Physiological Responses of Anoectochilus roxburghii to Salt Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement of Stem Diameter and Leaf Thickness
2.4. Measurement of Physiological Indicators
2.5. Measurement of Quality Indicators
2.6. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Salt Stress on Leaf Thickness and Stem Diameter of A. roxburghii
3.2. Effects of Salt Stress on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in A. roxburghii
3.3. Effects of Salt Stress on Membrane Lipid Peroxidation and Osmotic Adjustment Substances in A. roxburghii
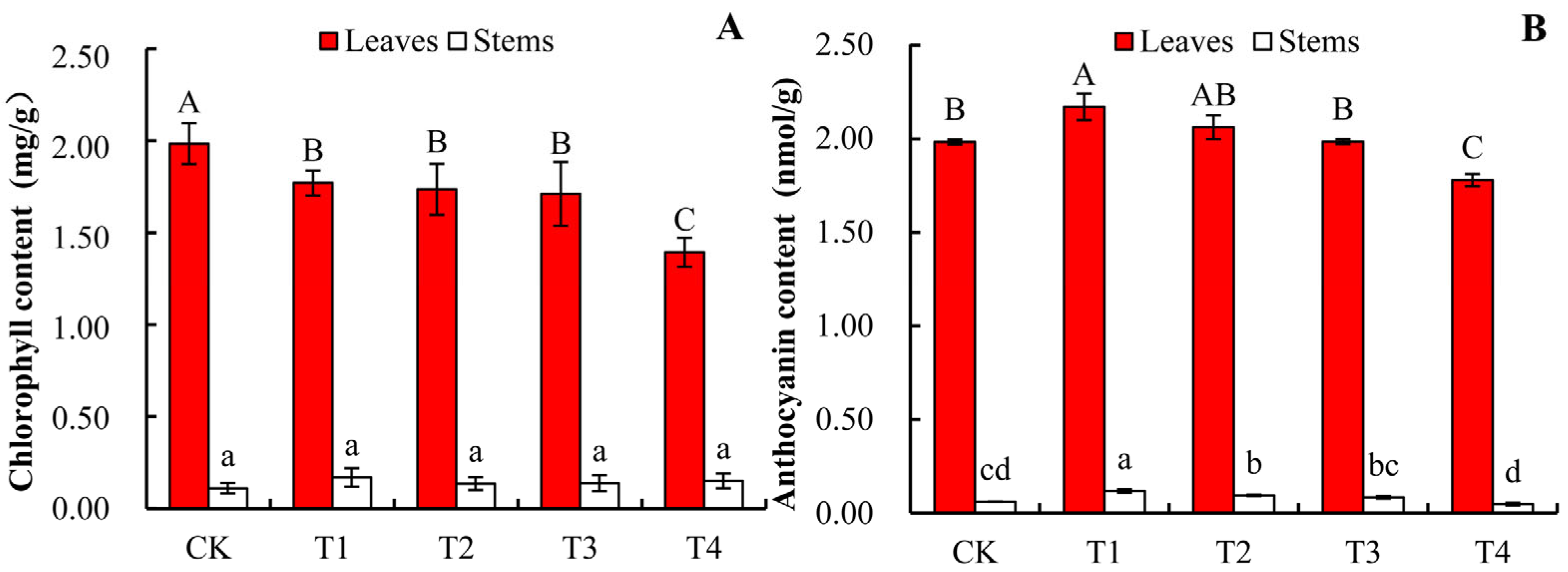
3.4. Effects of Salt Stress on Pigment Content in A. roxburghii
3.5. Effects of Salt Stress on Contents of Flavonoids and Total Phenols in A. roxburghii
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Different NaCl Concentrations in Leaves and Stems of A. roxburghii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, S.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, A. Anoectochilus roxburghii: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; He, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Antony, S.; Shao, Q.; Lin, D. Structure and pharmacological activities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zou, X. Effects of Different pH Values on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Anoectochilus roxburghii. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2025, 44, 4477–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils-Main Report; [R/OL]; [2025-4-2]; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, K.P.; Devkota, M.; Rezael, M.; Ezaei, M.; Roland Oosterbaan, R. Managing salinity for sustainable agricultural production in salt-affected soils of irrigated drylands. Agric. Syst. 2022, 198, 103390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kesawat, M.S.; Du, X.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Kant, S.; Chung, S.M. In silico analysis and expression profiling reveal the presence of abiotic stress and developmental stage specific Aconitase genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Tariq, F.; Ma, C. Integrative dynamics of cell wall architecture and plant growth under salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1644412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyimi, D.M.; Chemisto, J.K.; Buyela, D.K. Growth and physiological response of African nightshades (Solanum Scabrum Mill.) to Sodium chloride salinity stress. Int. J. Food Saf. Public Health 2021, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Hou, H. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, S.; Lan, Q.; Wang, Y. Research advancements in salt tolerance of cucurbitaceae: From salt response to molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.V.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Dambroz, C.; Dória, J.; Pasqual, M. Physiological and morphological responses of Selenicereus species to salt stress in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2025, 162, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, D.; Luo, L.; Hao, Y. Flavonoid profile of Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. Under short-term heat stress revealed by integrated metabolome, transcriptome, and biochemical analyses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gam, D.T.; Khoi, P.H.; Ngoc, P.B.; Linh, L.K.; Hung, N.K.; Anh, P.T.L.; Ha, C.H. LED lights promote growth and flavonoid accumulation of Anoectochilus roxburghii and are linked to the enhanced expression of several related genes. Plants 2020, 9, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Lu, Z.; Pang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, W. Gene expression profiles and flavonoid accumulation during salt stress in Ginkgo biloba seedlings. Plants 2020, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases: I. occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelAty, A.M.; Salama, W.H.; Fahmy, A.S.; Mohamed, S.A. Impact of Germination on Antioxidant Capacity of Garden Cress: New Calculation for Determination of Total Antioxidant Activity. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Marschner, H. Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Cui, M.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Tang, X. Salinity stress is beneficial to the accumulation of chlorogenic acids in honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica Thunb.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Qian, Y.; Rong, H.; Xie, T.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y. Analysis of the Transcriptome Provides Insights into the Photosynthate of Maize Response to Salt Stress by 5-Aminolevulinic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Study on the Molecular Mechanism of Petal Fading of Brunfelsia acuminata and the Technology of Adjusting Light and Temperature; Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Fuzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Lin, Y.; Yin, C. Research advances of salt exclusion, salt sequestration, salt secretion, and salt signaling regulation in plants. Plant Stress 2025, 17, 100952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.A.; Sarkhosh, A.; Khan, N.; Balal, R.M.; Ali, S.; Rossi, L.; Gómez, C.; Mattson, N.; Nasim, W.; Garcia-Sanchez, F. Insights into the Physiological and Biochemical Impacts of Salt Stress on Plant Growth and Development. Agronomy 2020, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiq, M.S.; Iqbal, S.; Hafeez, M.B.; Ibrahim, A.M.H.; Raza, A.; Fatima, E.M.; Baloch, H.; Jahanzai, B.; Woodrow, P.; Ciarmiello, L.F. Effect of Salinity Stress on Physiological Changes in Winter and Spring Wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, P.; Mounkaila, H.A.K.; Wan, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of Single and Combined Drought and Salinity Stress on the Root Morphological Characteristics and Root Hydraulic Conductivity of Different Winter Wheat Varieties. Plants 2023, 12, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bu, W.; Xu, Y.; Fei, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Zhu, G. Effects of salt stress on physiological and agronomic traits of rice genotypes with contrasting salt tolerance. Plants 2024, 13, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiao, Z.; Xu, A.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J. Investigating Salt Tolerance in Melon During Germination and Early Seedling Stages. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, K.; Hussain, K.; Majeed, A.; Khan, F.; Afghan, S.; Ali, K. Fatality of salt stress to plants: Morphological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 5475–5480. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Sajid, Z.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Ahmad, I.; Jamal, A.; Rizwana, H.; Almunqedhi, B.M.; Ronga, D. Characterization of Physiological and Biochemical Attributes of Neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) under Salinity Stress. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Razmjoo, J.; Karimmojeni, H.; Baldwin, T.C. Differential responses of Hollyhock (Alcea rosea L.) varieties to salt stress in relation to physiological and biochemical parameters. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y. Study on Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Metabolism of Avena sativa Lunder Salt Stress. Chin. Qinghai J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 51, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Eryılmaz, F. The relationships between salt stress and anthocyanin content in higher plants. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2006, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.N.; Sarker, U.; Raihan, M.S.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Oba, S. Influence of salinity stress on color parameters, leaf pigmentation, polyphenol and flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of Amaranthus lividus leafy vegetables. Molecules 2022, 27, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Arabidopsis LOS5 gene enhances chilling and salt stress tolerance in cucumber. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Zheng, B. The role of polyphenols in abiotic stress tolerance and their antioxidant properties to scavenge reactive oxygen species and free radicals. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Rong, H.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Jiang, Y. Physiological Responses of Anoectochilus roxburghii to Salt Stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101254
Li M, Rong H, Li H, Li N, Jiang Y. Physiological Responses of Anoectochilus roxburghii to Salt Stress. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(10):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Min, Hao Rong, Hongxia Li, Na Li, and Ying Jiang. 2025. "Physiological Responses of Anoectochilus roxburghii to Salt Stress" Horticulturae 11, no. 10: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101254
APA StyleLi, M., Rong, H., Li, H., Li, N., & Jiang, Y. (2025). Physiological Responses of Anoectochilus roxburghii to Salt Stress. Horticulturae, 11(10), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101254





