Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of a Medicinal Plant Launaea sarmentosa to Salinity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Salt Treatment and Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Growth Parameters
2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment Content
2.5. Determination of Relative Water Content, Proline and Total Phenolic Content
2.6. Determination of Ion Content
2.7. Determination of Malondialdehyde and Hydrogen Peroxide Content, and Electrolyte Leakage
2.8. Assays for the Enzymatic Activity of Catalase, Peroxidase, and Superoxide Dismutase
2.9. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
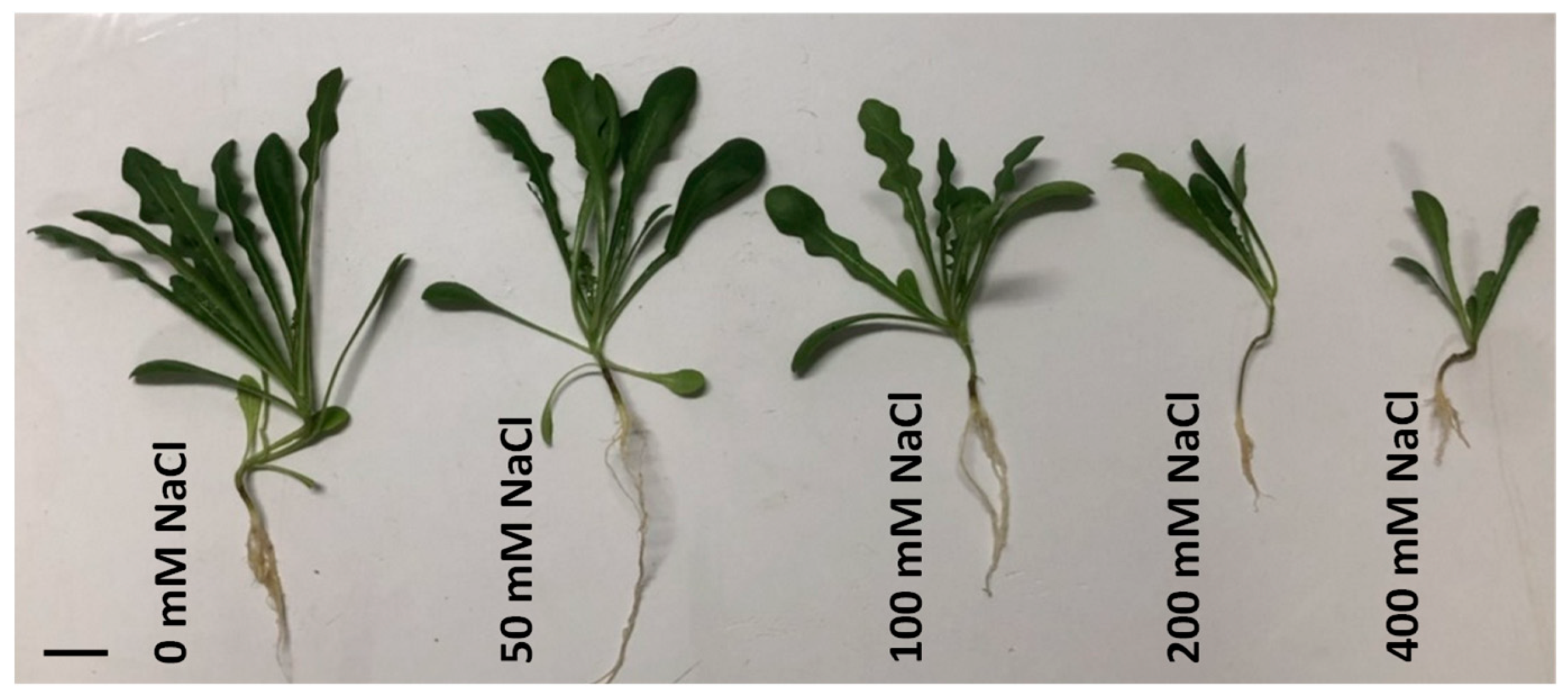
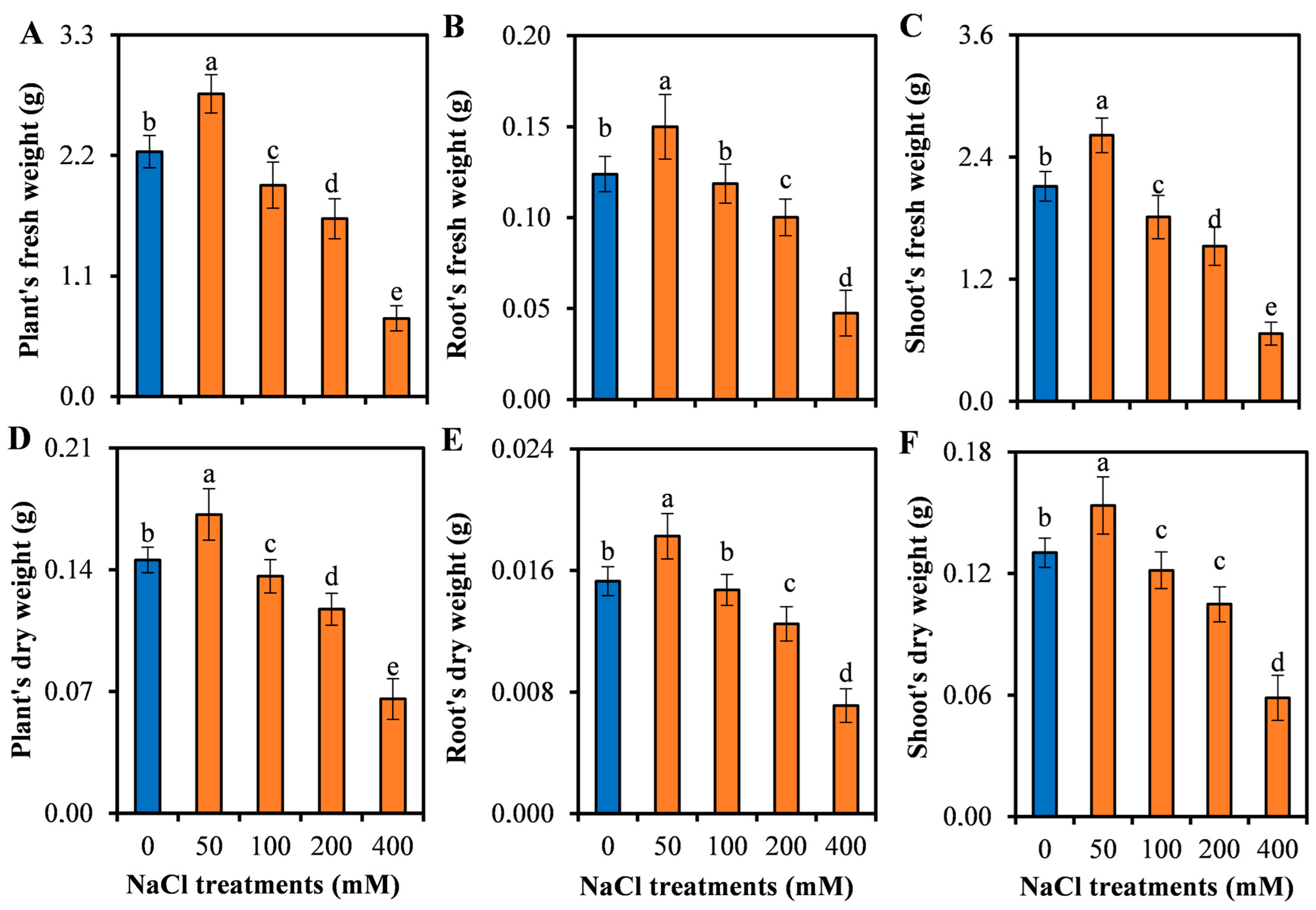
3.1. Growth Responses of L. sarmentosa to Salinity
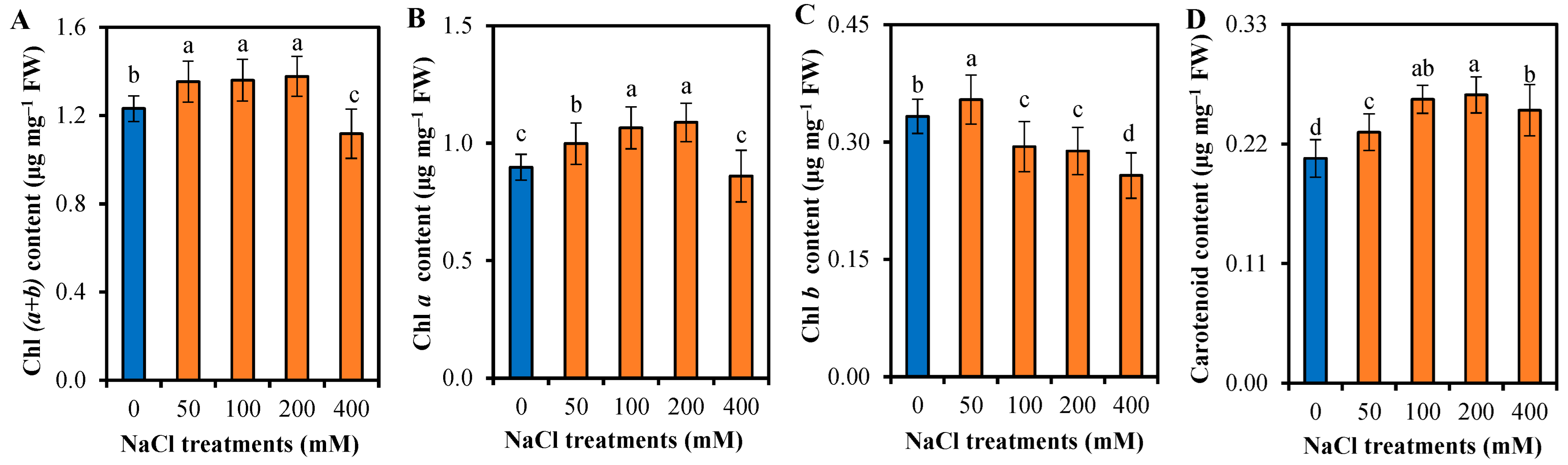
3.2. Photosynthetic Responses of L. sarmentosa to Salinity
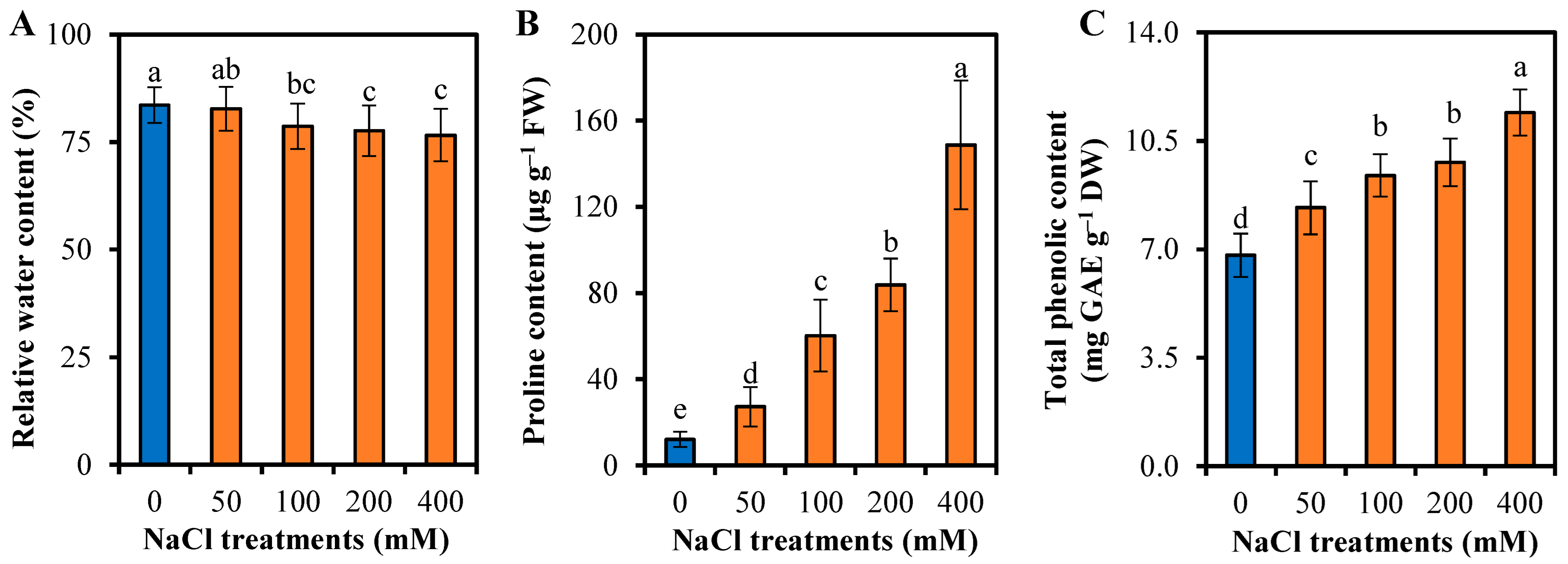
3.3. Reponses to Water Uptake and Osmotic Adjustment of L. sarmentosa to Salinity
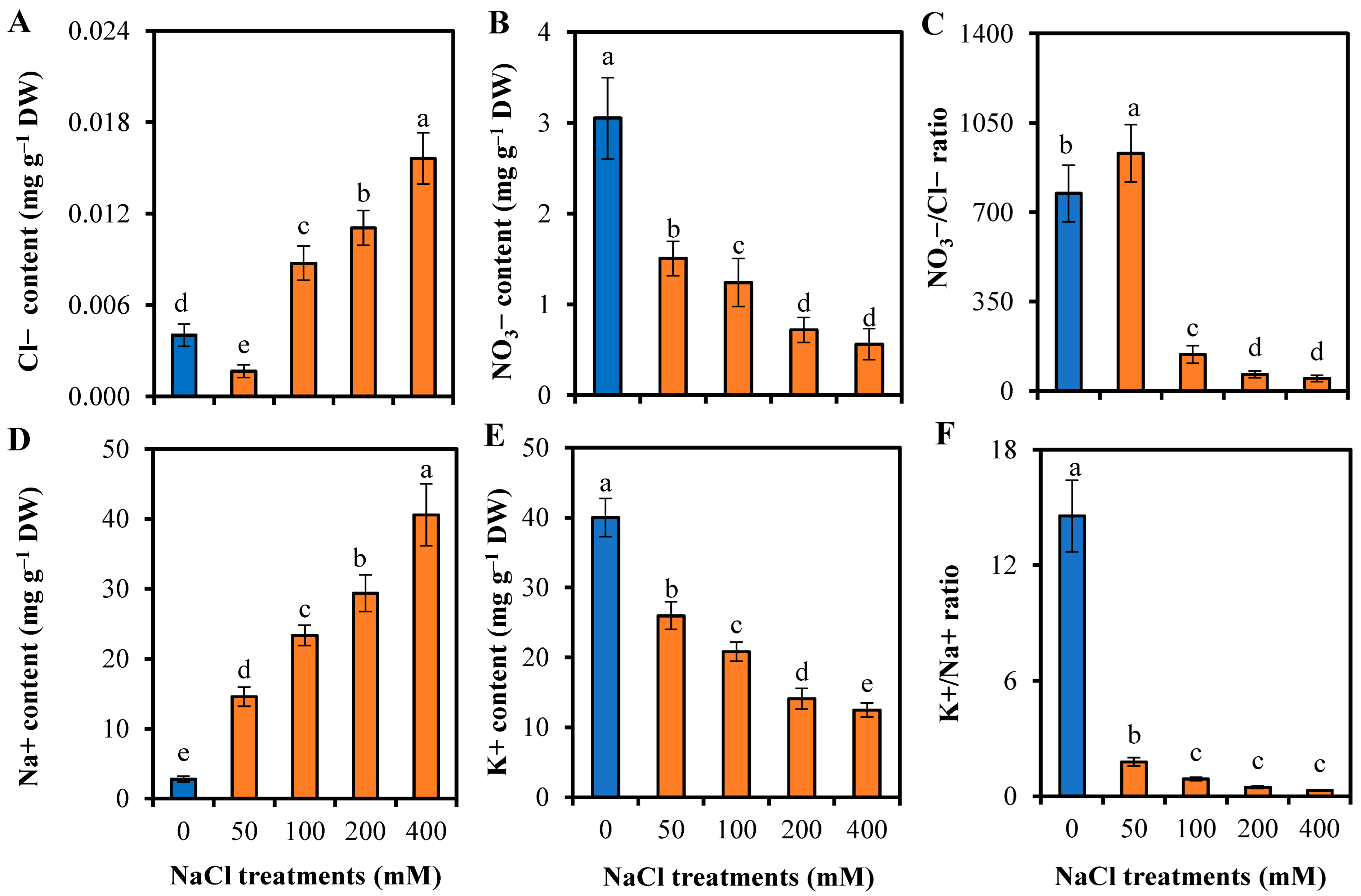
3.4. Responses to Ion Homeostasis of L. sarmentosa to Salinity
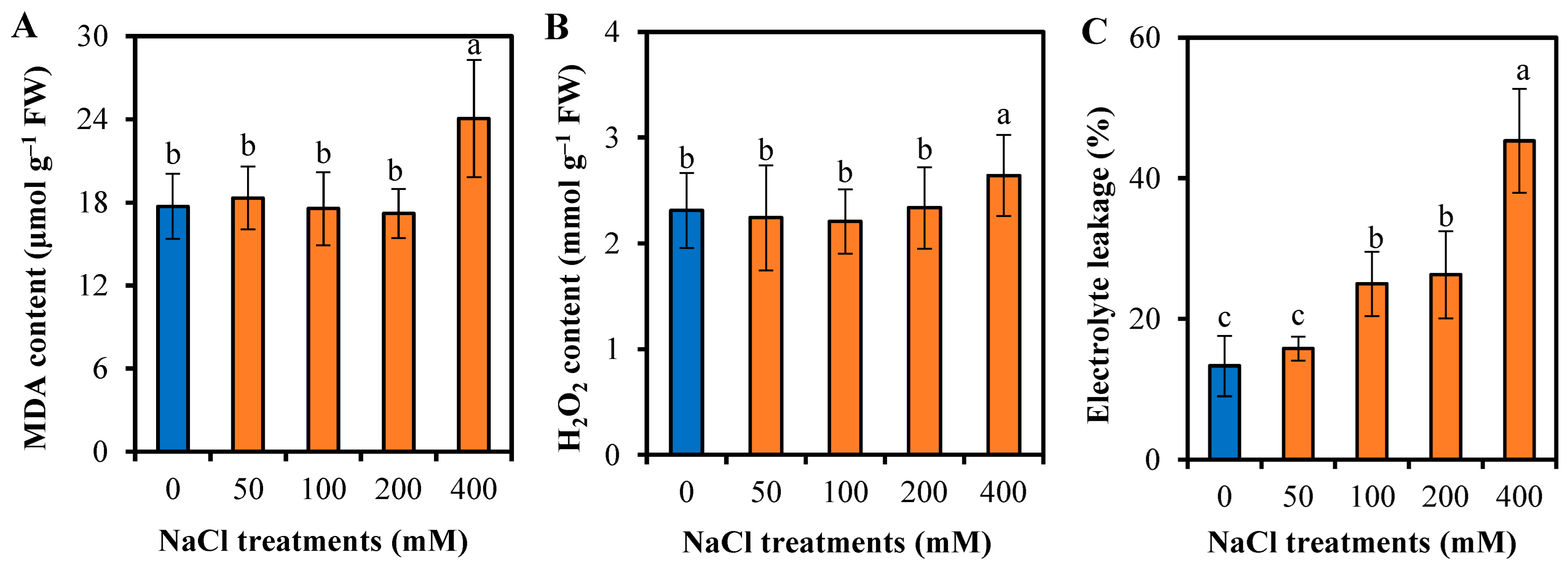
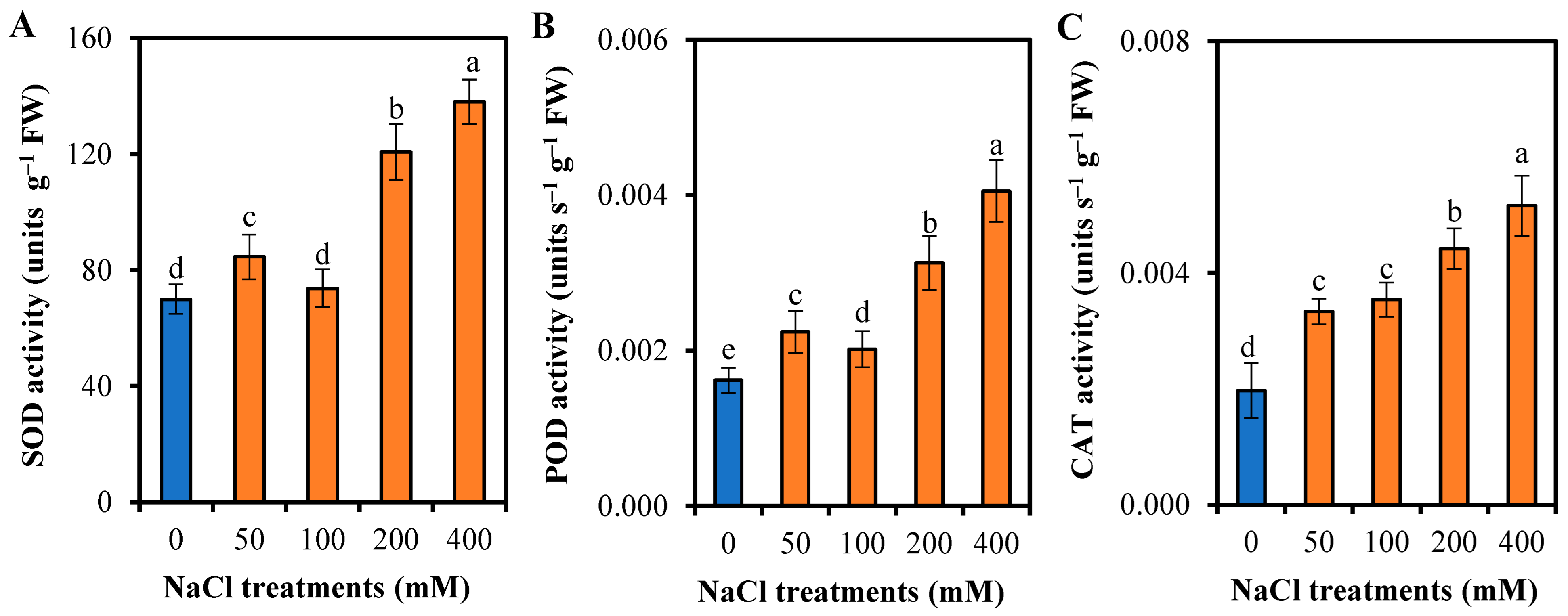
3.5. Responses of L. sarmentosa to Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Activity to Salinity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L.; Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil Salinity: Historical Perspectives and a World Overview of the Problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Zaman, M., Shahid, S.A., Heng, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, T.J.; Munns, R.; Colmer, T.D. Sodium chloride toxicity and the cellular basis of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, H.; Amin, A.; Shafiq, Y.; Ali, A.; Yasin, R.; Shoukat, A.; Hussan, M.U.; Sarwar, M.I. A review: Impact of salinity on plant growth. Nat. Sci. 2019, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hnilickova, H.; Kraus, K.; Vachova, P.; Hnilicka, F. Salinity stress affects photosynthesis, malondialdehyde formation, and proline content in Portulaca oleracea L. Plants 2021, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Ma, X.; Wan, P.; Liu, L. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.Q.; Konishi, A.; Cushman, J.C.; Morokuma, M.; Toyota, M.; Agarie, S. Ion accumulation and expression of ion homeostasis-related genes associated with halophilism, NaCl-promoted growth in a halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Plant Prod. Sci. 2020, 23, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mostofa, M.G.; Keya, S.S.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Ansary, M.M.U.; Das, A.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Tran, L.S.-P. Adaptive mechanisms of halophytes and their potential in improving salinity tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, T.; Shen, G.; Esmaeili, N.; Zhang, H. Plants’ response mechanisms to salinity stress. Plants 2023, 12, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.-K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zelm, E.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beentje, H.J. Flora of Tropical East Africa: Compositae (Part 1), 1st ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, R.J.; Sma-Air, S.; Limsathapornkul, N.; Pranama, N.; Nakkeaw, M.; Kaewnam, P.; Thongchumnum, P.; Kanjanachatree, K. Photosynthetic electron transport rate (ETR) in the littoral herb Launaea sarmentosa known as mole crab in Thailand. Photosynth. Res. 2021, 150, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makwana, H.T.; Pandya, D.J. Launaea pinnatifida Cass. A species of the controversial drug Gojihva: Comprehensive review. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2019, 11, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, S.; Jadhav, R.; Vikhe, S. Phytochemical and pharmacological activities of Launaea sarmentosa: A review. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2022, 14, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gunde, M.C.; Wani, J.S.; Pethe, A.M. Pharmacognostic and phytochemical studies on leaves of Launaea sarmentosa (Willd.) Schultz-Bip. Ex Kuntze. Int. J. Ayurvedic Med. 2022, 13, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Nguyen, T.M.; Nguyen, T.H.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Vu, T.D.; Tran, H.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, M.K.; Do, T.H. Chemical constituents from the aerial parts of Launaea sarmentosa (Asteraceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 110, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Binh, T.D.; Kusunoki, R.; Pham, T.L.; Nguyen, Y.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kanaori, K.; Kamei, K. Effects of Launaea sarmentosa extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via suppression of NF-κB/MAPK signaling and Nrf2 activation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meksuwan, Y.; Sutthinon, P. In vitro propagation and histochemical analysis of Launaea sarmentosa (Willd.) Kuntze. Trends Sci. 2023, 20, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U.; Ekinci, M.; Ors, S.; Turan, M.; Yildiz, S.; Yildirim, E. Effects of individual and combined effects of salinity and drought on physiological, nutritional and biochemical properties of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.; González-Vilar, M. Determination of Relative Water Content. In Handbook of Plant Ecophysiology Techniques; Manuel, J., Reigosa, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.A.; Teare, I. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, R.; Arzani, A.; Mirmohammady, M.S. Polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity involved in salt tolerance in wheat, Aegilops cylindrica and their amphidiploids. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 646221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Amaresan, N.; Sankaranarayanan, A.; Senthilkumar, M.; Amaresan, N.; Sankaranarayanan, A. Estimation of Malondialdehyde (MDA) by Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) Assay. In Plant-Microbe Interactions; Springer Protocols Handbooks; Springer Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; p. 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexieva, V.; Sergiev, I.; Mapelli, S.; Karanov, E. The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junglee, S.; Urban, L.; Sallanon, H.; Lopez-Lauri, F. Optimized assay for hydrogen peroxide determination in plant tissue using potassium iodide. Am. J. Analyt. Chem. 2014, 5, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, Y.; Nallamothu, V.; Balakrishnan, D.; Ramesh, P.; Desiraju, S.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Voleti, S.R.; Neelamraju, S. Increased catalase activity and maintenance of photosystem II distinguishes high-yield mutants from low-yield mutants of rice var. Nagina22 under low-phosphorus stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhindsa, R.S.; Plumb-Dhindsa, P.; Thorpe, T.A. Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.O.; Irfan, M.; Muhammad, A.; Ullah, I.; Nawaz, S.; Khalil, M.K.; Ahmad, M. A practical and economical strategy to mitigate salinity stress through seed priming. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 991977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Lata, C.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Sheoran, P. Halophytes as new model plant species for salt tolerance strategies. Front. Plant Sci 2023, 14, 1137211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kuroda, C.; Fujiyama, H. Function of sodium and potassium in growth of sodium-loving Amaranthaceae species. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsouna, A.B.; Ghneim-Herrera, T.; Romdhane, W.B.; Dabbous, A.; Saad, R.B.; Brini, F.; Abdelly, C.; Hamed, K.B. Early effects of salt stress on the physiological and oxidative status of the halophyte Lobularia maritima. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 47, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.K.; Bhandari, S.R.; Jo, J.S.; Song, J.W.; Cho, M.C.; Yang, E.Y.; Lee, J.G. Response to salt stress in lettuce: Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activities. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Hussain, T.; Aziz, I.; Ahmad, N.; Gul, B.; Nielsen, B.L. Effects of salinity stress on chloroplast structure and function. Cells 2021, 10, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddiq, M.S.; Iqbal, S.; Hafeez, M.B.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Raza, A.; Fatima, E.M.; Baloch, H.; Jahanzaib, W.P.; Ciarmiello, L.F. Effect of salinity stress on physiological changes in winter and spring wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïbi, K.; Taïbi, F.; Abderrahim, L.A.; Ennajah, A.; Belkhodja, M.; Mulet, J.M. Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 105, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffouo, V.D.; Nouck, A.E.; Nyemene, K.P.; Tonfack, B.; Meguekam, T.L.; Youmbi, E. Effects of salt stress on plant growth, nutrient partitioning, chlorophyll content, leaf relative water content, accumulation of osmolytes and antioxidant compounds in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) cultivars. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2017, 45, 481–490. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Wang, G.; Si, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jia, J. Effects of salt stress on photosynthetic pigments and activity of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Kalidium foliatum. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 65, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioli, S.; Koutalianou, M.; Gkafas, G.A.; Exadactylos, A.; Papathanasiou, V.; Katsaros, C.I.; Orfanidis, S.; Küpper, F.C. Responses of the Mediterranean seagrass Cymodocea nodosa to combined temperature and salinity stress at the ionomic, transcriptomic, ultrastructural and photosynthetic levels. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 175, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsai, O.; Hassan, M.A.; Negrușier, C.; Raigón, M.D.; Boscaiu, M.; Sestraș, R.E.; Vicente, O. Responses to salt stress in Portulaca: Insight into its tolerance mechanisms. Plants 2020, 9, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Nath, J.; Singh, A.K.; Pareek, A.; Joshi, R. Ion transporters and their regulatory signal transduction mechanisms for salinity tolerance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, E.; Razmjoo, J.; Zahedi, M. Effect of salt stress on growth and ion accumulation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, V.I.; Jacobsen, S.-E.; Shabala, S. Salt tolerance mechanisms in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. The response of salinity stress-induced A. tricolor to growth, anatomy, physiology, non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 559876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, K.; Al-Osaimi, A.A.; Alghamdi, B.A. Sodium chloride (NaCl)-induced physiological alteration and oxidative stress generation in Pisum sativum (L.): A toxicity assessment. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20819–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidchik, V.; Straltsova, D.; Medvedev, S.S.; Pozhvanov, G.A.; Sokolik, A.; Yurin, V. Stress-induced electrolyte leakage: The role of K+-permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, D.Q.; Pham, A.C.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Vo, T.C.; Vu, H.D.; Ho, G.T.; Mohsin, S.M. Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of a Medicinal Plant Launaea sarmentosa to Salinity. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040388
Tran DQ, Pham AC, Nguyen TTT, Vo TC, Vu HD, Ho GT, Mohsin SM. Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of a Medicinal Plant Launaea sarmentosa to Salinity. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(4):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040388
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Dan Quang, Anh Cong Pham, Trinh Thi Thanh Nguyen, Tuan Chau Vo, Hoang Duc Vu, Giap Ta Ho, and Sayed Mohammad Mohsin. 2024. "Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of a Medicinal Plant Launaea sarmentosa to Salinity" Horticulturae 10, no. 4: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040388
APA StyleTran, D. Q., Pham, A. C., Nguyen, T. T. T., Vo, T. C., Vu, H. D., Ho, G. T., & Mohsin, S. M. (2024). Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses of a Medicinal Plant Launaea sarmentosa to Salinity. Horticulturae, 10(4), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040388





