Abstract
Slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) has strong bactericidal activity and is relatively safe compared to other disinfectants. In vitro exposure of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to SAEW at a chlorine concentration of more than 25 mg/L for 3 min completely killed bacterial cells. When SAEW was sprayed in a greenhouse at a chlorine concentration of around 30 mg/L, the viability of airborne microorganisms was significantly reduced. On the other hand, SAEW spray did not affect the growth of eggplant and cucumber plants in the greenhouse. SAEW spray did not influence microorganisms in the soil or the plant leaf surface. SAEW could be used as a substitute for tap water to increase the relative humidity during the daytime, which is expected to increase photosynthesis. SAEW spraying reduces airborne microorganisms and improves the environmental conditions in the greenhouse.
1. Introduction
Bacteria can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants; therefore, disinfection and hygiene are important for improving the health of these living organisms [1]. Bacterial contamination of indoor air currently a public health problem, especially on agricultural farms and in the food industry [2]. On agricultural farms, in areas such as greenhouses and poultry houses, high-bacteria aerosols can cause infectious and non-infectious diseases in farmers and agricultural products [3]. Therefore, bacterial disinfection has become an essential topic of intense study in recent years [4]. The common practice to control bacterial contamination in the air is aerosol spraying. Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and chlorine dioxide (ClO2) are widely used as disinfectants to reduce contamination with pathogenic bacteria on agricultural farms, and in the food industry, markets, hospitals, nursing homes, residential environments, and households [5]. However, these compounds are potentially toxic to plants, animals, and humans [6]. For example, NaOCl has oxidizing potential, which can cause corrosion [7], and povidone-iodine causes hypersensitivity and skin discoloration [8]. It is crucial to develop alternative disinfectants that are effective, safe, and economical for environmental decontamination [9]. Slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) is now considered as such an alternative. SAEW has been increasingly used to prevent and control microorganisms in various agricultural fields [5].
SAEW, a highly concentrated hypochlorous acid with a pH of 5.0–6.5; it is prepared by electrolysis of aqueous hydrochloric acid (HCl) in a chamber without a membrane [10]. Compared with other disinfectants, SAEW has no adverse effects, such as corrosion of equipment, skin irritation, or phytotoxicity in plants, and no safety problems caused by Cl2 waste gas. SAEW has received more attention in agriculture and has been shown to prevent and control bacterial infection [11,12,13,14]. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) approved SAEW as a food additive in 2002, and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (MAFF) and the Ministry of Environment (MOE) approved it as a control agent in 2014 [1,15].
SAEW significantly reduced microorganisms on the skin of swine and in swine barns [16]. Spray application of SAEW for dust reduction has been tested in layer breeding houses [17]. Reducing airborne microorganisms is a critical approach to improving the indoor air in a greenhouse [18]. The number of microorganisms in a greenhouse should be controlled due to two aspects: farmer’s health and plant disease. Greenhouses with plants have been shown to have higher airborne bacteria and fungi concentrations than conventional farms [19]. The workers inside the greenhouses increase the possibility of exposure to airborne, potentially pathogenic microorganisms. Some minor diseases occurring under field conditions have become major in the closed greenhouses. Windblown spores and aerosols containing bacteria enter doorways and ventilators. Once inside a greenhouse, pathogens are difficult to eradicate [20]. In this study, SAEW mist was sprayed in the greenhouse to control airborne microorganisms. In addition, this study combined integrated pest management (IPM) and humidity using SAEW spraying. We also investigated the effects of SAEW spraying on the environment in the greenhouse, such as plant growth and bacterial community structures in the soil and on plant leaf surfaces.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SAEW Preparation
SAEW was freshly prepared by electrolysis of an aqueous dilute solution of HCl and tap water using a KC-5000 generator (Kowatech, Kochi, Japan). The available chlorine concentration was measured immediately after preparation using an AQUAB AQ-202P chlorine tester (Sibata Scientific Technology, Saitama, Japan). Different chlorine concentrations were used in this study: 5–25 mg/L for in vitro experiments and 25–40 mg/L for greenhouse spraying.
2.2. SAEW Treatment of Bacterial Cell Cultures in Vitro
In vitro experiments were performed with Gram-negative Escherichia coli (NBRC 3972) and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis (NBRC 3134). Overnight culture of bacteria in Luria-Bertani (LB, 10 g bacto peptone, 5 g yeast extract, 5 g NaCl in 1 L) media was pelleted by centrifugation (15,000 rpm for 2 min at 4 °C). The cells were washed twice with autoclaved distilled water (DW) and resuspended in autoclaved DW. Then, 0.2 mL of washed cells was mixed with 0.2 mL of SAEW. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for various times (30 s, 1, 2, and 3 min). At the end of each treatment period, 1 mL of LB was added, and cells were pelleted by centrifugation. Cells were diluted several times and spread on LB agar plates. After incubation at 37 °C for 24 h, bacterial colonies were counted.
2.3. Monitoring Temperature and Relative Humidity in the Greenhouse
The thermo recorder (TR-72wf, T&D Corporation, Nagano, Japan) was placed in the greenhouse, and temperature and relative humidity were recorded every 10 min.
2.4. Spraying SAEW in the Greenhouse
Experiments were conducted in a greenhouse (11 m × 12 m × 3 m) located on the Monobe campus of Kochi University, Japan (Figure 1). The experimental greenhouse was divided into area A for SAEW spray and area B for tap water spray. The mist was generated with a MUM602 Universal Mist Generator (Maruyama, Tokyo, Japan) using spray nozzle type CKBC 045 (H. Ikeuchi, Osaka, Japan). The mean droplet diameter was 10–30 μm. SAEW or tap water was sprayed for 2 h at a flow rate of 12.5 L/h at intervals of 1 min spraying and 30 s stop.
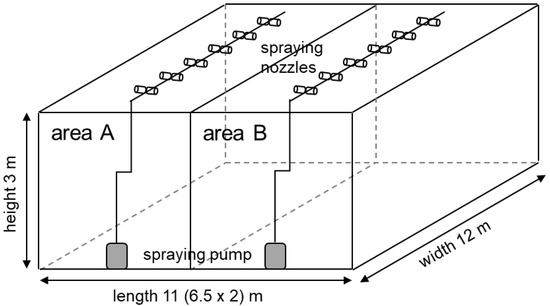
Figure 1.
Design of the greenhouse used in this study.
2.5. Counting Airborne Microorganisms
The air sample in the greenhouse was collected using an MP-Σ 500N air pump (Sibata Scientific Technology) equipped with an impinger filled with 10 mL of sterilized phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a flow rate of 2 L/min for 50 min. Then the collected air sample with 10 mL PBS was divided into two 5 mL tubes. The samples were stained with 4, 6-diamino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) at 15 µg/mL or propidium iodide at 3 µg/mL for 15 min, away from light. Stained samples were filtered through polycarbonate membrane filters (0.2 µm pore size, 25 mm diameter; Advantec, Tokyo, Japan) pre-stained with 0.0067% Sudan Black B. Microorganisms stained with DAPI or propidium iodide were observed under fluorescent microscopy with 100× objective lens using a UV excitation filter set (DM400, BP330-385, BA420; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) or a green excitation filter set (DM5665, BP520-550, BA580IF), respectively. The number of live cells was calculated by subtracting the number of dead cells based on propidium iodide staining from the number of total cells based on DAPI staining.
2.6. Effect of SAEW on Plant Growth
Cucumbers and eggplant were grown in the greenhouse. Tap water was sprinkled over the bedding once a day. Side shades were opened when the temperature was high. Six cucumber and six eggplant plants were selected for this experiment. The growth of four branches of cucumbers and two branches of eggplant on each plant was measured weekly for up to 70 days. The average of branch length was calculated.
2.7. Bacterial Community Structures in the Soil
Soil samples were collected from four locations in areas A and B before and after spraying SAEW and tap water in the greenhouse. Metagenomic DNA was extracted from the soil samples using the PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (MO BIO Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 0.7 g PowerBead, 750 μL PowerBead solution, and 0.25 g soil sample were added to a 2 mL tube with a screw cap. After adding 60 μL of Solution C1, the tube was smashed at 3000 rpm for 5 min with a MicroSmash MS-100 (TOMY Digital Biology, Tokyo, Japan). The tube was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 1 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a new 2 mL tube. Following the recommended procedure, the DNA was eluted with 100 μL Solution C6 into a new tube.
The first PCR amplified the V3–V4 regions of bacterial 16S rDNA with 341F-ill primer (5’-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3’) and 805R-ill primer (5’-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3’) using Tks Gflex DNA Polymerase (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). After the first PCR, products were purified using Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter, Tokyo, Japan), a second PCR was conducted using the first PCR products and index primers (Nextera XT index kit v2 set A, Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The DNA concentration of purified PCR products was measured using a QuantiFluor ONE dsDNA System with Quantus Fluorometer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA)
All libraries with 4 nM were mixed into a single tube and denatured with 0.2 N NaOH. Denatured DNA was diluted to 8 pM, loaded with 5% PhiX spike onto the cartridge of a MiSeq Reagent Nano Kit v2 (500 cycles), and analyzed with MiSeq (Illumina). The sequence reads were analyzed with the QIIME 2 next-generation microbiome bioinformatics platform [21] using a Silva database for 16S rDNA libraries.
2.8. Bacterial Community Structures on Plant Leaves
Discs were punched out from the leaves of three eggplants, repeatedly rinsed with 10 mL of PBS, and sonicated for 30 s, followed by shaking at 100 rpm for 30 min to remove the microorganisms residing on the leaf surface. Microorganisms recovered from the leaf surface were trapped on membranes of mixed cellulose esterase (0.45 µm pore size, 25 mm diameter; ADVANTEC), and metagenomic DNA was extracted using the PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit. Amplicon libraries of V3–V4 regions of 16S rDNA were prepared as described in Section 2.6 and sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq next-generation sequencer. The relative abundance at the genus level was analyzed with QIIME2.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were conducted with multiple replicates and data were analyzed using Student’s t-test at the 1% level.
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Disinfection Effect of SAEW
When E. coli or B. subtilis cells in LB media were mixed with SAEW at a high chlorine concentration, we could not observe bacterial disinfection (data not shown). This could be due to the rapid elimination of hypochlorous acid (HOCl), which has potent antimicrobial activity, with the organic compounds in LB media [22]. When we mixed the washed E. coli cells with SAEW at a chlorine concentration of more than 25 mg/L, the number of E. coli cells was dramatically reduced (Figure 2). However, lower chlorine concentrations of 5–10 mg/L of SAEW did not show bactericidal activity. In the case of B. subtilis cells, SAEW worked more effectively, even at lower chlorine concentrations (Figure 3).
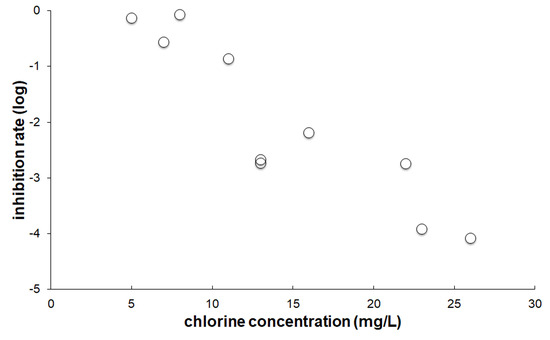
Figure 2.
In vitro disinfection activity of SAEW on E. coli. The inhibition rate was evaluated by dividing the number of cells treated with SAEW by those treated with DW.
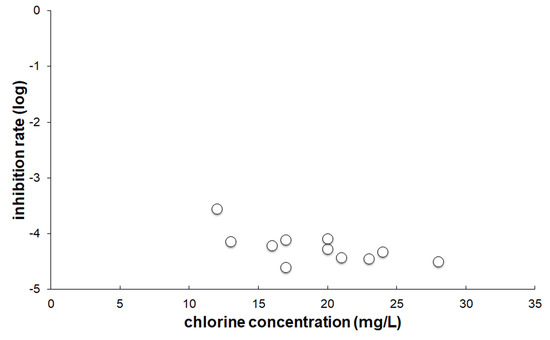
Figure 3.
In vitro disinfection activity of SAEW on B. subtilis. The inhibition rate was calculated the same way with E. coli.
3.2. Effect of SAEW Spraying on Airborne Bacteria in a Greenhouse
To distinguish live and dead airborne bacteria in the greenhouse, we first used a LIVE/DEAD BacLight Bacterial Viability Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), which uses SYTO 9 and propidium iodide for staining of live and dead cells, respectively. However, it was difficult to distinguish between live and dead cells in this system. Thus, in separate reactions, we used DAPI to count total cells, live and dead, and propidium iodide for dead cells. About half of the cells in the greenhouse air were dead (Figure 4). When SAEW was sprayed, the ratio of dead cells dramatically increased, while tap water spray did not change the number of dead cells (Figure 4).
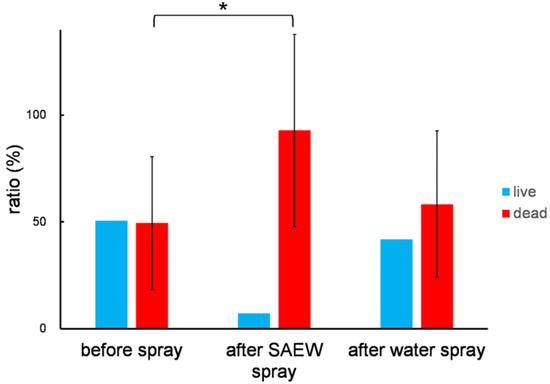
Figure 4.
Microorganism disinfection activity of SAEW in the greenhouse. The data was an average of six replicates with standard deviation. An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference (p < 0.01).
3.3. Effect of SAEW on Plant Growth in the Greenhouse
The effect of spraying SAEW on plant growth in the greenhouse was tested by measuring the growth of cucumbers (Figure 5A) and eggplants (Figure 5B). Plants grew well in both the SAEW-sprayed and tap water-sprayed areas. When the daily amount of SAEW was doubled, eggplants grew well, the same as in the tap water-sprayed area (data not shown). These results indicate that SAEW spraying did not affect plant growth in the greenhouse. There were no differences in seed weights between eggplants after 70 days of SAEW spraying and those sprayed with tap water (data not shown).
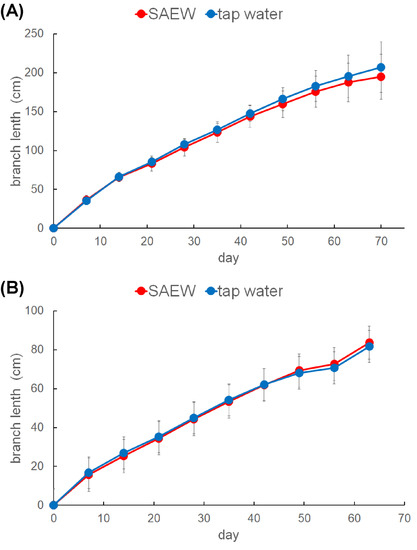
Figure 5.
Growth of plants in the greenhouse. (A) The growth of four branches of six cucumbers in greenhouse area A sprayed with SAEW (red circles), and area B sprayed with tap water (blue circles) was measured weekly. The average of branch lengths with SD was shown. (B) The growth of two branches of six eggplants was measured.
3.4. Effect of Spraying SAEW on Soil Microorganisms
Soil bacterial community structures in greenhouse areas A and B showed no difference (Figure 6). The dominant phyla were Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes. Bacteria belonging to these phyla are common in soil [23]. Even when SAEW was sprayed in area A, the bacterial community structures did not change (Figure 6). The control area B, sprayed with tap water, showed the same community structures. There was no overall difference in the beta diversity of soil bacterial communities by SAEW spraying (Figure 7A).
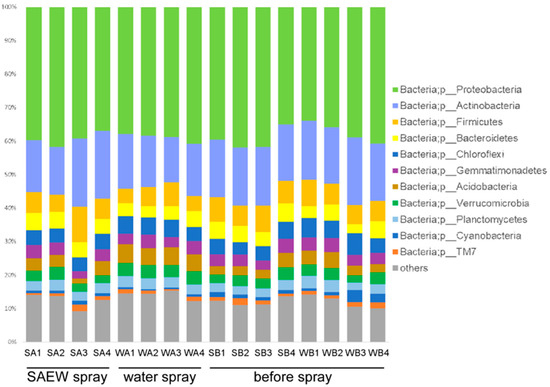
Figure 6.
Taxonomic analysis of bacteria in the greenhouse soil. Soil samples were taken from SB; area A before spray, WB; area B before spray, SA; area A after SAEW spray, WA; area B after tap water spray.
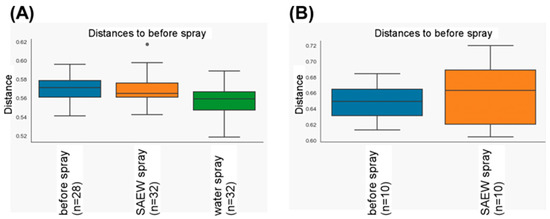
Figure 7.
Box plot of beta diversity of bacteria in the greenhouse. The box plot represented (A) the values of the distances to the soil bacterial community before spraying SAEW and tap water, and (B) the values of the distances to the eggplant leaf bacterial community before spraying SAEW and tap water, based on UniFrac distances. The box plots show medians (horizontal line in box), 25 and 75% quartiles, and max/min values, outliers marked as circles.
3.5. Effect of Spraying SAEW on Leaf Microorganisms
After washing out microorganisms loosely attached to the eggplant leaves, the microorganisms on the leaves were isolated. The dominant bacteria on the eggplant leaves in greenhouse areas A and B belonged to the genus Sphingobium (Figure 8). Sphingobium strains are known to colonize leaf surfaces [24]. The leaf bacterial community structures showed no difference between areas A and B. When SAEW was sprayed in area A, the bacterial community structures did not change (Figure 8). There was no overall difference in the beta diversity of leaf bacterial communities by SAEW spraying (Figure 7B).
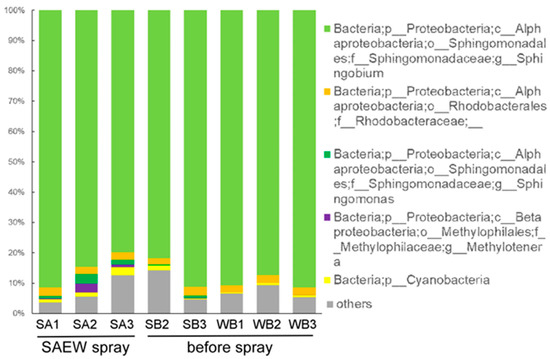
Figure 8.
Taxonomic analysis of bacteria on the eggplant leaves. Leaf discs were taken from SB; area A before spray, WB; area B before spray, and SA; area A after SAEW spray.
3.6. Environment Change in the Greenhouse by Spraying SAEW
Tomato yield was reported to be increased by a higher relative humidity [25]. We expected that SAEW spraying, like tap water spraying, could increase the relative humidity in the greenhouse. The relative humidity change was monitored after spraying SAEW in area A and tap water in area B. When the initial humidity was less than 60%, tap water spray increased the humidity close to 100% (Figure 9B). SAEW spraying showed the same effect as tap water. In the case of high humidity conditions, such as on a rainy day, spraying SAEW or tap water did not change the humidity, as expected (Figure 9B). The effect of spraying on temperature change was insignificant (Figure 9A). Although we expected that spraying would lower the temperature in the greenhouse by evaporative cooling, the temperature sometimes increased by up to 4 °C. Since the spraying continued for 2 h during the daytime while the outside temperature increased, this could have canceled out the evaporative cooling effect.
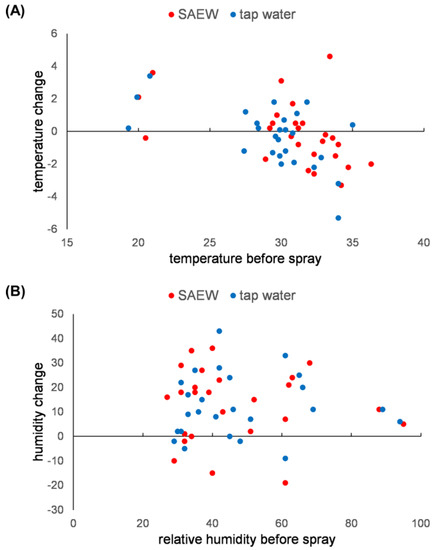
Figure 9.
Environmental change in the greenhouse by spraying SAEW. (A) The temperature in the greenhouse was monitored before and after SAEW and tap water spray. The temperature change was plotted against the temperature before spraying. (B) The relative humidity in the greenhouse was monitored before and after SAEW and tap water spray. The humidity change was plotted against the relative humidity before spraying.
4. Discussion
In vitro experiments using mixed E. coli and B. subtilis with SAEW in the solution demonstrated that although the antibacterial efficiency was different between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, SAEW at more than 25 mg/L completely killed bacteria. The disinfection mechanism of SAEW was demonstrated to be disrupting the permeability of the cell membrane and the cytoplasmic ultra-structures in Staphylococcus aureus cells [26]. The bactericidal mechanism of SAEW on Listeria monocytogenes was explained from two aspects including the damage to the cell membrane and the breaking of reactive oxygen species (ROS) balance [27]. The cell morphology and structure of Shewanella putrefaciens and Staphylococcus saprophyticus were demonstrated to be destroyed by SAEW. Besides, leakage of DNA and protein provided evidence that SAEW induced membrane permeabilization in cells [28]. SAEW worked the same way on E. coli and B. subtilis in this study and could be applied to control airborne microorganisms.
When SAEW was sprayed in the greenhouse for 2 h, dead cells dramatically increased by more than 90%. Even when the spraying time was up to 3 h, the dead cell ratio did not change, indicating that 2 h of spraying is enough to control airborne microorganisms. Although not many studies of SAEW application in the greenhouse have been reported, the spatial disinfection potential of SAEW has been demonstrated. A model clean chamber (length: 2.99 m, width: 3.96 m, height: 2.21 m) was used for SAEW spraying [15]. Staphylococcus epidermidis sprayed in the space was completely removed after 20 min of SAEW spraying. Spraying acidic electrolyzed oxidizing water significantly reduced powdery mildew in the greenhouse, which grew gerbera daisy [29]. Airborne microorganisms in swine barns decreased by 59 and 12% after 30 min exposure to SAEW and tap water, respectively [30].
Since SAEW was demonstrated to be an effective material for reducing airborne microorganisms in a greenhouse, we evaluated its negative effects. When eggplants and cucumbers growing in the greenhouse were treated with SAEW spraying, the plants grew normally and produced normal seeds, indicating that they were not affected by SAEW. When the broccoli seeds were submerged in SAEW solutions for 3 h, SAEW was demonstrated to inhibit the growth of broccoli sprouts [31]. Sprayed SAEW might be eliminated immediately after reaching the plant surfaces, and the negative effect was not observed. Soil bacteria are essential for plant growth [32]. Spraying SAEW did not affect the soil microorganisms in the greenhouse. Beneficial bacteria reside on plant leaves [33]. Spraying SAEW did not affect the leaf microorganisms in the greenhouse.
5. Conclusions
SAEW, a safe and effective disinfectant, successfully reduced airborne microorganisms in a greenhouse by spraying it in a fine mist. At the same time, SAEW spraying had no adverse effect. SAEW spraying did not affect plant growth in the greenhouse. Microorganisms in the soil and on the leaves were not affected by SAEW spraying in the greenhouse. SAEW spraying can improve the greenhouse environment by increasing relative humidity. As a result, SAEW spraying in the greenhouse could achieve IPM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B. and K.O.; methodology, B.B., S.Y. and K.O.; validation, J.N.B. and K.O.; formal analysis, B.B. and K.O.; investigation, B.B., S.Y. and K.O.; resources, S.Y.; data curation B.B. and K.O.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B. and K.O.; writing—review and editing, S.Y., J.N.B. and K.O.; supervision, K.O.; project administration J.N.B. and K.O.; funding acquisition, K.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a Cabinet Office grant in aid, the Advanced Next-Generation Greenhouse Horticulture by IoP (Internet of Plants), Japan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable for studies not involving humans.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Miho Satoh for her support with the Illumina MiSeq operation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naka, A.; Yakubo, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kurahashi, M. Effectiveness of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on bacteria reduction: In vitro and spray evaluation. Peer J. 2020, 8, e8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douwes, J.; Thorne, P.; Pearce, N.; Heederik, D. Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment: Progress and prospects. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2003, 47, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Yang, S.; Chang, M.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Luo, C.H.; Hung, P.C.; Fang, W. Inactivation efficiency to Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli bacterial aerosols of spraying neutral electrolyzed water. J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heederik, D.; Sigsgaard, T. Respiratory allergy in agricultural workers: Recent developments. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 5, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, S.; Shitanda, D.; Note, M.; Cao, W. Effects of mildly heated, slightly acidic electrolyzed water on the disinfection and physicochemical properties of sliced carrot. Food Control 2011, 22, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, F.; Oh, D.H. Hurdle enhancement of slightly acidic electrolyzed water antimicrobial efficacy on Chinese cabbage, lettuce, sesame leaf and spinach using ultrasonication and water wash. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumelzu, E.; Cabezas, C. Observations on the influence of cleaners on material corrosion in the food industry. Mater. Charact. 1996, 37, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.L. Chemical and microbiologic characteristics and toxicity of povidone-iodine solutions. Am. J. Surg. 1986, 151, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Cao, W.; Zheng, W.C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.M. Reduction of microbial contamination on the surfaces of layer houses using slightly acidic electrolyzed water. Poultry Sci. 2015, 94, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Shu, D.; Tang, X.; Zang, Y. Effects of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on the microbial quality and shelf life extension of beef during refrigeration. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H. Synergistic effect of low concentration electrolyzed water and calcium lactate to ensure microbial safety, shelf life and sensory quality of fresh pork. Food control 2013, 30, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Cao, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Ge, L. Slightly acidic electrolyzed water for reducing airborne microorganisms in a layer breeding house. J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Tango, C.N.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.H. Sanitization efficacy of slightly acidic electrolyzed water against pure cultures of Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus spores, in comparison with different water hardness. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, H.; Gates, R.S.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Soupir, M.L. Airborne particulate matter and culturable bacteria reduction from spraying slightly acidic electrolyzed water in an experimental aviary laying-hen housing chamber. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, M.; Ito, T.; Naka, A. Spatial disinfection potential of slightly acidic electrolyzed water. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, C.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Lin, B. Feasibility study of the sterilization of pigskin used as wound dressings by neutral electrolyzed water. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, B.; Cao, W.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Z. Application of neutral electrolyzed water spray for reducing dust levels in a layer breeding house. J. Air. Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichao, Z.; Li, N.; Xue, H.; Baoming, L.; Jiafa, Z. Optimization of slightly acidic electrolyzed water spray for airborne culturable bacteria reduction in animal housing. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Geng, X.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Abundant bacteria and fungi attached to airborne particulates in vegetable plastic greenhouses. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Song, W. Research on the feasibility of spraying micro/nano bubble ozonated water for airborne disease prevention. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.-Y.; Tango, C.N.; Oh, D.-H. Influence of different organic materials on chlorine concentration and sanitization of slightly acidic electrolyzed water. LWT 2018, 92, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Ali, S.; Amara, U.; Rabia Khalid, R.; Ahmed, I. Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, G.; Sbodio, A.; Tech, J.; Suslow, T.V.; Coaker, G.L.; Johan, H.J.; Leveau, J.H.L. Leaf microbiota in an agroecosystem: Spatiotemporal variation in bacterial community composition on field-grown lettuce. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, S.; Gary, C.; Leonardi, C.; Bertin, N. Analysis of growth and water relations of tomato fruits in relation to air vapor pressure deficit and plant fruit load. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2005, 24, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Xuan, X.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Shi, J.; Xue, S.J. Disinfection efficacy and mechanism of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on Staphylococcus aureus in pure culture. Food Control 2016, 60, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, D.; Huang, J.; Cui, C.; Rao, H.; Zhao, D.; Hao, J. The bactericidal efficacy and the mechanism of action of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on Listeria monocytogenes’ survival. Foods 2021, 10, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lan, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of slightly acidic electrolyzed water against Shewanella putrefaciens and Staphylococcus saprophytic. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 592, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.S.; Hung, Y.-C.; Oetting, R.D.; van Iersel, M.W.; Buck, J.W. Evaluation of electrolyzed oxidizing water for management of powdery mildew on gerbera daisy. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.X.; Li, B.M.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, B.Z.; Ge, L.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Cao, W. Disinfection effectiveness of slightly acidic electrolysed water in swine barns. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hao, J.; Song, S.; Nirasawa, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, H. Effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on bioactive compounds and morphology of broccoli sprouts. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ke, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; Qian, H. Effects of imazethapyr spraying on plant growth and leaf surface microbial communities in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).