Effects of Fertigation Management on the Quality of Organic Legumes Grown in Protected Cultivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Framework, Plant Species and Applied Treatments
2.2. Physical Traits
2.3. Chemical Traits
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Analysis
3.2. Physical Parameters
3.3. Nutritional Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CAPDER. Informe de Estadísticas de La Producción Ecológica a 31/12/16; Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2017.
- Rubio, L.A.; Molina, E. Las leguminosas en alimentación animal. Arbor 2016, 192, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldi, A.; Zanoni, C.; Lammi, C.; Boschin, G. The role of grain legumes in the prevention of hypercholesterolemia and hypertension. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 144–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Andrade, C.; Olías, R.; Jiménez-López, J.; Clemente, A. Aspectos de las legumbres nutricionales y beneficiosos para la salud humana. Arbor 2016, 192, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzano, L.A.; Thompson, A.M.; Tees, M.T.; Nguyen, C.H.; Winham, D.M. Non-soy legume consumption lowers cholesterol level: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Villar, C.; Clemente, A.; Lombó, F. Healthy effects of prebiotics and their metabolites against intestinal diseases and colorectal cancer. AIMS Microbiol. 2015, 1, 48–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, H.L.; Campbell, B.J. Dietary fibre-microbiota interactions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Mitchell, S.; Sahye-Pudaruth, S.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Chiavaroli, L.; Mirrahimi, A.; Ireland, C.; Bashyam, B.; et al. Effect of legumes as part of a low glycemic index diet on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Kumar, R.; Patel, N. Water and nitrate dynamics in baby corn (Zea mays L.) under different fertigation frequencies and operating pressures in semi-arid region of India. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 163, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, M.R.; Thompson, R.B.; Fernandez, M.D.; Martinez-Gaitan, C.; Gallardo, M. Prescriptive corrective nitrogen and irrigation management of fertigated and drip-irrigated vegetable crops using modelling and monitoring approaches. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 119, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Caparros, P.; Contreras, J.I.; Baeza, R.; Segura, M.L.; Lao, M.T. Integral Management of Irrigation Water in Intensive Horticultural Systems of Almería. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, M.C.; Céspedes, A.J.; Lorenzo, P.; Pérez-Parra, J.J.; Escudero, M.C.; Sánchez-Guerrero, M.C.; Medrano, E.; Baeza, E.; López, J.C.; Magán, J.J.; et al. El Sistema de Producción Hortícola de La Provincia de Almería; IFAPA (Instituto de Formación Agraria y Pesquera de Andalucía): Huelva, Spain, 2016; p. 179. [Google Scholar]
- Sezen, S.M.; Yazar, A.; Canbolat, M.; Eker, S.; Celikel, G. Effect of drip irrigation management on yield and quality of field grown green beans. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, M.; Ji, Y.; He, H.; Gruda, N. Effect of irrigation on growth, yield, and chemical composition of two green bean cultivars. Horticulturae 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.M.; Helmy, Y.I.; Karas, A.N.; Abou-Hadid, A.F. Influences of different water-stress treatments on growth, development and production of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Acta Hort. 2003, 614, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonachela, S.; González, A.M.; Fernández, M.D. Irrigation scheduling of plastic greenhouse vegetable crops based on historical weather data. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 25, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.A. Methods of Soils Analysis, Part II: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Kähkönen, M.P.; Hopia, A.I.; Vuorela, H.J.; Rauha, J.P.; Pihlaja, K.; Kujala, T.S. Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntornsuk, L.; Gritsanapun, W.; Nilkamhank, S.; Paochom, A. Quantitation of vitamin C content in herbal juice using direct titration. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Rojas, R.; Sánchez-Segarra, P.J.; García-Martínez, M.; Gordillo-Otero, M.J.; Amaro López, M.A. Mineral composition of skimmed milk fruit-added yoghurts, nutritional assessment. Milchwissenschaft 2000, 55, 510–512. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Esen, B. Heterogeneity of soybean and proteins: One dimensional electrophoretic profiles of six different solubility fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 297–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knabe, D.; Laure, D.; Gregg, E.; Martínez, G.; Tankley, T. Apparent digestibility of nitrogen and amino acids in protein feed stuffs by growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1989, 67, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. Arapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye banding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.I.; Baeza, R.; López, J.G.; Cánovas, G.; Alonso, F. Management of Fertigation in Horticultural Crops through Automation with Electrotensiometers: Effect on the Productivity of Water and Nutrients. Sensors 2021, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.I.; Alonso, F.; Cánovas, G.; Baeza, R. Irrigation management of greenhouse zucchini with different soil matric potential level. Agronomic and environmental effects. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 183, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.B.; Purves, J.V.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; Saker, L.R. Nitrogen assimilation and the control of ammonium and nitrate absorption by maize roots. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Tilliard, P.; Touraine, B. Nitrate fluxes in soybean seedling roots and their response to amino acids: An approach using 15N. Plant Cell Environ. 1995, 18, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dluzniewska, P.; Gessler, A.; Kopriva, S.; Strand, M.; Novak, O.; Dietrich, H.; Rennenberg, H. Exogenous supply of glutamine and active cytokinin to the roots reduces NO3 uptake rates in poplar. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oanzen, H.H.; Chang, C. Cation concentrations in the saturation extract and soil solution extract of soil salinized with various sulfate salts. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.I. Optimización de Las Estrategias de Fertirrigación de Cultivos Hortícolas en Invernadero Utilizando Aguas de Baja Calidad (Agua Salina y Agua Regenerada) en Condiciones Del Litoral de Andalucía. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Almería, Almería, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, M.L.; Contreras París, J.I.; Plaza, B.M.; Lao, M.T. Assessment of the Nitrogen and Potassium Fertilizer in Green Bean Irrigated with Disinfected Urban Wastewater. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelenbos, M.; Thybo, A.; Errichsen, L.; Wienberg, L.; Andersen, L. Relevant measurements of green pea texture. J. Food Qual. 2001, 24, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizana, C.; Wentworth, M.; Martinez, J.P.; Villegas, D.; Meneses, R.; Murchie, E.H.; Pastenes, C.; Lercari, B.; Vernieri, P.; Horton, P.; et al. Differential adaptation of two varieties of common bean to abiotic stress: I. Effects of drought on yield and photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelo-Nuñez, J.M.; Ruiz-Nogueira, B.; Sau-Sau, F. Prácticas de cultivo de la judía grano. Agricultura 1996, 767, 493–495. [Google Scholar]
- Droga, R.C.; Dudeja, S.S. Fertilizer N and Nitrogen Fixation in legume—Rhizobium Symbiosis. Ann. Biol. 1993, 9, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, G.; Rice, W.; Blade, S.; Grant, C.; Harker, N.; Johnston, A.; Lafond, G.; Lupwayi, N. Minimizing Risk and Increasing Yield Stability in Field Pea Production. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting, Conference and Trade Show of the Saskatchewan Soil Conservation Association, Regina, SK, Canada, 11–12 February 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kontopoulou, C.K.; Giagkou, S.; Stathi, E.; Savvas, D.; Iannetta, P.P.M. Responses of hydroponically grown common bean fed with nitrogen-free nutrient solution to root inoculation with N-2-fixing bacteria. Hortscience 2015, 50, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macák, M.; Candráková, E.; Đalović, I.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Farooq, M.; Korczyk-Szabó, J.; Kováčik, P.; Šimanský, V. The Influence of Different Fertilization Strategies on the Grain Yield of Field Peas (Pisum sativum L.) under Conventional and Conservation Tillage. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Rahman, M.A.; Hoque, A.K.M.S.; Zaman, S.; Noor, S. Response of Different Levels of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on the Growth and Yield of French Bean. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2010, 45, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, S.M.; Yazar, A.; Akyildiz, A.; Dasgan, H.Y.; Gencel, B. Yield and quality response of drip irrigated green beans under full and deficit irrigation. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 117, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.L.; Contreras, J.I.; García, I.I.; García, M.C.; Cuadrado, I.M. Fertilización nitrogenada de judía verde bajo invernadero con criterios agroecológicos. In VII Congreso SEAE Zaragoza; Sociedad Española de Agricultura Ecológica: Catarroja, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ntatsi, G.; Gutiérrez-Cortines, M.E.; Karapanos, I.; Barros, A.; Weiss, J.; Balliu, A.; Savvas, D. The quality of leguminous vegetables as influenced by preharvest factors. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 232, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mera, M.; Kehr, E.; Mejías, J.; Ihl, M.; Bifani, V. Arvejas (Pisum sativum) de Vaina Comestible Sugar Snap: Antecedentes y Comportamiento en el Sur de Chile. Agric. Tec. 2007, 67, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, N.E.P.; López, G.P.; Domínguez, C.R.; Peñuelas, V.M.L.; Izaguirre, S.C.O. Composición química, características funcionales y capacidad antioxidante de formulaciones de garbanzo (“Cicer arietinum” L.) Blanco Sinaloa 92. Agrociencia 2019, 53, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Khah, M.E.; Arvanitoyannis, S.I. Yield, nutrient content and physico-chemical and organoleptic properties en green bean are affected by N:K ratios. Food Agric. Environ. 2003, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dawo, M.; Wilkindon, J.M.; Sanders, F.; Pilbean, D.J. The yield and quality of fresh and ensiled plant material from intercropped maize (Zea mays) and beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Ros, G.; Periago, M.J.; López, G.; Ortuño, J. Physico-chemical and sensory quality criteria of green beans. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995, 28, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.M.; Garrido, C.; Flores, P.; Martínez, V. The effect of salinity on yield and fruit quality of pepper grown in perlite. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 8, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Suhaibani, N.A. Influence of early water deficit on seed yield and quality of faba bean under arid environment of Saudi Arabia. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Malleshi, N.G. Physical, chemical and nutritional characteristic of premature-processed and matured green legumes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siger, A.L.; Czubinski, J.; Kachlicki, P.; Dwiecki, K.; Lampart-Szczapa, E.; Nogala-Kalucka, M. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content in three Lupin species. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 25, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Information Council. Nutrition information & food labelling-results of the EUFIC consumer research conducted in May-June 2004. EUFIC Forum 2005, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ovaskainen, M.L.; Torronen, R.; Koponen, J.M.; Sinkko, H.; Hellstrom, J.; Reinivuo, H.; Mattila, P. Dietary intake and major food sources of polyphenols in finnish adults. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, E.S.; Young, S.I.; Ho, S.K.; Mizura, S.S. Determination of vitamin C in fresh fruits and vegetables using the dye-titration and microfluorometric methods. Pertanika 1988, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rekha, C.; Poornima, G.; Manasa, M.; Abhipsa, V.; Devi, J.P.; Kumar, V.H.T.; Kekuda, T.R.P. Ascorbic acid, total phenol content and antioxidant activity of fresh juices of four ripe and unripe citrus fruits. Chem. Sci. Trans. 2012, 1, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusciante, L.; Carli, P.; Ercolano, M.R.; Pernice, R.; Di Mateo, A.; Fogliano, V.; Pellegrini, N. Antioxidant nutritional quality of tomato. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreiras, O.; Carbajal, A.; Cabrera, L.; Cuadrado, C. Ingestas Recomendadas de energía y nutrientes (Revisadas 2002). In Tablas de Composición de Alimentos; Ediciones Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kalac, P.; Svoboda, L. A review of trace element concentrations in edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, M.; Abete, I.; Baladia, E.; Corbalán, M.; Manera, M.; Basulto, J. Ingestas Dietéticas de Referencia (IDR) para la Población Española; Ediciones Universidad de Navarra; Federación Española de Sociedades de Nutrición, Alimentación y Dietética (FESNAD): Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Genccelep, H.; Uzun, Y.; Tunctürk, Y.; Demirel, K. Determination of mineral contents of wild-grown edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serratos-Arévalo, J.C. Aislamiento y Caracterización de Proteínas de Las Semillas Maduras de Enterolobium Cyclocarpium Para Su Aprovechamiento Alimenticio. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Colima, Colima, Mexico, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, R.; Domoney, C. The protein composition of legume seeds its variability and potential. In Proceedings of the Ire Conference Europeenne sur les Proteagineux, Angers, France, 1–3 June 1992; pp. 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Jambunathan, R.; Singh, U.; Subramanian, V. Grain quality of sorghum, pearl millet, pigeon-pea, and chick-pea. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Interfaces between Agriculture, Nutrition, and Food Science, Hyderabad, India, 10–12 November 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, L.; Ordorica, F.; Guevara, L.; Covarrubias, A. Las proteínas vegetales. Presente y futuro de la alimentación. In Prospectiva de la Biotecnología en México; Quintero, R., Ed.; CONACYT: México, Mexico, 1985; pp. 331–349.
- El-Noemani, A.; El-Zeiny, H.; El-Gindy, A.; El-Sahhar, E.A.; El-Shawadfy, M. Performance of some bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties under different irrigation systems and regimes. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 4, 6185–6196. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.K.; Zaki, E.M.; Abou-Sedera, F.A.; Abdallah, A.S. Effect of sowing dates and plant cultivar on growth, development and pod production of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) during summerseason. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2016, 9, 231–242. [Google Scholar]

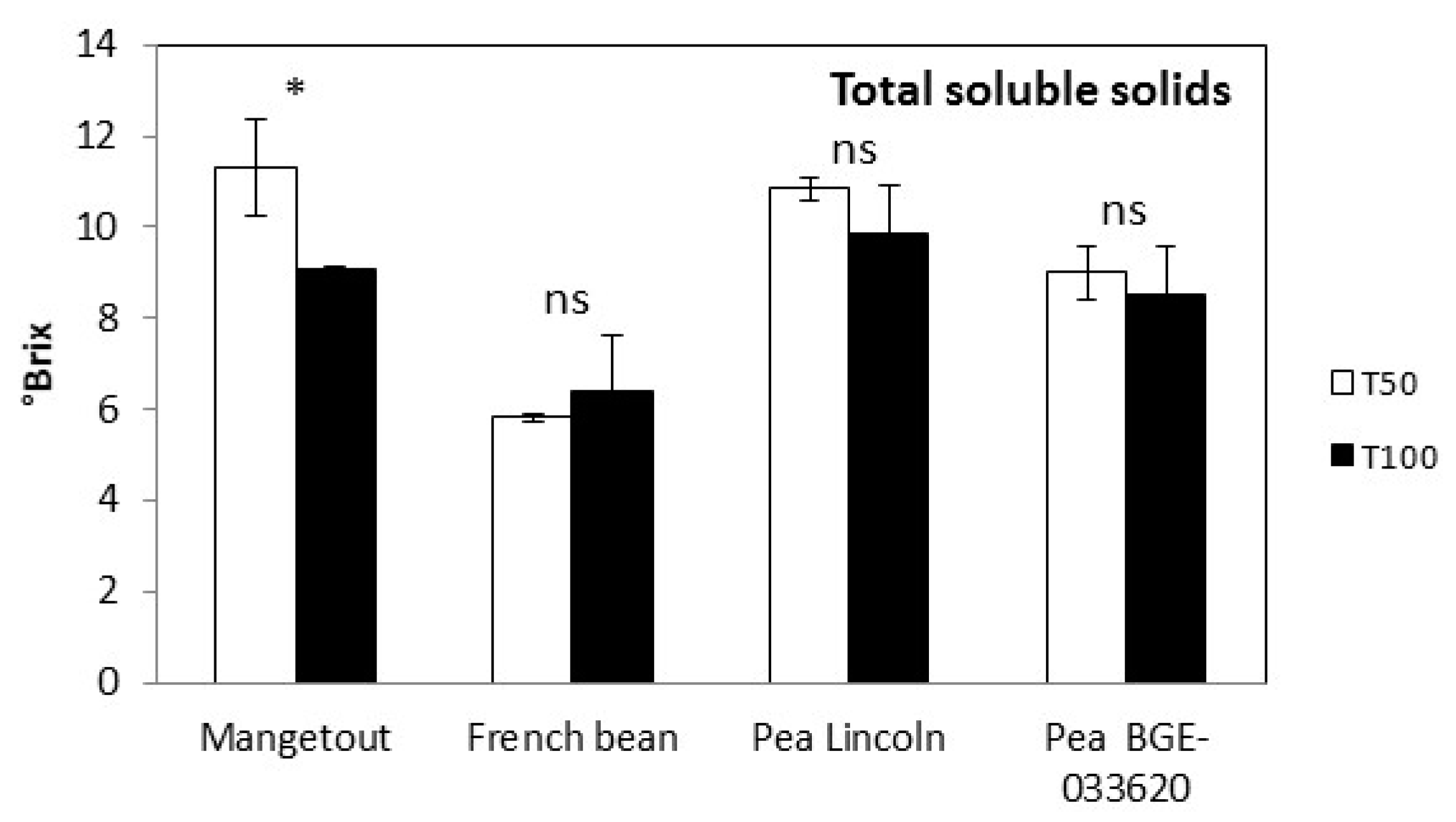

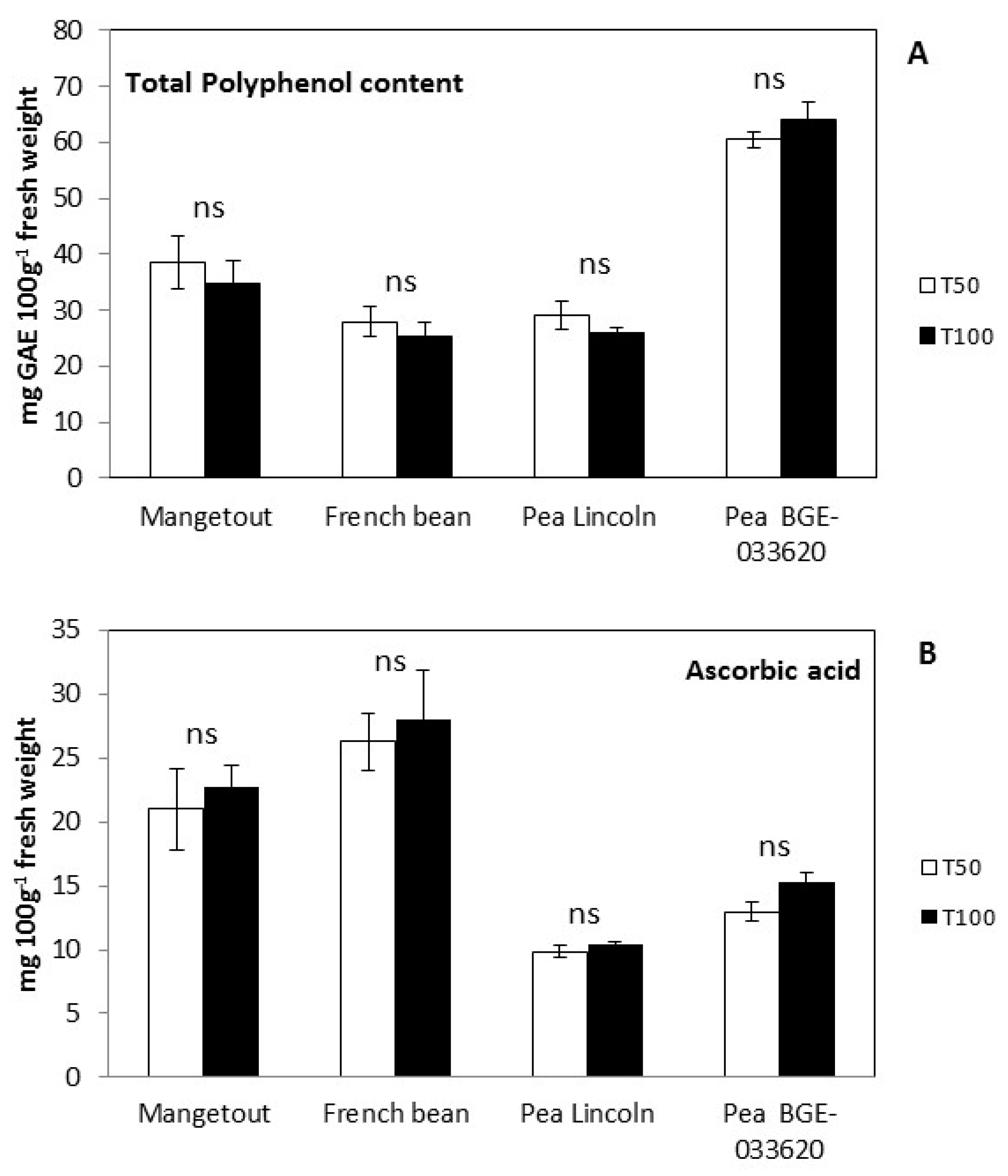
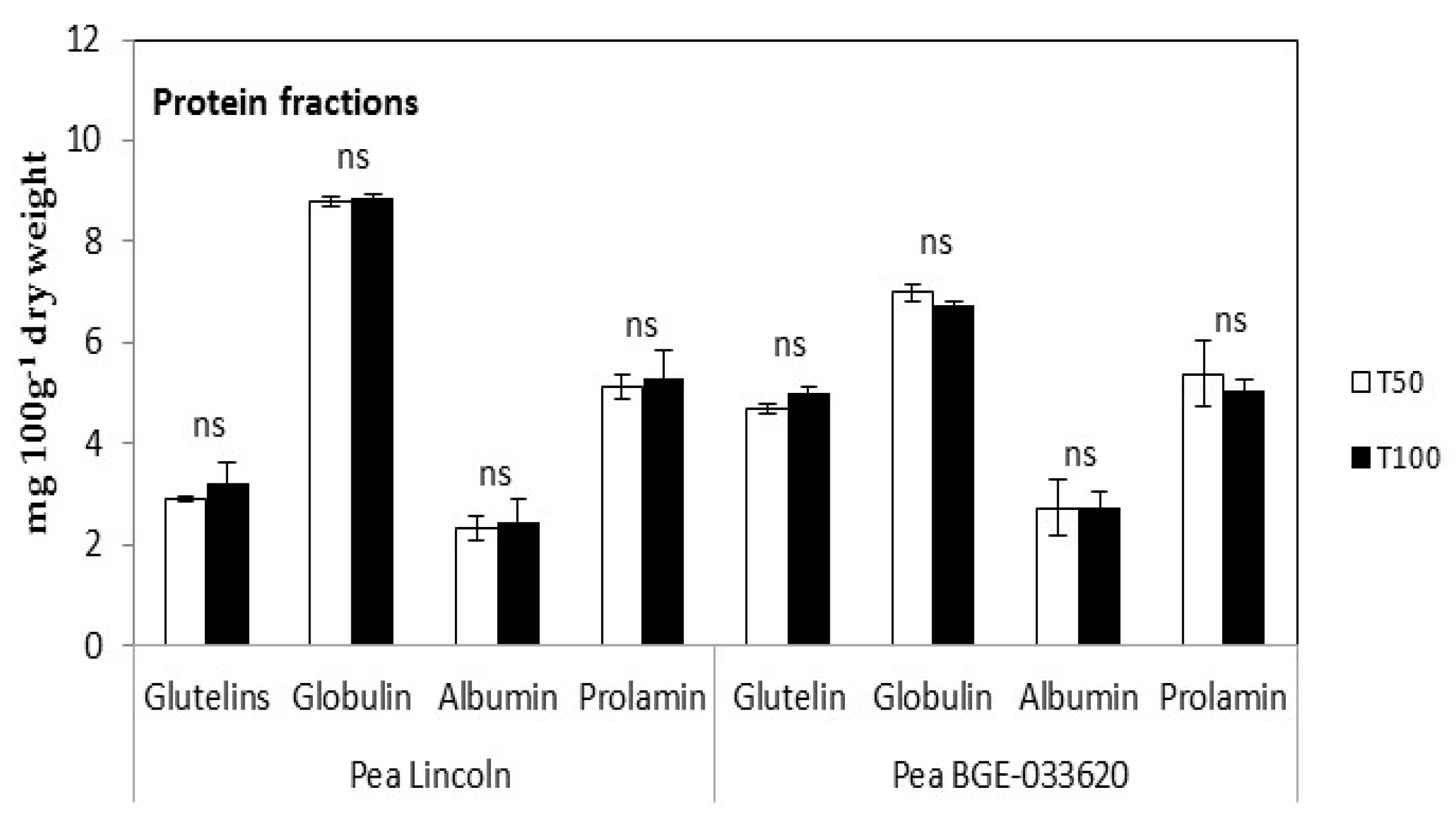
| Soil | EC | pH | Organic | Total | NO3− | P | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dS m−1) | Matter (%) | N (%) | (meq·L−1) | (meq·L−1) | (meq·L−1) | ||
| Before planting | 1.31 | 9.2 | 1.6 | 0.051 | 1.3 | 11 | 1.5 |
| After harvesting (T100) | 4.45 | 9.3 | 1.3 | 0.051 | 9.3 | 12.4 | 8.7 |
| After harvesting (T50) | 2.79 | 9.1 | 1.2 | 0.05 | 3.7 | 12 | 4.6 |
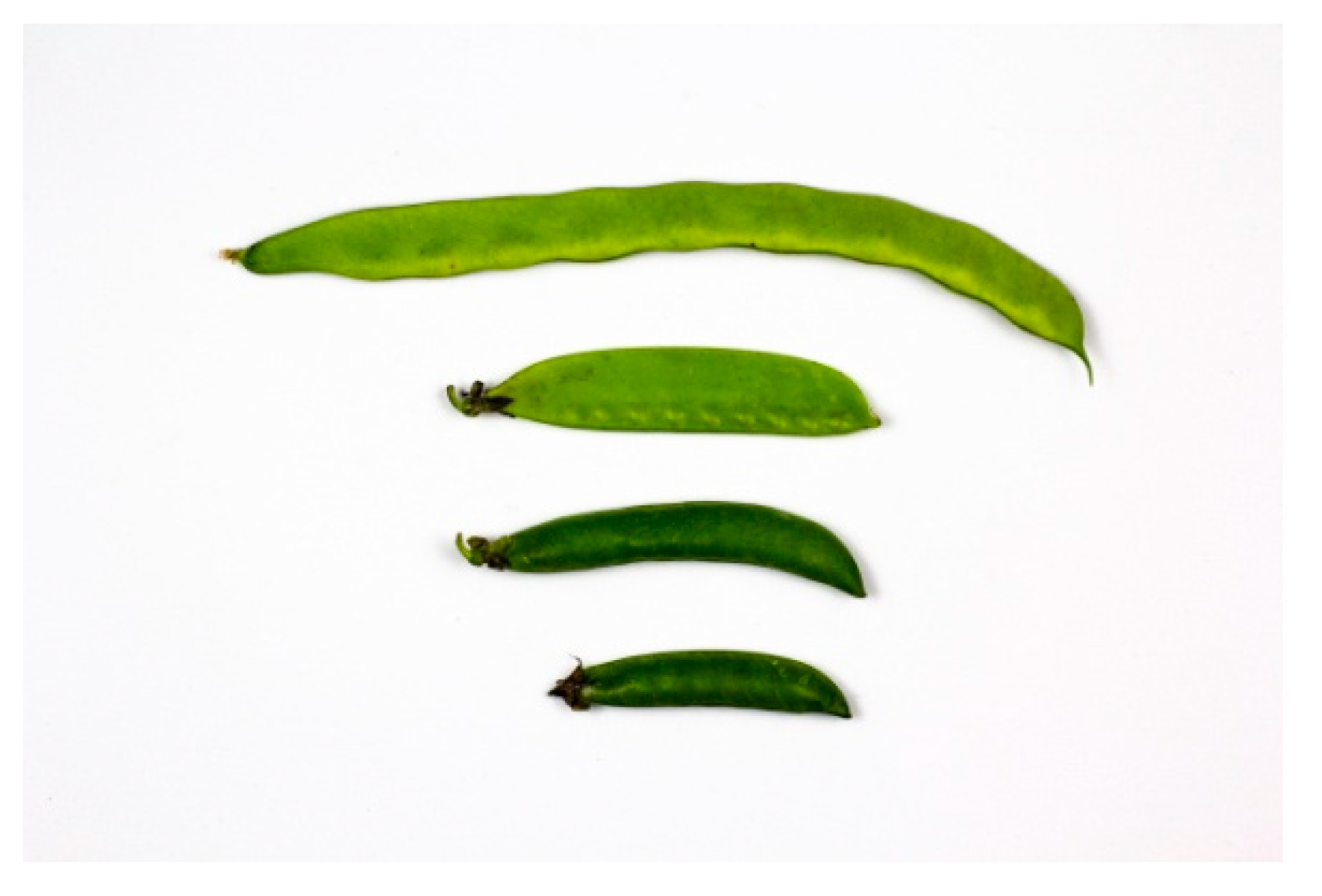
| Cultivar | Treatment | Length (mm) a | Width (mm) a | Height (mm) a | FW (g) b | Moisture (%) b | Firmness (N) b | C* b | Hue b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mangetout | T50 | 102.3 ± 0.4 | 23 ± 1.0 | 5.8 ± 0.5 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 85.2 ± 0.3 | 56.0 ± 3.0 | 33.0 ± 0.9 | 107.0 ± 0.6 |
| T100 | 104.7 ± 0.7 | 21.0 ± 1.0 *c | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | 84.2 ± 0.7 | 63.0 ± 7.3 | 32.0 ± 1.9 | 108.0 ± 0.2 | |
| French bean | T50 | 210.5 ± 0.2 | 18.6 ± 0.4 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 15.0 ± 0.8 | 91.1 ± 0.7 | 55.0 ± 3.5 | 27.0 ± 0.3 | 111.0 ± 0.1 |
| T100 | 229.7 ± 0.5 | 16.0 ± 1.8 *c | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 20.1 ± 1.8 *c | 91.2 ± 1.7 | 56.0 ± 11.1 | 29.0 ± 2.8 | 111.0 ± 1.7 | |
| Pea Lincoln | T50 | 10.9 ± 0.4 | 17.0 ± 0.8 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 24.4 ± 2.0 | 75.7 ± 2.1 | 33.0 ± 1.0 | 109.0 ± 0.5 | |
| T100 | 12.0 ± 0.8 | 15.0 ± 0.6 *c | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 24.2 ± 1.4 | 75.5 ± 1.5 | 34.0 ± 0.7 *c | 108.0 ± 0.4 | ||
| BGE-033620 | T50 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 12 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 20.2 ± 0.9 | 77.1 ± 0.8 | 39.0 ± 1.3 | 105.0 ± 0.5 | |
| T100 | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 12 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 22.9 ± 1.1 | 79.7 ± 1.9 *c | 39.0 ± 1.9 | 105.0 ± 0.2 |
| Cultivar | g 100g−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Protein | N | K | Ca | Mg | Na | Fe | Zn | Cu | Mn | |
| Mangetout | T50 | 20.0 ± 2.7 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.05 ± 0.0 | 44.6 ± 8.7 | 44.8 ± 6.5 | 3.7 ± 2.4 | 9.1 ± 1.6 |
| T100 | 21.1 ± 2.4 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.05 ± 0.0 | 44.5 ± 7.0 | 38.8 ± 1.9 | 3.2 ± 2.4 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | |
| French bean | T50 | 15.5 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.0 | 47.3 ± 6.3 | 26.8 ± 2.0 | 4.7 ± 1.3 | 17.8 ± 0.6 |
| T100 | 18.6 ± 1.6 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.0 | 44.0 ± 2,8 | 26.8 ± 1.2 | 5.0 ± 1.0 | 18.3 ± 2.5 | |
| Pea Lincoln | T50 | 25.6 ± 2.4 | 4.1 ± 0.8 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.0 | 52.5 ± 5.3 | 45.0 ± 3.0 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | 8.5 ± 0.9 |
| T100 | 27.8 ± 2.5 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.0 | 54.0 ± 2.5 | 49.0 ± 2.4 | 5.5 ± 0.8 | 7.5 ± 0.9 | |
| BGE-033620 | T50 | 24.7 ± 4.4 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.04 ± 0.0 | 54.5 ± 15.7 | 39.0 ± 10.8 | 2.8 ± 2.0 | 14.0 ± 0.5 *a |
| T100 | 23.8 ± 3.7 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.03 ± 0.0 | 47.1 ± 6.8 | 39.1 ± 8.8 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 12.5 ± 0.4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-García, M.d.C.; Font, R.; Gómez, P.; Valenzuela, J.L.; Fernández, J.A.; Del Río-Celestino, M. Effects of Fertigation Management on the Quality of Organic Legumes Grown in Protected Cultivation. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020028
García-García MdC, Font R, Gómez P, Valenzuela JL, Fernández JA, Del Río-Celestino M. Effects of Fertigation Management on the Quality of Organic Legumes Grown in Protected Cultivation. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-García, María del Carmen, Rafael Font, Pedro Gómez, Juan Luis Valenzuela, Juan A. Fernández, and Mercedes Del Río-Celestino. 2021. "Effects of Fertigation Management on the Quality of Organic Legumes Grown in Protected Cultivation" Horticulturae 7, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020028
APA StyleGarcía-García, M. d. C., Font, R., Gómez, P., Valenzuela, J. L., Fernández, J. A., & Del Río-Celestino, M. (2021). Effects of Fertigation Management on the Quality of Organic Legumes Grown in Protected Cultivation. Horticulturae, 7(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7020028









