A Comparative Study between Vis/NIR Spectroradiometer and NIR Spectroscopy for the Non-Destructive Quality Assay of Different Watermelon Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Assay Color Property
2.3. Assay Soluble Solids Content (SSC)
2.4. HPLC Determination of Carotenoids and Vitamin C
2.5. Spectra Acquisition
2.6. Spectral Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color Analysis of Watermelon Cultivars
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Watermelon Cultivars
3.3. Reflectance Spectra Analysis of Watermelon Cultivars
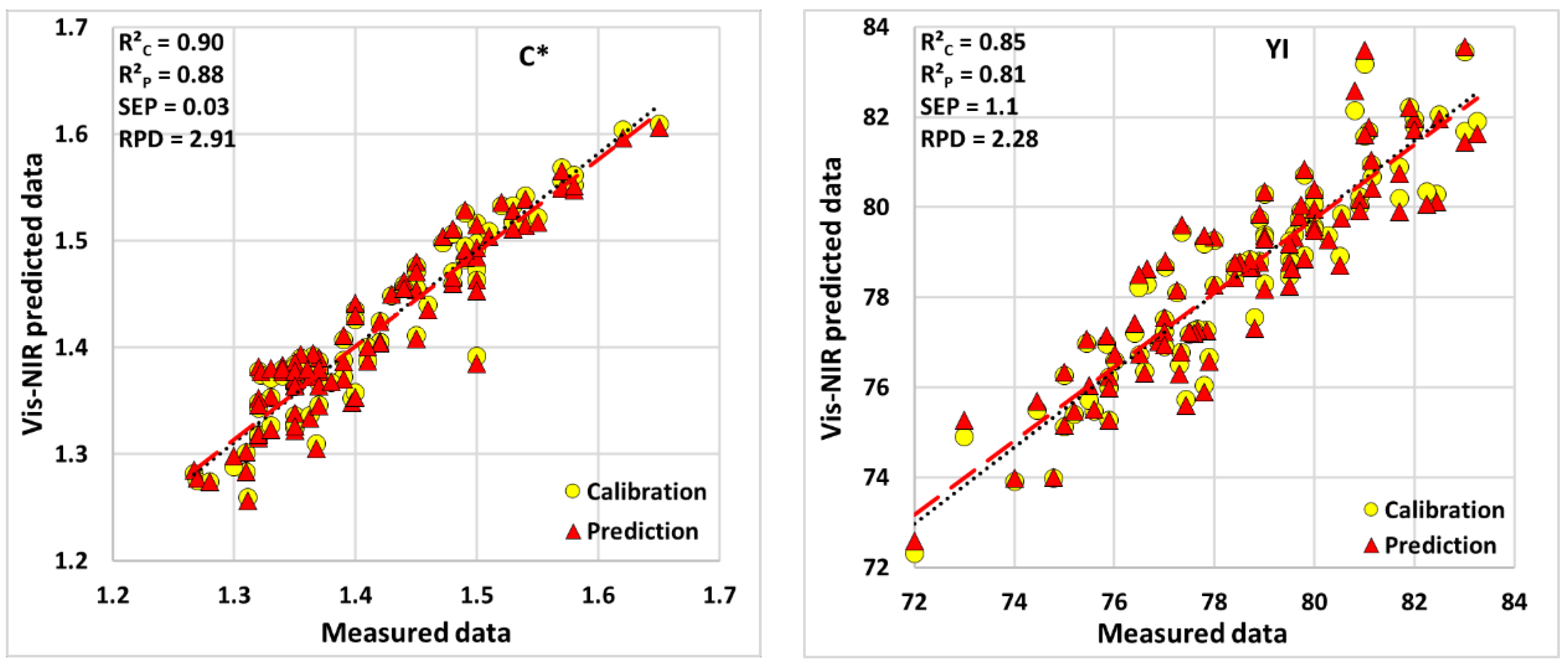
3.4. Spectral Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Fruit and Vegetables Watermelon Crop Information. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/crop-information/watermelon/en/ (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Mohd Ali, M.; Hashim, N.; Bejo, S.K.; Shamsudin, R. Rapid and nondestructive techniques for internal and external quality evaluation of watermelons: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins-Veazie, P.; Collins, J.K.; Davis, A.R.; Roberts, W. Carotenoid content of 50 watermelon cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maoto, M.M.; Beswa, D.; Jideani, A.I.O. Watermelon as a potential fruit snack. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jie, D.; Xie, L.; Rao, X.; Ying, Y. Using visible and near infrared diffuse transmittance technique to predict soluble solids content of watermelon in an on-line detection system. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, I.; Hdider, C.; Lenucci, M.S.; Ilahy, R.; Jebari, H.; Dalessandro, G. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities during fruit ripening of watermelon cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, Z.; Wan, X.; Yan, Z.; King, S.R. Lycopene and citrulline contents in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) fruit with different ploidy and changes during fruit development. Acta Hortic. 2010, 871, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semmelmeyer, E. OECD guidance on objective testing to determine the ripeness of fruit. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2006, 14, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins-Veazie, P. Composition of orange, yellow, and red fleshed watermelon. In Cucurbitacea; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2022; pp. 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins-Veazie, P.; Collins, J.K.; Clevidence, B. Watermelons and health. Acta Hortic. 2007, 731, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, E.; Costa, S.; Rugiero, I.; Pedrini, P.; Marchetti, M.G. Quantification of lycopene, β-carotene, and total soluble solids in intact red-flesh watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) using on-line near-infrared spectroscopy. Sensors 2017, 17, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawgien, K.; Kiattisin, S. Machine learning techniques for classifying the sweetness of watermelon using acoustic signal and image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 181, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Leskovar, D.I.; Colla, G.; Rouphael, Y. Watermelon and melon fruit quality: The genotypic and agro-environmental factors implicated. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriacou, M.C.; Soteriou, G.A.; Rouphael, Y.; Siomos, A.S.; Gerasopoulos, D. Configuration of watermelon fruit quality in response to rootstock-mediated harvest maturity and postharvest storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushita, A.A.; Daood, H.G.; Biacs, P.A. Change in carotenoids and antioxidant vitamins in tomato as a function of varietal and technological factors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, Y.; Dadomo, M.; Lucca, G.D.; Grolier, P.; Di Lucca, G. Effects of environmental factors and agricultural techniques on antioxidant content of tomatoes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovar, D.I.; Bang, H.J.; Crosby, K.; Maness, N.; Franco, J.A.; Perkins-Veazie, P. Lycopene, carbohydrates, ascorbic acid, and yield components of diploid and triploid watermelon cultivars are affected by deficit irrigation. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenucci, M.S.; Caccioppola, A.; Durante, M.; Serrone, L.; De Caroli, M.; Piro, G.; Dalessandro, G. Carotenoid content during tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit ripening in traditional and high-pigment cultivars. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2009, 4, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Sun, D.-W. Advanced applications of hyperspectral imaging technology for food quality and safety analysis and assessment: A review—part II: Applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Huang, K.; Xu, H.; Ying, Y. Research advances in nondestructive determination of internal quality in watermelon/melon: A review. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, D.J.; Scott, K.J. Development and evaluation of an HPLC method for the analysis of carotenoids in foods, and the measurement of the carotenoid content of vegetables and fruits commonly consumed in the UK. Food Chem. 1995, 54, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.; Helyes, L.; Romano, E.; Albandary, A.; Ibrahim, A. Thoughts for foods: Imaging technology opportunities for monitoring and measuring food quality. In Book Food Processing New Insights, 1st ed.; Var, D.I., Uzunlu, D.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, V.J.M.; Mascarin, G.M.; Silva, L.C.A.S.; Arthur, V.; Carstensen, J.M.; Boelt, B.; da Silva, C.B. Multispectral and X-ray images for characterization of Jatropha curcas L. seed quality. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Daood, H.; Friedrich, L.; Hitka, G.; Helyes, L. Monitoring, by high-performance liquid chromatography, near-infrared spectroscopy, and color measurement, of phytonutrients in tomato juice subjected to thermal processing and high hydrostatic pressure. J Food Process Preserv. 2021, 45, e15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Alghannam, A.; Eissa, A.; Firtha, F.; Kaszab, T.; Kovacs, Z.; Helyes, L. Preliminary study for inspecting moisture content, dry matter content, and firmness parameters of two date cultivars using an NIR hyperspectral imaging system. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 720630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Paillart, M.; Meesters, L.; Woltering, E.; Chauhan, A.; Polder, G. Assessing avocado firmness at different dehydration levels in a multi-sensor framework. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 118, 103901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; Verboven, P.; Nugraha, B.; Wang, Z.i.; Boone, M.; Josipovic, I.; Nicolaï, B.M. 3D pore structure analysis of intact ‘Braeburn’ apples using X-ray micro-CT. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 159, 111014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.B.; Blasco, J.; Zude-Sasse, M.; Sun, X. Visible-NIR ‘point’ spectroscopy in postharvest fruit and vegetable assessment: The science behind three decades of commercial use. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, B.; Verboven, P.; Janssen, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolaï, B.M. Non-destructive porosity mapping of fruit and vegetables using X-ray CT. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 150, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Tian, Y.; Song, P.; He, K.; Song, S. Analysis and detection of decayed blueberry by low field nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Kim, M.S.; Chao, K.; Dhakal, S.; Cho, B.-K.; Lohumi, S.; Mo, C.; Peng, Y.; Huang, M. Advances in Raman spectroscopy and imaging techniques for quality and safety inspection of horticultural products. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 149, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Landahl, S.; East, A.R.; Verboven, P.; Terry, L.A. Optical coherence tomography-A review of the opportunities and challenges for postharvest quality evaluation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 150, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cobo-Medina, M.; Lecourt, J.; Harrison, N.; Harrison, R.J.; Cross, J.V. Application of hyperspectral imaging for nondestructive measurement of plum quality attributes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 141, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwaliwale, N.; Singh, K.; Kalne, A.; Jha, S.N.; Seth, N.; Kar, A. X-ray imaging methods for internal quality evaluation of agricultural produce. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizrach, A. Ultrasonic technology for quality evaluation of fresh fruit and vegetables in pre- and postharvest processes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 48, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, E.; Ferrari, G.; Marchetti, M.G.; Pedrini, P.; Ferro, S. Development of FT-NIR models for the simultaneous estimation of chlorophyll and nitrogen content in fresh apple (Malus Domestica) leaves. Sensors 2015, 15, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamburini, E.; Marchetti, M.G.; Pedrini, P. Monitoring key parameters in bioprocesses using near-infrared technology. Sensors 2014, 14, 18941–18959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Ying, Y. Near Infrared Spectroscopy for on/in-line monitoring of quality in foods and beverages: A review. J. Food Eng. 2008, 87, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccher Zerbini, P. Emerging technologies for nondestructive quality evaluation of fruit. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2006, 14, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins-Veazie, P.; Collins, J.K. Flesh quality and lycopene stability of fresh-cut watermelon. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 31, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; El-Bialee, N. Internal quality assessment of tomato fruits using image color analysis. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2016, 18, 339–352. Available online: http://www.cigrjournal.org (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Arias, R.; Lee, T.C.; Logendra, L.; Janes, H. Correlation of lycopene measured by HPLC with the L*, a*, b* color readings of a hydroponic Tomato and the relationship of maturity with color and lycopene content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, M.; Singh, S.; Ingle, M. Lycopene concentration of tomato fruit can be estimated from chromaticity values. Hortscience 1992, 27, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins-Veazie, P.; Collins, J.K.; Pair, S.D.; Roberts, W. Lycopene content differs among red-fleshed watermelon cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S. Objective measurement of red grapefruit juice color. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.; Hobson, G.E. Compositional changes in normal and mutant tomato fruit during ripening and storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1987, 40, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.; Wu, Y.; Weller, C.; Schnepf, M. Physical characteristics of a composite film of soy protein isolate and propyleneglycol alginate. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daood, H.G.; Ráth, S.; Palotás, G.; Halász, G.; Hamow, K.; Helyes, L. Efficient HPLC separation on a core-c30 column with ms2 characterization of isomers, derivatives and unusual carotenoids from tomato products. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2022, 60, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A. ParLeS: Software for chemometric analysis of spectroscopic data. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2008, 90, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.C.; Sobering, D.C. How do we do it: A brief summary of the methods we use in developing near infrared calibrations. In Near Infrared Spectroscopy: The Future Waves, 2nd ed.; Davies, A.M.C., Williams, P.C., Eds.; NIR Publications: Chichester, UK, 1996; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaï, B.M.; Beullens, K.; Bobelyn, E.; Peirs, A.; Saeys, W.; Theron, I.K.; Lammertyn, J. Non-destructive measurement of fruit and vegetable quality by means of NIR spectroscopy: A review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 46, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyaka, A.W.; Oey, I.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. Application of thermal inactivation of enzymes during vitamin C analysis to study the influence of acidification, crushing and blanching on vitamin C stability in Broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheix, J.J.; Fleurient, A.; Billot, J. Phenolic compounds in fruit processing. In Fruit Phenolic; Mitra, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 295–342. [Google Scholar]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Remesy, C.; Jimenez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, R.; Bowser, T.J.; Weckler, P.; Maness, N.O.; McGlynn, W. Rapid estimation of lycopene concentration in watermelon and tomato puree by fiber optic visible reflectance -spectroscopy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, D.P.S.; Sogi, S. Utilization of watermelon pulp for lycopene extraction by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.P.; Nunes dos Santos, C.; Henriquesa, C.; Lima, G.; Quedas, F. Lycopene content and antioxidant capacity of Portuguese watermelon fruits. Elec. J. Environ. Agricult. Food Chem. 2011, 10, 2090–2097. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.15/637 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Jie, D.; Zhou, W.; Wei, X. Nondestructive detection of maturity of watermelon by spectral characteristic using NIR diffuse transmittance technique. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, B.; Pflanz, M.; Zude, M. Spectral shift as advanced index for fruit chlorophyll breakdown. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGlone, V.; Jordan, R.; Martinsen, P. Vis/NIR estimation at harvest of pre- and post-storage quality indices for ‘RoyalGala’ apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 25, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovenzana, V.; Beghi, R.; Romaniello, R.; Tamborrino, A.; Guidetti, R.; Leone, A. Use of visible and near infrared spectroscopy with a view to on-line evaluation of oil content during olive processing. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Norris, K.H. Variable affecting near infrared spectroscopic analysis. In Near infrared Technology in the Agriculture and Food Industries, 2nd ed.; Williams, P., Norris, K.H., Eds.; The American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2002; pp. 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavdir, I.; Buyukcan, M.B.; Lu, R.; Kocabiyik, H.; Seker, M. Prediction of olive quality using FT-NIR spectroscopy in reflectance and transmittance modes. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 103, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuvandzsiev, P.; Daood, H.G.; Posta, K.; Helyes, L.; Pék, Z. Application of VIS-NIR reflectance spectra for estimating soluble solid and lycopene content of open-field processing tomato fruit juice from irrigation and mycorrhiza treatments. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1159, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pék, Z.; Szuvandzsiev, P.; Daood, H.; Neményi, A.; Helyes, L. Effect of irrigation on yield parameters and antioxidant profiles of processing cherry tomato. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2014, 9, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenk, J.S.; Workman, J.J.; Westerhaus, M.O. Application of NIR spectroscopy to agricultural products. In Near Infrared Analysis; Burns, D.A., Ciurczak, R.W., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 419–469. [Google Scholar]
- Deák, K.; Szigedi, T.; Pék, Z.; Baranowski, P.; Helyes, L. Carotenoid determination in tomato juice using Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, G.A.; de Castilhos, F.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Bureau, S. Comparison of NIR and MIR spectroscopic methods for determination of individual sugars, organic acids and carotenoids in passion fruit. Food Res. Int. 2014, 60, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, S.; Ruiz, D.; Reich, M.; Gouble, B.; Bertrand, D.; Audergon, J.M.; Renard, C.M. Rapid and non-destructive analysis of apricot fruit quality using FT-near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Song, S.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Han, D. Establishment of a comprehensive indicator to nondestructively analyze watermelon quality at different ripening stages. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2014, 7, 1350034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, R. Optimization of soluble solids content prediction models in ‘Hami’ melons by means of Vis-NIR spectroscopy and chemometric tools. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, D.; Xie, L.; Fu, X.; Rao, X.; Ying, Y. Variable selection for partial least squares analysis of soluble solids content in watermelon using near-infrared diffuse transmission technique. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissard, A.; Fernández Pierna, J.A.; Baeten, V.; Sinnaeve, G.; Lognay, G.; Mouteau, A.; Dupont, P.; Rondia, A.; Lateur, M. Non-destructive measurement of vitamin C, total polyphenol and sugar content in apples using near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, K.; Sánchez, M.; Pérezmarín, D.; López, M.; Guerrero, J.; Garridovaro, A. Prediction of total soluble solid content in intact and cut melons and watermelons using near infrared spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2008, 16, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamar, P.D.; Caramês, E.T.S.; Poppi, R.J.; Pallone, J.A.L. Quality evaluation of frozen guava and yellow passion fruit pulps by NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.; Perez-Marin, D.; De la Haba, M.-J.; Sanchez, M.-T. Fast and accurate quality assessment of raf tomatoes using NIRS technology. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 107, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeys, W.; Mouazen, A.M.; Ramon, H. Potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 91, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
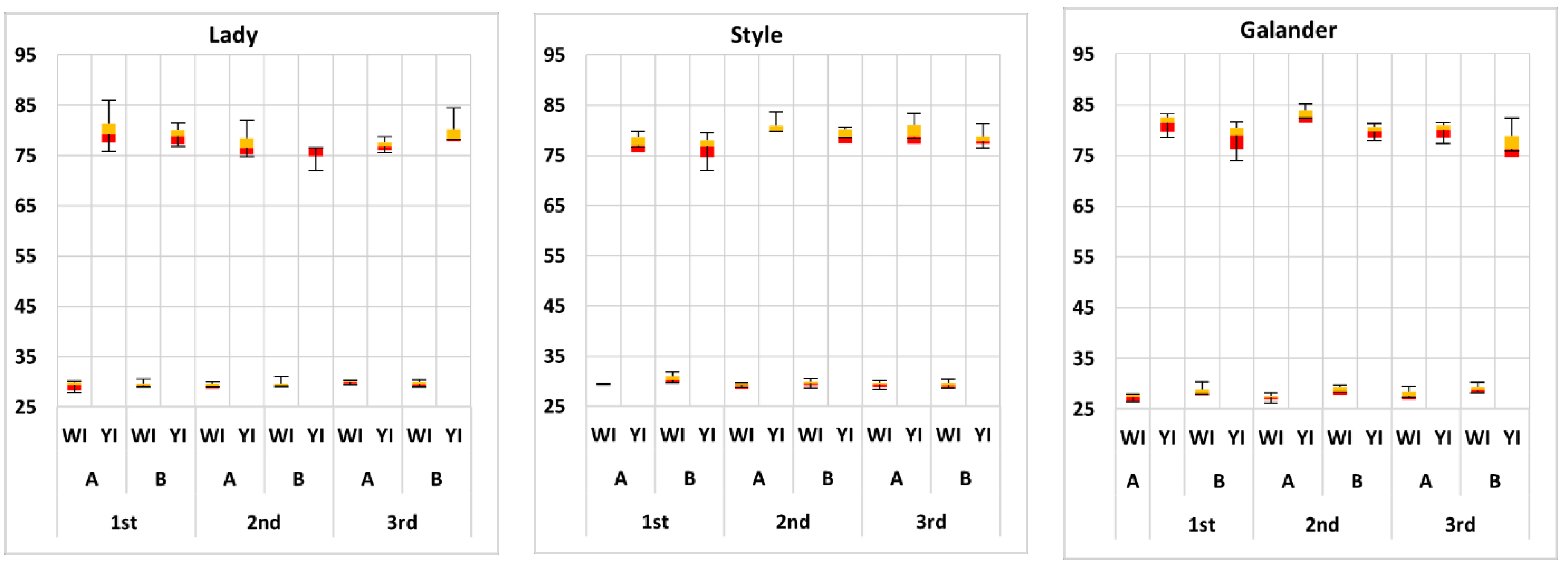
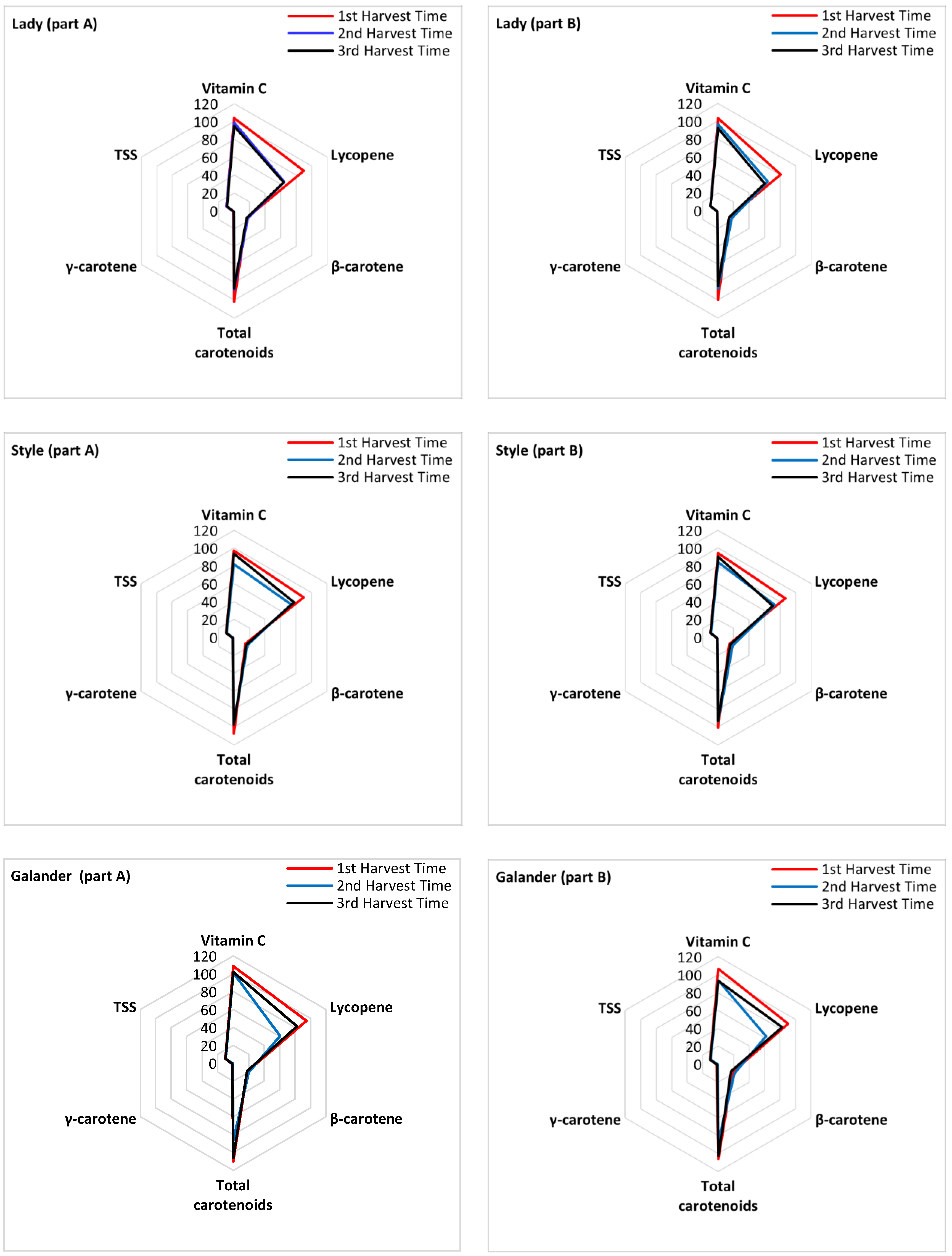


| Harvest Time | Cultivar | L* | a* | b* | a*/b* | C* | h* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Harvest time | Lady | A | 40.07 ± 1.56 | 30.30 ± 0.91 | 22.09 ± 0.80 | 1.37 ± 0.04 | 37.50 ± 1.1 | 36.11 ± 0.77 |
| B | 39.68 ± 1.80 | 29.88 ± 2.05 | 22.06 ± 1.40 | 1.35 ± 0.04 | 37.14 ± 2.43 | 36.46 ± 0.77 | ||
| 2nd Harvest time | A | 39.63 ± 0.75 | 30.08 ± 0.78 | 21.41 ± 0.88 | 1.41 ± 0.07 | 36.93 ± 0.84 | 35.46 ± 1.28 | |
| B | 39.51 ± 1.09 | 29.44 ± 0.50 | 20.72 ± 0.33 | 1.42 ± 0.03 | 36.00 ± 0.46 | 35.16 ± 0.61 | ||
| 3rd Harvest time | A | 40.00 ± 0.63 | 30.28 ± 0.76 | 22.33 ± 0.76 | 1.42 ± 0.06 | 36.32 ± 1.26 | 36.30 ± 1.13 | |
| B | 39.95 ± 0.66 | 29.61 ± 1.22 | 21.49 ± 0.80 | 1.45 ± 0.03 | 37.09 ± 1.02 | 37.04 ± 0.53 | ||
| 1st Harvest time | Style | A | 40.36 ± 0.31 | 30.95 ± 0.67 | 21.82 ± 0.60 | 1.42 ± 0.05 | 37.87 ± 0.62 | 35.20 ± 0.97 |
| B | 41.18 ± 0.90 | 30.17 ± 1.00 | 21.81 ± 0.85 | 1.38 ± 0.07 | 37.23 ± 0.99 | 35.88 ± 1.33 | ||
| 2nd Harvest time | A | 41.00 ± 0.34 | 32.02 ± 0.96 | 23.17 ± 0.35 | 1.38 ± 0.04 | 39.53 ± 0.87 | 35.92 ± 0.82 | |
| B | 41.17 ± 0.82 | 31.66 ± 0.90 | 22.72 ± 0.48 | 1.39 ± 0.10 | 38.98 ± 0.64 | 35.69 ± 1.16 | ||
| 3rd Harvest time | A | 39.50 ± 0.55 | 29.40 ± 0.93 | 21.97 ± 0.66 | 1.34 ± 0.03 | 36.70 ± 1.07 | 36.79 ± 0.59 | |
| B | 39.00 ± 0.78 | 28.92 ± 0.82 | 21.34 ± 0.19 | 1.36 ± 0.04 | 35.94 ± 0.71 | 36.45 ± 0.72 | ||
| 1st Harvest time | Galander | A | 38.76 ± 1.45 | 31.40 ± 0.59 | 21.32 ± 1.01 | 1.48 ± 0.09 | 37.96 ± 0.58 | 34.19 ± 1.54 |
| B | 37.76 ± 1.23 | 30.14 ± 0.53 | 21.04 ± 0.64 | 1.43 ± 0.05 | 36.76 ± 0.62 | 34.93 ± 0.86 | ||
| 2nd Harvest time | A | 39.93 ± 0.54 | 32.24 ± 0.56 | 22.41 ± 0.27 | 1.44 ± 0.04 | 39.27 ± 033 | 34.82 ± 0.77 | |
| B | 38.68 ± 1.03 | 31.61 ± 1.12 | 22.17 ± 0.26 | 1.43 ± 0.04 | 38.61 ± 1.03 | 35.07 ± 0.77 | ||
| 3rd Harvest time | A | 39.66 ± 0.57 | 31.61 ± 1.12 | 21.51 ± 0.19 | 1.47 ± 0.05 | 38.24 ± 0.98 | 34.27 ± 0.87 | |
| B | 38.78 ± 0.98 | 30.89 ± 1.63 | 21.44 ± 0.74 | 1.44 ± 0.09 | 37.61 ± 1.36 | 34.82 ± 1.77 | ||
| Quality Attributes | SD | N. PCs | Calibration | Cross-Validation | Prediction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2C | RMSEC | R2CV | RMSECV | R2P | SEP | RPD | |||
| Lycopene | 11.98 | 9 | 0.84 | 4.87 | 0.71 | 6.77 | 0.71 | 6.81 | 1.77 |
| Total carotenoids | 9.38 | 6 | 0.80 | 4.16 | 0.68 | 5.33 | 0.68 | 5.36 | 1.76 |
| Vitamin C | 8.59 | 3 | 0.74 | 3.72 | 0.68 | 4.19 | 0.68 | 4.21 | 2.05 |
| TSS | 0.26 | 3 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.172 | 1.50 |
| β-carotene | 4.22 | 6 | 0.87 | 1.53 | 0.78 | 1.98 | 0.78 | 1.99 | 2.13 |
| γ-carotene | 0.28 | 4 | 0.85 | 0.12 | 0.8 | 0.13 | 0.8 | 0.14 | 2.15 |
| a* | 1.48 | 3 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 1.74 |
| b* | 0.83 | 3 | 0.47 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.70 | 0.32 | 0.71 | 1.19 |
| h* | 1.18 | 3 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 1.61 |
| a*/b* | 1.96 | 3 | 0.62 | 1.21 | 0.52 | 1.37 | 0.52 | 1.38 | 1.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, A.; Daood, H.G.; Égei, M.; Takács, S.; Helyes, L. A Comparative Study between Vis/NIR Spectroradiometer and NIR Spectroscopy for the Non-Destructive Quality Assay of Different Watermelon Cultivars. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060509
Ibrahim A, Daood HG, Égei M, Takács S, Helyes L. A Comparative Study between Vis/NIR Spectroradiometer and NIR Spectroscopy for the Non-Destructive Quality Assay of Different Watermelon Cultivars. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(6):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060509
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Ayman, Hussein G. Daood, Márton Égei, Sándor Takács, and Lajos Helyes. 2022. "A Comparative Study between Vis/NIR Spectroradiometer and NIR Spectroscopy for the Non-Destructive Quality Assay of Different Watermelon Cultivars" Horticulturae 8, no. 6: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060509
APA StyleIbrahim, A., Daood, H. G., Égei, M., Takács, S., & Helyes, L. (2022). A Comparative Study between Vis/NIR Spectroradiometer and NIR Spectroscopy for the Non-Destructive Quality Assay of Different Watermelon Cultivars. Horticulturae, 8(6), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060509







