Dissecting Seed Proanthocyandin Composition and Accumulation under Different Berry Ripening Process in Wine Grapes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Information of Sub-Regions
2.1.2. Sample Collection
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Berry TSS and TA
2.2.2. Extraction and Determination of Seed PA
2.2.3. Analysis of Flavan-3-ol Units
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
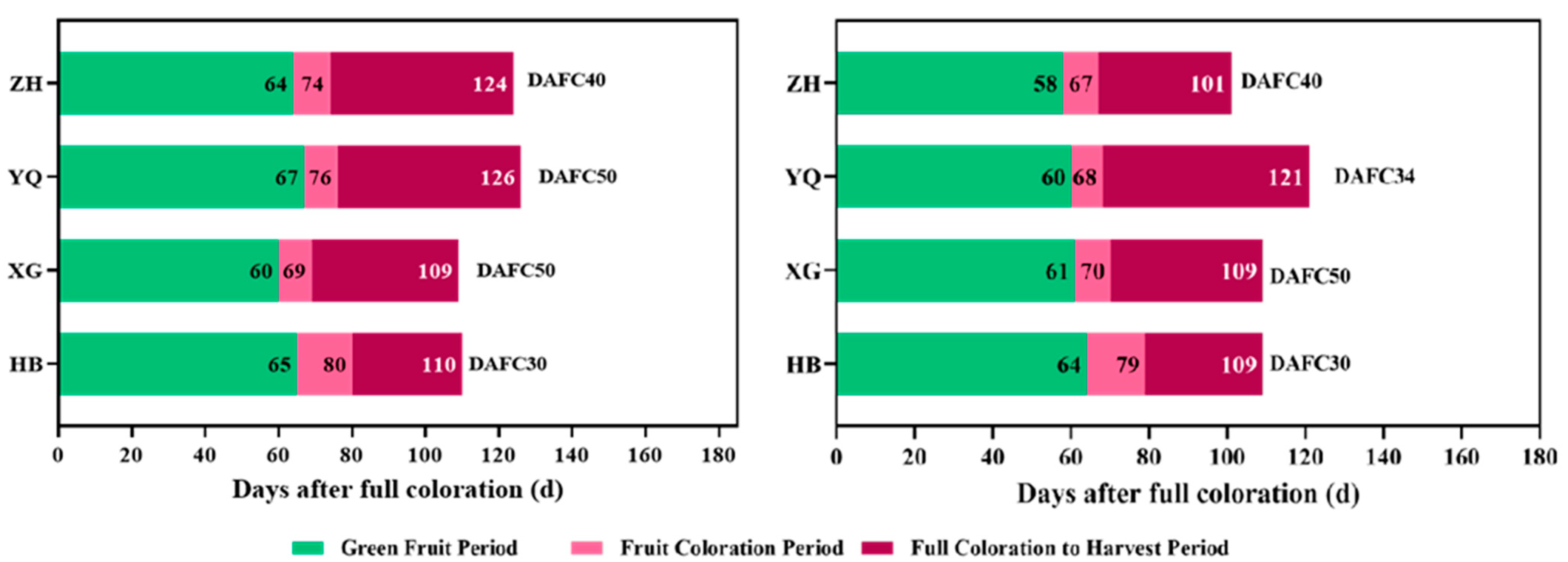
3.1. Differences in the Ripening Process of Grapes
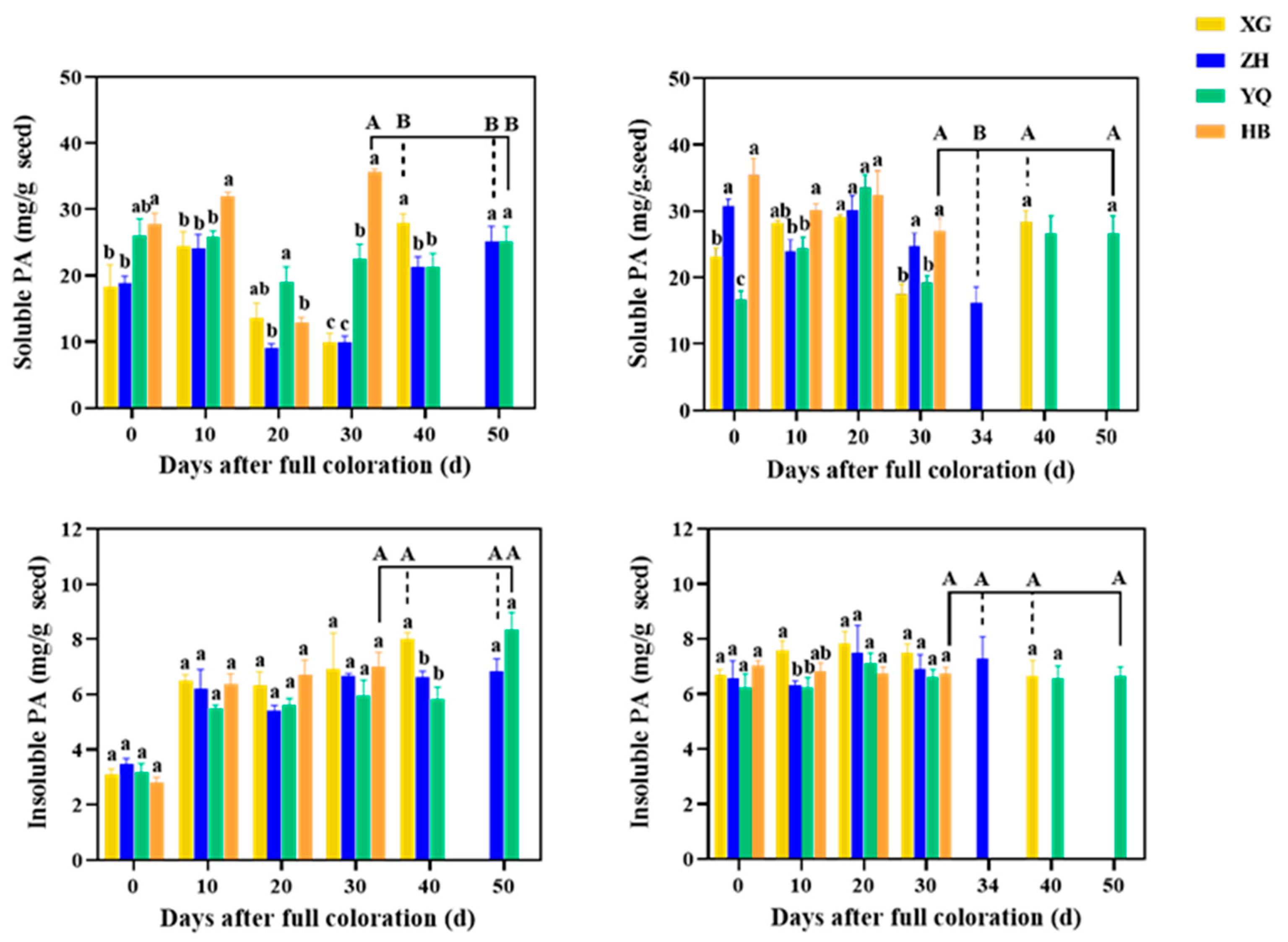
3.2. Differences in Soluble and Insoluble PA Accumulation in Seeds
3.3. Differences in Soluble and Insoluble PA Composition Units and Their Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, R.A.; Xie, D.Y.; Sharma, S.B. Proanthocyanidins—A Final Frontier in Flavonoid Research? New Phytol. 2005, 1651, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrussa, E.; Braidot, E.; Zancani, M.; Peresson, C.; Bertolini, A.; Patui, S.; Vianello, A. Plant Flavonoids-Biosynthesis, Transport and Involvement in Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14950–14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlin, R.L.; Kelm, M.A.; Wilkinson, K.L.; Downey, M.O. Detailed Characterization of Proanthocyanidins in Skin, Seeds, and Wine of Shiraz and Cabernet Sauvignon Wine Grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 13265–13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chira, K.; Schmauch, G.; Saucier, C.; Fabre, S.; Teissedre, P.L. Grape Variety Effect on Proanthocyanidin Composition and Sensory Perception of Skin and Seed Tannin Extracts from Bordeaux Wine Grapes (Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot) for Two Consecutive Vintages (2006 and 2007). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousserie, P.; Rabot, A.; Geny-Denis, L. From Flavanols Biosynthesis to Wine Tannins: What Place for Grape Seeds? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1325–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Muñoz, B.; Garrido-Vargas, F.; Pavez, C.; Osorio, F.; Chen, J.; Bordeu, E.; O’Brien, J.A.; Brossard, N. Wine Astringency: More Than Just Tannin–Protein Interactions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; Francis, L.; Guyot, S.; Marnet, N.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Gawel, R.; Cheynier, V.; Waters, E.J. The Mouth-Feel Properties of Grape and Apple Proanthocyanidins in a Wine-Like Medium. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheynier, V.; Duenas-Paton, M.; Salas, E.; Maury, C.; Souquet, J.M.; Sarni-Manchado, P.; Fulcrand, H. Structure and Properties of Wine Pigments and Tannins. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 2006, 57, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Peel, G.J.; Wright, E.; Wang, Z.; Dixon, R.A. Early Steps in Proanthocyanidin Biosynthesis in the Model Legume Medicago Truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindon, K.A.; Smith, P.A.; Holt, H.; Kennedy, J.A. Interaction between grape-derived proanthocyanidins and cell wall material. 2. Implications for vinification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10736–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcrand, H.; Dueñas, M.; Salas, E.; Cheynier, V. Phenolic Reactions During Winemaking and Aging. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 2006, 57, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, O.; Gonzalez-Royo, E.; Gil, M.; Gomez-Alonso, S.; Garcia-Romero, E.; Canals, J.M.; Hermosin-Gutierrez, I.; Zamora, F. Influence of Grape Seeds and Stems on Wine Composition and Astringency. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6555–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.A.; Troup, G.J.; Pilbrow, J.R.; Hutton, D.R.; Hewitt, D.; Hunter, C.R.; Ristic, R.; Iland, P.G.; Jones, G.P. Development of Seed Polyphenols in Berries from Vitis vinifera L. Cv. Shiraz. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2000, 6, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, R.; Iland, P.G. Relationships between Seed and Berry Development of Vitis vinifera L. Cv Shiraz: Developmental Changes in Seed Morphology and Phenolic Composition. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2005, 11, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. State of the Global Climate 2021; No. 1290; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Marotzke, J.; Bala, G.; Cao, L.; Corti, S.; Dunne, J.P.; Engelbrecht, F.; Fischer, E.; Fyfe, J.C.; Jones, C.; et al. 2021: Future Global Climate: Scenario-Based Projections and NearTerm Information. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 553–67217. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martínez, F.T. Variability in the Potential Effects of Climate Change on Phenology and on Grape Composition of Tempranillo in Three Zones of the Rioja Doca (Spain). Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 115, 126014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchêne, E.; Schneider, C. Grapevine and Climatic Changes: A Glance at the Situation in Alsace. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.R.; White, M.A.; Cayan, D.R.; Jones, G.V.; Running, S.W.; Coughlan, J.C.; Peterson, D.L. Asymmetric Warming over Coastal California and Its Impact on the Premium Wine Industry. Clim. Res. 2001, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.; Gerstengarbe, F.W.; Kartschall, T.; Werner, P.C. Reliability of Climate Change Impact Assessments for Viticulture. Acta. Hortic. 2005, 689, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, L. Impact of climate warming on heat resources and freezing injuries in wine grapes at the east foot of the Helan Mountains of Ningxia. Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2017, 37, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, F.; Urvieta, R.; Buscema, F.; Rasse, M.; Fontana, A.; Berli, F. Phenolic Characterization of Cabernet Sauvignon Wines from Different Geographical Indications of Mendoza, Argentina: Effects of Plant Material and Environment. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 700642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, C.; Fait, A.; Palumbo, F.; Lucchin, M.; Vannozzi, A. The Effect of Soil on the Biochemical Plasticity of Berry Skin in Two Italian Grapevine (V. vinifera L.) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtke, L.M.; Antalick, G.; Šuklje, K.; Blackman, J.W.; Boccard, J.; Deloire, A. Cultivar, Site or Harvest Date: The Gordian Knot of Wine Terroir. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R. Characteristics and evaluation of soil fertility in different sub-producing areas of wine grapes in the eastern foothills of Helan Mountain, Ningxia. Zhong Guo Tu Rang Yu Fei Liao 2021, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Niu, R.; Huang, X.; Shen, T.; Chen, W. Maturity Monitoring and Quality Comparison of Wine Grapes in the Typical Area of Eastern Foothills of Helan Mountain. Ning Xia Nong Lin Ke Ji 2020, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Gu, J.; Wu, H. Wine Grapes at the Eastern Foot of Helan Mountain of NingxiaExperimental Study on Integration of Water and Fertilizer of Drip Irrigation. Jie Shui Guan Gai 2016, 8, 76–81; 85. [Google Scholar]
- GBT15038-2006; Analytical Methods of Wine and Fruit Wine. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Yu, K.; Jun, J.; Duan, C.; Dixon, R.A. Vvlar1 and Vvlar2 Are Bifunctional Enzymes for Proanthocyanidin Biosynthesis in Grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, Q. Effects of different grapevine genotypes and micro-environments on concentrations of flavan-3-ols. J. Fruit Sci. 2014, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista-Ortín, A.B.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Gil-Muñoz, R.; Jiménez-Pascual, E.; Busse-Valverde, N.; Martínez-Cutillas, A.; López-Roca, J.M.; Gómez-Plaza, E. Influence of Berry Ripeness on Concentration, Qualitative Composition and Extractability of Grape Seed Tannins. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2012, 18, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.A.; Matthews, M.A.; Waterhouse, A.L. Changes in Grape Seed Polyphenols During Fruit Ripening. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geny, L.; Saucier, C.; Bracco, S.; Daviaud, F.; Glories, Y. Composition and Cellular Localization of Tannins in Grape Seeds During Maturation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8051–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, K. The Science of Grapevines: Anatomy and Physiology, 1st ed.; Wang, J., Duan, C., He, F., Zhu, B., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Allegro, G.; Pastore, C.; Valentini, G.; Muzzi, E.; Filippetti, I. Influence of Berry Ripeness on Accumulation, Composition and Extractability of Skin and Seed Flavonoids in Cv. Sangiovese (Vitis vinifera L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4553–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasy, L.L.; Swain, T. Structure of Condensed Tannins. Nature 1965, 208, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
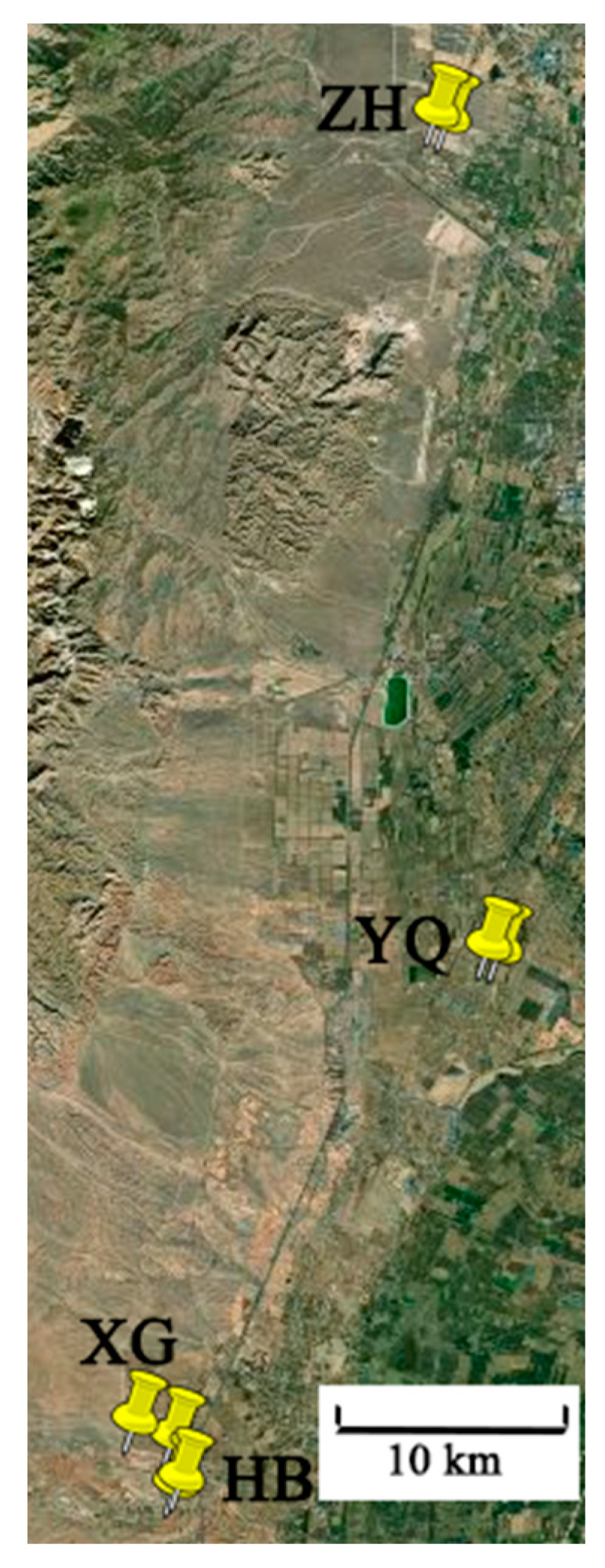

| Sub- Regions | Soil Type | Soil Conditions | ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ Grapevine Information | ‘Marselan’ Grapevine Information | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Organic Content g/kg | Available Nitrogen mg/kg | Available Phosphorus mg/kg | Available Kalium mg/kg | ||||
| ZH | Sandy loam | 7.84 | 16.40 | 82.00 | 15.00 | 220.00 | 6.35 ha, planted in 2013, spaced at 1.2 × 4 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, Vertical Shoot Positioning, yield 1.99 kg per extension meter. | 6.4 ha, planted in 2015, spaced at 2 × 4 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, Vertical Shoot Positioning, yield 1.77 kg per extension meter. |
| YQ | Sandy light sierozem | 8.66 | 8.58 | 9.55 | 27.16 | 104.39 | 2 ha, planted in 2012, spaced at 0.5 × 3.5 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, vertical shoot positioning, yield 2.00 kg per extension meter. | 4.73 ha, planted in 2018, spaced at 0.6 × 3.5 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, vertical shoot positioning, yield 2.19 kg per extension meter. |
| XG | Aeolian soil | 8.58 | 10.83 | 14.86 | 51.66 | 155.31 | 2.5 ha, planted in 2017, spaced at 1 × 3.5 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, inclined single cordon trellis system, yield 1.32 kg per extension meter. | 2 ha, planted in 2017, spaced at 1 × 3 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, Vertical Shoot Positioning, yielding 1.51 kg per extension meter. |
| HB | Newly accumulated light sierozem | 8.49 | 6.22 | 15.10 | 28.00 | 147.00 | 1.33 ha, planted in 2010, spaced at 0.4 × 3 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, single cordon trellis system, yield 3.47 kg per extension meter. | 2.13 ha, planted in 2017, spaced at 0.4 × 3.2 m (vine × row), orientated north–south rows, single cordon trellis system, yield 4.9 kg per extension meter. |
| Date after Full Coloration (DAFC) | Sub-Regions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH | YQ | XG | HB | ||
| DAFC0 | Cabernet sauvignon | 8/10 | 8/12 | 8/5 | 8/14 |
| Marselan | 8/5 | 8/7 | 8/5 | 8/14 | |
| DAFC10 | Cabernet sauvignon | 8/20 | 8/22 | 8/14 | 8/24 |
| Marselan | 8/15 | 8/16 | 8/14 | 8/24 | |
| DAFC20 | Cabernet sauvignon | 8/30 | 9/2 | 8/24 | 9/3 |
| Marselan | 8/25 | 8/27 | 8/24 | 9/3 | |
| DAFC30 | Cabernet sauvignon | 9/9 | 9/12 | 9/3 | 9/13 |
| Marselan | 9/4 | 9/7 | 9/3 | 9/13 | |
| DAFC40 | Cabernet sauvignon | 9/19 | 9/26 | 9/13 | / |
| Marselan | / | 9/17 | 9/13 | / | |
| DAFC50 | Cabernet sauvignon | 9/29 | 10/1 | / | / |
| Marselan | / | 9/26 | / | / | |
| Commercial harvest | Cabernet sauvignon | 9/29 | 10/1 | 9/13 | 9/13 |
| Marselan | 9/8 | 9/26 | 9/13 | 9/13 | |
| PA Composition | ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ | ‘Marselan’ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH | YQ | XG | HB | ZH | YQ | XG | HB | |
| Free monomers | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 2.19 ± 0.14 b | 2.02 ± 0.23 b | 2.07 ± 0.11 b | 3.06 ± 0.32 a | 1.89 ± 0.12 c | 2.01 ± 0.03 c | 2.32 ± 0.16 b | 2.86 ± 0.07 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 1.28 ± 0.09 b | 1.25 ± 0.12 b | 1.19 ± 0.05 b | 1.73 ± 0.13 a | 1.14 ± 0.09 b | 1.14 ± 0.07 b | 1.29 ± 0.15 ab | 1.42 ± 0.18 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 0.27 ± 0.03 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.02 b | 0.25 ± 0.02 b | 0.38 ± 0.02 a |
| Total | 3.63 ± 0.25 b | 3.44 ± 0.36 b | 3.40 ± 0.16 b | 5.06 ± 0.44 a | 3.28 ± 0.14 c | 3.44 ± 0.03 c | 3.87 ± 0.33 b | 4.66 ± 0.27 a |
| Soluble PA | ||||||||
| Terminal units | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 2.84 ± 0.17 bc | 2.63 ± 0.22 c | 3.14 ± 0.14 ab | 3.20 ± 0.16 a | 2.05 ± 0.17 a | 1.80 ± 0.76 a | 2.41 ± 0.23 a | 2.33 ± 0.18 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 1.61 ± 0.10 b | 1.67 ± 0.09 ab | 1.53 ± 0.13 b | 1.87 ± 0.09 a | 1.05 ± 0.13 ab | 0.77 ± 0.34 b | 1.23 ± 0.17 a | 0.98 ± 0.12 ab |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 3.29 ± 0.22 b | 2.92 ± 0.16 c | 3.3 ± 0.10 b | 4.19 ± 0.22 a | 3.71 ± 0.14 ab | 3.10 ± 0.47 b | 3.57 ± 0.45 ab | 4.02 ± 0.35 a |
| Total | 7.73 ± 0.46 b | 7.23 ± 0.39 b | 7.97 ± 0.37 b | 9.26 ± 0.33 a | 6.80 ± 0.21 a | 5.67 ± 1.58 a | 7.21 ± 0.78 a | 7.33 ± 0.42 a |
| Extension units | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 1.19 ± 0.11 a | 1.09 ± 0.22 a | 1.02 ± 0.14 a | 1.46 ± 0.40 a | 1.54 ± 0.10 a | 1.27 ± 0.14 a | 1.39 ± 0.08 a | 1.51 ± 0.32 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 51.97 ± 1.51 b | 53.24 ± 0.47 ab | 52.01 ± 1.99 b | 55.1 ± 1.17 a | 53.61 ± 1.23 a | 47.99 ± 6.09 a | 53.76 ± 1.89 a | 52.33 ± 1.17 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 8.47 ± 0.28 b | 8.77 ± 0.21 b | 8.28 ± 0.43 b | 9.55 ± 0.18 a | 11.84 ± 0.17 a | 10.72 ± 1.36 a | 11.07 ± 0.60 a | 11.84 ± 0.42 a |
| Total | 61.64 ± 1.55 b | 63.1 ± 0.19 ab | 61.31 ± 2.55 b | 66.11 ± 1.55 a | 66.99 ± 1.31 a | 59.98 ± 7.58 a | 66.22 ± 2.56 a | 65.68 ± 1.89 a |
| Total flavanols | 73.00 ± 2.14 b | 73.77 ± 0.64 b | 72.68 ± 2.81 b | 80.44 ± 1.25 a | 77.08 ± 1.45 a | 69.09 ± 9.13 a | 77.30 ± 3.59 a | 77.66 ± 2.56 a |
| mDP | 7.31 ± 0.25 b | 7.86 ± 0.37 a | 7.06 ± 0.10 bc | 6.70 ± 0.33 c | 9.10 ± 0.32 a | 10.12 ± 2.06 a | 8.44 ± 0.51 a | 8.37 ± 0.20 a |
| Insoluble PA | ||||||||
| Terminal units | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 0.21 ± 0.05 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 b | 0.23 ± 0.03 b | 0.38 ± 0.03 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 0.17 ± 0.02 ab | 0.15 ± 0.02 b | 0.22 ± 0.05 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 0.12 ± 0.03 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.01 ab | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.09 ± 0.02 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 0.14 ± 0.03 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 0.14 ± 0.00 ab | 0.18 ± 0.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 a |
| Total | 0.47 ± 0.10 b | 0.49 ± 0.02 b | 0.49 ± 0.04 b | 0.73 ± 0.06 a | 0.34 ± 0.03 b | 0.39 ± 0.03 ab | 0.34 ± 0.04 b | 0.46 ± 0.08 a |
| Extension units | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 0.22 ± 0.04 a | 0.24 ± 0.04 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.26 ± 0.07 a | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 6.17 ± 0.80 a | 7.15 ± 0.53 a | 6.34 ± 0.16 a | 7.17 ± 1.41 a | 6.91 ± 0.14 a | 6.82 ± 0.21 a | 6.21 ± 0.75 a | 6.49 ± 0.17 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 0.99 ± 0.19 a | 1.08 ± 0.08 a | 0.96 ± 0.03 a | 1.11 ± 0.28 a | 1.54 ± 0.04 a | 1.50 ± 0.09 a | 1.30 ± 0.18 b | 1.38 ± 0.04 ab |
| Total | 7.38 ± 1.02 a | 8.47 ± 0.56 a | 7.53 ± 0.19 a | 8.54 ± 1.71 a | 8.67 ± 0.18 a | 8.55 ± 0.27 a | 7.72 ± 0.96 a | 8.07 ± 0.20 a |
| Total flavanols | 7.85 ± 1.08 a | 8.96 ± 0.55 a | 8.02 ± 0.15 a | 9.27 ± 1.77 a | 9.01 ± 0.21 a | 8.93 ± 0.27 a | 8.05 ± 0.21 a | 8.53 ± 0.25 a |
| mDP | 13.03 ± 2.41 a | 14.11 ± 1.46 a | 12.66 ± 1.44 ab | 9.55 ± 1.15 b | 20.7 ± 1.41 a | 17.83 ± 1.55 a | 18.44 ± 0.47 a | 14.47 ± 2.34 a |
| PA Composition | ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ | ‘Marselan’ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH | YQ | XG | HB | ZH | YQ | XG | HB | |
| Soluble PA | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 5.81 ± 0.08 a | 5.29 ± 0.17 b | 6.01 ± 0.13 a | 6.18 ± 0.31 a | 4.88 ± 0.40 a | 4.60 ± 0.79 a | 5.17 ± 0.22 a | 5.25 ± 0.27 a |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 77.23 ± 0.45 a | 78.09 ± 0.34 a | 77.27 ± 0.22 a | 75.60 ± 0.68 b | 74.06 ± 0.46 ab | 74.32 ± 0.66 a | 74.91 ± 0.61 a | 73.03 ± 0.57 b |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 16.96 ± 0.46 b | 16.63 ± 0.50 b | 16.72 ± 0.12 b | 18.23 ± 0.40 a | 21.07 ± 0.07 a | 21.07 ± 0.30 a | 19.92 ± 0.50 b | 21.71 ± 0.43 a |
| Insoluble PA | ||||||||
| (+)-Catechin | 5.54 ± 0.69 b | 5.14 ± 0.01 b | 5.69 ± 0.31 ab | 6.99 ± 0.87 a | 3.95 ± 0.17 b | 4.48 ± 0.25 ab | 4.40 ± 0.10 a | 5.04 ± 0.57 ab |
| (-)-Epicatechin | 80.21 ± 1.26 ab | 81.25 ± 0.92 a | 80.52 ± 0.49 ab | 79.24 ± 1.12 b | 77.51 ± 0.13 b | 77.27 ± 0.12 b | 78.02 ± 0.43 a | 77.15 ± 0.13 b |
| (-)-Epicatechin-3-gallate | 14.26 ± 0.79 a | 13.60 ± 0.52 a | 13.79 ± 0.32 a | 13.77 ± 0.85 a | 18.54 ± 0.12 a | 18.25 ± 0.35 ab | 17.58 ± 0.38 b | 17.81 ± 0.47 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Xia, N.; Sun, Q.; Duan, C.; Pan, Q. Dissecting Seed Proanthocyandin Composition and Accumulation under Different Berry Ripening Process in Wine Grapes. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010061
Liu A, Wang J, Yao X, Xia N, Sun Q, Duan C, Pan Q. Dissecting Seed Proanthocyandin Composition and Accumulation under Different Berry Ripening Process in Wine Grapes. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Aoyi, Jingjing Wang, Xuechen Yao, Nongyu Xia, Qi Sun, Changqing Duan, and Qiuhong Pan. 2023. "Dissecting Seed Proanthocyandin Composition and Accumulation under Different Berry Ripening Process in Wine Grapes" Horticulturae 9, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010061
APA StyleLiu, A., Wang, J., Yao, X., Xia, N., Sun, Q., Duan, C., & Pan, Q. (2023). Dissecting Seed Proanthocyandin Composition and Accumulation under Different Berry Ripening Process in Wine Grapes. Horticulturae, 9(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010061








