Abstract
The application of beneficial microbial consortium can effectively improve plant disease resistance and its growth. Various fungi were compounded with Bacillus velezensis LJ02 and applied to watermelon plants in this paper. The results showed that the microbial consortium T2 (compounded Bacillus velezensis LJ02 with Aspergillus aculeatus 9) can effectively control gummy stem blight and powdery mildew in watermelon, while the control effect reached 83.56% and 70.93%, respectively (p < 0.05). Compound treatment improved the diversity and richness of the rhizosphere microbial community structure, and the relative abundance of Caulobacterales and Xanthomonadaceae significantly increased after applying T2 to the soil. Meanwhile, the internode length was significantly decreased 28% (p < 0.05), and the maximum leaf length increased 10.33% (p < 0.05). In addition, the microbial consortium delays the maturity of watermelon vegetables. By studying the effects of microbial consortium on watermelon seedlings, our study provides a theoretical basis for the popularization and application of the compound inoculant.
1. Introduction
Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. and Nakai), is one of the most important vegetables in the world, and its planting area has been expanded in recent years [1]. Gummy stem blight, a soil-borne fungal disease caused by Didymella bryoniae (Fuckel) Rehm, occurs during the whole growth and development of watermelon [2]. Gummy stem blight causes the stems and leaves of plants to wilt rapidly in humid environments, and then many vines die. Afterwards, there are visible damages to the vegetables, with surface tissue shriveling, which seriously affects its yield and quality [3,4]. Powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii), on the other hand, mainly affects the leaves, forming a white powdery layer on the foliage that interferes with photosynthesis, and if not treated in time, it develops rapidly and spreads to the vines of the melon, which severely reduce the yield and quality of the watermelon [5,6]. Watermelon plants are frequently affected by powdery mildew at all stages of development throughout the growing season, which leads to necrotic lesions on the leaves and reduces the net photosynthetic rate, resulting in impaired plant growth and a decrease in vegetable quality and total yield [7].
At present, chemical control can effectively control a variety of diseases. Because of the single site action of chemical agents, chemical control could result in different degrees of pathogen resistance to bactericide, and inevitably cause environmental pollution [8]. Compared with chemical control, biological control has the capability to suppress the growth of various pathogens through their own production of bacteriostatic substances to control plant diseases [9,10]. Furthermore, biological control is safe, environmentally friendly, and the pathogens are not prone to drug resistance, so it is gradually applied to agricultural production [11]. Bacillus velezensis LJ02 fermentation solution can effectively reduce the occurrence of powdery mildew [12,13,14]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 231-1 was able to effectively control gummy stem blight in watermelon through antimicrobial activity [15]. Traditional chemical bactericide and biological bactericide (Bacillus subtilis) was applied at the early stages of plant development, respectively, and the result revealed that Bacillus subtilis had a better preventive effect against powdery mildew of cucumber in the greenhouse [16]. Several fungi with biocontrol functions have also been used in agriculture. An amount of 350 endophytic fungi were isolated from asymptomatic watermelons, and it was found that two species of mycorrhizal fungi had a 93% inhibition rate against the pathogen in the double-culture test. Subsequently, they also had a preventive effect against the pathogen on watermelon [17]. Trichoderma asperelloides PSU-P1 was effective in controlling creeping blight and reduced severe diseases at the seedling stage [18]. Fermentation products of the endophytic fungus Aspergillus aculeatus GC-09, isolated from citrus, showed bacteriostatic activity against Penicillium italicum [19]. Aspergillus fumigatus is able to inhibit Pythium aphanidermatum oospores production, which leads to abnormal growth and consequently inhibits the occurrence of diseases [20].
Different beneficial microorganisms were compounded to form a beneficial microbiome through synergistic action, which in turn effectively controlled soil-borne diseases [21]. Furthermore, some studies have shown that the combined application of multiple biocontrol strains to control soil-borne diseases is widely used in modern agricultural production [22]. A typical example is provided by the combination of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus thuringiensis, which significantly increased the synthesis of defense enzymes in Cucurbitaceae and effectively prevented powdery mildew [23]. Combined application of Trichoderma harzianum Tr6 and Pseudomonas sp. Ps14 to cucumber plants enhances induced resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis cucumerinum by activating different signaling pathways [24]. Fermentation broth from the co-culture of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Trichoderma longibrachiatum showed a high inhibitory effect on a variety of pathogenic bacteria [25].
Watermelons are highly susceptible to gummy stem blight and powdery mildew. Infected watermelon seedlings exhibit significant decreases in their yield, quantity, and overall quality [4]. At present, there is limited progress in applying a microbial consortium for the control of these two diseases on watermelons [26]. Therefore, in this study, we used watermelon plants as research materials and investigated the effects of Bacillus velezensis LJ02 compounded with different fungi (Aspergillus aculeatus 9 and Aspergillus fumigatus F14) on the growth of watermelon, the control effect of gummy stem blight and powdery mildew, and we also analyzed the microbiome of the rhizosphere soil after different treatments. Overall, we analyzed the control effects of the microbial consortium on watermelon plants and provided a novel theoretical guidance for disease control.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
Bacillus velezensis LJ02, Aspergillus aculeatus 9 and Aspergillus fumigatus F14 were supplied by the Laboratory of Plant-Beneficial Microorganism Interaction, Tianjin Agricultural College. LJ02 was fermented at 200 r/min, 30 °C, and 168 h. Fungi were cultured with PDB medium and then fermented at 200 r/min, 32 °C, and 168 h.
The watermelon cultivar ‘Miduo’ was used in all experiments. The watermelon plants were cultivated in a greenhouse under controlled conditions, maintaining a temperature of 28 ± 2 °C, a humidity of 75% and a photoperiod of 16 h of light per day in Taitou Town, Jinghai District, Tianjin, China.
2.2. Experimental Design
In this experiment, the different bacterial suspensions were mixed uniformly, and 5 kg of wheat bran was added for mixing. Wheat bran is an inexpensive agricultural byproduct waste that is rich in proteins, carbs, minerals, and vitamins. At high-temperature, fungi decompose crop straw, turning it into nutrients for plants. This process also creates helpful microorganisms, boosting crop growth and quality [27], and is then applied to the colonization hole for planting, watering, and mulching. The microbial consortiums were applied after the seed had been sown. The combination methods and dosage are shown in Table 1. According to the random block design, the experiment was set up with 20 plots, 5 replications. Each plot has 15 plants, and the size of each plot was 11.52 m2. The cultivation method employed for the plots involved hanging vine cultivation, with double vine pruning. The subsequent management practices remained consistent with the field level.

Table 1.
The combination method and dosage of different bacterial suspensions.
2.3. Disease Survey
The five-point sampling method was used to investigate the control effect of gummy stem blight and powdery mildew on watermelon, which was calculated with reference to Ma’s method [28]. An experiment was conducted by randomly selecting seedlings within in the specified area. At each of these points, ten plants are chosen, and from each of these selected leaves, five upper-middle leaves are selected for disease statistics. The severity of wilt symptoms on watermelon plants was assessed and recorded based on the following scale: 0 indicated no symptoms, 1 indicated up to 25% wilt, 2 indicated wilt between 25% and 50%, 3 indicated wilt between 50% and 75%, and 4 indicated wilt between 75% and 100% of the foliage.
On the other hand, leaves were inoculated with fresh suspensions Podosphaera xanthii. The presence of powdery mildew was assessed through a visual examination that determined the extent of powdery mildew coverage on the leaves. This evaluation was carried out using a scale ranging from 0 to 11, where each value represented a specific range of leaf area affected by the disease. The scale was as follows: 0 indicated the absence of any symptoms, 1 represented a powdery mildew coverage of 0% to 5%, 3 indicated 5% to 15% coverage, 5 represented 15% to 25%, 7 indicated 25% to 50%, 9 represented 50% to 75%, and 11 indicated 75% to 100% coverage.
2.4. Growth Index
Ten watermelon plants were randomly selected for further experimentation, with the same number of measurements for the same agronomic traits. Biological traits such as stem length, stem diameter, internode length, maximum leaf length, and maximum leaf width were measured during the growth and development period of watermelon. Fruit quality, soluble sugar content and maturity were measured when the vegetables were ripe for picking [29].
The soluble sugar was estimated by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid reagent method [30]. To measure the soluble sugar content, 1 g of watermelon fruit was taken and ground with 3 milliliters of buffer. The resulting mixture was then transferred to a 10 milliliter centrifuge tube and centrifuged at a speed of 4000 revolutions per minute for a duration of 10 min. Following centrifugation, 1.5 milliliters of the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid reagent was added to 1 milliliter of the supernatant. The mixture was then subjected to a water bath for 5 min, and, after cooling, 16.5 milliliters of distilled water were added and thoroughly mixed. Thoroughly mix the solution and proceed to determine the OD520 using a spectrometer.
2.5. Rhizosphere Soil Metagenome Analysis
2.5.1. Sample Collection
The plants were randomly selected by a five-point random sampling method 30 days after the application. After removing the surface soil, the whole plant was uprooted; afterwards, the soil within two mm of the fibrous roots was collected by shaking off large pieces of soil from the roots. It was quickly stored in a refrigerator at −80 °C for backup and sent to the company for sequencing analysis [31].
2.5.2. Extraction of DNA from Rhizosphere Soil
An amount of 3.0 g of well-mixed rhizosphere soil was ground with liquid nitrogen. Rhizosphere microbial DNA was extracted using the Soil Microbial DNA Extraction Kit and stored at 4 °C. The quality of DNA was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. Genomic DNA from successful quality testing was used as a template for PCR amplification of the V3-V4 variable region of bacterial 16S rRNA using the universal primer 515F/806R. Afterwards, the products were purified, quantified and homogenized to construct a library [32].
2.5.3. Metagenomic Data Analysis and Processing
After the database was constructed, Qubit 2.0 was used for preliminary quantification. This was then followed by detection of the database using Agilent, and the database was sequenced by Illumina HiSeq 2500 after passing the quality control. The reads of each sample were first spliced using overlap to obtain the raw data, followed by filtering of the data. Finally, using UCHIME 4.1 software, the chimeric sequences were identified and removed to obtain the final valid data [33].
Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered, annotated for species classification, and Venn diagrams were drawn to analyze the number of common and unique OTUs between treatments using Vsearch 2.8.1 software [34]. Information on the top 30 species abundant at different taxonomic levels was labeled. LEfSe reveals the composition of different species in the biomes of different treatment groups [35].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Bar graphs were drawn using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA), statistically analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0 package (IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA), and images were typeset using Adobe Photoshop CS5 (Adobe Systems Inc, San Jose, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Treatments on the Growth of Watermelon Seedlings
After application of the microbial consortium, the length of the watermelon stem under different treatments increased to different degrees compared with the CK. The length of watermelon stem reached 2.3 m after T3 treatment, but the difference in stem length among other treatments was not significant (Figure 1a). There was no significant difference among the treatments regarding stem diameter (Figure 1b). Compared with CK, the internode length was significantly decreased after T1 and T2 treatment (p < 0.05) (Figure 1c).
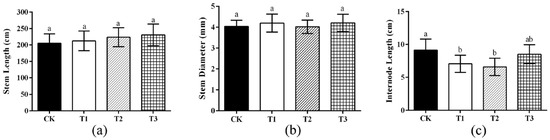
Figure 1.
Effects of different treatments on watermelon plants. (a) The steam length of watermelon. (b) The stem diameter of watermelon. Measurement of the diameter of the fourth stem section from the terminal bud toward the root. (c) The internode length of watermelon. The internode spacing was measured as the stem length of the fourth stem node from the terminal bud toward the root. Note: all analysis based on one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple tests, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; the columns with different letters indicate significant differences.
As can be seen in Figure 2, the maximum leaf length and maximum leaf width of watermelon after T3 treatment were the highest, reaching 16.86 cm and 14.33 cm, respectively, and the differences were significant compared with that of the CK (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the maximum leaf length and maximum leaf width of watermelon between CK and T1 treatment. T2 could promote the maximum leaf length, while there was no significant effect on the width of leaf size (p < 0.05).
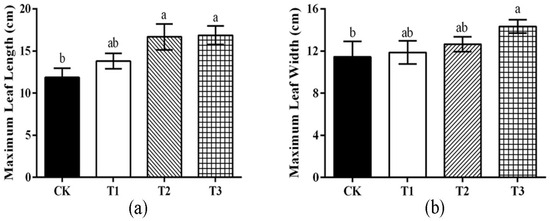
Figure 2.
Effects of different treatments on watermelon leaves. (a) The maximum leaf length of watermelon. Measured leaf length directly from leaf base to leaf tip, excluding petiole, using vernier caliper. (b) The maximum leaf width of watermelon. Measured leaf length at the widest point on the leaf blade perpendicular to the main vein directly with a vernier caliper. Note: all analysis based on one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple tests, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; the columns with different letters indicate significant differences.
3.2. Effect of Different Treatments on the Quality of Watermelon Fruits
Fruits quality, maturity and soluble sugar content were measured. We found that the fruit weight of watermelon after T1 treatment was significantly lower than that of the control group (p < 0.05) (Figure 3a). Similarly, watermelon ripeness after T1 treatment was significantly lower than that of the control group (p < 0.05), and there was no significant difference in maturity after T2 and T3 treatments (Figure 3b,d). Each group displayed different degrees of delayed ripening compared to the CK. Compared with CK, the soluble sugar content of watermelon fruit after different treatments was significantly reduced, and the soluble sugar content was decreased 21.9% after T2 treatment (Figure 3c).
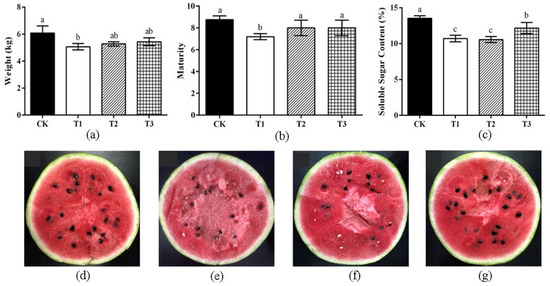
Figure 3.
Effects of different treatments on watermelon fruits. (a) The weight of watermelon. Fruits are weighed when they reach harvest time. (b) The maturity of watermelon. (c) The soluble sugar content of watermelon. Watermelon internal fruits from different treatments; control treatment (CK) (d), T1 treatment (e), T2 treatment (f), T3 treatment (g). Note: all analysis based on one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple tests, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; the columns with different letters indicate significant differences.
3.3. Effect of Different Treatments on Watermelon Gummy Stem Blight and Powdery Mildew
Microbial consortiums with different compounding methods were applied to the field (Table 1). The results showed that T2 had the best control effect among several treatments, and the control effect of gummy stem blight and powdery mildew reached 83.56% and 70.93%, respectively. Followed by T3, the control effect of gummy stem blight and powdery mildew was 79.44% and 68.40%, respectively. T1 also had a certain control effect against gummy stem blight and powdery mildew (Figure 4).
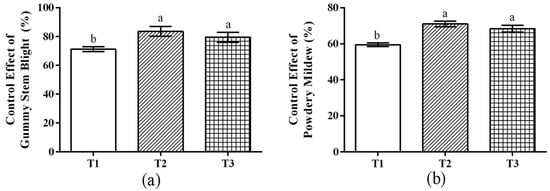
Figure 4.
Effect of different treatments on watermelon disease control. (a) Control effect of gummy stem blight. (b) Control effect of powdery mildew. Note: all analysis based on one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple tests, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; the columns with different letters indicate significant differences.
3.4. Effect of Different Treatments on Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms in the Watermelon
3.4.1. Microbial Community Structure
Venn diagram analysis showed that there were 36,462 OTUs and 214 unique OUTs in the CK, 36,164 OTUs and 220 unique OUTs in the T1 treatment, 36,159 OTUs and 156 unique OUTs in the T2 treatment, with 36,543 OTUs and 227 unique OUTs in the T3 treatment, which collectively possessed 32,891 OTUs across the four treatments (Figure 5a).

Figure 5.
Metagenomic analysis of rhizosphere microorganisms. (a) Venn diagram of the quantity of OTUs in bacteria from soils treated with different treatments. (b) The highest 30 phylum microbial abundance among samples from different treatments. (c) The highest 30 genius microbial abundance among samples from different treatments. Note: In (a), the numbers in the figure represent the number of OTUs in the different treatments. In (b,c), the columns in the picture represent each treatment, and the different colors represent different species.
Alpha diversity, including a Shannon index, Simpson index and Chao1 index, can reflect microbial community diversity and richness. The richness and community structure diversity of all treatments were analyzed (Table 2). Microbial community richness and diversity increased after different treatment compared with the CK. There was no significant difference in alpha diversity between treatments.

Table 2.
Soil microbial alpha diversity in watermelon rhizosphere.
The changes of microbial community composition in watermelon rhizosphere soil were analyzed by using the top 30 abundant phylum in different treatments (Figure 5b). Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Gemmatimonadetes, Planctomycetes, Chloroflexi, Candidatus_Rokubacteria, Actinobacteria, and Verrucomiccrobia were the nine most abundant phylum in the all samples. After application of the microbial consortium, the abundance of Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Verrucomiccrobia increased, and the abundance of Gemmatimonadetes, Chloroflexi, and Candidatus_Rokubacteria decreased. The abundance of Acidobacteria and Bacteroidetes increased after T1 treatment, while their abundance decreased after the T3 treatment; conversely, the abundance of Planctomycetes increased after the T3 treatment, while their abundance decreased after the T1 and T2 treatment.
The histograms of community structure of the top 30 most abundant sequences at the genius classification level in the different treatment groups are shown in Figure 5c. Compared with the CK, the abundance of Pseudomonas, Sphingomonas, Flavobacterium, Achromobacter, and Acidovorax increased after treatment, while the abundance of Steroidobacter, Lysobacter, Nitrospira, Pseudoxanthomonas, Algoriphagus, Arenimonas, and Nitrososphaera decreased.
3.4.2. LEfSe Analysis
To future illustrate the difference between various treatments, linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis was used to explore the contribution of different species to the difference. The results of the contribution analysis are shown in Figure 6 (LDA scores > 3.5). The CK contained eight abundant branches: Chitinophagia (class), Micromonosporales (order), Micromonosporaceae (family), Pseudomonadaceae (family), Pseudomonadales (order), Alphaproteobacteria (class), Actinobacteria (class), Actinobacteria (phylum). The T1 group contained nine abundant branches: Firmicutes (phylum), Moraxellaceae (family), Sphingomonadaceae (family), Sphingomonadales (order), Flavobacteriaceae (family), Flavobacteriia (class), Flavobacteriales (order), Bacteroidetes (phylum), Gammaproteobacteria (class). The T2 group contained five abundant branches: Caulobacterales (order), Caulobacteraceae (family), Xanthomonadaceae (family), Xanthomonadales (order), Enterobacterales (order). The T3 group contained four abundant branches: Proteobacteria (phylum), Betaproteobacteria (class), Deltaproteobacteria (class), Myxococcales (order).
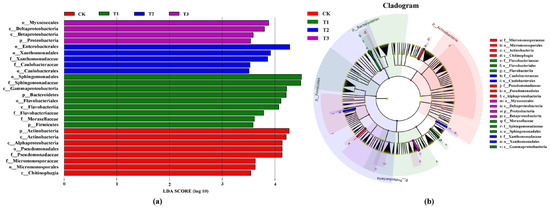
Figure 6.
LEfSe analysis in rhizosphere soil under different treatments. (a) Histogram of LDA value distribution. (b) Branch diagram annotation for different treatments. Note: different color bars represent species with higher abundance in different treatments.
4. Discussion
Stem diameter and stem length are the most important indicators that can directly reflect the vegetable growth status. In this study, T3 treatment increased the maximum leaf length and maximum leaf width of watermelon (p < 0.05) (Figure 2), while T2 treatment had the shortest internode length (Figure 1c). Consistent with the results of previous studies, shortening the distance between plants lead to a higher productivity in crops [36], and the application of compound microorganisms can effectively promote fruit quality [37]. In addition, watermelon fruits’ weight and maturity after T1 treatment were significantly lower than that of CK (p < 0.05) (Figure 3). We speculated that T1 treatment can delay the maturity of watermelon, so that the plant accumulates more organic matter and sugar during the reproductive growth process.
Many studies have shown that the application of biocontrol strain combinations can dramatically improve the ability to prevent disease [38,39]. Preliminary research found that Bacillus velezensis LJ02 reduces the occurrence of powdery mildew [12]. Bacillus mixed or compound with other biocontrol bacteria has a better disease control effect than a single strain [40]. The combined application of microbial agents with different mechanisms of action, different growth conditions and different ecological adaptability has stronger defense, coordination inhibition, and improve the disease prevention and stability [41]. Field tests showed that the application of single bacterial fertilizer of Bacillus velezensis LJ02 (T1 treatment) and microbial consortium T2 and T3 were effective in the control of gummy stem blight and powdery mildew in watermelon. The microbial consortiums were more effective than the T1 treatment in controlling these two diseases of watermelon (Figure 4). This result ties well with previous studies, which utilized a combination of biocontrol bacteria for the control of watermelon wilt [42]. Overall, the control effect of the combination treatment was better than that of the single treatment, and the control effect was higher than that of chemical pesticide control.
The rhizosphere is a diverse microbial ecosystem, many elements of which promote plant growth by inhibiting pathogen invasion and helping plants to extract nutrients from the soil [43,44]. In this experiment, different treatments could increase the species and abundance of soil microorganisms to various degrees (Figure 5). After treatment, the Shannon index of watermelon rhizosphere soil was higher than that of CK, which may be due to the large number of microorganisms in the treatment group, which could easily form a dominant bacterial community in the soil. The Simpson index of all treatments was higher than that of the CK, indicating that microbial agents significantly improved the abundance and diversity of microorganisms in soil (Table 2). Although it is not always beneficial to increase the microbial community in a soil infected with pathogens, the majority believed that soils with higher species diversity not only improve disease resistance but also increase productivity [45,46,47,48,49,50]. Based on this, different biocontrol bacteria were combined to achieve complementary advantages and enhance the biological control characteristics of pathogenic bacteria.
Former studies have demonstrated that soil microbes are critical components of soil, and the investigation into the diversity of microorganisms in soil has significantly contributed to the sustainable utilization of soil [51]. The dominating microorganisms that primarily responded to T1 treatment were the Firmicutes, Moraxellaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Flavobacteriia, Flavobacteriales, Bacteroidetes, Gammaproteobacteria, Pseudomonadaceae, Pseudomonadales. To suppress pathogen attacks, plants can recruit protective microorganisms in the rhizosphere as a supplement to the plant’s innate immune system [52]. It has been reported that Sphingomonas have a variety of functions, including the potential to improve plant growth under environmental stress, as well as to produce plant growth hormones [53]. The abundance of Sphingomonas after treatments was higher than that of CK. Furthermore, after T1 treatment, the maximum leaf width and leaf length of watermelon were significantly higher than those of the CK (Figure 2). A mixture of Sphingobacter A1 and Bacillus tequilensis C-9 can significantly improve the vegetable quality of field-processed tomatoes [54]. Sphingomonas has been reported to be able to efficiently release soluble phosphate from phosphate rock, which is beneficial to soil phosphorus solubility [55]. In addition, Sphingomonas can degrade harmful compounds, adapt to nutrient-poor environments by using special metabolic regulatory mechanisms, and resist many adverse environmental changes by adjusting its own growth [56].
The effect of T2 in preventing the disease was better (Figure 4), but its microbial abundance and species were lower than the CK and other treatments (Table 2). T2 only significantly increased the relative abundance of Xanthomonadaceae and Caulobacterales in the soil (Figure 6). Studies have shown that Caulobacterales was associated with the metabolism of cellulose, and the cellulose nanocomplex exhibits obvious disease resistance to plants [57,58]. We hypothesize that this might be due to the beneficial microorganisms in this treatment, which may have degraded harmful compounds while reducing the abundance of harmful organisms. The main microorganisms that responded to T3 were the Proteobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, Myxococcales, Deltaproteobacteria. The abundance of Proteobacteria in the soil was the highest, and the abundance of Proteobacteria increased after T3 treatment (Figure 5b). Proteobacteria feature a strong metabolism, degradation ability and good adaptability [59]. It also has been found to ameliorate heavy metal contaminated soils [60].
5. Conclusions
In this study, the application of microbial consortium in production and disease prevention and control were preliminarily discussed. The effects of compound microbial agents on soil biodiversity around the rhizosphere of watermelon were then studied through metagenomic analysis. In view of this, we found that the application of microbial consortium could transform the diversity of soil rhizosphere microbial community structure and effectively control the occurrence of disease. The combination of Bacillus velezensis LJ02 and Aspergillus aculeatus 9 had the best disease resistance effect, indicating potential application value for the development of green microbial preparations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and Y.Y.; methodology, W.Y.; software, T.W.; validation, W.Y. and T.W.; formal analysis, R.C.; investigation, R.C.; resources, Y.W.; data curation, T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Y. and T.W.; writing—review and editing, W.Y., T.W. and Y.Y.; visualization, Y.Y.; supervision, Y.W. and Y.Y.; project administration, Y.W.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific Project of Tianjin Municipal Education Commission (2023KJ002).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO. FAO Statistical Databases FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Han, J.; Dong, S.; Shi, Y.; Miao, H.; Liu, X.; Beckles, D.M.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of gummy stem blight resistance in cucumber stem. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3117–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, C.; Mao, C.; Zhang, C. Detection and characterization of difenoconazole resistance in Stagonosporopsis citrulli from watermelon and muskmelon in Zhejiang Province of China. Phytopathol. Res. 2023, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seblani, R.; Keinath, A.P.; Munkvold, G. Gummy stem blight: One disease, three pathogens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, M.K.; Suren, H.; Kousik, C. Elucidation of resistance signaling and identification of powdery mildew resistant mapping loci (ClaPMR2) during watermelon-Podosphaera xanthii interaction using RNA-Seq and whole-genome resequencing approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, A.G.; Taneja, J.; Yee, K.; Shi, X.; Haridas, S.; LaButti, K.; Singan, V.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Wildermuth, M.C. Spray-induced gene silencing to identify powdery mildew gene targets and processes for powdery mildew control. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 1168–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, P.K.; Virginia, B.D. Controlling powdery mildew on cucurbit rootstock seedlings in the greenhouse with fungicides and biofungicides. Crop Prot. 2012, 42, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.L.; Parker, J.E.; Warrilow, A.G.S.; Kelly, D.E.; Kelly, S.L. Azole fungicides—Understanding resistance mechanisms in agricultural fungal pathogens. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Tao, C.; Jousset, A.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; et al. Trophic interactions between predatory protists and pathogen-suppressive bacteria impact plant health. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, B.; Paul, E.; Gerardina, U. Defense-related gene expression in response to the application of biological control agents in banana. Biol. Control 2023, 186, 105317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlali, R.; Ezrari, S.; Radouane, N.; Kenfaoui, J.; Esmaeel, Q.; Hamss, H.E.; Belabess, Z.; Barka, E.A. Biological control of plant pathogens: A global perspective. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Y. Biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LJ02 induces systemic resistance against cucurbits powdery mildew. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, C.A.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Rooney, A.P. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum is a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus methylotrophicus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, C.A.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Rooney, A.P. Bacillus velezensis is not a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Bacillus methylotrophicus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum and ‘Bacillus oryzicola’ are later heterotypic synonyms of Bacillus velezensis based on phylogenomics. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nga, N.T.T.; Giau, N.T.; Long, N.T.; Lübeck, M.; Shetty, N.P.; Neergaard, E.D.; Thuy, T.T.T.; Kim, P.V.; Jørgensen, H.J.L. Rhizobacterially induced protection of watermelon against Didymella bryoniae. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meysam, S.; Abbas, J.; Jamalali, O. Chemical and biological products for control of powdery mildew on cucumber. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2022, 28, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, V.; Armijos, E.; Garcés-Claver, A. Fungal endophytes as biocontrol agents against the main soil-borne diseases of melon and watermelon in Spain. Agronomy 2020, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangwong, O.; Wonglom, P.; Phoka, N.; Suwannarach, N.; Lumyong, S.; Ito, S.; Sunpapao, A. Biological control activity of Trichoderma asperelloides PSU-P1 against gummy stem blight in muskmelon (Cucumis melo). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 115, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Kaliaperumal, K.; Zhong, B.; Jiang, Y. Evaluation of Aspergillus aculeatus GC-09 for the biological control of citrus blue mold caused by Penicillium italicum. Fungal Biol. 2022, 126, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshra, A.H.; Rashid, A.A.; Abdullah, M.A. Talaromyces omanensis and Aspergillus fumigatus endophytic fungi suppress Pythium aphanidermatum and its induced damping-off diseases of cucumber and radish. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2023, 56, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harveson, R.M.; Kimbrough, J.W.; Hopkins, D.L. Novel use of a Pyrenomycetous Mycoparasite for management of fusarium wilt of watermelon. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, W.; Ding, G.; et al. A Rhizosphere-derived consortium of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma harzianum suppresses common scab of potato and increases yield. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünlü, E.; Çalış, Ö.; Say, A.; Karim, A.A.; Yetisir, H.; Yilmaz, S. Investigation of the effect of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus thuringiensis as Bio-agents against powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii) disease in zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.). Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, H.; Behboudi, K.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Javan-Nikkhah, M.; Zamioudis, C.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A. Induced systemic resistance in cucumber and Arabidopsis thaliana by the combination of Trichoderma harzianum Tr6 and Pseudomonas sp. Ps14. Biol. Control 2013, 65, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cong, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, W.; Xin, Y.; Chen, K. Effects of mixed culture fermentation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Trichoderma longibrachiatum on its constituent strains and the biocontrol of tomato Fusarium wilt. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staropoli, A.; Vassetti, A.; Salvatore, M.M.; Andolfi, A.; Prigigallo, M.I.; Bubici, G.; Scagliola, M.; Salerno, P.; Vinale, F. Improvement of Nutraceutical Value of Parsley Leaves (Petroselinum crispum) upon Field Applications of Beneficial Microorganisms. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Kim, J.; Zhang, H.; Yoza, B.; Li, Q. Potential of wheat bran to promote indigenous microbial enhanced oil recovery. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Ke, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Li, B.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Oleozon: A novel control strategy against powdery mildew in cucumber. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, B.; He, Y.; Ying, Q.S.; Zhang, L.S. Study on mechanical properties and fruit quality analysis of watermelon (Cirtullus lanatus). Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2017, 29, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, S.; Bermejo, A.; Aleza, P.; Navarro, P.; Salvador, A. Phenolic composition, organic acids, sugars, vitamin c and antioxidant activity in the juice of two new triploid late-season mandarins. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Bai, T.; Fan, H.; He, P.; Zheng, S. A biological product of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 strain for promoting banana plant growth and modifying rhizosphere soil microbial diversity and community composition. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Effects of integrated biocontrol on bacterial wilt and rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørnsgaard, A.A.; Davey, M.L.; Kauserud, H. ITS all right mama: Investigating the formation of chimeric sequences in the ITS2 region by DNA metabarcoding analyses of fungal mock communities of different complexities. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruch, L.; Paruch, M.A.; Eiken, G.H.; Sørheim, R. Aquatic microbial diversity associated with faecal pollution of Norwegian waterbodies characterized by 16S rRNA gene amplicon deep sequencing. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sun, Z.; Sang, Q.; Qin, C.; Kong, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Su, T.; Li, H.; He, M.; et al. Soybean reduced internode 1 determines internode length and improves grain yield at dense planting. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, C.D.; Yagi, S.; Ijima, M.; Nashimoto, T.; Sawada, M.; Ikeda, S.; Asano, K.; Orikasa, Y.; Ohwada, T. Bacterial compatibility in combined inoculations enhances the growth of potato seedlings. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-García, L.F.; González-Almario, A.; Cotes, A.M.; Moreno-Velandia, C.A. Trichoderma virens Gl006 and Bacillus velezensis Bs006: A compatible interaction controlling Fusarium wilt of cape gooseberry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, S.; Bekkar, A.A.; Belabid, L. Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma harzianum combination on chickpea Fusarium wilt caused by F. oxysporum f. sp. ciceris. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2018, 51, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikova, V.S.; Tsvetkova, V.P.; Shelikhova, E.V.; Selyuk, M.P.; Alikina, T.Y.; Kabilov, M.R.; Dubovskiy, I.M. Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens mix suppresses rhizoctonia disease and improves rhizosphere microbiome, growth and yield of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Morita, A.; Koyama, H.; Suga, H.; Shimizu, M. Enhanced biocontrol of tomato bacteria wilt using the combined application of Mitsuaria sp. TWR114 and nonpathogenic Ralstonia sp. TCR112. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Tian, K.; Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zheng, L. A preliminary study on the effects of combination of biocontrol agents against watermelon fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Niveum. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2022, 49, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.R.; James, E.K.; Poole, P.S. The plant microbiome. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehra, A.; Raytekar, N.A.; Meena, M.; Swapnil, P. Efficiency of microbial bio-agents as elicitors in plant defense mechanism under biotic stress: A review. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brussaard, L.; Ruiter, P.C.; Brown, G.G. Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumova, N.; Baturina, O.; Nechaeva, T.; Kabilov, M. Root and Rhizosphere Microbiome of Tomato Plants Grown in the Open Field in the South of West Siberia under Mineral Fertilization. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruker, G.; Guidi, E.S.; Santos, J.M.d.S.d.; Mafra, Á.L.; Almeida, J.A.d. Quality of Bokashi-Type Biofertilizer Formulations and Its Application in the Production of Vegetables in an Ecological System. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Han, M.; Zhao, S. Microbial community structure and metabolome profiling characteristics of soil contaminated by TNT, RDX, and HMX. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzavecchia, G.; Frascarelli, G.; Rocchetti, L.; Bellucci, E.; Bitocchi, E.; Di Vittori, V.; Sillo, F.; Ferraris, I.; Carta, G.; Delledonne, M.; et al. Genotype Combinations Drive Variability in the Microbiome Configuration of the Rhizosphere of Maize/Bean Intercropping System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Xue, Q.; Guo, Q.; Lai, H. Widely targeted metabolomic, transcriptomic, and metagenomic profiling reveal microbe-plant-metabolic reprogramming patterns mediated by Streptomyces pactum Act12 enhance the fruit quality of Capsicum annuum L. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; You, P.; Hu, Q.; Leng, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wan, S.; Wang, B.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, R.; et al. Effects of co-contamination of heavy metals and total petroleum hydrocarbons on soil bacterial community and function network reconstitution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.; Kuramae, E.; Navarrete, A.; Veen, J.; Tsai, S. Taxonomical and functional microbial community selection in soybean rhizosphere. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhu, J. Mixed bacterial fermentation can control the growth and development of Verticillium dahliae. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, K.; Xue, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Inhibition effects of long-term calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer application Cd uptake in rice: Regulation of the iron-nitrogen coupling cycle driven by the soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Khurana, H.; Singh, D.N.; Negi, R.K. The genus Sphingopyxis: Systematics, ecology, and bioremediation potential—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verastegui, Y.; Cheng, J.; Engel, K.; Kolczynski, D.; Mortimer, S.; Lavigne, J.; Montalibet, J.; Romantsov, T.; Hall, M.; McConkey, B.J.; et al. Multisubstrate isotope labeling and metagenomic analysis of active soil bacterial communities. mBio 2014, 5, e01157-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yoshida, S.; Mitani, N.; Egusa, M.; Takagi, M.; Izawa, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Kaminaka, H.; Ifuku, S. Disease resistance and growth promotion activities of chitin/cellulose nanofiber from spent mushroom substrate to plant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Zhao, S.; Ai, Y.; Huang, D.; Yang, K.; Cheng, H. Soil microbial responses to simultaneous contamination of antimony and arsenic in the surrounding area of an abandoned antimony smelter in Southwest China. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emenike, C.U.; Agamuthu, P.; Fauziah, S.H.; Omo-Okoro, P.N.; Jayanthi, B. Enhanced bioremediation of metal-contaminated soil by consortia of proteobacteria. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).