Effect of Flavonoid Dynamic Changes on Flower Coloration of Tulipa gesneiana ‘Queen of Night’ during Flower Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Color Reactions of Petal Pigment
2.2.2. Identification and Measurement of Flavonoids
Extraction of Flavonoids
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
3. Results
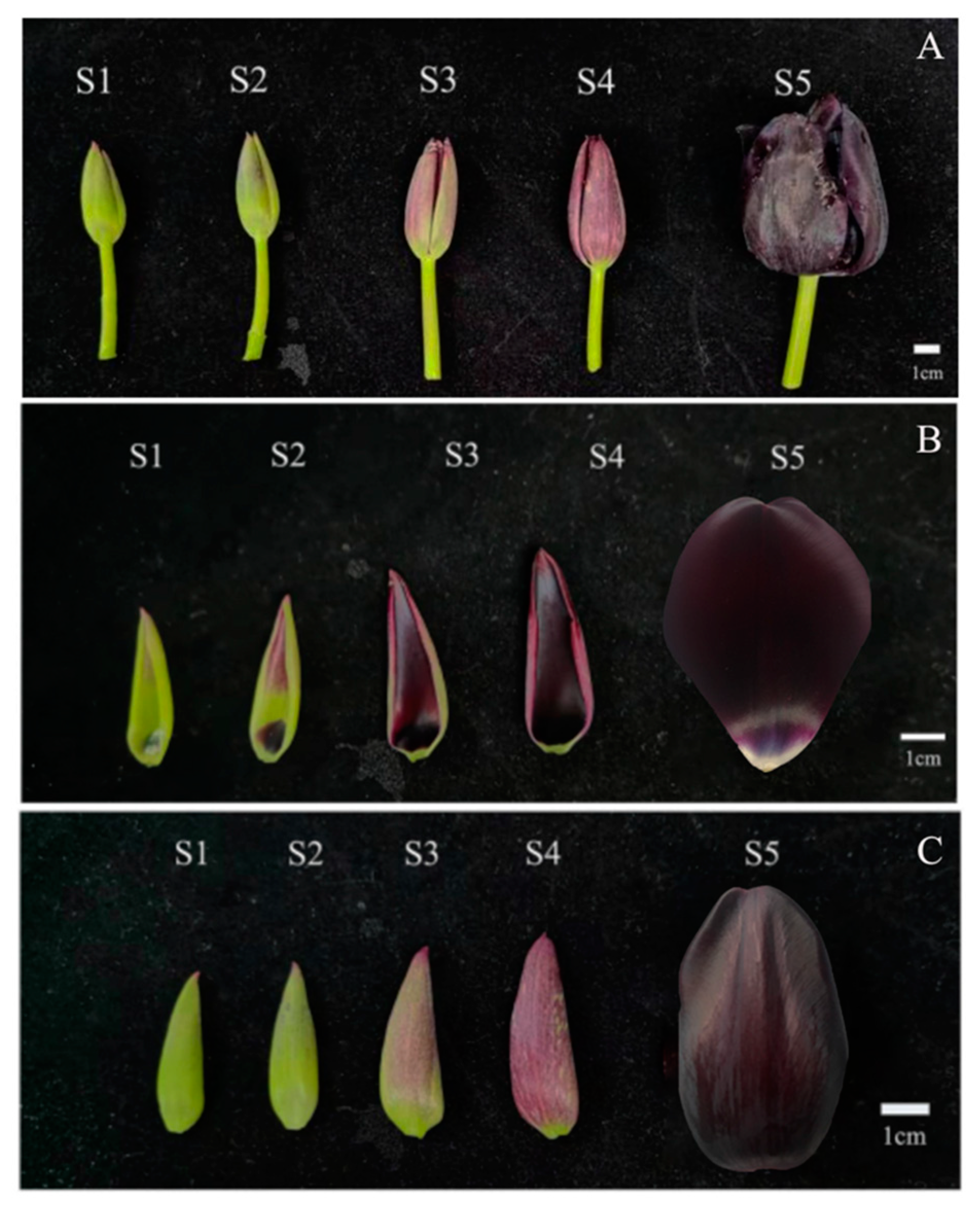
3.1. Color Reaction of Petal Pigment of ‘QN’
3.2. Analysis of Flavonoid Composition in the Petals of ‘QN’
3.2.1. Identification of Anthocyanins
3.2.2. Identification of Anthoxanthins
3.3. The Accumulation of Flavonoids along with the Process of Flower Opening
3.3.1. Dynamic Changes of Anthocyanins
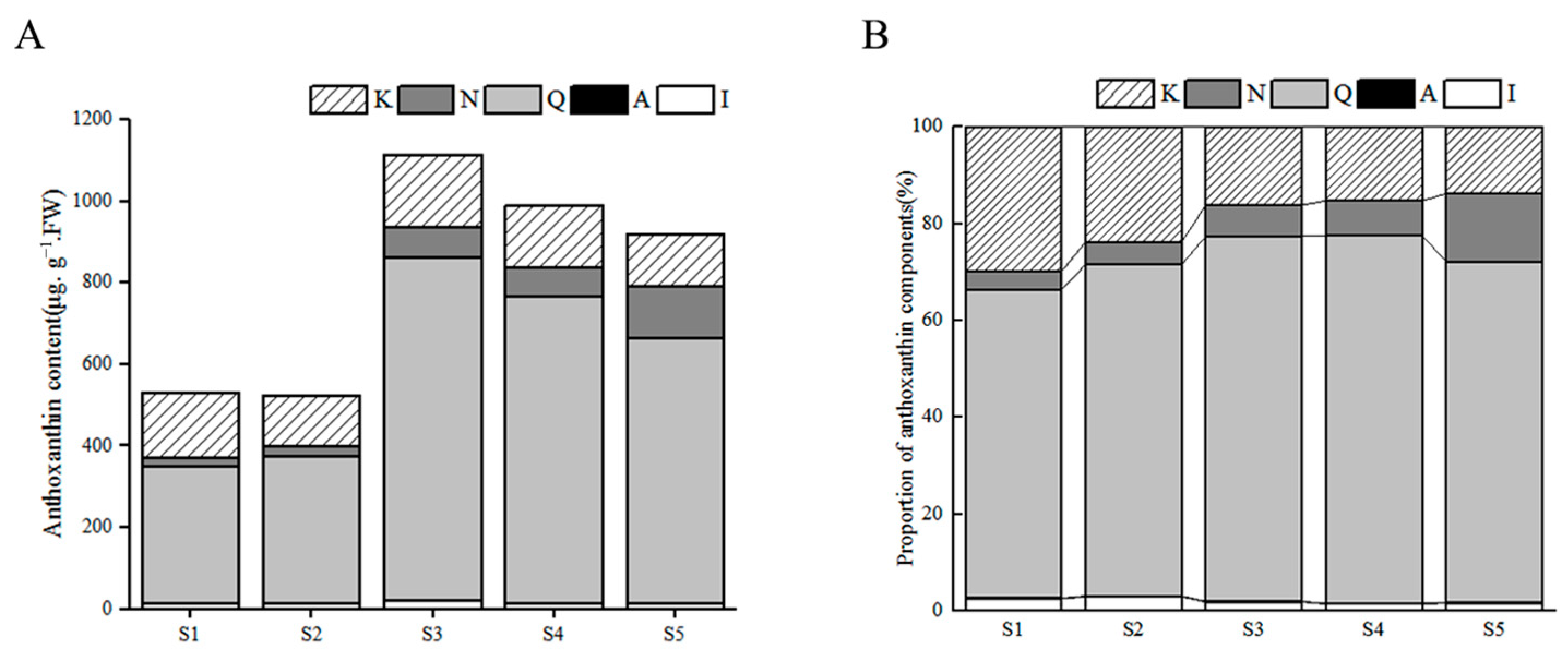
3.3.2. Dynamic Changes of Anthoxanthin Components
3.3.3. Dynamic Changes of Total Flavonoids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Dai, Z.; Dai, X.; Li, W.; Cao, M.; Li, C.; Tsai, W.-C.; Wu, X.; Zhai, J. Comparative transcriptomics provides insight into floral color polymorphism in a Pleione limprichtii orchid population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Irfan, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Integrated metabolic profiling and transcriptome analysis of pigment accumulation in diverse petal tissues in the lily cultivar ‘Vivian’. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F.; Chandler, S. Recent progress of flower colour modification by biotechnology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5350–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, A.; Das, G.; Das, S.K. Roles of flavonoids in plants. Carbon 2011, 100, 12–35. [Google Scholar]
- Iwashina, T. The structure and distribution of the flavonoids in plants. J. Plant Res. 2000, 113, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lei, J. Flower pigment inheritance and anthocyanin characterization of hybrids from pink-flowered and white-flowered strawberry. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 200, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lewis, D.; Shi, R.; McGhie, T.; Wang, L.; Arathoon, S.; Schwinn, K.; Davies, K.; Qian, X.; Zhang, H. The colour variations of flowers in wild Paeonia delavayi plants are determined by four classes of plant pigments. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2022, 50, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, C.; Meng, J.; Lin, S.; Ding, W.; Tao, J. Transcriptome sequencing of a chimaera reveals coordinated expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes mediating yellow formation in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F. Flower colour and cytochromes P450. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, H.; Mizuno, T.; Iwashina, T. Flavonoid pigments and color expression in the flowers of black Hollyhock (Alcea rosea ‘nigra’). Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. B 2012, 38, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Murai, Y.; Yangzom, R.; Gyeltshen, C.; Dorji, K.; Wangmo, C.; Iwashina, T. Flower pigments of black pea Thermopsis barbata (Fabaceae) in Bhutan. Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser. B 2017, 43, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Amamiya, K.; Iwashina, T. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of flower pigments in chocolate Cosmos, Cosmos atrosanguineus, and its hybrids. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, K.R.; Bloor, S.J.; Nicholson, R.; Rivera, R.; Shemluck, M.; Kevan, P.G.; Michener, C. Black flower coloration in wild Lisianthius nigrescens: Its chemistry and ecological consequences. Z. Nat. C 2004, 59, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Li, S.; Feng, C.; Hong, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Dai, S. Metabolite and gene expression analysis reveal the molecular mechanism for petal colour variation in six Centaurea cyanus cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 142, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Song, Y.; Jin, X.; Su, T.; Pu, Y. Effects of pigment constituents and their distribution on spathe coloration of Zantedeschia hybrida. HortScience 2017, 52, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Shikazono, N.; Tanaka, A. TRANSPARENT TESTA 19 is involved in the accumulation of both anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004, 37, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Asif, M.; Naveed, M.; Qadri, R.W.K.; Faried, N.; Anjum, F. Postharvest exogenous application of various bacterial satrains improves the longevity of cut ‘royal virgin’ tulip flowers. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Mogollón, N. Propagación in vitro de los cultivares de Etlingera hemisphaerica ‘Red Tulip’ y ‘Black Tulip’. Rev. Fac. Agron. Univ. Zulia 2007, 24, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Van Raamsdonk, L. Flower pigment composition in Tulipa. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1993, 40, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Guo, P.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G. New insight into the pigment composition and molecular mechanism of flower coloration in tulip (Tulipa gesneriana L.) cultivars with various petal colors. Plant Sci. 2022, 317, 111193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torskangerpoll, K.; Norbaek, R.; Nodland, E.; Ovstedal, D.O.; Andersen, O.M. Anthocyanin content of Tulipa species and cultivars and its impact on tepal colours. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2005, 33, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Tang, D.; Shi, Y. Comparison of anthocyanin components, expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic structural genes, and TfF3′ H1 sequences between Tulipa fosteriana ‘Albert heijn’ and its reddish sport. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 175, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Okada, M.; Taya-Kizu, M.; Urashima, O.; Kan, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Koshioka, M. Coloration and anthocyanin profile in tulip flowers. JARQ-Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2004, 38, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Momonoi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Mano, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nakamori, C.; Shoji, K.; Nitta, A.; Nishimura, M. A vacuolar iron transporter in tulip, TgVit1, is responsible for blue coloration in petal cells through iron accumulation. Plant J. 2009, 59, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Nishihara, M.; Mishiba, K.; Yamamura, S. Temporal expression of flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes regulates flower pigmentation in gentian plants. Plant Sci. 2005, 168, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, H.; Miao, M.; Che, D. Components of flower pigments in petals of lily. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2016, 23, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Tang, D. Composition of flavonoids in the petals of Freesia and prediction of four novel transcription factors involving in Freesia flavonoid pathway. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 756300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, C.; Wang, M. Rapid characterization of the chemical constituents of Yinchen Wuling powder by UPLC coupled with fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 198, 114022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeraik, M.; Yariwake, J. Quantification of isoorientin and total flavonoids in Passiflora edulis fruit pulp by HPLC-UV/DAD. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, M.; Tang, D.; Shi, Y. Composition of carotenoids and flavonoids in narcissus cultivars and their relationship with flower color. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Cuyckens, F.; Heuvel, H.V.D.; Claeys, M. Mass spectrometric methods for the characterisation and differentiation of isomeric O-diglycosyl flavonoids. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Shu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Relationship between the composition of flavonoids and flower colors variation in tropical water lily (Nymphaea) cultivars. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-J.; Su, S.; Wu, J.; Du, H.; Li, S.-S.; Huo, J.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.-S. Variation of anthocyanins and flavonols in Vaccinium uliginosum berry in Lesser Khingan Mountains and its antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rabaneda, F.; Jáuregui, O.; Casals, I.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Liquid chromatographic/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric study of the phenolic composition of cocoa (Theobroma cacao). J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, W.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for rapid analysis of constituents of Suanzaoren decoction. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, M.E. UPLC™: An introduction and review. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, I.; Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A. Comparison of UPLC and HPLC methods for determination of vitamin C. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchwell, M.I.; Twaddle, N.C.; Meeker, L.R.; Doerge, D.R. Improving LC–MS sensitivity through increases in chromatographic performance: Comparisons of UPLC–ES/MS/MS to HPLC–ES/MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 825, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, H.-J.; Feng, C.-Y.; Yin, D.-D.; Wu, R.-Y.; Wang, L.-S. Transcriptome sequencing and metabolite analysis for revealing the blue flower formation in waterlily. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Du, H.; Wang, L.; Shu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Ge, Y. Flavonoid composition and antioxidant activity of tree peony (Paeonia section Moutan) yellow flowers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8496–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Tang, W.; Hao, Z.; Tao, J. Identification of flavonoids and expression of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in two coloured tree peony flowers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, A.; Ohno, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Tatsuzawa, F.; Doi, M. Endogenous post-transcriptional gene silencing of flavone synthase resulting in high accumulation of anthocyanins in black dahlia cultivars. Planta 2013, 237, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, A.; Tatsuzawa, F.; Hosokawa, M.; Doi, M.; Ohno, S. Quantitative evaluation of the contribution of four major anthocyanins to black flower coloring of Dahlia petals. Hortic. J. 2016, 85, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitonga, V.W.; Stolker, R.; Koning-Boucoiran, C.F.; Aelaei, M.; Visser, R.G.; Maliepaard, C.; Krens, F.A. Inheritance and QTL analysis of the determinants of flower color in tetraploid cut roses. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Young, J.C.; Rabalski, I. Anthocyanin composition in black, blue, pink, purple, and red cereal grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4696–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F. Flavonoids: A colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, Y.; Suzuki, K.-I.; Fukuchi-Mizutani, M.; Fukui, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Ohkawa, H.; Kusumi, T.; Tanaka, Y. Molecular and biochemical characterization of torenia flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase and flavone synthase II and modification of flower color by modulating the expression of these genes. Plant Sci. 2002, 163, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, K.; Momonoi, K.; Tsuji, T. Alternative expression of vacuolar iron transporter and ferritin genes leads to blue/purple coloration of flowers in Tulip cv. Murasakizuisho. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, K.; Miki, N.; Nakajima, N.; Momonoi, K.; Kato, C.; Yoshida, K. Perianth bottom-specific blue color development in Tulip cv. Murasakizuisho requires ferric ions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.Y.; Wang, C.K. Molecular breeding of flower color. Floric. Ornam. Plant Biotechnol. 2006, 1, 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Yang, C.-L.; Jiang, G. Effects of the coupling between electrode and GQD-anthoxanthin nanocomposites for dye-sensitized solar cell: DFT and TD-DFT investigations. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 407, 113080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Bian, S.; Chang, P.; Xuan, L.; Fan, L.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Gu, C.; Zhang, S. Flavonoid components of different color Magnolia flowers and their relationship to cultivar selections. HortScience 2019, 54, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Suzuki, T.; Harada, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Dohra, H.; Ohno, H. Floral organ-and temperature-dependent regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Cymbidium hybrid flowers. Plant Sci. 2019, 287, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, A.; Appelhagen, I.; Martin, C. Natural blues: Structure meets function in anthocyanins. Plants 2021, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.H.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, S.H. Increased flavonol levels in Tobacco expressing AcFLS affect flower color and root growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Ning, G.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, P.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Bao, M. Disequilibrium of flavonol synthase and dihydroflavonol-4-reductase expression associated tightly to white vs. red color flower formation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Identification | tR (min) | ESI-(+)-MS (m/z) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Delphinidin 3-o-rutinoside | 5.26 | 611 [M + H]+, 303 [Y0+] | [23] |
| A2 | Cyanidin 3-o-rutinoside | 5.73 | 595 [M + H]+, 287 [Y0+] | [23,24] |
| A3 | Pelargonidin 3-o-rutinoside | 6.20 | 579 [M + H]+, 271 [Y0+] | [23,24] |
| No. | Identification/Tentative Identification | tR (min) | ESI-(+)-MS (m/z) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Isorhamnetin-7-succinylrutinoside-rhamnoside | 0.79 | 869 [M-H]−, 461, 315 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F2 | Isorhamnetin-3-succinylrutose-galactoside | 1.17 | 881 [[M-H]−, 473, 315 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F3 | Apigenin-3-acetylrhamnose-7-sambubiose | 1.31 | 745 [M-H]−, 451, 269 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F4 | Isorhamnetin-3-sophoroside-7-gallicacylglucoside | 3.63 | 953 [M-H]−, 627, 315 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F5 | Quercetin-3-acetylpentose-7-sambubiose | 4.16 | 771 [M-H]−, 593, 301 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F6 | Kaempferol-3-sophoroside | 4.42 | 769 [M-H]−, 447, 285 [Y0−] | [32,35,36] |
| F7 | Quercetin-3-galactose-sambubiose | 5.12 | 755 [M-H]−, 591, 301 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F8 | Naringin-3-acetylrutinoside | 5.22 | 627 [M-H]−, 316, 271 [Y0−] | [32,34] |
| F9 | Kaempferol-3- rhamnoside- sambubiose | 5.32 | 726 [M-H]−, 579, 285 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F10 | Quercetin-3-sambubiose | 5.42 | 595 [M-H]−, 301 [Y0−] | [32,37] |
| F11 | Naringenin-3-sophoroside | 5.54 | 595 [M-H]−, 271 [Y0−] | [32,35,36] |
| F12 | Kaempferol-3-galactose-sambubiose | 5.60 | 741 [M-H]−, 575, 285 [Y0−] | [32,33,34] |
| F13 | Quercetin-7-rutinoside | 5.85 | 609 [M-H]−, 301 [Y0−] | [32,37] |
| F14 | Rutin(Quercetin-3-rutinoside) | 5.92 | 609 [M-H]−, 301 [Y0−] | std |
| F15 | Kaempferol-7-malonylgalactose | 6.09 | 691 [M-H]−, 447, 285 [Y0−] | [32,34] |
| F16 | Kaempferol-3-sambubiose | 6.21 | 579 [M-H]−, 285 [Y0−] | [32,37] |
| F17 | Kaempferol-3-rutinoside | 6.36 | 593 [M-H]−, 285 [Y0−] | [32,37] |
| F18 | Isorhamnetin-3-succinylsophoricoside | 6.74 | 737 [M-H]−, 415, 315 [Y0−] | [32,34] |
| F19 | Quercetin-3-sophoroside | 6.84 | 624 [M-H]−, 301 [Y0−] | [32,35,36] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Tang, D. Effect of Flavonoid Dynamic Changes on Flower Coloration of Tulipa gesneiana ‘Queen of Night’ during Flower Development. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060510
Guo X, Fu X, Li X, Tang D. Effect of Flavonoid Dynamic Changes on Flower Coloration of Tulipa gesneiana ‘Queen of Night’ during Flower Development. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(6):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060510
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xueying, Xueqing Fu, Xin Li, and Dongqin Tang. 2022. "Effect of Flavonoid Dynamic Changes on Flower Coloration of Tulipa gesneiana ‘Queen of Night’ during Flower Development" Horticulturae 8, no. 6: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060510
APA StyleGuo, X., Fu, X., Li, X., & Tang, D. (2022). Effect of Flavonoid Dynamic Changes on Flower Coloration of Tulipa gesneiana ‘Queen of Night’ during Flower Development. Horticulturae, 8(6), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060510






