Silicon Foliar Spray and Substrate Drench Effects on Plant Growth, Morphology, and Resistance to Wilting with Container-Grown Edible Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment #1: Evaluation of Si Foliar Spray Concentrations with Basil
2.2. Experiment #2: Edible Plant Species Supplied with Si Foliar Sprays and Substrate Drenches
3. Results
3.1. Experiment #1: Evaluation of Si Foliar Spray Concentrations with Basil
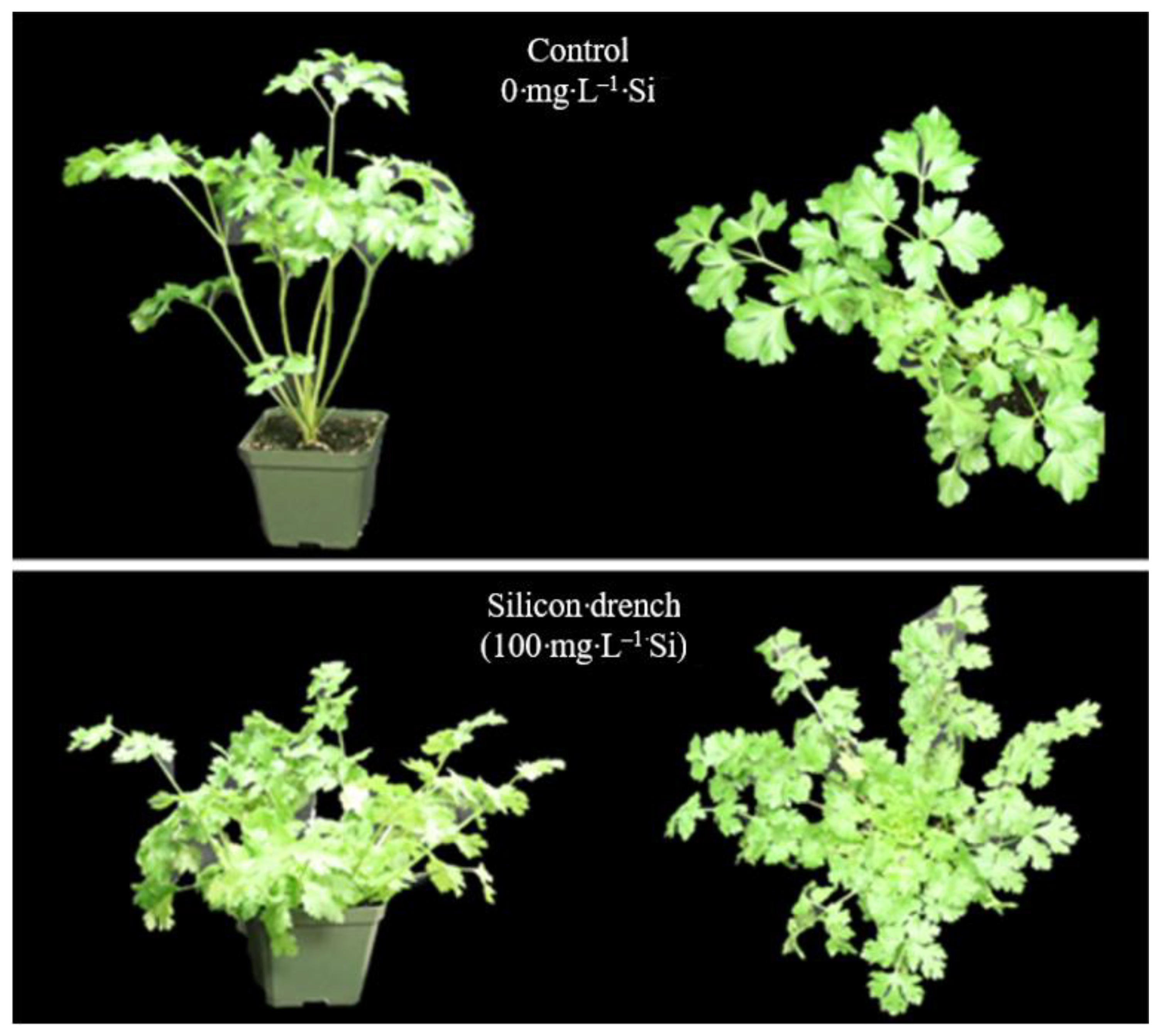
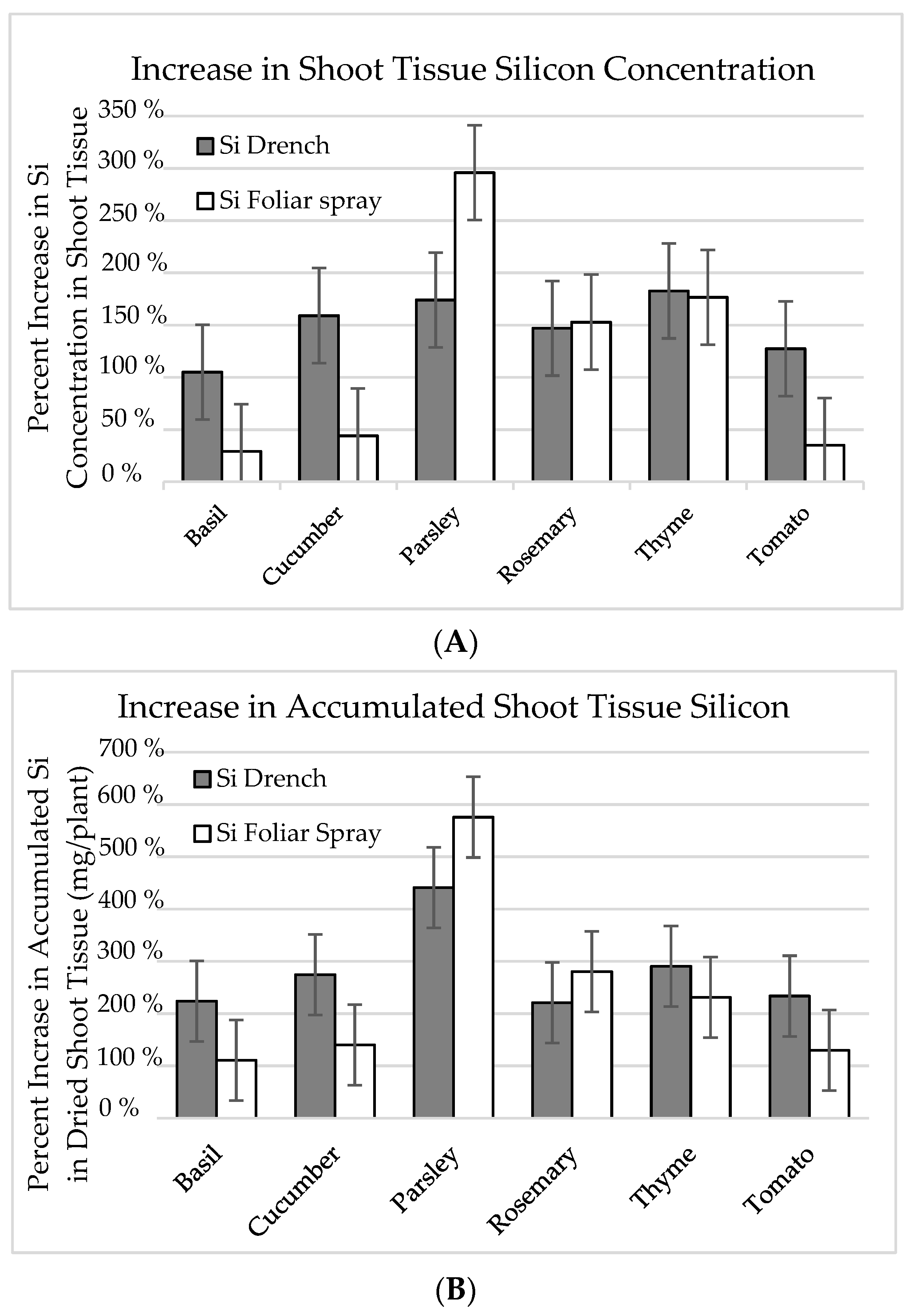
3.2. Experiment #2: Edible Plant Species Supplied with Si Foliar Sprays and Substrate Drenches
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Epstein, E. Silicon. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Voogt, W.; Sonneveld, C. Silicon in horticultural crops grown in soilless culture. In Silicon in Agriculture; Datnoff, L.E., Snyder, G.H., Korndörfer, G.H., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Datnoff, L.E.; Nell, T.A.; Leonard, R.T.; Rutherford, B.A. Effect of silicon on powdery mildew development on miniature potted rose. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Gillman, J.H.; Zlesak, D.C.; Smith, J.A. Applications of potassium silicate decrease black spot infection in Rosa hybrida ‘Meipelta’ (Fuchsia Meidiland). HortScience 2003, 38, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, N.; Leatherwood, W.R. Potassium silicate drenches increase leaf silicon content and affect morphological traits of several floriculture crops grown in a peat-based substrate. Hortscience 2010, 45, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamenidou, S.; Calvins, T.; Marek, S. Silicon supplements affect horticultural traits of greenhouse produced ornamental sunflowers. HortScience 2008, 43, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamenidou, S.; Calvins, T.; Marek, S. Evaluation of silicon as a nutritional supplement for greenhouse zinnia production. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 119, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenidou, S.; Cavins, J.; Marek, S. Silicon supplements affect floricultural quality traits and elemental nutrient concentrations of greenhouse produced gerbera. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenidou, S.; Calvins, T.; Marek, S. Correlation between tissue and substrate silicon concentration of greenhouse produced ornamental sunflowers. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 34, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenidou, S. Silicon Supplementation Affects Greenhouse Produced Cut Flowers. Master’s Thesis, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pozo, J.; Urrestarazu, M.; Morales, I.; Sanchez, J.; Santos, M.; Dianez, F.; Alvaro, J. Effects of silicon in the nutrient solution for three horticultural plant families on the vegetative growth, cuticle, and protection against Botrytis cinerea. HortScience 2015, 50, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, G.; Tikum, G.; Horst, W.J. The effect of silicon on the infection by and spread of Pythium aphanidermatum in single roots of tomato and bitter gourd. J. Expt. Bot. 2007, 58, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAvoy, R.J.; Bible, B.B. Silica sprays reduce the incidence and severity of bract necrosis in poinsettia. HortScience 1996, 31, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, J.M.; Locke, J.C.; Mattson, N. Research update: Does silicon have a role in ornamental crop production? OFA Res. 2010, 924, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- E-GRO Edible Alerts: Control Plant Growth and Height for Potted Herbs, 2.10. Available online: http://www.e-gro.org/alerts.php#EDIBLE (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Gómez, C.; Currey, C.J.; Dickson, R.W.; Kim, H.J.; Hernández, R.; Sabeh, N.C.; Raudales, R.E.; Brumfield, R.G.; Laury-Shaw, A.; Wilke, A.K.; et al. Controlled environment food production for urban agriculture. HortScience 2019, 54, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Produce Grower. Available online: https://www.producegrower.com/article/from-seed-to-store/ (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Cavins, T.J.; Whipker, B.E.; Fonteno, W.C. Establishment of calibration curves for comparing pour-through and saturated media extract nutrient values. HortScience 2004, 39, 1635–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarie, S.; Uchida, H.; Qgata, W.; Kubota, F.; Kaufman, P.B. Effects of silicon on transpiration and leaf conductance in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1998, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zou, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F. Silicon improves water use efficiency in maize plants. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnveld, C.; Voogt, W. Plant Nutrition of Greenhouse Crops; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Loomis, W.D.; Durst, R.W. Boron and cell walls. Curr. Top. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 1991, 10, 149–178. [Google Scholar]
- Loomis, W.D.; Durst, R.W. Chemistry and biology of boron. BioFactors 1992, 3, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Miyake, Y.; Takahashi, E. Silicon as a beneficial element for crop plants, In Silicon in Agriculture: Studies in Plant Science; Datnoff, L.E., Snyder, G.H., Korndörfer, G.H., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mitani, N.; Ma, J.F. Uptake system of silicon in different plant species. J. Expt. Bot. 2005, 56, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frantz, J.M.; Khandahar, S.; Leisner, S. Silicon differentially influences copper toxicity response in silicon-accumulator and non-accumulator species. J. Am. Hort. Sci. 2011, 136, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Silicon Foliar Treatment (mg∙L–1 Si) | F-Statistic z | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf SPAD chlorophyll content | 50 | 26.68 | 0.0001 |
| 100 | 17.05 | 0.0009 | |
| 200 | 19.52 | 0.0005 | |
| 400 | 15.14 | 0.0014 | |
| Shoot dry weight (g) | 50 | 1.66 | 0.2177 |
| 100 | 0.68 | 0.4239 | |
| 200 | 2.36 | 0.1451 | |
| 400 | 4.60 | 0.0488 | |
| Shoot Si concentration (mg∙kg−1) | 50 | 0.60 | 0.4514 |
| 100 | 13.59 | 0.0022 | |
| 200 | 78.93 | <0.0001 | |
| 400 | 146.16 | <0.0001 | |
| Number of days until wilting | 50 | 2.22 | 0.1569 |
| 100 | 4.19 | 0.0586 | |
| 200 | 4.60 | 0.0488 | |
| 400 | 5.81 | 0.0292 |
| Si Foliar Treatment (mg∙L−1 Si) | Leaf SPAD Chlorophyll Content | Shoot Dry Weight (g) | Shoot Si Concentration (mg∙kg−1) | Number of Days until Wilting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 34.2 z | 5.5 | 466.3 | 11.6 | ||||
| 50 | 41.8 | *** y | 6.4 | NS | 439.6 | NS | 13.1 | NS |
| 100 | 40.3 | ** | 6.1 | NS | 593.2 | * | 13.7 | NS |
| 200 | 40.7 | ** | 6.6 | NS | 772.3 | *** | 13.8 | * |
| 400 | 40.0 | ** | 7.0 | * | 882.7 | *** | 14.1 | * |
| Species | Supplemental Si Treatment | Canopy Height (cm) | Canopy Width (cm) | Stem Diameter at Shoot Tip (mm) | Stem Diameter at Plant Base (mm) | Shoot Dry Weight (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basil | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 29.3 | a | 33.7 | a | 3.1 | a | 5.6 | a | 4.10 | ab |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 32.7 | a | 34.2 | a | 2.8 | a | 6.0 | a | 4.47 | a | |
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 27.3 | a | 31.7 | a | 2.7 | a | 5.9 | a | 3.52 | b | |
| NS | NS | NS | NS | * | |||||||
| Cucumber | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 64.3 | a | 40.3 | a | 3.5 | a | 8.3 | a | 6.10 | a |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 58.7 | a | 42.7 | a | 3.7 | a | 8.0 | a | 6.44 | a | |
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 63.0 | a | 41.7 | a | 3.3 | a | 7.9 | a | 5.92 | a | |
| NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |||||||
| Parsley | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 5.0 | a | 41.0 | a | 5.8 | b | 12.0 | a | 3.15 | b |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 2.3 | a | 48.2 | a | 10.2 | a | 13.3 | a | 5.09 | a | |
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 3.0 | a | 46.8 | a | 9.1 | ab | 13.0 | a | 4.60 | a | |
| NS | NS | * | NS | * | |||||||
| Rosemary | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 11.7 | a | 13.2 | a | 1.8 | a | 3.3 | a | 0.92 | a |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 11.7 | a | 11.2 | a | 1.9 | a | 2.7 | a | 0.83 | a | |
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 15.7 | a | 13.0 | a | 1.8 | a | 3.1 | a | 1.01 | a | |
| NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |||||||
| Thyme | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 19.7 | a | 23.2 | a | 1.0 | a | 2.7 | a | 1.71 | a |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 17.0 | a | 21.5 | a | 0.9 | a | 2.5 | a | 1.73 | a | |
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 14.7 | a | 23.0 | a | 1.0 | a | 2.4 | a | 1.43 | a | |
| NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |||||||
| Tomato | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | 51.7 | a | 53.2 | a | 2.3 | a | 7.9 | 7.68 | a | |
| Si drench (100 mg∙L−1 Si) | 50.0 | a | 54.0 | a | 2.5 | a | 7.4 | 7.91 | a | ||
| Si spray (500 mg∙L−1 Si) | 54.3 | a | 56.0 | a | 2.2 | a | 7.5 | 7.48 | a | ||
| NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Plant Species | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | Si Foliar Spray (500 mg∙L–1 Si) | Si Substrate Drench (100 mg∙L–1 Si) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si concentration in shoot tissue (mg∙kg–1) | ||||||
| Basil | 459.7 z | b | 593.5 | b | 943.0 | b |
| Cucumber | 1095.3 | a | 1577.3 | a | 2838.4 | a |
| Parsley | 124.9 | c | 494.5 | b | 342.3 | c |
| Rosemary | 142.3 | bc | 359.9 | b | 351.6 | c |
| Thyme | 232.1 | bc | 641.9 | b | 656.0 | bc |
| Tomato | 254.4 | bc | 343.4 | b | 578.6 | bc |
| Accumulated Si in shoot tissue (mg/plant) | ||||||
| Basil | 1.85 | b | 2.09 | bc | 4.21 | bc |
| Cucumber | 6.66 | a | 0.32 | a | 18.28 | a |
| Parsley | 0.40 | cd | 2.28 | b | 1.75 | cd |
| Rosemary | 0.13 | d | 0.37 | d | 0.29 | d |
| Thyme | 0.40 | cd | 0.92 | cd | 1.16 | d |
| Tomato | 1.96 | b | 2.54 | b | 4.57 | b |
| Plant Species | Control (0 mg∙L–1 Si) | Si Foliar Spray (500 mg∙L–1 Si) | Si Substrate Drench (100 mg∙L–1 Si) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si uptake efficiency in shoot tissue (%) | ||||||
| Basil | 27.3 z | b | 8.0 | b | 6.3 | b |
| Cucumber | 95.6 | a | 27.2 | a | 27.3 | a |
| Parsley | 6.0 | c | 8.7 | b | 2.3 | c |
| Rosemary | 2.0 | c | 2.3 | c | 0.4 | c |
| Thyme | 5.7 | c | 5.0 | bc | 1.7 | c |
| Tomato | 28.3 | b | 7.3 | b | 6.7 | b |
| *** y | *** | *** | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tebow, J.B.; Houston, L.L.; Dickson, R.W. Silicon Foliar Spray and Substrate Drench Effects on Plant Growth, Morphology, and Resistance to Wilting with Container-Grown Edible Species. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090263
Tebow JB, Houston LL, Dickson RW. Silicon Foliar Spray and Substrate Drench Effects on Plant Growth, Morphology, and Resistance to Wilting with Container-Grown Edible Species. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(9):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090263
Chicago/Turabian StyleTebow, Joshua B., Lauren L. Houston, and Ryan W. Dickson. 2021. "Silicon Foliar Spray and Substrate Drench Effects on Plant Growth, Morphology, and Resistance to Wilting with Container-Grown Edible Species" Horticulturae 7, no. 9: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090263
APA StyleTebow, J. B., Houston, L. L., & Dickson, R. W. (2021). Silicon Foliar Spray and Substrate Drench Effects on Plant Growth, Morphology, and Resistance to Wilting with Container-Grown Edible Species. Horticulturae, 7(9), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7090263






