Study of 15 Varieties of Herbaceous Peony Pollen Submicroscopic Morphology and Phylogenetic Relationships
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials and Sampling
2.2. Electron Microscope
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. External Pollen Forms
3.2. Surface Ornamentation Characteristics of Pollen
3.3. Apertures of the Pollen Grains
3.4. Pollen Grain Size
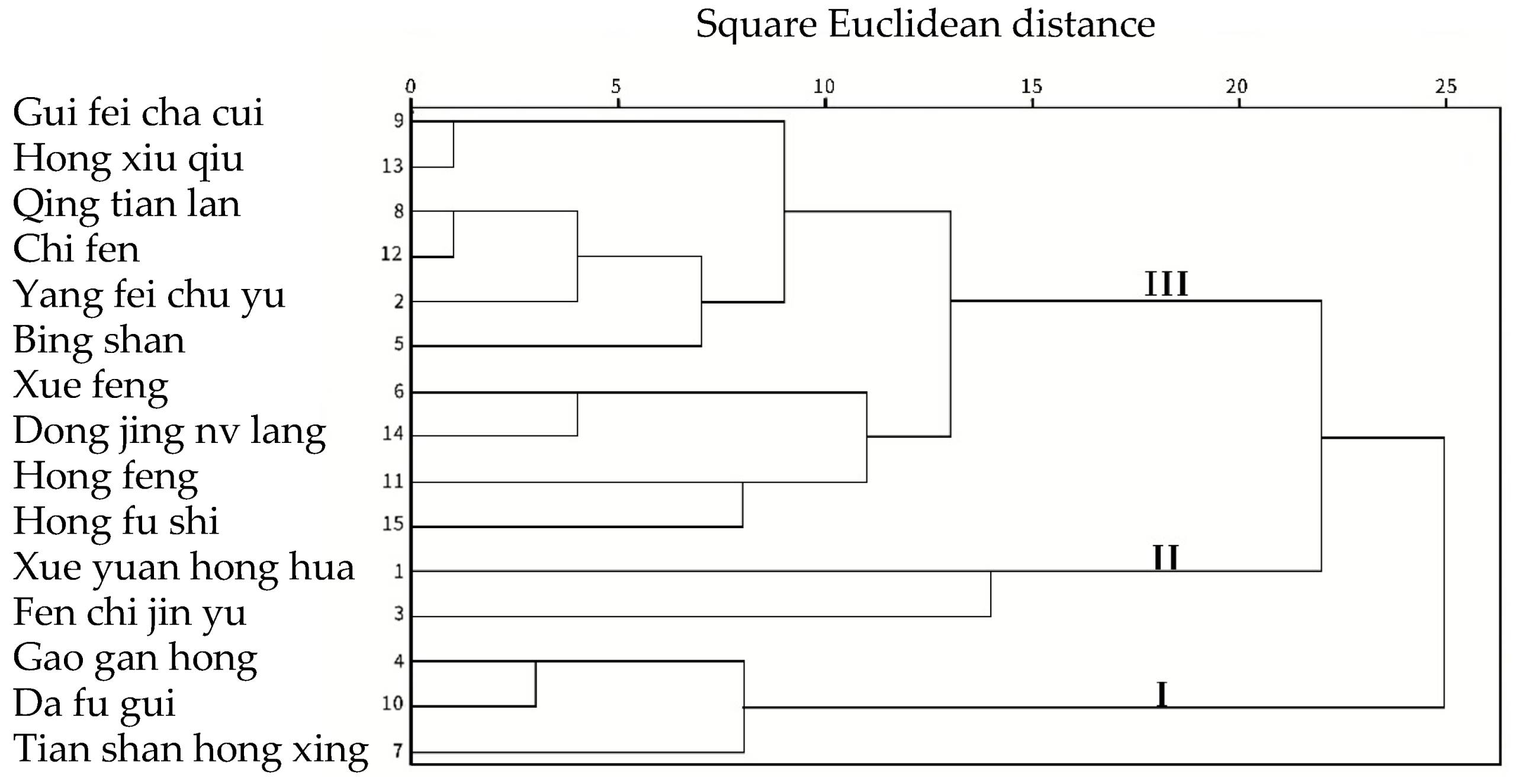
3.5. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Similarities and Differences in Pollen Submicroscopic Morphological Characteristics among Herbaceous Peony Varieties
4.2. Kinship
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wodehouse, R.P. Pollen Grains; McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Agababian, V.S. Pollen morphology of the family Magnoliaceae. Grana 1972, 12, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praglowski, J. World Pollen and Spore Flora; Almqvist & Widsell: Stockholm, Sweden, 1974; Volume 3, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, S.; Costa, M. Pollen grain development is compromised in Arabidopsis agp6 agp11 null mutants. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.A.; Le Thomas, A. Evolution and phylogenetic significance of pollen in Annonaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 169, 190–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Garcıá, S.A.; Figueroa-Castro, D.M.; Castañeda-Posadas, C. Pollen morphology of Pachycereus weberi (Cactaceae): An evaluation of variation in pollen size. Plant Syst. Evol. 2012, 298, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, W.; Hoen, P.P.; Blackmore, S.; Nilsson, S.; Le Thomas, A. Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2007, 143, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdtman, G. Handbook of Palynology; Translation by Academy of Sciences in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; pp. 1–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- House, A.; Balkwill, K. FIB-SEM: An additional technique for investigating internal structure of pollen walls. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.U.; Zafar, M.; Ahmad, M.; Anjum, F.; Sultana, S.; Kilic, O.; Ozdemir, F.A.; Nazir, A.; Yaseen, G.; Aabidin, S.Z.U. Pollen micromorphological analysis of tribe Acacieae (Mimosaceae) with LM and SEM techniques. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Yuan, T. Studies on the pollen morphology of 4 species of wild herbaceous peony. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2005, 41, 184–188. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.H.; Ma, H.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Yu, X.N. Pollen morphology of herbaceous peonies (Paeonia L.) with different ploidy levels. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 141, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, Q. Southern China the main crop and vegetable and fruit modern pollen morphology and agriculture archaeology research value. Acta Micropalaeontol. Sin. 2012, 29, 80–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mert, C. Pollen morphology and anatomy of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) varieties. HortScience 2009, 44, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, L. Discussion on several peony pollen morphology and evolution of wild species of classification. J. Beijing Univ. 1999, 21, 17–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; Xiong, Y.M.; Liu, R.Z.; Huang, X.F.; Yang, L.; Shen, C.G. Morphological characteristics of pollen grains from 16 germplasms of pitaya. Fresenius Environ. Bul. 2020, 29, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Piwowarczyk, R.; Rura, K.; Krasylenko, Y.; Kasińska, J.; Pedraja, S.S. Seed micromorphology of representatives of holoparasitic Orobanchaceae genera from the Caucasus region and its taxonomic significance. Phytotaxa 2020, 432, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y. The pollen morphology and exine ultrastructure of China Paeonia. Acta Bot. Sin. 1984, 26, 241–246. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, R.P. Pollen heteromorphism is pervasive in Thalictrum (Ranunculaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2016, 302, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; He, X.; Wu, J.; Ding, L. The relationship between morphological characteristics of pollen and cultivar evolution. Jiangsu J. Ag. Sci. 2005, 21, 63–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Guan, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Peng, L.C.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Wang, J.H.; Song, J. Cytology and pollen morphology of Bougainvillea glabra ‘Elizabeth Angus,’ a cultivar with low pollen fertility. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 301, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
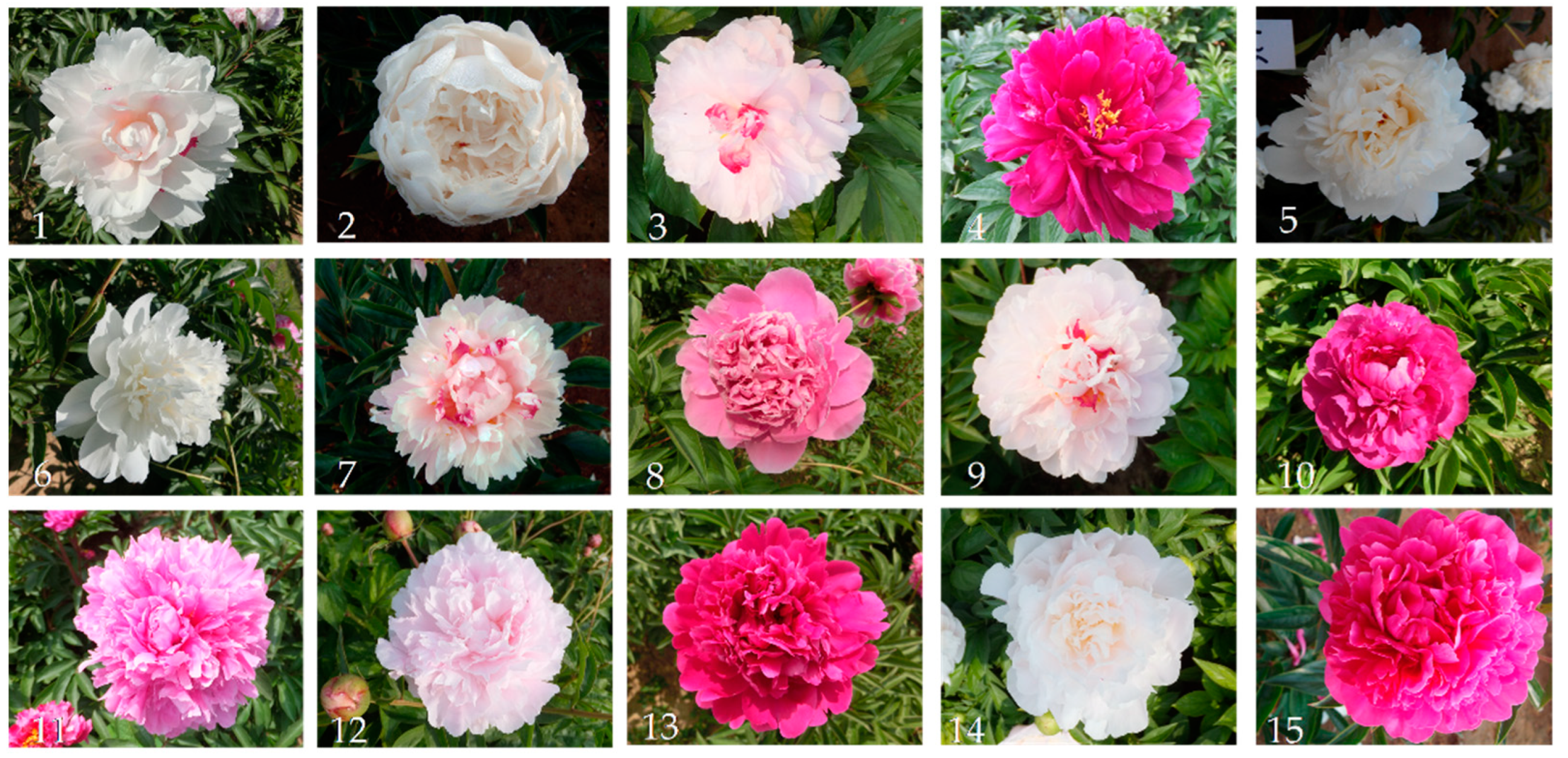


| Pollen Code | Cultivar Type | Bulbil Shape | Bud Shape | Flower Color | Petal Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pavilion type | Brush-shaped | Inclined sharp-pointed peach-shaped | White | Papery |
| 2 | Crown type | Projectile-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | White | Papery |
| 3 | Rose type | Bamboo-shaped | Inclined sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Pink | Leathery |
| 4 | Colorful-ball type | Projectile-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Red | Waxy |
| 5 | Crown type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | White | Papery |
| 6 | Crown type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | White | Papery |
| 7 | Rose type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | White | Waxy |
| 8 | Rose type | Brush-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Soft red | Papery |
| 9 | Crown type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Pink | Papery |
| 10 | Rose type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Red | Waxy |
| 11 | Colorful-ball type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Red | Papery |
| 12 | Rose type | Brush-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Pink | Papery |
| 13 | Crown type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Red | Waxy |
| 14 | Rose type | Bamboo-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Pink | Leathery |
| 15 | Colorful-ball type | Brush-shaped | Sharp-pointed peach-shaped | Burgundy | Waxy |
| Pollen Code | Length of Polar Axis (μm) | Length of Equatorial Axis (μm) | P/E | Perforation Number per 100 μm2 | Lumina Diameter (μm) | Ridge Width (μm) | D/W | Shape of Two Poles | Type of Exine Sculpture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 (18.5–26.4) | 25.3 (21.2–28.4) | 0.91 | 140 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 1.46 | circular and elliptical | reticular |
| 2 | 24.14 (21.6–26) | 26.3 (21.6–29.4) | 0.92 | 145 | 0.60 | 0.51 | 1.18 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 3 | 24.3 (22–27.2) | 26.4 (23.8–28.6) | 0.92 | 85 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 1.39 | circular and elliptical | reticular |
| 4 | 26.7 (22.4–29.6) | 26.9 (21.6–30.2) | 0.99 | 102 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.95 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 5 | 27.2 (23–31.5) | 27.8 (24.8–30.2) | 0.98 | 140 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 1.20 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 6 | 24.3 (20–28.2) | 25.4 (23.6–26.8) | 0.96 | 170 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.86 | circular | pit |
| 7 | 27 (21.6–31.2) | 26.3 (21.6–29.2) | 1.03 | 70 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.83 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 8 | 25 (32.1–22.2) | 25.6 (20.6–28.5) | 0.98 | 130 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 1.12 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 9 | 25.4 (20.8–29.6) | 25.7 (19–30.8) | 0.99 | 125 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.86 | circular and elliptical | pit |
| 10 | 28.3 (24.4–31.6) | 27.8 (22.6–31.4) | 1.02 | 100 | 0.50 | 0.61 | 0.82 | circular and elliptical | small pit |
| 11 | 22.62 (17.8–26) | 23.9 (14.8–28.4) | 0.95 | 145 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.97 | circular | pit |
| 12 | 25.7 (20.8–28.87) | 26.6 (22–28.4) | 0.97 | 125 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 1.22 | circular | pit |
| 13 | 25.2 (21.8–27.8) | 25.3 (20.4–27.6) | 1.00 | 125 | 0.48 | 0.57 | 0.84 | circular | small pit |
| 14 | 22.4 (17.8–25.8) | 24.3 (17.6–29.6) | 0.92 | 160 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.88 | circular and elliptical | small pit |
| 15 | 24.7 (19–29.2) | 26.2 (23–29) | 0.94 | 160 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 1.2 | circular and elliptical | pit |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Xie, A.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Dong, L.; Lei, F.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Study of 15 Varieties of Herbaceous Peony Pollen Submicroscopic Morphology and Phylogenetic Relationships. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121161
Zhang D, Xie A, Yang X, Shi Y, Yang L, Dong L, Lei F, Wu J, Sun X. Study of 15 Varieties of Herbaceous Peony Pollen Submicroscopic Morphology and Phylogenetic Relationships. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(12):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121161
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dongliang, Anqi Xie, Xiao Yang, Yajie Shi, Lijin Yang, Lingling Dong, Fuling Lei, Jingyue Wu, and Xia Sun. 2022. "Study of 15 Varieties of Herbaceous Peony Pollen Submicroscopic Morphology and Phylogenetic Relationships" Horticulturae 8, no. 12: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121161
APA StyleZhang, D., Xie, A., Yang, X., Shi, Y., Yang, L., Dong, L., Lei, F., Wu, J., & Sun, X. (2022). Study of 15 Varieties of Herbaceous Peony Pollen Submicroscopic Morphology and Phylogenetic Relationships. Horticulturae, 8(12), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121161






