Influence of Agricultural Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Apple Orchards in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Soil DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Management Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties
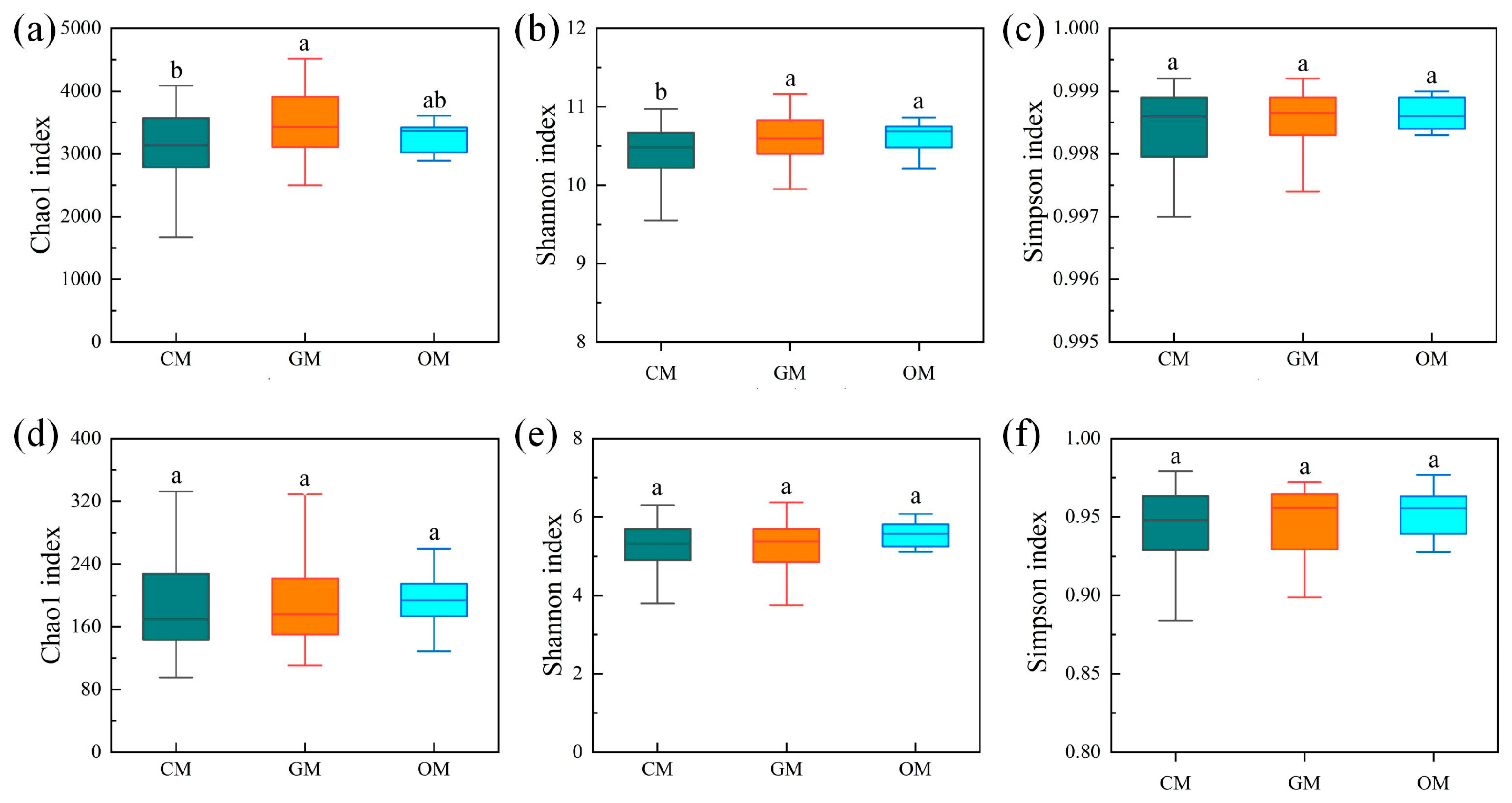
3.2. Impactt of Management Practices on Microbial Alpha Diversity in Inter-Root Soils
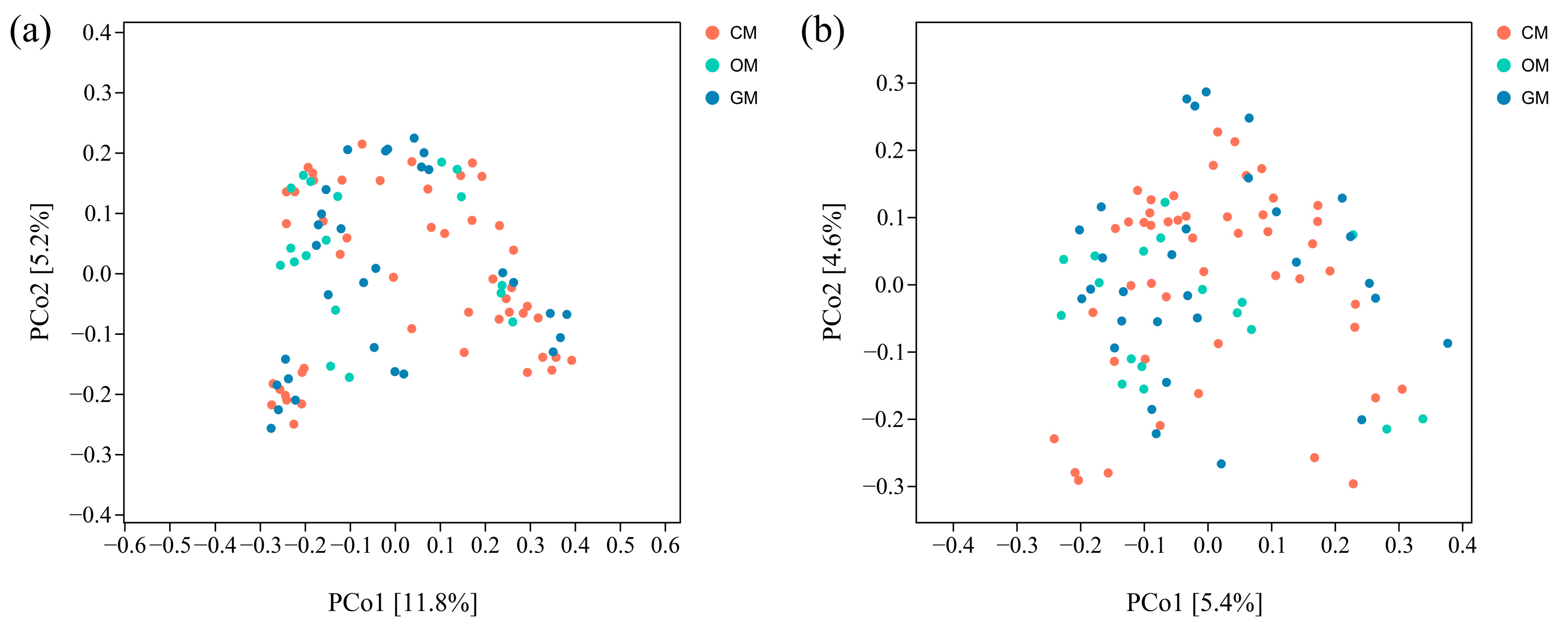
3.3. Impact of Management Practices on Inter-Root Soil Microbial Community Structure
3.4. Differences in Soil Fungal and Bacterial Biomarkers Across Management Practices
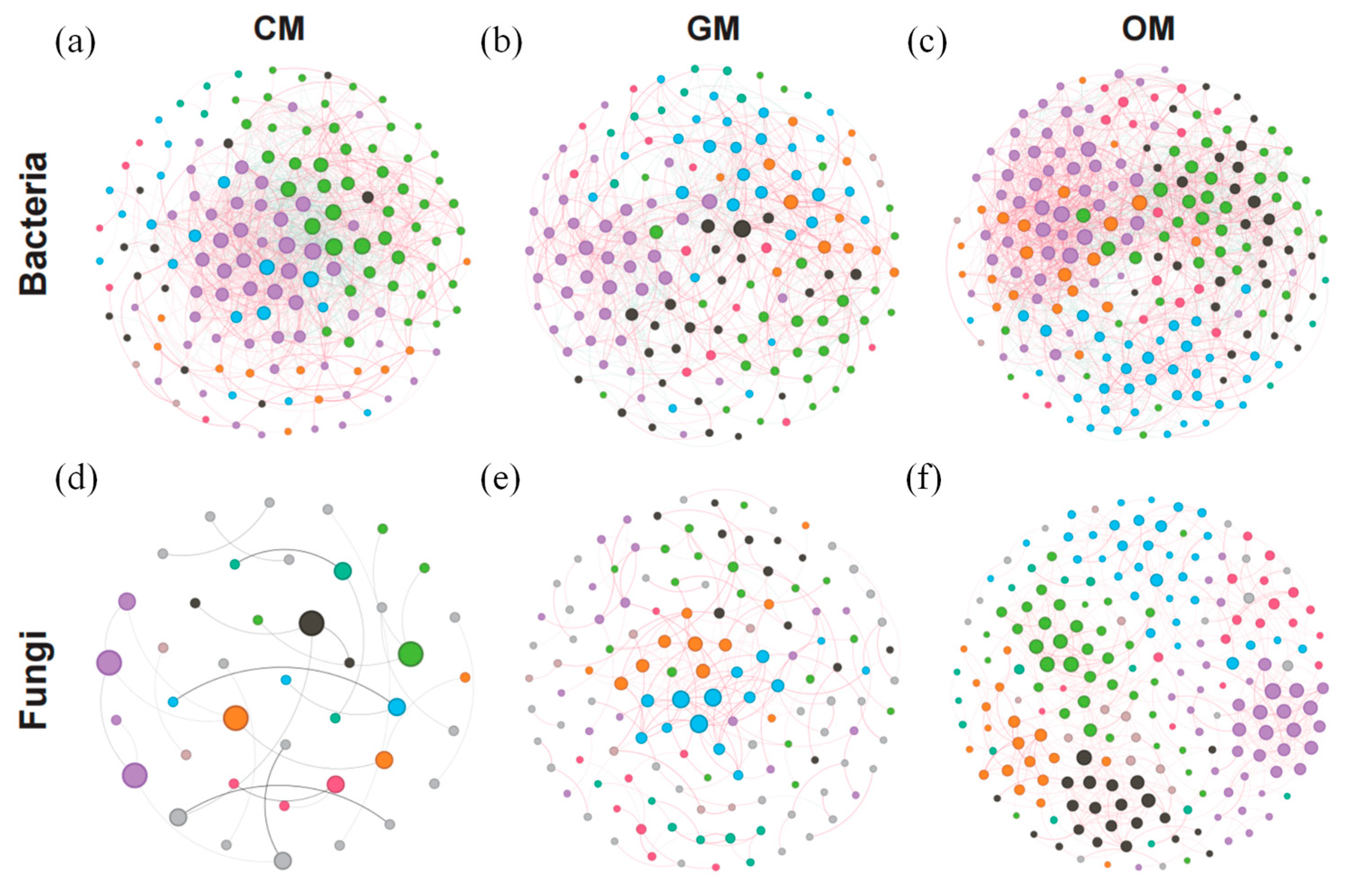
3.5. Microbial Community Network Characterization
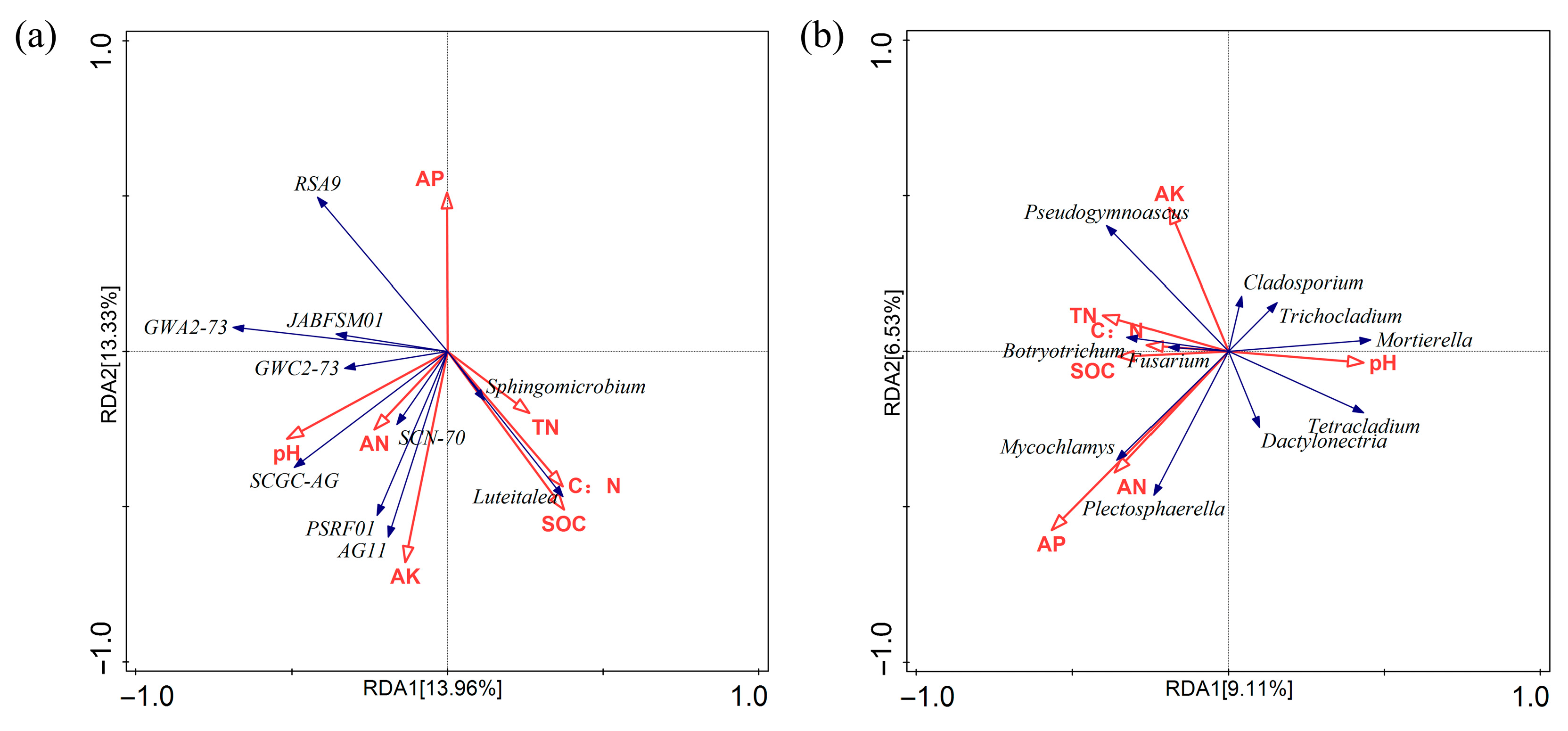
3.6. Relationship Between Microbial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Management Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Impact of Management Practices on Microbial Diversity and Community Composition
4.3. Impact of Soil Physicochemical Properties on Soil Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sukayat, Y.; Setiawan, I.; Suharfaputra, U.; Kurnia, G. Determining Factors for Farmers to Engage in Sustainable Agricultural Practices: A Case from Indonesia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, G.; Maucieri, C.; Squartini, A.; Stevanato, P.; Tolomio, M.; Toffanin, A.; Borin, M. Soil indicators for comparing medium-term organic and conventional agricultural systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjar, R.M.; Vasile Scăețeanu, G.; Sandu, M.A. Nutrient Water Pollution from Unsustainable Patterns of Agricultural Systems, Effects and Measures of Integrated Farming. Water 2024, 16, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Hülsbergen, K.-J. A new method for analyzing agricultural land-use efficiency, and its application in organic and conventional farming systems in southern Germany. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 83, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Voluntary Guidelines for Sustainable Soil Management; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; p. 16. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i6874en/I6874EN (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Szymańska, M.; Gubiec, W.; Smreczak, B.; Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Sosulski, T. How Does Specialization in Agricultural Production Affect Soil Health? Agriculture 2024, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, M. Effects of land-use conversion from paddy field to orchard farm on soil microbial genetic diversity and community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 64, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Sha, X. Effect of plant-soil feedback on soil microbial co-occurrence network depends on the stage of secondary succession. Rhizosphere 2023, 27, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.M.; Wittwer, R.; Hartmann, M.; Keller, T.; Buchmann, N.; van der Heijden, M.G. Effects of conventional, organic and conservation agriculture on soil physical properties, root growth and microbial habitats in a long-term field experiment. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Zhang, S.; He, P. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, G.; Celano, G.; Dichio, B.; Xiloyannis, C. Effects of soil-protecting agricultural practices on soil organic carbon and productivity in fruit tree orchards. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Zang, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Huang, L. The Influence of Organic and Conventional Cultivation Patterns on Physicochemical Property, Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community Characteristics of Paddy Soil. Agriculture 2022, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, S.; Long, J.; Mao, H.; Dong, Y.; Hou, Y. Differences in microbial community structure and metabolic activity among tea plantation soils under different management strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1219491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, C.; Marcello, C.; Marco, C.; Emilio, C.; Lucilla, I. Organic vs. conventional: Impact of cultivation treatments on the soil microbiota in the vineyard. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1242267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Mayra, M. Research on the development strategy of green organic fruit and vegetable industry cluster in Xinjiang. Chin. Fruit Tree 2024, 6, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.F.; Lu, L.; Tang, J. Current status, problems and countermeasures of apple variety selection in Xinjiang. J. Fruit Tree Resour. 2023, 4, 67–71+79. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Hussain, S.; Guo, R.; Sarwar, M.; Ren, X.; Krstic, D.; Aslam, Z.; Zulifqar, U.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; et al. Carbon Sequestration to Avoid Soil Degradation: A Review on the Role of Conservation Tillage. Plants 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19630-2019; Organic Products—Production, Processing, Labelling and Management System. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- NY/T 391-2021; Green Food—Environmental Quality for Production Areas. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Sun, M.; Xiao, T.; Ning, Z.; Xiao, E.; Sun, W. Microbial community analysis in rice paddy soils irrigated by acid mine drainage contaminated water. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Balance between community assembly processes mediates species coexistence in agricultural soil microbiomes across eastern China. ISME J. 2020, 14, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; De Filippis, F.; Cesarano, G.; La Storia, A.; Ercolini, D.; Scala, F. Organic farming induces changes in soil microbiota that affect agro-ecosystem functions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yuan, D.; Qin, S.; Hu, C. Influence of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric ratios on the stimulation effect of soil organic carbon mineralization. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric. 2023, 31, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, P.; Cui, J.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Organic management increases beneficial microorganisms and promotes the stability of microecological networks in tea plantation soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Wei, X.M.; Wu, C.F.; Deng, Y.W.; Liao, J.L.; Huang, D.F.; Wu, J.S.; Ge, T.D. Effects of different years of organic cultivation on soil biological nitrogen fixation activity. Soil Bull. 2021, 52, 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Tian, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, B. Tillage Changes Vertical Distribution of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Jiao, X.; Wu, F. Effects of continuous cucumber cropping and alternative rotations under protected cultivation on soil microbial community diversity. Plant Soil 2006, 284, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, M.W.; Peng, H.L.; Feng, Y.; Geng, S.G. Soil fungal diversity in solar greenhouse vegetable cultivation under long-term organic cultivation. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 32, 641–654. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Wei, D.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Cao, F.; Li, J. Long-term fertilization changes bacterial diversity and bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere of Chinese Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sha, C.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Li, P.; Tan, J.; Huang, S.F. Comparison of Bacterial Community in Paddy Soil after Short-Term Application of Pig Manure and the Corresponding Organic Fertilizer. Land 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Yang, Y.; Bissett, A.; Behrens, T.; Dixon, K.; Nevil, P.; Li, S. Environmental controls of soil fungal abundance and diversity in Australia’s diverse ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 17, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Vineyard reclamation alters soil properties and microbial community in desertified land. Catena 2024, 246, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, K.; Philipp, W.; Henry, M.; Robert, M.; Hans, U.; Tomislav, C.; Gabriele, B. Unraveling the Complexity of Soil Microbiomes in a Large-Scale Study Subjected to Different Agricultural Management in Styria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.F.; Wu, N.; Liu, J.L.; Xu, X. Effects of different fertiliser treatments on soil physico-chemical properties and bacterial diversity in willow jik. Soil Fertil. China 2022, 3, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Meena, M.C.; Agarwal, B.K.; Mahapatra, P.; Shahi, D.K.; Salwani, R.; Agnihorti, R. Temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition as affected by long-term fertilization under a soybean based cropping system in a sub-tropical Alfisol. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 233, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, J.L.; Wu, N.; Wan, M.H.; Ma, F.L.; Liu, H. Effects of charcoal-based fertiliser on soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities and microbial communities of maize farmland in dry areas. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.P.; Meenakshi, S.; Nath, T.B. Glomalin: An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal soil protein. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Becerril, F.; Van Tuinen, D.; Chatagnier, O.; Rouard, N.; Béguet, J.; Kuszala, C.; Soulas, G.; Gianinazzi-Pearson, V.; Martin-Laurent, F. Impact of a pesticide cocktail (fenhexamid, folpel, deltamethrin) on the abundance of Glomeromycota in two agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, P.; Rodríguez, I.; Fernández, V.F.; Ramil, M.; Castrillo, D.; Albiac, M.A.; Adamo, I.; Trujillo, C.F.; Jiménez, B.G.; Acedo, A.; et al. Physicochemical Properties and Microbiome of Vineyard Soils from DOP Ribeiro (NW Spain) Are Influenced by Agricultural Management. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, P.; Guo, X.L.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.J. Fifteen-year no tillage of a Mollisol with residue retention indirectly affects topsoil bacterial community by altering soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Akhter, A.W.; Tarique, Z.M.; Arjun, S.; Hillol, C.; Adarsh, K.; Samir, F.M.; Anu, S.; Sudhir, S.; Kumar, S.A. Core microbiota of wheat rhizosphere under Upper Indo-Gangetic plains and their response to soil physicochemical properties. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1186162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Ecological responses of soil microbial abundance and diversity to cadmium and soil properties in farmland around an enterprise-intensive region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zuo, J.; Dong, H. Changes in Soil Properties and Bacterial Community Composition with Biochar Amendment after Six Years. Agronomy 2020, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Zou, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, D.; Han, C.; Duan, Y. Long-term conservation tillage enhances microbial carbon use efficiency by altering multitrophic interactions in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Waqas, M.; Kang, S.-M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Hussain, J.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Al-Khiziri, S.; Ullah, I.; Ali, L.; Jung, H.-Y.; et al. Bacterial endophyte Sphingomonas sp. LK11 produces gibberellins and IAA and promotes tomato plant growth. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.M.; Zhi, H.T.; Yu, X.M.; Zhang, D.S.; Xu, S.X. Influence of soil salinity on the structure of inter-root microbial communities of facility vegetables. Soil Bull. 2024, 55, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Du, N.; Li, Q.; Wei, G. Soil microbiomes with distinct assemblies through vertical soil profiles drive the cycling of multiple nutrients in reforested ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
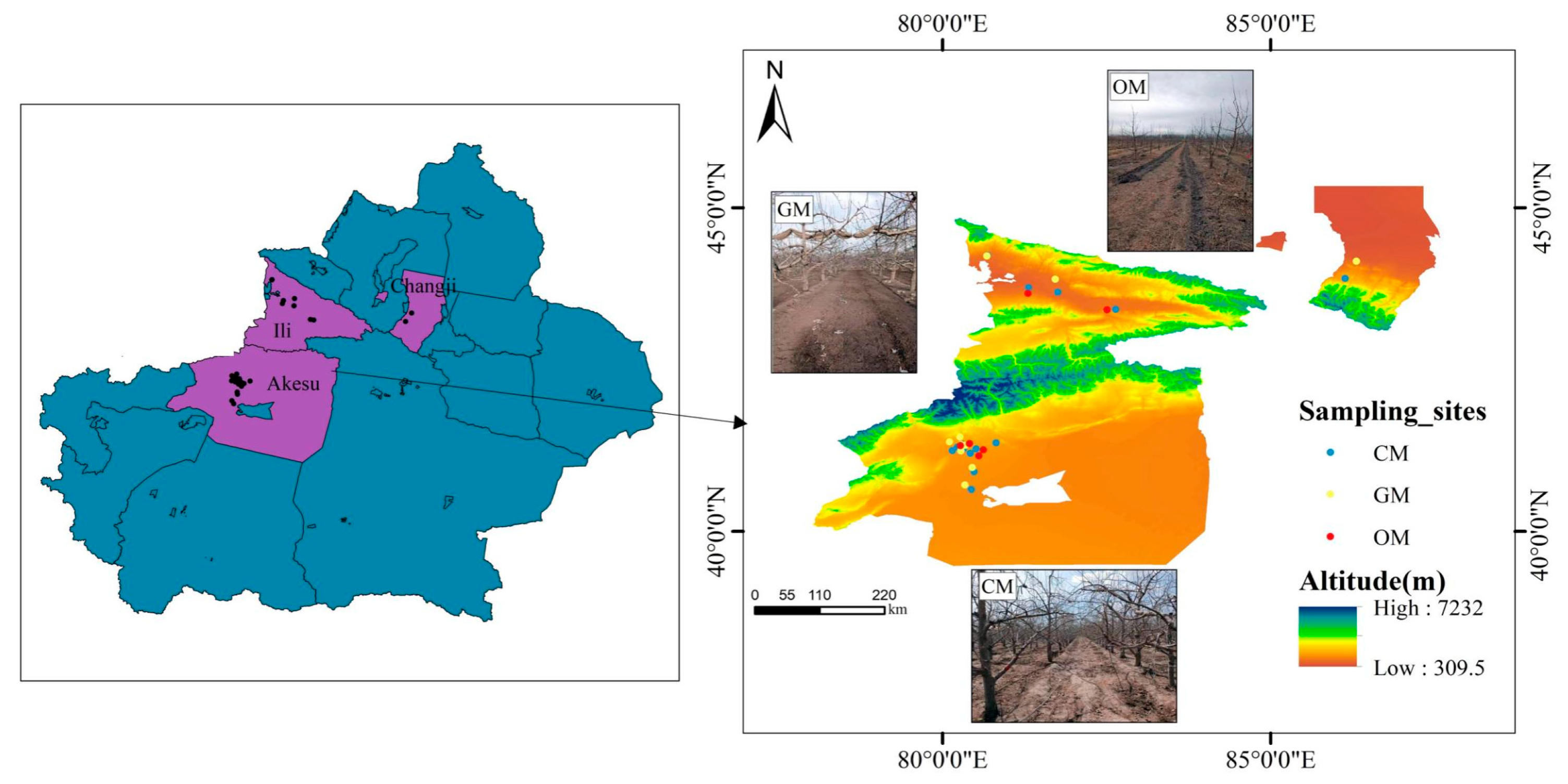



| Orchard Number | Longitude and Latitude | Management Practice | Years of Management Practice Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E 80°15′, N 41°27′ | GM | 2 |
| 2 | E 80°6′, N 41°23′ | GM | 2 |
| 3 | E 80°16′, N 41°14′ | GM | 2 |
| 4 | E 80°16′, N 41°20′ | GM | 3 |
| 5 | E 80°20′, N 41°19′ | GM | 2 |
| 6 | N 80°27′, N 40°59′ | GM | 4 |
| 7 | E 80°20′, N 40°42′ | GM | 3 |
| 8 | E 80°40′, N 44°15′ | GM | 2 |
| 9 | E 81°42′, N 43°53′ | GM | 2 |
| 10 | E 86°18′, N 44°10′ | GM | 2 |
| 11 | E 80°16′, N 41°19′ | OM | 2 |
| 12 | E 80°33′, N 41°10′ | OM | 2 |
| 13 | E 80°24′, N 41°21′ | OM | 3 |
| 14 | E 80°37′, N 41°15′ | OM | 2 |
| 15 | E 81°18′, N 43°40′ | OM | 3 |
| 16 | E 82°30′, N 43°25′ | OM | 2 |
| 17 | E 80°13′, N 41°18′ | CM | |
| 18 | E 80°8′, N 41°14′ | CM | |
| 19 | E 80°16′, N 41°19′ | CM | |
| 20 | E 80°17′, N 41°20′ | CM | |
| 21 | E 80°19′, N 41°16′ | CM | |
| 22 | E 80°28′, N 40°55′ | CM | |
| 23 | E 80°26′, N 40°38′ | CM | |
| 24 | E 80°41′, N 44°15′ | CM | |
| 25 | E 81°18′, N 43°45′ | CM | |
| 26 | E 86°8′, N 43°54′ | CM | |
| 27 | E 80°48′, N 41°22′ | CM | |
| 28 | E 80°25′, N 41°12′ | CM | |
| 29 | E 80°30′, N 41°16′ | CM | |
| 30 | E 80°19′, N 41°19′ | CM | |
| 31 | E 81°45′, N 43°41′ | CM | |
| 32 | E 82°38′, N 43°25′ | CM |
| Sample | pH | SOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | C:N | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) | AN (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM | 7.94 ± 0.21b | 9.75 ± 3.86a | 0.49 ± 0.10a | 21.48 ± 6.26b | 35.10 ± 27.43b | 216.00 ± 92.16ab | 54.38 ± 25.08ab |
| OM | 8.07 ± 0.21a | 10.90 ± 2.58a | 0.46 ± 0.12a | 24.53 ± 5.41a | 41.64 ± 32.94b | 170.50 ± 43.41b | 49.21 ± 20.39b |
| CM | 8.01 ± 0.15ab | 9.75 ± 2.44a | 0.42 ± 0.06a | 22.92 ± 4.72ab | 64.13 ± 33.59a | 239.15 ± 117.50a | 61.46 ± 17.52a |
| Features | Bacteria | Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | GM | OM | CM | GM | OM | |
| Nodes | 152 | 157 | 206 | 41 | 133 | 206 |
| Edges | 1362 | 863 | 1917 | 29 | 206 | 673 |
| Degree | 17.921 | 10.994 | 18.612 | 1.415 | 3.098 | 6.534 |
| Network diameter | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 17 | 11 |
| Modularity | 0.52 | 0.545 | 0.55 | 0.848 | 0.77 | 0.782 |
| Average clustering coefficient | 0.571 | 0.464 | 0.481 | 0.139 | 0.326 | 0.411 |
| Positive links | 71.39% | 76.13% | 73.45% | 89.66% | 99.03% | 100% |
| Negative links | 27.61% | 23.87% | 26.55% | 10.34% | 0.97% | 0.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, K.; Yu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, F. Influence of Agricultural Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Apple Orchards in Xinjiang, China. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080891
Zhang G, Wang Z, Zhang H, Li X, Liu K, Yu K, Zheng Z, Zhao F. Influence of Agricultural Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Apple Orchards in Xinjiang, China. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080891
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guangxin, Zili Wang, Huanhuan Zhang, Xujiao Li, Kun Liu, Kun Yu, Zhong Zheng, and Fengyun Zhao. 2025. "Influence of Agricultural Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Apple Orchards in Xinjiang, China" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080891
APA StyleZhang, G., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Li, X., Liu, K., Yu, K., Zheng, Z., & Zhao, F. (2025). Influence of Agricultural Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Apple Orchards in Xinjiang, China. Horticulturae, 11(8), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080891






