Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Growth Regulatory Factor (GRF) and Growth-Regulating Interacting Factor (GIF) Gene Families in Cassava
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the MeGRFs and MeGIFs Gene in the Cassava Genome
2.2. Phylogenetic, Conserved Motif, and Gene Structure Analysis
2.3. Cis-Acting Element Analysis of the MeGRFs and MeGIFs Promoters
2.4. Expression Profiles of MeGRFs and MeGIFs Genes
2.5. Synteny Analysis of MeGRFs and MeGIFs Family Genes
2.6. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.7. Interaction Analysis Between MeGRFs and MeGIFs Family Proteins
2.8. Coexpression Analysis of MeGRFs and MeGIFs
2.9. Plasmid Construction and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing
2.10. Statistical Method
3. Results
3.1. Identification Analysis of the MeGRFs and MeGIFs Gene in the Cassava Genome
3.2. Phylogenetic, Conserved Motif, and Gene Structure Analysis
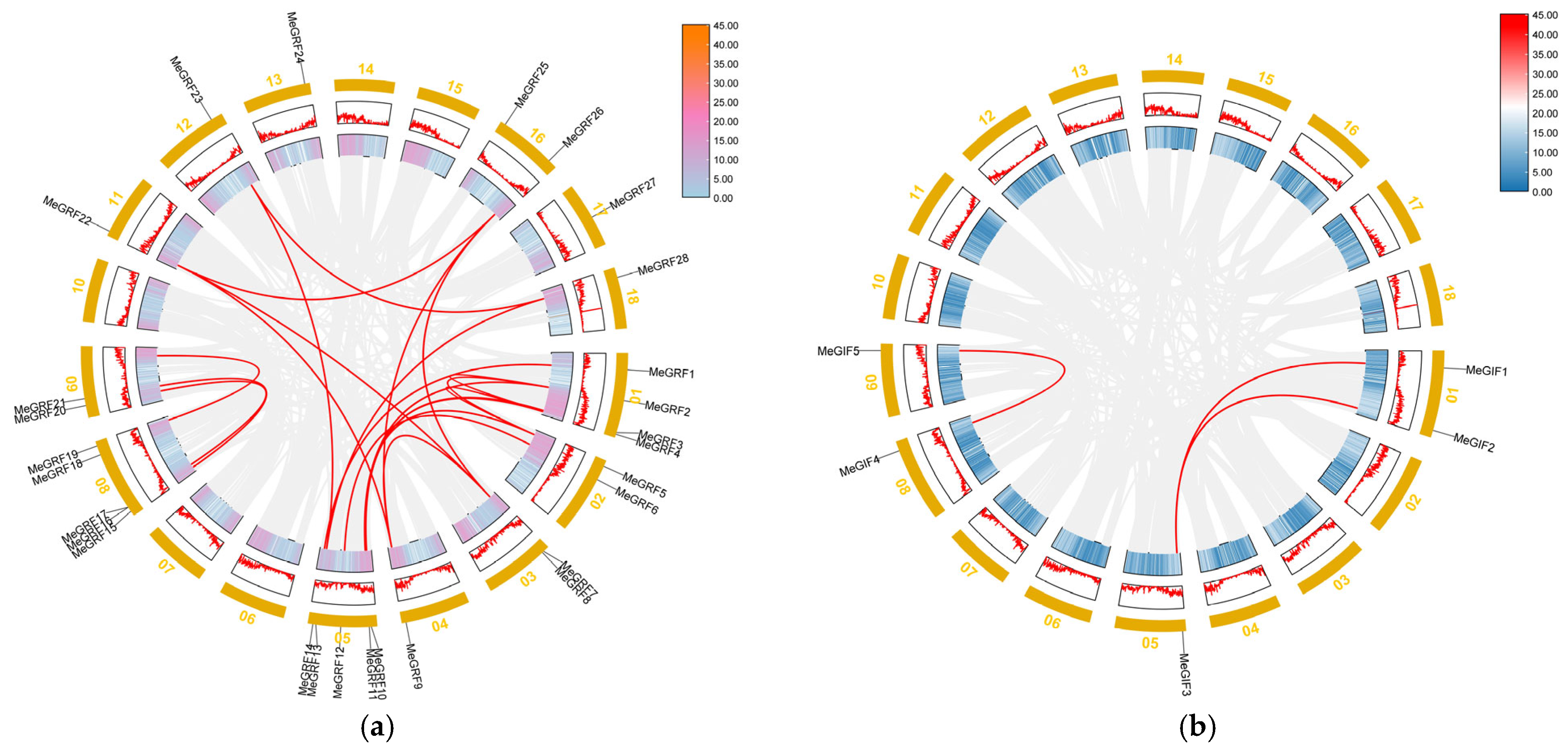
3.3. Synteny Analysis of MeGRFs and MeGIFs Genes
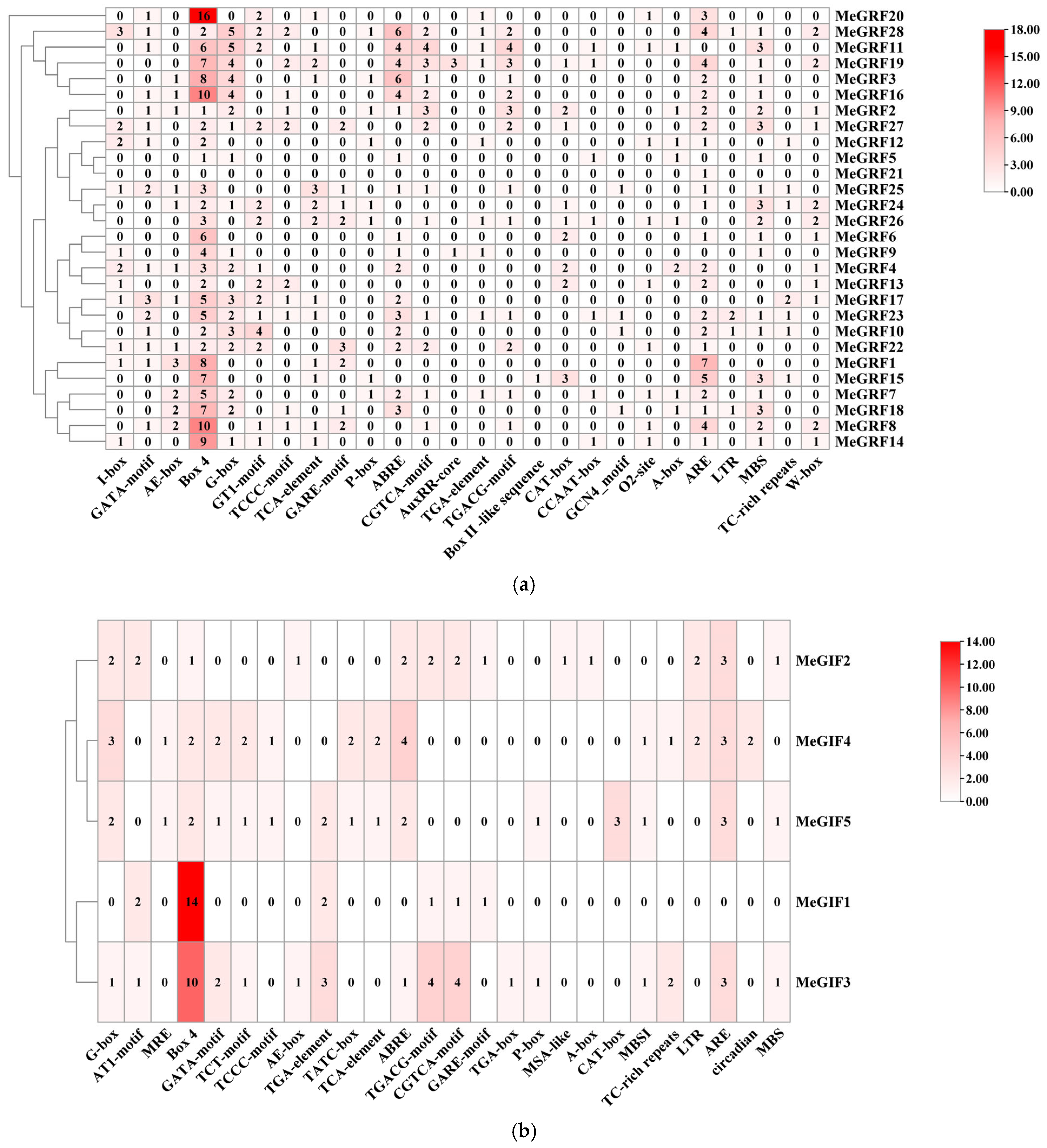
3.4. Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of MeGRFs and MeGIFs Genes
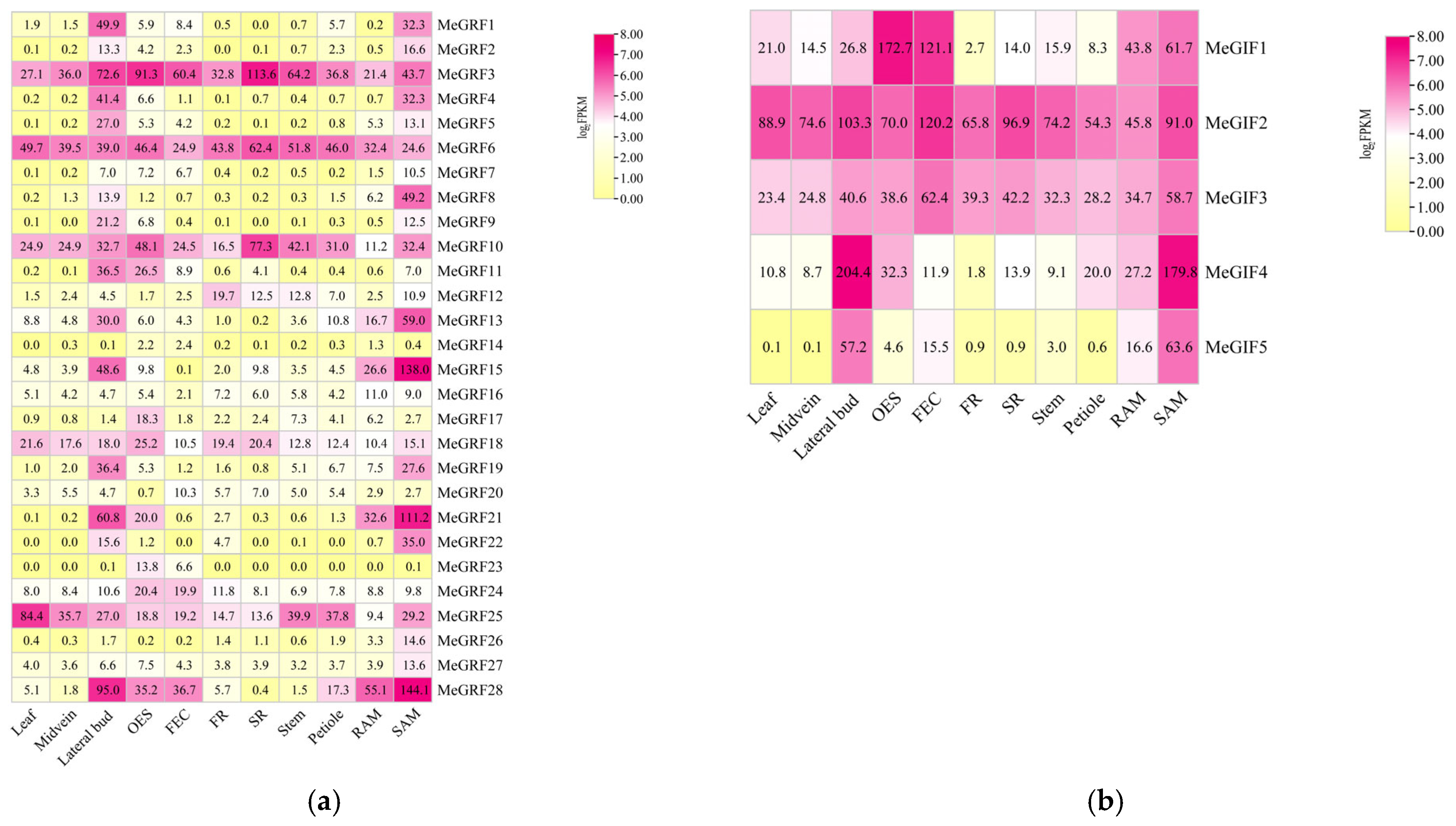
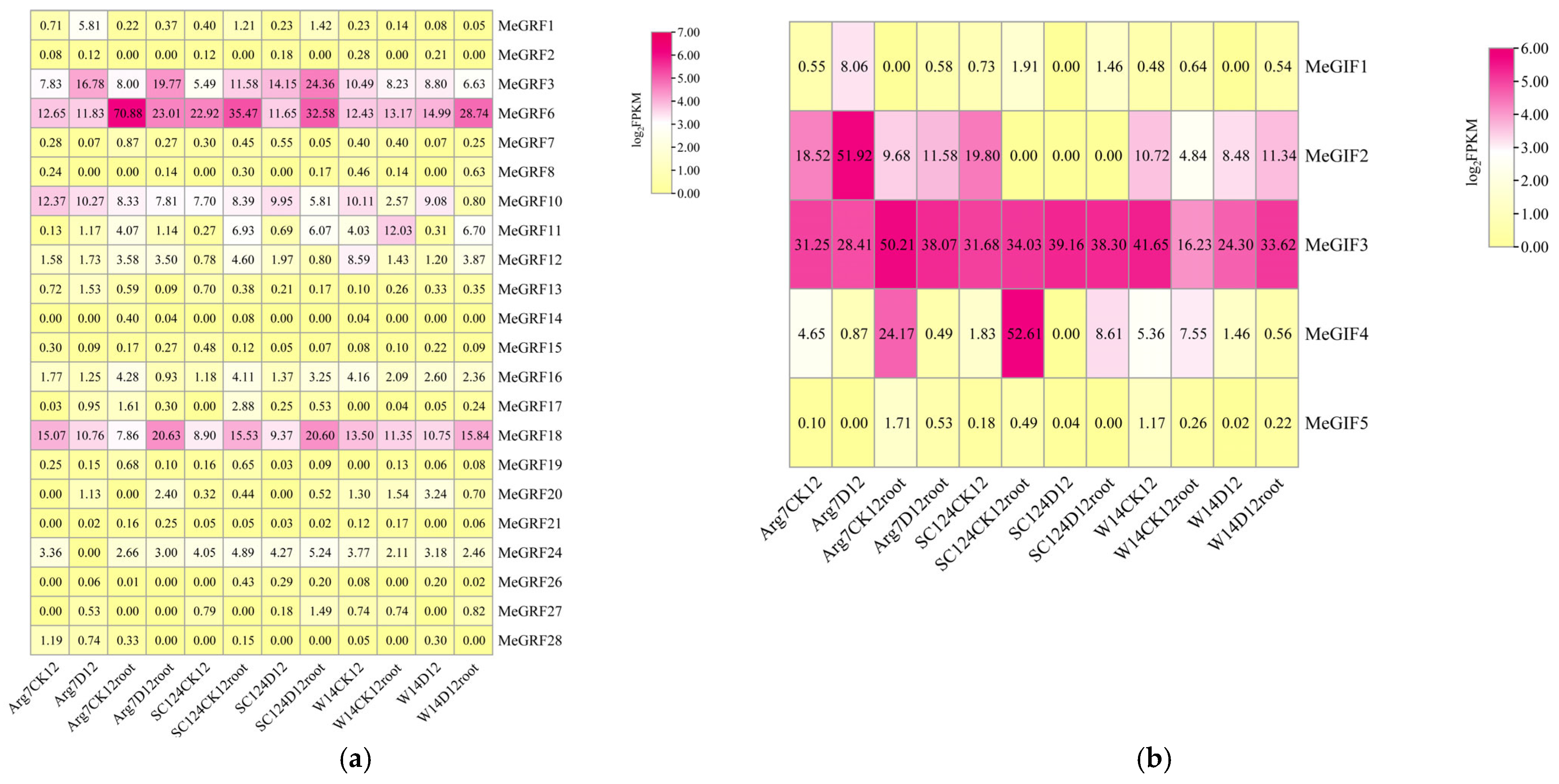
3.5. Tissue-Specific Expression of MeGRFs and MeGIFs in Cassava
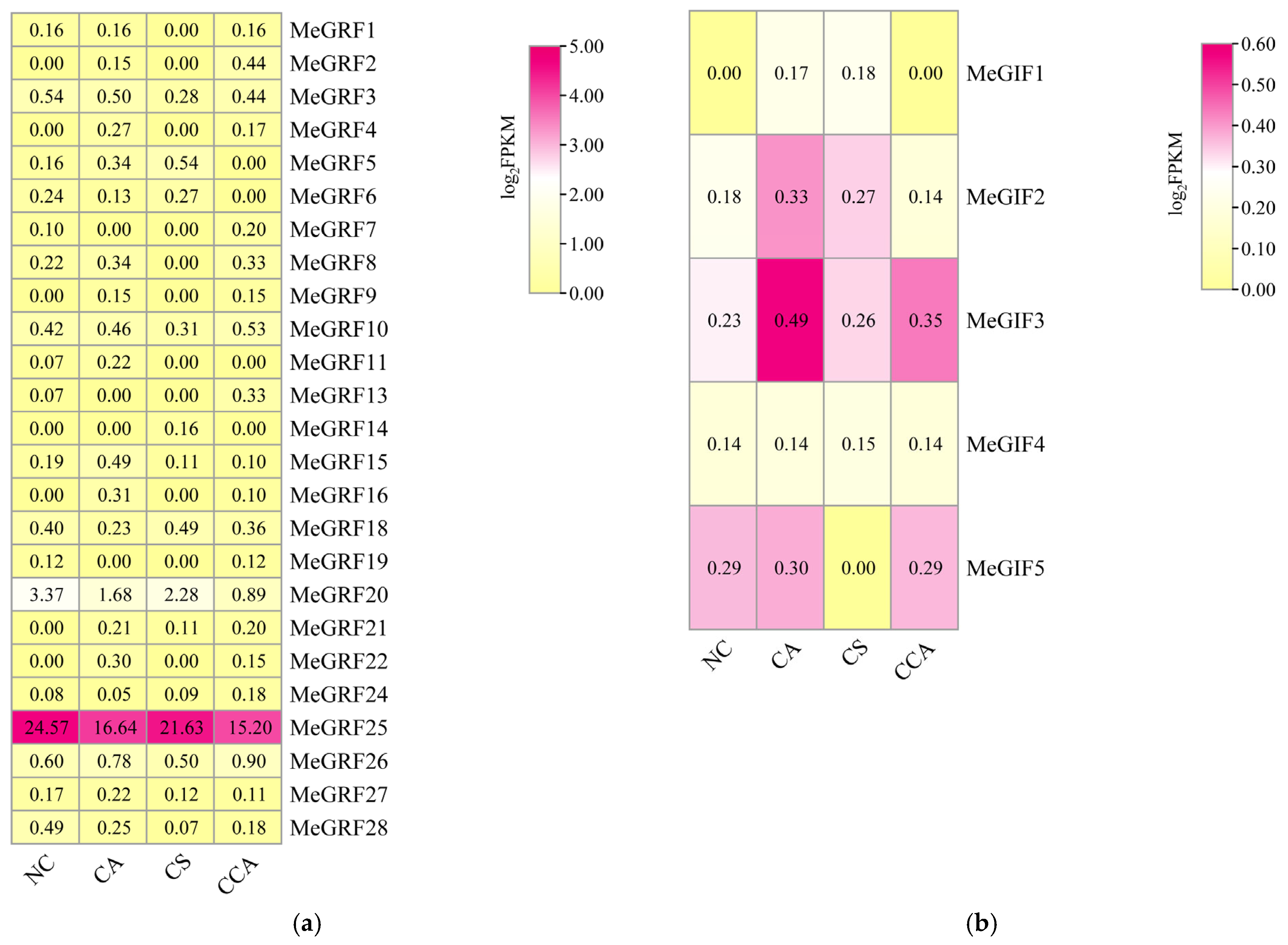
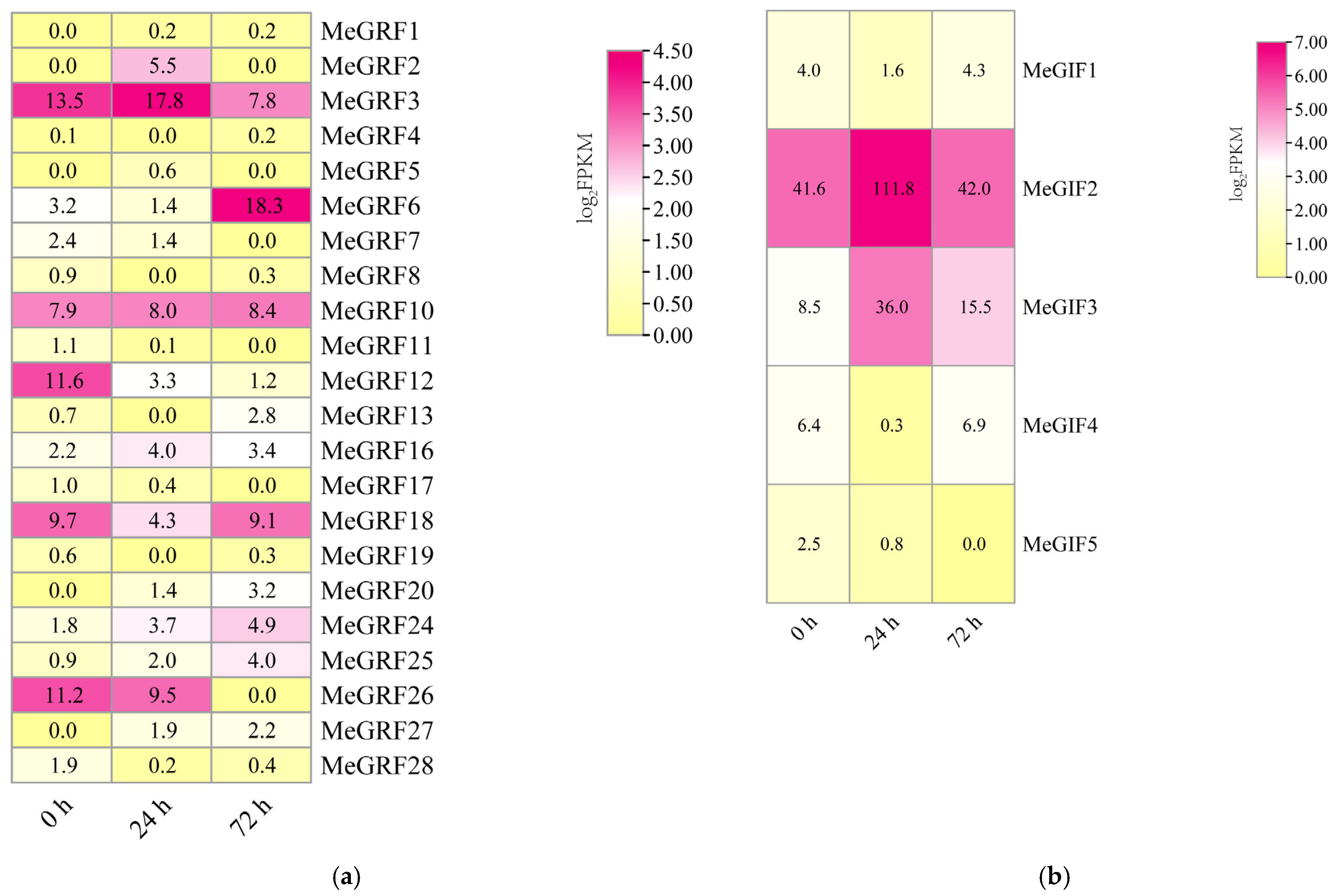
3.6. Expression Analysis of MeGRFs and MeGIFs Under Different Biotic and Abiotic Stresses
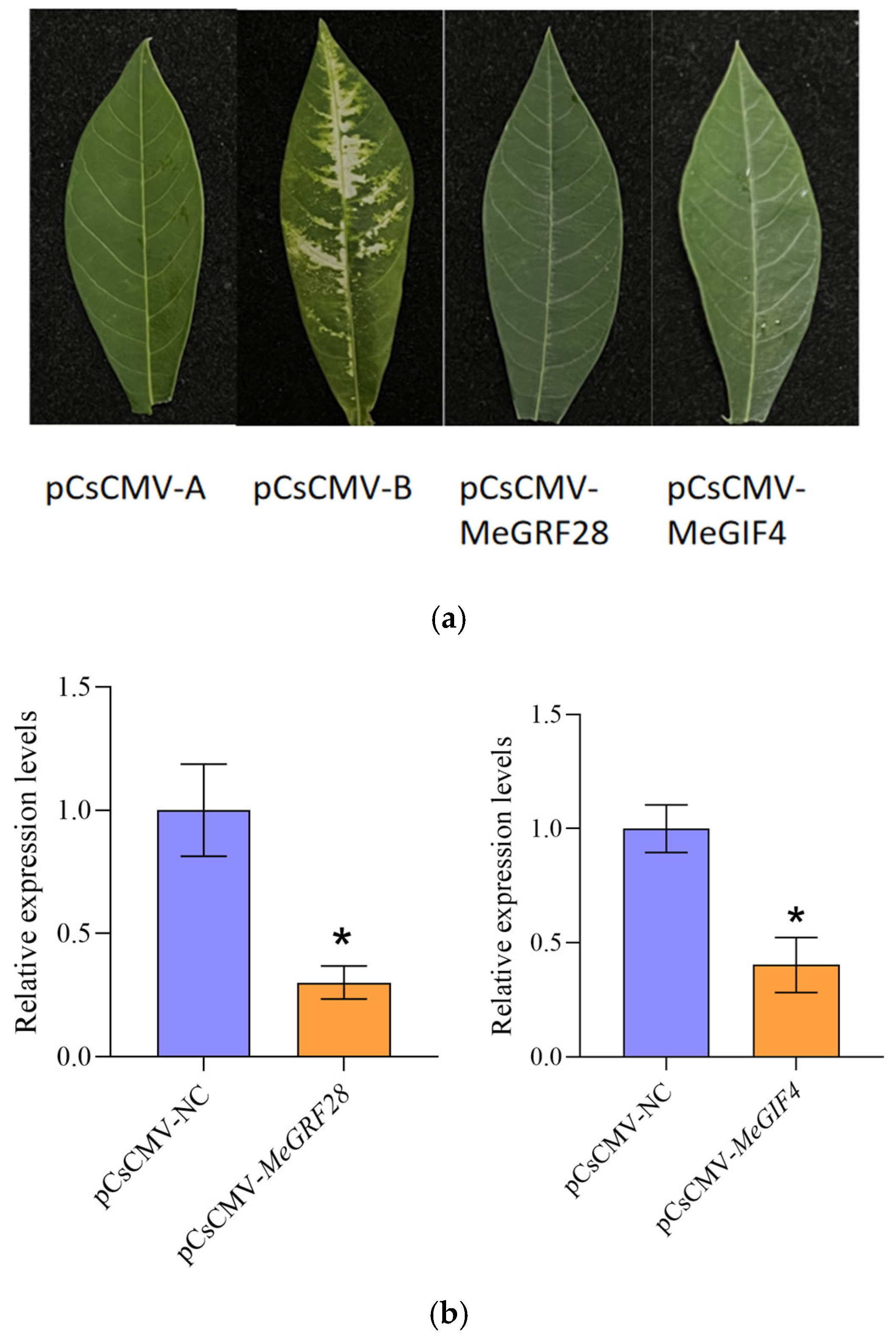
3.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
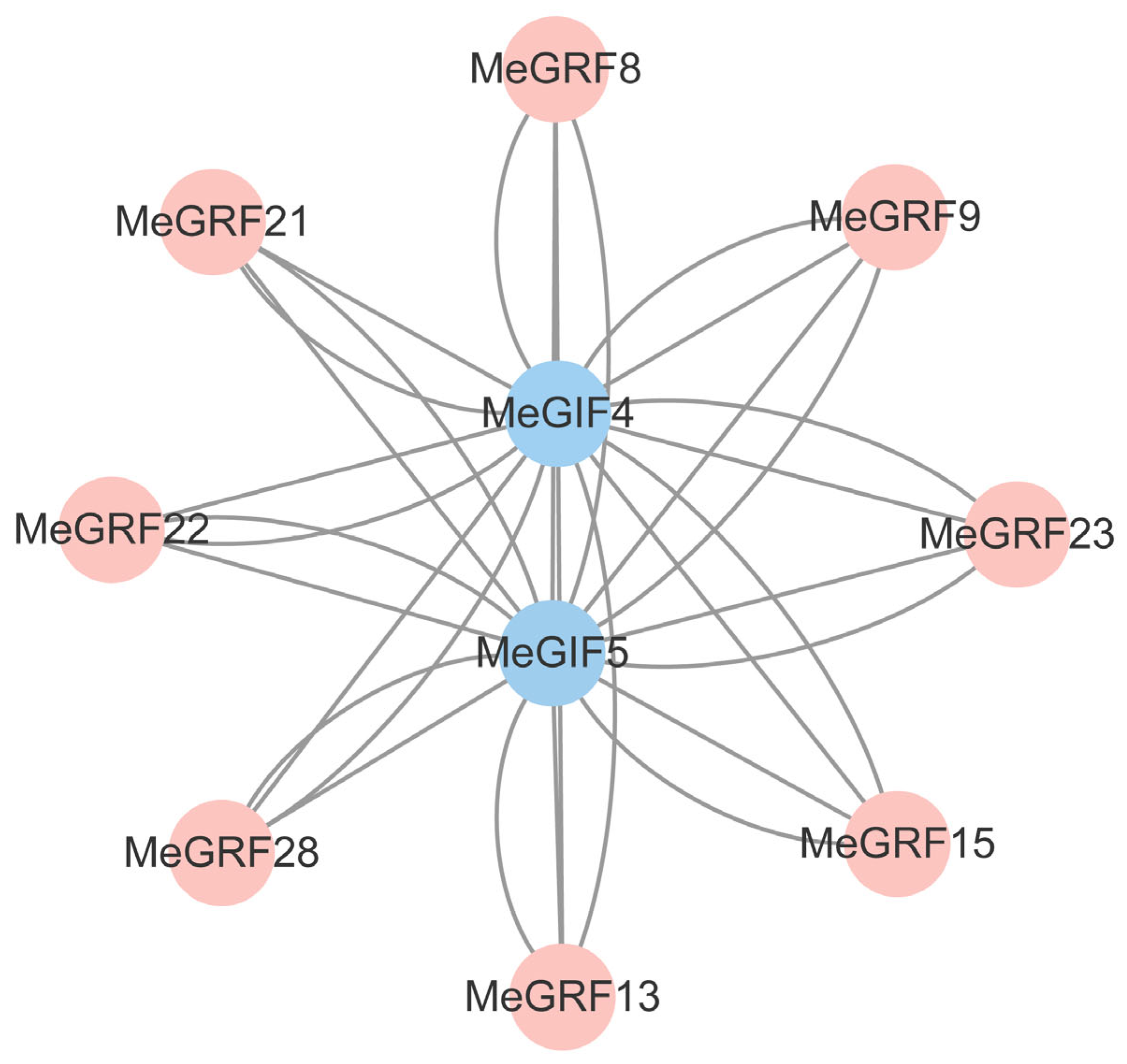
3.8. Interaction Analysis Between MeGRFs and MeGIFs Family Proteins
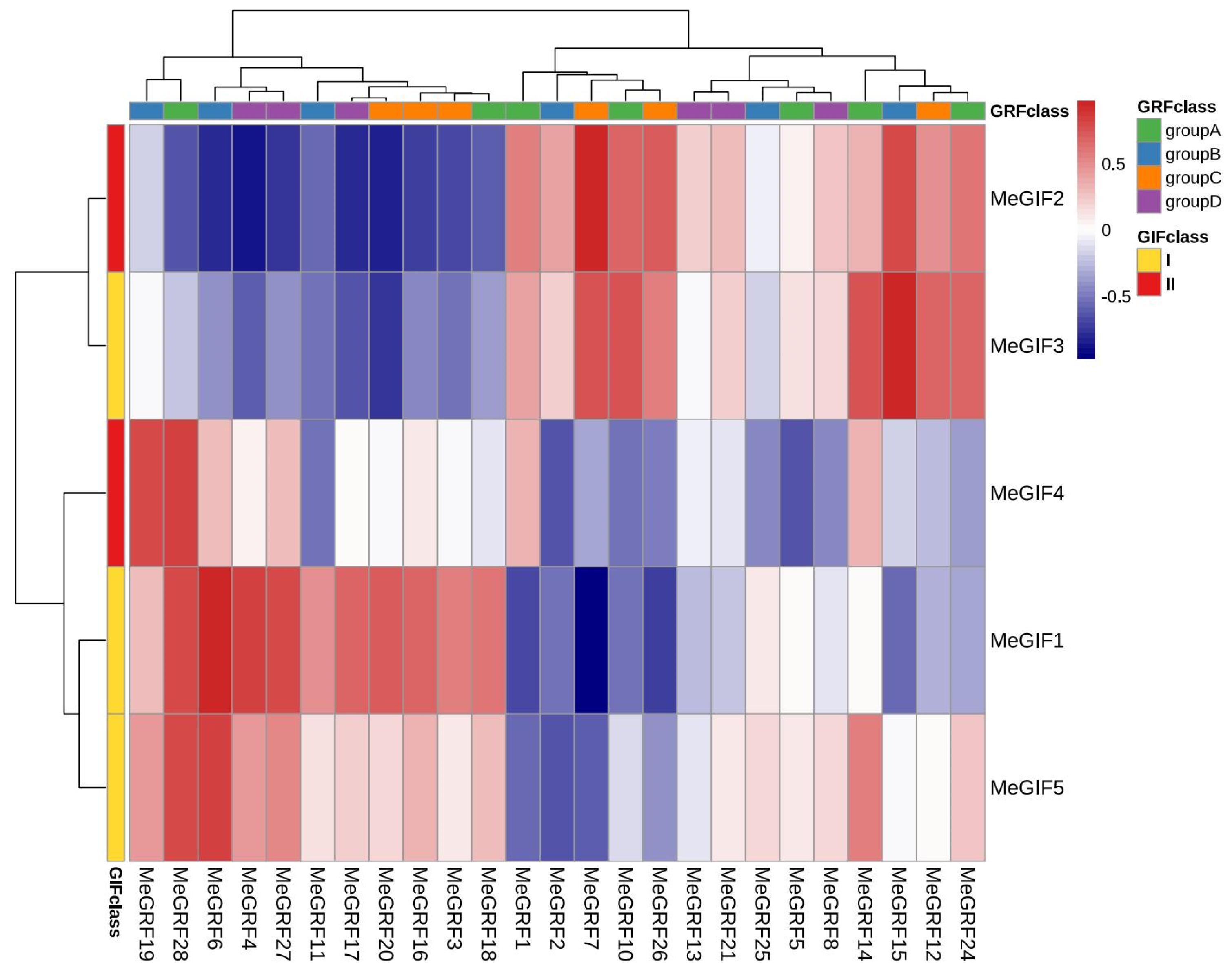
3.9. Coexpression Analysis Between MeGRFs and MeGIFs
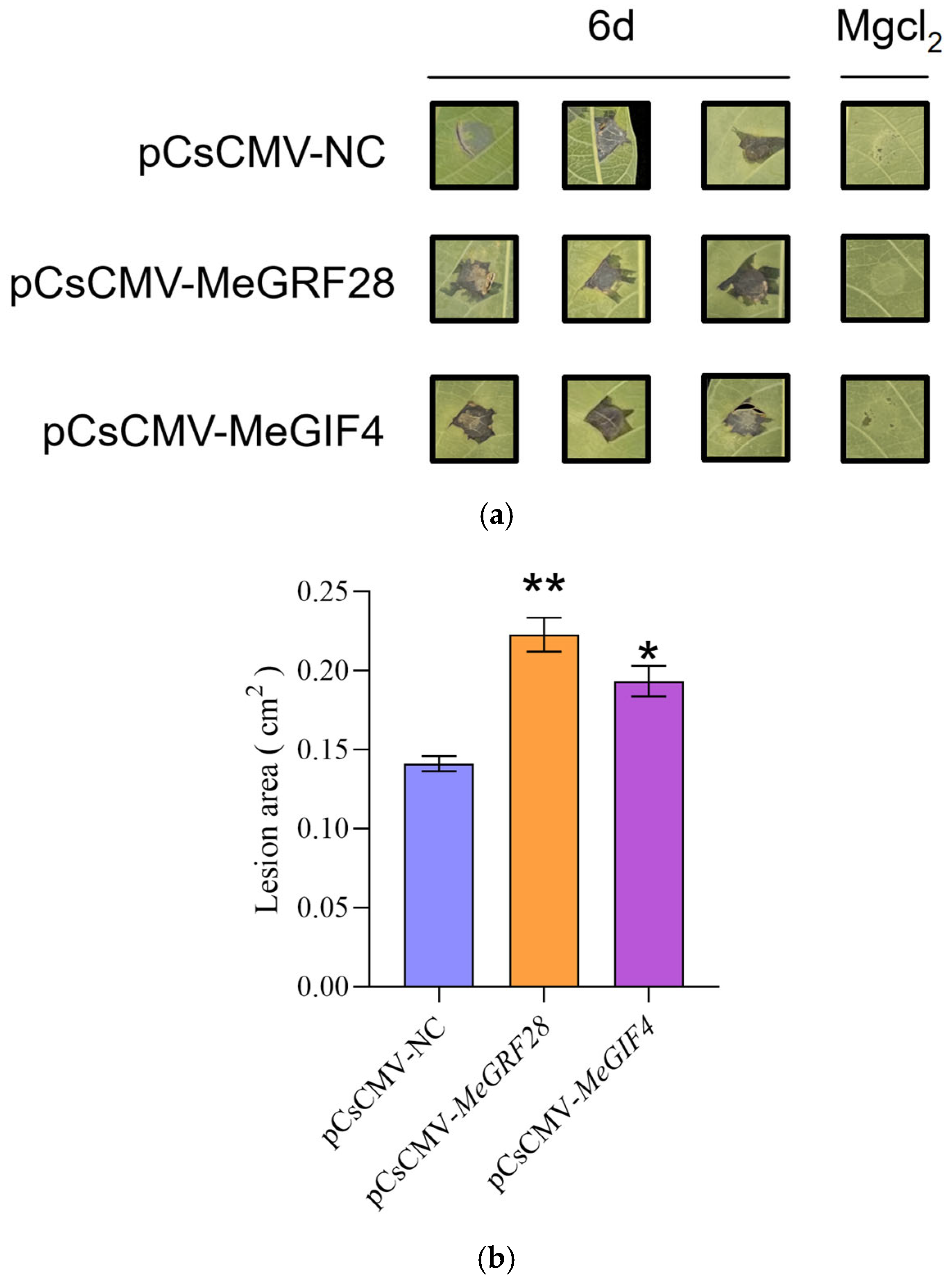
3.10. The Resistance of Cassava Plants to Bacterial Wilt Was Changed After Silencing MeGRF28 and MeGIF4 Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. MeGRFs and MeGIFs: An Overview of Evolution and Function
4.2. The Role of MeGRF and MeGIF in Growth and Development
4.3. Expression Changes Under Pathogen Stress (XpmCNH11 Infection)
4.4. GRF-GIF Coexpression and Interaction Networks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dufour, D.L. Cyanide content of cassava (Manihot esculenta, Euphorbiaceae) cultivars used by Tukanoan Indians in Northwest Amazonia. Econ. Bot. 1988, 42, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essers, A.J.A. Removal of Cyanogens from Cassava Roots Studies on Domestic Sun-Drying and Solid-Substrate Fermentation in Rural Africa; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Montagnac, J.A.; Davis, C.R.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Nutritional Value of Cassava for Use as a Staple Food and Recent Advances for Improvement. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Gleadow, R.; Cliff, J.; Zacarias, A.; Cavagnaro, T. Cassava: The Drought, War and Famine Crop in a Changing World. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3572–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howeler, R.H.; Lutaladio, N.; Thomas, G. Save and Grow: Cassava: A Guide to Sustainable Production Intensification; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wydra, K.; Zinsou, V.; Jorge, V.; Verdier, V. Identification of Pathotypes of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Africa and Detection of Quantitative Trait Loci and Markers for Resistance to Bacterial Blight of Cassava. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, E.J.; Anjanappa, R.B.; Gruissem, W. Tackling agriculturally relevant diseases in the staple crop cassava (Manihot esculenta). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, G.; He, C.; Shi, H. Functional characterization of WHY-WRKY75 transcriptional module in plant response to cassava bacterial blight. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veley, K.M.; Elliott, K.; Jensen, G.; Zhong, Z.; Feng, S.; Yoder, M.; Gilbert, K.B.; Berry, J.C.; Lin, Z.D.; Ghoshal, B.; et al. Improving cassava bacterial blight resistance by editing the epigenome. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Brugger, A.; Lamotte, O.; Vandelle, E.; Bourque, S.; Lecourieux, D.; Poinssot, B.; Wendehenne, D.; Pugin, A. Early signaling events induced by elicitors of plant defenses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Functional analysis of transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscaill, P.; Rivas, S. Transcriptional control of plant defence responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 20, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Xie, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Ruan, M. MeWRKY30, a cassava stress-responsive WRKY transcription factor, confers drought resistance to transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; He, Q.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, P.F.; Xu, J.M.; Zheng, S.J.; Fan, W.; Yang, J.L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) during aluminum stress. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborough, W.; Gentle, N.; Rey, M.E.C. WRKY Transcription Factors in Cassava Contribute to Regulation of Tolerance and Susceptibility to Cassava Mosaic Disease through Stress Responses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Hai, M.; Guo, Y.; Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Ding, X.; Yan, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. The ERF transcription factor family in cassava: Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses against drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; An, F.; Chen, S.; Qin, X. Expression Pattern and Functional Analysis of MebHLH149 Gene in Response to Cassava Bacterial Blight. Plants 2024, 13, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Gou, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Pi, E. Regulatory Mechanisms of bHLH Transcription Factors in Plant Adaptive Responses to Various Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 677611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, K.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Si, H. MYB transcription factors: Acting as molecular switches to regulate different signaling pathways to modulate plant responses to drought stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 226, 120676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokolia, M.; Tv, N.; Priya, J.C.; Singh, B. GRAS transcription factor-Genome-wide identification characterization expression analysis in Avena sativa, L. under salinity stress. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. Whole genome analysis of the OsGRF gene family encoding plant-specific putative transcription activators in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Knaap, E.; Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. A novel gibberellin-induced gene from rice and its potential regulatory role in stem growth. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treich, I.; Cairns, B.R.; de los Santos, T.; Brewster, E.; Carlson, M. SNF11, a new component of the yeast SNF-SWI complex that interacts with a conserved region of SNF2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perani, M.; Ingram, C.J.; Cooper, C.S.; Garrett, M.D.; Goodwin, G.H. Conserved SNH domain of the proto-oncoprotein SYT interacts with components of the human chromatin remodelling complexes, while the QPGY repeat domain forms homo-oligomers. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8156–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. Biological roles and an evolutionary sketch of the GRF-GIF transcriptional complex in plants. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): A Small Transcription Factor Family with Important Functions in Plant Biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, M.; Dong, Y. Genome-wide molecular evolution analysis of the GRF and GIF gene families in Plantae (Archaeplastida). BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.; Kende, H. The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 36, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Park, J.I.; Nath, U.K.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, K.B.; Nou, I.S.; Chung, M.Y. Molecular Characterization and Expression Profiling of Tomato GRF Transcription Factor Family Genes in Response to Abiotic Stresses and Phytohormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Mizoi, J.; Kidokoro, S.; Maruyama, K.; Nakajima, J.; Nakashima, K.; Mitsuda, N.; Takiguchi, Y.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Kondou, Y.; et al. Arabidopsis growth-regulating factor7 functions as a transcriptional repressor of abscisic acid- and osmotic stress-responsive genes, including DREB2A. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3393–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baucher, M.; Moussawi, J.; Vandeputte, O.M.; Monteyne, D.; Mol, A.; Pérez-Morga, D.; El Jaziri, M. A role for the miR396/GRF network in specification of organ type during flower development, as supported by ectopic expression of Populus trichocarpa miR396c in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biol. 2013, 15, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pei, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Kou, G.; Niu, W.; He, R.; Gong, R. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the GRF and GIF Gene Families in Prunus avium. Agronomy 2025, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-F.; Li, B.; Jia, G.-Q.; Zhang, T.-F.; Dai, J.-R.; Li, J.-S.; Wang, S.-C. Isolation and characterization of genes encoding GRF transcription factors and GIF transcriptional coactivators in Maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13374–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Qiu, N.; Ding, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, J. Genome-wide identification analysis of the growth-regulating factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa, L. ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Lv, K.; Du, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Kang, X.; Wei, H. Growth-regulating factor 5 (GRF5)-mediated gene regulatory network promotes leaf growth and expansion in poplar. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Molecular mechanism of microRNA396 mediating pistil development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Chong, K. OsmiR396d-regulated OsGRFs function in floral organogenesis in rice through binding to their targets OsJMJ706 and OsCR4. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xie, K.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.; et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewezi, T.; Maier, T.R.; Nettleton, D.; Baum, T.J. The Arabidopsis microRNA396-GRF1/GRF3 regulatory module acts as a developmental regulator in the reprogramming of root cells during cyst nematode infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernardi, J.M.; Mecchia, M.A.; Vercruyssen, L.; Smaczniak, C.; Kaufmann, K.; Inze, D.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 79, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijt, S.J.; Greco, R.; Agalou, A.; Shao, J.; t Hoen, C.C.; Overnäs, E.; Osnato, M.; Curiale, S.; Meynard, D.; van Gulik, R.; et al. Interaction between the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX families of transcription factors. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1952–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.Y. Growth-regulating factors: Conserved and divergent roles in plant growth and development and potential value for crop improvement. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 113, 1122–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Cheng, M.; Fan, F.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Si, F.; Luo, X.; Li, N.; Li, S. OsGRF6-OsYUCCA1/OsWRKY82 Signaling Cascade Upgrade Grain Yield and Bacterial Blight Resistance in Rice. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2407733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Tan, C.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, J.; Xu, N.; Han, Y.; et al. A new gain-of-function OsGS2/GRF4 allele generated by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing increases rice grain size and yield. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Cheng, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Fan, F.; Wang, W.; Si, F.; Gao, F.; Li, S. miR396b/GRF6 module contributes to salt tolerance in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Tang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsGRF6 interacts with SLR1 to regulate OsGA2ox1 expression for coordinating chilling tolerance and growth in rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 260, 153406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, G.; Kim, G.T.; Tsukaya, H. The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 43, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Tsukaya, H. Regulation of plant growth and development by the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR duo. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6093–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Pak, J.H.; Kim, J.H. The Arabidopsis GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR gene family performs an overlapping function in determining organ size as well as multiple developmental properties. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, G.; Zhang, D.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Ahiakpa, J.K.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Growth-Regulating Factors-Interacting Factor Gene Family in Tomato. Genes 2020, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruyssen, L.; Verkest, A.; Gonzalez, N.; Heyndrickx, K.S.; Eeckhout, D.; Han, S.K.; Jégu, T.; Archacki, R.; Van Leene, J.; Andriankaja, M.; et al. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 binds to SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes to regulate transcription during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, H.; Eeckhout, D.; Demuynck, K.; Persiau, G.; Walton, A.; van Bel, M.; Vervoort, M.; Candaele, J.; De Block, J.; Aesaert, S.; et al. Dynamic Changes in ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Complex Composition Reveal a Growth Regulatory Mechanism in the Maize Leaf. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, W.; Singh, R.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, M.; Lunde, C.; Hake, S.; Zhang, Z. GRF-interacting factor1 Regulates Shoot Architecture and Meristem Determinacy in Maize. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernardi, J.M.; Tricoli, D.M.; Ercoli, M.F.; Hayta, S.; Ronald, P.; Palatnik, J.F.; Dubcovsky, J. A GRF-GIF chimeric protein improves the regeneration efficiency of transgenic plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruyssen, L.; Tognetti, V.B.; Gonzalez, N.; Van Dingenen, J.; De Milde, L.; Bielach, A.; De Rycke, R.; Van Breusegem, F.; Inzé, D. GROWTH REGULATING FACTOR5 stimulates Arabidopsis chloroplast division, photosynthesis, and leaf longevity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Ji, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Yang, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Generation of novel bpm6 and dmr6 mutants with broad-spectrum resistance using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system in Brassica oleracea. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2025, 67, 1214–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Ekramoddoullah, A.K. Identification and characterization of the WRKY transcription factor family in Pinus monticola. Genome 2009, 52, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, M.; Yan, Y.; Lei, X.; Di, P.; Wang, Y. Whole-genome identification and expression profiling of growth-regulating factor (GRF) and GRF-interacting factor (GIF) gene families in Panax ginseng. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Han, Y.; Jin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Cai, Y. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the GRF Genes in Chinese Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd), Poplar (Populous), Grape (Vitis vinifera), Arabidopsis and Rice (Oryza sativa). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Wu, C.; Huang, C.; Tie, W.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xia, Z.; Wang, W.; Peng, M.; Tian, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the GRF Family Reveals Their Involvement in Abiotic Stress Response in Cassava. Genes 2018, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Functional conservation and divergence in plant-specific GRF gene family revealed by sequences and expression analysis. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł-Sommer, A.; Gaj, M.D. The miR396-GRF Regulatory Module Controls the Embryogenic Response in Arabidopsis via an Auxin-Related Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadegesin, M.A.; Beeching, J.R. Isolation and partial characterization of a root-specific promoter for stacking multiple traits into cassava (Manihot esculenta CRANTZ). Genet. Mol. Res. GMR 2011, 10, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y.; Liang, Z. Transcriptome Sequencing in Response to Salicylic Acid in Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Fu, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, G.; Yan, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W. Strand-specific RNA-seq based identification and functional prediction of drought-responsive lncRNAs in cassava. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, G.; Nakayama, H.; Ishikawa, N.; Kubo, M.; Demura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Tsukaya, H. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 plays roles in adaxial/abaxial patterning and growth in leaf morphogenesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Q. The Rice miR396-GRF-GIF-SWI/SNF Module: A Player in GA Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 786641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zeng, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Gao, F.; Cao, Y.; Luo, T.; Yuan, G.; Wu, X.; et al. OsGIF1 Positively Regulates the Sizes of Stems, Leaves, and Grains in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
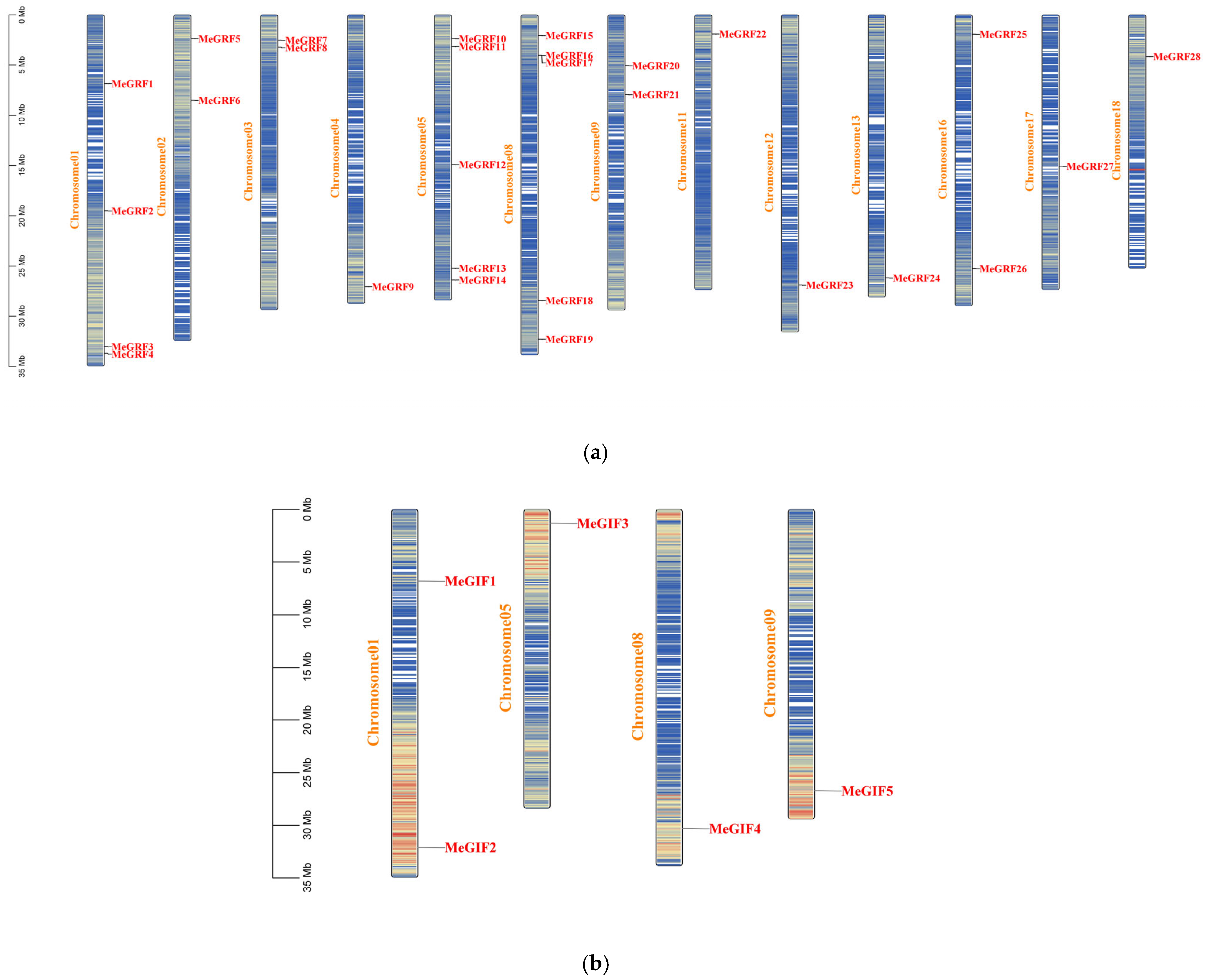
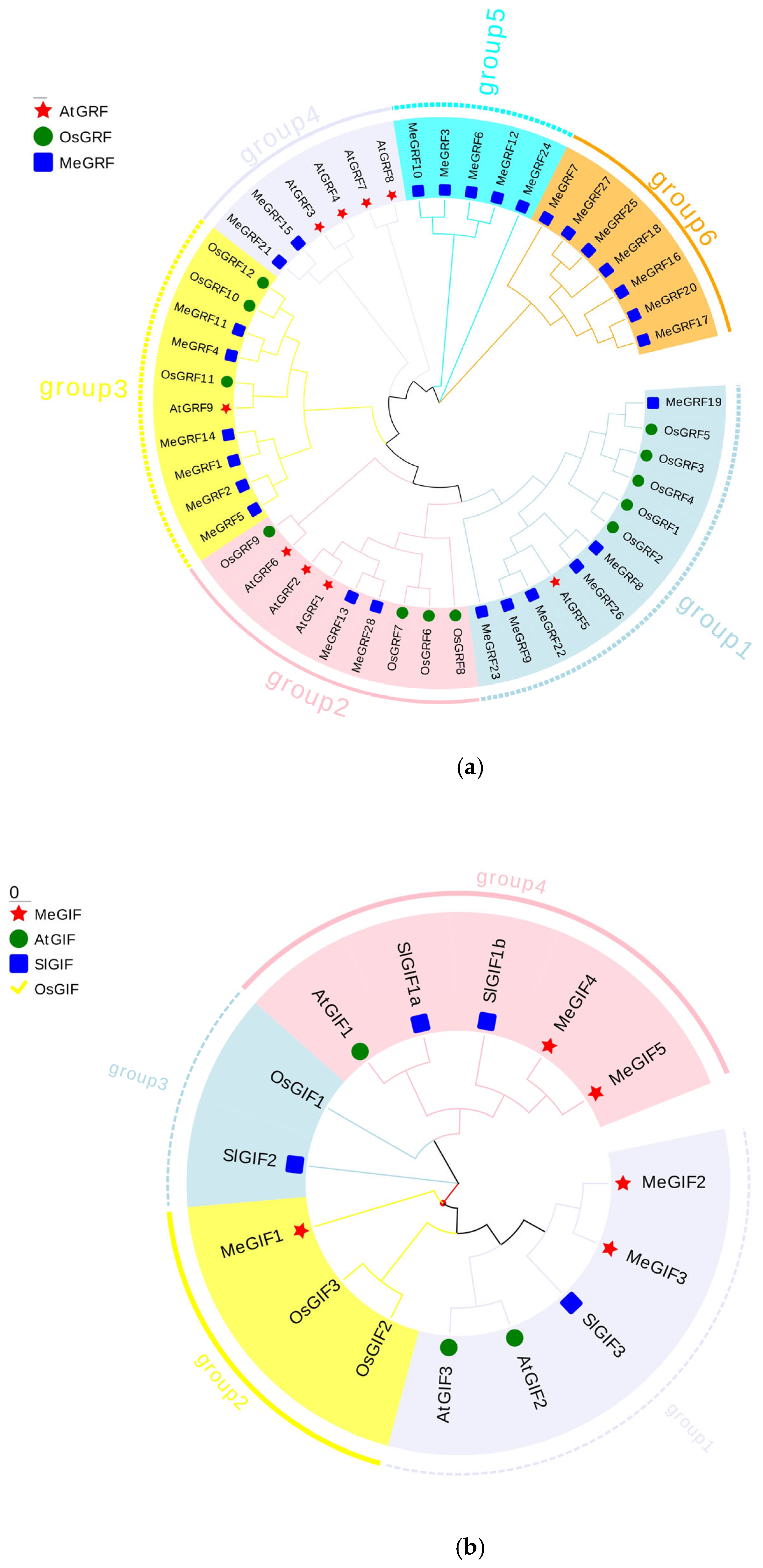
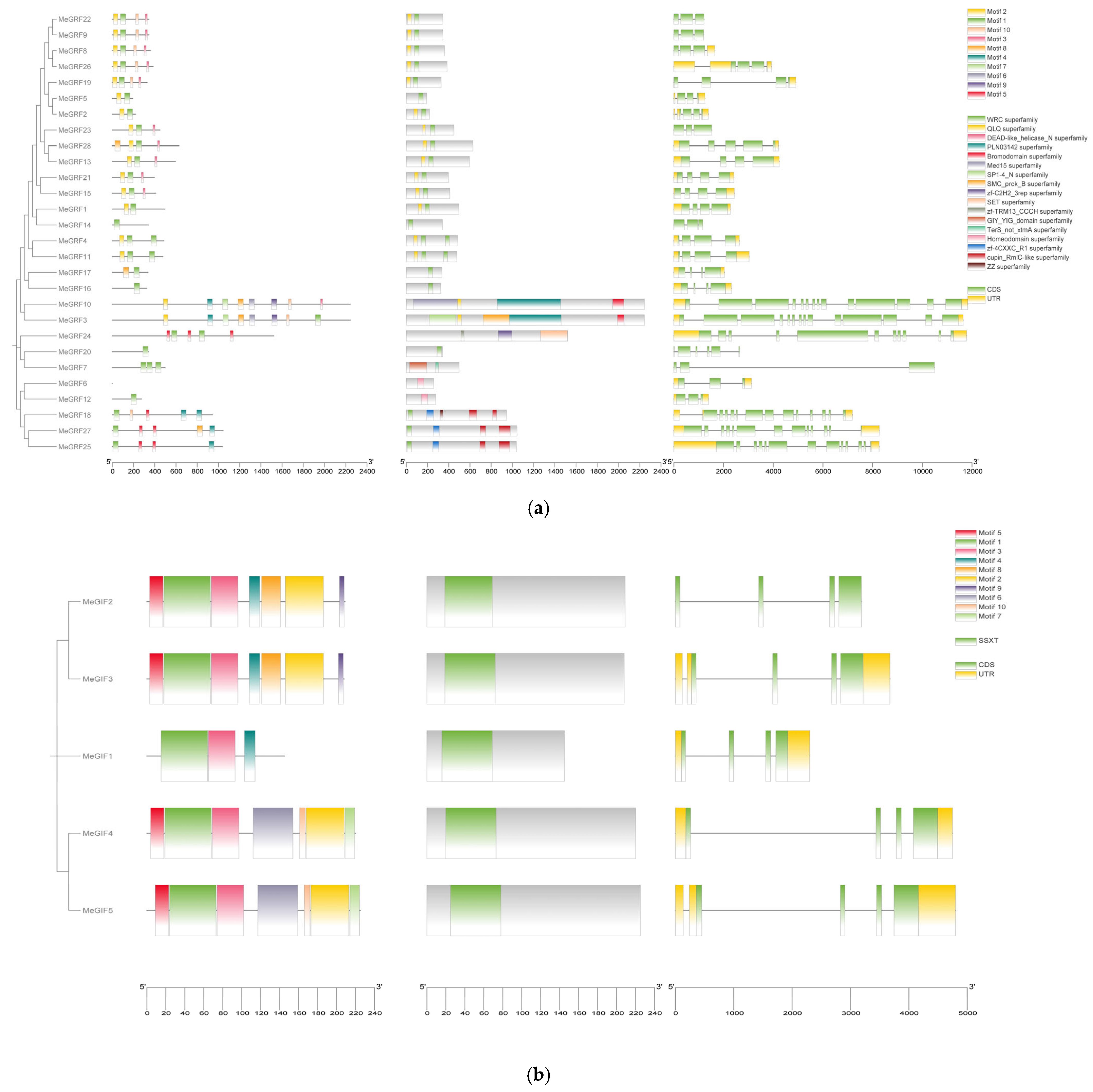
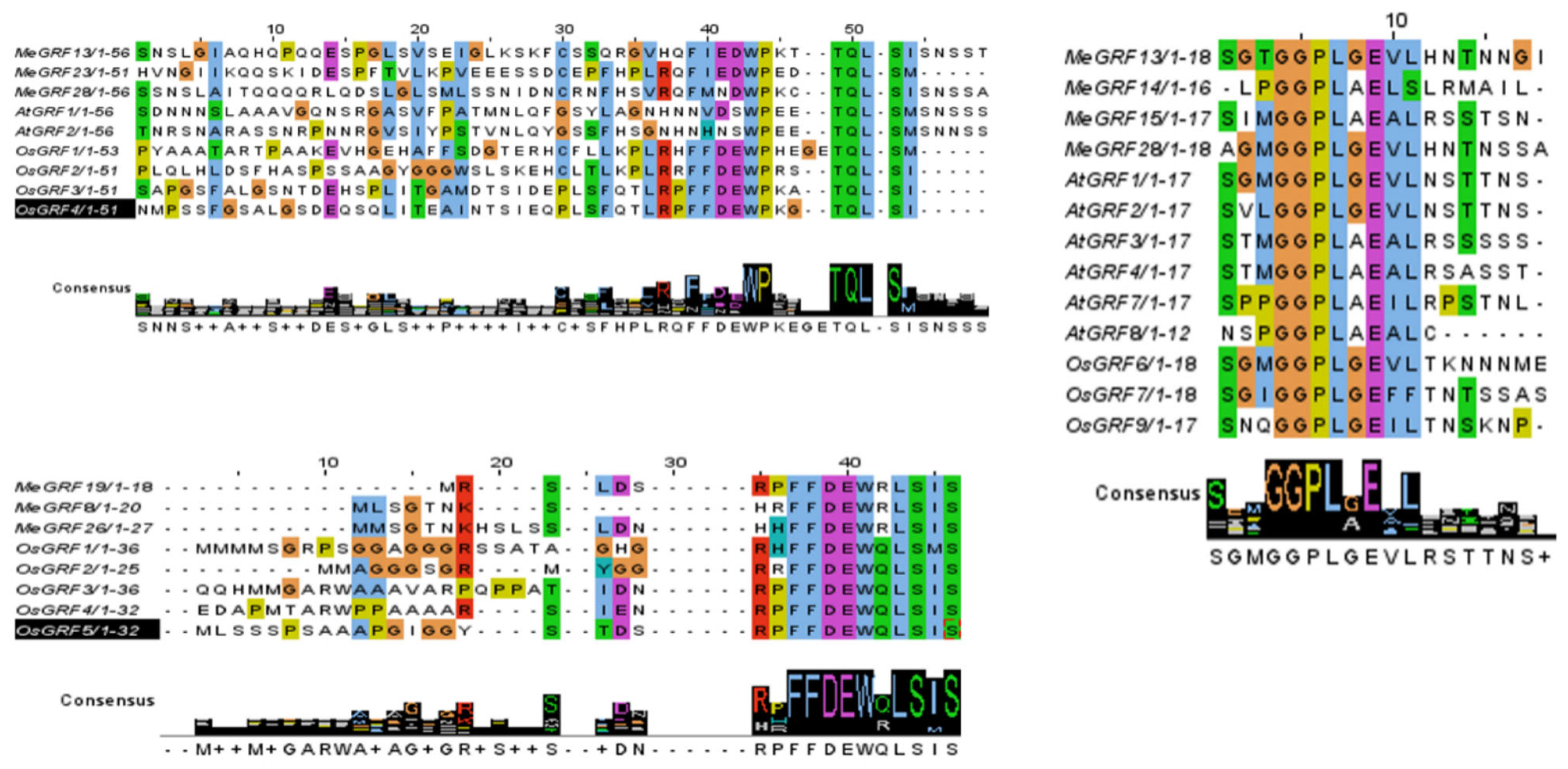


| Gene ID | Number of Amino Acid | Molecular Weight | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeGRF1 | 495 | 52,400.94 | 6.32 | 55.07 | 61.58 | −0.507 |
| MeGRF2 | 218 | 23,968.14 | 8.99 | 53.19 | 72.02 | −0.544 |
| MeGRF3 | 2243 | 250,934.06 | 9.08 | 55.41 | 72.58 | −0.706 |
| MeGRF4 | 480 | 51,734.08 | 9.29 | 39.8 | 65.25 | −0.604 |
| MeGRF5 | 191 | 20,990.78 | 9.21 | 61.39 | 69.95 | −0.609 |
| MeGRF6 | 257 | 29,154.26 | 5.65 | 47.84 | 65.64 | −0.962 |
| MeGRF7 | 496 | 54,818.67 | 9.17 | 48.77 | 61.33 | −0.695 |
| MeGRF8 | 359 | 40,723.21 | 8.69 | 56.36 | 55.99 | −0.85 |
| MeGRF9 | 345 | 38,959.98 | 8.22 | 58.33 | 52.61 | −0.866 |
| MeGRF10 | 2243 | 251,011.23 | 8.93 | 58.16 | 70.4 | −0.746 |
| MeGRF11 | 475 | 51,559.57 | 9.54 | 47.05 | 73.87 | −0.471 |
| MeGRF12 | 276 | 31,666.05 | 6.51 | 53.13 | 75.22 | −0.522 |
| MeGRF13 | 595 | 64,651.39 | 6.63 | 56.15 | 66.87 | −0.588 |
| MeGRF14 | 339 | 37,222.87 | 8.32 | 45 | 66.25 | −0.502 |
| MeGRF15 | 409 | 44,355.41 | 8.61 | 53.14 | 62.32 | −0.581 |
| MeGRF16 | 323 | 35,901.59 | 9.57 | 56.67 | 60.93 | −0.909 |
| MeGRF17 | 335 | 37,622.51 | 9.67 | 61.43 | 53.28 | −1.018 |
| MeGRF18 | 944 | 107,236.37 | 6.11 | 42.81 | 75.67 | −0.647 |
| MeGRF19 | 327 | 36,385.27 | 8.74 | 57.02 | 45.29 | −0.784 |
| MeGRF20 | 340 | 38,313.39 | 9.32 | 54.09 | 59.06 | −0.695 |
| MeGRF21 | 396 | 43,061.93 | 7.81 | 47.56 | 62.37 | −0.624 |
| MeGRF22 | 344 | 38,540.8 | 9.01 | 57.02 | 49.39 | −0.798 |
| MeGRF23 | 448 | 49,554.39 | 5.97 | 59.41 | 61.61 | −0.552 |
| MeGRF24 | 1520 | 172,018.07 | 5.94 | 46.36 | 75.61 | −0.488 |
| MeGRF25 | 1036 | 117,794.42 | 8.56 | 53.77 | 75.81 | −0.543 |
| MeGRF26 | 384 | 43,073.87 | 8.84 | 53.73 | 56.88 | −0.783 |
| MeGRF27 | 1043 | 118,549.18 | 8.3 | 51.52 | 78.68 | −0.519 |
| MeGRF28 | 627 | 68,086.34 | 8.68 | 51.04 | 61.18 | −0.635 |
| MeGIF1 | 144 | 16,790.96 | 6.12 | 77.37 | 68.54 | −0.88 |
| MeGIF2 | 208 | 22,243.16 | 5.63 | 69.46 | 60.24 | −0.606 |
| MeGIF3 | 207 | 21,958.62 | 5.83 | 58.59 | 54.98 | −0.676 |
| MeGIF4 | 219 | 23,066.56 | 5.72 | 64.57 | 54.11 | −0.582 |
| MeGIF5 | 224 | 23,706.29 | 5.8 | 62.54 | 56.34 | −0.617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Abdoulaye, A.H.; Feng, Y.; Wen, W.; Chen, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Growth Regulatory Factor (GRF) and Growth-Regulating Interacting Factor (GIF) Gene Families in Cassava. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091046
Xu R, Li T, Zheng L, Chen Y, Abdoulaye AH, Feng Y, Wen W, Chen Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Growth Regulatory Factor (GRF) and Growth-Regulating Interacting Factor (GIF) Gene Families in Cassava. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091046
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Rou, Tianyu Li, Linling Zheng, Yuhua Chen, Assane Hamidou Abdoulaye, Yating Feng, Wenlong Wen, and Yinhua Chen. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Growth Regulatory Factor (GRF) and Growth-Regulating Interacting Factor (GIF) Gene Families in Cassava" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091046
APA StyleXu, R., Li, T., Zheng, L., Chen, Y., Abdoulaye, A. H., Feng, Y., Wen, W., & Chen, Y. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Growth Regulatory Factor (GRF) and Growth-Regulating Interacting Factor (GIF) Gene Families in Cassava. Horticulturae, 11(9), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091046






