Unraveling Diversity in Physical and Mineral Traits of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Landraces Harvested at Immature Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Field Experiment
2.2. External Quality Assessment
2.3. Internal Quality Assessment
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Mineral Composition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Faba Beans Volume
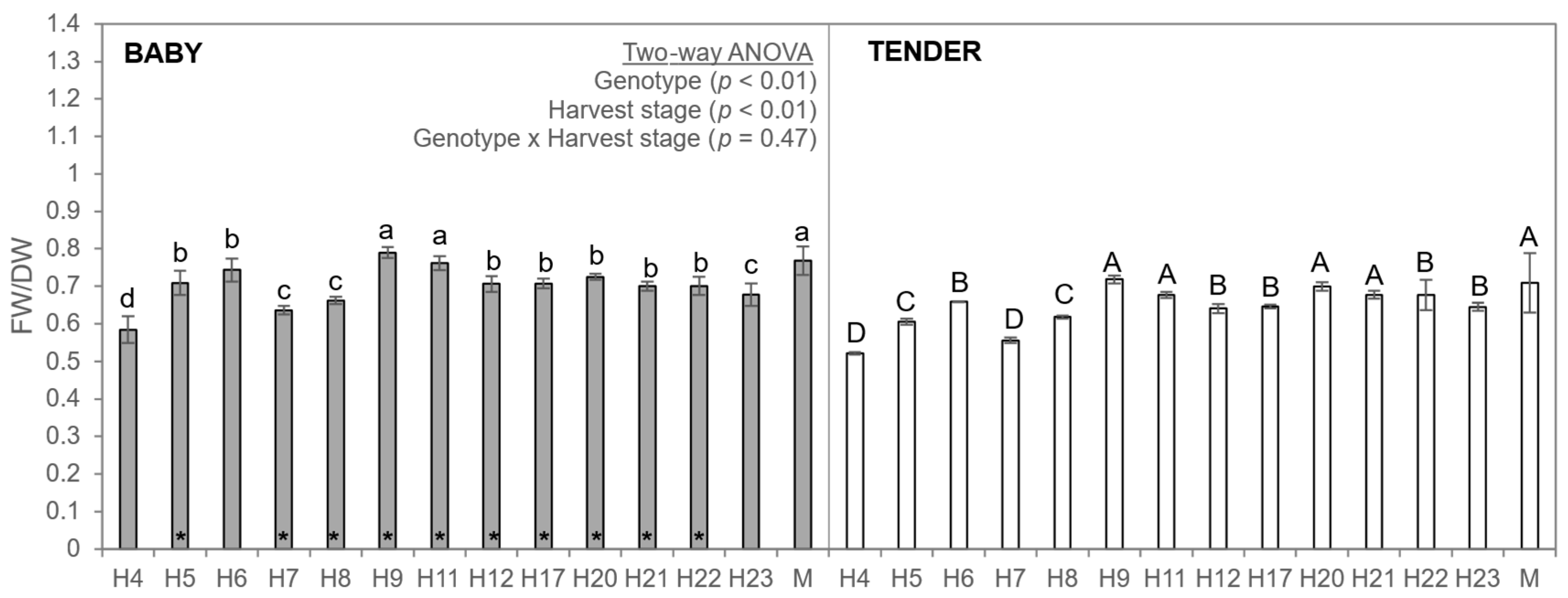
3.2. Fresh-to-Dry Weight Ratio of Faba Beans
3.3. Mineral Content
3.3.1. Total Mineral Content
3.3.2. Macro-Elements
Calcium (Ca)
Magnesium (Mg)
Potassium (K)
| ID | Ca (g 100 g−1) | Mg (g 100 g−1) | K (g 100 g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | |
| H4 | 0.167 ± 0.003 c * | 0.147 ± 0.001 b | 0.143 ± 0.001 f * | 0.128 ± 0.003 h | 1.734 ± 0.015 e | 1.603 ± 0.060 e |
| H5 | 0.123 ± 0.002 f | 0.122 ± 0.005 d | 0.188 ± 0.004 e | 0.176 ± 0.001 e | 2.167 ± 0.043 c * | 1.985 ± 0.017 c |
| H6 | 0.126 ± 0.001 f * | 0.113 ± 0.001 e | 0.218 ± 0.001 b * | 0.177 ± 0.002 e | 2.355 ± 0.021 b * | 2.044 ± 0.031 c |
| H7 | 0.155 ± 0.004 d | 0.150 ± 0.002 b | 0.187 ± 0.001 e * | 0.152 ± 0.002 g | 2.036 ± 0.008 d * | 1.834 ± 0.027 d |
| H8 | 0.127 ± 0.003 f * | 0.110 ± 0.002 e | 0.224 ± 0.005 b * | 0.189 ± 0.004 d | 2.458 ± 0.047 a * | 2.140 ± 0.039 b |
| H9 | 0.136 ± 0.003 e | 0.149 ± 0.004 b * | 0.193 ± 0.004 e | 0.189 ± 0.005 d | 2.410 ± 0.046 b | 2.333 ± 0.051 a |
| H11 | 0.082 ± 0.002 h | 0.096 ± 0.002 f * | 0.239 ± 0.001 a * | 0.224 ± 0.005 a | 2.470 ± 0.012 a * | 2.306 ± 0.047 a |
| H12 | 0.186 ± 0.004 b * | 0.135 ± 0.000 c | 0.213 ± 0.004 c * | 0.203 ± 0.001 b | 2.142 ± 0.033 c | 2.140 ± 0.010 b |
| H17 | 0.137 ± 0.003 e | 0.129 ± 0.003 c | 0.200 ± 0.003 d * | 0.169 ± 0.004 f | 2.293 ± 0.040 b * | 2.040 ± 0.050 c |
| H20 | 0.123 ± 0.002 f | 0.131 ± 0.000 c | 0.182 ± 0.004 e | 0.166 ± 0.001 f | 2.197 ± 0.056 c | 2.175 ± 0.022 b |
| H21 | 0.110 ± 0.001 g | 0.125 ± 0.003 d * | 0.209 ± 0.004 c | 0.208 ± 0.006 b | 2.494 ± 0.048 a | 2.362 ± 0.065 a |
| H22 | 0.203 ± 0.007 a | 0.189 ± 0.005 a | 0.199 ± 0.006 d | 0.197 ± 0.003 c | 2.192 ± 0.063 c | 2.094 ± 0.028 c |
| H23 | 0.109 ± 0.001 g | 0.114 ± 0.002 e | 0.211 ± 0.002 c * | 0.185 ± 0.003 d | 2.378 ± 0.025 b * | 2.201 ± 0.043 b |
| M | 0.150 ± 0.003 d * | 0.124 ± 0.003 d | 0.218 ± 0.002 b * | 0.160 ± 0.003 g | 2.408 ± 0.017 b * | 2.168 ± 0.025 b |
| Average | 0.138 ± 0.009 | 0.131 ± 0.006 | 0.202 ± 0.006 | 0.180 ± 0.007 | 2.267 ± 0.056 | 2.102 ± 0.054 |
| 0.134 ± 0.005 | 0.191 ± 0.005 | 2.184 ± 0.041 | ||||
| G | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| G × HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
Phosphorus (P)
Sulfur (S)
Sodium (Na)
| ID | P (g 100 g−1) | S (g 100 g−1) | Na (g 100 g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | |
| H4 | 0.528 ± 0.004 e | 0.502 ± 0.023 d | 0.155 ± 0.001 d * | 0.144 ± 0.004 f | 0.032 ± 0.000 c * | 0.020 ± 0.000 f |
| H5 | 0.728 ± 0.013 b * | 0.678 ± 0.005 a | 0.182 ± 0.002 c | 0.174 ± 0.002 c | 0.026 ± 0.000 e | 0.034 ± 0.000 c * |
| H6 | 0.676 ± 0.005 c * | 0.620 ± 0.009 c | 0.205 ± 0.002 a * | 0.172 ± 0.003 c | 0.049 ± 0.000 b | 0.053 ± 0.001 b * |
| H7 | 0.684 ± 0.004 c * | 0.606 ± 0.008 c | 0.179 ± 0.001 c | 0.168 ± 0.002 d | 0.019 ± 0.001 f | 0.016 ± 0.000 h |
| H8 | 0.653 ± 0.013 d * | 0.589 ± 0.013 c | 0.189 ± 0.004 c * | 0.156 ± 0.003 e | 0.057 ± 0.001 a | 0.058 ± 0.001 a |
| H9 | 0.636 ± 0.013 d | 0.607 ± 0.015 c | 0.192 ± 0.004 b | 0.178 ± 0.005 c | 0.016 ± 0.000 g | 0.019 ± 0.000 f * |
| H11 | 0.680 ± 0.003 c * | 0.639 ± 0.011 b | 0.180 ± 0.001 c * | 0.169 ± 0.003 d | 0.028 ± 0.000 d * | 0.024 ± 0.001 e |
| H12 | 0.662 ± 0.008 d | 0.638 ± 0.005 b | 0.184 ± 0.002 c | 0.185 ± 0.002 b | 0.018 ± 0.000 f | 0.028 ± 0.000 d * |
| H17 | 0.761 ± 0.014 a * | 0.675 ± 0.015 a | 0.193 ± 0.004 b * | 0.164 ± 0.004 d | 0.010 ± 0.000 i | 0.010 ± 0.000 i |
| H20 | 0.704 ± 0.018 b | 0.676 ± 0.009 a | 0.182 ± 0.004 c | 0.178 ± 0.002 c | 0.007 ± 0.000 j | 0.009 ± 0.000 j * |
| H21 | 0.718 ± 0.014 b | 0.681 ± 0.016 a | 0.192 ± 0.003 b | 0.193 ± 0.005 a | 0.011 ± 0.000 h | 0.018 ± 0.001 g * |
| H22 | 0.643 ± 0.020 d | 0.668 ± 0.006 a | 0.186 ± 0.006 c | 0.179 ± 0.003 c | 0.006 ± 0.000 k | 0.006 ± 0.000 k |
| H23 | 0.647 ± 0.008 d * | 0.595 ± 0.010 c | 0.188 ± 0.002 c * | 0.173 ± 0.002 c | 0.008 ± 0.000 j | 0.010 ± 0.000 i * |
| M | 0.764 ± 0.003 a * | 0.648 ± 0.010 b | 0.199 ± 0.001 a * | 0.175 ± 0.003 c | 0.018 ± 0.000 f * | 0.017 ± 0.000 g |
| Average | 0.678 ± 0.016 | 0.630 ± 0.013 | 0.189 ± 0.003 | 0.172 ± 0.003 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 0.023 ± 0.004 |
| 0.654 ± 0.011 | 0.179 ± 0.003 | 0.022 ± 0.003 | ||||
| G | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| G × HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
3.3.3. Micro-Elements
Copper (Cu)
Iron (Fe)
Manganese (Mn)
| ID | Cu (mg kg−1) | Fe (mg kg−1) | Mn (mg kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | |
| H4 | 17.68 ± 0.18 d | 17.97 ± 0.23 b | 43.53 ± 0.90 g | 48.37 ± 2.52 e | 23.94 ± 0.14 d * | 21.66 ± 0.09 f |
| H5 | 17.78 ± 0.29 d | 16.99 ± 0.16 c | 67.38 ± 0.95 d * | 61.46 ± 0.39 d | 26.87 ± 0.44 c | 25.48 ± 0.19 d |
| H6 | 19.47 ± 0.22 b * | 16.57 ± 0.33 c | 92.00 ± 5.17 a * | 67.16 ± 0.82 c | 30.08 ± 0.27 a * | 25.52 ± 0.37 d |
| H7 | 17.58 ± 0.10 d * | 15.59 ± 0.27 d | 64.85 ± 0.82 e * | 60.60 ± 0.67 d | 26.28 ± 0.15 c * | 23.28 ± 0.32 e |
| H8 | 17.38 ± 0.27 d * | 15.63 ± 0.33 d | 63.02 ± 1.31 e * | 58.14 ± 1.06 d | 30.32 ± 0.49 a | 28.51 ± 0.47 b |
| H9 | 15.78 ± 0.35 e | 15.59 ± 0.40 d | 58.74 ± 1.20 f | 69.17 ± 3.41 c * | 27.11 ± 0.57 c | 29.62 ± 0.66 a * |
| H11 | 21.15 ± 0.06 a * | 18.76 ± 0.30 a | 70.03 ± 0.75 c | 79.80 ± 5.69 b | 28.55 ± 0.21 b | 29.83 ± 0.50 a |
| H12 | 18.33 ± 0.27 c * | 17.11 ± 0.08 c | 64.28 ± 0.85 e | 108.94 ± 1.30 a * | 29.33 ± 0.45 a | 29.63 ± 0.12 a |
| H17 | 14.88 ± 0.24 f | 15.25 ± 0.44 d | 72.22 ± 1.48 c | 80.02 ± 2.59 b * | 28.44 ± 0.41 b | 25.76 ± 1.11 d |
| H20 | 15.67 ± 0.14 e | 15.30 ± 0.32 d | 64.80 ± 4.02 e | 72.80 ± 2.41 c | 27.17 ± 0.43 c | 25.94 ± 0.15 d |
| H21 | 14.24 ± 0.24 f | 14.26 ± 0.44 e | 61.31 ± 1.40 f | 65.01 ± 2.72 d | 29.84 ± 0.95 a | 30.00 ± 0.78 a |
| H22 | 15.48 ± 0.48 e | 17.47 ± 0.13 c * | 66.65 ± 1.84 d | 68.30 ± 1.85 c | 29.87 ± 0.99 a | 30.31 ± 0.37 a |
| H23 | 14.79 ± 0.17 f | 14.64 ± 0.22 e | 60.41 ± 0.74 f * | 58.30 ± 1.31 d | 28.83 ± 0.27 b * | 27.17 ± 0.43 c |
| M | 18.76 ± 0.09 c * | 15.77 ± 0.31 d | 83.79 ± 2.24 b * | 70.06 ± 1.25 c | 30.23 ± 0.19 a * | 24.49 ± 0.48 d |
| Average | 17.07 ± 0.54 | 16.21 ± 0.35 | 66.64 ± 3.03 | 69.15 ± 3.82 | 28.35 ± 0.50 | 26.94 ± 0.74 |
| 16.64 ± 0.32 | 67.90 ± 2.40 | 27.64 ± 0.46 | ||||
| G | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| G × HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
Molybdenum (Mo)
Nickel (Ni)
Zinc (Zn)
| ID | Mo (mg kg−1) | Ni (mg kg−1) | Zn (mg kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | Baby | Tender | |
| H4 | 5.59 ± 0.07 h | 6.15 ± 0.33 j | 1.71 ± 0.04 c | 1.88 ± 0.07 d | 48.19 ± 0.51 f | 47.82 ± 1.03 f |
| H5 | 6.52 ± 0.13 g | 7.28 ± 0.03 i * | 2.52 ± 0.15 a * | 1.96 ± 0.06 d | 58.54 ± 0.88 c | 56.46 ± 1.53 c |
| H6 | 5.94 ± 0.05 h | 7.67 ± 0.13 i * | 2.35 ± 0.20 b | 1.84 ± 0.04 d | 63.33 ± 0.46 b * | 55.03 ± 0.85 c |
| H7 | 10.2 ± 0.07 e | 12.6 ± 0.18 e * | 1.58 ± 0.06 c * | 1.33 ± 0.03 e | 59.29 ± 0.40 c * | 49.98 ± 0.54 e |
| H8 | 9.80 ± 0.42 e | 10.8 ± 0.24 f | 2.14 ± 0.08 b | 2.18 ± 0.07 c | 60.61 ± 1.81 b | 55.07 ± 1.19 c |
| H9 | 6.56 ± 0.13 g | 8.99 ± 0.77 h * | 1.80 ± 0.03 c | 2.23 ± 0.05 c * | 51.56 ± 1.21 e | 53.00 ± 1.19 d |
| H11 | 4.40 ± 0.04 i | 6.43 ± 0.39 j * | 1.71 ± 0.05 c | 1.86 ± 0.04 d | 67.70 ± 1.58 a * | 60.35 ± 0.90 b |
| H12 | 8.89 ± 0.10 f | 9.98 ± 0.10 g * | 1.63 ± 0.03 c | 3.20 ± 0.02 a * | 71.44 ± 1.98 a | 66.85 ± 0.38 a |
| H17 | 24.5 ± 0.45 a | 38.7 ± 0.47 a * | 2.34 ± 0.04 a | 2.66 ± 0.05 b * | 55.19 ± 1.08 d | 53.47 ± 0.86 d |
| H20 | 18.6 ± 0.41 b | 21.0 ± 0.27 b * | 2.04 ± 0.18 b | 2.06 ± 0.13 d | 41.67 ± 0.52 g * | 39.37 ± 0.63 h |
| H21 | 14.1 ± 0.26 d * | 10.2 ± 0.21 g | 2.10 ± 0.07 b | 2.29 ± 0.18 c | 40.82 ± 0.54 g | 45.64 ± 1.12 g * |
| H22 | 14.7 ± 0.49 d | 16.2 ± 0.16 d * | 2.69 ± 0.07 a | 2.69 ± 0.12 b | 44.08 ± 1.44 g | 41.54 ± 0.53 h |
| H23 | 15.4 ± 0.15 c | 18.2 ± 0.30 c * | 2.52 ± 0.05 a | 2.50 ± 0.12 b | 42.30 ± 0.46 g * | 40.04 ± 0.46 h |
| M | 8.77 ± 0.16 f | 11.3 ± 0.20 f * | 2.51 ± 0.09 a * | 1.91 ± 0.10 d | 68.48 ± 1.09 a * | 61.15 ± 1.06 b |
| Average | 11.00 ± 1.54 | 13.26 ± 2.29 | 2.12 ± 0.10 | 2.18 ± 0.12 | 55.23 ± 2.83 | 51.84 ± 2.21 |
| 12.13 ± 1.37 | 2.15 ± 0.08 | 53.53 ± 1.79 | ||||
| G | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
| HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.08 | p < 0.01 | |||
| G × HS | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | |||
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.4.1. Overall Correlations
3.4.2. Baby Stage
3.4.3. Tender Stage
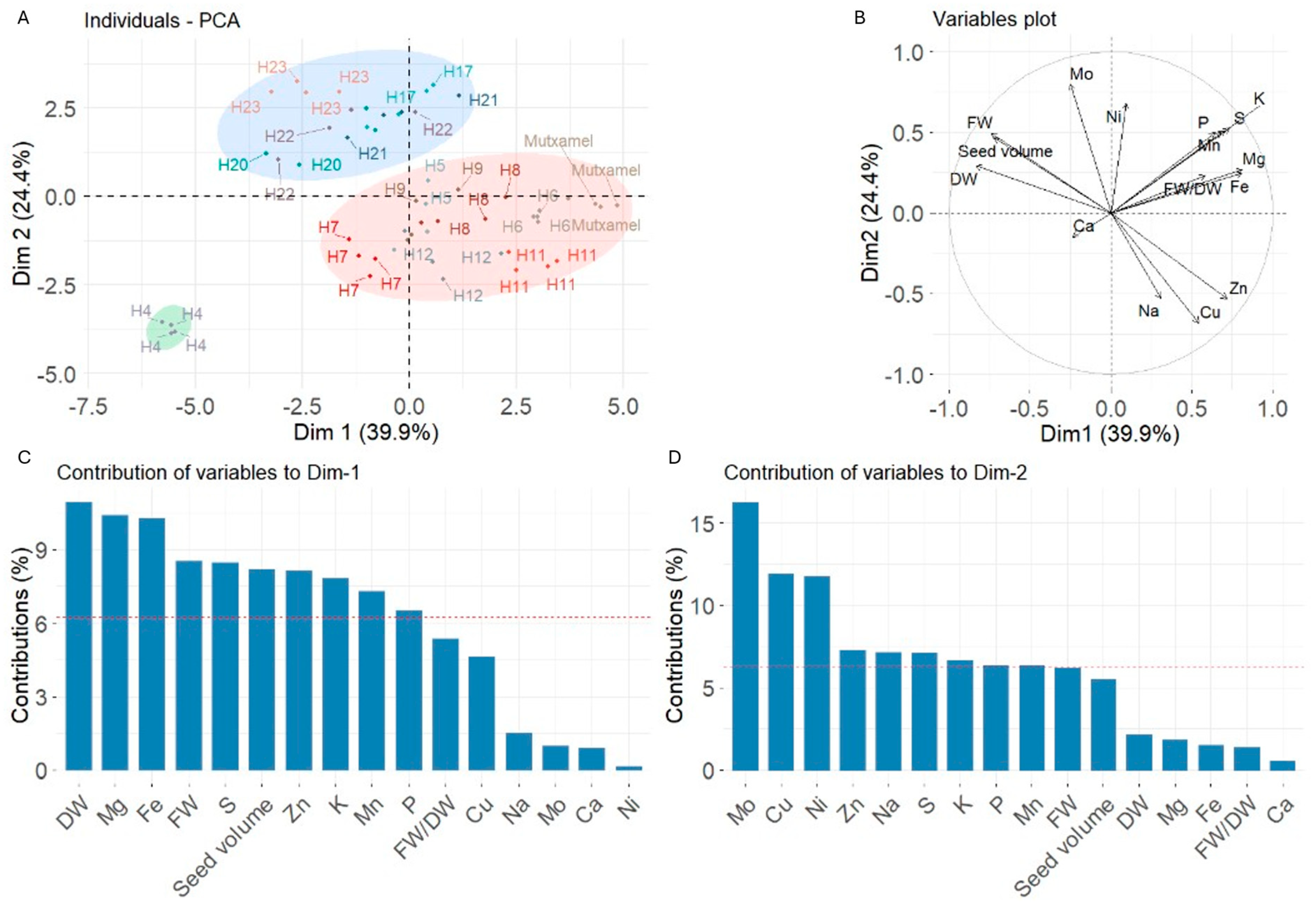
3.5. PCA
3.5.1. Baby Stage PCA
3.5.2. Tender Stage PCA
3.6. Hierarchical Heatmap Visualization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FW | Fresh weight |
| DW | Dry weight |
| FW/DW | Fresh-to-dry weight ratio |
| Ca | Calcium |
| K | Potassium |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Na | Sodium |
| P | Phosphorus |
| S | Sulfur |
| Cu | Copper |
| Fe | Iron |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Mo | Molybdenum |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Zn | Zinc |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Skovbjerg, C.K.; Angra, D.; Robertson-Shersby-Harvie, T.; Kreplak, J.; Ecke, W.; Windhorst, A.; Nielsen, L.K.; Schiemann, A.; Knudsen, J.; Gutierrez, N.; et al. Genetic analysis of global faba bean diversity, agronomic traits and selection signatures. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gela, T.; Khazaei, H.; Podder, R.; Vandenberg, A. Dissection of genotype–by–environment interaction and simultaneous selection for grain yield and stability in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Agron. J. 2023, 115, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alla, M.; Al-Amri, S.; El-Enany, A. Enhancing rhizobium–legume symbiosis and reducing nitrogen fertilizer use are potential options for mitigating climate change. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau-Côté, D.; Achouri, A.; Karboune, S.; L’Hocine, L. Faba bean: An untapped source of quality plant proteins and bioactives. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, G. Analysis of nutritional traits: Natural variation within 90 diverse faba bean (Vicia faba) genotypes and daily value contribution. Crops 2024, 4, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanis, A.; Ntatsi, G.; Lepse, L.; Fernández, J.A.; Vågen, I.M.; Rewald, B.; Alsiņa, I.; Kronberga, A.; Balliu, A.; Olle, M.; et al. Faba bean cultivation: Revealing novel managing practices for more sustainable and competitive European cropping systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, H.; Vandenberg, A. Seed mineral composition and protein content of faba beans (Vicia faba L.) with contrasting tannin contents. Agronomy 2020, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenz, L.; Grebenteuch, S.; Zocher, K.; Rohn, S.; Pleißner, D. Valorization of faba bean (Vicia faba) by-products. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 14, 26663–26680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, G.; Aleksić, J.M.; Marget, P.; Mikić, A.; Paull, J.; Redden, R.J.; Sass, O.; Stoddard, F.L.; Vandenberg, A.; Vishnyakova, M. Faba bean. In Grain Legumes; de Ron, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 10, pp. 141–178. [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi, F.; Barker, A.V.; Hashemi, M.; Zandvakili, O.R.; Park, Y. Nutrient accumulation in faba bean varieties. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 2064–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, K.; Zaragoza, I.; Knecht, J.; Munster, R.; Coulter, H.; Potter, A.; Enke, E.; Fox, A.; Mosqueda, E.; Zakeri, H. Potential of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) for dual-purpose vegetable production and cover cropping. HortScience 2023, 58, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cillis, F.; Leoni, B.; Massaro, M.; Renna, M.; Santamaria, P. Yield and Quality of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L. var. major) Genotypes as a Vegetable for Fresh Consumption: A Comparison between Italian Landraces and Commercial Varieties. Agriculture 2019, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualone, A.; Abdallah, A.; Summo, C. Symbolic meaning and use of broad beans in traditional foods of the Mediterranean Basin and the Middle East. J. Ethn. Foods 2020, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Morton, J.D.; Maes, E.; Kumar, L.; Serventi, L. Exploring faba beans (Vicia faba L.): Bioactive compounds, cardiovascular health, and processing insights. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 4354–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, A.; Bhutta, Z. Global micronutrient deficiencies in childhood and impact on growth and survival: Challenges and opportunities. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouis, H.E.; Saltzman, A. Improving nutrition through biofortification: A review of evidence from HarvestPlus, 2003 through 2016. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 12, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, R.M.; Graham, R.D. Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, N.; Islam, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ercişli, S.; Ullah, R.; Bari, A.; Munir, I. Rice seeds biofortification using biogenic iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by using Glycyrrhiza glabra: A study on growth and yield improvement. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Yadav, H.K.; Raiya, R.; Singh, R.K.; Jha, U.C.; Sathee, L.; Singh, P.; Thudi, M.; Singh, A.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; et al. Integrated breeding approaches to enhance the nutritional quality of food legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 984700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roorkiwal, M.; Pandey, S.; Thavarajah, D.; Hemalatha, R.; Varshney, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and biochemical pathways for micronutrient acquisition and storage in legumes to support biofortification for nutritional security. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 682842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzopoulos, P.J.; Kaltsikes, P.J.; Bebeli, P.J. Determining the sources of heterogeneity in Greek faba bean local populations. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramidou, E.; Ganopoulos, I.; Mylona, P.; Abraham, E.M.; Nianiou-Obeidat, I.; Osathanunkul, M.; Madesis, P. Comparative analysis of the genetic diversity of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Sustainability 2023, 15, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Amro, A.; Mourad, A.M.I.; Rafeek, A.; Boerner, A.; Eltaher, S. Molecular genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium structure of the Egyptian faba bean using single primer enrichment technology (SPET). BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridi, E.; Kapazoglou, A.; Gerakari, M.; Kleftogianni, K.; Passa, K.; Sarri, E.; Bebeli, P.J. Crop landraces and indigenous varieties: A valuable source of genes for plant breeding. Plants 2024, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbe, E.; Morard, M.; Rausell-Moreno, A.; Calatayud, Á.; Penella, C. Exploring nutritional quality and bioactive compounds in Mediterranean bean landraces. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 142, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, A.; Martínez-Ispizua, E.; Morard, M.; Crespo-Sempere, A.; Albiach-Marti, M.R.; Calatayud, Á.; Penella, C. Optimizing sweet potato production: Insights into the interplay of plant sanitation, virus influence, and cooking techniques for enhanced crop quality and food security. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1357611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, F.; Hu, J.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Zong, X.; Hamwieh, A.; Kumar, S.; Baum, M. Breeding and genomics status in faba bean (Vicia faba). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazas, M.; González-Orenga, S.; Nguyen, H.T.; Morar, I.M.; Fita, A.; Boscaiu, M.; Prohens, J.; Vicente, O. Growth and antioxidant responses triggered by water stress in wild relatives of eggplant. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Navarro, J.D.; Padilla, Y.G.; Álvarez, S.; Calatayud, Á.; Colmenero-Flores, J.M.; Gómez-Bellot, M.J.; Hernández, J.A.; Martínez-Alcalá, I.; Penella, C.; Pérez-Pérez, J.G.; et al. Advancements in water-saving strategies and crop adaptation to drought: A comprehensive review. Physiol. Plant. 2025, 177, e70332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, J.; Bartual, J.; Garcia, J.; Ortiz, M. Selección de material vegetal autóctono en habas de verdeo (Vicia faba var. major). In Proceedings of the XLVIII Seminario de Técnicos y Especialistas en Horticultura, Muriedas, Spain, 11–14 June 2018; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food: Madrid, Spain, 2022; pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. Corrplot: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.92) [R Package]. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses (Version 1.0.7) [R Package]. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K. Cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions (Version 2.1.4) [R Package]. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cluster (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex Heatmaps Reveal Patterns and Correlations in Multidimensional Genomic Data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuero, A.G.; Sayago, A.; González, A.G. The correlation coefficient: An overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Han, Y.; Du, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, L.; Sun, G.; Li, W. QTL analyses of seed weight during the development of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Heredity 2009, 102, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, J.D.; Bradford, K.J.; Hilhorst, H.W.M.; Nonogaki, H. Development and Maturation. In Seeds: Physiology of Development, Germination and Dormancy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 133–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Møller, I.M.; Murphy, A. Plant Physiology and Development, 6th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Borisjuk, L.; Rolletschek, H.; Radchuk, R.; Weschke, W.; Wobus, U.; Weber, H. Seed development and differentiation: A role for metabolic regulation. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripathy, K.V.; Groot, S.P.C. Seed development and maturation. In Seeds: Physiology of Development, Germination and Dormancy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, J.A. Mineral contents of soybean seed coats and embryos during development. J. Plant Nutr. 1990, 13, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, P.; Burslem, D. Mineral nutrient concentrations as a function of seed size within seed crops: Implications for competition among seedlings and defence against herbivory. J. Trop. Ecol. 1998, 14, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, D.B. Seed water relations and the regulation of the duration of seed growth in soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 1990, 41, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Dibley, K.E.; Tyerman, S.D.; Furbank, R.T.; Patrick, J.W. Nutrient loading of developing seeds. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarah, N.; Abu-Yahya, A.; Grusak, M. Effect of maturity stages for winter- and spring-sown chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) on seed mineral content. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.B.; Grusak, M.A. Mineral accumulation in vegetative and reproductive tissues during seed development in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipcevic, V.; Vedrina-Dragojevic, I.; Balint, L. Dynamics of the cumulation of iron, copper and sodium during development to maturity of soybean seed. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 1993, 170, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Irving, L.J.; McGill, C.; Matthew, C.; Zhou, D.; Kemp, P. The effects of salinity and osmotic stress on barley germination rate: Sodium as an osmotic regulator. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R. Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets—Iron, zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, selenium and iodine. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Calabozo, R.; Martínez-Martín, I.; Rodríguez-Fernández, M.; Absi, Y.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M.; Revilla, I. The influence of the nutritional and mineral composition of vegetable protein concentrates on their functional properties. Foods 2025, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.S.; Vanaja, M.; Shankar, M.; Siddiqua, A.; Sharma, K.L.; Girijaveni, V.; Singh, V.K. Change in mineral composition and cooking quality in legumes grown on semi-arid Alfisols due to elevated CO2 and temperature. Front. Nutr. 2025, 11, 1444962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.; Fortunato, G.; Barilli, E.; Rubiales, D.; Pinto, E.; Vasconcelos, M.W. Establishing the effects of climate and soil on the nutritional composition of an array of faba bean varieties grown in two different zones of Andalusia, Spain. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursakov, S.A.; Kroupin, P.Y.; Karlov, G.I.; Divashuk, M.G. Tracing the element: The molecular bases of molybdenum homeostasis in legumes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Nath, R. Prospects of molybdenum fertilization in grain legumes—A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 45, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Li, J.; Yahya, M.; Wang, M.; Ali, A.; Cheng, A.; Wang, X.; Ma, C. Grain legumes and fear of salt stress: Focus on mechanisms and management strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzroud, S.; Henkrar, F.; Fahr, M.; Smouni, A. Salt stress responses and alleviation strategies in legumes: A review of the current knowledge. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, F.S.; Karaköy, T.; Demirbaş, A.; Toklu, F.; Özkan, H.; Hatipoğlu, R. Variation of some seed mineral contents in open pollinated faba bean (Vicia faba L.) landraces from Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Grusak, M.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Tonnis, B.; Barkley, N.A.; Evans, S.; Pinnow, D.; Davis, J.; Phillips, R.D.; Holbrook, C.C.; et al. Seed protein percentage and mineral concentration variability and their correlation with other seed quality traits in the U.S. peanut mini-core collection. Peanut Sci. 2016, 43, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Branch, W.D.; Gaines, T.P. Seed mineral composition of diverse peanut germplasm. Peanut Sci. 1983, 10, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreugdenhil, D.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Koornneef, M.; Nelissen, H.; Ernst, W.H.O. Natural variation and QTL analysis for cationic mineral content in seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. (Ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, T.; Takahashi, M.; Oda, K.; Terada, Y.; Yoshida, K.T. Dynamic changes in the distribution of minerals in relation to phytic acid accumulation during rice seed development. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanha, G.S.; Carvalho Mendes, N.A.; Perez, L.C.; Oliveira Cunha, M.L.; Santos, E.; Pérez, C.A.; de Almeida, E.; Marques, J.P.; Umburanas, R.C.; Linhares, F.S.; et al. Unfolding the dynamics of mineral nutrients and major storage protein fractions during soybean seed development. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karley, A.J.; White, P.J. Moving cationic minerals to edible tissues: Potassium, magnesium, calcium. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Drought and salinity: A comparison of their effects on mineral nutrition of plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.W.G.; Campbell, L.C. Patterns of mineral nutrient accumulation in soybean seed. Field Crops Res. 1980, 3, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A.K.; Gaur, P.M.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Chibbar, R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108 (Suppl. 1), S11–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerche, S.; Ewald, A. Seed potassium concentration decline during maturation is inversely related to subsequent germination of primrose. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, J.W.; Offler, C.E. Compartmentation of transport and transfer events in developing seeds. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, L.J.; Palmer, L.T.; Rutzke, M.A.; Graham, R.D.; Stangoulis, J.C. Nutrient variability in phloem: Examining changes in K, Mg, Zn and Fe concentration during grain loading in common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Grant, J.; Cooper, P.; Tegeder, M. Increased phloem transport of S-methylmethionine positively affects sulfur and nitrogen metabolism and seed development in pea plants. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo, M.A.; Boldrin, P.F.; Hart, J.J.; de Andrade, M.J.; Guilherme, L.R.; Glahn, R.P.; Li, L. Zinc and selenium accumulation and their effect on iron bioavailability in common bean seeds. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhull, S.B.; Kidwai, M.; Noor, R.; Chawla, P.; Rose, P. A review of nutritional profile and processing of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Legume Sci. 2022, 4, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| ID | Local Name | Code | Origin | Institution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H4 | Haba valenciana | IVIA-O19G | Catarroja (Valencia) | IVIA |
| H5 | Haba valenciana | IVIA-263 | Foios (Valencia) | IVIA |
| H6 | Haba valenciana | IVIA-475 | Millares (Valencia) | IVIA |
| H7 | Haba de Elche | BGV-9859 | Novelda (Alicante) | COMAV-UPV |
| H8 | Haba Valenciana tardía | BGV-15037 | El Perelló (Valencia) | COMAV-UPV |
| H9 | Haba valenciana | BGV-15620 | Valencia | COMAV-UPV |
| H11 | Haba valenciana | BGV-16035 | Moncada (Valencia) | COMAV-UPV |
| H12 | Haba valenciana | BGV-16094 | Moncada (Valencia) | COMAV-UPV |
| H17 | Haba de Mutxamel | 17-152 | Mutxamel (Alicante) | IVIA |
| H20 | Haba valenciana | H68-LG | Turis (Valencia) | IVIA |
| H21 | Haba de Bétera | LG10-69 | Bétera (Valencia) | IVIA |
| H22 | Haba del terreno | Var-303 | Valencia | IVIA |
| H23 | Haba valenciana | BGV-9886 | Valencia | COMAV-UPV |
| Mutxamel | Mutxamel comercial | Mutxamel (Alicante) | BATLLE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorbe, E.; Moreno-Valle, I.; Calatayud, Á.; Penella, C. Unraveling Diversity in Physical and Mineral Traits of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Landraces Harvested at Immature Stages. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121411
Gorbe E, Moreno-Valle I, Calatayud Á, Penella C. Unraveling Diversity in Physical and Mineral Traits of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Landraces Harvested at Immature Stages. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(12):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121411
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorbe, Elisa, Irene Moreno-Valle, Ángeles Calatayud, and Consuelo Penella. 2025. "Unraveling Diversity in Physical and Mineral Traits of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Landraces Harvested at Immature Stages" Horticulturae 11, no. 12: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121411
APA StyleGorbe, E., Moreno-Valle, I., Calatayud, Á., & Penella, C. (2025). Unraveling Diversity in Physical and Mineral Traits of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Landraces Harvested at Immature Stages. Horticulturae, 11(12), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121411







