Molecular and Metabolic Changes under Environmental Stresses: The Biosynthesis of Quality Components in Preharvest Tea Shoots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
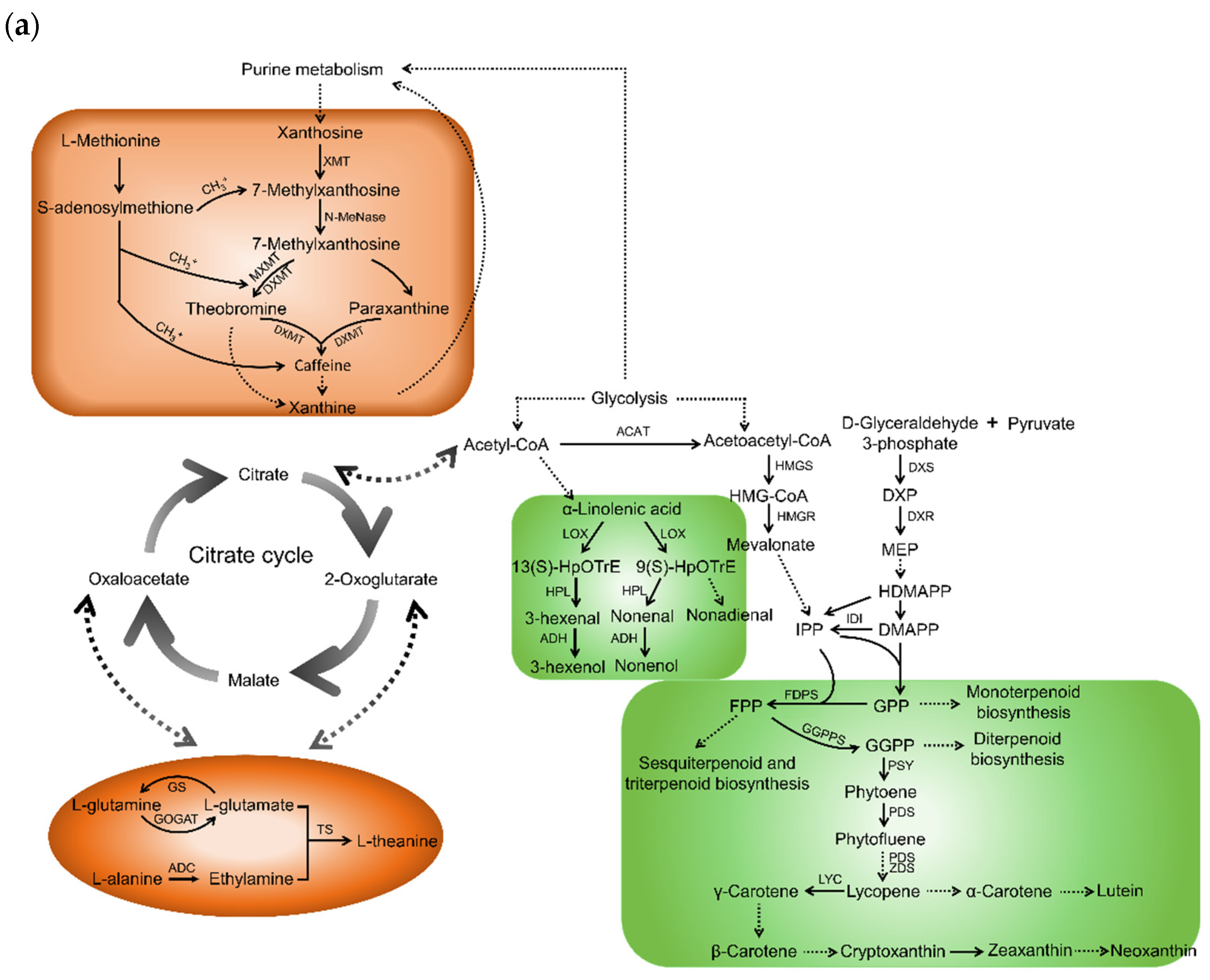
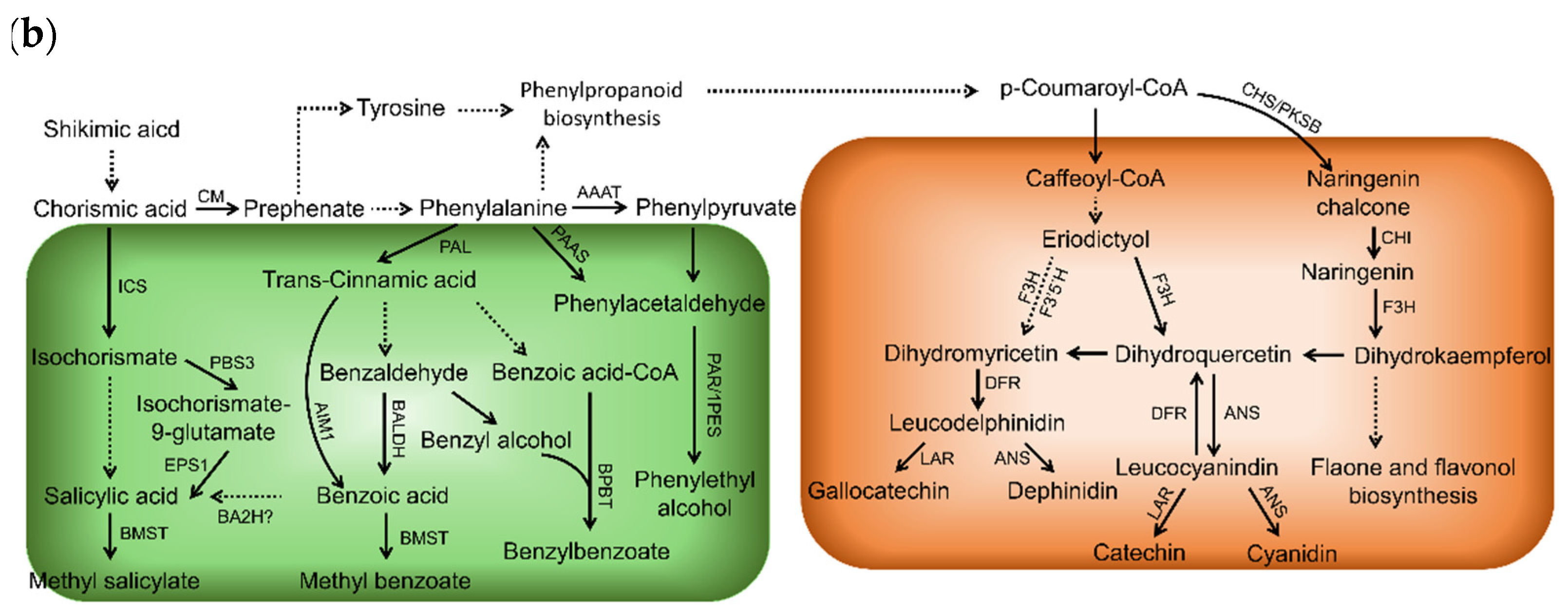
2. Quality Components and Their Metabolic Pathways in Tea Shoots
2.1. Taste Contributors and Their Biosynthetic Pathways in Tea Shoots
2.2. Aroma Contributors and Their Biosynthetic Pathways
3. Molecular and Metabolic Responses of Tea Shoots to Environmental Stresses
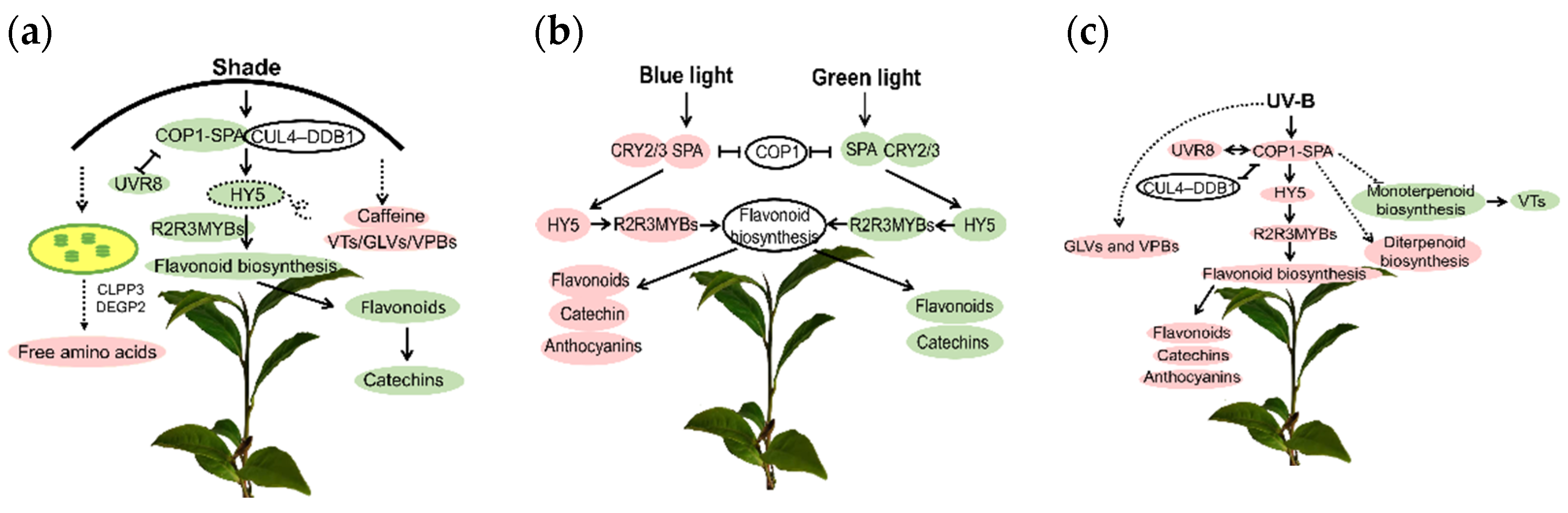
3.1. Changes of Quality Components in Tea Shoots under Light Stress and the Associated Molecular Mechanisms
3.2. Changes in the Quality Components in Tea Shoots under Drought Stress and Their Associated Molecular Mechanisms
3.3. Changes in the Quality Components in Tea Shoots under Temperature Stress and the Associated Molecular Mechanisms
3.4. Changes in the Quality Components in Tea Shoots under Elevated Levles of Carbon Dioxide and Their Associated Molecular Mechanisms
3.5. Changes in the Quality Components in Tea Shoots under Salt Stress and Their Associated Molecular Mechanisms
4. Discussion and Prospects
4.1. Changes in Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism Are Critical to the Levels of Quality Components in Tea Shoots
4.2. Artificial Environments Could Be Created to Affect the Metabolic Biosyntheis of Preharvest Tea Shoots
4.3. The Prospects of Studying the Co-Regulated Genes to Improve Quality Components and Multiresistance in Breeding and Field Cultivation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Stepp, J.R.; Orians, C.; Griffin, T.; Matyas, C.; Robbat, A.; Cash, S.; Xue, D.; Long, C.; Unachukwu, U.; et al. Effects of extreme climate events on tea (Camellia sinensis) functional quality validate indigenous farmer knowledge and sensory preferences in tropical China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munivenkatappa, N.; Sarikonda, S.; Rajagopal, R.; Balakrishnan, R.; Nagarathana, C.K. Variations in quality constituents of green tea leaves in response to drought stress under south Indian condition. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 233, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Fritschi, F.B.; Mittler, R. Global warming, climate change, and environmental pollution: Recipe for a multifactorial stress combination disaster. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.P.; Mattoo, A.K. Sustainable agriculture—enhancing environmental benefits, food nutritional quality and building crop resilience to abiotic and biotic stresses. Agriculture 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.-T.; Ma, S.-L.; Bai, L.-P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Jia, P.; Liu, J.; Zhong, M.; Guo, Z.-F. Signal transduction during cold, salt, and drought stresses in plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakabe, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tran, L.-S.P. Sensing the environment: Key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, M.K.; Kumar, M.; Li, W.; Luo, Y.; Burritt, D.J.; Alkan, N.; Tran, L.-S.P. Enhancing salt tolerance of plants: From metabolic reprogramming to exogenous chemical treatments and molecular approaches. Cells 2020, 9, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, N.G.; Curtis, T.Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J. Effects of abiotic stress and crop management on cereal grain composition: Implications for food quality and safety. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, R. Lower levels of UV-B light trigger the adaptive responses by inducing plant antioxidant metabolism and flavonoid biosynthesis in Medicago sativa seedlings. Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, J.-P.; Ahammed, G.J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Han, W.-Y. Brassinosteroids attenuate moderate high temperature-caused decline in tea quality by enhancing theanine biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis L. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, N.; Gao, T.; Jin, J.; Jing, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Schwab, W.; Song, C. Sesquiterpene glucosylation mediated by glucosyltransferase UGT91Q2 is involved in the modulation of cold stress tolerance in tea plants. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Nesi, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Stitt, M. Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 973–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ouyang, X.; Yang, P.; Lau, O.S.; Chen, L.; Wei, N.; Deng, X.W. Conversion from CUL4-based COP1–SPA E3 apparatus to UVR8–COP1–SPA complexes underlies a distinct biochemical function of COP1 under UV-B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16669–16674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qian, W.; Qiu, C.; Xie, H.; Sun, L.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Exogenous abscisic acid induces the lipid and flavonoid metabolism of tea plants under drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Zhao, A. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling unveiled mechanisms of tea (Camellia sinensis) quality improvement by moderate drought on pre-harvest shoots. Phytochemistry 2020, 180, 112515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Li, F.; Yang, T.; Feng, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Li, W.; Xu, G.; Bao, S.; Wan, X.; et al. Theanine transporters identified in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Plant J. 2020, 101, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.; Ling, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; She, G.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Wan, X. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals regulatory mechanisms of theanine synthesis in tea (Camellia sinensis) and oil tea (Camellia oleifera) plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10235–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Deng, R.; Yang, Z. Stable isotope-labeled precursor tracing reveals that L-alanine is converted to L-theanine via L-glutamate not ethylamine in tea plants in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15354–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Kato, T.; Xu, H.L. Transport of nitrogen assimilation in xylem vessels of green tea plants fed with NH4-N and NO3-N. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Salvador, P.; Uscola, M.; Jacobs, D.F. The role of stored carbohydrates and nitrogen in the growth and stress tolerance of planted forest trees. New For. 2015, 46, 813–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D. Transcriptional profiling of catechins biosynthesis genes during tea plant leaf development. Planta 2017, 246, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, B.; Chen, Z. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic strategies to understand the effects of dark stress on tea callus flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, A.-D.; Lian, S.-B.; Wu, N.-N.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Zhang, L.-M.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, H.-Y. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of catechins, caffeine and theanine biosynthesis in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) over the course of seasons. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Chen, L.-B.; Lu, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, J.; Deng, W.-W.; Zhang, Z.-Z. Caffeine content and related gene expression: Novel insight into caffeine metabolism in Camellia plants containing low, normal, and high caffeine concentrations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3400–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Barman, T.; Dutta, J.; Devi, A.; Tamuly, P.; Kumar Paul, R.; Karak, T. Catechin and caffeine content of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) leaf significantly differ with seasonal variation: A study on popular cultivars in north east India. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2021, 96, 103684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, T.; Tsushida, T. Changes in lipoxygenase activity in relation to lipid degradation in plucked tea shoots. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2521–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudareva, N.; Klempien, A.; Muhlemann, J.K.; Kaplan, I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox-Georgian, D.; Ramadoss, N.; Dona, C.; Basu, C. Therapeutic and medicinal uses of terpenes. In Medicinal Plants; Joshee, N., Dhekney, S.A., Parajuli, Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 333–359. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.-T.; Zheng, X.; Li, S. Tea aroma formation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Lin, Q.; Yan, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D.; Guo, F. Relationship between secondary metabolism and miRNA for important flavor compounds in different tissues of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) as revealed by genome-wide miRNA analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncan, D.A.T.; Tsang, S.S.K.; Li, C.; Lee, I.H.T.; Lam, H.-M.; Chan, T.-F.; Hui, J.H.L. Terpenes and terpenoids in plants: Interactions with environment and insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kobayashi, E.; Katsuno, T.; Asanuma, T.; Fujimori, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Tomomura, M.; Mochizuki, K.; Watase, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Characterisation of volatile and non-volatile metabolites in etiolated leaves of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants in the dark. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, S.; Zeng, L.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z. Characterization of enzymes specifically producing chiral flavor compounds (R)- and (S)-1-phenylethanol from tea (Camellia sinensis) flowers. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlemann, J.K.; Klempien, A.; Dudareva, N. Floral volatiles: From biosynthesis to function. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1936–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevere, H.; Bauters, L.; Gheysen, G. Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhter, D.; Lüdke, D.; Ding, Y.; Feussner, K.; Zienkiewicz, K.; Lipka, V.; Wiermer, M.; Zhang, Y.; Feussner, I. Isochorismate-derived biosynthesis of the plant stress hormone salicylic acid. Science 2019, 365, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zeng, L.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z. Study of the biochemical formation pathway of aroma compound 1-phenylethanol in tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) flowers and other plants. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hauer, R.J.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; He, X. Growth, nutrient assimilation, and carbohydrate metabolism in Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) seedlings in response to light spectra. Forests 2020, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; She, G.; Zhang, X.; Jordan, B.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wan, X. Metabolite profiling and transcriptomic analyses reveal an essential role of UVR8-mediated signal transduction pathway in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in response to shading. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Dong, F.; Watanabe, N.; Yang, Z. Transformation of catechins into theaflavins by upregulation of CsPPO3 in preharvest tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves exposed to shading treatment. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, X.; Mei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zeng, L.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z. Proteolysis of chloroplast proteins is responsible for accumulation of free amino acids in dark-treated tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves. J. Proteom. 2017, 157, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Fei, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, X.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Hu, X.-Y. Effect of shade treatment on theanine biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 71, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, S.; Takemoto, T.; Ogihara, A.; Suzuki, K.; Masumura, T.; Satoh, S.; Takano, K.; Mimura, Y.; Morita, S. Stress responses of shade-treated tea leaves to high light exposure after removal of shading. Plants 2020, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owuor, P.O.; Othieno, C.O.; Howard, G.E.; Robinson, J.M.; Cooke, R.D. Studies on the use of shade in tea plantations in Kenya: Effects on chemical composition and quality of made Tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1988, 46, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Mei, X.; Katsuno, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Dong, F.; Watanabe, N.; Yang, Z. Regulation of formation of volatile compounds of tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves by single light wavelength. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Ma, J.-Q.; Ma, C.-L.; Shen, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-F.; Chen, L. Regulation of growth and flavonoid formation of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) by blue and green light. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Gu, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Ye, N. Exploration of the effects of different blue LED light intensities on flavonoid and lipid metabolism in tea plants via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-D.; Sun, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Fu, H.-W.; Cui, L.; Chen, R.-Z.; Zhang, D.-W.; Tian, J.-K. UV-B induced changes in the secondary metabolites of Morus alba L. leaves. Molecules 2010, 15, 2980–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazari, M.; Zarinkamar, F. Ultraviolet-B induced changes in Mentha aquatica (a medicinal plant) at early and late vegetative growth stages: Investigations at molecular and genetic levels. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 154, 112618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamala, L.F.; Zhou, H.-C.; Han, Z.-X.; Wei, S. UV-B induces distinct transcriptional re-programing in UVR8-signal transduction, flavonoid, and terpenoids pathways in Camellia sinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Tan, L.; Zou, Y.; Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, W.; Tang, Q. The effects of ultraviolet A/B treatments on anthocyanin accumulation and gene expression in dark-purple tea cultivar ‘Ziyan’ (Camellia sinensis). Molecules 2020, 25, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menon, C.; Sheerin, D.J.; Hiltbrunner, A. SPA proteins: SPAnning the gap between visible light and gene expression. Planta 2016, 244, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoecker, U. The activities of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1/SPA, a key repressor in light signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 37, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dien, D.C.; Thu, T.T.P.; Moe, K.; Yamakawa, T. Proline and carbohydrate metabolism in rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) under various drought and recovery conditions. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2019, 24, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Xu, Y.; Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Xu, Q. CsCYT75B1, a citrus CYTOCHROME P450 gene, is involved in accumulation of antioxidant flavonoids and induces drought tolerance in transgenic arabidopsis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, L. Global transcriptional analysis reveals the complex relationship between tea quality, leaf senescence and the responses to cold-drought combined stress in Camellia sinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, I.; Alegre, L.; Munné-Bosch, S. Enhanced oxidation of flavan-3-ols and proanthocyanidin accumulation in water-stressed tea plants. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xin, H.; Wang, M.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Kaleri, N.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of drought-stress-induced decreases in Camellia sinensis leaf quality. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, E.R.; Li, X.; Kfoury, N.; Morimoto, J.; Han, W.-Y.; Ahmed, S.; Cash, S.B.; Griffin, T.S.; Stepp, J.R.; Robbat, A.; et al. Interactive effects of drought severity and simulated herbivory on Tea (Camellia sinensis) volatile and non-volatile metabolites. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 157, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Z.; Tang, M.; Yan, P.; Han, W. Decreased biosynthesis of jasmonic acid via lipoxygenase pathway compromised caffeine-induced resistance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides under elevated CO2 in tea seedlings. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safaei Chaeikar, S.; Marzvan, S.; Jahangirzadeh Khiavi, S.; Rahimi, M. Changes in growth, biochemical, and chemical characteristics and alteration of the antioxidant defense system in the leaves of tea clones (Camellia sinensis L.) under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 265, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Ming, R.; Zhang, J. Transcriptome dynamics of Camellia sinensis in response to continuous salinity and drought stress. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copolovici, L.; Kännaste, A.; Remmel, T.; Niinemets, Ü. Volatile organic compound emissions from Alnus glutinosa under interacting drought and herbivory stresses. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 100, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szabó, K.; Zubay, P.; Németh-Zámboriné, É. What shapes our knowledge of the relationship between water deficiency stress and plant volatiles? Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinwächter, M.; Selmar, D. New insights explain that drought stress enhances the quality of spice and medicinal plants: Potential applications. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, V.; Joshi, R.; Gulati, A. Seasonal clonal variations and effects of stresses on quality chemicals and prephenate dehydratase enzyme activity in tea (Camellia sinensis). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.L. Functional Analysis of Green Leaf Volatile and Histone H3K4 Methylation in Response to Drought Stress in Tea Plant. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Shamala, L.F.; Yi, X.-K.; Yan, Z.; Wei, S. Analysis of terpene synthase family genes in Camellia sinensis with an emphasis on abiotic stress conditions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Sales, C.; Beltrán, J.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Arbona, V. Activation of secondary metabolism in citrus plants is associated to sensitivity to combined drought and high temperatures. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamloo, M.; Babawale, E.A.; Furtado, A.; Henry, R.J.; Eck, P.K.; Jones, P.J.H. Effects of genotype and temperature on accumulation of plant secondary metabolites in Canadian and Australian wheat grown under controlled environments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Liao, J.; Duan, Y.; Wen, B.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling of Camellia sinensis L. cv. ‘Suchazao’ exposed to temperature stresses reveals modification in protein synthesis and photosynthetic and anthocyanin biosynthetic pathways. Tree Physiol. 2019, 39, 1583–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.-H.; Deng, W.-W.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wei, J.-P.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Fu, J.-Y.; Han, W.-Y. Exogenous melatonin improves tea quality under moderate high temperatures by increasing epigallocatechin-3-gallate and theanine biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis L. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 253, 153273–153280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, J.A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Tan, X. Transcriptomic analyses of Camellia oleifera ‘Huaxin’ leaf reveal candidate genes related to long-term cold stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sang, Z.; Yuan, H. Comparative metabolomics analysis of the response to cold stress of resistant and susceptible Tibetan hulless barley (Hordeum distichon). Phytochemistry 2020, 174, 112346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, B.; Yue, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Integrative transcriptional and metabolic analyses provide insights into cold spell response mechanisms in young shoots of the tea plant. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1655–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Ban, Q.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wei, C.; Bennetzen, J.L. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals gene expression associated with cold adaptation in the tea plant Camellia sinensis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 624–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Jin, J.; Gao, T.; Zhang, N.; Jing, T.; Wang, J.; Ban, Q.; Schwab, W.; Song, C. Glucosyltransferase CsUGT78A14 regulates flavonols accumulation and reactive oxygen species scavenging in response to cold stress in Camellia sinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cai, B.; Jin, J.; Zhang, N.; Jing, T.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. Cold stress-induced glucosyltransferase CsUGT78A15 is involved in the formation of eugenol glucoside in Camellia sinensis. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Z.-X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.-P.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Han, W.-Y. Freezing stress deteriorates tea quality of new flush by inducing photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in mature leaves. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 230, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarina, L.S.; Malyukova, L.S.; Efremov, A.M.; Simonyan, T.A.; Matskiv, A.O.; Koninskaya, N.G.; Rakhmangulov, R.S.; Gvasaliya, M.V.; Malyarovskaya, V.I.; Ryndin, A.V.; et al. Physiological, biochemical and genetic responses of caucasian tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) genotypes under cold and frost stress. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, M.; Moser, G.; Raschi, A.; Kammann, C.; Grünhage, L.; Müller, C. Carbon dioxide fertilization and suppressed respiration induce enhanced spring biomass production in a mixed species temperate meadow exposed to moderate carbon dioxide enrichment. Funct. Plant Biol. 2015, 43, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Haake, V.; Ludewig, F.; Sonnewald, U.; Stitt, M. The nitrate and ammonium nitrate supply have a major influence on the response of photosynthesis, carbon metabolism, nitrogen metabolism and growth to elevated carbon dioxide in tobacco. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 1177–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, D.; Thompson, M.; Sutherland, M.; Hirotsu, N.; Makino, A.; Seneweera, S. New insights into the cellular mechanisms of plant growth at elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, R.; Pérez, P.; Martínez-Carrasco, R.; Usadel, B.; Kostadinova, S.; Morcuende, R. Quantitative RT–PCR platform to measure transcript levels of C and N metabolism-related genes in durum wheat: Transcript profiles in elevated [CO2] and high temperature at different levels of N supply. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1556–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Z.-X.; Wei, J.-P.; Shen, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Han, W.-Y. Stimulation in primary and secondary metabolism by elevated carbon dioxide alters green tea quality in Camellia sinensis L. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, M.; Pokharel, S.S.; Li, C.; Parajulee, M.N.; Chen, F.; Fang, W. Effects of elevated CO2 on foliar soluble nutrients and functional components of tea, and population dynamics of tea aphid, Toxoptera aurantii. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 145, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of carbon dioxide enrichment on health-promoting compounds and organoleptic properties of tomato fruits grown in greenhouse. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Kläring, H.-P. CO2 enrichment can produce high red leaf lettuce yield while increasing most flavonoid glycoside and some caffeic acid derivative concentrations. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Y.-T.; Wei, J.-P.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Han, X.; Han, W.-Y. Salicylic acid acts upstream of nitric oxide in elevated carbon dioxide-induced flavonoid biosynthesis in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO₂ concentration and temperature on photosynthesis system and quality components in tea plant. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2016, 39, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. The impact of elevated CO2 and temperature on grain quality of rice grown under open-air field conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.-F.; Qiu, C.-W.; Ding, G.; Vincze, E.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F. Agriculture organic wastes fermentation CO2 enrichment in greenhouse and the fermentation residues improve growth, yield and fruit quality in tomato. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Response of carbon and nitrogen metabolism and secondary metabolites to drought stress and salt stress in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Zou, C.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal mechanisms of adaptation to salinity in which carbon and nitrogen metabolism is altered in sugar beet roots. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 138–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, M.; Yadav, S.K. Overexpression of a tea flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene confers tolerance to salt stress and Alternaria solani in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 551–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Hu, X.-Y. Effect of salt treatment on theanine biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 56, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Liao, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhu, X. The protective effect of exogenous putrescine in the response of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) to salt stress. HortScience 2018, 53, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Pu, G.; Gao, T.; Liu, W. Influence of AM on the growth of tea plant and tea quality under salt stress. J. Tea Sci. 2013, 33, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otori, K.; Tanabe, N.; Maruyama, T.; Sato, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Tamoi, M.; Shigeoka, S. Enhanced photosynthetic capacity increases nitrogen metabolism through the coordinated regulation of carbon and nitrogen assimilation in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igamberdiev, A.U.; Kleczkowski, L.A. The glycerate and phosphorylated pathways of serine synthesis in plants: The branches of plant glycolysis linking carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yao, Q.; Gao, X.; Jiang, C.; Harberd, N.P.; Fu, X. Shoot-to-root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wu, T.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. Effect of LED spectrum on the quality and nitrogen metabolism of lettuce under recycled hydroponics. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Ni, D. Impact of light irradiation on black tea quality during withering. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Tang, M.; Zhai, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, S. Effect of different withering light-wave bands on chlorophyll fluorescence parameter and biochemical quality of black tea. J. Tea Sci. 2019, 39, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, J.; Lai, Z.; Sun, Y. Transcriptome analysis reveals the effect of short-term sunlight on aroma metabolism in postharvest leaves of oolong tea (Camellia sinensis). Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, P.; Ni, D. Nonvolatile metabolism in postharvest tea (Camellia sinensis L.) leaves: Effects of different withering treatments on nonvolatile metabolites, gene expression levels, and enzyme activity. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 126992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Z.; Shen, C. Pre- and post-harvest exposure to stress influence quality-related metabolites in fresh tea leaves (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaramraja, P.; Pius, P.; Raj Kumar, R.; Jayakumar, D. Soil moisture stress-induced alterations in bioconstituents determining tea quality. J. Sci Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, P.J.; Carr, M. Responses of young tea (Camellia sinensis) clones to drought and temperature. II. dry matter production and partitioning. Exp. Agric. 1996, 32, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, A.; Hoecker, U. COP1/SPA ubiquitin ligase complexes repress anthocyanin accumulation under low light and high light conditions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e970440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, M.; Agarwal, P.; Roy, S. The N-terminal MYB domains affect the stability and folding aspects of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB4 transcription factor under thermal stress. Protoplasma 2021, 258, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Tigchelaar, M.; Battisti, D.S.; Merrill, S.C.; Huey, R.B.; Naylor, R.L. Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 2018, 361, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, G.-J.; Xue, X.-Y.; Mao, Y.-B.; Wang, L.-J.; Chen, X.-Y. Arabidopsis MYC2 interacts with DELLA proteins in regulating sesquiterpene synthase gene expression. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2635–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Sun, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.-S.; Deng, X.W.; et al. Red-light is an environmental effector for mutualism between begomovirus and its vector whitefly. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.A.; Nemchenko, A.; Borrego, E.; Murray, I.; Sobhy, I.S.; Bosak, L.; DeBlasio, S.; Erb, M.; Robert, C.A.; Vaughn, K.A. The maize lipoxygenase, Zm LOX 10, mediates green leaf volatile, jasmonate and herbivore-induced plant volatile production for defense against insect attack. Plant J. 2013, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Han, S.-W.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, B.K.; Lee, S.C. The pepper lipoxygenase CaLOX1 plays a role in osmotic, drought and high salinity stress response. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wen, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Molecular and Metabolic Changes under Environmental Stresses: The Biosynthesis of Quality Components in Preharvest Tea Shoots. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020173
Liu J, Wen B, Liu X, Yang Y, Li M, Wang X. Molecular and Metabolic Changes under Environmental Stresses: The Biosynthesis of Quality Components in Preharvest Tea Shoots. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianjun, Beibei Wen, Xiaobo Liu, Yun Yang, Meifeng Li, and Xiaojing Wang. 2022. "Molecular and Metabolic Changes under Environmental Stresses: The Biosynthesis of Quality Components in Preharvest Tea Shoots" Horticulturae 8, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020173
APA StyleLiu, J., Wen, B., Liu, X., Yang, Y., Li, M., & Wang, X. (2022). Molecular and Metabolic Changes under Environmental Stresses: The Biosynthesis of Quality Components in Preharvest Tea Shoots. Horticulturae, 8(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020173




