The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
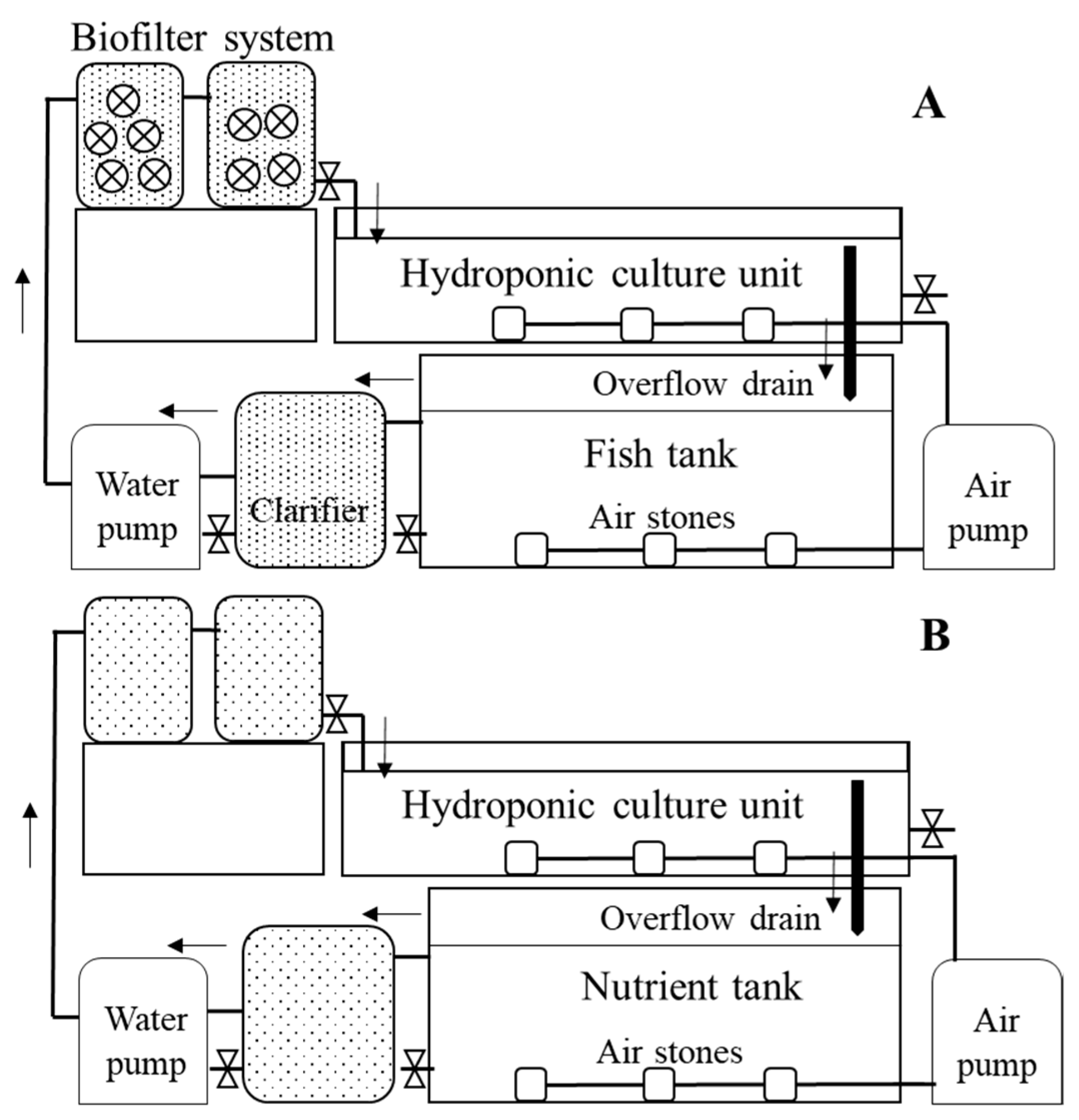
2.1. System Design
2.2. Plant Materials and Growing Conditions
2.3. Plant Sample Collection and Microbial Isolation
2.4. Microbial Detection in Water and Fish Feces Samples
2.5. PCR Assay for Detection of Virulence Genes
2.6. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Conditions for Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems
3.2. The occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC), Listeria Monocytogenes, and Salmonella spp.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redmond, E.C.; Griffith, C.J. Consumer perceptions of food safety risk, control and responsibility. Appetite 2004, 43, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, M.C.; Clarke, R.; Jaykus, L.A.; McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Frank, J.M. Climate change and food safety: A review. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1745–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, L.; Ximenes, E.; Seockmo, K.; Ladisch, M. Foodborne pathogens in horticultural production systems: Ecology and mitigation. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, A.J.; Mauer, L.J.; Pruitt, R.E. Internalization of E. coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. in plants: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, L.K.; Gröhn, Y.T.; Warchocki, S.; Worobo, R.W.; Bihn, E.A.; Wiedmann, M. Risk factors associated with salmonella and listeria monocytogenes contamination of produce fields. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7618–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadias, M.; Alegre, I.; Oliveira, M.; Altisent, R.; Viñas, I. Growth potential of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on fresh-cut fruits (melon and pineapple) and vegetables (carrot and escarole) stored under different conditions. Food Control 2012, 27, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashears, M.M.; Durre, W.A. Antagonistic Action of Lactobacillus lactis toward Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli O157:H7 during Growth and Refrigerated Storage. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.J.; Archer, P.; Banks, J.G. Growth of Listeria monocytogenes at refrigeration temperatures. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, J.A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Ayers, T.; Tauxe, R.V.; Braden, C.R.; Angulo, F.J.; Griffin, P.M. attribution of foodborne illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths to food commodities by using outbreak data, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey-Mattia, D.; Manikonda, K.; Hall, A.J.; Wise, M.E.; Crowe, S.J. Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States, 2009–2015. MMWR Surveill Summ 2018, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey-Mattia, D.; Kisselburgh, H.; Manikonda, K.; Silver, R.; Subramhanya, S.; Sundararaman, P.; Whitham, H.; Crowe, S. Surveillance for Foodborne Disease Outbreaks. Annual Report 2017; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fdoss/pdf/2017_FoodBorneOutbreaks_508.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Singleton, I.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Sources and contamination routes of microbial pathogens to fresh produce during field cultivation: A review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despommier, D. The vertical farm: Controlled environment agriculture carried out in tall buildings would create greater food safety and security for large urban populations. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 2011, 6, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Yang, T.; Lin, M.-Y.; Langenhoven, P. Plant propagation for successful hydroponic production. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1212, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Currey, C.J.; Dickson, R.W.; Kim, H.-J.; Hernández, R.; Sabeh, N.C.; Raudales, R.E.; Brumfield, R.G.; Laury-Shaw, A.; Wilke, A.K.; et al. Controlled environment food production for urban agriculture. HortScience 2019, 54, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; van Iersel, M.W.; Chen, J.; Brackett, R.E.; Beuchat, L.R. Evidence of association of Salmonellae with tomato plants grown hydroponically in inoculated nutrient solution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3639–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warriner, K.; Ibrahim, F.; Dickinson, M.; Wright, C.; Waites, W.M. Interaction of Escherichia coli with Growing Salad Spinach Plants. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, E.; Visser, A.; Vandiepeningen, A.; Klerks, M.; Termorshuizen, A.; Vanbruggen, A. Quantification of contamination of lettuce by GFP-expressing Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarisin, D.; Patel, J.; Sharma, V.K. Role of curli and plant cultivation conditions on Escherichia coli O157:H7 internalization into spinach grown on hydroponics and in soil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 173, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagrainie, K.K.; Flores, R.M.V.; Kim, H.-J.; McClain, V. Economic analysis of aquaponics and hydroponics production in the U.S. Midwest. J. Appl. Aquac. 2018, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Kim, H.-J. Nutrient management regime affects water quality, crop growth, and nitrogen use efficiency of aquaponic systems. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.A. Aquaponics and Food Safety. 2004. Available online: http://www.backyardaquaponics.com/Travis/Aquaponics-andFood-Safety.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Rakocy, J.E. Aquaponics—Integrating Fish and Plant Culture. In Aquaculture Production Systems; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 344–386. [Google Scholar]
- Enduta, A.; Jusoh, A.; Ali, N.; Wan Nik, W.B. Nutrient removal from aquaculture wastewater by vegetable production in aquaponics recirculation system. Desalin. Water Treat 2011, 32, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldreich, E.E.; Clarke, N.A. Bacterial Pollution Indicators in the Intestinal Tract of Freshwater Fish. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health Guidelines for the Use of Wastewater in Agriculture and Aquaculture; (WHO Technical Report Series No. 778), Report of a World Health Organization, (WHO) Scientific Group; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, T.V.R. Aquaculture and the Environment, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Pub: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-4051-0167-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, J.M.; Sparling, P.H.; Crowe, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Swerdlow, D.L. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Outbreaks, United States, 1982–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, B.J.; Mahon, B.E.; Griffin, P.M.; Gould, L.H.; Tauxe, R.V.; Crim, S.M.; Jackson, K.A.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Herman, K.M.; Henao, O.L. Vital Signs: Listeria Illnesses, Deaths, and Outbreaks—United States, 2009–2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 448–452. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, B.R.; Griffin, P.M.; Cole, D.; Walsh, K.A.; Chai, S.J. Outbreak-associated Salmonella enterica Serotypes and Food Commodities, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Popp, B.N.; Kim, H.-J.; Khanal, S.K. Fate of nitrogen in floating-raft aquaponic systems using natural abundance nitrogen isotopic compositions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 125, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, M.; Moreira, R.G.; Omac, B.; Castell-Perez, M.E. Quantifying the effectiveness of washing treatments on the microbial quality of fresh-cut romaine lettuce and cantaloupe. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.H.; Wang, H.; Jacobson, A.; Hammack, T. Bacteriological Analytical Manual (BAM) Chapter 5: Salmonella; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.; Weagant, S.D.; Grant, M.A.; Burkhardt, W. BAM 4: Enumeration of Escherichia coli and the Coliform bacteria; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fode-Vaughan, K.A.; Maki, J.S.; Benson, J.A.; Collins, M.L.P. Direct PCR detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemer, C.J.; Steadham, S.R. Evaluation of the specificity of Salmonella PCR primers using various intestinal bacterial species*. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaza, M.S.; Dhraïef, M.N.; Kraïem, M.M. Effects of water temperature on growth and sex ratio of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) reared in geothermal waters in southern Tunisia. J. Therm. Biol. 2008, 33, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, R.M.; Becker, N.G.; Hall, G.; Moodie, K.B.A. Does Ambient Temperature Affect Foodborne Disease? Epidemiology 2004, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadbolt, C.; Ross, T.; McMeekin, T.A. Differentiation of the effects of lethal pH and water activity: Food safety implications. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.Y.; Holley, R.A. Pathogen survival in Swine manure environments and transmission of human enteric illness—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, T.E.; Larkin, M.J.; Frost, J.P.; Levett, P.N. Survival of pathogenic bacteria during mesophilic anaerobic digestion of animal waste. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993, 75, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellajosyula, K.R.; Doores, S.; Mills, E.W.; Wilson, R.A.; Anantheswaran, R.C.; Knabel, S.J. Destruction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in Lebanon bologna by interaction of fermentaron pH, heating temperature, and time. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matches, J.R.; Liston, J. Effect of pH on low temperature growth of Samonella. J. Milk Food Technol. 1972, 35, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, B.; Ricke, S.C.; Johnson, M.G. Growth, survival, proliferation and pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes under low oxygen or anaerobic conditions: A review. Anaerobe 2009, 15, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukuku, D.O.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L. Growth parameters of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, and aerobic mesophilic bacteria of apple cider amended with Nisin–EDTA. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.R.S.; Beuchat, L.R. Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in broth and processed Salami as influenced by pH, water activity, and temperature and suitability of media for Its recovery. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Van Elsas, J.D.; Semenov, A.V.; Costa, R.; Trevors, J.T. Survival of Escherichia coli in the environment: Fundamental and public health aspects. ISME J. 2011, 5, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, L.; Miceli, A.; Francesca, N.; Cruciata, M.; Moschetti, G. Microbiological investigation of Raphanus sativus L. grown hydroponically in nutrient solutions contaminated with spoilage and pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 160, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allende, A.; Monaghan, J. Irrigation Water Quality for Leafy Crops: A Perspective of Risks and Potential Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7457–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.M.; Bisha, B.; Newman, S.E.; Bunning, M.; Goodridge, L.D. Transmission and Persistence of Salmonella enterica in Nutrient Solution of Hydroponic Greenhouse Grown Tomatoes. HortScience 2017, 52, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.V.; van Overbeek, L.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Influence of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in Luria–Bertani broth, farm-yard manure and slurry. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, E.; Bruggen, A.H.C. van Ecology of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica in the primary vegetable production chain. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 34, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagadala, S.; Marine, S.C.; Micallef, S.A.; Wang, F.; Pahl, D.M.; Melendez, M.V.; Kline, W.L.; Oni, R.A.; Walsh, C.S.; Everts, K.L.; et al. Assessment of region, farming system, irrigation source and sampling time as food safety risk factors for tomatoes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 196, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, P.; Kozyra, I.; Lazic, S.; Söderberg, K.; Vasickova, P.; Bouwknegt, M.; Rutjes, S.; Willems, K.; Moloney, R.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; et al. Virological Quality of Irrigation Water in Leafy Green Vegetables and Berry Fruits Production Chains. Food Environ. Virol. 2017, 9, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, N.; Duek, L.; Niv, S.; Hepher, B.; Sandbank, E. Microbiological aspects of fish grown in treated wastewater. Water Res. 1987, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apun, K.; Yusof, A.M.; Jugang, K. Distribution of bacteria in tropical freshwater fish and ponds. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1999, 9, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Doyle, M.P. Survival of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in water. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.; El-Timawy, A.K.; Ahmed, S. Role of aerobic intestinal pathogens of fresh water fish in transmission of human diseases. J. Food Prot. 1992, 55, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Maertens, M. Do private standards benefit workers in horticultural export chains in Peru? J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2392–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, H.; Chen, L.-J.; Jiang, R.; Wu, Y.-N. Food Safety Knowledge, Attitudes and Behavior among Dairy Plant Workers in Beijing, Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Shelton, D.R.; McLain, J.E.T.; Patel, J.; Mandrell, R.E. Irrigation Waters as a Source of Pathogenic Microorganisms in Produce: A Review. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2011; pp. 75–141. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, E.B.; Schoeni, J.L.; Wong, A.C.L. Effect of trisodium phosphate on biofilm and planktonic cells of Campylobacter jejuni, Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1994, 22, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanti, R.; Wong, A.C.L. Influence of culture conditions on biofilm formation by Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1995, 26, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlich, G.A.; Cooke, P.H.; Solomon, E.B. Analyses of the Red-Dry-Rough Phenotype of an Escherichia coli O157:H7 Strain and Its Role in Biofilm Formation and Resistance to Antibacterial Agents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, R.; Iturriaga, M.H.; Tamplin, M.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Call, J.E.; Luchansky, J.B.; Escartin, E.F. Animal and environmental impact on the presence and distribution of Salmonella and Escherichia coli in hydroponic tomato greenhouses. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 676–683. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, A.; Timmons, M.; Goddek, S.; Pentz, T. Bacterial Relationships in Aquaponics: New Research Directions. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Goddek, S., Joyce, A., Kotzen, B., Burnell, G.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 145–161. ISBN 978-3-030-15943-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, B.K.; Tamaru, C.S.; Hollyer, J.; Castro, L.F.; Fonseca, J.M.; Jay-Russell, M.; Low, T. A Preliminary Study of Microbial Water Quality Related to Food Safety in Recirculating Aquaponic Fish and Vegetable Production Systems. 2012. Available online: https://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/oc/freepubs/pdf/FST-51.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Joyce, T.M.; Mcguigan, K.G.; Elmore-Meegan, M.; Conroy, R.M. Inactivation of fecal bacteria in drinking water by solar heating. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, S.R.; Moore, J.A. Modeling enteric bacterial die-off: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut 1986, 27, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, C.; Barnhart, C.; Ringle, D. Food Safety Hazards Associated with Smooth Textured Leafy Greens Produced in Aquaponic, Hydroponic, and Soil-Based Systems with and Without Roots in Retail. Minnesota Aquaponics Conference Posters, MN, USA. 2015. Available online: https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/172223 (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Saylor, L.R.; Turkon, P. Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Presence in Hydroponic and Aquaponic Systems: An Exploratory Case Study. 2018. Available online: https://digitalcommons.ithaca.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1397&context=whalen (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Wachtel, M.R.; Whitehand, L.C.; Mandrell, R.E. Association of Escherichia coli O157:H7 with preharvest leaf lettuce upon exposure to contaminated irrigation water. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.H.; Walsh, K.A.; Vieira, A.R.; Herman, K.; Williams, I.T.; Hall, A.J.; Cole, D. Surveillance for Foodborne Disease Outbreaks—United States, 1998–2008; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, J.M.; Sumner, S.S.; Boyer, R.R.; Williams, R.C.; Latimer, J.G.; McKinney, J.M. Internalization of Salmonella enterica serovar Montevideo into greenhouse tomato plants through contaminated irrigation water or seed stock. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sequence | PCR Program | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) | |||
| stx1-F | CAGTTAATGTGGTGGCGAAG | 95 °C for 3 min, 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min, repeat steps 2–4 30 times, 72 °C for 10 min | [35] |
| stx1-R | CACCAGACAATGTAACCGCTG | ||
| Salmonella spp. | |||
| iroB-F | TGCGTATTCTGTTTGTCGGTCC | 95 °C for 3 min, 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min, repeat steps 2–4 30 times, 72 °C for 10 min | [36] |
| iroB-R | TACGTTCCCACCATTCTTCCC |
| Production System | Vegetable | DO z (mg/L) | pH | Temperature (°C) | EC (dS/m) | NH4+ (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaponics | Lettuce | 6.1 ± 0.7 y | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 27.5 ± 1.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 74.7 ± 10.8 |
| Basil | 6.2 ± 0.7 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 25.9 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 50.8 ± 4.9 | |
| Tomato | 6.1 ± 0.7 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 27.5 ± 1.7 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 83.1 ± 13.8 | |
| Hydroponics | Lettuce | 10.0 ± 0.4 | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 20.3 ± 1.4 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | nd x | 77.5 ± 7.8 |
| Basil | 10.0 ± 0.4 | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 20.2 ± 1.2 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | nd | 73.9 ± 7.0 | |
| Tomato | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 5.8 ± 0.6 | 20.5 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | nd | 95.5 ± 9.4 | |
| Significance | ||||||||
| System | *** w | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| Vegetable | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| System × Vegetable | ns | ns | ns | ns | *** | ns | ns | |
| Vegetable | Tissue Type | Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli | L. monocytogenes | Salmonella spp. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaponics | Hydroponics | Aquaponics | Hydroponics | Aquaponics | Hydroponics | ||
| Lettuce | Internal leaf | – z | – | – | – | – | – |
| Leaf surface | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Internal root | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Root surface | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Water | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Fish feces | + | NA | – | NA | – | NA | |
| Basil | Internal leaf | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Leaf surface | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Internal root | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Root surface | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Water | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Fish feces | + | NA | – | NA | – | NA | |
| Tomato | Fruit | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Internal root | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Root surface | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Water | + | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Fish feces | + | NA | – | NA | – | NA | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-J.; Deering, A.J.; Kim, H.-J. The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6010001
Wang Y-J, Deering AJ, Kim H-J. The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems. Horticulturae. 2020; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Ju, Amanda J. Deering, and Hye-Ji Kim. 2020. "The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems" Horticulturae 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6010001
APA StyleWang, Y.-J., Deering, A. J., & Kim, H.-J. (2020). The Occurrence of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli in Aquaponic and Hydroponic Systems. Horticulturae, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6010001






