Characteristics of Rotary Sprinkler Water Distribution under Dynamic Water Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
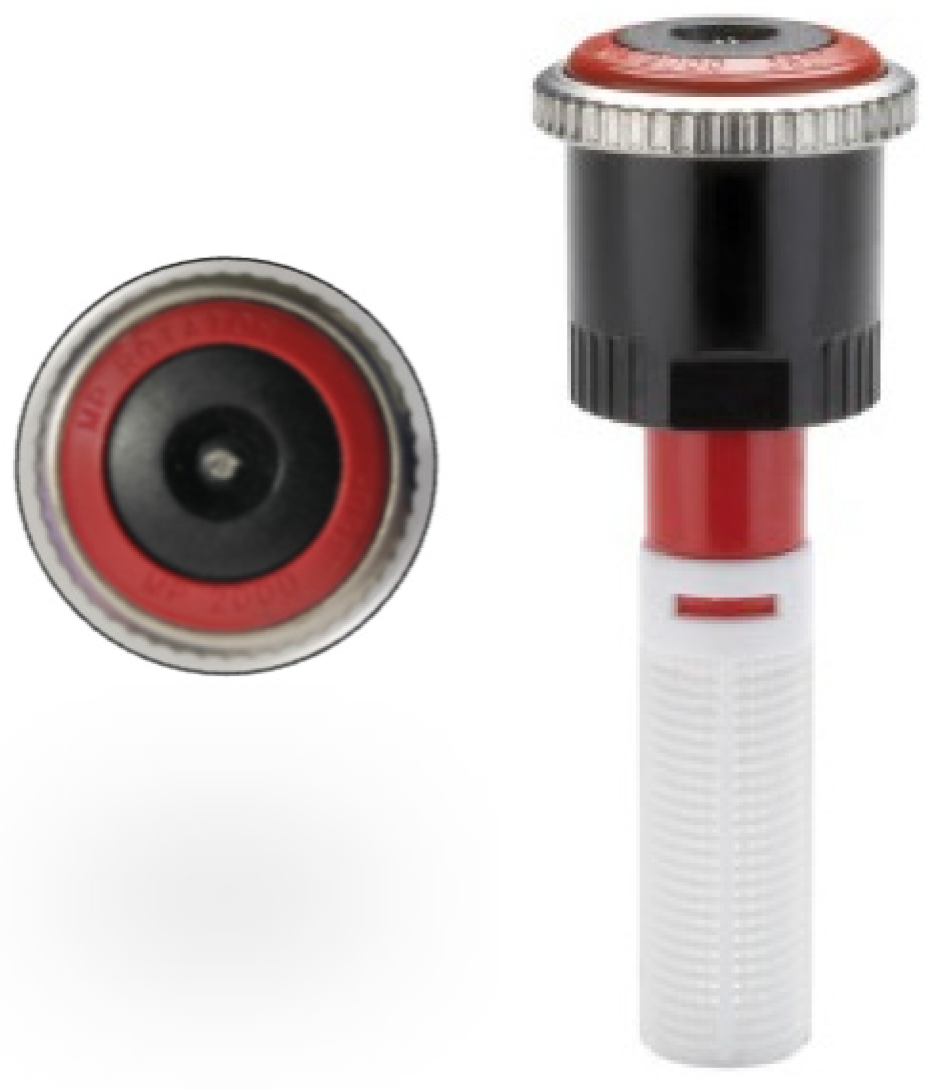
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Dynamic and Constant Pressure Changes
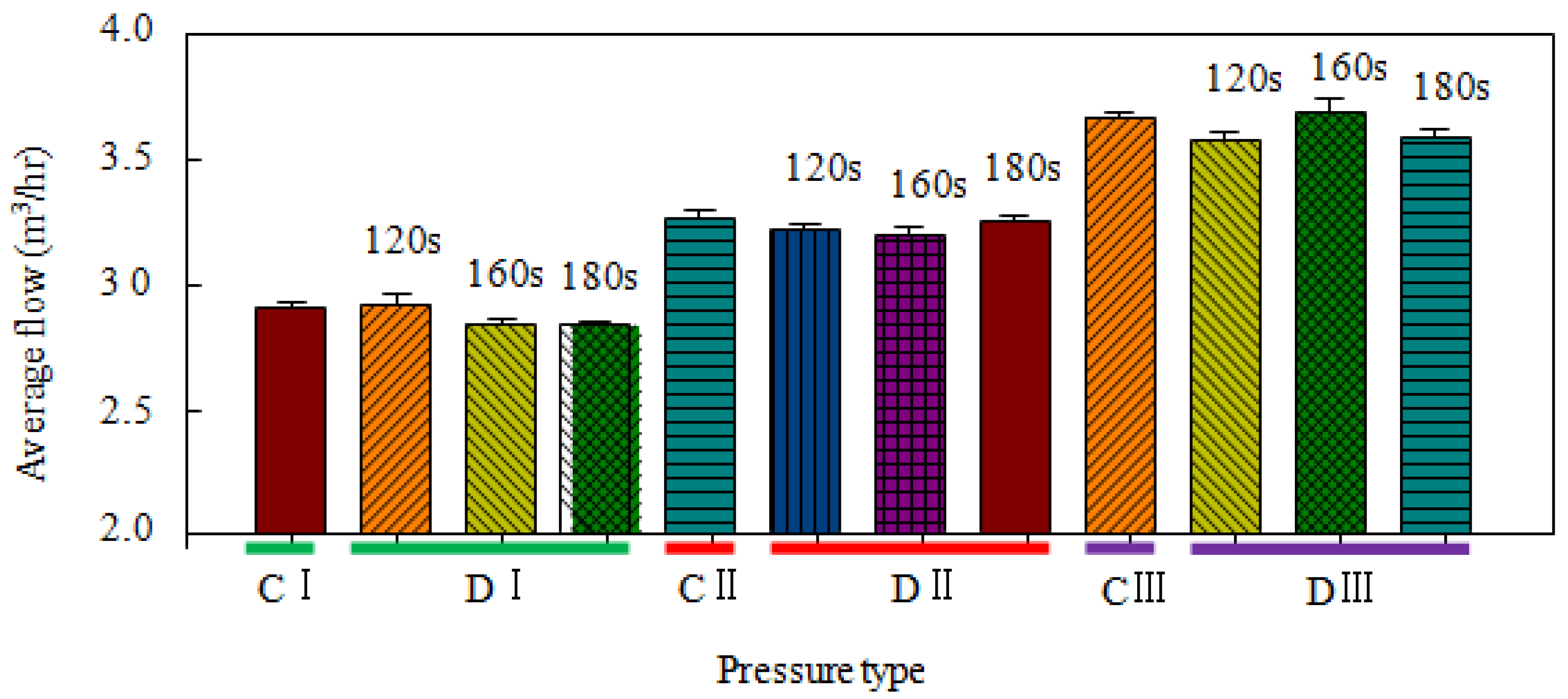
2.3. Comparison of the Sprinkler Flow Rates
2.4. Calculation Model of Combined Water Volume
2.4.1. Water Distribution Calculation Theory of Single Sprinkler
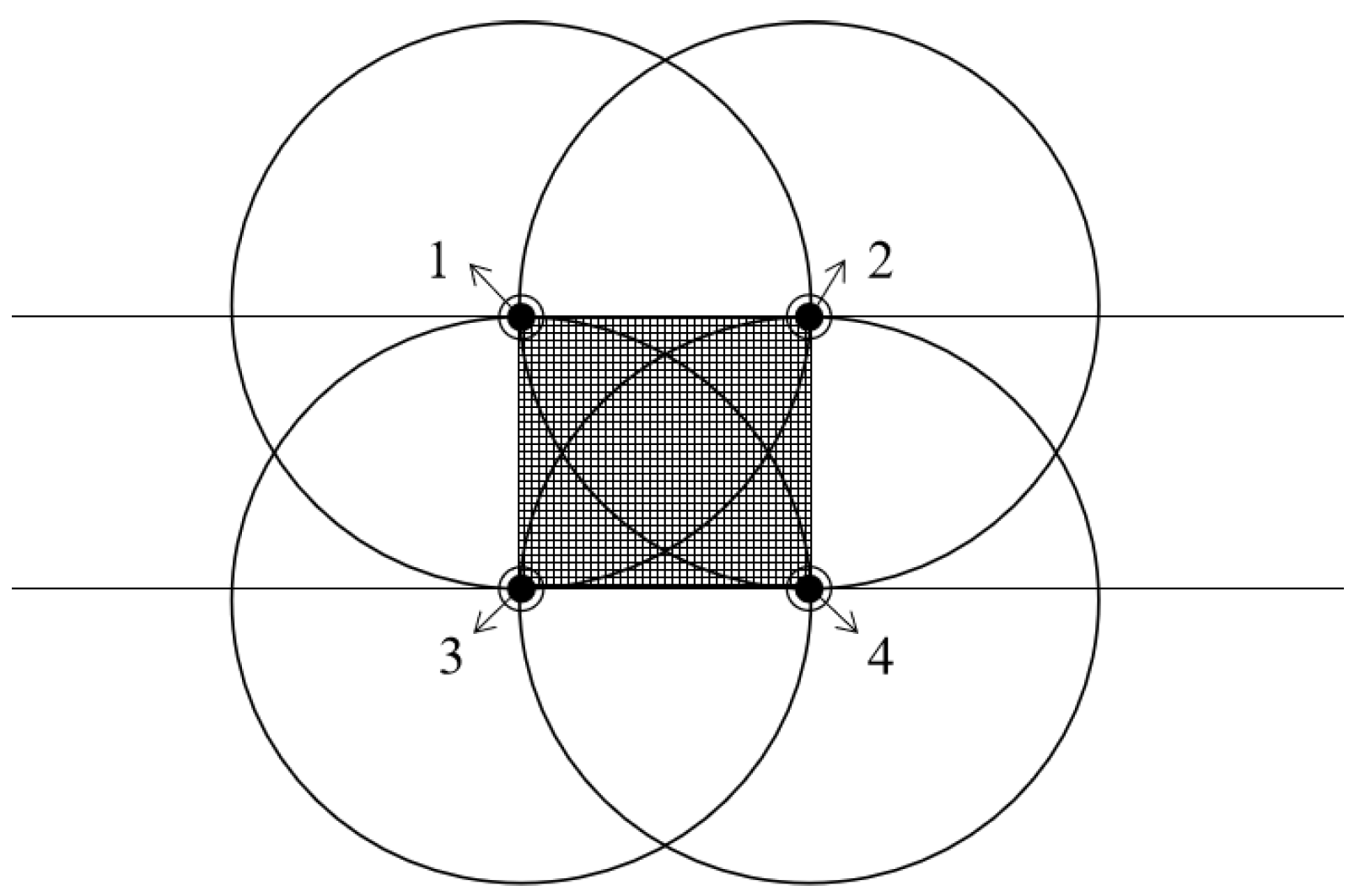
2.4.2. Multi-Sprinkler Combination Mode
2.5. Evaluation Indicators
- (1)
- Coefficient of variation (CV) is used to measure the discrete degree of water distribution in the spraying area [27]. The calculation formula is shown in Formula (4);
- (2)
- Average intensity () refers to the average precipitation in a typical calculated area [27]. Since the permeable speed should be higher than the sprinkler irrigation intensity in actual engineering experience, the smaller the intensity is, the better it is within a certain range. The calculation formula is shown in Formula (5);
- (3)
2.6. Establishment of Dynamic Pressure Evaluation Index Prediction Model
3. Test results and Analysis
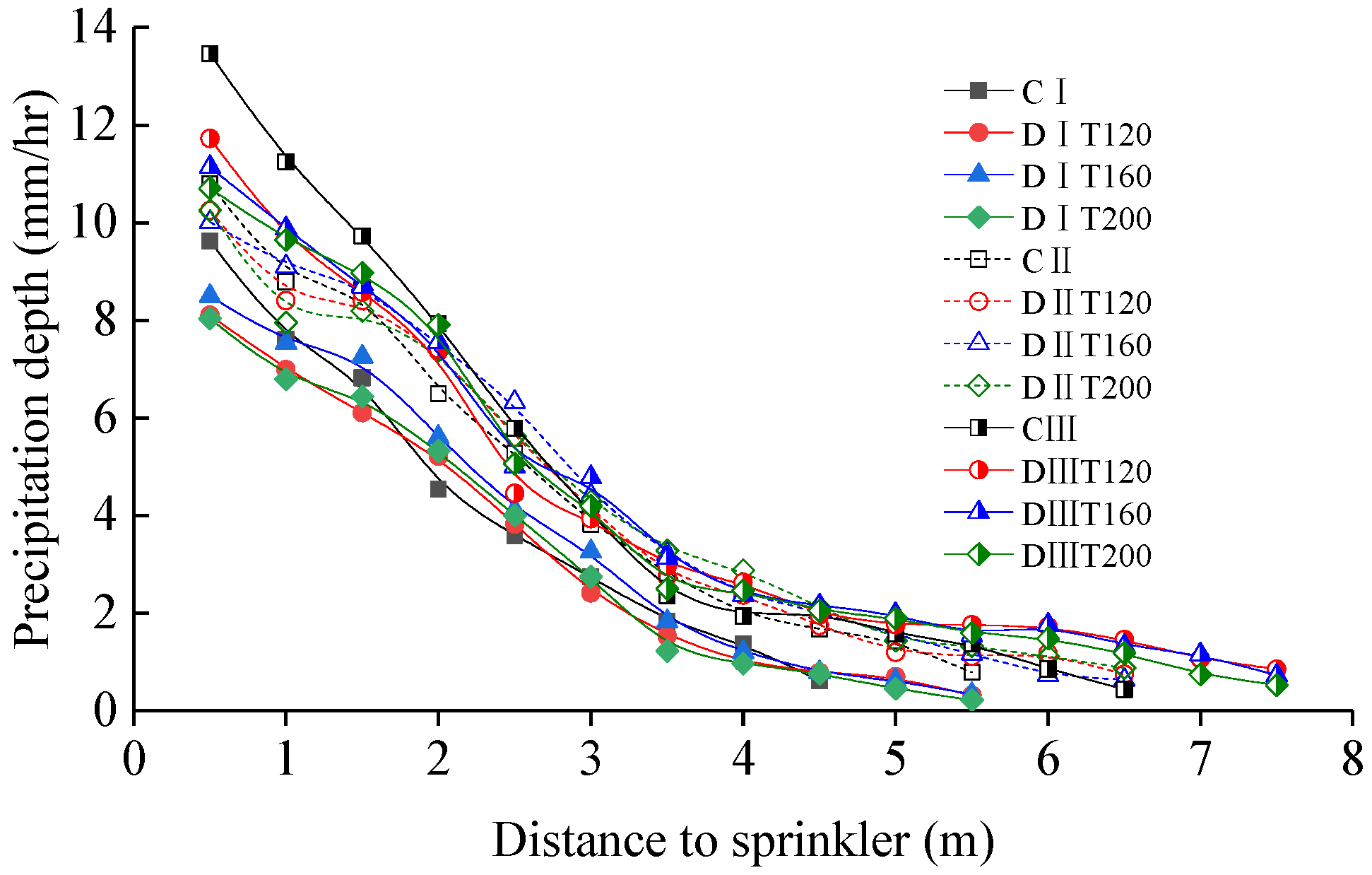
3.1. Radial Water Distribution Curve of Single Sprinkler
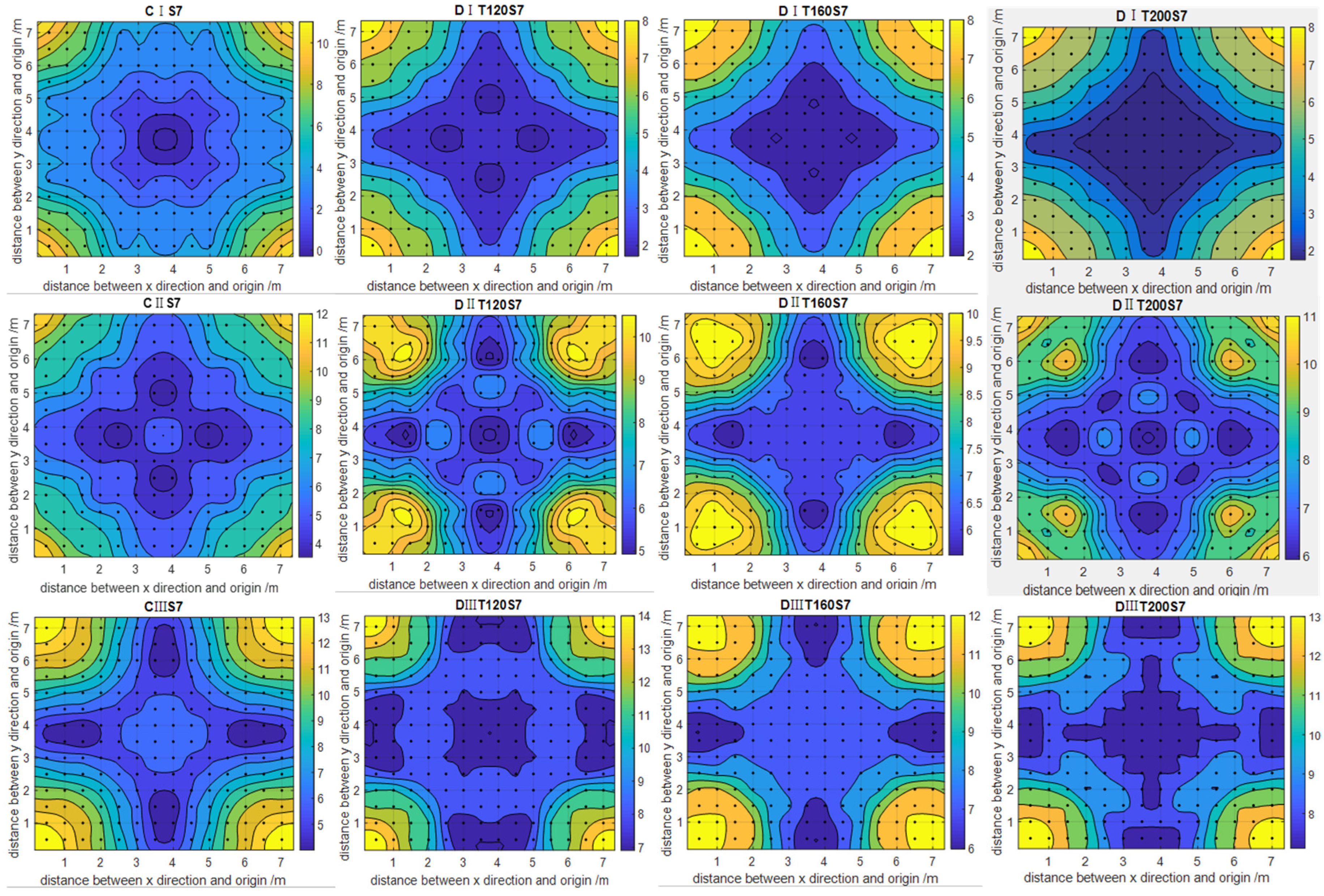
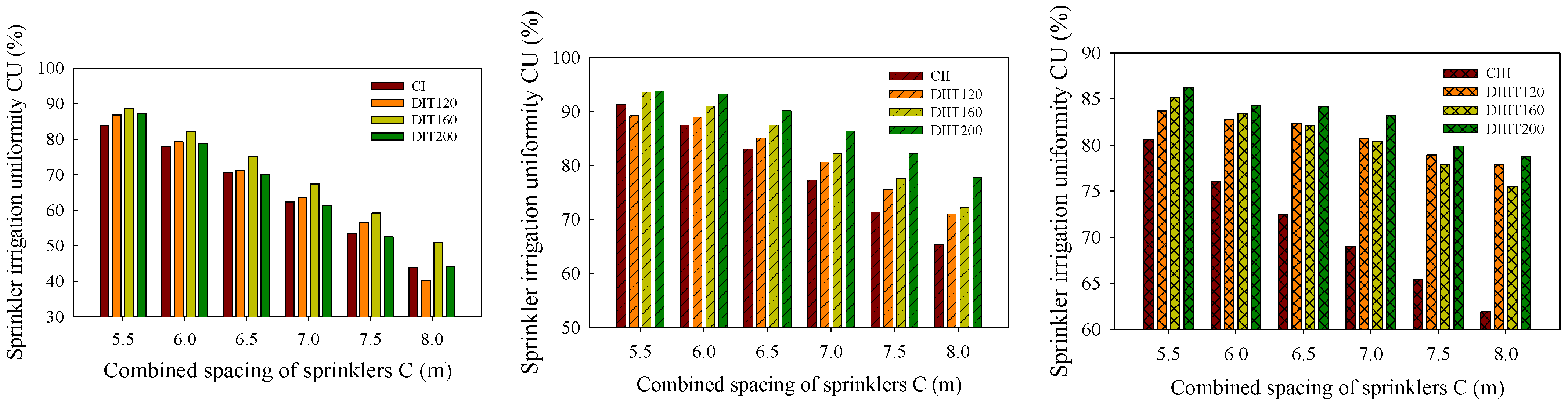
3.2. Water Distribution of Combined Sprinkler
3.3. Comprehensive Test under Dynamic Pressure
3.3.1. Comprehensive Test Design
3.3.2. Variance Analysis
3.3.3. Positive and Normalized Analysis of Indicators
3.4. Verification Test
3.5. Establishment of Dynamic Pressure Evaluation Index Prediction Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Feasibility of Sprinkler Irrigation and Analysis of Factors Affecting Water Distribution under Dynamic Pressure
4.2. Influence of Dynamic Pressure Water Supply on Sprinkler Irrigation and Optimization Ideas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, Y.; Shengde, C.; Fritz, B.K. Current status and future trends of precision agricultural aviation technologies. International J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Sun, W.; Fan, Y. Application prospect of sprinkler irrigation technology in water-short areas of northern China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 1–6, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Chikangaise, P.; Shi, W.; Chen, W.-H.; Yuan, S. Review of intelligent sprinkler irrigation technologies for remote autonomous system. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branscheid, V.O.; Hart, W.E. Predicting field distribution of sprinkler systems. Trans. ASAE 1968, 11, 801–803. [Google Scholar]
- Seginer, I.; Kostrinsky, M.W. Wind, sprinkler patterns, and system design. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1975, 101, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.L. The effect of spray head sprinklers with different deflector plates on irrigation uniformity, runoff and sediment yield in a Mediterranean soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Comparison of fluidic and impact sprinklers based on hydraulic performance. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Yuan, S.Q.; Liu, J.P. Effect of sprinkler head geometrical parameters on hydraulic performance of fluidic sprinkler. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Burguete, J.; Zapata, N.; Serreta, A.; Playán, E. A photographic method for drop characterization in agricultural sprinklers. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 27, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Montero, J.; Valiente, M.; Honrubia, F.T.; Ortiz, J. Irrigation uniformity with medium size sprinklers part i:characterization of water distribution in no-wind conditions. Trans. ASAE 1999, 42, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Clark, G.A.; Rogers, D.H.; Martin, V.L. Evaluation of Collector Size for the Measurement of Irrigation Depths; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2003; pp. 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Wan, J.H.; Alexander, F. Experiment of Water Distribution and Uniformity of Rotating Plate Sprinkler. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 145–152, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Assouline, S.; Möller, M.; Cohen, S.; Ben-Hur, M.; Grava, A.; Narkis, K.; Silber, A. Soil-Plant System Response to Pulsed Drip Irrigation and Salinity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaloglou, S.; Diamantopoulos, E. Wetting front advance patterns and water losses by deep percolation under the root zone as influenced by pulsed drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G. Research on Influence Laws of the Operating Water Pressure on Hydraulic Properties of Drip Emitters. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Research on Experiment of the Effect of Dynamic Pressure on the Hydraulic Properties of Drip Emitters. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Hui, X.; Ren, N.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Water Distribution and Application Uniformity of Sprinkler Irrigation with Pulsating Pressure on Sloping Land. Water Sav. Irrig. 2019, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Wu, P.T.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, X. Hydraulic Performance of Fixed Spray Plate Sprinklerunder Dynamic Water Pressure. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 27–33, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- King, B.A.; Wall, R.W. Distributed instrumentation for optimum control of variable speed electric pumping plants with center pivots. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2000, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.H.; Rosentreter, E.E. ANSI/ASAE.S330.1; Procedure for Sprinkler Distribution Testing for Research Purposes. Agricultural Engineers Yearbook: St Joseph, MI, USA, 2003.
- GB/T 27612.3-2011; Sprinkler Heads for Agricultural Irrigation Equipment-Part 3: Water Distribution Characteristics and Test Methods. China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Yuge, K.; Anan, M. Quantification of the crop stem flow in the sprinkler irrigated field. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.; Faci, J.M.; Zapata, N. The effects of pressure, sprinkler diameter and meteorological conditions on the per-formance of agricultural impact sprinklers. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 102, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Ooi, S.; Wang, X. A dynamic model for sprinkler irrigation water distribution. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2013, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.S.; Liu, J.L. Using Fourier transforms to express sprinkler overlapping uniformity. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 10, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.M.; Wu, P.T.; Niu, W.Q. Influence of the Combination Distance, Work Pressure and Layout Form of Sprinkler Head on Uniformity Coefficient in Irrigation. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 9, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Sun, C. Optimization and experiment of adjustable structural parameters for vertical impact sprinkler with working pressure. Trans. CSAE 2016, 32, 99–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mateos, L. A simulation study of comparison of the evaluation procedures for three irrigation methods. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 25, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, M.; Urrego, Y.; Isla, R.; Cavero, J. Effect of non-uniform sprinkler irrigation and plant density on simulated maize yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, G.H. Improve the method of multi-criteria comprehensive evaluation. Coll. Math. 2009, 25, 199–202. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, R.; Adolfo, R. Multiple nontrivial solutions of a semilinear elliptic problem with asymmetric nonlinearity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2020, 484, 123720. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.Y.; Liu, G.S.; Guo, L.T. Multiple positive solutions for a kirchhoff type problem with a critical nonlinearity. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2016, 31, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Xiang, Q.; Liu, J. Orthogonal experimental on design and performance of a rotational jet sprinkler. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2008, 39, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Burillo, G.S.; Delirhasannia, R.; Playán, E.; Paniagua, P.; Latorre, B.; Burguete, J. Initial Drop Velocity in a Fixed Spray Plate Sprinkler. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, D.W. Drop and Energy Characteristics of a Rotating Spray-Plate Sprinkler. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2002, 128, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faci, J.M.; Salvador, R.; Playán, E.; Sourell, H. Comparison of Fixed and Rotating Spray Plate Sprinklers. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2001, 127, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourell, H.; Faci, J.M.; Playán, E. Performance of Rotating Spray Plate Sprinklers in Indoor Experiments. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Bai, G.; He, J.; Lin, G. Influence of droplet kinetic energy flux density from fixed spray-plate sprinklers on soil infiltration, runoff and sediment yield. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, C.; Xiao, J.; Li, W. Simulation of sprinkler water distribution with droplet dynamics and evaporation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 127–132, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Jin, H.; Qian, Y. Characterizing center pivot irrigation with fixed spray plate sprinklers. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Moreno, J.M.; Callejón-Ferre, A.J.; Pérez-Alonso, J.; Velázquez-Martí, B. Review of the mathematical models for predicting the heating value of biomass materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3065–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhai, C.; Wang, W.; Fan, X. Optimization and flow numerical simulation of flow passage of square spray field impact sprinkler. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 71–79, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]




| Levels | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A (kPa) | B (s) | C (m) | |
| 1 | 200 | 120 | 6 |
| 2 | 250 | 160 | 7 |
| 3 | 300 | 200 | 8 |
| Treatment | Test Factors | Coefficient of Variation CV | Average Irrigation Intensity /(mm) | Coefficient of Uniformity CU/(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||||
| T1 | 200 | 120 | 6 | 0.2390 | 5.682 | 79.20 |
| T2 | 250 | 120 | 6 | 0.1156 | 10.01 | 88.90 |
| T3 | 300 | 120 | 6 | 0.1469 | 11.51 | 82.80 |
| T4 | 200 | 160 | 6 | 0.2100 | 6.378 | 82.20 |
| T5 | 250 | 160 | 6 | 0.08819 | 10.53 | 91.00 |
| T6 | 300 | 160 | 6 | 0.1460 | 11.32 | 83.40 |
| T7 | 200 | 200 | 6 | 0.2499 | 5.590 | 78.80 |
| T8 | 250 | 200 | 6 | 0.07936 | 10.54 | 93.20 |
| T9 | 300 | 200 | 6 | 0.1412 | 13.01 | 84.70 |
| T10 | 200 | 120 | 7 | 0.4147 | 4.174 | 63.70 |
| T11 | 250 | 120 | 7 | 0.2248 | 7.497 | 80.60 |
| T12 | 300 | 120 | 7 | 0.2078 | 9.195 | 80.70 |
| T13 | 200 | 160 | 7 | 0.3919 | 4.686 | 67.40 |
| T14 | 250 | 160 | 7 | 0.1948 | 7.845 | 82.20 |
| T15 | 300 | 160 | 7 | 0.2165 | 8.870 | 80.40 |
| T16 | 200 | 200 | 7 | 0.4478 | 4.107 | 61.40 |
| T17 | 250 | 200 | 7 | 0.1576 | 7.806 | 86.30 |
| T18 | 300 | 200 | 7 | 0.1835 | 9.479 | 83.20 |
| T19 | 200 | 120 | 8 | 0.6055 | 3.196 | 40.20 |
| T20 | 250 | 120 | 8 | 0.3343 | 5.740 | 71.00 |
| T21 | 300 | 120 | 8 | 0.2802 | 7.153 | 77.90 |
| T22 | 200 | 160 | 8 | 0.5944 | 3.588 | 51.00 |
| T23 | 250 | 160 | 8 | 0.3130 | 6.006 | 72.20 |
| T24 | 300 | 160 | 8 | 0.2952 | 6.863 | 75.50 |
| T25 | 200 | 200 | 8 | 0.6543 | 3.145 | 44.00 |
| T26 | 250 | 200 | 8 | 0.2657 | 5.976 | 77.80 |
| T27 | 300 | 200 | 8 | 0.2638 | 7.368 | 78.80 |
| k1 | 0.4231 | 0.2854 | 0.1574 | Coefficient of variation CV | ||
| k2 | 0.1970 | 0.2722 | 0.2710 | |||
| k3 | 0.2090 | 0.2715 | 0.4007 | |||
| R | 0.2260 | 0.0140 | 0.2434 | |||
| k1 | 4.505 | 7.129 | 9.273 | Average irrigation intensity /(mm) | ||
| k2 | 7.994 | 7.343 | 7.073 | |||
| k3 | 9.295 | 7.323 | 5.448 | |||
| R | 4.790 | 0.2143 | 3.825 | |||
| k1 | 63.10 | 73.89 | 84.91 | Coefficient of uniformity CU/(%) | ||
| k2 | 82.58 | 76.14 | 76.21 | |||
| k3 | 80.82 | 76.47 | 65.38 | |||
| R | 19.48 | 2.578 | 19.53 | |||
| Factors | CV | CU | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Pressure A | 181.60 ** | 559.5 ** | 112.8 ** |
| Dynamic Pressure Period B | 0.69 | 1.28 | 1.92 |
| Combined Spacing of Sprinkler C | 166.5 ** | 336.0 ** | 93.05 ** |
| Basic pressure A × Combined sprinkler spacing C | 15.40 ** | 9.080 ** | 17.06 ** |
| Dynamic pressure period × Combined sprinkler spacing C | 0.086 | 0.1 | 0.11 |
| Number of Test | Positive Values | Normalized Values | Comprehensive Evaluation Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | CU | CV1 | 1 | CU1 | |||
| T1 | −0.2309 | −5.682 | 79.20 | 0.7364 | 0.7428 | 0.7358 | 0.7381 |
| T2 | −0.1156 | −10.01 | 88.90 | 0.9370 | 0.3041 | 0.9189 | 0.7399 |
| T3 | −0.1469 | −11.51 | 82.80 | 0.8825 | 0.1521 | 0.8038 | 0.6319 |
| T4 | −0.2100 | −6.378 | 82.20 | 0.7728 | 0.6723 | 0.7925 | 0.7505 |
| T5 | −0.08819 | −10.53 | 91.00 | 0.9846 | 0.2514 | 0.9585 | 0.7542 |
| T6 | −0.1460 | −11.32 | 83.40 | 0.8841 | 0.1713 | 0.8151 | 0.6427 |
| T7 | −0.2499 | −5.590 | 78.80 | 0.7034 | 0.7522 | 0.7283 | 0.7280 |
| T8 | −0.07936 | −10.54 | 93.20 | 1.0000 | 0.2504 | 1.000 | 0.7751 |
| T9 | −0.1412 | −13.01 | 84.70 | 0.8924 | 0 | 0.8396 | 0.6036 |
| T10 | −0.4147 | −4.174 | 63.70 | 0.4167 | 0.8957 | 0.4434 | 0.5711 |
| T11 | −0.2248 | −7.497 | 80.60 | 0.7470 | 0.5588 | 0.7623 | 0.6967 |
| T12 | −0.2078 | −9.195 | 80.70 | 0.7766 | 0.3867 | 0.7642 | 0.6547 |
| T13 | −0.3919 | −4.686 | 67.40 | 0.4564 | 0.8438 | 0.5132 | 0.5953 |
| T14 | −0.1948 | −7.845 | 82.20 | 0.7992 | 0.5236 | 0.7925 | 0.7138 |
| T15 | −0.2165 | −8.870 | 80.40 | 0.7615 | 0.4197 | 0.7585 | 0.6577 |
| T16 | −0.4478 | −4.107 | 61.40 | 0.3592 | 0.9025 | 0.4000 | 0.5385 |
| T17 | −0.1576 | −7.806 | 86.30 | 0.8639 | 0.5275 | 0.8698 | 0.7654 |
| T18 | −0.1835 | −9.479 | 83.20 | 0.8189 | 0.3579 | 0.8113 | 0.6776 |
| T19 | −0.6055 | −3.196 | 40.20 | 0.08488 | 0.9948 | 0 | 0.3239 |
| T20 | −0.3343 | −5.740 | 71.00 | 0.5566 | 0.7369 | 0.5811 | 0.6205 |
| T21 | −0.2802 | −7.153 | 77.90 | 0.6507 | 0.5937 | 0.7113 | 0.6578 |
| T22 | −0.5944 | −3.588 | 51.00 | 0.1042 | 0.9551 | 0.2038 | 0.3993 |
| T23 | −0.3130 | −6.006 | 72.20 | 0.5936 | 0.7100 | 0.6038 | 0.6326 |
| T24 | −0.2952 | −6.863 | 75.50 | 0.6246 | 0.6231 | 0.6660 | 0.6407 |
| T25 | −0.6543 | −3.145 | 44.00 | 0 | 1.000 | 0.07170 | 0.3287 |
| T26 | −0.2657 | −5.976 | 77.80 | 0.6759 | 0.7130 | 0.7094 | 0.7005 |
| T27 | −0.2638 | −7.368 | 78.80 | 0.6792 | 0.5719 | 0.7283 | 0.6667 |
| A (kPa) | x(s) | y(m) | f(x,y) | Binary Function Constant | R2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | β1 | β2 | β3 | β4 | β5 | |||||
| 200 | 120 | 6 | CV | 0.1910 | 0.1441 | −0.1492 | 0.007383 | 0.03643 | 0.009475 | 0.9999 |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 250 | 120 | 6 | 0.02715 | 0.09332 | −0.002747 | 0.006958 | −0.002437 | −0.00809 | 0.9967 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 300 | 120 | 6 | 0.05969 | 0.03440 | 0.05895 | 0.009617 | −0.002675 | −0.01533 | 0.9916 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 200 | 120 | 6 | 6.209 | −2.404 | 2.218 | 0.2742 | −0.5683 | 0.01025 | 0.9967 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 250 | 120 | 6 | 12.22 | −3.557 | 1.315 | 0.3861 | −0.2306 | −0.1210 | 0.9999 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 300 | 120 | 6 | 15.23 | −2.821 | −1.430 | 0.1710 | 0.4165 | −0.04370 | 0.9999 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 200 | 120 | 6 | CU | 77.77 | −13.20 | 20.68 | −1.600 | −5.650 | 1.050 | 0.9913 |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
| 250 | 120 | 6 | 98.46 | −7.200 | −3.117 | −0.6833 | 1.167 | 0.6250 | 0.9969 | |
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 300 | 200 | 8 | ||||||||
| 120 | 6 | 86.51 | 1.050 | −4.950 | −0.9167 | −0.2500 | 1.583 | 0.9656 | ||
| 160 | 7 | |||||||||
| 200 | 8 | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Yang, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of Rotary Sprinkler Water Distribution under Dynamic Water Pressure. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8090804
Li N, Liu J, Zhou N, Yang Q, Liang J, Li J, Yu L, Liu X, Zhang W. Characteristics of Rotary Sprinkler Water Distribution under Dynamic Water Pressure. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(9):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8090804
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Na, Jia Liu, Ningshan Zhou, Qiliang Yang, Jiaping Liang, Jianian Li, Liming Yu, Xiaogang Liu, and Wenqian Zhang. 2022. "Characteristics of Rotary Sprinkler Water Distribution under Dynamic Water Pressure" Horticulturae 8, no. 9: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8090804
APA StyleLi, N., Liu, J., Zhou, N., Yang, Q., Liang, J., Li, J., Yu, L., Liu, X., & Zhang, W. (2022). Characteristics of Rotary Sprinkler Water Distribution under Dynamic Water Pressure. Horticulturae, 8(9), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8090804









