An Assessment of Treated Greywater Reuse in Irrigation on Growth and Protein Content of Prosopis and Albizia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
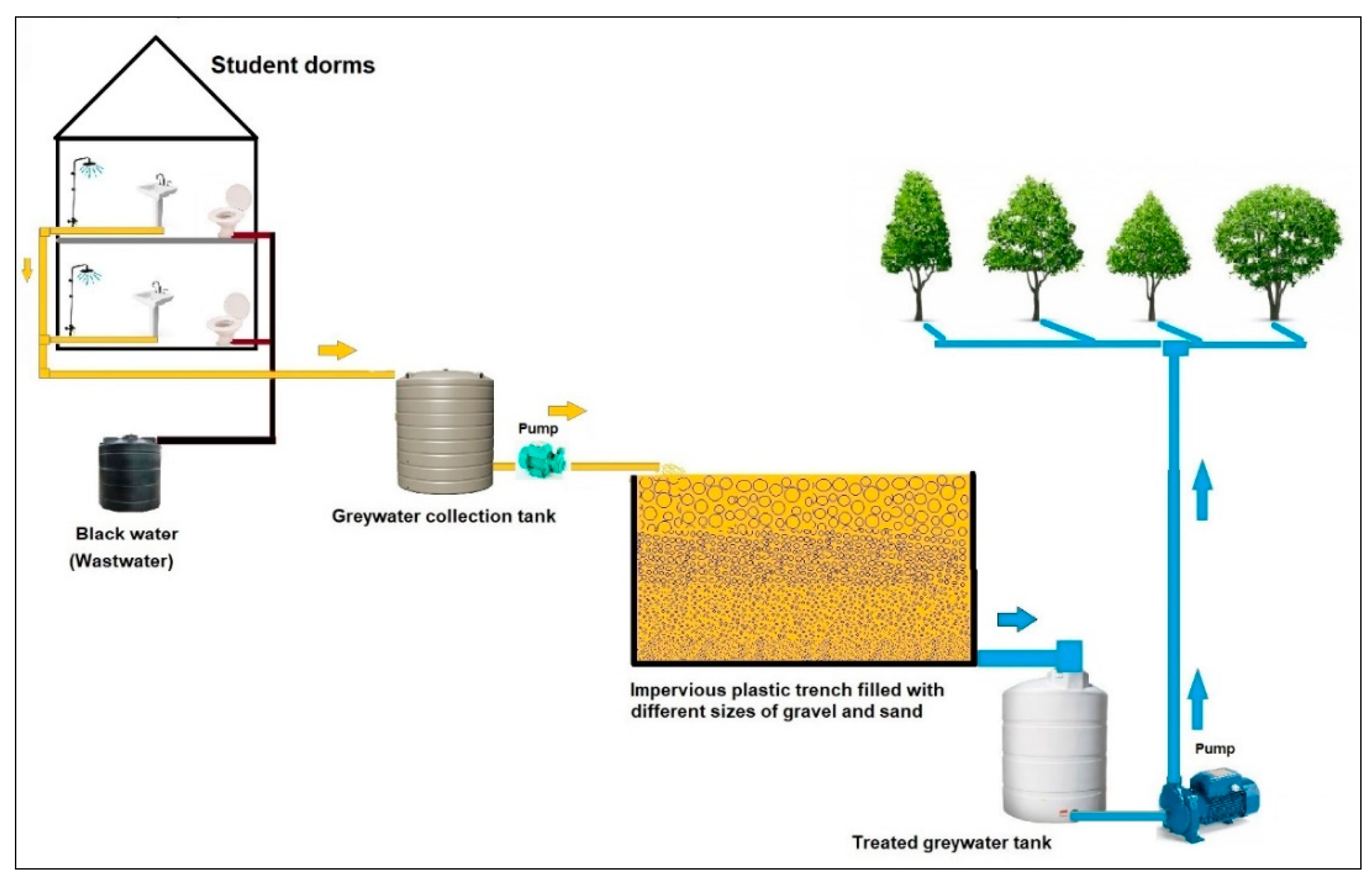
2.1. Experiment Setup and Plant Material
2.2. Greywater Sources and Quality Analyses
2.3. Treatment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
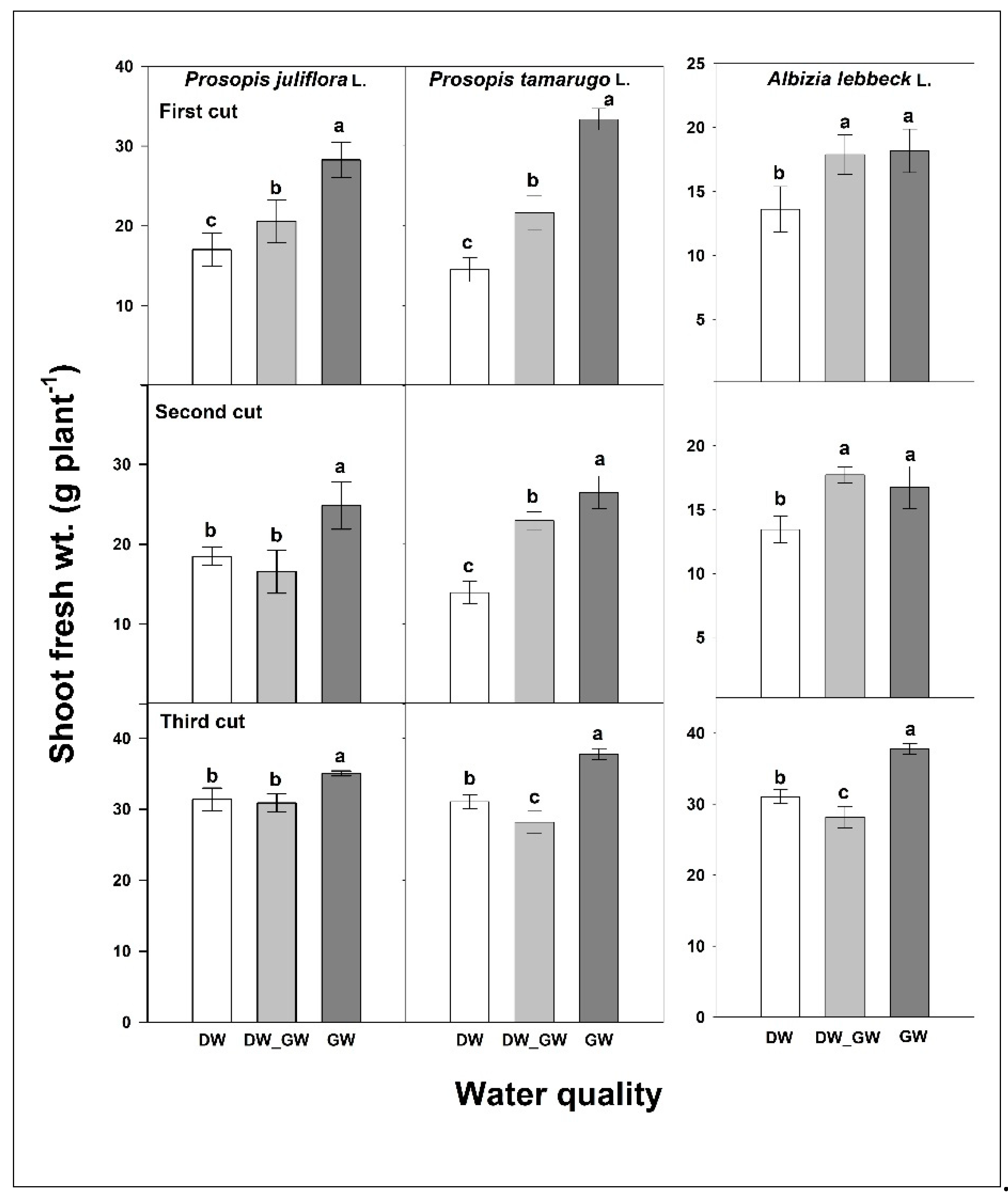
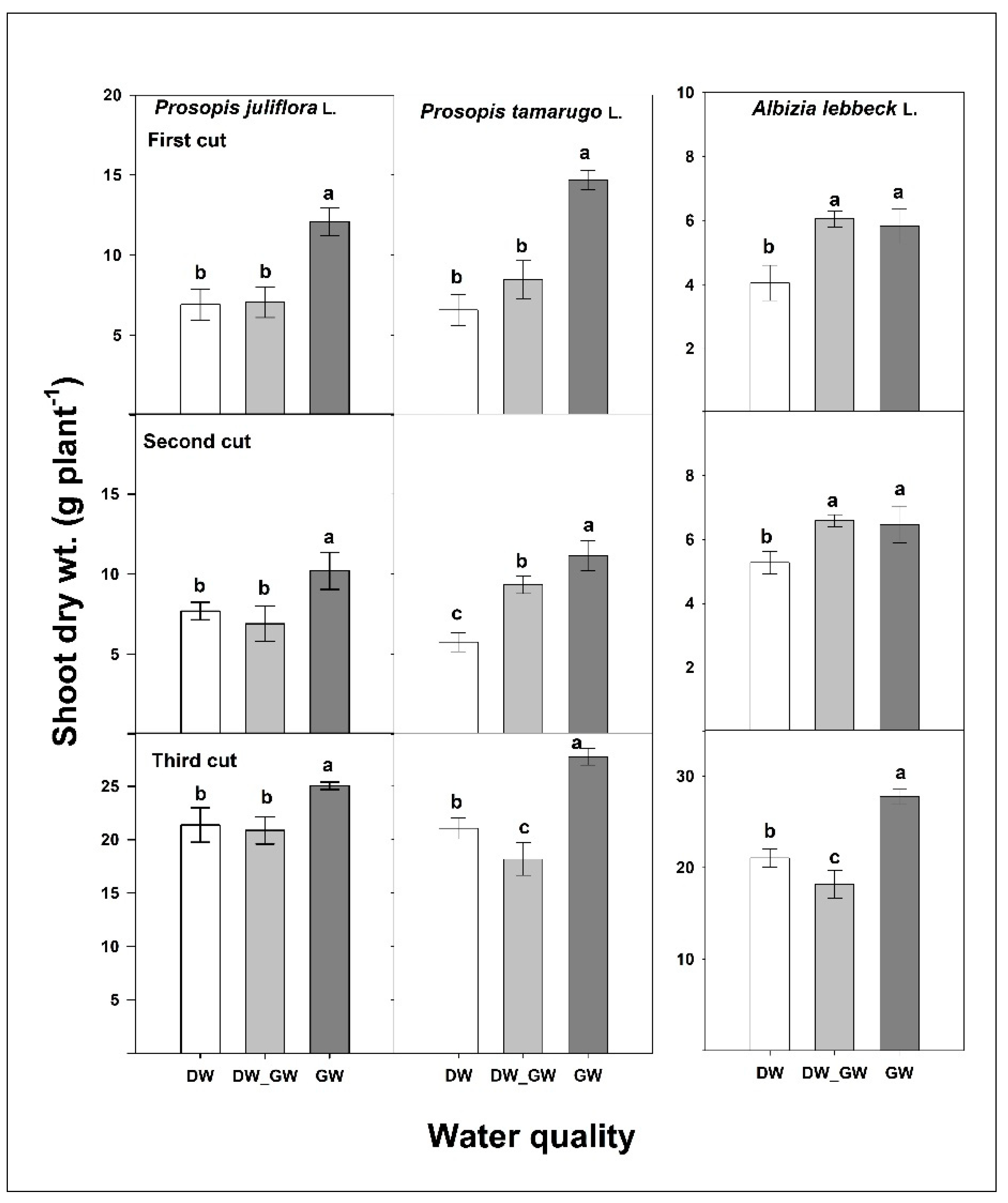
3.1. Greywater Quality and Plant Yield
3.2. Reuse of Greywater for Irrigation of Multipurpose Trees—Prosopis and Albizia
3.2.1. Food and Forage Production
3.2.2. Ornamentals, Fuel, and Wood Production
3.3. Ways for Improvement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadros, M.; Al-Mefleh, N.; Othman, Y.; Al-Assaf, A. Water harvesting techniques for improving soil water content, and morpho-physiology of pistachio trees under rainfed conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.; Niazi, N. A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.; Balan, P.; Chong, M.; Poh, P. Life-cycle assessment and life-cycle cost analysis of decentralized rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling and hybrid rainwater-greywater systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.; Auffarth, K.; Henze, M.; Ledin, A. Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water 2002, 4, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Hadari, M. Economic feasibility of on-site greywater reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination 2006, 190, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boano, F.; Caruso, A.; Costamagna, E.; Ridolfi, L.; Fiore, S.; Demichelis, F.; Gavão, A.; Pisoeiro, J.; Rizzo, A.; Masi, F. A review of nature-based solutions for greywater treatment: Applications, hydraulic design, and environmental benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radingoana, M.; Dube, T.; Mazvimavi, D. Progress in greywater reuse for home gardening: Opportunities, perceptions and challenges. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 116, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.; Soeter, A.; Kools, S.; Kraak, M.; Parsons, J.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C. Ecotoxicological assessment of greywater treatment systems with Daphnia magna and Chironomus riparius. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamaiedeh, H.; Bino, M. Effect of treated grey water reuse in irrigation on soil and plants. Desalination 2010, 256, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzini, L.; Winter, K. Analysis of grey-water used for irrigating vegetables and possible effects on soils in the vicinity of Umtata Dam, Eastern Cape. Water SA 2015, 41, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assaf, A.; Tadros, M.J.; Al-Shishany, S.; Stewart, S.; Majdalawi, M.; Tabieh, M.; Othman, Y.A. Economic Assessment and Community Management of Prosopis juliflora Invasion in Sweimeh Village, Jordan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagg, C.W.; Stewart, J.L. The value of Acacia and Prosopis in arid and semi-arid environments. J. Arid Environ. 1994, 27, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.P.; Prince, W.; Sivakumar, S.; Subbhurram, C. Prosopis juliflora—A green solution to decontaminate heavy metal (Cu and Cd) contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakie, T.; Laituri, M.; Evangelista, P. Assessing the distribution and impacts of Prosopis juliflora through participatory approaches. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 66, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qrunfleh, M.; Othman, Y. Ornamental Landscape Plants Grown in Jordan and Neighbouring Countries: Woody Ornamental Trees, 1st ed.; Dar Wael for Publishing: Amman, Jordan, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Tadros, M.; Al-Assaf, A.; Othman, Y.; Makhamreh, Z.; Taifour, H. Evaluating the effect of Prosopis juliflora, an alien invasive species, on land cover change using remote sensing approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankhwar, A.; Srivastava, R. Biomass production through grey water fertigation in Eucalyptus hybrid and its economic significance. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesny, R.; Stanturf, J.; Evett, S.; Kandil, N.; Sorianos, C. Opportunities for woody crop production using treated wastewater in Egypt. I. Afforestation strategies. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2011, 13, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamamre, Z.; Saidan, M.; Hararah, M.; Rawajfeh, K.; Alkhasawneh, H.; Al-Shannag, M. Wastes and biomass materials as sustainable-renewable energy resources for Jordan. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USAID. Water Resources and Environment: Investing in a Water-Secure Future in Jordan. 2020. Available online: https://www.usaid.gov/jordan/water-and-wastewater-infrastructure#:~:text=Jordan%20is%20one%20of%20the,as%20it%20can%20be%20recharged (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- JISM. Water—Reclaimed Grey Water (JS 1776:2013); Jordan Institution for Standards and Meteorology: Amman, Jordan, 2013; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Radingoana, M.; Dube, T.; Mazvimavi, D. An assessment of irrigation water quality and potential of reusing greywater in home gardens in water-limited environments. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 116, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siggins, A.; Burton, V.; Ross, C.; Lowe, H.; Horswell, J. Effects of long-term greywater disposal on soil: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disha, A.; Al Harun, M.; Akter, S.; Billah, S.; Abdullah-Al-Noman, M. Reusing greywater for cultivation of Capsicum frutescens and Calendula officinalis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mzini, L.; Winter, K. Effects of irrigation water quality on vegetables Part 1: Yield and aesthetical appeal. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2015, 32, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajlouni, M.; Ayad, J.; Othman, Y. Increasing nutrient levels promote growth and flower quality in lilies grown under soilless culture. Hort. Sci. 2017, 44, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovar, D.; Othman, Y.; Dong, X. Strip tillage improves soil biological activity, fruit yield and sugar content of triploid watermelon. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovar, D.; Othman, Y. Nitrogen management for improving root and shoot components of young ‘Arbequina’ olives. HortScience 2019, 54, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, Y.; Leskovar, D. Nitrogen management influenced root length intensity of young olive trees. Sci. Hort. 2019, 246, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahat, M.; Alananbeh, K.; Othman, Y.; Leskovar, D. Soil health and sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrell, W.; Beverly, R. The dilution effect in plant nutrition studies. Adv. Agron. 1981, 34, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, I.; Ahammed, M. Quantity and quality characteristics of greywater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, S.; Barrington, S.; Lyew, D. Reuse of domestic greywater for the irrigation of food crops. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 199, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S. Quantitative microbial risk assessment of Greywater on-site reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggeman, S.; van den Brink, N.; Van Praet, N.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L. Metal exposure and accumulation patterns in free-range cows (Bos taurus) in a contaminated natural area: Influence of spatial and social behavior. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoreanu, L.; Phillips, C. Modeling cadmium uptake and accumulation in plants. Adv. Agron. 2004, 84, 121–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinuthia, G.; Ngure, V.; Beti, D.; Lugalia, R.; Wangila, A.; Kamau, L. Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: Community health implication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alonso, M. Animal feed contamination by toxic metals. In Animal Feed Contamination, Effects on Livestock and Food Safety; Fink-Gremmels, J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 183–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; McCrory, D.; Powell, J.; Saam, H.; Jackson-Smith, D. A survey of selected heavy metal concentrations in Wisconsin dairy feeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaganapathy, V.; Xavier, F.; Sreekumar, D.; Mandal, P. Heavy metal contamination in soil, water and fodder and their presence in livestock and products: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamse, A.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.; de Jong, J. Cadmium, lead, mercury and arsenic in animal feed and feed materials–trend analysis of monitoring results. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajmi, A.; Salih, A.; Kadim, I.; Othman, Y. Chemical constituents and heavy metals contents of barley fodder produced under hydroponic system in GCC countries using tertiary treated sewage effluents. J. Phytol. 2009, 1, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Prodanovic, V.; Hatt, B.; McCarthy, D.; Zhang, K.; Deletic, A. Green walls for greywater reuse: Understanding the role of media on pollutant removal. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanovic, V.; McCarthy, D.; Hatt, B.; Deletic, A. Designing green walls for greywater treatment: The role of plants and operational factors on nutrient removal. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, H.; Panthi, S.; Rjoub, Y.; Lipchin, C.; Sapkota, A.; Sapkota, A. Antibiotic and herbicide concentrations in household greywater reuse systems and pond water used for food crop irrigation: West Bank, Palestinian Territories. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.; Oh, K.; Poh, P.; Chong, M. Prospects of hybrid rainwater-greywater decentralised system for water recycling and reuse: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3014–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Warne, M.; Dawes, L.; Thompson, K.; Will, G. Greywater irrigation as a source of organic micro-pollutants to shallow groundwater and nearby surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.; Donner, E. Metals in greywater: Sources, presence and removal efficiencies. Desalination 2009, 248, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Warne, M.; Dawes, L.; Vardy, S.; Will, G. Irrigated greywater in an urban sub-division as a potential source of metals to soil, groundwater and surface water. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaris, G.; Dawson, R.; Gironás, J.; Hess, S.; Ortúzar, J. Understanding the preferences for different types of urban greywater uses and the impact of qualitative attributes. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assaf, A.; Nawash, O.; Mmari, M. Identifying forest ecosystem services through socio-ecological bundles a case study from northern Jordan. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2014, 21, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, S.; Stevens, P.; Arnold, R. Hidden assets: Asia’s smallholder wood resources, and their contribution to supply chains of commercial wood. Aust. For. 2017, 80, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, H.; Alamirew, T.; Dzikiti, S.; Bewket, W.; Zeleke, G.; Schaffner, U. Water use of Prosopis juliflora and its impacts on catchment water budget and rural livelihoods in Afar Region, Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Muscolo, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, W. Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources for rehabilitation of marginal lands in arid and semiarid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Treated Greywater | JISM | WHO |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.9 | 6.0–9.0 | 6.5–8.0 |
| ECw (dS m−1) | 0.7 | 1.0–3.0 | 0.7–3.0 |
| N (mg L−1) | 17.7 | 50 | 5–30 |
| Ca+2 (mg L−1) | 71.9 | 400 | - |
| Mg+2 (mg L−1) | 17.3 | 60 | - |
| K+ (mg L−1) | 5.1 | 80 | - |
| Na+ (mg L−1) | 43.5 | 230 | 69–207 |
| Cl- (mg L−1) | 85.1 | 400 | 140–350 |
| Zn (mg L−1) | 0.7 | 2.0 | <2.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.1 | 5.0 | 0.1–1.5 |
| B (mg L−1) | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.7–3.0 |
| As (mg L−1) | <0.002 | 0.1 | <0.1 |
| Cd (mg L−1) | <0.002 | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Pb (mg L−1) | <0.01 | 5.0 | <5.0 |
| BOD5 (mg L−1) | 12.9 | 60 | - |
| COD (mg L−1) | 29.6 | 120 | - |
| PO4 (mg L−1) | 0.2 | 30 | - |
| NO3 (mg L−1) | 2.0 | 45 | 50 |
| TDS (mg L−1) | 429 | <2000 | 450–2000 |
| SAR (ratio) | 21.9 | 9.0 | <13 |
| ESP (%) | 0.5 | - | - |
| E. coli (no. 100 mL−1) | 408 | <103 | 104–105 |
| Water Source (W) | Species (S) | Shoot Fresh wt. (g plant−1) | Shoot Dry wt. (g plant−1) | Crude Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distilled water | 60.9 b | 32.7 b | 11.2 | |
| Distilled+greywater | 68.3 b | 34.0 b | 11.6 | |
| Greywater | 84.8 a | 45.7 a | 10.9 | |
| Prosopis juliflora L. | 74.4 a | 39.4 a | 8.80 b | |
| Prosopis tamarugo L. | 76.6 a | 41.0 a | 9.00 b | |
| Albizia lebbeck L. | 63.0 b | 32.0 b | 16.0 a | |
| p-value | W | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.68 |
| S | 0.006 | 0.001 | <0.001 | |
| W × S | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mefleh, N.K.; Othman, Y.A.; Tadros, M.J.; Al-Assaf, A.; Talozi, S. An Assessment of Treated Greywater Reuse in Irrigation on Growth and Protein Content of Prosopis and Albizia. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030038
Al-Mefleh NK, Othman YA, Tadros MJ, Al-Assaf A, Talozi S. An Assessment of Treated Greywater Reuse in Irrigation on Growth and Protein Content of Prosopis and Albizia. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mefleh, Naji K., Yahia A. Othman, Maher J. Tadros, Amani Al-Assaf, and Samer Talozi. 2021. "An Assessment of Treated Greywater Reuse in Irrigation on Growth and Protein Content of Prosopis and Albizia" Horticulturae 7, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030038
APA StyleAl-Mefleh, N. K., Othman, Y. A., Tadros, M. J., Al-Assaf, A., & Talozi, S. (2021). An Assessment of Treated Greywater Reuse in Irrigation on Growth and Protein Content of Prosopis and Albizia. Horticulturae, 7(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030038






