Research Progress of Plant Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
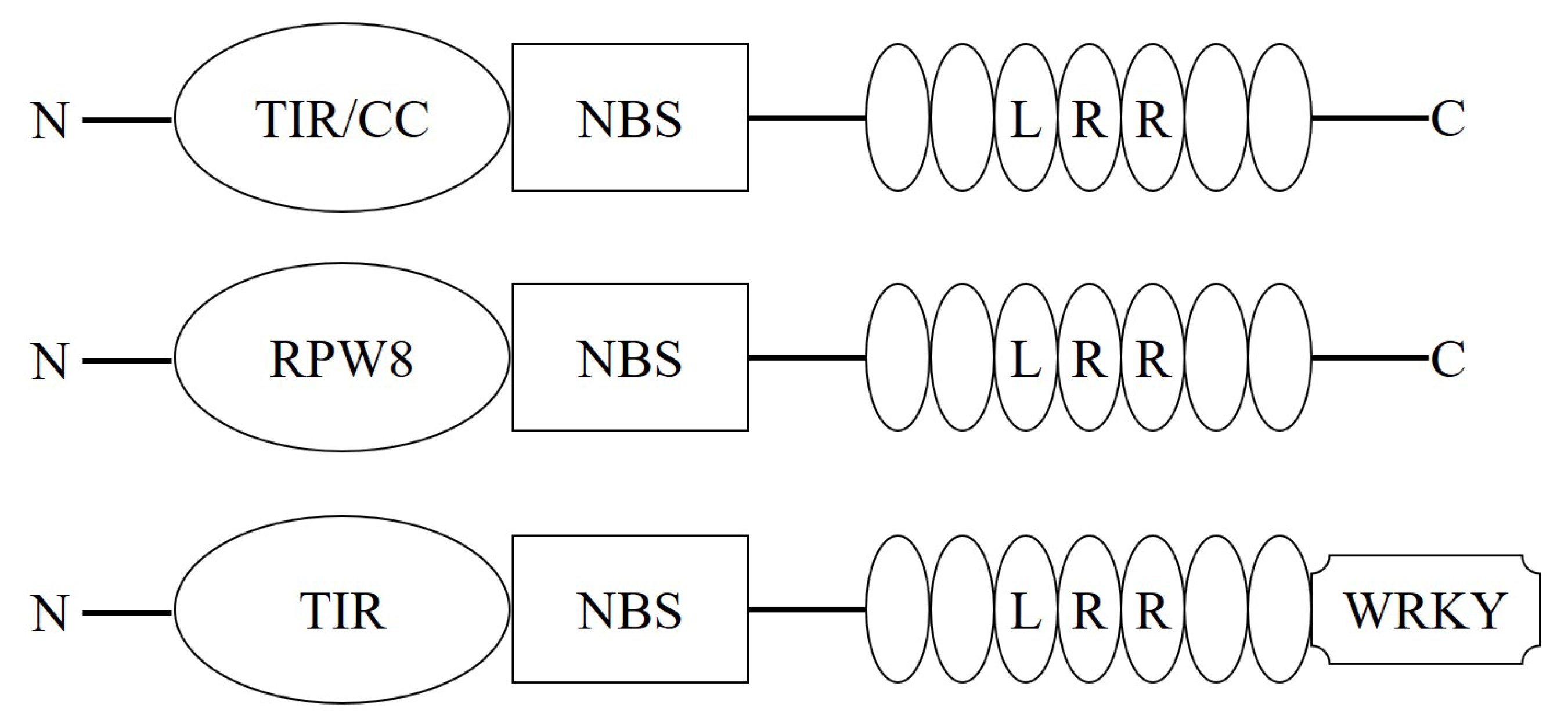
2. Plant NBS-LRR Protein
3. Domain and Function of Plant NBS-LRR Protein
3.1. NBS Domain
3.2. LRR Domain
3.3. TIR/CC Domain
4. Molecular Mechanism of Immune Response Induced by Plant NBS-LRR Protein
4.1. Immune Response Induced by Plant NBS-LRR Protein after Recognizing Pathogen Effector Protein
4.2. Immune Response Induced by Interaction between Plant NBS-LRR Protein and Molecules in Signal Transduction Process
4.3. Other Ways of Plant NBS-LRR Protein Inducing Immune Response
5. Application of Plant NBS-LRR Protein in Disease-Resistant Breeding
6. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Su, X.; Muleke, E.M.; Liu, L. Identification and characterization of expressed TIR- and non-TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene analogous sequences from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) de novo transcriptome. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.; Zipfel, C. Plant pattern recognition receptor complexes at the plasma membrane. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H.; Shim, S.; Yoon, M.Y.; Sun, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Van, K.; Lee, S.H. Genome-wide mapping of NBS-LRR genes and their association with disease resistance in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andras, K.; Renata, B.; Gabor, G.; Mohamed, H.Y.; Lorant, K. Staying alive-is cell death dispensable for plant disease resistance during the hypersensitive response. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 93, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Monosi, B.; Wisser, R.J.; Pennill, L.; Hulbert, S.H. Full-genome analysis of resistance gene homologues in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Chen, L. Identification and analysis of NBS-LRR gene family in sugar beet. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 1642–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, X.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Kang, J. Identification and expression profiling analysis of NBS–LRR genes involved in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans resistance in cabbage. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NBS-LRR gene family in Setaria italica. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2020, 49, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Xuan, H.; Gao, Z. Functional analysis of plant NB-LRR gene L3 by using E. coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traut, T.W. The function and consensus motifs of nine types of peptide segments that form different types of nucleotide-binding sites. J. Biochem. 1994, 222, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Prunet, N.; Gan, E.S.; Wang, Y.; Stewart, D.; Wellmer, F.; Huang, J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Tatsumi, Y.; Kojima, M.; et al. SUPERMAN regulates floral whorl boundaries through control of auxin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, C.; Center, B. Cloning and preliminary analysis of NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs in flower konjac. Mol. Plant Breed. 2019, 17, 2486–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Kobe, B.; Kajava, A.V. The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, K.U. Lucine-rich repeat receptor kinase in plants: Structure, function, and signal transduction pathways. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004, 234, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ausubel, F.M. Are innate immune signaling pathways in plants, animals conserved. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 6, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, P.; Farnham, G.; Peart, J.; Baulcombe, D.C. Interaction between domains of a plant NBS-LRR protein in disease resistance-related cell death. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4511–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, M.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.Q.; Hang, Y.Y. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of NBS-LRR genes from Dioscorea rotundata. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslandes, L.; Olivier, J.; Theulieres, F.; Hirsch, J.; Feng, D.X.; Bittner-Eddy, P.; Beynon, J.; Marco, Y. Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis thaliana is conferred by the recessive RRS1-R gene, a member of a novel family of resistance genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calil, I.P.; Fontes, E.P.B. Plant immunity against viruses: Antiviral immune receptors in focus. Ann. Bot. 2016, 119, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasset, C.; Bernoux, M.; Jauneau, A.; Pouzet, C.; Brière, C.; Kieffer-Jacquinod, S.; Rivas, S.; Marco, Y.; Deslandes, L. Autoacetylation of the Ralstonia solanacearum effector PopP2 targets a lysine residue essential for RRS1-R-mediated immunity in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Yu, D.; Jiao, J.; Jing, S.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Shen, Q. Barley MLA immune receptors directly interfere with antagonistically acting transcription factors to initiate disease resistance signaling. Plant Cell. 2013, 25, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, K.; Wirthmueller, L.; Tasset, C.; Pouzet, C.; Deslandes, L.; Parker, J.E. Arabidopsis EDS1 connects pathogen effector recognition to cell compartment specific immune responses. Science 2011, 334, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slootweg, E.; Roosien, J.; Spiridon, L.N.; Petrescu, A.J.; Tameling, W.; Joosten, M.; Pomp, R.; Schaik, C.V.; Dees, R.; Borst, J.W.; et al. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution is required for activation of resistance by the potato NB-LRR receptor Rx1 and is balanced by its functional domains. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 4195–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowen, R.H.; Engel, J.L.; Shao, F.; Ecker, J.R.; Dixon, J.E. A family of bacterial cysteine protease type III effectors utilizes acylation-dependent and -independent strategies to localize to plasma membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15867–15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Elmore, J.M.; Lin, Z.J.; Coaker, G. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase phosphorylates the host target RIN4, leading to the activation of a plant innate immune receptor. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Kaneko-Kawano, T.; Shimamoto, K. Rho family GTPase dependent immunity in plants and animals. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Pang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Q.; Yin, D.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Importance of OsRac1 and RAI1 in signalling of nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat protein-mediated resistance to rice blast disease. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, T.; Xing, L.; Han, G.; Ma, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, L.; et al. PM2b, a CC-NBS-LRR protein, interacts with TaWRKY76-D to regulate powdery mildew resistance in common wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 973065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Kosami, K.I.; Uno, K.; Nagawa, S.; Tan, L.; Du, J.; Shimamoto, K.; Kawano, Y. Resistance protein Pit interacts with the GEF OsSPK1 to activate OsRac1 and trigger rice immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11551–E11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Gu, F.; Liu, W.; Yang, G.; Huang, M.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, H.; et al. NBS-LRR protein Pik-H4 interacts with OsBIHD1 to balance rice blast resistance and growth by goordinating Ethylene-Brassinosteroid pathway. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, D.G.; Mota, A.P.Z.; Santos, I.R.; Arraes, F.B.M.; Grynberg, P.; Fontes, W.; Castro, M.S.; Sousa, M.V.; Lisei-de-Sá, M.E.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F.; et al. NBS-LRR-WRKY genes and protease inhibitors (PIs) seem essential for cowpea resistance to root-knot nematode. J. Proteom. 2022, 261, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; et al. SH3P2, an SH3 domain-containing protein that interacts with both Pib and AvrPib, suppresses effector-triggered, Pib-mediated immunity in rice. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Lapin, D.; Feehan, J.M.; Stolze, S.C.; Kramer, K.; Dongus, J.A.; Rzemieniewski, J.; Blanvillain-Baufumé, S.; Harzen, A.; Bautor, J.; et al. Pathogen effector recognition-dependent association of NRG1 with EDS1 and SAG101 in TNL receptor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Tian, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. TIR signal promotes interactions between lipase-like proteins and ADR1-L1 receptor and ADR1-L1 oligomerization. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, V.M.; Kumar, A. Nematode resistance in plants: The battle underground. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Lu, D.; Niu, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, C.; McCormack, M.; Sheen, J.; et al. Bifurcation of Arabidopsis NLR immune signaling via Ca(2+)-dependent protein kinases. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, W.; Agarwal, S.K.; Huang, H.D.; Raikhel, N.; Jin, H. Arabidopsis Argonaute 2 regulates innate immunity via miRNA393(∗)-mediated silencing of a Golgi-localized SNARE gene, MEMB12. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Deng, S.; Xuan, H.; Fan, X.; Sun, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, N.; Xing, H. A novel TIR-NBS-LRR gene regulates immune response to Phytophthora root rot in soybean. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, H.; Tang, X.; Chen, G. GauCNL18 mediates Verticillium wilt resistance by activating the salicylic acid immunity pathway. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 116, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Kong, Z.; Tang, D. The NB-LRR gene Pm60 confers powdery mildew resistance in wheat. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Bao, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a wild eggplant Solanum aculeatissimum NBS-LRR gene, involved in plant resistance to Meloidogyne incognita. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Cui, J.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. A tomato NBS-LRR gene is positively involved in plant resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Lu, C.; Du, L.; Ye, X.; Liu, X.; Coules, A.; Zhang, Z. The wheat NB-LRR gene TaRCR1 is required for host defence response to the necrotrophic fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Cai, T.; Deng, Y.; Zhuang, R.; Zhang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, R.; Pan, R.; et al. Overexpression of a novel peanut NBS-LRR gene AhRRS5 enhances disease resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, S.; Li, X. The maize NBS-LRR gene ZmNBS25 enhances disease resistance in Rice and Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xing, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. RppM, encoding a typical CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to southern corn rust in Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 951318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Fengler, K.; Bolar, J.; Llaca, V.; Wang, X.; Clark, C.B.; Fleury, T.J.; Myrvold, J.; Oneal, D.; et al. A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; et al. The Sm gene conferring resistance to gray leaf spot disease encodes an NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat) plant resistance protein in tomato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Kong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, A.; Zou, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of rice NLR genes responsive to the infections of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Magnaporthe oryzae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, G. Genome-wide characterization of NBS-LRR family genes and expression analysis under powdery mildew stress in Lagenaria siceraria. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 118, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotze, H.U.; Mitrousia, G.K.; Wit, D.; Fitt, B.D.L. Effector-triggered defence against apoplastic fungal pathogens. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Fan, H.; Cui, N.; Meng, X.; He, J.; Ran, N.; Yu, Y. Research Progress of Plant Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010122
Wang X, Xu Y, Fan H, Cui N, Meng X, He J, Ran N, Yu Y. Research Progress of Plant Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(1):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010122
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xue, Yuanfan Xu, Haiyan Fan, Na Cui, Xiangnan Meng, Jiajing He, Nana Ran, and Yang Yu. 2023. "Research Progress of Plant Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein" Horticulturae 9, no. 1: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010122
APA StyleWang, X., Xu, Y., Fan, H., Cui, N., Meng, X., He, J., Ran, N., & Yu, Y. (2023). Research Progress of Plant Nucleotide-Binding Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein. Horticulturae, 9(1), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010122




