A Fast and Sensitive Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification Method for Field Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematode Populations
2.2. Wood Samples
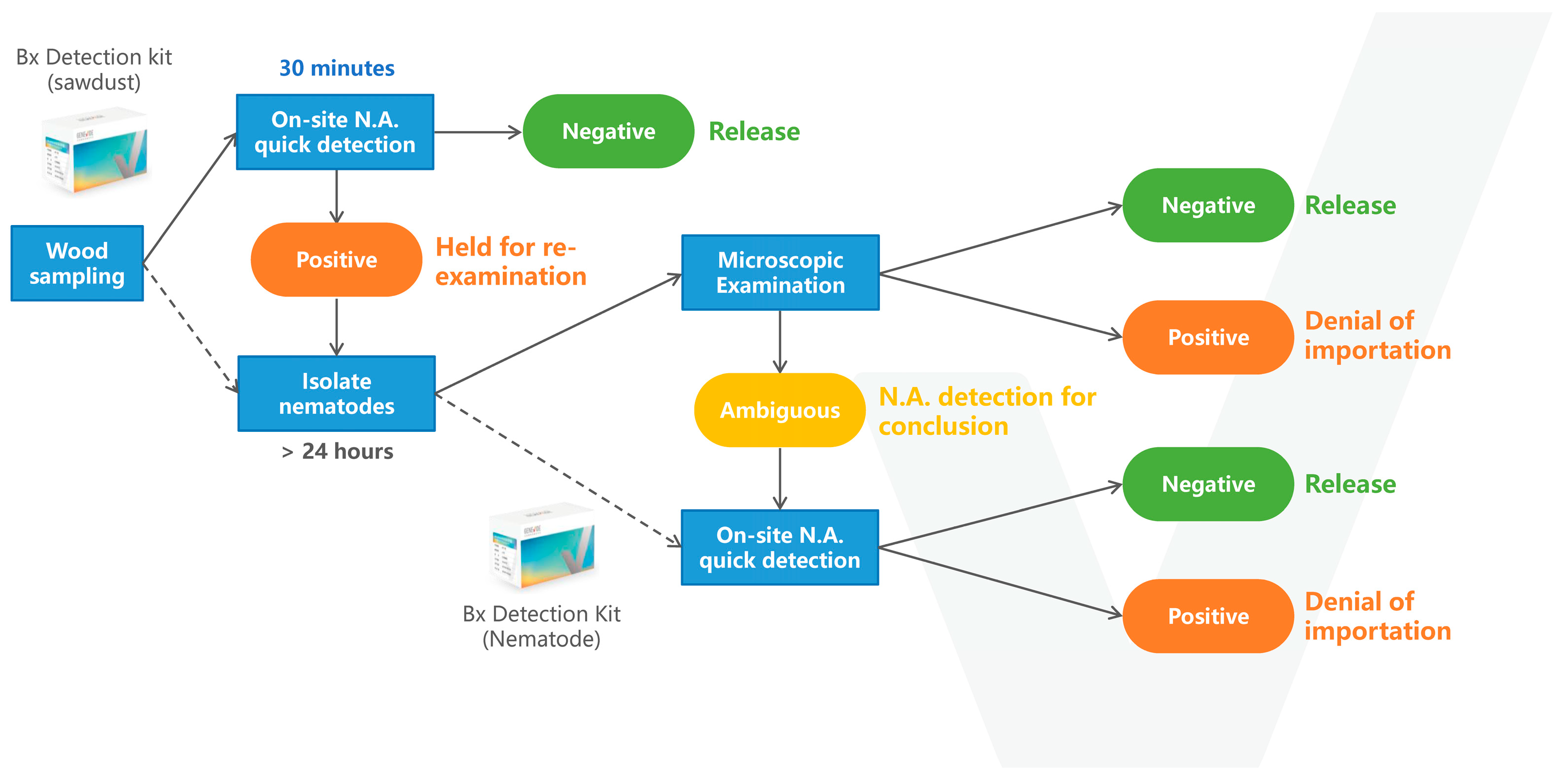
2.3. Portable Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification (EmDEA) Instrument and Commercial Kit
2.4. Genomic DNA (gDNA) Extraction from Nematodes
2.5. Genomic DNA Extraction from Pinewood Sawdust
2.6. Isothermal Fluorescence Amplification Assay
2.7. Evaluation of EmDEA Assay Specificity
2.8. Evaluation of EmDEA Assay Sensitivity and Stability
2.9. Comparison of the Baermann Funnel Technique and the Sawdust Method
3. Results
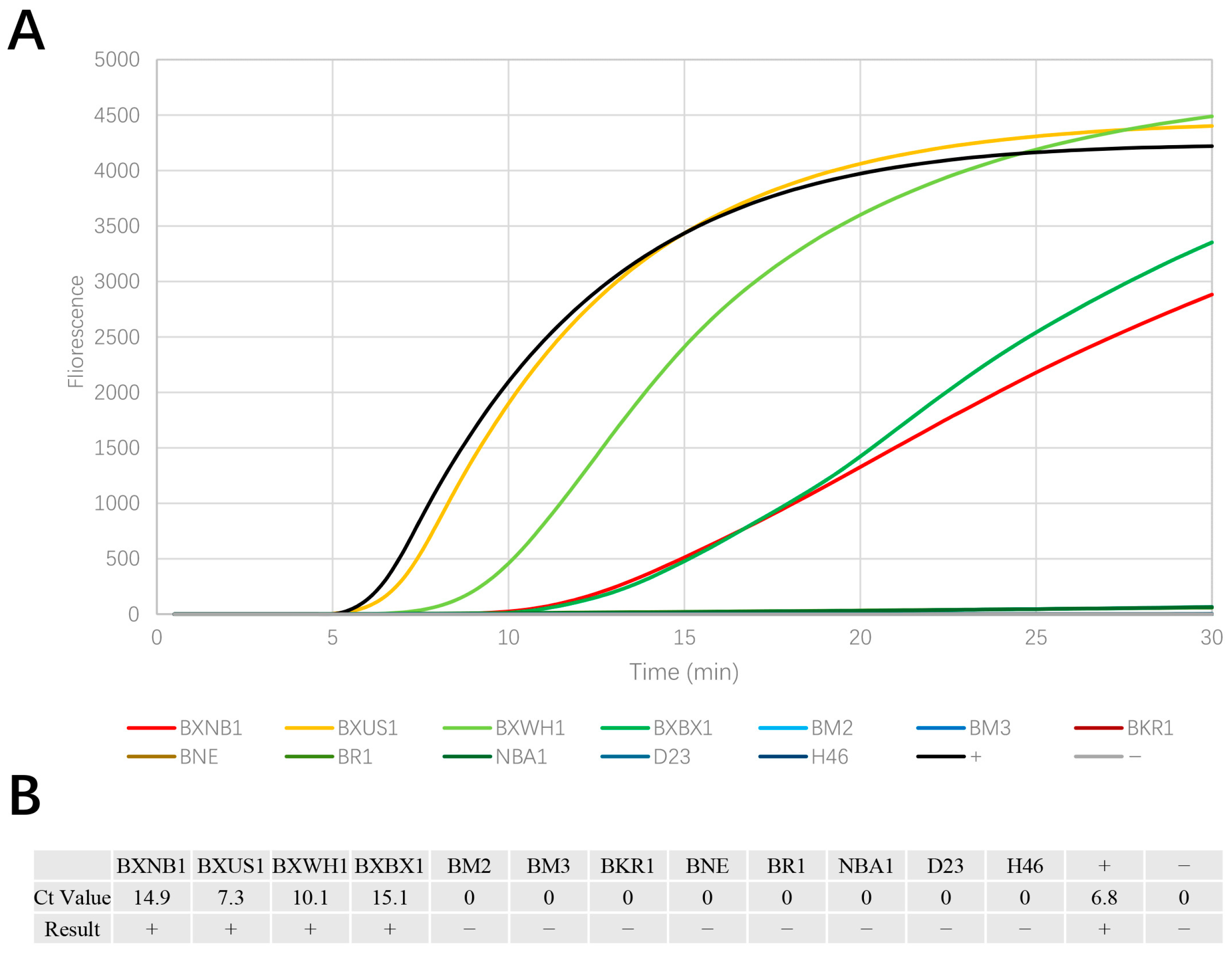
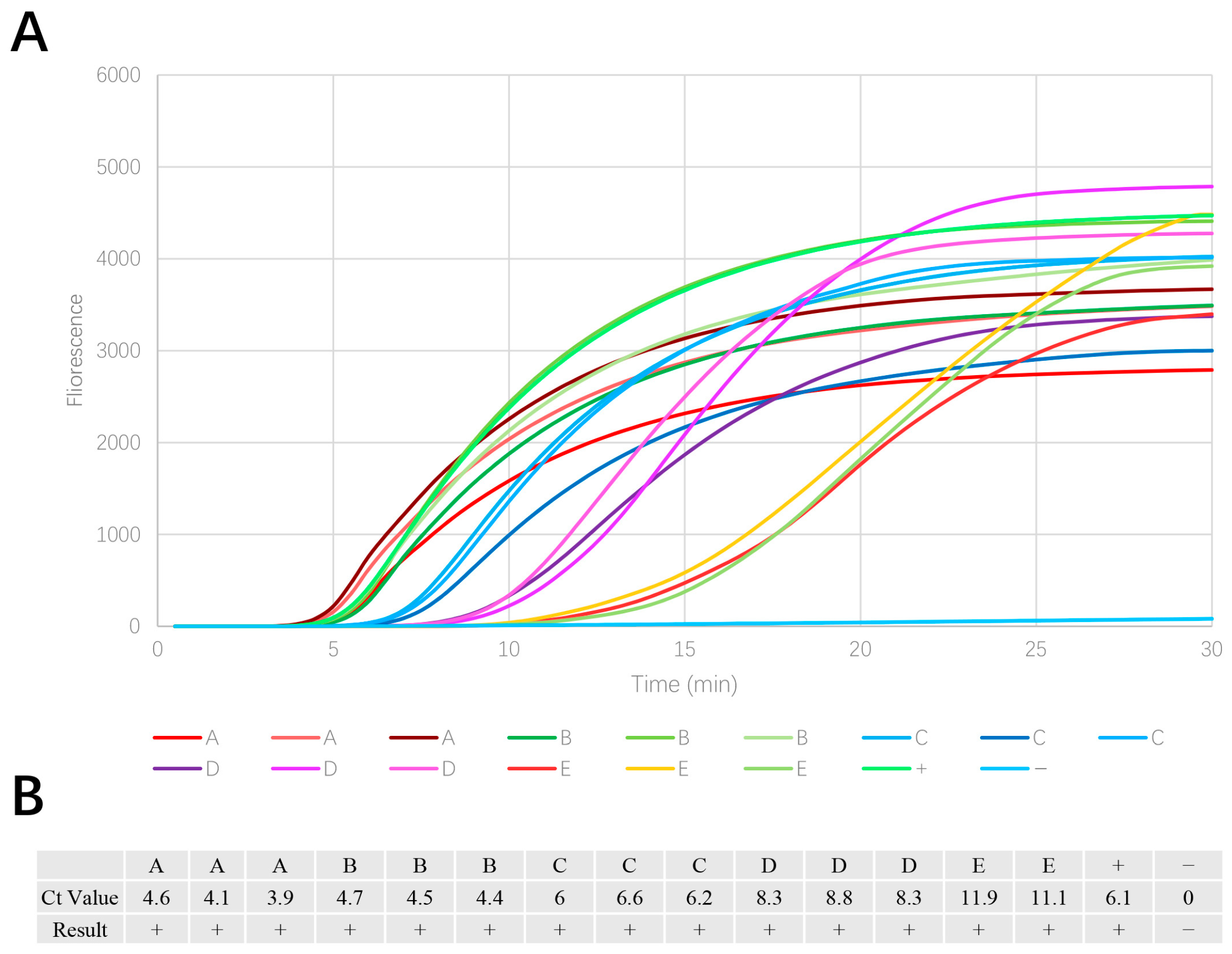
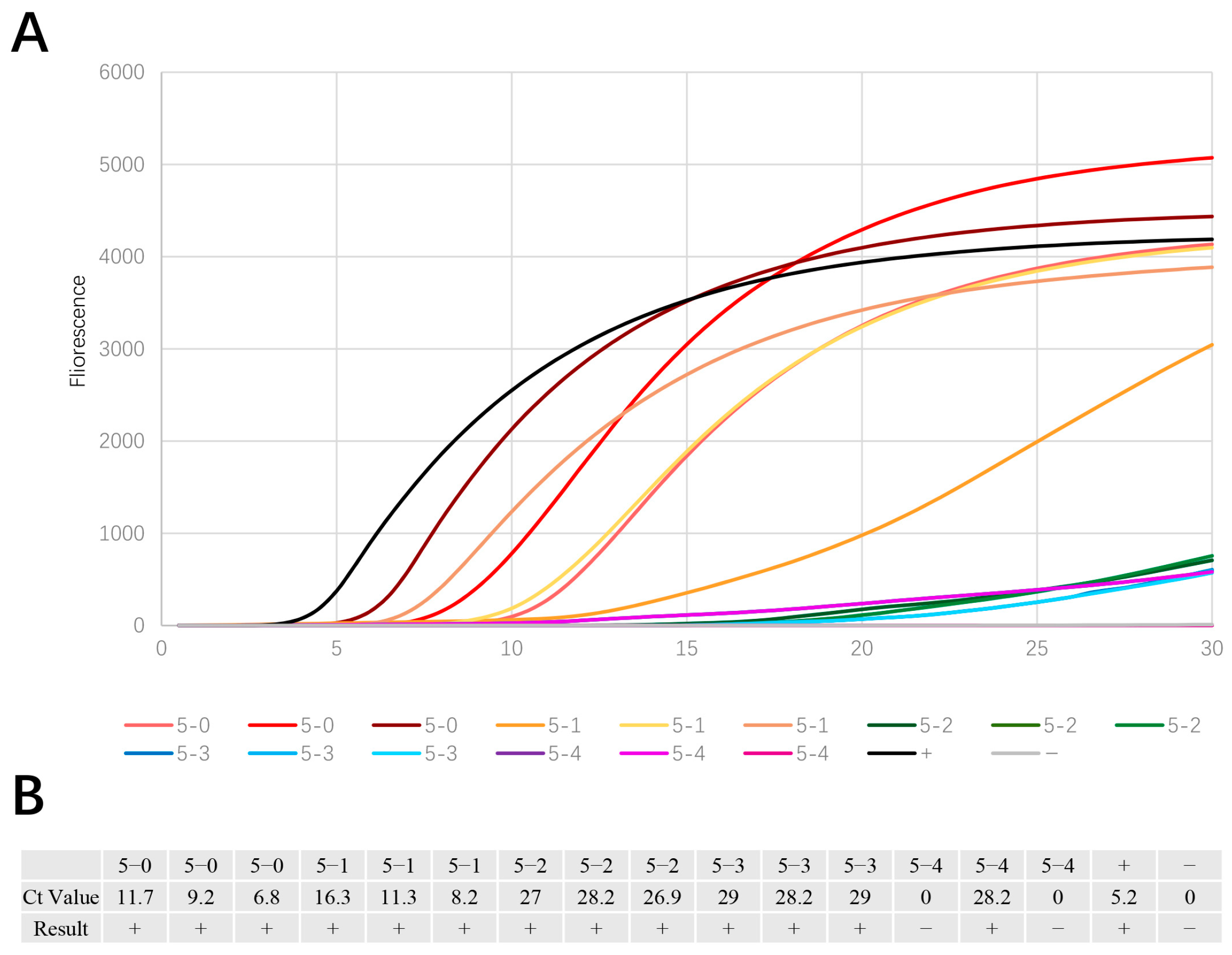
3.1. EmDEA Assay Specificity
3.2. Gradient Dilution Tests on PWN Plasmid DNA
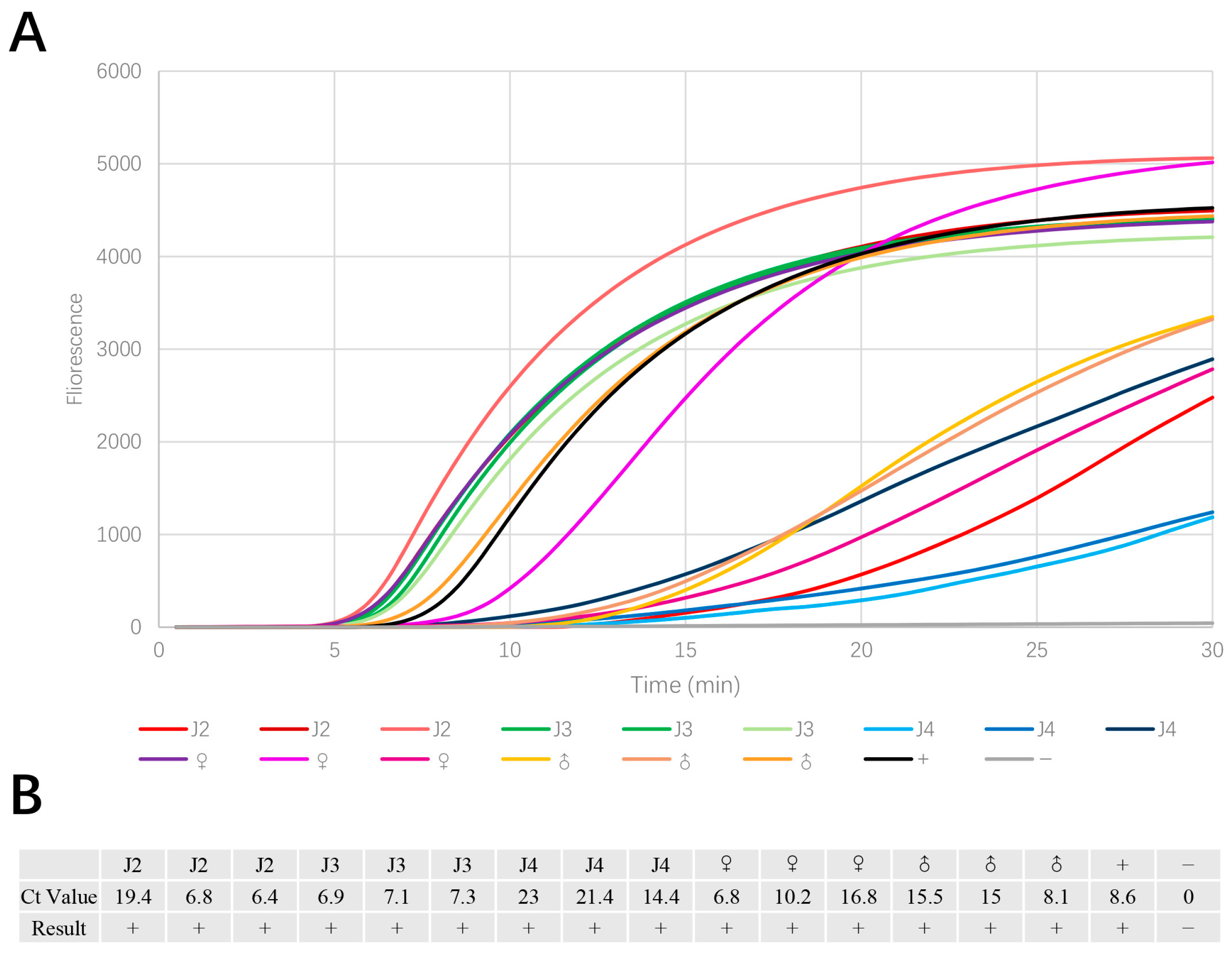
3.3. Dilution Test for Single Adult PWN
3.4. Stability Test of Single PWN in Different Juvenile Stages
3.5. Mixed Nematode Liquid Test
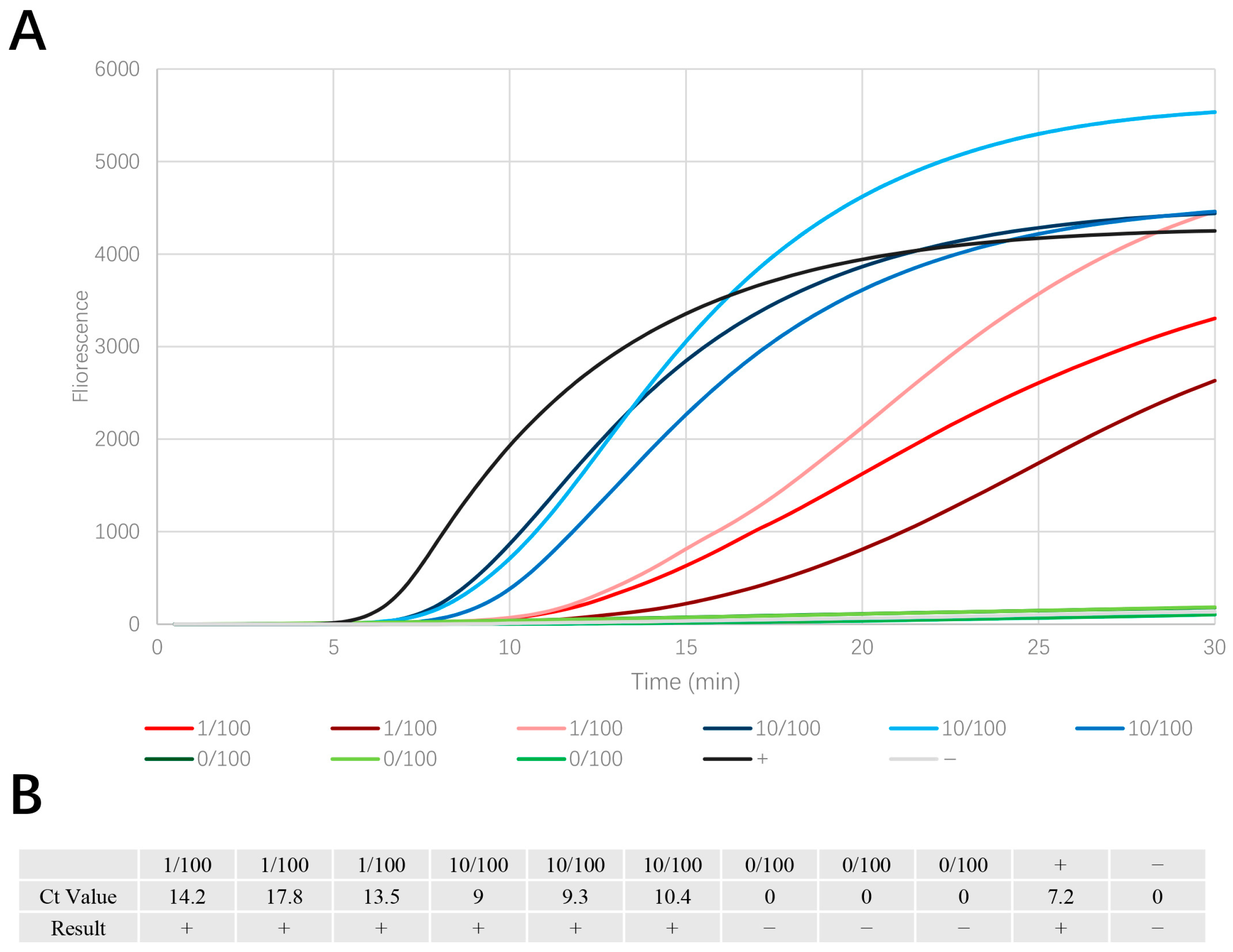
3.6. Comparison of the Baermann Funnel Technique and the Sawdust EmDEA Method Based on Real Pinewood Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWN | pinewood nematode |
| EmDEA | enzyme-mediated duplex exponential amplification |
References
- Nickle, W.R. A taxonomic review of the genera of the Aphelenchoidea (Fuchs, 1937) Thorne, 1949 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). J. Nematol. 1970, 2, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Futai, K. Pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, K.; Arakawa, Y. Horizontal transmission of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus between the sexes of Monochamus alternatus. J. Nematol. 2003, 35, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, M.M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgermeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Cobacho, A.S.; Escuer, M.; Santiago, M.R.; Esparrago, G.; Abelleira, A.; Navas, A. Incidence of the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Steiner & Buhrer, 1934 (Nickle, 1970) in Spain. Nematology 2011, 13, 755–757. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, D.J.; Evans, K. Extraction, identification, and control of plant-parasitic nematodes. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Temperate Agriculture; Evans, K., Trudgill, D., Webster, J., Eds.; CAB International: Wellingford, UK, 1993; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Fang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Guo, K. Identification of a Bursaphelenchus xylophilus form with mucronated tips in most females. J. Plant Prot. 2021, 48, 434–441. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahori, H.; Kanzaki, N.; Futai, K. A simple polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism-aided diagnosis method for pine wilt disease. For. Pathol. 2000, 30, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Aikawa, T.; Oeda, Y.; Karim, N.; Kanzaki, N. A rapid and precise diagnostic method for detecting the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Kanzaki, N.; Futai, K. A nested PCR-based method for detecting the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pine wood. Nematology 2005, 7, 775–782. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.S.; Kim, A.Y.; Han, H.R.; Moon, Y.S.; Koh, Y.H. Development of two alternative Loop-mediated isothermal amplification tools for detecting pathogenic pine wood nematodes. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, I.; Allen, E.; Humble, L.; Green, M.; Rott, M. Application of Conventional PCR and Real-Time PCR Diagnostic Methods for Detection of the PineWood Nematode, Bursaphe-lenchus xylophilus in Wood Samples from Lodgepole Pine. In Pine Wilt Disease: A Worldwide Threat to Forest Ecosystems; Mota, M.M., Vieira, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, D.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.K.; Han, H.R. A new on-site detection method for Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in infected pine trees. For. Pathol. 2019, 49, e12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.; Kim, D.; Choi, W.; Park, S.; Han, H. Point-of-care diagnostic (POCD) method for detecting Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pinewood using recombinase polymerase amplifi-cation (RPA) with the portable optical isothermal device (POID). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.C.; Li, M.; Sheng, R.C.; Chen, F.M. Enzyme-Mediated Amplification (EMA) to detect the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Forests 2022, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Rapid detection of the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus using recombinase polymerase amplification combined with CRISPR/Cas12a. Crop Prot. 2023, 170, 106–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Fonseca, L.; Abrantes, I. Direct molecular detection of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, from pine wood, bark and insect vector. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, C.; Castagnone, C.; Boonham, N.; Tomlinson, J.; Lawson, R.; Hockland, S.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Satellite DNA as a target for TaqMan real-time PCR detection of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Q.; Kong, X.C.; Wang, X.R.; Zhong, T.K.; Zhu, X.W.; Mota, M.M.; Ma, C. Direct PCR-based method for detecting Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the pine wood nematode in wood tissue of Pinus massoniana. For. Pathol. 2011, 41, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Choi, K.S.; Shin, S.C.; Moon, I.S.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, S.H. Development of an efficient PCR-based diagnosis protocol for the identification of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). Nematology 2004, 6, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, W.; Long, L.; Qi, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for rapid visual detection of cry2Ab and cry3A genes in genetically modified crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15109–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, I.; Allen, E.; Foord, B.; Anema, J.; Reisle, C.; Uzunovic, A.; James, D. Detection of living Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in wood, using reverse transcriptase loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
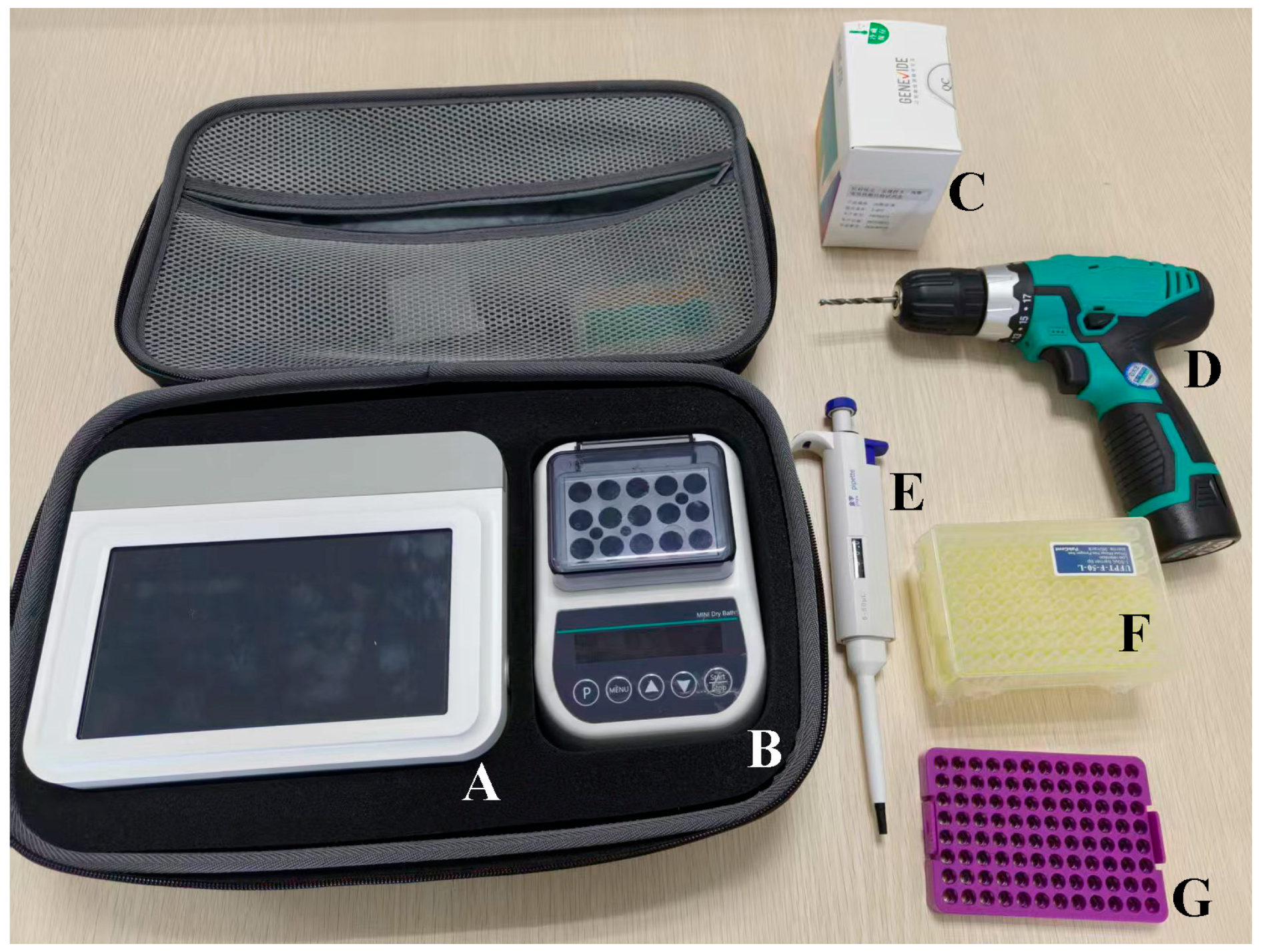
| No. | Species | Isolation Number | Source | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BXNB1 | Ningbo, China | Pinus massoniana Lamb. |
| 2 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BXUS1 | USA | Pinus taeda L. |
| 3 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BXWH1 | Weihai, China | Pinus massoniana |
| 4 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | BXBX1 | Benxi, China | Pinus koraiensis Siebold et Zuccarini |
| 5 | Bursaphelenchus mucronatus kolymensis (Braasch, Gu & Burgermeister, 2011) | BM2 | Turkey | Pinus packaging wood |
| 6 | Bursaphelenchus mucronatus mucronatus (Mamiya & Enda, 1979) | BM3 | Huzhou, China | Pinus massoniana |
| 7 | Bursaphelenchus doui (Brassch, Gu, Burgermeister & Zhang, 2004) | BKR1 | Republic of Korea | Pinus packaging wood |
| 8 | Bursaphelenchus fungivorus (Franklin & Hooper, 1962) | BNE | The Netherlands | Peat |
| 9 | Bursaphelenchus rainulfi (Brassch & Burgermeister, 2002) | BR1 | Ningbo, China | Pinus massoniana |
| 10 | Aphelenchoides sp. | NBA1 | Ningbo, China | Pinus massoniana |
| 11 | Pseudaphelenchus sp. | D23 | USA | Pinus taeda |
| 12 | Ektaphelenchoides sp. | H46 | USA | Pinus taeda |
| Region (Country/Province) | Host Species | No. of Samples | EmDEA Results | Baermann Results | Result Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang, China | Pinus massoniana | 25 | 15 +, 10 − | 13 +, 12 − | Nematodes not isolated by the Baermann method in 2 EmDEA-positive samples |
| Pinus tabuliformis | 1 | 1 + | 1 − | Detected by EmDEA only | |
| Jilin, China | Pinus sylvestris | 2 | 2 + | 2 + | Full agreement |
| Pinus tabuliformis | 2 | 2 + | 1 +, 1 − | Nematodes not isolated by the Baermann method in 1 EmDEA-positive samples | |
| USA | Pinus taeda | 6 | 6 + | 4 +, 2 − | Nematodes not isolated by the Baermann method in 2 EmDEA-positive samples |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, K.; Ma, X.; Fang, Y.; Duan, W.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Ye, W.; Gu, J. A Fast and Sensitive Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification Method for Field Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060602
Guo K, Ma X, Fang Y, Duan W, Wu Y, Hu Z, Ye W, Gu J. A Fast and Sensitive Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification Method for Field Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(6):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060602
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Kai, Xinxin Ma, Yiwu Fang, Weijun Duan, Yao Wu, Zhenxin Hu, Weimin Ye, and Jianfeng Gu. 2025. "A Fast and Sensitive Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification Method for Field Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus" Horticulturae 11, no. 6: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060602
APA StyleGuo, K., Ma, X., Fang, Y., Duan, W., Wu, Y., Hu, Z., Ye, W., & Gu, J. (2025). A Fast and Sensitive Enzyme-Mediated Duplex Exponential Amplification Method for Field Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Horticulturae, 11(6), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060602






