Abstract
Citrus depressa Hayata is the native and widespread citrus species in Taiwan. The notable character is that C. depressa has a distinct aroma different from local citrus. The ex situ germplasm of scions from different collection regions has variant leaf shapes and different odor characteristics. Establishing volatile biomarkers for classifying the local C. depressa is beneficial to commercial development. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) of fresh leaves from seven C. depressa accessions which were collected from different locations in Taiwan were extracted by headspace solid-phase microextraction and analyzed by GC-MS. The volatile compositions from each season showed the diversity, and linalool, of which the average relative content is 52.7%, was the most volatile component in any season. The other main VOCs of leaves of C. depressa were γ-terpinene, limonene, β-ocimene, and α-terpineol. The result of linear discriminant analysis by VOC markers shows that there are two main different types which are (1) accessions from the central and the east of Taiwan and (2) accessions which are closer to C. depressa in Okinawa, Japan. Five major VOC-related synthase genes were selected and the gene expression was used to classify the varieties. The clustering result is the same with VOC-based discrimination. Our results reveal leaf volatile profiling is capable of being the discrimination markers, and the possibility for constructing molecular markers is directly related to characteristics from secondary metabolites phenotyping.
1. Introduction
Citrus depressa Hayata is a citrus species native to Taiwan. The small and flat fruit with a sour taste is the typical characteristic of C. depressa, and also the reason for the name hirami lemon or shiikuwasha. Besides the morphology, the aroma from the peel makes C. drpressa fruit unique and impressive, and that is why it is also named as “Taiwan scented lemon”. According to the first introduction of C. depressa by Dr. Tyozaburo Tanaka [1], the description in Flora of Taiwan [2] (pp. 513–517), and the collected recordings of the biospecimen stored in the herbarium of National Taiwan University, C. depressa plants were widely distributed in the low-altitude forests of Taiwan Island. In old times, the peel of C. depressa was used as the main source of Chenpi, which is an aged citrus peel in traditional Chinese medicine [3]. In modern times, C. depressa is widely used to make juices and food additives because of the high contents of polymethoxyflavones [4,5] and its unique aroma [6]. It has been proved to have many benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects [7,8].
Classification of the citrus family has been discussed for decades from morphological traits to molecular features. Two important but distinct systems by Swingle [9] (pp. 190–430) and Tanaka [10] were established by morphological characteristics in the 1980s. DNA markers are more informative and unaffected by environmental factors in comparison to morphological data. Many molecular markers applications, such as the random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD), simple sequence repeats (SSR), and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), were used to expound citrus classification and evolution [11,12]. Those molecular markers assist in figuring out the phylogeny and possible evolution among citrus species. However, these DNA markers have a weak linkage to functional characteristics.
Speaking of the representative features of the citrus family, citrus peels are rich in flavonoids and the aromatic traits of essential oil are the crucial characteristics. These secondary metabolites have been used as chemical patterns for classification and flavonoids have been developed as inter-species chemotaxonomy markers [13,14]. Besides the inter-specific differences, secondary metabolite profiles also reflected the complex genetic backgrounds of the hybrids. A pattern of inheritance of Poncirus chemical traits could be revealed in the case of Citrus × Poncirus hybrids by flavonoids, limonoids, and volatile-compound analysis [15]. Fruit peels and juice were the most used materials in numerous pieces of research. Citrus leaves are also rich in essential oils. The volatile components are different among citrus species, and they also have classification potential with the genetic relationship of the citrus family [16,17].
C. depressa has a unique scent that is present not only in fruits but also in leaves. Leaves are more easily obtained than fruits and are suitable for determining classification markers. The long domestication histories and spontaneous mutations may create the diversity of citrus species. The nucleotide polymorphisms were applied to identify relationships among the local accessions of shiikuwasha in Okinawa [18,19]. Four major maternal lineages were detected among the landraces of shiikuwasha. However, there is no study that has explored the accessions of C. depressa in Taiwan, where the origin of this citrus species is.
The aromatic characteristics of C. depressa are exceptional and important to their products. Using aroma profiles to establish chemical markers for phenotyping may develop the characteristic-specific index but also help to understand the relationship among landraces in Taiwan. In this study, using the grafted plants in official citrus germplasm with different scions, which were collected from three regions, we explored the leaf volatile components in each season. To further understand the relationship between the aroma markers and their relevant gene involved in biosynthesis, we used the gene expression as classification markers and evaluated the classification capability of volatile markers to figure out the similarity among the accessions of C. depressa in Taiwan.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
Citrus depressa potted plants were kept in the Taiwan citrus germplasm (Chiayi Agricultural Experiment Station, Chiayi, Taiwan). They were grafted on Citrus sunki Hort. and grown in the same greenhouse for more than 3 years. There were seven grafted plants, including two scions from Ouwanda, Nantou County (OWD-1 and OWD-2), one from Hualien County (HLN), and another two scions collected from Okinawa in Japan (OKN-1 and OKN-2). Two grafted plants preserved in germplasm over 30 years were marked as GS-1 and GS-2, respectively, whose scion sources were not available.
Mature leaves from spring shoots at three to five nodes were collected in spring (March 2019) and used as samples for investigating morphological characteristics. Ten leaves of one potted tree were measured for leaf length, broadness, leaf petiole wing (WL) length, and WL broadness with a digital Vernier caliper (Mitutoyo Co., Kanagawa, Japan). The leaf shape ratio and WL broadness ratio were calculated as follows:
(length of leaf (WL)/broadness of leaf (WL)) × 100%
2.2. Leaf Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Analysis
Ten mature leaves from the current shoots each season were collected in March (spring), June (summer), September (autumn), and December (winter) in 2019 and were immediately stored at −20 °C after harvest. Leaf volatile compounds which were easily released by injury were the representative aromatic composition of the citrus leaf. The extraction method of those VOCs was modified from the previous research [17]. A hole punch was used to collect three 5 mm-diameter leaf discs (approximately 0.05 g), which were placed in a 20 mL airtight bottle. An internal standard of 1 μL tridecane (5 ng μL−1) was added to the vial using a micro injector. The leaf discs were heated to 40 °C for 5 min to release VOCs. Headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) was applied for leaf VOCs’ extraction. The SPME fiber with 50/30 μm divinylbenzene (DVB)–carboxen-polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was conditioned at 250 °C for 10 min before use. Leaf VOCs were extracted for 10 min of compound adsorption. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate.
The VOC profiles were analyzed by Agilent-6890 GC coupled with Agilent-5975 mass spectrometer (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a capillary column (30 m× 0.25 mm and 0.25 μm-thickness; Agilent J&W DB-5MS) having a split ratio of 5:1. The GC-MS system was operated using the following temperature program: (a) oven temperature set at 40 °C for 2 min, (b) temperature increased to 100 °C at a rate of 15 °C·min−1, (c) temperature increased to 110 °C at a rate of 2 °C·min−1, (d) temperature increased to 220 °C at 20 °C·min−1, and (e) temperature held for 2 min. The injection temperature was set at 250 °C, and the temperature of the transfer line and ion source was 250 °C and 230 °C, respectively. Helium (>99.999%) was used as the carrier gas at a constant pressure of 6 psi. The electron energy was 70 eV. Mass spectra were obtained by automatic scanning at m/z 40–300 amu. Compounds were identified by comparing the mass spectra with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST 11) library at a match factor of ≥85%. The retention index (RI) of VOCs was calculated with the retention time of compounds and standard saturated n-alkanes mixture (C8-C20) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) obtained under the same GC–MS condition, and was compared with the Kovats retention indices in NIST library.
The characteristic volatile compounds of the samples were represented as relative concentrations based on internal standard (IS):
2.3. Selection of VOC-Relevant Genes
Eight mature leaves collected from the current shoots were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. For each sample, 4.0 g of frozen tissue was ground in liquid nitrogen with mortar and pestle. Total RNA was extracted using a LabPrepTM RNA Plus Mini Kit (LabTurbo, NJ, USA). The RNA samples of Citrus depressa OWN and GS-1 and Citrus × microcarpa (calamondin) were entrusted to Tri-I Biotech Inc. (Taipei, Taiwan) for high-throughput sequencing analysis.
There are 65,972 contigs and we selected 48 contigs related to the biosynthesis of critical VOCs of classification according to the gene annotation with Blast analysis. The comparison of contig fold change to reference sample was further investigated. Contigs related to β-ocimene synthase, limonene synthase, linalool synthase, γ-terpinene synthase, and α-terpineol synthase were selected as candidates. Primer construction was entrusted to Tri-I Biotech Inc, with reference to citrus pan-genome breeding database (CPBD, http://citrus.hzau.edu.cn/index.php, accessed on 8 June 2021) (Table S1).
2.4. Relative Gene Expression with RT-qPCR Analysis
cDNA was synthesized with 1 μL of 50 μM Oligo (dT) primer, 1 μL of 10 mM dNTP, and 2000 ng μL-1 of RNA in a final reaction volume of 10 μL by the following program: (a) reaction carried out at 65 °C for 5 min and then cooled on ice for 5 min, (b) addition of 4 μL of 5X FS buffer, 2 μL of 0.1 M DTT, 0.5 μL of double-distilled water, and 0.5 μL RNase, (c) reaction mixture incubated at 37 °C for 2 min, (d) 1 μL of M-MLV reverse transcriptase added, and (e) reaction carried out at 37 °C for 50 min and heated to 70 °C for 15 min. The resulting product was diluted 200 times with RNase-free water before use in the reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assays.
RT-qPCR was performed using 5 μL fluorescent dye SYBR®Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with 2 μL of cDNA, 1 μL of forward primer, and 1 μL of reverse primer to a final reaction volume of 10 μL on a CFX Connect real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The primers of preference genes and actin are listed in Table S1. The experiment was performed with three biological and technical replicates. PCR reaction conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, and 60 °C for 60 s. The melting curve was checked to ensure the specificity of each primer pair. Gene actin was used as the reference gene to calculate the relative fold difference based on the comparative cycle threshold (2−ΔΔCt) value.
2.5. Statistical and Multivariate Analysis
The leaf morphological traits and the relative concentration of VOCs in different accessions and seasons were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with least significant difference (LSD) test (p < 0.05). The relative concentration of VOCs was also analyzed using linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and LDA scatter plots were generated. The statistical analysis was conducted by software SYSTAT 13 (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) and the graph was drawn by SigmaPlot (ver. 14.0; Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The relative gene expression of VOCs was visualized in a heatmap and as the multivariate data to cluster the accessions using the Clustvis web tool [20].
3. Results
3.1. Diversity in Leaf Characteristics of Citrus Depressa Accessions
The average leaf length of Taiwanese C. depressa accessions was 75.4 ± 7.8 mm and 39.3 ± 3.7 mm in average leaf broadness. The leaf petiole wing (WL) in all accessions was all narrow-winged with an average broadness of 1.9 ± 0.3 mm. The average length-to-broadness ratio of the leaves was 1.9 and of the WL was 4.9. It indicated the leaf was elliptic-shaped. However, the collected varieties which are grown in the same greenhouse showed diversity in leaf morphology. The leaves of Taiwanese accessions were smaller than OKN-1 and OKN-2, especially the leaves of OWD-1 and OWD-2 (Table 1). The leaf shape of the Taiwanese accession was closer to ovate with a leaf shape ratio between 1.8 and 1.9. Besides GS-1 and GS-2, the Taiwan accession OWD and HLN had very narrow-winged WL, and the ratio of the WL shape was close to linear (Figure 1). Leaf morphology is the basic tool for citrus distinction. However, more valuable and remarkable characteristics should be developed to differentiate the accessions. The odor of the leaf is a specific character in citrus species and is worthy to be further evaluated.

Table 1.
Leaf characteristics of Taiwanese accessions of Citrus depressa.
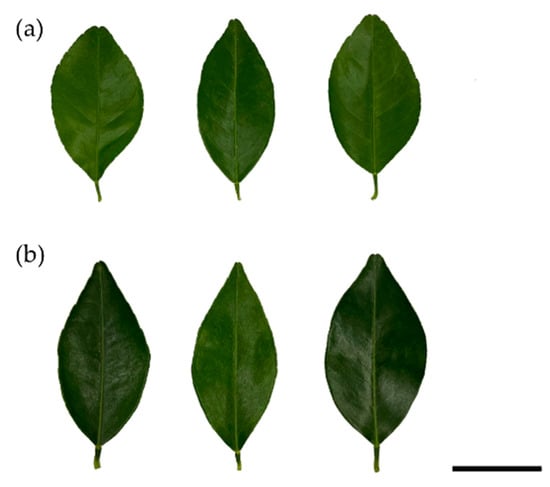

Figure 1.
The ovate leaf and narrow-winged leaf petiole of two accessions (a) OWD and (b) GS-1 of Citrus depressa in Taiwan. The line represents 3 cm in scale.
3.2. Featured Volatile Compositions of Citrus Depressa Fresh Leaf and Its Seasonal Variation
There are 22 stable detected VOCs by HS-SPME extraction that contributed to the leaf aroma of C. depressa (Table S2). Except for trans-2-hexenal, all selected VOCs were terpenoids, and more than 90% were monoterpenes including monoterpene hydrocarbons or oxygenated monoterpenes. Linalool, of which the average content ratio is 52.7% among Taiwanese accessions of the leaf, has the highest concentrations of all accessions in every season (Tables S2 and S3). It is considered the characteristic citrus aroma. The highest content of linalool was detected in spring; OWDs and HLN had higher linalool composition in all seasons (Figure 2). Besides linalool, γ-terpinene is the other remarkable volatile compound of C. depressa fresh leaf, and also several terpinene-related VOCs such as terpinen-4-ol and α-terpineol contribute to the aromatic pattern of C. depressa fresh leaf. The relative concentration of γ-terpinene was 590.48 and 770.99 ng·g−1, respectively, in spring and summer and it was higher than the other seasons (Table S2). Although, no matter which season, OKNs always showed higher relative concentrations of γ-terpinene than other accessions (Figure 3).
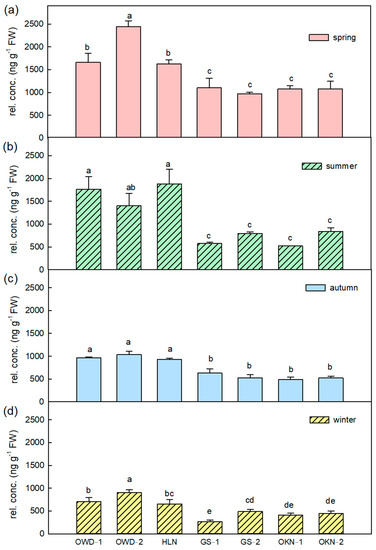
Figure 2.
The linalool variations in Citrus depressa fresh leaf among all accessions in each season, which is (a) spring; (b) summer; (c) autumn; and (d) winter. Each bar shows the average (n = 3) of the relative concentration (rel. conc.) The error bar was calculated by standard errors, and the different letters show a significant difference (LSD p < 0.05).
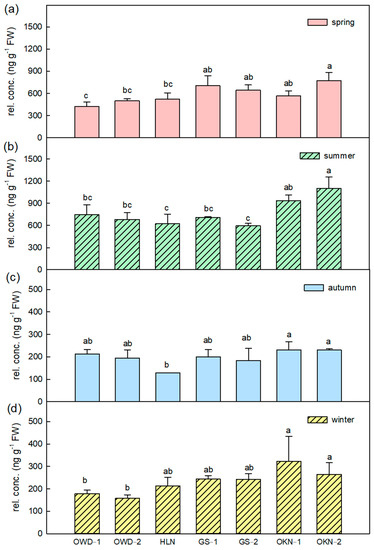
Figure 3.
The γ-terpinene variations in Citrus depressa fresh leaf among all accessions in each season, which is (a) spring; (b) summer; (c) autumn; and (d) winter. Each bar showed the average (n = 3) of the relative concentration (rel. conc.) The error bar was calculated by standard errors, and the different letters showed a significant difference (LSD p < 0.05).
The VOCs β-ocimene and limonene are important compounds of the fresh leaf aroma, and the average content ratios of the two VOCs are 2.4% and 1.8%, respectively. They contribute the fresh, herbal and citrus scents in citrus leaves. Fresh leaves of C. depressa had more β-ocimene in summer, and the detected content decreased when the climate was getting cold. However, GS samples and OKN samples always had a lower composition of β-ocimene (Figure 4). Most monoterpenes showed higher content in spring or summer, and then decreased. However, caryophyllene, a major sesquiterpene in citrus leaf, increased in cold days (Figure 5). The accessions GS-1 and GS-2 had very low caryophyllene content compared to other accessions in all seasons. However, GS had a significantly higher concentration in α-farnesene than other Taiwanese accessions (OWD and HLN) (Table S2). Leaf volatile profiling of C. depressa accessions revealed vital volatile compounds contributing to the smell of the leaf, and the aroma patterns differed in accessions. In spite of the seasonal variations in volatile contents, key VOCs showed a consistent compositional ratio among each season (Figure 6).
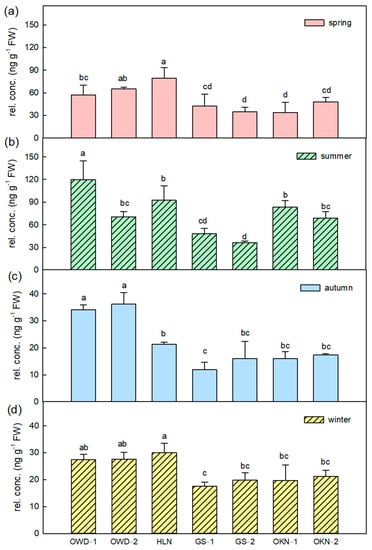
Figure 4.
The β-ocimene variations in Citrus depressa fresh leaf among all accessions in each season, which is (a) spring; (b) summer; (c) autumn; and (d) winter. Each bar shows the average (n = 3) of the relative concentration (rel. conc.) The error bar was calculated by standard errors, and the different letters show a significant difference (LSD p < 0.05).
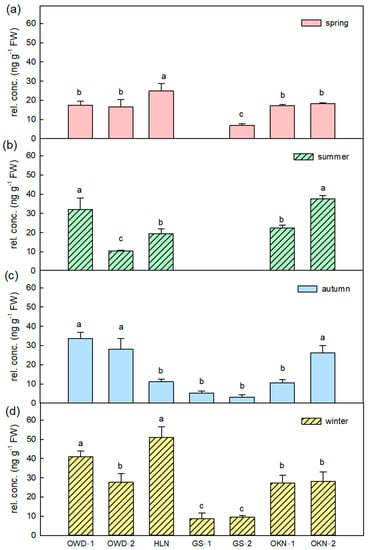
Figure 5.
The caryophyllene variations in Citrus depressa fresh leaf among all accessions in each season, which is (a) spring; (b) summer; (c) autumn; and (d) winter. Each bar shows the average (n = 3) of the relative concentration (rel. conc.) The error bar was calculated by standard errors, and the different letters show a significant difference (LSD p < 0.05).
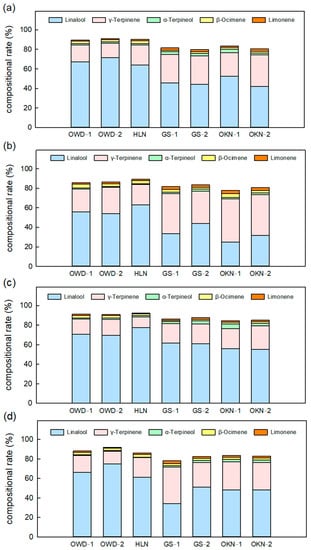
Figure 6.
The compositional rate of major volatile compounds of Citrus depressa fresh leaf among all accessions in all seasons, which is (a) spring; (b) summer; (c) autumn; and (d) winter. Each bar shows the average (n = 3) of the relative concentration (rel. conc.) The error bar was calculated by standard errors, and the different letters show a significant difference (LSD p < 0.05).
3.3. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) by Fresh Leaf VOCs and Clustering Analysis by Relevant Gene Expression
The volatile composition profiles of each accession in every season were revealed. The result of the LDA scatter plot by leaf VOCs showed that three main groups were distributed. The first group including OWD-1, OWD-2, and HLN was close to each other and distant from other groups (Figure 7). The original specimens of C. depressa, GS-1, and GS-2 was grouped together, and was closer to the Japanese variety OKN-1 and OKN-2 (Figure 7). The average of the classification correction value was 86% in the LDA result, and the correction rate for GS-1, HLN, and OKN-1 was even over 90%. The impactful determinant VOCs in score 1 and score 2 included β-thujene, (+)-4-carene, β-ocimene, linalool, α-terpineol, and α-pinene (Table S4). Among those VOCs, β-ocimene, linalool, and α-terpineol had a higher compositional ratio in leaf VOC.
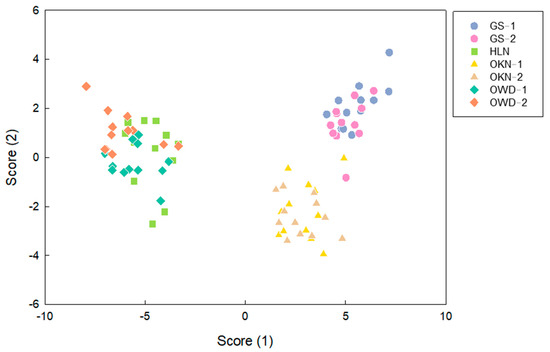
Figure 7.
The canonical scores plot of LDA by volatile compositions in Citrus depressa varieties. Each spot represents each analytical replicate. Blue dots (GS-1) and purple dots (GS-2) represent the original sample trees in germplasm; green square (HLN) represents the scion from Hualien; yellow triangle (OKN-1) and brown triangle (OKN-2) are the scion of Okinawa; cyan diamond (OWD-1) and orange diamond (OWD-2) represent the scions collected from Ouwanda.
Leaf VOC profiling showed the differentiation in accessions of C depressa. We further selected five VOC index candidates by discriminant analysis and gene fold change expression and annotation in high-throughput analysis. These selected genes were synthases related to VOCs including linalool, γ-terpinene, α-terpinol, β-ocimene, and limonene. The gene expression heatmap shows the most active gene expression was α-terpinol synthase (Figure 8). The pattern of OKN accessions had stronger expression of β-ocimene synthase gene (OS gene), but weaker α-terpinol synthase (alpha-TPS gene) when compared to the Taiwanese accessions (Table S5). The gene of γ-terpinene synthase showed similar expression levels in all accessions, which was the same as the compositional ratio of γ-terpinene VOC. The clustering by gene expression separated Taiwanese accessions into two groups: OWDs and HLN were in one group; GS-1 and GS-2 were another group (Figure 4). The GS group was closer to OKNs. The clustering result revealed the same as LDA using VOC profiles. Two distinguishable groups of C. depressa by leaf aroma characteristics were distributed on Taiwan Island. The same clustering results by VOC profiling and gene expression of relevant genes to VOC synthase indicated that gene expression may be strongly linked to smell. Leaf aromatic grouping not only has an effect on phenotype, but also has a corresponding result on gene expression.
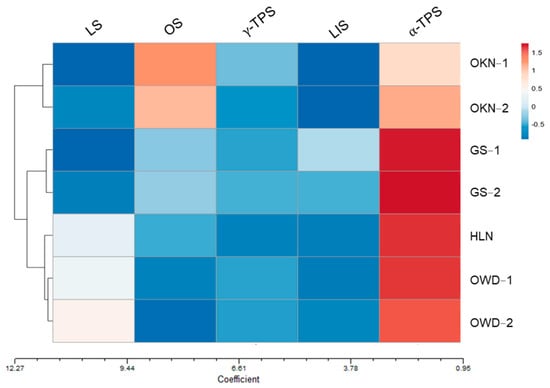
Figure 8.
The heatmap of relative gene expression of volatile-compound-synthesis-relevant genes, and the clustering analysis to the accessions of Citrus depressa in Taiwan. Clustering distances for varieties are the Euclidean coefficient, and the clustering method uses the average value. Accessions include OWD-1 and OWD-2 (Ouwanda, Nantou), HLN (Hualien), GS-1 and GS-2 (original sample trees in germplasm), and OKN-1 and OKN-2 (Okinawa, Japan). The gene abbreviations, respectively, represent as follows: LS, gene of limonene synthase; OS, gene of β-ocimene synthase; γ-TPS and α-TPS, genes of γ-terpinene synthase and α-terpinol synthase; and LIS, gene of linalool synthase.
4. Discussion
Both Taiwan island and Okinawa, Japan are two original distributed locations of C. depressa by Tanaka [1]. The high interspecific diversity of shiikuwasha in Okinawa has been revealed depending on fruit characteristics and molecular evidence [18,21,22,23]. However, molecular phylogeny studies require well-trained techniques and specific laboratory equipment. Establishing the relationships between genotyping and phenotyping takes years, heavy work, and high costs. In the food and fragrance industries, secondary metabolites are the central targets to distinguish the materials. Flavonoids in citrus peel [13,24,25] and essential oils [26,27,28] have been investigated regarding the differences among inter- or intra-species.
Leaf characteristics are the basic but essential traits in citrus discrimination. The wild distribution of C. depressa in Taiwan is unclear but we found diverse leaf characteristics, and they also have different leaf aromatic types among the collected samples in the official germplasm. Visual and olfactory phenotypes are the direct index for classification. Morphological traits, especially from leaves, have been used for variety discrimination in citrus species for years [29,30]. The narrow-winged WL is an important feature of mandarins and is consistent with the character description of C. depressa which is less than 3 mm in the Flora of Taiwan [2]. These morphological biomarkers are easier to investigate and are genetically foundational.
The distinct aroma composition of shiikuwasha fruit peel has been evaluated and showed diversity in their cultivation lines in Japan [6]. The fruit is harvested only once a year. The odor pattern of fresh citrus leaves is mostly discussed in plant defense [31]. However, the odor compositions of fresh leaves showed an inter-specific difference and the clustering with aromatic profiles reflected the reasonable similarity to phylogeny relations in citrus species [17,32]. Using leaf volatile compounds develops a metabolomic and functional database and has the potential as a classification index. An easy and eco-friendly extraction method, headspace solid-phase micro-extraction (HS-SPME), was applied for this study. It improves the VOC extraction efficiency and greatly keeps the fresh VOCs similar under the growing conditions [33]. Our analytical results revealed that citrus leaf volatiles have immense potential as character-specific markers for intra-specific diversity (Figure 1 and Figure 2; Table S2).
The leaf scent of C. depressa is composed of linalool, γ-terpinene, β-ocimene, α-terpineol, and limonene. Linalool and limonene are the most common VOCs in citrus aroma compositions. They contribute to the citrus floral fragrance and the lemon-like scent of fruits, and they have the potential to be botanical pesticides because of their insecticidal activity [34]. The scent of β-ocimene is fresh and herbal, and is responsible for citrus scents in citrus leaves. There are several terpinene-related VOCs, such as γ-terpinene, terpinen-4-ol, and α-terpineol, which also contribute to the aromatic pattern of C. depressa fresh leaf. The scent of γ-terpinene is a terpenic herbal and lemon-like aroma. The volatile α-terpineol, which has pine-like and resinous scent with a slight cooling lemon nuance, has been used in many medical applications because of its antimicrobial activity, and it is the important major component in tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) oil [35]. The major function of these VOCs is their use for defense, especially for floral buds and young parts of trees, and that may be why they have a high relative concentration in spring than in other seasons (Table S3). The different composition ratios of major VOCs result in different aromatic patterns for fresh leaves. The VOC pattern is a useful index to distinguish the differences from Taiwanese accessions. The LDA result indicated that using VOC characteristics as the classification factor allows distinguishing the diversity, not only inter-species but also within a species.
Volatile fingerprints may be affected by tissue, developmental stages, and environmental factors [36]. Floral VOCs displayed different compositions when harvested at different blooming stages in citrus [32]. The predominant compounds of shiikuwasha fruit pulp were limonene and γ-terpinene [6], but the predominant VOC of the fresh leaf was linalool (Table S2). Although the predominant compounds may not be the same in different tissue, the leading VOC group including linalool, limonene, and γ-terpinene was consistent in fruits or in leaves of C. depressa. Volatile profiles showed seasonal variations and most VOCs had the highest relative concentration in summer (Table S3). High light intensity, more ultraviolet radiation, and high temperature may increase the contents of most secondary metabolites [37]. Currently, there is little research on the effects of light and temperature on VOCs’ variation. Our seasonal citrus leaf VOC variation provides preliminary results to discover the changing pattern.
Realizing the correlation between chemical fingerprints and genetic markers may be a useful starting point for marker-assisted selection [38]. Through the bioinformatics of C. depressa, synthase genes related to a few major volatile compounds were first tried for the transcript to cDNA and quantifying the gene expression. Our results displayed the same grouping by VOCs, the secondary metabolites (Figure 3), and the clustering by VOC-relevant gene expression (Figure 4). They revealed that phenotypic characteristics and genetic performance were connected to each other. Understanding VOC composition may develop a specific characteristic marker to differentiate the varieties. This demonstrates the feasibility of working backward from metabolomics to functional genes and constructing functional auxiliary molecules for marker selection.
5. Conclusions
Citrus depressa, also called shiikuwasha in Okinawa, is a small-fruit citrus with a distinct scent and sour taste. Using the aroma from fresh leaves as the fingerprint has been verified a valuable character-specific index for the classification of citrus species, no matter whether inter-species or for variety discrimination. Linalool, γ-terpinene, β-Ocimene, α-terpineol, and limonene are the five major volatile components in the fresh leaf of C. dpressa. According to the leaf volatile profiles, Taiwanese accessions of C. depressa have two aromatic types. One group, OWNs and HLN, is native in Taiwan, and the original germplasm samples, GS-1 and GS-2, are much more similar to shiikuwasha in Okinawa (OKNs). Volatile patterns varied in seasons, but the variation did not affect the variety discrimination based on the distinct grouping by LDA analysis. The gene expression levels of five VOC-relevant synthase genes were quantified and were used as the character-specific index. The clustering result showed the same grouping as the VOC-dependent discrimination. Our results revealed the connection between secondary metabolites and relevant gene expression, and the possibility for working backward from metabolomics to functional genes to construct a functional auxiliary for a molecule marker selection method.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae8090773/s1. Table S1: qPCR primers used in the gene expression analysis; Table S2: Volatile composition profiles in varieties of Citrus depressa in Taiwan; Table S3: Volatile composition profiles in seasonal variation of Citrus depressa in Taiwan; Table S4: Standardized determinant function coefficient of volatile components; Table S5: The relative gene expression of volatile components.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-Y.L. and P.-A.C.; methodology, S.-Y.L.; validation, S.-Y.L. and P.-A.C.; formal analysis, Y.-Y.L.; investigation, Y.-Y.L.; data curation, S.-Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-Y.L.; writing—review and editing, S.-Y.L. and P.-A.C.; visualization, S.-Y.L.; supervision, P.-A.C.; project administration, S.-Y.L.; funding acquisition, S.-Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, R.O.C. (Taiwan), grant number 108AS-1.2.1-ST-a4.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Joint Center for Instruments and Researches, College of Bioresources and Agriculture, National Taiwan University, who provided the GC-MS instruments for our analysis, and Technology Commons, College of Life Science, National Taiwan University, who provided the RT-qPCR instruments. We are also grateful to the Taiwan citrus germplasm in Chiayi Agricultural Experiment Branch, Taiwan Agricultural Research Institute, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, who provided the plant materials for our study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Tanaka, T. Wild citri of the Japanese territories. Bul. Sci. Fak. Terk. Kjusu. Imp. Univ. 1926, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.E.; Hartley, T.G. Citrus. In Flora of Taiwan; Flora of Taiwan Editorial Committee, Ed.; Epoch Pub. Co.: Taipei, Taiwan, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Wang, Y. Citrus phytochemicals and their potential effects on the prevention and treatment of obesity: Review and progress of the past 10 years. J. Food Bioact. 2018, 4, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogata, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Ishii, T.; Yano, M.; Ohta, H. Flavonoid composition of fruit tissues of citrus species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inafuku-Teramoto, S.; Suwa, R.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Kawamitsu, Y. Polymethoxyflavones, synephrine and volatile constitution of peels of citrus fruit grown in Okinawa. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 80, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Maeda, G.; Tamaki, H.; Mizu, M.; Oku, H.; Wada, K. Cultivation line and fruit ripening discriminations of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) peel oils using aroma compositional, electronic nose, and antioxidant analyses. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 67, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Wei, C.C.; Huang, J.; Pan, M.H.; Shahidi, F.; Ho, C.T. Anti-inflammatory effects of polymethoxyflavones from citrus peels: A review. J. Food Bioact. 2018, 3, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, S.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, Q. Citrus polymethoxyflavones as regulators of metabolic homoeostasis: Recent advances for possible mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swingle, W.T.; Reece, P.C. History, world distribution, botany and varieties. In The Citrus Industry, 2nd ed.; Reuther, E.W., Webber, H.J., Batchelor, L.D., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 190–430. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T. Fundamental discussion of Citrus classification. Studia Citrol. 1977, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolosi, E.; Deng, Z.N.; Gentile, A.; La Malfa, S.; Continella, G.; Tribulato, E. Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, B.; Roy, A.; Annamalai, A.; Lakshmi, P.T.V. A molecular perspective on the taxonomy and journey of Citrus domestication. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2021, 53, 125644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M.; Koizumi, M.; Ito, C.; Furukawa, H. Quantitative study of flavonoids in leaves of Citrus plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukawa, T.; Nito, N. Metabolic fingerprinting of citrus cultivars and related genera using HPLC and multivariate analysis. J. Plant Stud. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deterre, S.C.; McCollum, G.; Leclair, C.; Manthey, J.A.; Bai, J.; Baldwin, E.A.; Plotto, A. Effect of Poncirus trifoliata on the chemical composition of fruits in pedigrees of Citrus scion hybrids. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 277, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lota, M.L.; de Rocca Serra, D.; Casanova, J.; Tomi, F. Chemical variability of peel and leaf essential oils of sour orange. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2001, 16, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Roan, S.F.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, I.Z. Volatile organic components of fresh leaves as indicators of indigenous and cultivated citrus species in Taiwan. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 90891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urasaki, N.; Yoshida, K.; Uehara, T.; Inoue, H.; Onda, S.; Kinjyo, H.; Kawano, S. Single nucleotide polymorphism in shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) chloroplast DNA, trnL-trnF. J. Trop. Agric. 2005, 49, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.T.; Ishikawa, R. Molecular discrimination of landraces of Citrus species in the Okinawa, Japan. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Inafuku-Teramoto, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Mimura, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Yamamoto, M. Characterization of chloroplast matK sequences of Citrus tachibana and Citrus depressa, two indigenous species in Japan. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 28, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, R.; Badenoch, N.; Miyagi, K.; Medoruma, K.; Osada, T.; Onishi, M. Multi-lineages of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) evaluated by using whole chloroplast genome sequences and its bio-diversity in Okinawa, Japan. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takakura, A.; Tanabe, A.; Teramoto, S.; Kita, M. Diversity of Citrus depressa Hayata (Shiikuwasha) revealed by DNA analysis. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, D.; Tan, C.; Hu, Y.; Sundararajan, B.; Zhou, Z. Profiling of flavonoid and antioxidant activity of fruit tissues from 27 Chinese local citrus cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An overview of bioactive flavonoids from Citrus fruits. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clery, R.A.; Armendi, A.; Franco, V.; Furrer, S.; Genereux, J.C.; Kahn, T.L.; Koshiro, K. Chemical diversity of citrus leaf essential oils. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, V.; Costantino, G.; Paoli, M.; Paymal, N.; Quinton, C.; Ollitrault, P.; Luro, F. Intercultivar diversity of sour orange (Citrus aurantium L.) based on genetic markers, phenotypic characteristics, aromatic compounds and sensorial analysis. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petretto, G.L.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Piroddi, M.; Pintore, G.; Mannu, A. Classification of pummelo (Citrus grandis) extracts through UV-VIS-based chemical fingerprint. Beverages 2022, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penjor, T.; Mimura, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagano, Y. Characterization of limes (Citrus aurantifolia) grown in Bhutan and Indonesia using high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.U.; Zhin, K.L.; Oh, E.U.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.B.; Song, K.J. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of three different types of Dangyooza (Citrus grandis), Korean landrace Citrus. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.T.L.; Van Hung, P.; Le Thanh, H.; Phi, N.T.L. Valorization of citrus leaves: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 4849–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xu, C.; Chen, K. Citrus leaf volatiles as affected by developmental stage and genetic type. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17744–17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, J.; Ke, Y.; Huang, S.; Zeng, F.; Luan, T.; Ouyang, G. Applications of in vivo and in vitro solid-phase microextraction techniques in plant analysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 794, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyedeji, A.O.; Okunowo, W.O.; Osuntoki, A.A.; Olabode, T.B.; Ayo-Folorunso, F. Insecticidal and biochemical activity of essential oil from Citrus sinensis peel and constituents on Callosobrunchus maculatus and Sitophilus zeamais. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.; Felipe, L.D.O.; Bicas, J.L. Production, properties, and applications of α-terpineol. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.; Bhardwaj, S.; Sharma, N.R. Fragrance stimulation mechanisms of flowers and their regulation under environmental constraints. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamine, M.; Rahali, F.Z.; Hamdaoui, G.; Selmi, S.; Mliki, A.; Gargouri, M. Associating chemical analysis to molecular markers for the valorization of Citrus aurantium leaves: A useful starting point for marker-assisted selection. Euphytica 2017, 213, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).