Abstract
Leaf samples of 226 cultivated olive trees were collected from traditionally managed olive orchards and genotyped with eleven consensual SSR markers. The proportion of shared allele distance was used for the estimation of distances between olive genotypes. Cluster analyses were performed using a Fitch–Margoliash least-squares algorithm. The number of different genetic subgroups of olive genotypes (K) was investigated using STRUCTURE analysis. The standardization of allele lengths was performed to enable the comparison SSR profiles of Croatian olive genotypes with olive profiles obtained with the same SSR primers in OleaDB and WOGB databases. Overall, 73 SSR profiles of known Croatian varieties and 53 profiles of unknown olive genotypes were differentiated. Synonyms were detected in 18 varieties, and we found intra-varietal differences in 15 varieties. Three genetic subgroups of olive genotypes were determined. Following allele length standardization achieved using nine referral samples, the genetic profiles of 126 cultivated olive genotypes were compared to OleaDB and WOGB databases, out of which 92 genotypes were found to be unique to Croatian olive germplasm. The results revealed the wide genetic diversity of olive germplasm beyond the known, registered varieties. The FAZ_oliveDB database containing the profiles of 126 Croatian olive genotypes was created and made available for public use.
1. Introduction
The olive tree crop (Olea europaea L.) is widely cultivated, generally being grown in the area of the Eastern region of Mediterranean basin along the European and African coasts [1]. Olive was domesticated during the Chalcholitic Levant, about 6800–6300 years BP, and spread over the Mediterranean basin [2]. However, our understanding of the heartland of primary olive domestication must be enlarged to the Levant and not only focus on the Jordan Valley [3]. Shortly after these conclusions, Besnard et al. [4] pointed out that the northern Levant is the primary area of olive domestication. Since the period of olive domestication began, large numbers of cultivated olive varieties have spread until now thanks to the vegetative propagation of plants with the best trait combinations. This previously occurred as a result of random crosses between cultivated (ssp. sativa) and wild (ssp. oleaster) olive plants (i.e., feral forms of olive [5]) or as natural mutations. The “Olive Germplasm: Cultivars and World-Wide Collections” includes data on 1250 cultivars in 54 countries, conserved in more than hundred collections [6].
The olive is a species of great economic importance, not only in the countries of Mediterranean basin. Total world production in 2021 was 3,010,000 tons of olive oil [7]. European production led the way, with the combined production of Spain, Italy, Greece, and Portugal standing at around 1,974,000 tones, and non-EU but IOC members such as Algeria, Argentina, Morocco, Egypt, Tunisia, and Turkey were estimated to have collectively produced 936,000 tons of olive oil. The olive tree has been cultivated in Croatia for over 2000 years [8]. The early division of olive-growing regions in Croatia into southern, middle, and northern Dalmatia, the Kvarner islands, Istria, and inner Dalmatia [9] was largely supported by local microclimate regions. The production of olives in Croatia is proportional to the size of the Mediterranean part of the country, which is smaller comparing to the leading producing countries but still very significant in terms of germplasm diversity. Olive oil production was 32,026 hl [10] in 2021. In 2020, olives were grown on an area of 20,282 hectares, with an average yield of 1.6 t/ha and a total production of 33,230 tons of fruit. However, in the last 15 years, Croatian olive oil producers have won numerous silver and gold awards in international competitions for the organoleptic qualities of their olive oil.
There are more than 40 autochthonous olive varieties in Croatia [11], which may be grouped by their impact on economy and biodiversity. In the region of Dalmatia, Croatian varieties with a significant economic impact, such as ‘Oblica’, ‘Lastovka’, ‘Levantinka’, ‘Drobnica’ and ‘Bjelica’, dominate. The second group includes varieties such as ‘Karbunčela’, ‘Krvavica’, ‘Paštrica’, ‘Crnica’, ‘Želudarica’, ‘Mezanica’, and ‘Uljarica’, which are important just for the local economies. The third group consists of varieties that are represented in a very small number and are threatened, with extinction such as ‘Brindićanka’, ‘Jeruzalemka’, ‘Kamasa’, ‘Krivulja’, and ‘Duška’ i ‘Vrhuljača’ [12].
Numerous studies of the local olive germplasm in Croatian territory were based on morphology [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. However, their morphological characterization was not strong enough for the precise differentiation of cultivars, especially of synonyms and homonyms, due to limitations caused by environmental influences. A great leap forward in the characterization of varieties was achieved using PCR-based DNA markers, which proved to be applicable for the investigation of genetic diversity, the identification of olive germplasm, and the investigation of intra-varietal variability. Among the others, the use of SSRs is one of the molecular techniques that may provide useful information on the level of polymorphism and diversity in the characterization of olive germplasm accessions [21] and may be applied for the discrimination of closely related cultivars and association mapping [22]. SSR markers are far and away the ideal markers, being abundant and uniformly distributed over the genome, codominant, highly polymorphic and informative, highly reproducible, easily produced by PCR, and relatively simple to interpret. They produce data that are easily exchangeable among laboratories [23,24].
Olive genotypes from Croatia, either autochthonous or introduced, were genotyped only partly with different sets of SSR markers, comprising varieties from south Dalmatia [25] and Istria [26,27]. Several studies focused only on the molecular characterization of distinct varieties [28,29], the relationships among olive varieties native to Croatia and Turkey [30], the clarification of possible cases of synonymy and homonymy [11], and the determination of intra-varietal diversity [31]. In some reports, Croatian varieties were represented only by one or several of the most common varieties as part of other studies comprising genotypes directly sampled from the wider Mediterranean area [32,33,34,35], or by genotypes originating from Croatia that were sampled at olive collections in other countries [36,37,38]. However, no comprehensive and systematic work on Croatian germplasm has been performed yet. Many other studies from the Mediterranean basin have been conducted recently in order to determine genetic variability and perform genotype identification. These studies cover different areas, from those locally focused on just one country, like Albania [39,40], Montenegro [35], Italy [41,42,43], Turkey [44,45,46,47], Greece [48], Iran [49], Lebanon [50], Tunisia [51,52,53], or Algeria [54], or even narrow producing areas like the West Bank [55], southern Anatolia [56], Sicily [57,58], southern Italy [59,60], parts of Spain [21,61], or Madeira [62], to those comprising several countries, but with fewer samples per country [34,63,64,65,66]. Gomes et al. [67] analyzed the main Portuguese varieties, comparing them with several Italian and Spanish varieties using SSR and ISSR markers. This was carried out after a comparison had already been performed between the main Italian and Spanish varieties using SSR markers [68]. With the objective of the standardization and the consensual application of SSR markers, and due to the need for more convenient methods of result exchange and data comparison, markers and protocols were proposed for the improvement of the application of SSRs in order to develop a robust method with which to track the origin of olive cultivars [69,70]. These were overviewed [71] alongside the other molecular-marker techniques applied in olive germplasm studies.
The SSR markers are also widely used for the assessment of intra-varietal differences. There were studies that aimed to assess the on-farm variability of only two local cultivars of olives in the Alentejo region [72], to compare Iranian ecotypes and varieties with cultivars from the Mediterranean basin [73], and to compare olive clones from Morocco with varieties from other countries [74]. The other studies analyzed the intra-varietal differences between three major Italian cultivars [75], the range of variability within the three major Iranian cultivars [76], and the intra-varietal differences and genetic relationships of some of the most widespread homonymic olive cultivars in the East Adriatic region [77].
Our hypothesis assumes the presence of huge genetic variability within the existing olive germplasm in Croatia. The objectives of the study are as follows:
- To genotype a large and representative number of olive samples using SSR markers, including olive traditional varieties and unnamed genotypes of economic importance;
- To identify synonyms and homonyms of Croatian varieties;
- To create a database of olive SSR profiles comparable to publicly available olive SSR databases and to detect genotypes which are unique only to the Croatian part of the Mediterranean.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Isolation
In collaboration with the local community and olive producers, we localized, labelled, and sampled 226 cultivated trees of old varieties with uncertain status of synonymy, trees of the same variety with obvious in situ variability, and trees of unknown identity. All the trees were localized in old, extensive or traditionally managed olive orchards, covering five olive-growing zones in Croatia: 26 trees in Istria, 27 trees in Kvarner, 86 trees in northern Dalmatia, 21 trees in middle Dalmatia, and in 66 trees in southern Dalmatia. The age of the labelled trees ranged from at least 50 years to even more than 1000 years. The trees were selected and attributed according to the best practice and knowledge, respecting the descriptions published by previous authors [6,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Additionally, nine foreign varieties (‘Ascolana tenera’, ‘Frantoio’, ‘Gentile di Chieti’, ‘Grossa di Spagna’, ‘Leccino’, ‘Moraiolo’, ‘Nostrana di Brisighella’, ‘Pendolino’, and ‘Picholine’), obtained from the nursery in Italy [Vivai Pietro Pacini, Via L. Galeotti, 1-51017 Pescia (PT)], were used as referral samples. Six of them (‘Ascolana Tennera’, ‘Frantoio’, ‘Leccino’, ‘Pendolino’, and ‘Picholine’) were introduced varieties that have been traditionally cultivated in Croatia for a long time. These referral varieties were chosen as the most appropriate options for covering the whole allele range of the primers applied in this research and enabling allele standardization among the databases.
Samples of fresh leaf tissues were collected in situ from the canopy and immediately put in zip bags with silica gel (in a ratio of 1 g of a fresh leaf sample to 5 g of silica gel) and dried for three weeks in the fridge at +4 °C. Dried leaves were ground into fine powder for 30 s at the vibrational frequency of 30 Hz using a mixer mill MM400 (Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany). Genomic DNA was isolated using a DNA plant isolation kit (DNeasy Plant Mini Kit; Qiagene, Venlo, The Netherlands) following the protocol provided by manufacturer. The quality of the isolated DNA was checked in 0.8% agarose gel in a 0.5 × TBE buffer (45 mM Tris, 45 mM Boric acid, and 1 mM EDTA). The quantity of isolated DNA was measured in VersaFluorTM Fluorimeter (ver. 170-2402EDU; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA), and diluted with millipore water to a working concentration of 5 ng µL−1 for further molecular analysis.
2.2. Molecular Analysis
Among the markers previously designed by different authors [1,41,78,79], Baldoni et al. [70] suggested a consensus list of 11 the most effective markers for characterizing olive accessions and proved their use for comparison of the results obtained among different laboratories regarding different PCR conditions and techniques, cycling conditions, separation and visualization methods. Forward primers were labelled with fluorescent dyes (6FAM, VIC, and NED; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) (Table 1).

Table 1.
SSR primers (fluorescently dye-labelled) used for olive genotyping.
The PCR reaction was performed in a VeritiTM 96 Well Thermal Cycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) in a reaction mix with a total volume of 10 µL (Table S1) at 72 °C; for 28 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 55 °C, and 30 s at 72 °C; and a final extension step of 5 min at 72 °C. Amplified fragments were separated in the four capillary electrophoresis (Genetic Analyzer 3130; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) using GeneScan™ 500 LIZ™ dye of standard size (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The PCR products of the 11 SSR primers of each olive DNA sample were mixed together two or three at a time, according to the dye and expected allele size, and put through capillary electrophoresis in the following combinations: standardization DCA3/DCA18/UDO43; DCA9/DCA14/DCA16; DCA5/GAPU71B/GAPU103A; and EMO90/GAPU101. The allele size of the amplified fragments was scored using the GeneMapper 4.0 software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
2.3. Allele Lenght Standardization
The standardization of allele lengths of Croatian olive genotypes based on the allele lengths of the 80 most important Mediterranean olive varieties from 11 Mediterranean countries, with data available in OleaDB [6], was accomplished using referral varieties of specific alleles for each locus. The standardization of allele lengths was performed to enable the comparison of the SSR profiles of Croatian olive genotypes obtained from the combinations of the eleven consensual SSR markers, with olive profiles obtained using the same SSR markers on the Olea database (Table S2). The standardized data of SSR allele lengths of Croatian olive genotypes were additionally standardized with the allele lengths of olive accessions of the Worldwide Olive Germplasm Banks of Córdoba (WOGBC) [37] and Worldwide Olive Germplasm Banks of Marrakech databases (WOGBM) [36]. To standardize the length of alleles, we used the genotypes present in our research as referral samples, and those which are also present in the databases OleaDB, WOGBC, and WOGBM.
2.4. Data Analysis
Olive trees with identical genotypes were identified using the GenClone programme [80] and excluded from further analysis, with the exception of the analysis of variability within varieties. Information index (I) scores, the number of alleles (Na), the number of effective alleles (Ne), the number of rare alleles per locus (Nu), and the number of distinguished genotypes (NDG) were calculated for each SSR locus. The expected (He) and observed (Ho) heterozygosity for each SSR locus were estimated according to the work of Nei [81], while the polymorphic information content (PIC) was estimated according to the research of Botstain et al. [82]. I, Na, Ne, Nu, NDG, He, Ho and PIC were calculated using GenAlEx 6.501 software [83]. The probability of identity [84] for each SSR locus and the overall probability were estimated using software IDENTITY 1.0 [85]. The power of discrimination—PD [86] was calculated for each SSR locus, where the allele frequency was replaced by the genotype frequency [1].
The proportion of shared allele distance (Dps, [87]) was used for the estimation of distances between olive genotypes using MICROSAT v.1.5 software [88]. Allele differences between pairs of Croatian olive genotypes were estimated using GenAlex 6.501 software [83]. Cluster analyses were performed on SSR loci using a least-squares algorithm [89] with 1000 bootstraps using the FITCH programme of the Phylip software, ver. 3.695 [90]. The relationships among olive genotypes were visualized using Display Newick Trees constructed in MEGA7 [91].
For the analysis of intra-varietal variability, a matrix of allele differences among trees was used for the construction of a dendrogram using the UPGMA (unweighted pair group method using an arithmetic average) algorithm. Matrices of allele differences were calculated using GeneAlex program, ver. 6.5 [83]. UPGMA analysis was conducted using NTSYSpc software, ver. 2.21 L [92].
A number of different genetic subgroups of olive genotype K (the modal value of ΔK) were investigated using STRUCTURE, ver. 2.3.4 software [93]. STRUCTURE analyses included a burn-in period (the initial stage of the sampling process) of 200,000 replicates, followed by 600,000 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) replicates for each run. Twenty repeat runs were carried out to quantify the amount of variation in the likelihood for each K (from K = 1 to K = 8) using an ADMIXTURE model and correlated allele frequencies. The posterior probability of the data lnP(K) for a given K can be used as an indication of the most likely number of real genetic groups [94]. Therefore, the height of the modal value of the ΔK distribution was calculated in order to detect the number of real genetic subgroups K using Structure Harvester, v 0.6.92 [95]. The K that best described the data was chosen by examining the lnP(K) [96] and by calculating ΔK [94]. The value of K with the highest mean log likelihood [lnP(K)] and ΔK statistic was selected. An olive genotype having a membership probability of Q > 75% indicated its belonging to a specific genetic group (K), while genotypes with membership probabilities of Q < 75% belonged to admixed groups of genotypes of mixed origin [97].
3. Results
We analyzed 226 olive trees grown in Croatia and assessed additional foreign referral samples of 9 trees (in total 235 trees) at eleven SSR loci. Duplicates (91 trees) were excluded from further statistical analyses, reducing the number of trees to 135 trees of different genotypes (Table S3). The analyses of these 135 genotypes resulted in 138 polymorphic and reproducible alleles, out of which 30% (42) had a frequency of less than 1%. Allele frequencies varied from 0.004 to a maximum of 0.567 for the allele 191 bp at the locus DCA14. The mean number of alleles per SSR locus was 12.5 (Table 2). The number of alleles obtained ranged from 5 (EMO90) to 19 (UDO43), while allele size ranged from 117 bp (GAPU71B) to 259 bp (DCA3). The number of effective alleles (Ne) per locus ranged from 1.36 (EMO90) to 7.20 (DCA9). The expected heterozygosity (He) ranged from 0.611 (DCA5) to 0.861 (DCA9), with a mean value of 0.766. The observed heterozygosity (Ho) was lowest at locus DCA14 (0.622), and highest at locus UDO43 (0.985). Loci DCA9 and DCA16 showed lower value Ho in relation to He. The mean value of Ho was higher (0.823) than the mean value of He (0.766), indicating high genetic variability within analyzed the germplasm. Most of SSR loci (9) have higher Ho then He, which is also reflected in the negative value of fixation index (F) (Table 2). The PIC value of the 11 SSR loci was above 0.5 and ranged from 0.56 (DCA5) to 0.86 (DCA9), with a mean value of 0.74. The average number of distinguished genotypes per SSR locus (NDG) was 27. The SSR locus DCA9 showed the highest number of identified genotypes (NDG = 42) while the loci EMO90 showed the lowest (NDG = 11). The probability of identity (PI) of genotypes varied from 0.019 (DCA14) to 0.210 (DCA5), while the cumulative PI value for all SSR loci was 5.86 × 10−15. The obtained PIC, NDG and PI values indicated that the SSR loci had very good discriminating power, successfully differentiating 73 SSR profiles of known Croatian varieties (including the cases of intra-varietal variability), 9 profiles of foreign varieties, and 53 profiles of unknown olive genotypes, from a total 135 SSR profiles (Table S3). The unknown (UNK) olive genotypes are the genotypes not documented or known by name. They also belong to the Olea europaea subsp. europaea species (not the Oleaster) and they are normally cultivated, but their genetic profiles are not identical to the profiles of any native Croatian or introduced variety.

Table 2.
Genetic diversity parameters estimated for 11 SSR primer pairs (loci) in 135 olive genotypes. The parameters reported for each SSR primer pair: the number of different (Na), effective (Ne) and rare or unique (Nu) alleles; the number of distinguished genotypes (NDG); the observed (Ho) and expected (He) heterozygosity; polymorphic information content (PIC); the fixation index or inbreeding coefficient (F); and the probability of identity (PI).
Within Croatian germplasm, 34 alleles were detected as rare or private (Table 3). These alleles were confirmed via repeated amplification. There were 34 private alleles within the set of 138 polymorphic alleles detected within Croatian germplasm, and 25 out of 135 genotypes possessed one to five private alleles.

Table 3.
List of genotypes with rare alleles within Croatian germplasm. The rare alleles unique to Croatian germplasm are marked with asterisk (*).
However, comparing SSR profiles of Croatian olive germplasm with the profiles of olive varieties in the Olea database and olive accessions in the WOGBC and WOGBM databases, we found that the number of rare alleles decreased from the initial 34 to 12 rare alleles, only represented within and unique to germplasm originating from the Croatian part of Mediterranean (Table 3).
3.1. Synonyms and Homonyms
Synonyms were detected in 18 cultivars, mostly in ‘Oblica’ (9 synonyms), ‘Drobnica’ (7 synonyms), and ‘Plominka’ (7 synonyms). Few synonyms were detected in the remaining 15 varieties of local significance (Table 4), the production of which is limited to small geographic areas. Homonyms were not detected in this research, but we did detect numerous cases of intra-varietal variability (Table 5).

Table 4.
Croatian olive varieties analyzed, with the number of sampled trees, common names of varieties, and its synonyms detected as a result of SSR analyses.

Table 5.
Allele combinations (in bp) within genotype at loci with observed intra-varietal variation. The number of tree samples (n) with defined allelic combinations are presented in brackets.
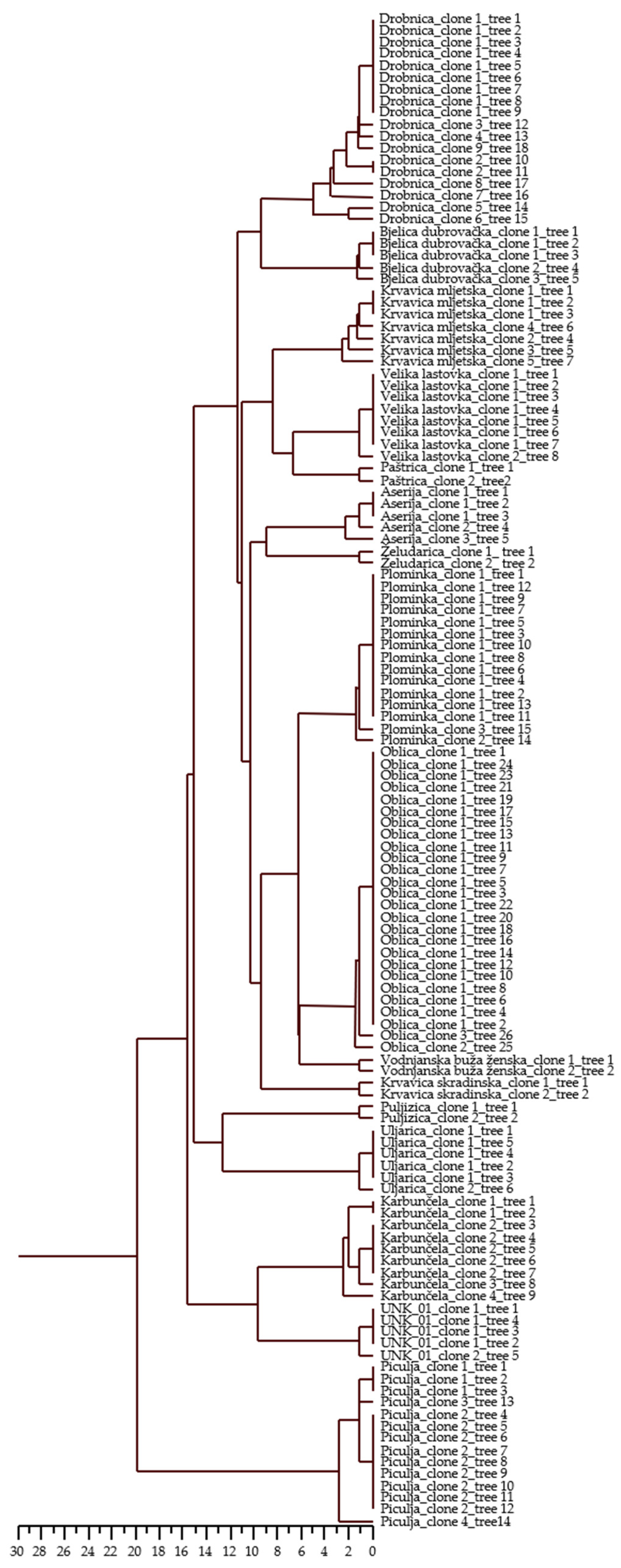
Intra-varietal differences were detected for a variable number of loci in 15 varieties and for one unknown genotype (Table 5). The number of variable loci ranged from one locus in seven varieties and one unknown genotype to two loci in ‘Plominka’, ‘Oblica’, ‘Bjelica dubrovačka’, and ‘Aserija’, three loci in ‘Piculja’ and ‘Karbunčela’, four loci in ‘Krvavica mljetska’, and five loci in ‘Drobnica’. The loci DCA9 (27 allelic combinations), UDO43 (18 allelic combinations), and Gapu103A (8 allelic combinations) proved to be the most sensitive in terms of the detection of differences within varieties. Some of the alleles were differentiated in only two base pairs per locus. These small variations were proved by repeated PCR amplification. UPGMA clustering (Figure 1) based on allelic differences showed variation in olive trees within 15 varieties and one unknown genotype.
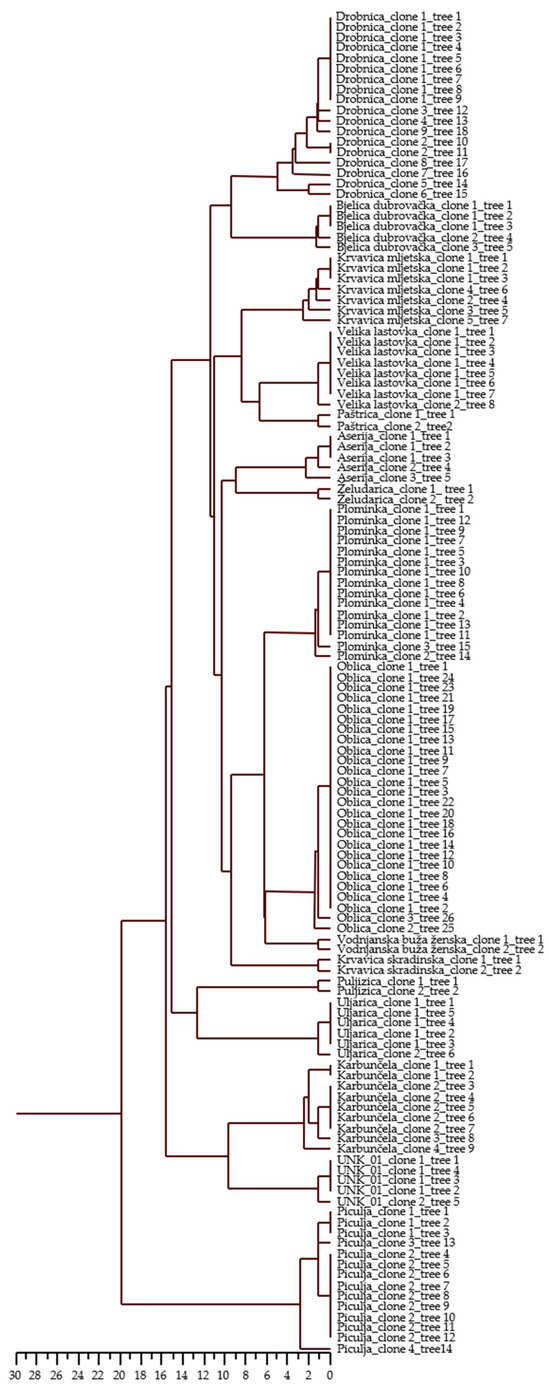
Figure 1.
Dendrogram of 128 olive trees of 16 Croatian olive varieties based on Squared Euclidean distances (i.e., allelic differences) using UPGMA method. Dendrogram represents variation among trees within varieties.
3.2. Genetic Distances and Relationships of Croatian Olive Germplasm
The proportion of shared allele distance (Dps) between 135 olive genotypes ranged from 0.045 (27 pairs of genotypes) to 0.955 (12 pairs of genotypes) with a mean value of 0.629.
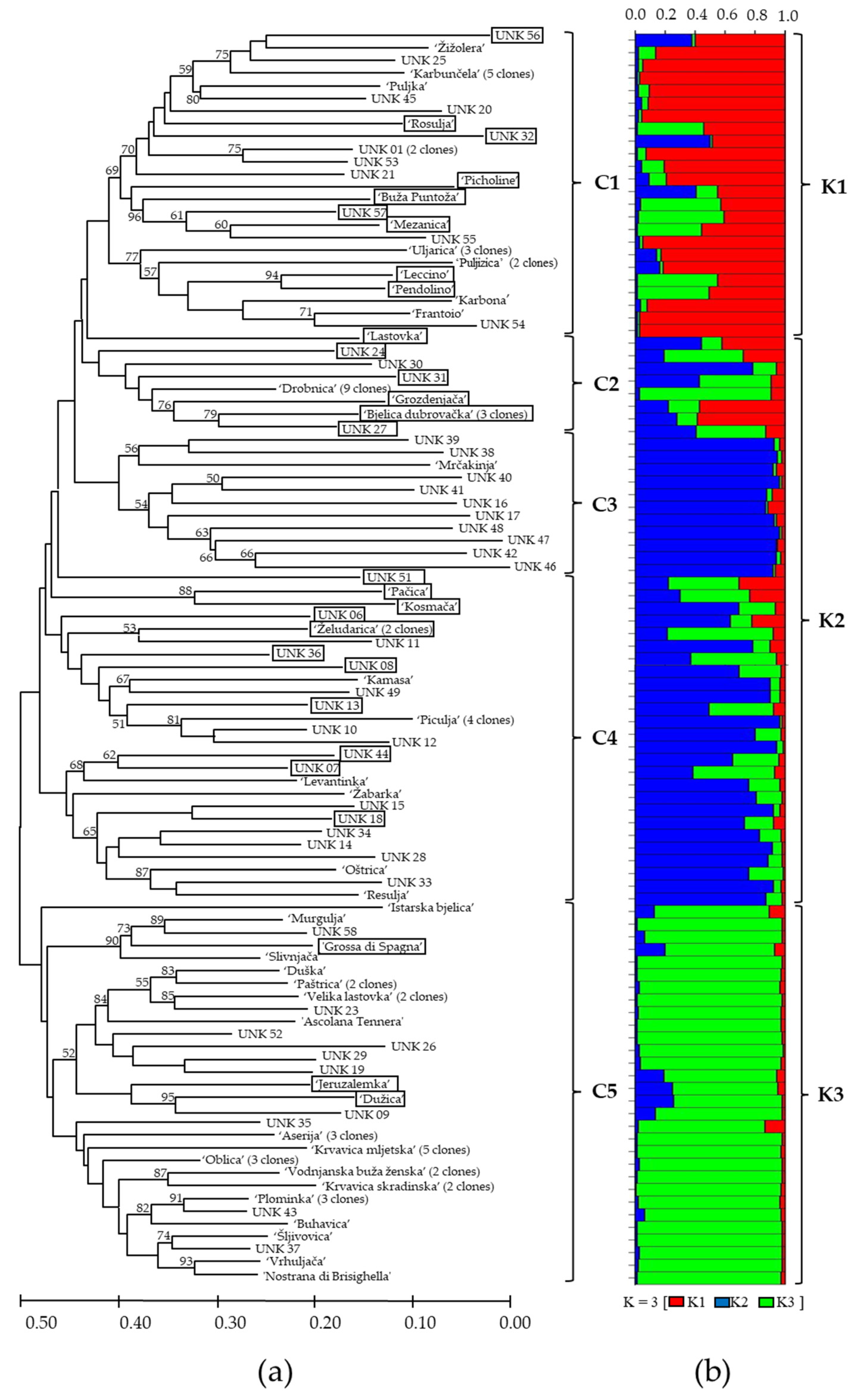
Olive genotypes were divided into five clusters (C1–C5) usinge Fitch–Margoliash least-squares algorithm cluster analysis (Figure 2a). Varieties and unknown genotypes with intra-varietal variability are only represented by one representative in the cluster. The genotypes from the same region clustered mostly into the same cluster, but some of them were grouped into other clusters, mostly with the genotypes from another regions. The genotypes from Istria and Kvarner (46% of genotypes) clustered mostly within the cluster C1. Genotypes from the northern Dalmatia clustered mostly within the cluster C2 (50% of genotypes), and those from southern Dalmatia clustered within cluster C3 (45% of genotypes). The genotypes from middle Dalmatia mostly clustered into the clusters C3 (27%) and C4 (27%). The traditional varieties ‘Drobnica’, ‘Oblica’, and ‘Plominka’, cultivated in a wide area from Kvarner to southern Dalmatia, were grouped in separate clusters. ‘Drobnica’ a variety mostly presented in Kvarner, middle and southern Dalmatia, was grouped within the cluster C2. Recently, the trees of ‘Drobnica’ were found even in Istria, in the north. ‘Oblica’, the leading autochthonous variety in Dalmatia, and partially produced also in Kvarner, was grouped within cluster C5. The variety ‘Plominka’, mainly cultivated in Kvarner region, Istria, and southern Dalmatia, was also grouped within cluster C5.
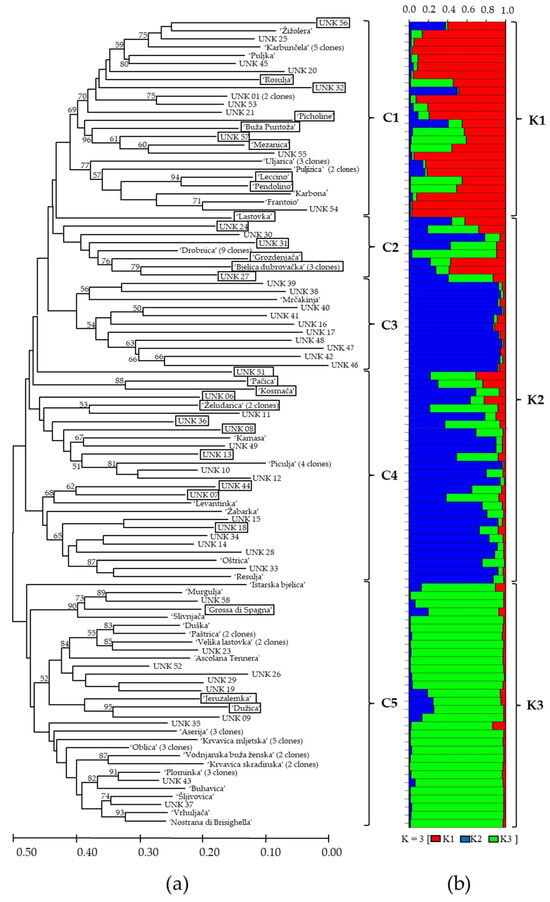
Figure 2.
The dendrogram: (a) based on the proportion of shared allele distance (Dps) and cluster analysis using Fitch–Margoliash least-squares algorithm of 99 genotypes of Olea europaea based on 11 consensus SSR markers. Olive genotypes were divided into five clusters (C1–C5). Bootstrap values over 50% based on 1000 resamplings of the data set are indicated based on the branches of the dendrogram. (b) Bayesian cluster analysis of the 99 samples of Olea europaea. Genetic subgroups (K) are indicated at the right side of the bar plot. The strips of different colors represent membership coefficient for K = 3 (genetic subgroup K1 (red), K2 (blue), and K3 (green)), calculated using STRUCTURE v.2.3.4 software. The length of colored strips represents the estimated membership proportion of genotype in corresponding genetic subgroup. Genotypes of mixed origin (with membership probabilities of Q < 75%) are graphically marked by black frame in the dendrogram.
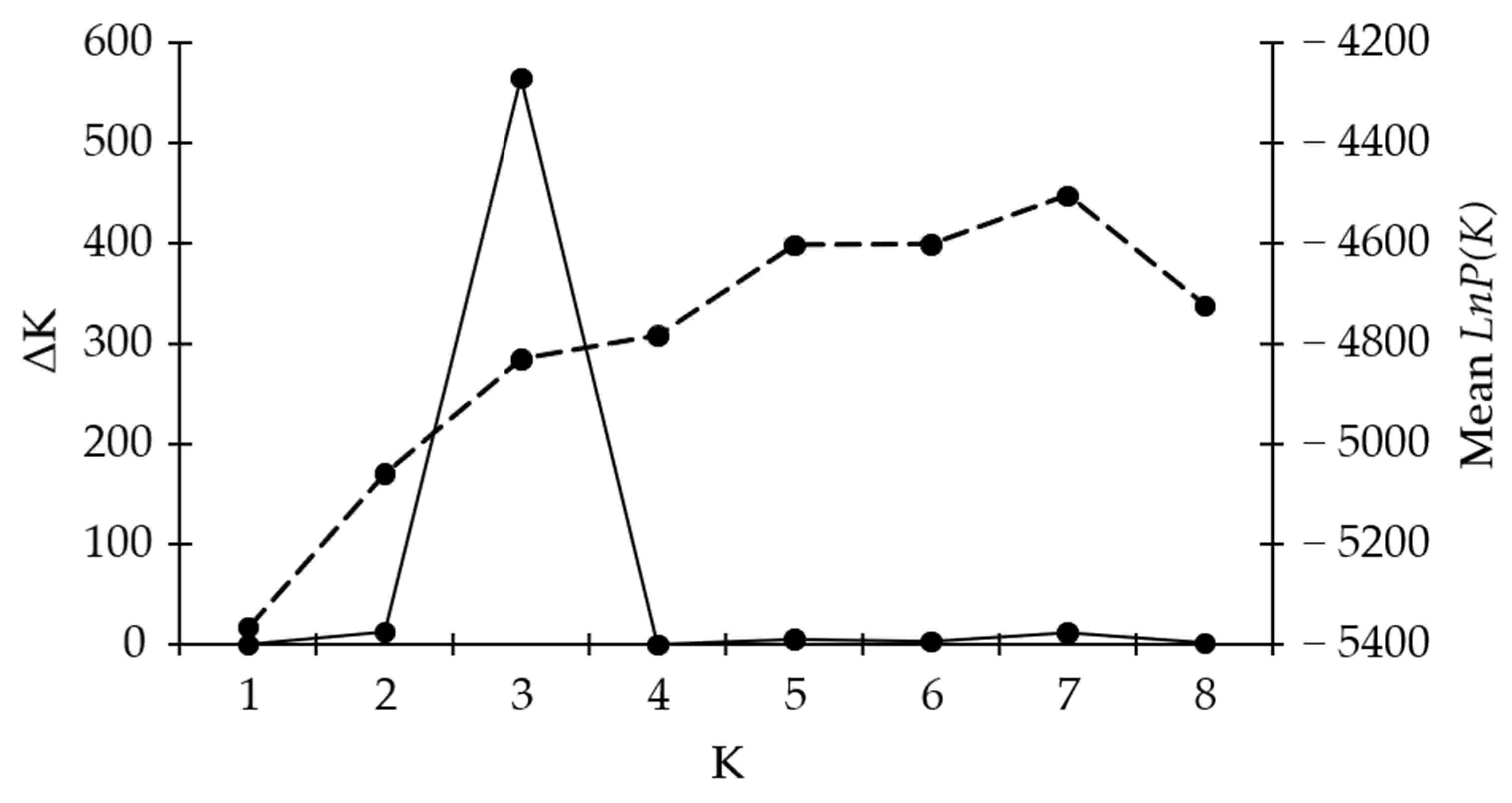
Bayesian clustering analysis was used to test the genetic structures of Croatian olive germplasm, and one to eight clusters (K) were tested. The average log probability lnP(K) values increased up to the third testing cluster, after which the rate of change in the log probability value decreased (Figure 3). The relationship between K and ΔK indicated the clustering of olive genotypes into three distinctive genetic groups (Figure 2b). Genotypes of mixed origin (with membership probabilities of Q < 75%) are marked by black frames in Figure 2b. Genetic subgroups K1 (marked in red), K2 (blue), and K3 (green) consisted of 32, 59, and 44 genotypes, respectively. The varieties were mostly represented within the genetic subgroup K3 (43%), followed by genetic subgroup K2 (35%), and the least represented within genetic subgroup K1 (22%) (Figure 2b). The unknown genotypes were mostly distributed within the subgroup K2 (60%), while a slightly smaller part of unknown genotypes were distributed within genetic subgroups K1 (21%, and K3 (19%). The majority of olive genotypes originating from Istria and Kvarner were distributed within genetic subgroup K1, the majority of genotypes from the north and some genotypes from the middle Dalmatia were within the subgroup K3, while the majority of genotypes from the middle and all genotypes from southern Dalmatia were distributed within the subgroup K2.
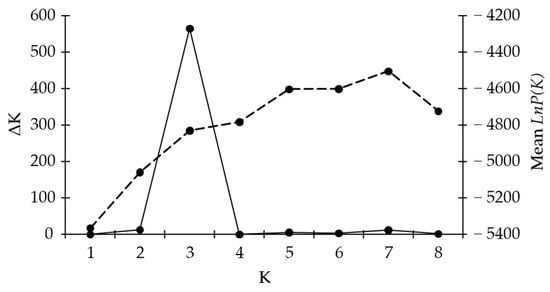
Figure 3.
Bayesian clustering of Croatian olive genotypes. The average log probability value LnP(K) (dashed line) and modal value of ΔK (solid line) or distinctive genetic subgroups K are shown. The ΔK values are based on 20 replicates for each value of K using the ADMIXTURE method.
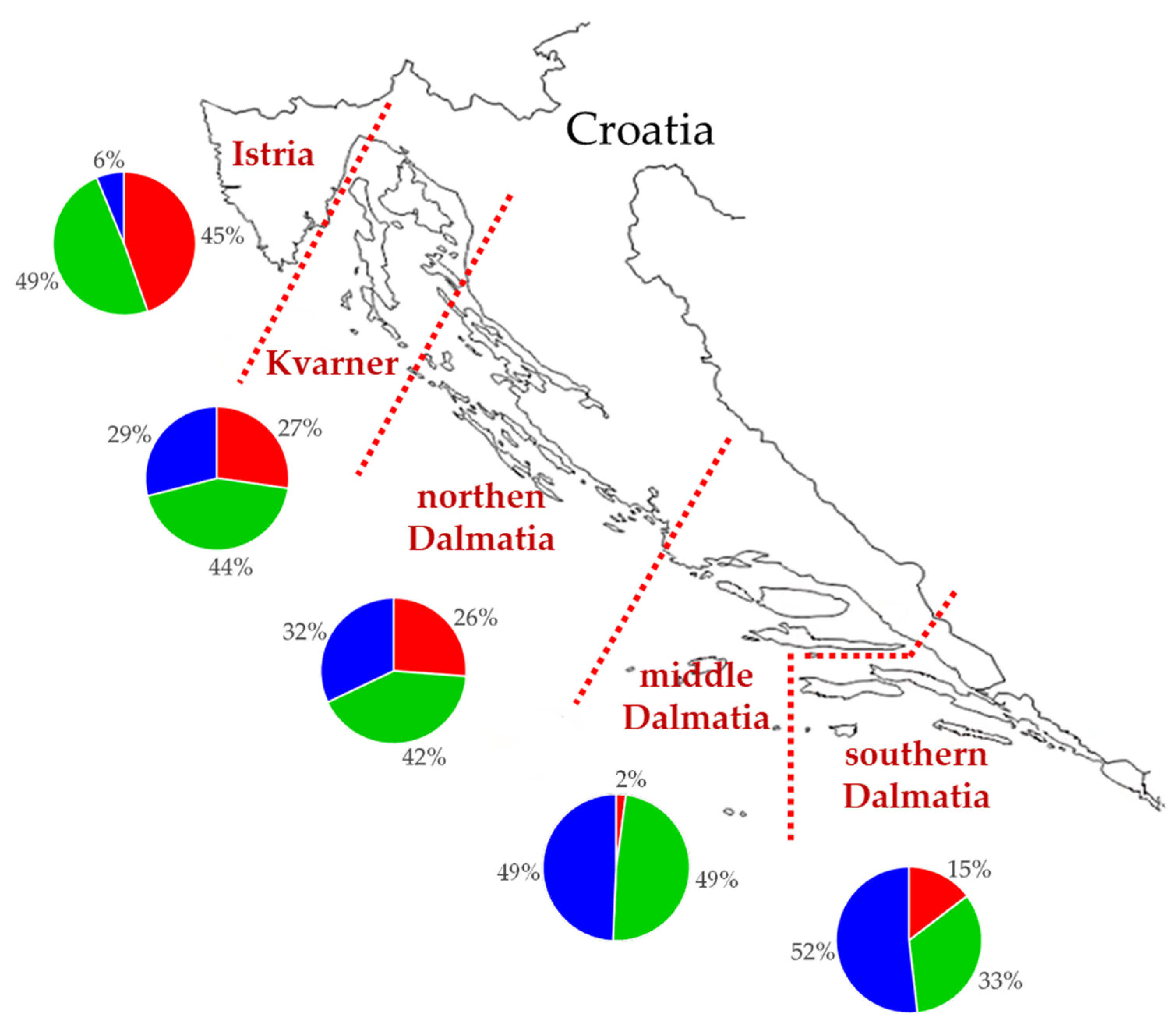
The mean value of membership coefficients of Croatian olive genotypes, sampled in five olive-growing areas in Croatia, was calculated by each growing area on the basis of membership coefficients for K = 3 for olive genotypes (pie charts, Figure 4). The genetic basis of the plants originated from the three genetic subgroups. The most represented genetic subgroup in southern Dalmatia was K2 (blue) (52%). Moving northward, the share of that genetic subgroup dropped drastically to only 6% in Istria. The share of genetic subgroup K1 (red) was lower in southern Dalmatia (15%) than Istria (45%). The share of genetic subgroup K3 (green) was stable compared to remaining genetic subgroups, with the share between 33% in southern Dalmatia and 49% in Istria and middle Dalmatia (Figure 4).
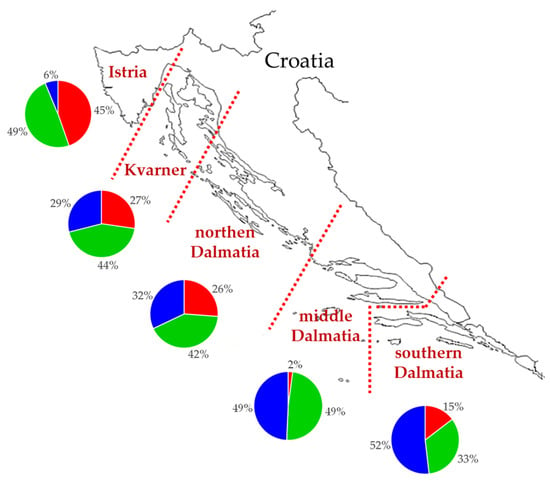
Figure 4.
Map of Croatian Adriatic region with the five main olive-growing regions (Istria, Kvarner, northern, middle, and southern Dalmatia) marked. Pie charts representing membership coefficient for K = 3 (genetic subgroup K1 (red), K2 (blue), and K3 (green)), calculated using STRUCTURE averaged by areas designated by growing conditions.
4. Discussion
In addition to the reports on global olive germplasm based on collections in situ [37,38], there are many published papers with a focus on olive germplasm ex situ and its diversity within certain geographic areas [46,48,50,53,54,58,60,72,98,99]. Regarding Croatian olive germplasm, different sets of SSR loci were used to genotype traditional olive varieties cultivated in southern Dalmatia [25] and in Istria [27]. Our report was based on the first comprehensive research on the Croatian olive germplasm using 11 SSR markers, which were suggested and recommended as consensual markers for the genetic characterization of olive germplasm [70]. The variation in the allele size in the comparison of SSR profiles of domestic germplasm with other established international databases of SSR profiles was standardized, using referral genotypes that possess specific alleles for each locus as a standardization bridge.
The focus of this research was the determination of the genetic diversity of olives in Croatian part of the Mediterranean, with a special emphasis on the DNA identification of lesser-known varieties and unknown genotypes found in old and extensive olive orchards. Lesser-known varieties and unknown genotypes are mainly of local significance, but they are still important, not only as a pool of genetic variability, but also as an economic niche for the production of virgin olive oils, and as a basis for branding the final product with a mark of local origin authentic to the region (island, town) where it is produced. The results of this research represent an important contribution in terms of establishing a database of SSR profiles of domestic olive germplasm comparable with the databases of olive germplasm OleaDB [6], WOGBC [37], and WOGBM [36,38].
The results of SSR analyses revealed high genetic diversity within the olive germplasm in Croatia. Altogether, 126 genotypes originating from Croatian part of the Mediterranean were identified using 11 SSR loci. The major of SSR loci (nine out of 11) showed higher values of observed heterozygosity (Ho) compared to expected heterozygosity (He), as well as negative values of the inbreeding coefficient (F). These parameters indicate the existence of high genetic variability within the analyzed germplasm. The existence of high genetic variability within the germplasm is explained by the emergence and accumulation of spot mutations during the long period of the clonal reproduction of olive varieties [37,54,70,100].
The mean value of PIC (>0.7) for the set of consensual SSR loci was high, and as such was suitable for the assessment of molecular diversity and the identification of olive genotypes [27,64]. These SSR loci proved to be enough powerful for the separation of genotypes within Croatian olive germplasm. The average number of distinguished genotypes per SSR locus was multiple times higher (NDGavg = 27) in comparison to the SSR loci applied in previous reports [54,58,59]. The cumulative probability of the identity value (PI) of these loci was very low, and this showed that SSR loci used in this study had high discriminating power in genotyping of Croatian olive genotypes, which was in accordance with previous reports [36,60,101].
The grouping of the olive genotypes based on the results of the SSR analyses was not related to their geographic distribution along the Adriatic coast. Despite being grouped into three genetic subgroups according to their genetic origin, the results confirmed the high discriminatory ability of the consensus SSR markers. The high diversity of the genotypes in our research was a result of their different genetic origin and probably a lack of selection pressure.
Three genetic subgroups (K = 3) were determined via Bayesian clustering analysis, which was used to test the genetic structure of Croatian olive genotypes. All olive genotypes were distributed within these three genetic subgroups. Three fundamental genetic subgroups were also determined in previous studies of the olive genotypes from the whole Mediterranean [33,36,70]. These three genetic subgroups are distributed in the eastern, middle, and western Mediterranean. The presence of the three genetic subgroups was determined in middle Mediterranean [36] and the values obtained corresponded to our results for the Croatian part of the middle Mediterranean. The main reason for that was probably the possibility of the spreading of generative and vegetative propagation material within the entire Mediterranean basin [36].
In our research, consensual SSR primers proved to be a tool of choice for distinguishing variable genotypes within a variety. In that sense, the loci DCA9, UDO43, and Gapu103A were the most effective, which corresponded with the identical conclusion [70] reached on the usefulness of this subset of markers in terms of segregating variable genotypes within the same variety. Considering the variability within several olive varieties in eastern Adriatic, the loci DCA9 and Gapu103A were the most effective [77]. In our research, the intra-varietal variability was noticed in the very old and important varieties cultivated today, like ‘Oblica’, ‘Drobnica’, ‘Karbunčela’, and ‘Piculja’. The variety ‘Oblica’ is the most represented olive variety along the whole Adriatic, counting for 60% of the total olive trees in Croatia [8].
The variety ‘Drobnica’ is mostly represented in northern Dalmatia [102], but is also present in southern Dalmatia [18]. The name ‘Drobnica’ is mostly used in the northern part of Dalmatia, while the name ‘Sitnica’ is mostly used in southern part of Dalmatia [9]. This research shows that the variety ‘Drobnica’ is also represented in Istria, that ‘Karbunčela’ is mostly represented in northern Dalmatia, in the islands and in the area around Zadar, while ‘Piculja’ is mostly represented in southern Dalmatia [13]. The highest intra-varietal variability was detected for the variety ‘Drobnica’. The clones of ‘Drobnica’ differed in as much as six out of 22 alleles. This kind of variability might be explained as polyclonal variations that arise as a consequence of the vegetative propagation of different genotypes [75,77].
Within ‘Piculja’ and ‘Karbunčela’, both varieties of local importance, variations were found in up to three out of 22 alleles. This variation might be explained as a result of the accumulation of somatic mutations [36]. Variation was found within ‘Oblica’, the most represented variety in Croatia [8], in up to 1 out of the total of 22 alleles. ‘Oblica’ is probably the variety that does not tend to accumulate somatic mutations. The variation in up to two alleles among clones is due to somatic mutation occurring in different branches of the ancient mother plants used for vegetative propagation [75].
A list of varieties, their names, and synonyms is provided in one of the first documented sources on olive varieties [13]. Working based on descriptions and data collected in situ, Bulić [13] states that ‘Dužica’ and ‘Duška’ are synonyms. Also, synonymy was attributed to following three pairs of varieties: ‘Mrčakinja’ and ‘Piculja’, ‘Paštrica’ and ‘Žutica’, ‘Puljizica’ and ‘Puljka’ [13]. In our research, we found unique genetic profiles for all of these putative synonyms, and hence established their varietal uniqueness, in spite of similar names and previous statements. Contrary to the attribution to varieties ‘Murgulja’ and ‘Krvavica’ of the characteristic of being synonyms [13,16], we found unique genetic profile for all of these varieties. However, there are two different varieties, known as ‘Krvavica’: ‘Krvavica mljetska’, found in southern Damlatia (island if Mljet), and ‘Krvavica skradinska’, found in middle Dalmatia (region of Skradin). With the addition of ‘Murgulja’, which was considered as a synonym [13], these genotypes are three different varieties, each with unique genetic profiles. The variety ‘Velika lastovka’ is cultivated in southern Dalmatia, but we discovered this variety far away in the Kvarner region and northern Dalmatia.
Within the scope of this research, for the first time, we created a comprehensive database of SSR profiles of Croatian olive germplasm FAZ_OliveDB (University of Zagreb, Faculty of Argiculture Olive Database) (Table S3) using the set of consensual SSR primers [70]. The length of the alleles was standardized with the alleles in OleaDB [6], WOGBC [37], and WOGBM [36,38], enabling the comparison of SSR profiles of Croatian origin with SSR profiles of olives in these databases, contributing to the accurate determination of the identity of genotypes from the Adriatic coast of Croatia.
The matching of the SSR profiles of the varieties used as referral samples was performed via the comparison of genotypes on the basis of different SSR data, except for varieties ‘Grossa di Spagna’ and ‘Picholine’. The profile of ‘Grossa di Spagna’ in the databases OleaDB [6] and WOGBC [37] is identical to the profile of variety ‘Konservolia’, while in the database WOGBM [36,38] it is identical to the variety ‘Amphisis’, which is considered as a local synonym of the variety ‘Konservolia’ [34]. The SSR profile of variety ‘Picholine’ from OleaDB [6] is different from the profile in WOGBC [37] and WOGBM [36] by six alleles, but the difference with the results in our research is five alleles.
In the continuation of the discussion, when comparing the SSR profiles of olive genotypes obtained in our research with the SSR profiles of olive genotypes in the world databases, in addition to the OleaDB [6], we will use the WOGB database [38] because it combines the SSR profiles from both the WOGBC [37] and WOGBM [36] databases.
The WOGB database [38] shows the SSR profiles of 23 Croatian accessions which were analyzed by SSR markers and attributed to 12 varieties really originating from Croatia (‘Buga’, ‘Crnica’, ‘Istarska bjelica’, ‘Istarska crnica’, ‘Karbuncela’, ‘Lastovka’, ‘Levantinka’, ‘Oblica’, ‘Plemenita bjelica’, ‘Puntoza’, ‘Simjaca’ and ‘Velika Lastovka’). By comparing those Croatian cultivars in the WOGB database with the SSR profiles found in our studies, non-matching was noticed in the SSR profiles of several cultivars. The SSR profile of variety ‘Puntoža’ (MAR00499) (abbreviated from ‘Buža puntoža’) in the WOGB database is not identical to the SSR profile of variety ‘Buža puntoža’ in our studies, but it is identical to the SSR profile of UNK_56, which was also determined here. Therefore, the accession named ‘Puntoža’ (MAR00499) in the WOGB database is not, as it is supposed to be, a variety ‘Puntoža’ or ‘Buža puntoža’.
The SSR profile of the variety ‘Karbuncela’ (MAR00513) in the WOGB database differs from the SSR profile of ‘Karbunčela’ found in our studies. According to Bulić [13], the variety ‘Karbunčela’ is probably identical to the variety ‘Carboncella’, which was introduced from Southern Italy to the Zadar area, where it has spread in cultivation. According to our analyses, the SSR profiles of varieties ‘Karbunčela’ and ‘Moraiolo’ (syn. Carboncella [34]) match, confirming previous assumptions [13] about the origin of the variety and the origin of the name of the variety. By comparing the SSR profile of variety ‘Karbuncela’ (MAR00513) in the WOGB database with the SSR profile of ‘Karbunčela’ in our studies, we determined that the SSR profile of ‘Karbuncela’ in the WOGB database is actually identical to the SSR profile of variety ‘Paštrica’ found in our studies. Therefore, the accession named ‘Karbuncela’ (MAR00513) in WOGB database is actually the variety ‘Paštrica’.
The SSR profiles of both variety ‘Mezanica’ (MAR00511) and variety ‘Sitnica’ (MAR00514) in the WOGB database are identical, but their profile differs from the SSR profile of variety ‘Mezanica’ tested in our research. The SSR profiles of variety ‘Drobnica’, together with its clonal variants identified in our research, are very similar to the SSR profiles of varieties ‘Mezanica’ and ‘Sitnica’ in the WOGB database. Also, the name of variety ‘Sitnica’ is a synonym of the variety ‘Drobnica’ [9]. Taking into account these two facts, it is most likely that the WOGB database consists of clonal variants of ‘Drobnica’, but not ‘Mezanica’ (MAR00511), whose SSR profile is different in our studies.
The varieties ‘Uljarica’ (MAR00512) and ‘Žabarka’ (MAR00505), included in the WOGB database, also have the same SSR profile. However, in our research we determined that it is not Uljarica/Žabarka in WOGB, but ‘Bijelica dubrovačka’. In our research, different SSR profiles were determined for ‘Žabarka’ and ‘Uljarica’ (Table S3). The SSR profile of ‘Uljarica’ was identical to the SSR profile of ‘Gentile di Chieti’, which was the reference variety in our research. The profile of our referral variety was also identical to the SSR profile of ‘Gentile di Chieti’ (MAR0015) in WOGB database. With the profiles of both accessions, MAR00512 and MAR00505 probably correspond to the variety ‘Bjelica dubrovačka’.
The SSR profile of variety ‘Oblica’ determined in our study matches the SSR profile of ‘Oblica’ in OleaDB [6] and in WOGB database (‘Oblica’; COR000706). The SSR profile of variety ‘Lumbardeška’ (MAR00500) in the WOGB database is the same as the SSR profile of ‘Oblica’ in the WOGB database and OleaDB [6]. This profile is also identical to the profile of ‘Oblica’ in our research. According to previous statements [13], the variety ‘Lumbardeška’ is a synonym of ‘Oblica’, as confirmed here.
The SSR profiles of varieties ‘Istarska bjelica’, ‘Oblica’ and ‘Simjaca’ (syn. of ‘Slimjača’ in our research), taken from the databases Olea and WOGB, are identical to the SSR profiles in our research, while the profiles of varieties ‘Drobnica’, ‘Lastovka’, and ‘Plominka’ from these three databases differ in a range from one to a maximum of three alleles per locus compared to the profiles of the same varieties in our research.
The SSR profile of the genotype UNK_56 determined in our study differs in just one allele from both, the SSR profile of variety ‘Frangivento’ (syn. ‘Cipressino’ [34]) in the OleaDB [6], and the profile of variety ‘Cipressino’ (COR000090) in WOGB database. Therefore, the genotype UNK_56 from our study is probably variety ‘Cipressino’, which is sporadically present in Istria, the origin of the genotype for our research.
By comparing the SSR profiles of 135 olive genotypes analyzed in our study with the SSR profiles of olive samples in the OleaDB [6] and WOGB [38] database, we found a total of 92 olive varieties and unknown genotypes with unique genetic profiles in the producing area of the Mediterranean part of Croatia.
5. Conclusions
This study is the first systematic genotyping of olive germplasm in the Croatian part of Mediterranean. We performed our genetic analyses of Croatian olive germplasm by applying a set of consensus SSR primers, and we conducted our study among a representative number of samples, fully covering the five olive-producing regions in Croatia, results in a comprehensive database of SSR profiles of Croatian olive germplasm “FAZ_OliveDB”. The SSR profiles reveal high genetic diversity within the Croatian olive germplasm. Out of a total of 226 analyzed trees, a total of 132 genotypes were determined, including foreign introduced varieties. Wide genetic diversity was revealed among the unknown genotypes represented in production, but genetic uniqueness was confirmed for 73 local varieties and 53 unknown genotypes, latter being presented mainly in extensive production. Three different genetic subgroups were determined by STRUCTURE analysis. The varieties were mostly represented in the genetic subgroup K3, while unknown genotypes were mainly distributed in subgroup K2. Synonyms were found in 18 varieties, but the majority of them were synonymous with the varieties ‘Oblica’, ‘Drobnica’ and ‘Plominka’. No homonyms were discovered. Small allele variations responsible for clonal variability were discovered in 15 varieties. The lengths of the alleles among databases were standardized in order to enable the comparison of SSR profiles of Croatian germplasm with the olive germplasm from OleaDB and WOGB databases. Out of 132 different genotypes, the profiles of 92 of them are shown for the first time in our database after not being determined in any of the previous reports. These genotypes are local varieties, or genotypes without name that are unique to producing regions in Croatia. Also, several cases of varietal mismatches were detected among the olive databases. Regarding the economic potential of many of Croatian olive genotypes in extensive production, this research is a contribution to their characterization, and is significant for claiming varietal uniqueness. It is an important step for further recognition of the olive oils specific to certain geographic regions or production zone. Knowing the exact genetic profile is important for nurseries in the production of authentic varieties, but also for the introduction and spread of interesting genotypes to wider production. Further work should be focused on the propagation of all the identified genotypes with unique SSR profiles and planting them into collection olive groves, where phenotypic data can be collected with due accuracy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10040417/s1, Table S1: Final concentrations of components in PCR reactions.; Table S2: The alleles obtained on 11 SSR loci standardized among all three olive databases using referral genotypes.; Table S3: The FAZ_OliveDB (University of Zagreb, Faculty of Agriculture Olive Database) containing the genetic profiles of genotypes of Croatian olive germplasm, including the referral genotypes analyzed on 11 SSR loci from the consensus list of the SSR markers for olive genotyping [70]. The table indicates the sites and geographic data for samples collected in Croatia. The last two columns indicate the presence of the same genotypes and their names as present in the databases WOGB and OleaDB, i.e., the synonyms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B., K.B.L., A.V. and Đ.B.; methodology, S.B. and K.B.L.; software, S.B. and A.V.; validation, S.B. and Đ.B.; formal analysis, S.B., A.V. and K.B.L.; investigation, K.B.L. and Đ.B.; resources, A.V and Đ.B.; data curation, S.B. and Đ.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B., A.V. and K.B.L.; writing—review and editing, S.B., A.V., K.B.L. and Đ.B.; visualization, S.B., A.V. and K.B.L.; supervision, S.B. and Đ.B.; project administration, K.B.L. and Đ.B.; funding acquisition, Đ.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research, named “Genetic identification and collecting of Croatian autochthonous olive genotypes’’ was funded by the Adris foundation.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cipriani, G.; Marrazo, M.T.; Marconi, R.; Cimato, A.; Testolin, R. Microsatellite markers isolated in olive (Olea europaea L.) are suitable for individual fingerprinting and reveal polymorphism within ancient cultivars. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M.; Weiss, E. Domestication of Plants in the Old World-The Origin and Spread of Domesticated Plants in South-West Asia, Europe, and the Mediterranean Basin, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; p. 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, D.; Van Campo, E.; Boiy, T.; Terral, J.F.; Khadari, B.; Besnard, G. Primary domestication and early uses of the emblematic olive tree: Palaeobotanical, historical and molecular evidence from the Middle East. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, G.; Khadari, B.; Navascués, M.; Fernández-Mazuecos, M.; El Bakkali, A.; Arrigo, N.; Baali-Cherif, D.; Brunini-Bronzini de Caraffa, V.; Santoni, S.; Vargas, P.; et al. The complex history of the olive tree: From Late Quaternary diversification of Mediterranean lineages to primary domestication in the northern Levant. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2013, 280, 20122833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, A.; Mencuccini, M.; Baldoni, L. Olive genetic diversity assessed using amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 98, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, G. Olea Databases. 2007. Available online: www.oleadb.it (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- IOC International Olive Council. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/the-world-of-olive-oil/ (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Miljković, I. Suvremeno Voćarstvo; Nakladni zavod Znanje: Zagreb, Hrvatska, 1991; pp. 491–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zec, J. Sortiment maslina u Dalmaciji. Biljn. Proizv. 1951, 1, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Croatian Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://web.dzs.hr/ (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Šatović, Z.; Liber, Z.; Belaj, A.; Radosavljević, I.; Šindrak, Z.; Benčić, Đ. Genetic diversity of Croatian olive cultivars. In Proceedings of the 46th Croatian and 6th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 14–18 February 2011; Pospišil, M., Ed.; University of Zagreb, Faculty of Agriculture: Zagreb, Croatia, 2011; pp. 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ozimec, R.; Karoglan Kontić, J.; Maletić, E.; Matotan, Z.; Strikić, F. Tradicijske Sorte i Pasmine Dalmacije; UNDP Croatia: Zagreb, Croatia, 2015; pp. 90–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bulić, S. Građa za Dalmatinsku Elajografiju; Poljoprivredno odjeljenje Pokrajinske uprave za Dalmaciju: Šibenik, Kingdom of Serbs Croats and Slovenes, 1921; pp. 2–32. [Google Scholar]
- Marčić, M. Uzgoj Maslina na Istočnim Obalama Jadrana; Zadružni savez. Leonova Tiskara: Split, Kingdom of Serbs Croats and Slovenes, 1923; pp. 5–158. [Google Scholar]
- Bakarić, P. Olive cultivars in the Dubrovnik littoral. Pomol. Croat. 1995, 8, 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bakarić, P. Sorte Maslina Dubrovačkog Primorja; Alfa 2: Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2002; pp. 7–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bakarić, P. Stare Konavoske Sorte Maslina; Samizdat: Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2005; pp. 5–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bakarić, P. Main olive varieties in the area of Dubrovnik-Neretva County with special reference to autochtonous varieties of the Pelješac peninsula. Pomol. Croat. 2005, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bakarić, P. Autohtone Sorte Maslina Elafita; Samizdat: Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007; pp. 7–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hugues, C. Elaiografia Istriana; Ceres: Zagreb, Hrvatska, 1999; pp. 7–159. [Google Scholar]
- Belaj, A.; Satovic, Z.; Cipriani, G.; Baldoni, L.; Testolin, R.; Rallo, L.; Trujillo, I. Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and of their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationships in olive. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Perri, E. Genetic characterizationof olive germplasm by molecular markers. Eur. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 2, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rafalski, J.A.; Vogel, J.M.; Morgante, M.; Powell, W.; Andre, C.; Tingey, S.V. Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In Nonmammalian Genomic Analysis; Birren, B., Lai, E., Eds.; Academic Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 75–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, V.K.; Misra, A.K.; Modi, D.R.; Pandey, B.K. Potential of molecular markers in plant biotechnology. Plant Omics 2009, 2, 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Štambuk, S.; Sutlović, D.; Bakarić, P.; Petričević, S.; Anđelinović, Š. Forensic botany: Potential usefulness of microsatellite-based genotyping of Croatian olive (Olea europaea L.) in forensic casework. Croat Med. J. 2007, 48, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Poljuha, D.; Sladonja, B.; Bubola, K.B.; Radulović, M.; Brščić, K.; Šetić, E.; Krapac, M.; Milotić, A. A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Characterisation of Autochthonous Istrian Olive (Olea europaea L.) Varieties. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 46, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Poljuha, D.; Sladonja, B.; Šetić, E.; Milotić, A.; Bandelj, D.; Jakše, J.; Javornik, B. DNA fingerprinting of olive varieties in Istria (Croatia) by microsatellite markers. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 115, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolarić, S.; Kauf, Z.; Kožarić Silov, G.; Šindrak, Z.; Kozumplik, V.; Benčić, Đ.; Vokurka, A. Morphological and genetic characterization of olive variety of hinterland of Skradin. In Proceedings of the 46th Croatian and 6th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 14–18 February 2011; Pospišil, M., Ed.; University of Zagreb, Faculty of Agriculture: Zagreb, Croatia, 2011; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Miljković, I.; Žužić, I.; Pucci, C.; Baldoni, L.; Mariotti, M.; Cultrera, N.G.M. Molecular characterization of an ancient Olea europaea tree located on the Brijuni islands of (Croatia) by SSR markers analysis. Pomol. Croat. 2010, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercisli, S.; Bencic, D.; Ipek, A.; Barut, E.; Liber, Z. Genetic relationships among olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars native to Croatia and Turkey. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2012, 85, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Vokurka, A.; Batelja Lodeta, K.; Bolarić, S.; Hropić, L.; Majić, M.; Benčić, Đ. Determination of genetic variability within the olive variety ‘Piculja’ by molecular and morphological markers. In Proceedings of the 46th Croatian and 16th International Symposium on Agriculture, Vodice, Croatia, 5–11 September 2021; Rozman, V., Antunović, Z., Eds.; University Josip Juraj Strossmayer, Faculty of Agrobiotechnical Sciences: Osijek, Croatia, 2021; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Contento, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Gelati, M.T.; Maggini, F.; Baldoni, L.; Cionini, P.G. Diversity of Olea genotypes and the origin of cultivated olives. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, V.; Baldoni, L.; Porceddu, A.; Cultrera, N.G.M.; Contento, A.; Frediani, M.; Belaj, A.; Trujillo, I.; Cionini, P.G. Microsatellite markers are powerful tools for discriminating among olive cultivars and assigning them to geographically defined populations. Genome 2006, 49, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Perri, E. Genetic diversity in olive tree cultivars from Italy and other countries of the Mediterranean basin as revealed by RAPD and SSR molecular marker. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2009, 23, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Lazović, B.; Adakalić, M.; Pucci, C.; Perović, T.; Bandelj, D.; Belaj, A.; Mariotti, R.; Baldoni, L. Characterizing ancient and local olive germplasm from Montenegro. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 209, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouane, H.; El Bakkali, A.; Moukhli, A.; Tollon, C.; Santoni, S.; Oukabli, A.; Al Modafar, C.; Khadari, B. Genetic structure and core collection of the World Olive Germplasm Bank of Marrakech, towards the optimised management and use of Mediterranean olive genetic resources. Genetica 2011, 139, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, I.; Ojeda, M.A.; Urdiroz, N.M.; Potter, D.; Barranco, D.; Rallo, L.; Díez, C.M. Identification of the Worldwide Olive Germplasm Bank of Córdoba (Spain) using SSR and morphological markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 10, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bakkali, A.; Essalouh, L.; Tollon, C.; Rivallan, R.; Mournet, P.; Moukhli, A.; Zaher, H.; Mekkaoui, A.; Hadidou, A.; Sikaoui, L.; et al. Characterization of Worldwide Olive Germplasm Banks of Marrakech (Morocco) and Córdoba (Spain): Towards management and use of olive germplasm in breeding programs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Muto, A.; Badolati, G.; Veizi, A.; Chiappetta, A. Genotyping of Albania olive (Olea europaea) germplasm by SSR molecular marker. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2018, 30, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervishi, A.; Jakše, J.; Ismaili, H.; Javornik, B.; Štajner, N. Genetic structure and core collection of olive germplasm from Albania revealed by microsatellite markers. Genes 2021, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriero, E.; Fontanazza, G.; Cellini, F.; Giorio, G. Identification of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in olive (Olea europaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Stefanizzi, F.; Salimonti, A.; Falabella, R.; Perri, E. Microsatellite markers for identification of a group of italian olive accessions. Sci. Agric. 2009, 66, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Vendramin, G.G.; Chiapetta, A. Genetic biodiversity of Italian olives (Olea europaea) germplasm analyzed by SSR markers. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 296590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercisli, S.; Ipek, A.; Barut, E. SSR Marker-Based DNA Fingerprinting and Cultivar Identification of Olives (Olea europaea). Biochem. Genet. 2011, 49, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işık, N.; Doğanlar, S.; Frary, A. Genetic Diversity of Turkish Olive Varieties Assessed by Simple Sequence Repeat and Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism Markers. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, A.; Barut, E.; Gulen, H.; Ipek, M. Assessment of inter- and intra-cultivar variations in olive using SSR markers. Sci. Agric. 2012, 69, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, H.; Sakar, E.; Ulas, M.; Ercisli, S.; Bekir Erol, A.K. Molecular characterization of indigenous olive genotypes based on SSR analysis. Genetika 2016, 48, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubos, K.; Moustakas, M.; Aravanopoulos, F.A. Molecular identification of Greek olive (Olea europaea) cultivars based on microsatellite loci. Genet. Mol. Res. 2010, 9, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noormohammadi, Z.; Hosseini-Mazinani, M.; Trujillo, I.; Rallo, L.; Belaj, A.; Sadeghizadeh, M. Identification and classification of main Iranian olive cultivars using microsatellite markers. HortScience 2007, 42, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rony, C.; Baalbaki, R.; Kalaitzis, P.; Talhouk, S.N. Molecular characterization of Lebanese olive germplasm. Tree Genet. Genomes 2009, 5, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, I.; Salimonti, A.; Kamoun, N.G.; Muzzalupo, I.; Lepais, O.; Gerber, S.; Perri, E.; Rebai, A. Characterization and Identification of Tunisian Olive Tree Varieties by Microsatellite Markers. HortScience 2008, 43, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendri, M.; Trujillo, I.; Trigui, A.; Rodrıguez-Garcıa, M.I.; Ramırez, J.D.A. Simple Sequence Repeat Identification and Endocarp haracterization of Olive Tree Accessions in a Tunisian Germplasm Collection. HortScience 2010, 45, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, S.; Omri, A.; Grati-Kamoun, N.; Paolo Marra, F.; Caruso, T. Molecular characterization and genetic relationships of cultivated Tunisian olive varieties (Olea europaea L.) using SSR markers. J. New Sci. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 40, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Abdessemed, S.; Muzzalupo, I.; Benbouza, H. Assessment genetic diversity among Algerian olive (Olea europaea L) cultivars using SSR marker. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 192, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, R.; Abu-Qaoud, H.; Arafeh, R. Molecular characterization of three common olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars in Palestine, using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakar, E.; Unver, H.; Ercisli, S. Genetic Diversity Among Historical Olive (Olea europaea L.) Genotypes from Southern Anatolia Based on SSR Markers. Biochem Genet. 2016, 54, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, M.; Lain, O.; Caruso, T.; Testolin, R. SSR-based DNA fingerprints reveal the genetic diversity of Sicilian olive (Olea europaea L.) germplasm. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Casas, G.; Scollo, F.; Distefano, G.; Continella, A.; Gentile, A.; La Malfa, S. Molecular characterization of olive (Olea europaea L.) Sicilian cultivars using SSR markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, V.; Montemurro, C.; Sabetta, W.; Pasqualone, A.; Blanco, A. SSR-based identification key of cultivars of Olea europaea L. diffused in Southern-Italy. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 123, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.P.; Caruso, T.; Costa, F.; Di Vaio, C.; Mafrica, R.; Marchese, A. Genetic relationships, structure and parentage simulation among the olive tree (Olea europaea L. subsp. europaea) cultivated in Southern Italy revealed by SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genomes. 2013, 9, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, C.M.; Trujillo, I.; Barrio, E.; Belaj, A.; Barranco, D.; Rallo, L. Centennial olive trees as a reservoir of genetic diversity. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, G.; Loureiro, J.; Lopes, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Santos, C. Genetic characterisation of olive trees from Madeira Archipelago using flow cytometry and microsatellite markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelj, D.; Jakše, J.; Javornik, B. DNA fingerprinting of olive varieties by microsatellite markers. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 40, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelj, D.; Jakše, J.; Javornik, B. Assessment of genetic variability of olive varieties by microsatellite and AFLP markers. Euphytica 2004, 136, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Mariotti, R.; Regni, L.; Nasini, L.; Bufacchi, M.; Pandolfi, S.; Baldoni, L.; Proietti, P. The first molecular identification of an olive collection applying standard simple sequence repeats and novel expressed sequence Tag markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Rienzo, V.; Sion, S.; Taranto, F.; D’Agostino, N.; Montemurro, C.; Fanelli, V.; Sabetta, W.; Boucheffa, S.; Tamendjari, A.; Pasqualone, A.; et al. Genetic flow among olive populations within the Mediterranean basin. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Lopes, J.; Guedes-Pinto, H. Assessing Genetic Diversity in Olea europaea L. Using ISSR and SSR Markers. Plant. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 27, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaj, A.; Cipriani, G.; Testolin, R.; Rallo, L.; Trujillo, I. Characterization and identification of the main Spanish and Italian olive cultivars by simple-sequence repeat markers. HortScience 2004, 39, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, S.; Gil, F.S.; Dıaz, A.; Reale, S.; Busconi, M.; Machado, A.D.; Martın, A.; Fogher, C.; Donini, P.; Lee, D. Standardization of a set of microsatellite markers for use in cultivar identification studies in olive (Olea europaea L.). Sci. Hortic. 2008, 116, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoni, L.; Cultrera, N.G.; Mariotti, R.; Riccioloni, C.; Arcioni, S.; Vendramin, G.G.; Buonamici, A.; Porceddu, A.; Sarri, V.; Ojeda, M.A.; et al. A consensus list of microsatellites markers for olive genotyping. Mol. Breed. 2009, 24, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracci, T.; Busconi, M.; Fogher, C.; Sebastiani, L. Molecular studies in olive (Olea europaea L.): Overview on DNA markers applications and recent advances in genome analysis. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso, M.M.; Simões-Costa, M.C.; Carneiro, L.C.; Guimarães, J.B.; Mateus, C.; Fevereiro, P.; Pinto-Ricardo, C. Olive tree (Olea europaea L.) diversity in traditional small farms of Ficalho, Portugal. Diversity 2018, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Mazinani, M.; Mariotti, R.; Torkzaban, B.; Sheikh-Hassani, M.; Ataei, S.; Cultrera, N.G.; Pandolfi, S.; Baldoni, L. High genetic diversity detected in olives beyond the boundaries of the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, H.; Boulouha, B.; Baaziz, M.; Sikaoui, L.; Gaboun, F.; Udupa, S.M. Morphological and genetic diversity in olive (Olea europaea subsp. europaea L.) clones and varieties. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzalupo, I.; Russo, A.; Chuappetta, A.A.; Benincasa, C.; Perri, E. Evaluation of genetic diversity in Italian olives (Olea europaea L.) cultivars by SSR markers. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormohammadi, Z.; Hosseini-Mazinani, M.; Trujillo, I.; Belaj, A. Study of intracultivar variation among main Iranian olive cultivars using SSR markers. Acta. Biol. Szeged 2009, 53, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lazović, B.; Klepo, T.; Adakalić, M.; Šatović, Z.; Baruca Arbeiter, A.; Hladnik, M.; Strikić, F.; Liber, Z.; Bandelj, D. Intra-varietal variability and genetic relationships among the homonymic East Adriatic olive (Olea europaea L.) varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefc, K.M.; Lopes, M.S.; Mendonça, D.; Rodrigues Dos Santos, M.; Laimer Da Câmara Machado, M.; Da Câmara Machado, A. Identification of microsatellite loci in olive (Olea europaea) and their characterization in Italian and Iberian olive trees. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1171–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Rosa, R.; James, C.; Tobutt, K.R. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite in olive Olea europaea L. and their transferability to other genera in the Oleaceae. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud-Haond, S.; Belkhir, K. Genclone: A computer program to analyse genotypic data, test for clonality and describe spatial clonal organization. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Analysis of Gene Diversity in Subdivided Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 3321–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Sholnick, M.; David, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paetkau, D.; Calvert, W.; Stirling, I.; Strobeck, C. Microsatellite analysis of population structure in Canadian polar bears. Mol. Ecol. 1995, 4, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.W.; Sefc, K.M. Identity 1.0; Centre for Applied Genetics, University of Agricultural Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kloosterman, A.D.; Budowe, B.; Riley, E.L. Population data of the HLA DQα locus in Dutch caucasians. Int. J. Leg. Med. 1993, 105, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowcock, A.M.; Ruiz-Linarez, A.; Tomfhorde, J.; Minch, E.; Kidd, J.R.; Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. High resolution human evolutionary trees with polamorphic microsatellites. Nature 1994, 368, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minch, E.; Ruiz-Linares, A.; Goldstein, D.; Feldman, M.; Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. MICROSAT: A Computer Program for Calculating Various Statistics on Microsatellite Allele Data, Ver.1.5; Stanford University Medical Center: Stanford, CA, USA, 1996; Available online: https://hpgl.stanford.edu/projects/microsat/microsat.html (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Fitch, W.M.; Margoliash, E. Construction of phylogenetic trees: A method based on mutation distances as estimated from cytochrome C sequences is of general applicability. Science 1967, 155, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 1989, 5, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohlf, F.J. Exeter Software NTSYS-Pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System; Applied Biostatistics, Inc. Exeter Software: Setauket, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Dominant markers and null alleles. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, E.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Vigouroux, Y.; Goodman, M.M.; Sanchez, J.G.; Buckler, E.; Doebley, J. A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6080–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiolillo, A.; Reale, S.; Pilla, F.; Baldoni, L. Molecular analysis of olive cultivars in the Molise region of Italy. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, G.; La Mura, M.; Ambrosino, O.; Pugliano, G.; Varricchio, P.; Rao, R. Relationships of Campanian olive cultivars: Comparative analysis of molecular and phenotypic data. Genome 2009, 52, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkett, F.; Simon, J.C.; Balloux, F. Tackling the population genetics of clonal and partially clonal organisms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervishi, A.; Jakše, J.; Ismaili, H.; Javornik, B.; Štajner, N. Comparative assessment of genetic diversity in Albanian olive (Olea europaea L) using SSRs from anonymous and transcribed genomic regions. Tree Genet. Genomes 2018, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strikić, F.; Gugić, J.; Klepo, T. Stanje hrvatskog maslinarstva. Glas. Zaštite Bilja 2012, 12, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).