles, blood pressure, inflammation, and oxidative stress in women over the age of 70: A pilot study. HortScience 2017, 52, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filingeri, D.; Fournet, D.; Hodder, S.; Havenith, G. Why wet feels wet? A neurophysiological model of human cutaneous wetness sensitivity. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 112, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragsig Peschardt, K.; Karlsson Stigsdotter, U. Associations between park characteristics and perceived restorativeness of small public urban green spaces. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 112, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Lee, J. Nature therapy. Designing Our Future: Perspectives on Bioproduction, Ecosystems and Humanity; Osaki, M.B.A., Nakagami, K., Eds.; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 407–412. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20113192530 (accessed on 30 December 2011).
- Miyazaki, Y. Shinrin-Yoku: The Japanese Way of Forest Bathing for Health and Relaxation; Aster: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, R.S. Health benefits of gardens in hospitals. In Proceedings of the Plants for People International Exhibition Floriade, Haarlemmermeer, The Netherlands, 6 April–20 October 2002; Available online: https://jardinessanadores.cl/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Health_Benefits (accessed on 30 January 2002).
- Velarde, M.D.; Fry, G.; Tveit, M. Health Effects of Viewing Landscapes: Landscape Types in Environmental Psychology. Urban For. Urban Green. 2007, 6, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.; Jorgensen, A.; Wilson, E.R. Evaluating restoration in urban green spaces: Does setting type make a difference? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 127, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Igarashi, M.; Namekawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Physiological and psychological relaxing effects of visual stimulation with foliage plants in high school students. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 28, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A.; Song, C.; Choi, J.Y.; Son, K.C.; Miyazaki, Y. Foliage plants cause physiological and psychological relaxation as evidenced by measurements of prefrontal cortex activity and profile of mood states. HortScience 2016, 51, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.O.; Jeong, J.E.; Oh, Y.A.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S.A. Comparing Concentration Levels and Emotional States of Children Using Electroencephalography During Horticultural and Nonhorticultural Activities. HortScience 2021, 56, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, Y.; van den Berg, A. Restorative environments: An introduction. In Environmental Psychology; Steg, L., van den Berg, A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumann, K.; Gärling, T.; Morten Stormark, K. Rating scale measures of restorative components of environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T.; Mitchell, R.; de Vries, S.; Frumkin, H. Nature and health. Ann. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlucchi, G.; Vallar, G. The history of the neurophysiology and neurology of the parietal lobe. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 151, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Variable | Male (n = 7) | Female (n = 23) | Total (N = 30) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||
| Age (years) | 26.71 ± 2.56 | 32.57 ± 11.28 | 31.20 ± 10.21 |
| Height 1 (cm) | 173.50 ± 2.19 | 161.50 ± 4.46 | 164.40 ± 6.58 |
| Body weight 2 (kg) | 75.90 ± 8.78 | 59.10 ± 11.66 | 63.20 ± 13.12 |
| Body mass index 3 (kg∙m−2) | 25.20 ± 2.80 | 22.60 ± 4.34 | 23.30 ± 4.13 |
| Variable | No Touch (Control) | Geranium | Tiny Ardisia | Decomposed Granite Soil | Log Hardwood | Culture Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD 1 | ||||||
| Pulse rate | 77.73 ± 9.87 | 76.63 ± 9.49 | 77.73 ± 9.16 | 78.10 ± 9.50 | 77.07 ± 9.40 | 77.93 ± 8.80 |
| Significance 2 | 0.317 | 1.000 | 0.724 | 0.487 | 0.857 | |
| Systolic pressure | 117.07 ± 16.60 | 114.37 ± 12.95 | 113.97 ± 13.95 | 116.33 ± 16.43 | 115.40 ± 15.46 | 118.37 ± 15.38 |
| Significance 2 | 0.066 | 0.012 * | 0.532 | 0.206 | 0.255 | |
| Diastolic pressure | 75.30 ± 11.82 | 73.33 ± 10.04 | 73.07 ± 9.41 | 74.93 ± 9.70 | 72.87 ± 10.81 | 74.80 ± 10.93 |
| Significance 2 | 0.045 * | 0.034 * | 0.712 | 0.020 * | 0.644 | |
| Variable | No Touch (Control) | Grass | Moss | Pebbles | Bark | Culture Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD 1 | ||||||
| Pulse rate | 75.73 ± 9.67 | 75.47 ± 10.36 | 76.50 ± 10.64 | 75.70 ± 11.35 | 75.93 ± 9.62 | 77.30 ± 11.00 |
| Significance 2 | 0.813 | 0.473 | 0.978 | 0.861 | 0.266 | |
| Systolic pressure | 114.03 ± 14.28 | 116.83 ± 15.24 | 116.07 ± 15.14 | 114.53 ± 14.08 | 114.90 ± 13.66 | 118.27 ± 16.83 |
| Significance 2 | 0.036 * | 0.047 * | 0.725 | 0.416 | 0.001 ** | |
| Diastolic pressure | 73.97 ± 10.72 | 74.90 ± 10.10 | 75.43 ± 11.49 | 75.50 ± 11.49 | 74.37 ± 8.97 | 75.13 ± 10.42 |
| Significance 2 | 0.358 | 0.165 | 0.201 | 0.660 | 0.325 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, S.-W.; Park, S.-A. Effects of Tactile Stimulation Using an Assortment of Natural Elements on the Psychophysiological Responses of Adults. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121293
Kim Y-J, Choi S-W, Park S-A. Effects of Tactile Stimulation Using an Assortment of Natural Elements on the Psychophysiological Responses of Adults. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(12):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121293
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yun-Jin, Soo-Wan Choi, and Sin-Ae Park. 2023. "Effects of Tactile Stimulation Using an Assortment of Natural Elements on the Psychophysiological Responses of Adults" Horticulturae 9, no. 12: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121293
APA StyleKim, Y.-J., Choi, S.-W., & Park, S.-A. (2023). Effects of Tactile Stimulation Using an Assortment of Natural Elements on the Psychophysiological Responses of Adults. Horticulturae, 9(12), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9121293







