Recommendations for Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes Suitable for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear in Jiangxi Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Quantification of Pesticide Residues and Heavy Metals
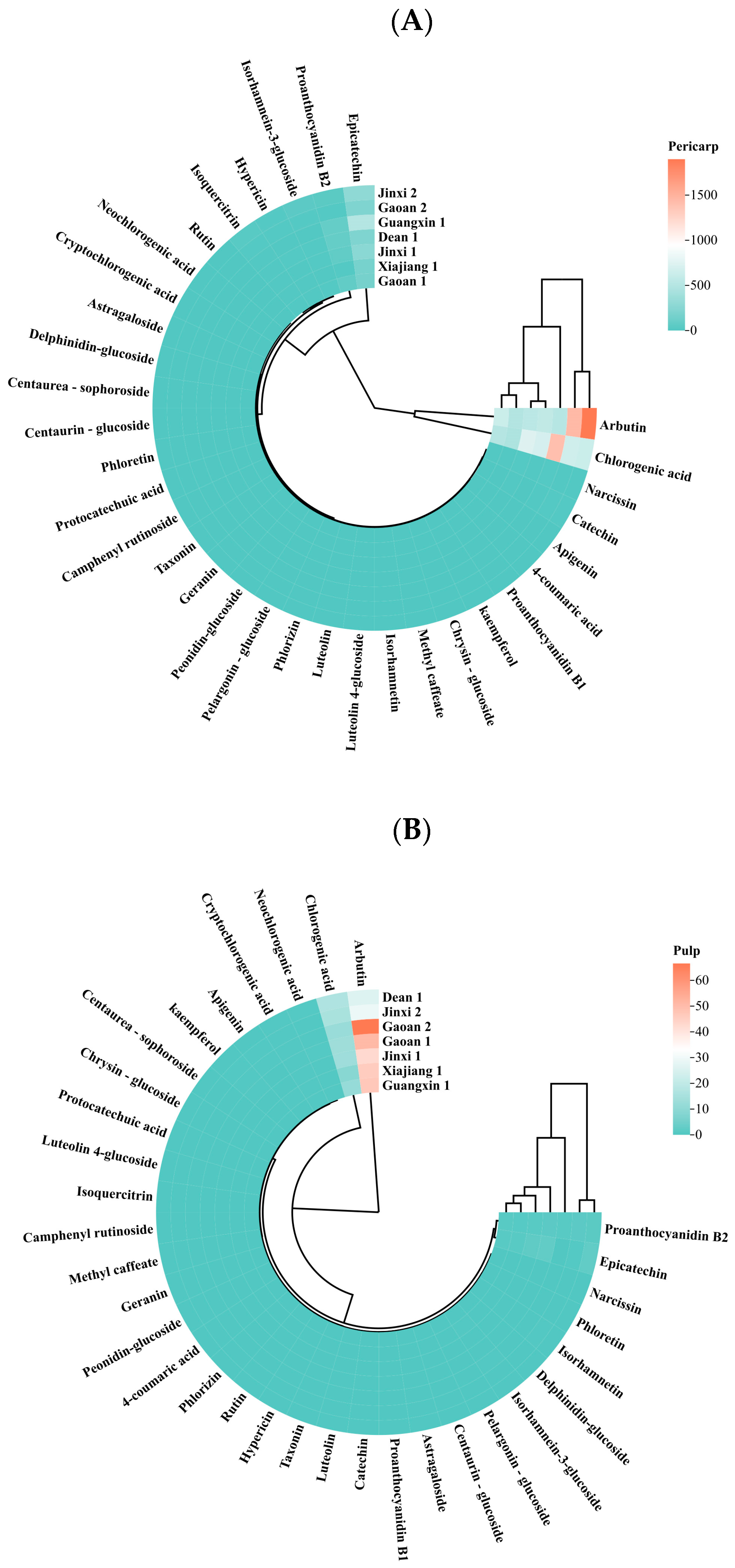
2.2.2. Determination of Chemical Components and Metabolites
2.2.3. Sensory Analysis
- Fruit size (Too small; Middling; Large; Too large);
- Smoothness of fruit surface (Rough; Middling; Smooth);
- Pulp texture (Coarse; Middling; Appropriate; Delicate);
- Pulp type (Soft; Sandy; Loose; Crispy; Hard);
- Fruit juice (Not much; Middling; Much; Too much).
- Flavor (Slight acid; Tasteless; Appropriate; Sweet; Quite sweet);
- Retronasal aroma (Hardly; Perfumed; Fragrant);
- Purchase intention (No purchase intention; Possible purchase; Willing to buy; Buy at a high price).
2.2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analyses
3. Results
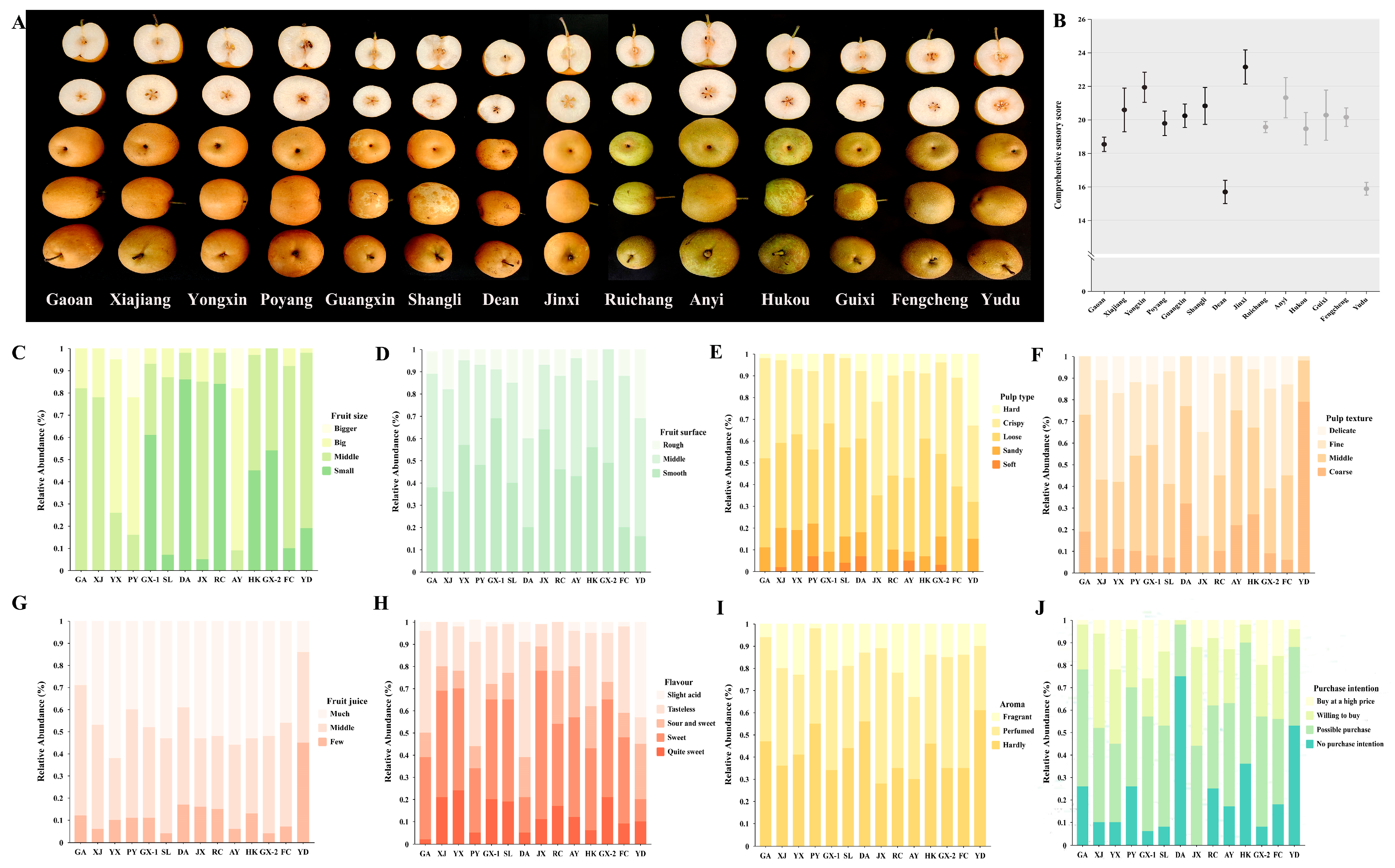
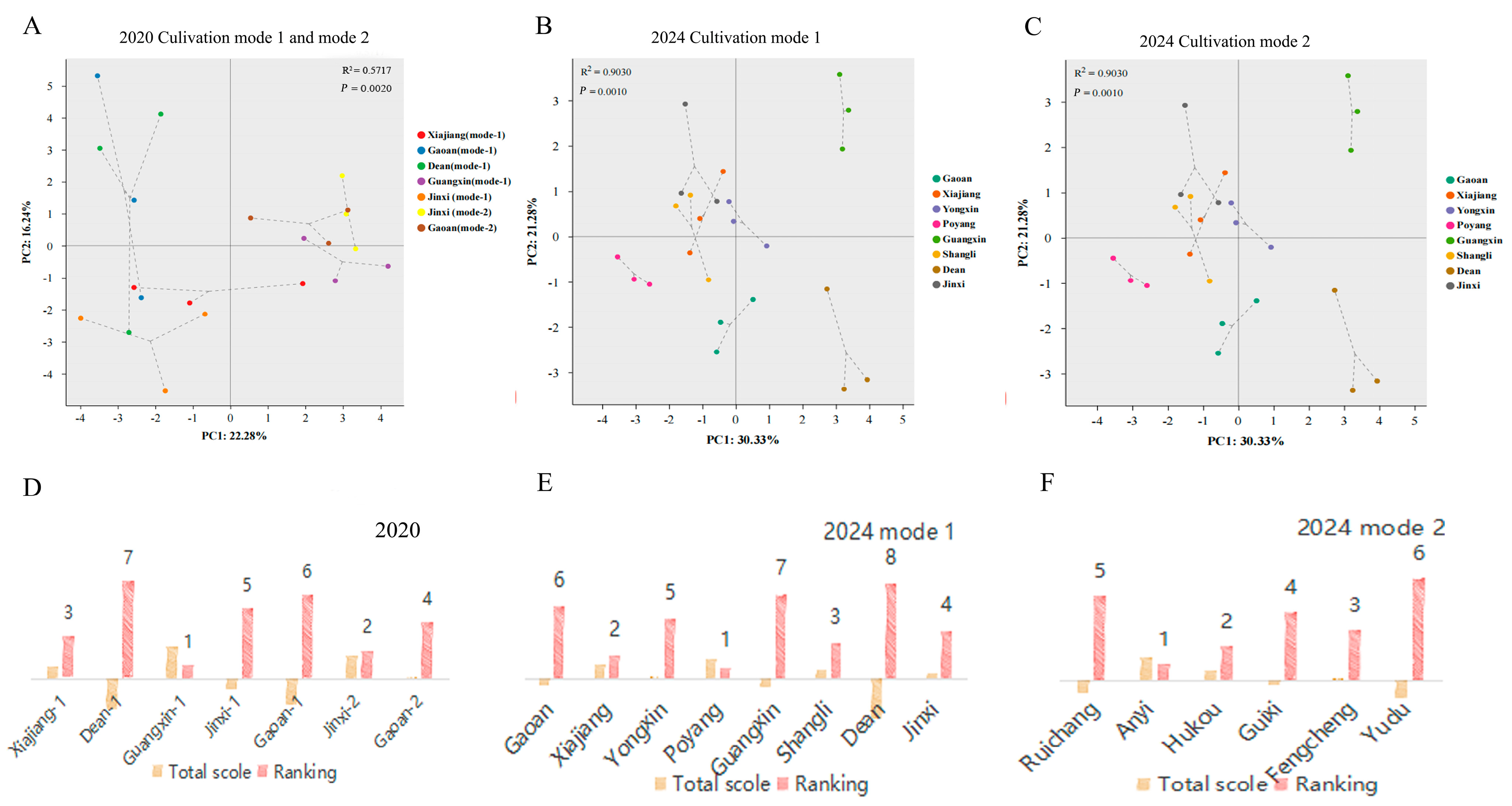
3.1. Quality Attributes Are Strongly Influenced by the Location and Cultivation Mode
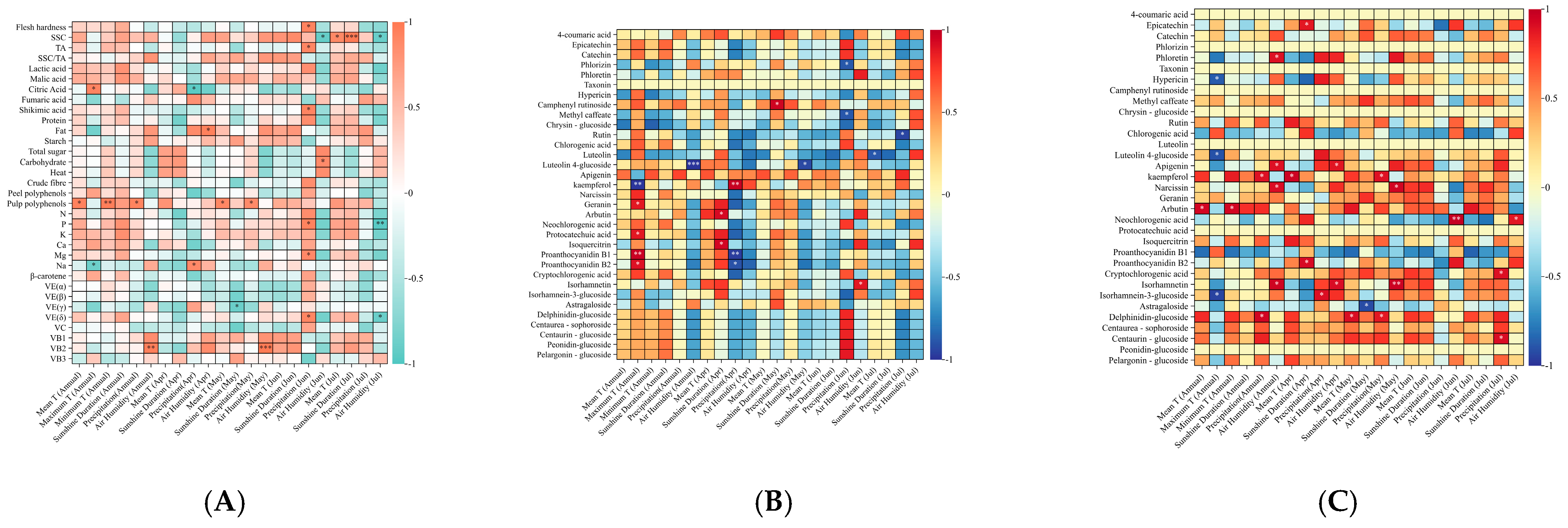
3.2. Analysis of Quality Attributes, Polyphenols, and Meteorological Parameters
3.3. Sensory Analysis
3.4. Recommendations for Suitable Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes for ‘Cuiguan’ Pear
4. Discussion
4.1. Pear Phytochemical Profile and Secondary Metabolites Are Influenced by Cultivation Mode and Most Prominently by Climate
4.2. Sensory Analysis
4.3. Discussion of Suitable Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.G.; Zh, S.L. Pears in China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.X.; Fu, J.; Qin, J.X.; Su, B.L.; Hong, Y. Effects of climate variability and urbanization on spatiotemporal patterns of vegetation in the middle and lower Yangtze River Basin, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1459058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Cheng, Y.S.; Nie, X.S.; Wu, T. Comparative physiological, metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the mechanisms of differences in pear fruit quality between distinct training systems. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, R.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, X. Study on Fine Zoning of Maize Variety Suitability in Huang-Huai-Hai Area. J. Agric. 2015, 46, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Han, F.R.; Shu, S.F. Meteorological condition analysis for growth of pear variety Cuiguan and its blossoming prediction. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2022, 63, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Balasundaram, A.; Aziz, B.A.; Gupta, A.; Shaik, A.; Kavitha, M.S. A fusion approach using GIS, green area detection, weather API and GPT for satellite image based fertile land discovery and crop suitability. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaos, K.; Thomas, K.A.; George, B.; Serafeim, T.; Stefanos, K. Delineating Natural Terroir Units in Wine Regions Using Geoinformatics. Agriculture 2023, 13, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.D.; Pan, S.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.F.; Han, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Zhao, C.J. Precise Recommendation Method of Suitable Planting Areas of Maize Varieties Based on Knowledge Graph. Agriculture 2023, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; Yang, S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of tree shape on the microclimate and fruit quality parameters of Camellia Oleifera Abel. Forests 2019, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngao, J.; Martinez, S.; Marquier, A.; Bluy, S.; Saint-Joanis, B.; Costes, E. Spatial variability in carbon- and nitrogen-related traits in apple trees: The effects of the light environment and crop load. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahnd, C.; Arend, M.; Kahmen, A.; Hoch, G. Microclimatic gradients cause phenological variations within temperate tree canopies in autumn but not in spring. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 331, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.; De Vos, R.C.H.; Conde, A.; Cunha, A. Light microclimate-driven changes at transcriptional level in photosynthetic grape berry tissues. Plants 2021, 10, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, B.M.; Minas, I.S. Redefining the impact of preharvest factors on peach fruit quality development and metabolism: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 297, 110919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Application of exogenous melatonin improves tomato fruit quality by promoting the accumulation of primary and secondary metabolites. Foods 2022, 11, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.Q.; Qin, X.L.; Wei, C.Q.; Feng, Y.X.; Cheng, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, J.F. Influence of Bagging on Fruit Quality, Incidence of Peel Browning Spots, and Lignin Content o ‘Huangguan’Pears. Plants 2024, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Y. Responses of Soil Microbial Traits to Ground Cover in Citrus Orchards in Central China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Li, X.G.; Blanco-Ulate, B.; Yang, Q.S.; Yao, G.F.; Wei, Y.D.; Wu, J.; Sheng, B.L.; Chang, Y.H.; et al. A pear S1-bZIP transcription factor PpbZIP44 modulates carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid, and flavonoid accumulation in fruits. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.F.; Li, L.T.; Jugpreet, S.; Sun, M.Y.; Bai, B.; Li, S.W.; Ni, J.P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, W.L.; et al. Construction of a high-density bin-map and identification of fruit quality-related quantitative trait loci and functional genes in pear. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marija, K.; Mateja, B.; Jasna, J.; Ante, N.; Tomislav, R.; Tihomir, K.; Ivana, D.Š.; Šarkanj, B. Mycotoxins, Pesticide Residues, and Heavy Metals Analysis of Croatian Cereals. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kamitakahara, H.; Sasaki, R.; Oikawa, A.; Saito, K.; Murayama, H. Effect of exogenous GA4+7 and BA+CPPU treatments on fruit lignin and primary metabolites in Japanese pear gold Nijisseiki. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Z.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T. Effects of hydrogen water treatment on antioxidant system of litchi fruit during the pericarp browning. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.J.; Dobson, P.; Smith, P.; Blake, A.; Stewart, D. Assessing potential bioavailability of raspberry anthocyanins using an in vitro digestion system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallarino, J.G.; Abreu, L.F.; Soria, C.; Tong, H.; Pott, D.M.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R.; Nikoloski, Z.; Osorio, S. Genetic diversity of strawberry germplasm using metabolomic biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Experiments; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.6-2016; Food Safety National Standard—Determination of Fat in Food. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China; The State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Dai, L.G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Liu, J.S. Method for Determining Total Starch Content in Grains. Chin. Food Nutr. 2013, 19, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Xiao, X.H. Comparison of Three Extraction Methods for Soluble Carbohydrates in Forage Grasses. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2018, 19, 206–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.K.; Zheng, D.F. Improvement of the Method for Measuring Vegetable Crude Fiber—The Enhancement of the Acid-Soaping Method. Shandong Agric. Sci. 1990, 6, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.82-2016; Food Safety National Standard—Determination of Vitamins A, D and E in Food. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China; The State Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Reinholds, I.; Pugajeva, I.; Bavrins, K.; Kuckovska, G.; Bartkevics, V. Mycotoxins, pesticides and toxic metals in commercial spices and herbs. Food Addit. 2017, 10, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.S.; Tao, S.T.; Zhang, S.L. Characterization and Quantification of Polyphenols and Triterpenoids in Thinned Young Fruits of Ten Pear Varieties by UPLC-Q TRAP-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, D.M.; Osorio, S.; Vallarino, J.G. From central to specialized metabolism: An overview of some secondary compounds derived from the primary metabolism for their role in conferring nutritional and organoleptic characteristics to fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisosto, C.H.; Mitchell, F.G.; Johnson, R.S. Factors in fresh market stone fruit quality. Post Harvest. News Infor. 1995, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.H.; Quilot, B.; Kervella, J.; Genard, M.; Li, S.H. Analysis of genotypic variation of sugar and acid contents in peaches and nectarines through the principle component analysis. Euphytica 2003, 32, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaudanskas, M.; Zymonė, K.; Viškelis, J.; Klevinskas, A.; Janulis, V. Determination of the phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of pear extracts. J. Chem. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.R.; Reddy, S.V.R.; Jhalegar, M.J. Pre-harvest fruit bagging: A useful approach for plant protection and improved post-harvest fruit quality-a review. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotech. 2014, 89, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Liu, L.; Ming, M.L.; Hu, H.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Fan, J. Comparative transcriptomic analysis provides insight into the domestication and improvement of pear (P. pyrifolia) fruit. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, L.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Wu, T.; Li, X.M.; Tu, J.F. Comparative physiological and transcriptomic analysis of pear leaves under distinct training systems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, D.M.; Durán-Soria, S.; Allwood, J.W.; Pont, S.; Gordon, S.L.; Jennings, N.; Austin, C.; Stewart, D.; Brennan, R.M.; Masny, A.; et al. Dissecting the impact of environment, season and genotype on blackcurrant fruit quality traits. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Dong, T.; Qiu, X.; Rong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J. Nitrogen nutrition is a key modulator of the sugar and organic acid content in citrus fruit. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Chen, R.; Xue, X. Effects of Spraying Calcium Fertilizer on Photosynthesis, Mineral Content, Sugar–Acid Metabolism and Fruit Quality of Fuji Apples. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Guo, N.; He, W.T.; Naeem, A.; Abbasi, Y.R.; Qu, X.L.; Zhang, S.X. Transformation of Soil Accumulated Phosphorus and Its Driving Factors across Chinese Cropping Systems. Agronomy 2023, 13, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Nakamura, K.; Ma, L.; Li, J.Z.; Kayahara, H. Analyses of arbutin and chlorogenic acid, the major phenolic constituents in Oriental pear. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3882–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, B.; Gao, W.; Cao, J.; Huang, L. Chemical composition and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of peels and flesh from 10 different pear varieties (Pyrus spp.). Food Chem. 2014, 152, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asima, A.; Amila, O.; Fuad, G.; Mekjell, M.; Pakeza, D.; Senad, M.; Nermina, S.; Oručević, Ž.S.; Igor, J.; Osman, M.; et al. A Comparative, Study of Ten Pear (Pyrus communis L.) Cultivars in Relation to the Content of Sugars, Organic Acids, and Polyphenol Compounds. Foods 2022, 11, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, J.W.; Woznicki, T.L.; Xu, Y.; Foito, A.; Aaby, K.; Sungurtas, J.; Sønsteby, A. Application of HPLC–PDA–MS metabolite profiling to investigate the effect of growth temperature and day length on blackcurrant fruit. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.Q.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.P.; Meinhardt, L.; Cao, B.; Li, Y.J.; Song, L.H. Elevated temperature and drought stress significantly affect fruit quality and activity of anthocyanin-related enzymes in jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. ‘Lingwuchangzao’). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samykanno, K.; Pang, E.; Marriott, P.J. Genotypic and environmental effects on flavor attributes of ‘Albion’and ‘Juliette’strawberry fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Pu, Y.Y. Study on the relationship between apple quality and meteorological conditions. Acta Hortic. Sin. 1987, 02, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Du, H.B.; Wu, Z.F.; He, H.S.; Wang, L.; Zong, S.W. Recent and future changes in the combination of annual temperature and precipitation throughout China. Climate 2017, 37, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.X.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, Z.B. Climatic factors determine the yield and quality of Honghe fue-cured tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, F.; Fisherfleming, R.; Hogue, E.J. Ideal pear sensory attributes and fruit characteristics. HortScience. 1995, 30, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predieri, S.; Missere, D.; Gatti, E. Studies on sensory evaluation and quality of pear fruits in Emilia-Romagna. Acta Hortic. 2002, 596, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, H.J.; Tieman, D.M. The genetics of fruit flavour preferences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colantonioa, V.; Ferrao, L.F.V.; Tieman, D.M.; Bliznyuk, N.; Sims, C.; Klee, H.J.; Munoz, P.; Resende, M.F.R. Metabolomic selection for enhanced fruit flavor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115865119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudina, M.; Stampar, F.; Orazem, P.; Petkovsek, M.M.; Veberic, R. Phenolic compounds profile, carbohydrates and external fruit quality of the ‘Concorde’ pear (Pyrus communis L.) after bagging. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tieman, D.; Zhu, G.; Resende, M.F., Jr.; Lin, T.; Nguyen, C.; Bies, D.; Rambla, J.L.; Beltran, K.S.O.; Taylor, M.; Zhang, B.; et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor. Science 2017, 355, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiwasa, K.; Rose, J.K.C.; Nakano, R.; Inaba, A.; Kubo, Y. Differential expression of seven α-expansin genes during growth and ripening of pear fruit. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 117, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, M.A.; Ross, C.F.; Pitts, M.; Kupferman, E.; Swanson, B. Relationship between instrumental and sensory determination of apple and pear texture. J. Food Qual. 2010, 33, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Zhang, L.W.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.G. Amino acid composition and principal component analysis of 11 kinds of jujube. Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 16, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Vagiri, M.; Ekholm, A.; Oberg, E.; Johansson, E.; Andersson, S.C.; Rumpunen, K. Phenols and ascorbic acid in black currants (Ribes nigrum L.): Variation due to genotype, location, and year. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9298–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
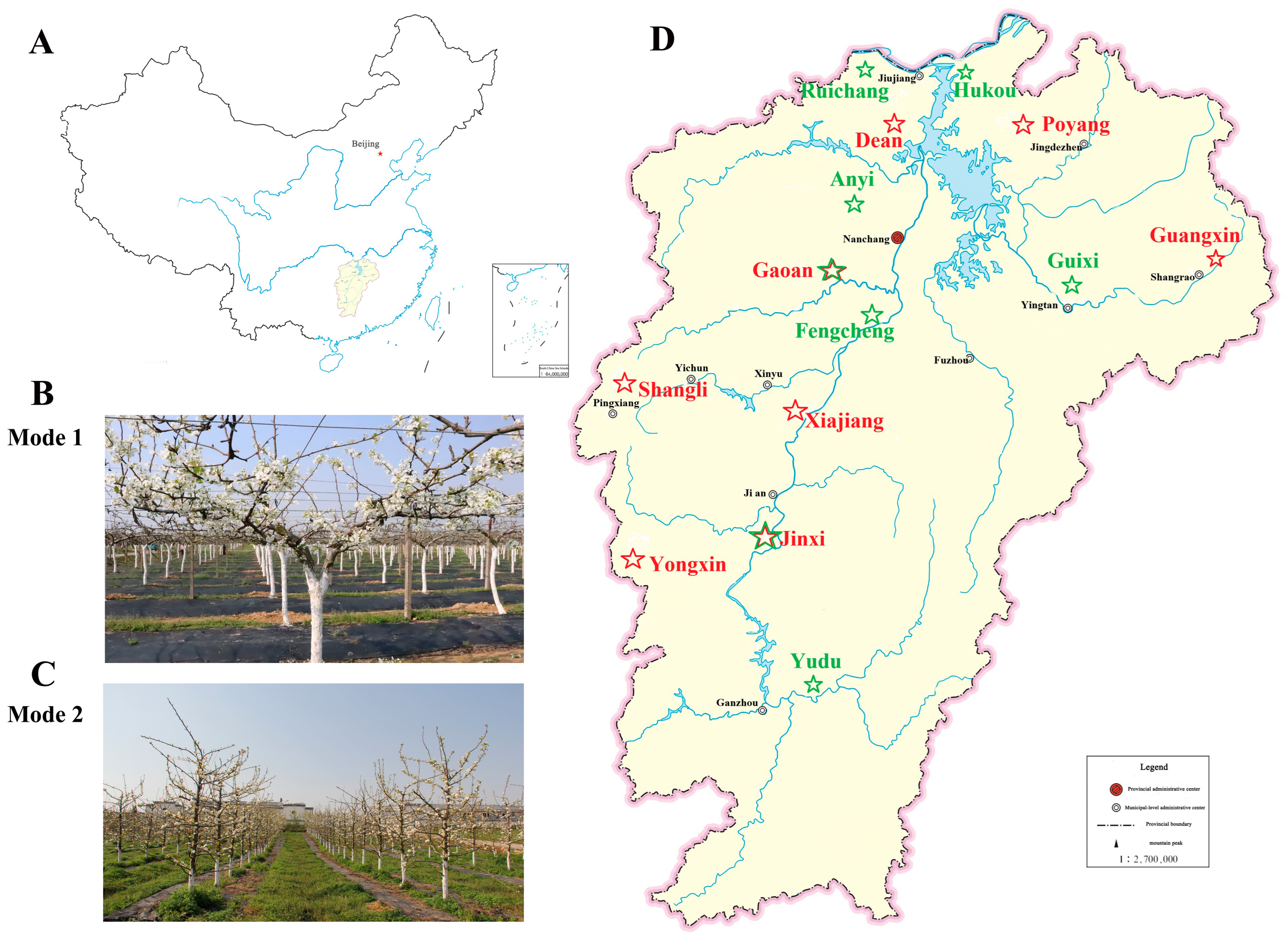
| Year | Cultivation Mode | Planting Sites: City (County) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Mode 1 | 5 (5): Jinan (Xiajiang), Fuzhou (Jinxi), Yichun (Gaoan), Shangrao (Guangxin), Jiujiang (Dean) |
| Mode 2 | 2 (2): Fuzhou (Jinxi), Yichun (Gaoan) | |
| 2024 | Mode 1 | 6 (8): Yichun (Gaoan), Jian (Xiajiang, Yongxin), Shangrao (Poyang, Guangxin), Pingxiang (Shangli), Jiujiang (Dean), Fuzhou (Jinxi) |
| Mode 2 | 5 (6): Jiujiang (Ruichang, Hukou), Nanchang (Anyi), Yingtan (Guixi), Yichun (Fhengcheng), Ganzhou (Yudu) |
| Locations | Xiajiang-1 | Jinxi-1 | Gaoan-1 | Dean-1 | Guangxin-1 | Jinxi-2 | Gaoan-2 | Mean | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flesh hardness (kg/cm2) | 5.07 ± 0.21 bc | 4.93 ± 0.12 abc | 4.53 ± 0.06 d | 4.63 ± 0.21 cd | 6.40 ± 0.26 a | 5.30 ± 0.46 b | 4.77 ± 0.21 cd | 5.09 | 12% |
| SSC (%) | 11.83 ± 0.23 ab | 12.10 ± 0.26 a | 11.10 ± 0.75 bcd | 10.53 ± 0.76 cd | 11.57 ± 0.32 abc | 10.92 ± 0.77 bcd | 10.33 ± 0.35 d | 11.2 | 7% |
| TA (g/kg) | 0.86 ± 0.03 bc | 0.79 ± 0.02 c | 0.83 ± 0.03 bc | 0.80 ± 0.10 c | 0.91 ± 0.05 bc | 1.05 ± 0.12 a | 0.94 ± 0.08 ab | 0.88 | 12% |
| SSC/TA | 13.84 ± 0.76 ab | 15.28 ± 0.77 a | 13.36 ± 0.72 b | 13.27 ± 0.86 b | 12.84 ± 0.94 b | 10.4 ± 0.47 c | 11.04 ± 0.82 c | 12.86 | 13% |
| Lactic acid (mg/kg) | 273.16 ± 70.45 bc | 324.29 ± 46.16 abc | 247.73 ± 21.63 c | 237.92 ± 40.26 c | 376.03 ± 24.12 ab | 409.38 ± 110.05 a | 430.32 ± 9.65 a | 328.4 | 27% |
| Tartaric acid (mg/kg) | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | <50 | 0 | 0 |
| Malic acid (mg/kg) | 1187.65 ± 27.00 ab | 1400.18 ± 112.62 a | 1229.00 ± 26.36 ab | 1168.85 ± 198.65 ab | 1320.64 ± 125.69 b | 1264.68 ± 203.91 ab | 1265.01 ± 79.88 ab | 1262.29 | 10% |
| Citric acid (mg/kg) | 450.27 ± 65.46 bc | 634.59 ± 137.48 ab | 608.36 ± 131.8 ab | 704.68 ± 278.03 ab | 742.5 ± 89.79 a | 299.59 ± 11.36 c | 334.19 ± 45.78 c | 539.17 | 38% |
| Succinic acid (mg/kg) | <250 | <250 | <250 | <250 | <250 | <250 | <250 | 0 | 0 |
| Fumaric acid (mg/kg) | 8.36 ± 2.50 ab | 5.68 ± 2.65 abc | 8.83 ± 4.37 a | 6.74 ± 1.84 abc | 2.47 ± 0.44 c | 3.39 ± 2.62 bc | 1.86 ± 0.18 c | 5.33 | 63% |
| Shikimic acid (mg/kg) | 103.63 ± 17.52 bcd | 88.94 ± 20.5 cd | 66.38 ± 18.58 d | 77.57 ± 44.71 cd | 143.68 ± 18.97 ab | 117.1 ± 15.90 abc | 161.17 ± 13.34 a | 108.35 | 35% |
| Protein (g/kg) | 4.40 ± 0.26 ab | 3.90 ± 0.36 ab | 3.70 ± 0.61 ab | 3.67 ± 0.64 b | 4.43 ± 0.55 ab | 4.47 ± 0.12 a | 3.77 ± 0.25 ab | 4.05 | 13% |
| Fat (g/kg) | 3.00 ± 0 a | 2.67 ± 0.58 ab | 2.67 ± 0.58 ab | 2.33 ± 0.58 ab | 2.33 ± 0.58 ab | 2.33 ± 0.58 ab | 2.00 ± 0 b | 2.48 | 21% |
| Starch (g/kg) | 1.99 ± 0.83 a | 2.59 ± 0.40 a | 2.05 ± 0.79 a | 2.06 ± 1.37 a | 1.48 ± 0.97 a | 1.85 ± 0.24 a | 1.86 ± 0.74 a | 1.98 | 39% |
| Total sugar (g/kg) | 64.80 ± 3.86 b | 62.80 ± 1.56 b | 78.43 ± 10.08 a | 70.9 ± 2.52 ab | 69.27 ± 4.59 ab | 76.53 ± 4.39 a | 64.87 ± 2.65 b | 69.66 | 10% |
| Carbohydrate (g/kg) | 66.77 ± 4.45 c | 65.40 ± 1.84 c | 80.50 ± 9.35 a | 72.93 ± 1.57 bc | 70.80 ± 4.65 bc | 78.40 ± 4.31 ab | 66.73 ± 2.99 c | 71.65 | 10% |
| Heat (kcal/kg) | 311.77 ± 17.57 c | 301.17 ± 11.96 c | 360.7 ± 34.15 a | 327.5 ± 8.13 bc | 321.73 ± 17.01 bc | 352.4 ± 19.86 ab | 299.97 ± 11.28 c | 325.03 | 8% |
| Crude fiber (%) | 1.63 ± 0.15 ab | 1.30 ± 0.17 b | 1.40 ± 0.17 ab | 1.37 ± 0.46 b | 1.73 ± 0.15 a | 1.77 ± 0.06 a | 1.50 ± 0 ab | 1.53 | 16% |
| Peel phenols (mg/kg) | 1139.04 ± 128.58 c | 1645.78 ± 130.26 bc | 1382.73 ± 509.72 bc | 1581.91 ± 282.01 bc | 2546.68 ± 1450.82 ab | 2972.08 ± 834.12 a | 2404.01 ± 267.55 ab | 1953.17 | 44% |
| Pulp phenols (mg/kg) | 57.89 ± 18.75 ab | 59.9 ± 14.32 ab | 68.84 ± 13.92 ab | 46.61 ± 12.37 b | 61.14 ± 8.92 ab | 48.16 ± 0.96 b | 80.89 ± 18.69 a | 60.49 | 27% |
| N (mg/kg) | 704.00 ± 42.33 ab | 624.00 ± 57.69 ab | 592.00 ± 97.32 ab | 586.67 ± 102.87 b | 709.33 ± 88.12 ab | 714.67 ± 18.48 a | 602.67 ± 40.27 ab | 647.62 | 13% |
| P (mg/kg) | 158.00 ± 14.18 ab | 157.67 ± 16.04 ab | 136.97 ± 34.17 b | 123.00 ± 19.47 b | 179.00 ± 11 a | 133.67 ± 22.01 b | 134.00 ± 4.36 b | 146.04 | 17% |
| K (mg/kg) | 862.16 ± 291.68 a | 1061.36 ± 273.55 a | 850.32 ± 104.55 a | 802.35 ± 471.59 a | 1049.65 ± 296.10 a | 1095.98 ± 273.09 a | 810.75 ± 470.69 a | 933.22 | 33% |
| Ca (mg/kg) | 22.09 ± 3.18 b | 27.92 ± 9.83 ab | 27.08 ± 7.76 ab | 25.79 ± 5.04 ab | 36.06 ± 14.38 ab | 34.88 ± 2.95 ab | 39.62 ± 13.09 a | 30.49 | 32% |
| Mg (mg/kg) | 62.48 ± 12.53 a | 62.37 ± 6.98 a | 50.86 ± 19.89 a | 53.91 ± 16.28 a | 75.55 ± 13.25 a | 65.68 ± 4.29 a | 61.57 ± 19.67 a | 61.77 | 23% |
| Na (mg/kg) | 10.10 ± 1.83 a | 5.03 ± 0.62 b | 5.25 ± 1.77 b | 5.95 ± 2.05 b | 4.57 ± 0.82 b | 6.24 ± 1.15 b | 5.81 ± 0.79 b | 6.13 | 34% |
| Se (mg/kg) | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0 | 0% |
| β-carotenoid (mg/kg) | 0.03 ± 0.02 b | 0.05 ± 0.02 ab | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 0.08 ± 0.03 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.05 | 58% |
| VA (µg/kg) | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| VE (α) (mg/kg) | 12.06 ± 2.81 ab | 8.84 ± 2.76 bc | 12 ± 3.12 ab | 12.12 ± 4.51 ab | 14.93 ± 0.61 a | 8.14 ± 2.71 bc | 6.56 ± 3.96 c | 10.67 | 36% |
| VE (β) (mg/kg) | 0.53 ± 0.22 ab | 0.23 ± 0.14 bc | 0.46 ± 0.17 abc | 0.48 ± 0.21 abc | 0.67 ± 0.04 a | 0.28 ± 0.07 c | 0.22 ± 0.07 c | 0.41 | 50% |
| VE (γ) (mg/kg) | 0.06 ± 0.03 a | 0.01 ± 0 b | 0.02 ± 0.02 ab | 0.03 ± 0.02 ab | 0.03 ± 0.01 ab | 0.06 ± 0.04 a | 0.06 ± 0.05 a | 0.04 | 75% |
| VE (δ) (mg/kg) | 0.22 ± 0.08 a | 0.21 ± 0.13 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.05 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.18 ± 0.08 a | 0.19 | 35% |
| VC (mg/kg) | 83.57 ± 32.5 a | 72.9 ± 13.16 a | 75.83 ± 20.93 a | 80.6 ± 35.49 a | 88.80 ± 1.30 a | 89.73 ± 28.44 a | 72.83 ± 10.25 a | 80.61 | 26% |
| VB1 (mg/kg) | 0.09 ± 0.02 ab | 0.13 ± 0.04 a | 0.07 ± 0.02 bc | 0.07 ± 0.02 bc | 0.05 ± 0.01 c | 0.07 ± 0.02 bc | 0.07 ± 0.02 bc | 0.08 | 38% |
| VB2 (mg/kg) | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.02 a | 0.05 | 20% |
| VB3 (mg/kg) | 0.20 ± 0.05 b | 0.49 ± 0.17 a | 0.33 ± 0.09 ab | 0.44 ± 0.17 a | 0.14 ± 0.04 b | 0.17 ± 0.04 b | 0.18 ± 0.03 b | 0.28 | 57% |
| Location | L | a | b | Weight (g) | Tare/Weight | LD (cm) | TD (cm) | LD/TD | Core Size (cm) | Core Size/TD | TSS (%) | TA (mol/L) | TSS/TA | Hardness (kg/cm2) | Stone Cell (g/200 g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode-1 | Gaoan | 59.00 ± 1.17 bc | 13.03 ± 1.10 a | 39.85 ± 0.63 a | 266.44 ± 41.86 cb | 0.11 ± 1.48 a | 77.35 ± 5.45 a | 78.83 ± 2.78 c | 0.98 ± 0.04 a | 28.95 ± 1.33 bc | 0.37 ± 0.03 c | 10.73 ± 0.15 c | 18.93 ± 0.40 cd | 0.57 ± 0.02 de | 4.08 ± 0.33 c | 1.03 ± 0.03 c |
| Xiajiang | 61.29 ± 0.79 bc | 12.15 ± 1.20 a | 41.65 ± 0.90 a | 307.53 ± 15.29 b | 0.11 ± 0.21 a | 75.96 ± 5.82 abc | 84.28 ± 4.48 ab | 0.9 ± 0.09 a | 31.63 ± 0.84 ab | 0.38 ± 0.03 abc | 12.23 ± 0.85 ab | 17.73 ± 0.70 de | 0.69 ± 0.04 bc | 4.99 ± 0.57 b | 1.06 ± 0.16 c | |
| Yongxin | 62.28 ± 0.83 abc | 11.78 ± 0.84 a | 39.20 ± 0.14 a | 270.56 ± 7.50 bc | 0.09 ± 0.78 b | 76.06 ± 2.92 ab | 77.61 ± 0.97 c | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 30.7 ± 2.47 ab | 0.4 ± 0.03 ab | 11.8 ± 0.00 b | 16.6 ± 0.30 ef | 0.71 ± 0.01 b | 4.34 ± 0.41 bc | 1.81 ± 0.2 a | |
| Poyang | 63.52 ± 5.43 ab | 11.34 ± 0.92 a | 39.69 ± 0.62 a | 383.03 ± 29.58 a | 0.10 ± 0.62 b | 81.29 ± 2.05 a | 89.32 ± 3.45 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 a | 32.5 ± 3.05 a | 0.36 ± 0.05 c | 10.73 ± 0.51 c | 20.53 ± 0.30 bc | 0.52 ± 0.04 ef | 4.94 ± 0.05 b | 0.98 ± 0.02 c | |
| Guangxin | 66.68 ± 2.83 a | 8.20 ± 2.54 b | 41.40 ± 1.6 a | 172.06 ± 22.58 d | 0.12 ± 0.29 a | 60.93 ± 4.44 e | 69.14 ± 1.74 d | 0.88 ± 0.08 a | 27.03 ± 0.82 c | 0.39 ± 0.01 abc | 12.17 ± 0.15 ab | 15.73 ± 0.13 f | 0.78 ± 0.01 a | 4.36 ± 0.42 bc | 1.79 ± 0.01 a | |
| Shangli | 62.71 ± 3.09 ab | 11.76 ± 1.98 a | 39.15 ± 2.44 a | 243.96 ± 22.65 c | 0.10 ± 0.48 b | 68.49 ± 2.93 cd | 75.65 ± 0.70 c | 0.91 ± 0.05 a | 31.79 ± 1.57 ab | 0.42 ± 0.02 a | 10.73 ± 0.67 c | 22.73 ± 2.00 a | 0.47 ± 0.03 f | 4.67 ± 0.75 bc | 1.3 ± 0.15 b | |
| D an | 57.06 ± 3.11 c | 12.18 ± 1.57 a | 36.25 ± 1.78 b | 164.35 ± 22.24 d | 0.12 ± 0 a | 65.39 ± 2.25 de | 68.97 ± 5.45 d | 0.96 ± 0.07 a | 23.80 ± 1.74 d | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | 10.2 ± 0.26 c | 15.93 ± 0.40 ef | 0.64 ± 0.01 c | 4.19 ± 0.26 c | 1.14 ± 0.04 bc | |
| Jinxi | 60.62 ± 3.73 bc | 9.96 ± 2.53 b | 41.34 ± 2.03 a | 230.58 ± 7.01 c | 0.1 ± 0.36 b | 68.6 ± 1.55 cd | 74.41 ± 0.18 cd | 0.92 ± 0.03 a | 29.67 ± 1.13 abc | 0.40 ± 0.02 ab | 12.73 ± 0.15 a | 21.98 ± 1.63 ab | 0.58 ± 0.04 d | 5.77 ± 0.40 a | 0.59 ± 0.11 d | |
| Mean | 61.65 | 11.3 | 39.82 | 254.81 | 0.11 | 71.76 | 77.28 | 0.93 | 29.51 | 0.38 | 11.42 | 18.77 | 0.62 | 4.67 | 1.21 | |
| CV | 6.10% | 18.05% | 5.25% | 27.75% | 11.38% | 10.21% | 9.25% | 6.45% | 10.68% | 7.84% | 8.41% | 14.56% | 16.28% | 13.88% | 33.57% | |
| Mode-2 | Ruichang | 59.24 ± 2.52 a | −11.99 ± 1.03 d | 43.61 ± 2.57 a | 135.04 ± 3.85 d | 0.13 ± 0.74 a | 58.14 ± 1.69 d | 61.39 ± 1.89 d | 0.95 ± 0.05 ab | 29.65 ± 1.00 ab | 0.48 ± 0.03 a | 12.23 ± 0.06 a | 16.93 ± 0.5 d | 0.72 ± 0.02 a | 4.07 ± 0.12 b | 0.83 ± 0.05 e |
| Anyi | 51.46 ± 4.02 bc | −2.74 ± 2.80 c | 37.37 ± 2.16 bc | 374.37 ± 7.86 a | 0.09 ± 0.30 e | 80.5 ± 4.45 a | 90.52 ± 2.13 a | 0.89 ± 0.06 b | 30.25 ± 0.93 ab | 0.33 ± 0.01 e | 12.37 ± 0.12 a | 24.73 ± 1 b | 0.5 ± 0.02 b | 3.8 ± 0.35 b | 1.23 ± 0.03 cd | |
| Hukou | 55.00 ± 0.56 b | −9.12 ± 2.09 d | 39.55 ± 1.30 b | 207.58 ± 28.07 b | 0.12 ± 0.81 ab | 68.98 ± 3.88 b | 73.51 ± 3.17 b | 0.94 ± 0.04 ab | 24.65 ± 0.16 c | 0.34 ± 0.02 de | 11.67 ± 1.12 a | 17.00 ± 0.3 d | 0.69 ± 0.07 a | 4.5 ± 0.65 b | 1.94 ± 0.24 b | |
| Guixi | 52.46 ± 1.28 bc | −2.23 ± 2.88 bc | 37.57 ± 2.09 bc | 170.45 ± 5.44 c | 0.10 ± 0.65 cd | 60.98 ± 2.42 cd | 68.21 ± 1.06 c | 0.89 ± 0.05 b | 27.99 ± 1.89 b | 0.41 ± 0.02 bc | 12.60 ± 0.72 a | 17.62 ± 0.57 cd | 0.72 ± 0.06 a | 4.56 ± 0.15 b | 1.07 ± 0.05 de | |
| Fengcheng | 51.29 ± 1.45 bc | 1.27 ± 1.00 ab | 35.55 ± 1.43 c | 220.04 ± 15.57 b | 0.10 ± 0 d | 67.93 ± 2.40 bc | 73.93 ± 1.31 b | 0.92 ± 0.03 ab | 27.83 ± 1.47 b | 0.38 ± 0.03 cd | 12.20 ± 0.26 a | 18.65 ± 0.57 c | 0.66 ± 0.02 a | 4.83 ± 1.18 b | 1.46 ± 0.03 c | |
| Yudu | 49.99 ± 1.07 c | 4.00 ± 0.12 a | 33.92 ± 0.99 c | 212.31 ± 23.27 b | 0.11 ± 0.33 bc | 71.77 ± 5.08 b | 73.02 ± 0.88 b | 0.98 ± 0.06 a | 31.36 ± 2.11 a | 0.43 ± 0.03 b | 12.57 ± 0.4 a | 29.60 ± 1.04 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 b | 6.2 ± 0.60 a | 2.6 ± 0.3 a | |
| Mean | 53.24 | −3.47 | 37.93 | 219.96 | 0.11 | 68.05 | 73.43 | 0.93 | 28.62 | 0.39 | 12.27 | 20.76 | 0.62 | 4.66 | 1.52 | |
| CV | 6.87% | 171.30% | 9.31% | 35.64% | 12.51% | 11.84% | 12.53% | 5.76% | 8.81% | 14.51% | 4.76% | 23.86% | 19.70% | 20.32% | 41.09% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiong, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, C.; Xu, L. Recommendations for Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes Suitable for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear in Jiangxi Province. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070771
Li Y, Yang S, Xiong C, Wang Y, Hu X, Zhou C, Xu L. Recommendations for Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes Suitable for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear in Jiangxi Province. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(7):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070771
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanting, Sichao Yang, Chuanyong Xiong, Yun Wang, Xinlong Hu, Chaohua Zhou, and Lei Xu. 2025. "Recommendations for Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes Suitable for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear in Jiangxi Province" Horticulturae 11, no. 7: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070771
APA StyleLi, Y., Yang, S., Xiong, C., Wang, Y., Hu, X., Zhou, C., & Xu, L. (2025). Recommendations for Planting Sites and Cultivation Modes Suitable for High-Quality ‘Cuiguan’ Pear in Jiangxi Province. Horticulturae, 11(7), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070771






