Complementary Nutrients in Decoupled Aquaponics Enhance Basil Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Greenhouse Description
2.3. Growing System
2.4. Aquaculture and Mineralization Systems
2.5. Treatment Solutions
2.6. Performance Parameters
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
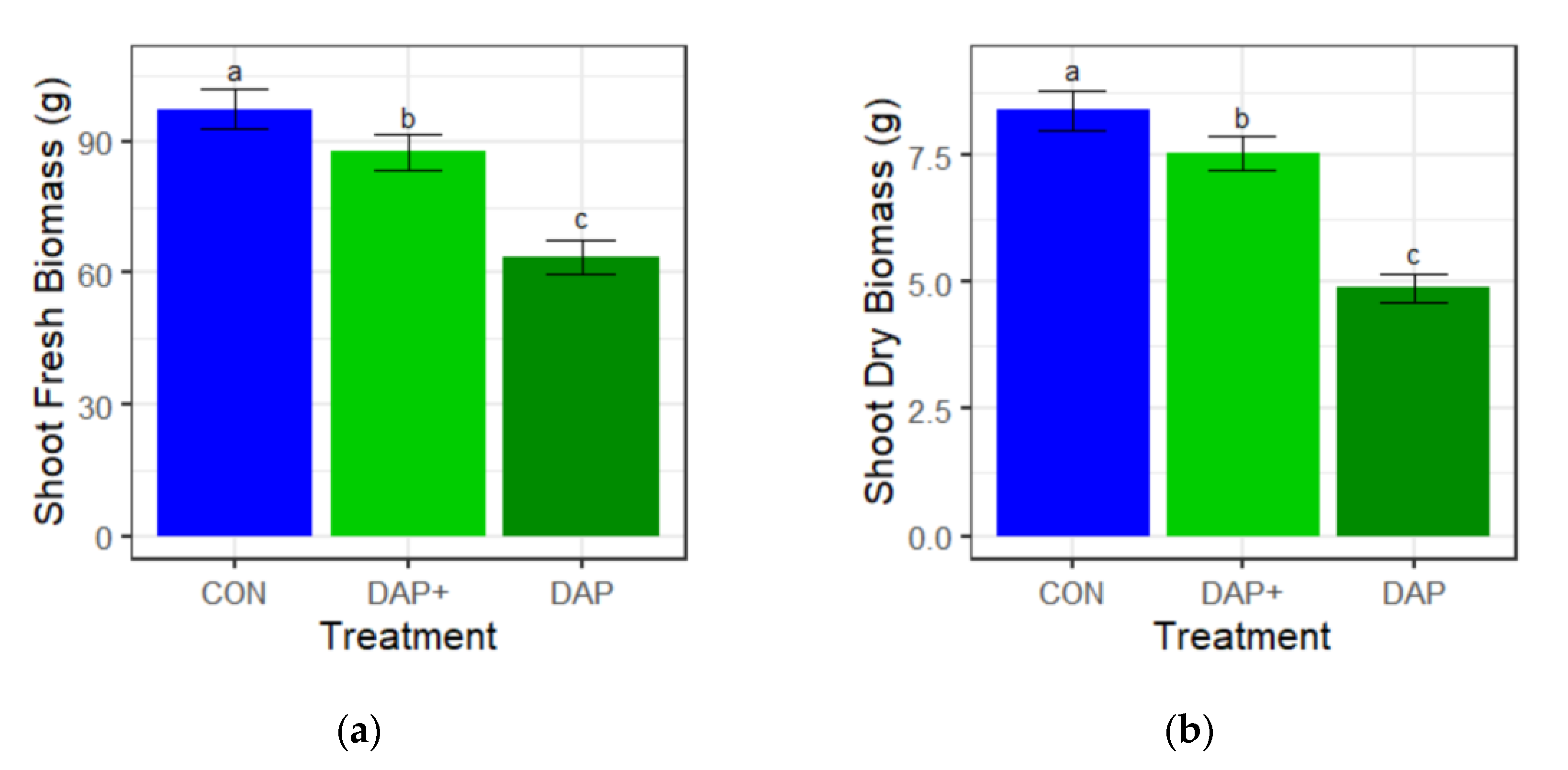
3.1. Shoot Fresh and Dry Biomass
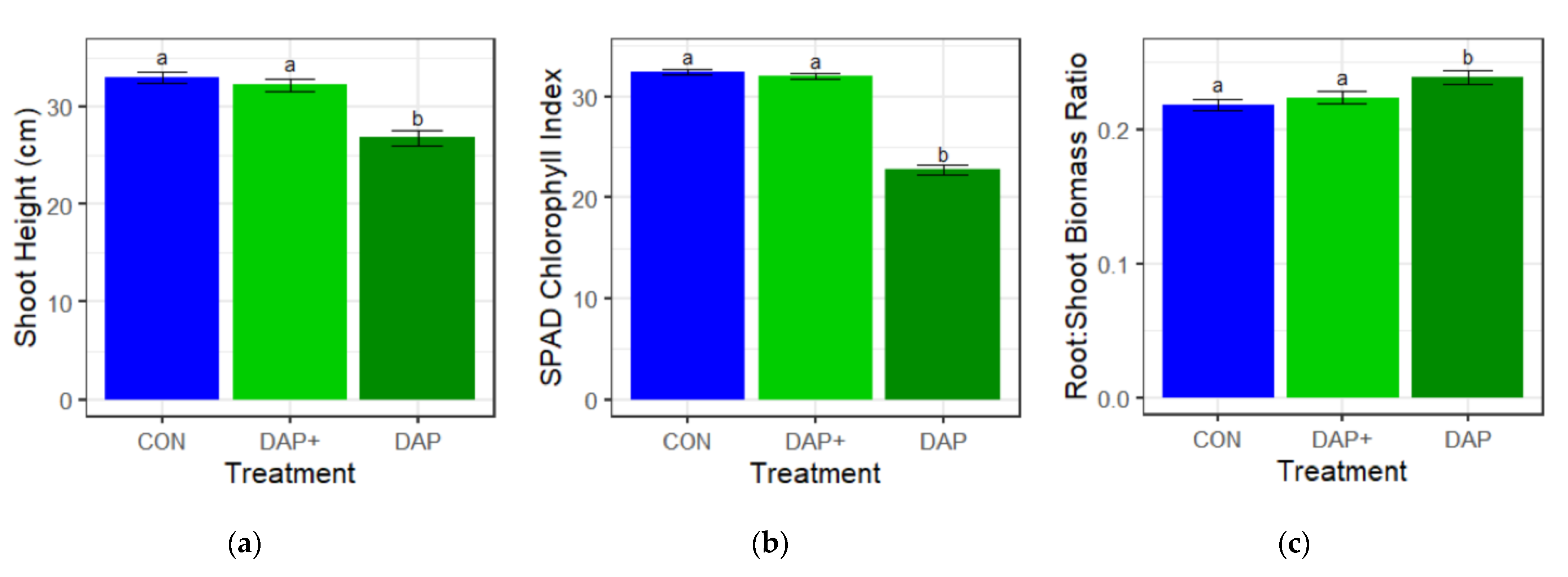
3.2. Height, SPAD Chlorophyll Index, and Root:Shoot Biomass Ratio
3.3. Height over Time
3.4. Treatment Nutrient Solution Analysis
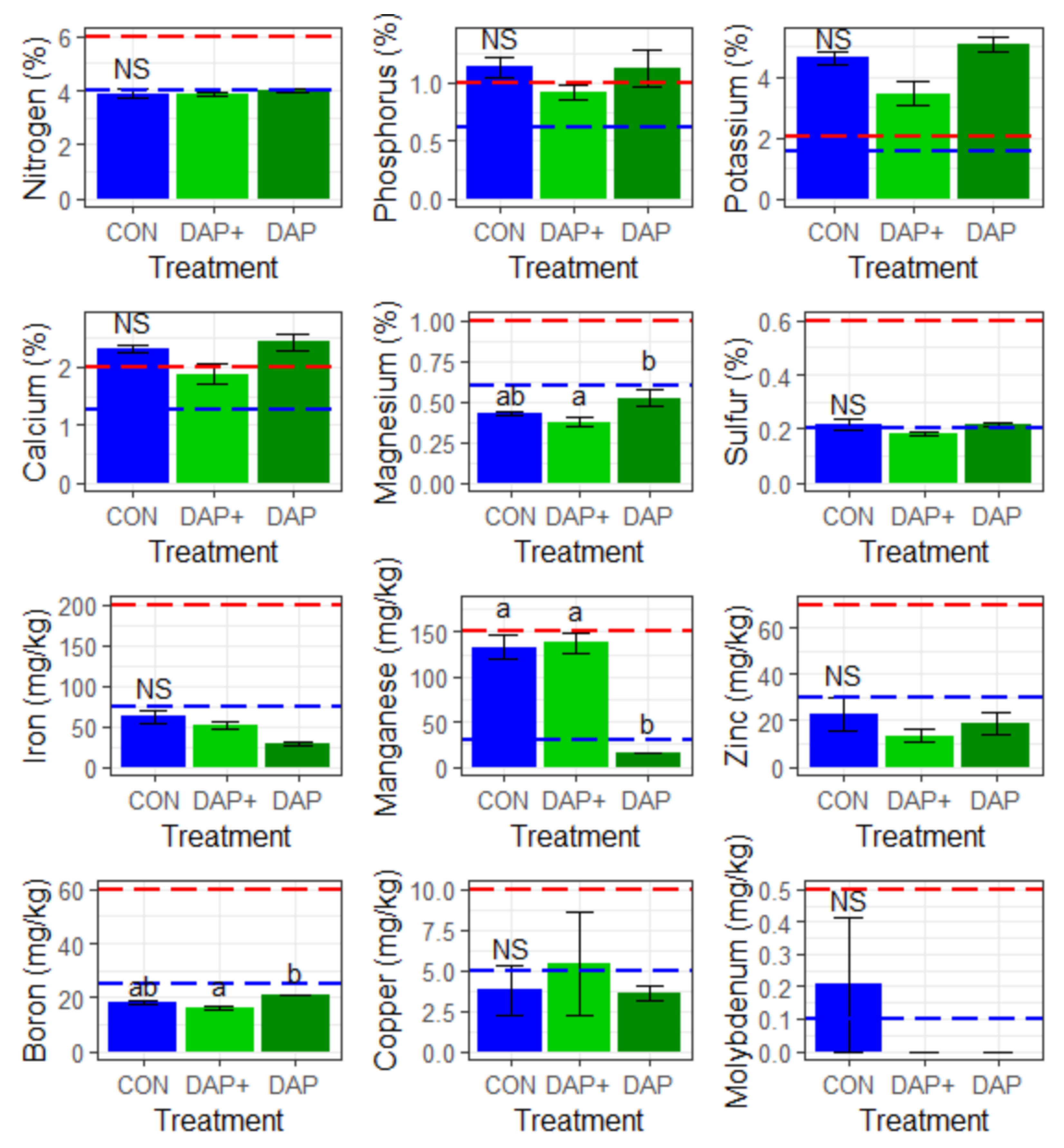
3.5. Leaf Tissue Nutrient Analysis
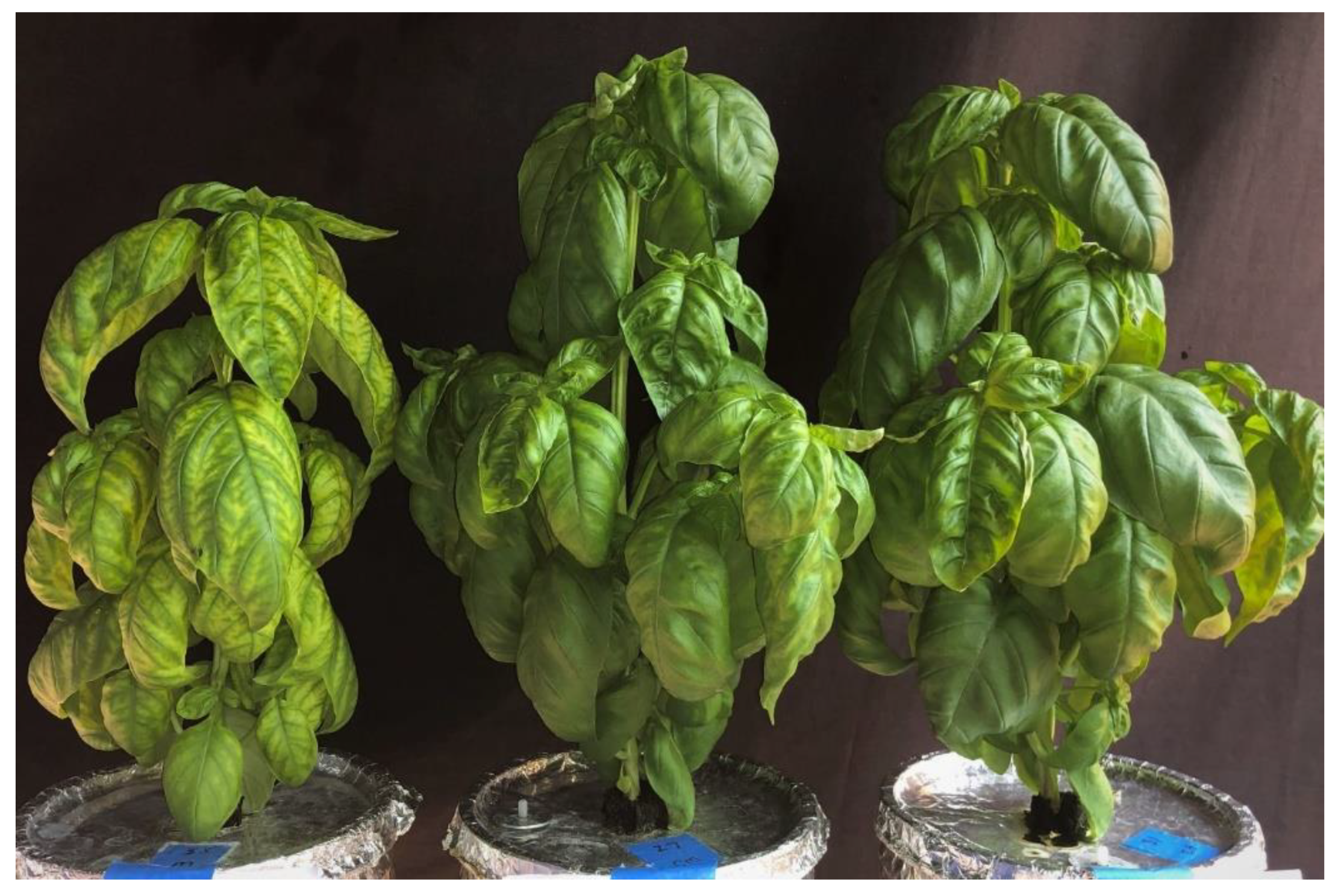
3.6. Visual Observation
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis
4.2. Previous Research
4.3. Adjustments to the Complemented Blend
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakocy, J.E. Aquaponics-Integrating Fish and Plant Culture. In Aquaculture Production Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Ames, IA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Joyce, A.; Kotzen, B.; Burnell, G. Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 163–267. ISBN 978-3-030-15943-6. [Google Scholar]
- Timmons, M.B. Recirculating Aquaculture, 4th ed.; Ithaca Publishing Company LLC: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 663–709. [Google Scholar]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.; Mankasingh, U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Jijakli, H.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Challenges of Sustainable and Commercial Aquaponics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4199–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, R. Carbon Emission from Farm Operations. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Emissions Due to Agriculture. Global, Regional and Country Trends 2000–2018; FAOSTAT Analytical Brief Series No. 18; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cripps, S.; Bergheim, A. Solids Management and Removal for Intensive Land-Based Aquaculture Production Systems. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 22, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayipio, E.; Wells, D.; McQuilling, A.; Wilson, A. Comparisons between Aquaponic and Conventional Hydroponic Crop Yields: A Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suhl, J.; Dannehl, D.; Kloas, W.; Baganz, D.; Jobs, S.; Scheibe, G.; Schmidt, U. Advanced Aquaponics: Evaluation of Intensive Tomato Production in Aquaponics vs. Conventional Hydroponics. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallenave, R.; Shultz, C.R. Decoupled Aquaponics: A Comparison to Single-Loop Aquaponics; New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Delaide, B.; Goddek, S.; Gott, J.; Soyeurt, H.; Jijakli, M.H. Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L. Var. Sucrine) Growth Performance in Complemented Aquaponic Solution Outperforms Hydroponics. Water 2016, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industry Research. Global Basil Leaves Market Research Report 2021; Industry Research: Los Angelos, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rakocy, J.; Shultz, R.C.; Bailey, D.S.; Thoman, E.S. Aquaponic Production of Tilapia and Basil: Comparing Batch and Staggered Cropping System. Acta Hortic. 2004, 448, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwoody, R.K. Aquaponics and Hydroponics: The Effect of Nutrient Source and Hydroponic Subsystem Design on Sweet Basil Production. Master’s Thesis, Masters of Science, University of Central Missouri, Warrensburg, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Monroe, A.; Day, M.R. Growth, Yield, Plant Quality and Nutrition of Basil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) under Soilless Agricultural Systems. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.; Pribbernow, M.; Xu, L.; Appelaum, S.; Palm, H. Basil (Ocimum Basilicum) Cultivation in Decoupled Aquaponics with Three Hydro-Components (Grow Pipes, Raft, Gravel) and African Catfish (Clarias Gariepinus) Production in Northern Germany. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosta, H.R. Comparison of the Vegetative Growth, Eco-Physiological Characteristics and Mineral Nutrient Content of Basil Plants in Different Irrigation Ratios of Hydroponic:Aquaponic Solutions. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 1782–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.; Kubota, C.; Miller, S. Effects of Low pH of Hydroponic Nutrient Solution on Plant Growth, Nutrient Uptake, and Root Rot Disease Incidence of Basil (Ocimum Basilicum L.). HortScience 2020, 55, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, N.S.; Peters, C. A Recipe for Hydroponic Success. Inside Grower 2014, 2014, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.; Panda, P.; Ghadamgahi, F.; Rosberg, A.; Vetukuri, R.R. Comparison of Two Commercial Recirculated Aquacultural Systems and Their Microbial Potential in Plant Disease Suppression. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, N.; Merrill, T. Nutrient Deficiencies in Hydroponic Basil. e-Gro Res. Update. 2016, 1–10. Available online: http://www.e-gro.org/pdf/2016-4.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. LmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Soft. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, W.G.; Cockson, P.; Henry, J.; Whipker, B.; Currey, C.J. Basil (Ocimum Basilicum). e-Gro Nutr. Monit. 2018, 1, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Wielgosz, Z.; Anderson, T.; Timmons, M.B. Microbial Effects on the Production of Aquaponically Grown Lettuce. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Espinoza, F.H.; Murillo-Amador, B.; García-Hernández, J.L.; Fenech-Larios, L.; Rueda-Puente, E.O.; Troyo-Diéguez, E.; Kaya, C.; Beltrán-Morales, A. Field Evaluation of the Relationship Between Chlorophyll Content in Basil Leaves and A Portable Chlorophyll Meter (SPAD-502) Readings. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Marschner, P.; Rengel, Z. Chapter 13—Effect of Internal and External Factors on Root Growth and Development. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Marschner, P., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 331–346. ISBN 978-0-12-384905-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.-G.; van Iersel, M.W. Nutrient Solution Concentration Affects Shoot: Root Ratio, Leaf Area Ratio, and Growth of Subirrigated Salvia (Salvia Splendens). HortScience 2004, 39, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, E.; Park, K. Effect of Different Concentrations of Nutrient Solutions on the Growth, Yield, and Quality of Basil. Acta Hortic. 1999, 483, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.J.; Currey, C.J. Effects of Nutrient Solution Concentration and Daily Light Integral on Growth and Nutrient Concentration of Several Basil Species in Hydroponic Production. HortScience 2018, 53, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Toapanta, E.; Fisher, P.; Gómez, C. Growth Rate and Nutrient Uptake of Basil in Small-Scale Hydroponics. HortScience 2020, 55, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattson, N.S. Magnesium Deficiency of 2018 Sponsors Hydroponic and Container Grown Basil. e-Gro Edible Alert 2018, 3, 6. [Google Scholar]


| Chemical | Grams 50 L−1 |
|---|---|
| Calcium Nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) | 10 |
| Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4·7H2O) | 7 |
| Sprint 330 (10% DTPA Fe) | 1.5 |
| Boric Acid (H3BO3) | 0.15 |
| Manganese Sulfate (MnSO4· H2O) | 0.1 |
| Total | 18.75 |
| Concentrations | N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Fe | Mn | Zn | B | Cu | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target (CON) | 150 | 39 | 162 | 139 | 47 | 64 | 2.3 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.075 |
| DAP 1 | 81.3 | 29.1 | 178.9 | 49 | 17.9 | 28.7 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0 |
| Complementary | 31 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 14.4 | 19.1 | 3 | 0.65 | 0 | 0.53 | 0 | 0 |
| Calculated DAP+ 2 | 112.3 | na 3 | na | 87 | 32.3 | 57.8 | 3 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 0.01 | 0 |
| Trtmt 1 | N 2 | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Fe | Mn | Zn | B | Cu | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target 3 | 150 | 39 | 162 | 139 | 47 | 64 | 2.3 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.075 |
| CON | 138.6 a (4.05) | 90.4 a (3.6) | 177.1 (10.1) | 176.1 a (3.0) | 47.0 a (0.7) | 91.8 a (4.5) | 2.40 a (0.17) | 0.42 a (0.02) | 0.22 a (0.01) | 0.43 (na) | 0.20 a (0.02) | 0.07 a (0) |
| DAP+ | 102.6 b (6.95) | 26.8 b (2.9) | 179.4 (20.7) | 81.8 b (2.1) | 20.2 b (0.9) | 52.3 b (3.1) | 3.37 b (0.25) | 0.73 b (0.11) | 0.03 b (0) | 0.63 (na) | 0.01 b (0) | 0 b (0) |
| DAP | 81.3 c (5.1) | 29.1 b (2.9) | 178.9 (19.6) | 49 c (2.1) | 17.9 c (0.7) | 28.7 c (2.1) | 0 c (0) | 0 c (0) | 0.02 b (0) | 0.09 (na) | 0.01 b (0) | 0 b (0) |
| (N) 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodgers, D.; Won, E.; Timmons, M.B.; Mattson, N. Complementary Nutrients in Decoupled Aquaponics Enhance Basil Performance. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020111
Rodgers D, Won E, Timmons MB, Mattson N. Complementary Nutrients in Decoupled Aquaponics Enhance Basil Performance. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(2):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020111
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodgers, Dylan, Eugene Won, Michael B. Timmons, and Neil Mattson. 2022. "Complementary Nutrients in Decoupled Aquaponics Enhance Basil Performance" Horticulturae 8, no. 2: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020111
APA StyleRodgers, D., Won, E., Timmons, M. B., & Mattson, N. (2022). Complementary Nutrients in Decoupled Aquaponics Enhance Basil Performance. Horticulturae, 8(2), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020111








