Abstract
Fertilizer application is a decisive measure for the productivity of medicinal chrysanthemum plants. Therefore, determining the optimal doses of nutrients required for the growth and yield is crucial. In this study, we set out to investigate the effect of various nutrients on the growth, yield, and functional components of chrysanthemum under eight different fertilization levels at seedling, branching, and flowering growth periods. The results show that plant height, stem diameter, and leaf area under the balance fertilization treatment were the highest (82 cm, 0.78 cm, and 38.50 cm2, respectively), while the flower size and yield under the high potassium treatment were significantly increased compared to using balance fertilization. Chlorophyll content was also highest under the high potassium treatment. Moreover, plant defensive antioxidant peroxidase (POD) was responsive to low nitrogen treatment and low phosphorus treatment, while high potassium treatment enhanced the phenylalanine aminolase (PAL) activity and increased the content of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in Chrysanthemum morifolium. In addition, low phosphorus treatment promoted the accumulation of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid content. Convincingly, the results show that growth, flowering, and functional indicators of chrysanthemum may thrive best under high potassium and balanced fertilization dosages, which will contribute to the development of a new economical chrysanthemum fertilizer ratio.
1. Introduction
Throughout history, plant species have been utilized for medicinal purposes. In the wild, certain plants are innately consumed by wild animals as a kind of self-medication. Moreover, the world’s population is said to rely primarily on plants and plant extracts for medical treatment and therapeutic purposes. The annual demand for medicinal plant raw materials was USD 60 billion in 2000 and is estimated to reach USD 5 trillion by 2050 [1]. Furthermore, it is predicted that up to 25% of all medications are plant-based in industrialized nations like the United States, compared to up to 80% in fast-developing nations like China and India [2]. Medicinal plants are effectively employed and extensively used on every continent. However, herbal medicine has a very well established and recorded history in Asia [3]. As a result, the bulk of the medicinal plants that are recognized internationally are found in China and India.
Chrysanthemum morifolium is a well-known Asian medicinal plant that has a wide range of health benefits, including stress and anxiety reduction, cardiovascular health improvement, oxidative damage prevention, inflammation inhibition, support of healthy immunological function, eye health improvement, and osteoporosis risk reduction [3]. Chrysanthemum has developed over time, from wild to cultivated and from edible to decorative and medicinal purposes. As a key raw material for clinical medicine [4] and food [4,5], chrysanthemum is widely used in many aspects of medicine and life, and there is substantial research on the chemical composition and pharmacological effects of medicinal chrysanthemum [5].
Indeed, chrysanthemum cultivars are heavy feeders and are frequently planted in fertile soils; however, nourishment is still essential because of their short root system, which allows the plant to extract nutrients from a very shallow layer of the soil [6]. Furthermore, although floral quality is mostly a varietal attribute, climatic, regional, and nutritional variables also have a significant impact [6]. Therefore, applying chemical fertilizers is the most crucial factor that directly affects the development and productivity of flower crops [7]. As a result, the choice and required dosage of nutrients are closely related to the choice of cultivar, initial soil fertility, stage of plant growth, climate [6], etc.
Plant nutrition has a direct influence on crop physiology, and the most significant inputs are optimal fertilizer application, which has a direct impact on plant development, growth, output, and quality. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the main components of chemical and organic fertilizers necessary for plant development. Nitrogen boosts photosynthetic activity and vegetative development in plants and is a necessary component of amino acids and nucleic acids [8,9,10]. Conversely, phosphorus (P), which is present in enzymes, phospholipids, and nucleic acids, is necessary for the best possible metabolism [11]. Potassium (K) enriches a range of floral crops and is essential for respiration, transpiration, and the synthesis of proteins, amino acids, and chlorophyll [8]. Past research indicates that Chrysanthemum morifolium growth, production, and quality are influenced by plant nitrogen, phosphate fertilizer, potash, and organic fertilizer. For instance, it was found that the best amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus for greater flower output were 300 and 150 kg⸳ha−1 in chrysanthemum cv. Nilima [7]. Furthermore, potassium treatment of 75 kg P2O5/ha was shown to be promising for flowering and the production of cut Chrysanthemum cv. Thai Chen Queen [7]. A recent study also showed that NPK applied by drip fertigation may enhance chrysanthemum inflorescence characteristics, such as yield, biochemical activity, and soil nutrient status [8]. In other studies, potassium increased stalk thickness [12], and organic fertilizer promoted growth and improved crop quality [13]. Similarly, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, through with different ratios of use, prompt plant mass efficiency [14].
The Chinese Pharmacopoeia categorizes medicinal “Chrysanthemum flower” into five groups according to the primary production zones and distinguishes regional cultivars, i.e., “Boju”, “Chuju”, “Gongju”, “Hangju”, and “Huaiju”, based on their macro-morphology as well as processing techniques [4]. The Boju cultivar, a specialty of Bozhou city in Anhui province, is the classic cultivar of a medicinal C. morifolium with a white dry head of chrysanthemum. Grown in the north of the Yangtze River, Boju has been cultivated for medicinal purposes for at least 240 years. Furthermore, it is recognized to be similar to the Gongju cultivar and other cultivars of Hangju, as well as closely linked to the Qiju, Huaiju, and Jiju cultivars [15]. Cultivation of chrysanthemum is a well-established practice in China [5], but research into the fertilizing impact of the Boju cultivar of chrysanthemum and culture area depth is insufficient.
Different nitrogen and phosphorus treatment doses have been proven to be extremely effective in achieving good growth and quality flowers in various chrysanthemum varieties and other plant genotypes [7,8,10,16]. Thus, determining the optimal fertilizer dose is likely to increase chrysanthemum flower output [8]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of different fertilization dosages on the growth, yield, and active composition of the chrysanthemum cultivar Boju. To test this hypothesis, we conducted an analysis comparing different NPK fertilizer treatments’ effects on chrysanthemum morphological (plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, fresh weight, and dry weight) characteristics, physiological parameters (chlorophyll content), biochemical properties (peroxidase and phenylalanine aminolase activities), and antioxidant metabolite contents (flavonoids and chlorogenic acid) to determine the optimal and economical NPK doses for maximizing chrysanthemum yield.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Design
Chrysanthemum morifolium variety Boju was acquired from Bozhou Xinghe Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. (Bozhou, China). Field experiments were conducted in 2021 at the Anhui Northwest Experimental Station of Anhui Agricultural University (Linquan County, Anhui province, China). The physical and chemical properties of the soil were as follows: pH 5.4, organic matter 28.40 g∙kg−1, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen 149.13 mg∙kg−1, available phosphorus 23.86 mg∙kg−1, and available potassium 283.33 mg∙kg−1. Fertilizer selection included urea (N 46%), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (P2O5 52%), potassium chloride (K2O 60%), organic fertilizer (organic matter 40.0%), and inorganic fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O:15–15–15, total nutrients 45%). They were all purchased from Hubei Ezhong Ecological Engineering Co., Ltd. (Jingmen, China).
A total of 24 plots were randomly arranged for the experiment, with each plot measuring 25 m2 (5 m × 5 m). The plant spacing and planting density were set at 40 cm × 40 cm and 156 plants/plot, respectively. The experiments consisted of eight fertilization levels (Table 1), which included non-fertilization (negative control, NON−, 0 kg∙ha−1), organic (positive control 1, O+, 1666 kg∙ha−1) or inorganic (positive control 2, I+, 1666 kg∙ha−1), low nitrogen (LN, 0–196–300 kg∙ha−1), low phosphorus (LP, 330–0–300 kg∙ha−1), low potassium (LK, 330–196–0 kg∙ha−1), and high potassium (HK, 330–196–450 kg∙ha−1), and the balance fertilization (BF, 330–196–300 kg∙ha−1). Specific application period and amount of fertilizer: Nitrogen fertilizer was applied at 110 kg∙ha−1 before transplanting, branching, and current bud stages. Phosphate fertilizer was applied as the base fertilizer all before transplanting. The 180 kg∙ha−1 of potash were applied as base fertilizer, and the remaining potash was applied at 135 kg∙ha−1 in both the branching and current bud stages. The 666 kg∙ha−1 of organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer were applied as base fertilizer, and the remaining 500 kg∙ha−1 of fertilizer were applied during branching and current bud stages. Water management according to the weather, temperature, and other conditions of watering according to routine management was consistent.

Table 1.
Amounts of fertilizers applied in different pots (kg∙ha−1).
2.2. Measurement of Parameters
2.2.1. Plant Height, Stem Diameter, and Leaf Area
At the full flowering stage, six plants with good and consistent growth rates were selected to measure plant height and stem diameter with a vernier caliper at 5 cm above the root, and leaf area indexes were measured with a portable leaf area meter CI-202 (CID Corporation, Miami, FL, USA).
2.2.2. Flower Diameter and Size
After harvesting in full bloom, 10 chrysanthemums with the same growth in each plot were selected, and the flower diameter and size indexes of each treatment were measured. Each plot was selected, and the flower diameter and size indexes of each treatment were measured.
2.2.3. Yield
Flowers of six plants from different treatments were collected and weighed individually after drying (120 °C for 10 min, 55 °C for constant weight). The yield per plant was calculated by dividing the measured weight by the number of plants, and the yield per single plant was multiplied by planting density to get the yield per unit area of chrysanthemum.
2.2.4. Chlorophyll Content
Chlorophyll content was measured using the SPAD method. Briefly, leaves of each treatment group were selected at the seedling stage, dividing stage, and flowering period; the chlorophyll content of each treatment repeat group was determined using a chlorophyll meter SPAD-502 PLUS (Konica Minolta, Tokyo, Japan); and the average value was taken.
2.2.5. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
The activities of plant antioxidant enzymes POD and PAL were assessed using protocols provided in the manufacturer’s directions for test kits (Beijing Solarbio Science and Technology, Beijing, China), similar to prior research by Hua et al. [17] and Luan et al. [18], repeated three times.
2.2.6. Flavonoids and Chlorogenic Acid
The flavonoid content was determined according to Ai et al. [19] with a few modifications. Briefly, dried samples of each treatment at a constant weight were crushed, sieved, and closely weighed to 0.02 g of chrysanthemum powder. Next, 2 mL of extract were added, shaken at 60 °C for 2 h, and centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min. The supernatant was extracted, a microplate analyzer was used to obtain the OD value to make a standard curve (Figure 1a), and the total flavonoid content of each treatment was calculated. For chlorogenic acids, 0.25 g of chrysanthemum powder was accurately weighed, and 70% methanol was added to 25 mL. Ultrasonic treatment (120 W, 40 kHz) was conducted for 40 min followed by cooling, shaking, and filtering. The filtrate was evaporated by rotation to dryness and then dissolved in 2.5 mL of 70% methanol, filtered by a 0.22 μm organic microporous membrane, and the sample solution was obtained. A standard curve (Figure 1b) was made to calculate the chlorogenic acid content of each treatment.
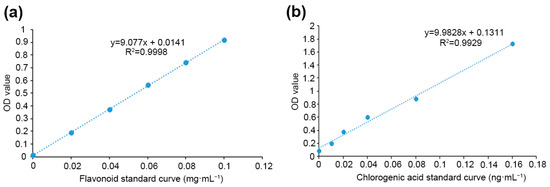
Figure 1.
Standard linear regression curve. (a) Standard curve for flavonoids, (b) standard curve for chlorogenic acid.
2.3. Data Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2018, Prism 8.0, and SPSS 27.0 software. Data for each treatment were expressed as mean values ± S.D., with three replicates. Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine which means differed significantly, with p-values (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Influence on the Growth of Chrysanthemum with Different Treatments at Seedling Stage
The effect of different doses of fertilizers on chrysanthemum seedling growth period was studied (Table 2). As shown in Table 2, morphological changes including plant height, stem thickness, and leaf area were highest with high potassium (HK) compared to other treatments at the seedling stage, with 45 cm, 0.45 cm, and 25.37 cm2, respectively. Following BF treatment, plant height, stem thickness, and leaf area increased significantly by 40 cm, 0.42 cm, and 21.47 cm2, respectively (Table 2). In comparison with the controls (O+ and I+), HK treatments showed significant percent increases in plant height of 28.57% and 33.36%, while BF treatments showed an increase of 14.28% and 21.21%, respectively. Contrarily, treatment result comparisons between NON−, O+, and I+ showed a percent decrease in plant height of −27.27% and −31.43%, respectively, while no significant changes were observed between the control treatments LP and LN (Table 2). The stem diameter exhibited a significant increase of 18.42% and 25% after HK and when compared with the control results, O+ and I+, respectively. A similar trend was observed between BF and the control, with a percent increase of 10.53% and 16.68%, respectively (Table 2). However, negative control treatment showed a significant decrease of −18.42% and −13.88% in stem diameter in comparison with O+ and I+, respectively. In regard to leaf area and response to different fertilizer treatments, HK, BK, LN, LP, and LK showed significantly increasing levels compared to the NON−, O+, and I+ controls (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effects of different treatments on the growth of chrysanthemum during seedling.
3.2. Influence on the Growth of Chrysanthemum with Different Treatments at Branching Stages
The effect of different fertilizer concentrations on chrysanthemum branching periods is presented in Table 3. All fertilization treatments at the branching period were higher than the control treatment (Table 3). Moreover, among all treatments, BF had a significant increase in plant height, stem thickness, and leaf area at 66 cm2, 0.49 cm2, and 29.45 cm2, respectively. HK treatment showed similar results, with a significant increase in plant height, stem thickness, and leaf area; however, there were no significant differences compared to O+ during the branching period at the plant height growth stage (Table 3).

Table 3.
Effects of different treatments on the growth of chrysanthemum during branching.
3.3. Influence of Different Treatments on the Chrysanthemum Flowering Period
Different fertilization treatments had a substantial influence on chrysanthemum development during the flowering period. The order of plant height, stem diameter, and leaf area from high to low were as follows: BF > HK > O+ > I+ > LN > LP > LK > NON− (Table 4). Moreover, at the full flowering stage, the plant height, stem diameter, and leaf area of various fertilization treatments were higher than those of NON−, and the BF treatment outperformed (82 cm, 0.78 cm, and 38.50 cm2) the other groups in terms of these metrics, followed by HK (Table 4). Chrysanthemum flower width and diameter in the HK treatment were considerably greater than those in the other groups, measuring 1.93 cm and 4.94 cm, followed by BF. Furthermore, there was no significant difference between the BF treatment and O+ treatments. In addition, the flower diameters of the HK, BF, and LN organic fertilizer treatments were higher than those of the NON−, LK, and LP inorganic fertilizer treatments (Figure 2; Table 4).

Table 4.
Effects of different treatments on the growth of chrysanthemum during flowering.

Figure 2.
Observable changes in chrysanthemum flowers under different fertilization treatments. NON−, negative control; LN, low nitrogen; LK, low potassium; BF, balance fertilization; HK, high potassium; LP, low phosphorus.
3.4. Influence on the Biomass and Yield of Chrysanthemum under Different Fertilization Levels
The results of measuring the fresh and dry weight of chrysanthemum indicate that different fertilization treatments had a substantial impact on flower output based on the fresh and dry weight (Figure 3). The treatments in each group of LK, BF, and HK, among others, were greater than those in NON−. Further, HK-treated flower weight and dry weight was the highest at 707.65 kg/666.67 m2 and 117.04 kg/666.67 m2. The yield of chrysanthemum increased as the K content increased, while N treatment was slightly greater than that of P treatment. Additionally, the flower weight and dry flower weight of O+ were 6.65% and 11.28% higher than those of I+.
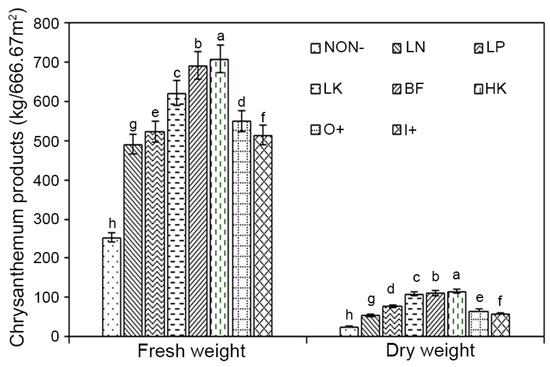
Figure 3.
Effect of different fertilization on the fresh and dry weight of chrysanthemum. Different letters in the same column represent significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level. NON−, negative control; LN, low nitrogen; LK, low potassium; BF, balance fertilization; HK, high potassium; LP, low phosphorus; O+, positive control 1; I+, positive control 2.
3.5. Effects on the Chlorophyll Content
The chlorophyll content of chrysanthemum plants after 60, 120, and 180 days following planting with varied dosages of NPK treatment was determined. As displayed in Figure 4, chrysanthemum had considerably greater chlorophyll content in HK than NON−, indicating that a higher N content might also raise chrysanthemum’s chlorophyll content (Figure 4). Chlorophyll concentration increased from 60 to 120 days after transplantation. After 60 days of treatment, LN (29.03%), LP (80%), LK (93%), BF (75%), and HK (88.7%) showed a significant increase in chlorophyll content in comparison with NON− (Figure 4). In comparison with O+ and I+, LN, LP, LK, BF, and HK treatments showed similar trends of increase in chlorophyll content at 60 days. Furthermore, after 120 days, HK treatment (62.43) showed the maximum chlorophyll concentration with a SPAD score, followed by BF (59.7), LK (59.02), LP (53.65), O+ (48.4), I+ (46.6), LN (40.1), and NON− (30.23) (Figure 4). The chlorophyll concentrations in LN, LP, LK, BF, HK, O+, and I+ decreased after 180 days. However, expression levels were significantly higher when compared to NON−, ranging from 24.13% to 96%.
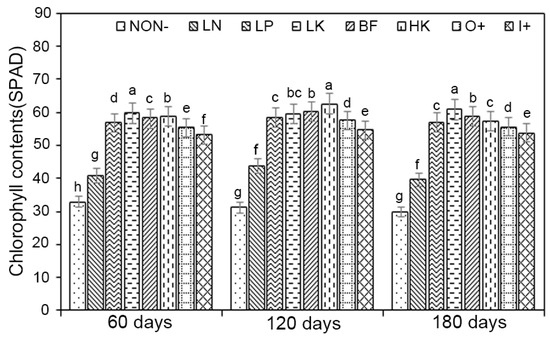
Figure 4.
Effects of different fertilization on the chlorophyll content of chrysanthemum. Different letters in the same column represent significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level. NON−, negative control; LN, low nitrogen; LK, low potassium; BF, balance fertilization; HK, high potassium; LP, low phosphorus; O+, positive control 1; I+, positive control 2.
3.6. Effects on POD and PAL Activities
POD activity was measured in flower, and the results indicate that it varied from 17.43 to 24. 33 U∙g−1∙min−1 (Figure 5). All treatments had higher POD activity than the control group; the BF treatment had the greatest POD activity at 24.33 U∙g−1∙min−1, followed by HK, and the LN treatment had the lowest POD activity at 18.63 U∙g−1∙min−1. The POD activity of LK was much lower than that of HK and BF compared to LN. Consequently, an increase in N content increased the chrysanthemum’s POD activity, while the increase in P content was not conducive to the increase in POD activity. In addition, POD activity of O+ and I+ was higher than that of LK, LP and LN, and O+ was 5.01% higher than that of I+. The PAL activity in flower ranged from 3.014 to 5.342 U∙g−1∙min−1. PAL activity of all treatments was higher than that of NON−, and the highest score (5.34 U∙g−1∙min−1) was recorded in HK treatment followed by BF. For LP treatment, the PAL activity was 14.13% and 5.77% higher than that of LK and LN. As a result, we hypothesized that both LK and LN could reduce PAL activity, its demand for K is high, and LP may boost PAL activity.
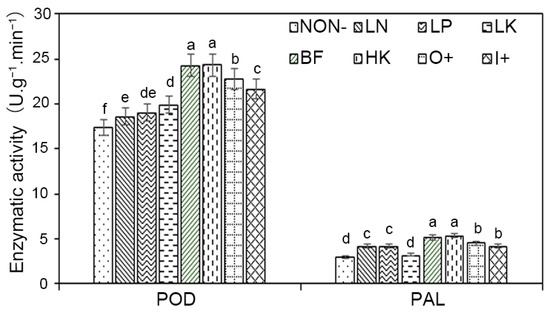
Figure 5.
Effects of different fertilization on POD and PAL activity of chrysanthemum. Different letters in the same column represent significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level. NON−, negative control; LN, low nitrogen; LK, low potassium; BF, balance fertilization; HK, high potassium; LP, low phosphorus; O+, positive control 1; I+, positive control 2.
3.7. Effects on Contents of Flavonoids and Chlorogenic Acids
The levels of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid under different treatments were considerably different. The flavonoid concentration in flower ranged from high to low as follows: HK > LP > O+ > BF > LN > I+ > LK > NON− (Figure 6). No significant difference in flavonoid content was observed between the BF, O+, LN, and LP treatments. However, in comparison with NON−, BF, O+, LN, and LP, there were significant increases in flavonoid content ranging from 47.65% to 61.1% (Figure 6). Similarly, the contents of chlorogenic acid in flower from high to low were as follows: HK > LN > LP > O+ > BF > LK > I+ > NON−. Among them, the concentrations of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in the HK treatment were 34.89 mg∙g−1 and 13.82 mg∙g−1, respectively, and HK > BF, indicating that the higher the potassium content, the higher the contents of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid. The contents of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in LP treatment were higher than those in BF treatment, indicating that LP would increase the contents of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid. In addition, the flavonoids and chlorogenic acid concentrations in LN treatment were higher than those in LK treatment. Similarly, the contents of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in O+ treatment were 10.26% and 29.60% higher than those in I+ treatment.
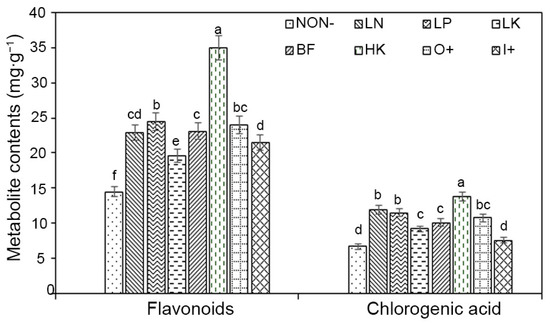
Figure 6.
Effects of different treatments on the flavonoids and chlorogenic acid of chrysanthemum. Different letters in the same column represent significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level. NON−, negative control; LN, low nitrogen; LK, low potassium; BF, balance fertilization; HK, high potassium; LP, low phosphorus; O+, positive control 1; I+, positive control 2.
4. Discussion
4.1. Different Treatments’ Effects on the Growth of Chrysanthemum
Plant growth in response to fertilizers has been extensively studied [10,20]. Significant morphological and physiological changes in the leaf, stem, and root are typically attributed to plant growth. Available data indicate that excessive N application promotes vegetative growth [10]. Moreover, the findings according to [8,21] revealed that nitrogen concentration at 300 kg⸳ha−1 resulted in a significant increase in plant height, number of branches per plant, leaf area, fresh and dry weight, flowering span, and total fresh and dry weight of the flower. In accordance with the present study, the BF fertilization dose (N-P-K, 330-196-300 kg⸳ha−1) displayed a significant increase in chrysanthemum growth parameters, including plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, and flower diameter (Table 4; Figure 2). Similar tendencies were seen during branching growth; however, vegetative growth in response to BF was greatest when compared to HK at N concentrations of 450 kg⸳ha−1 during the seedling growth stage (Table 3). Nitrogen is thought to be a component of protein, which is required for protoplasmic development, effecting cell division and enlargement and, ultimately, leading to greater vegetative growth [22]. As a consequence, we hypothesize that the considerable increase in vegetative and branching development of chrysanthemum during BF fertilization may be due to an increase in cell division and cell enlargement at the branching growth phase (Table 3). In our results, 450 kg⸳ha−1 of K2SO4 also increased growth qualities such as plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, and flower diameter during flowering (Table 4). However, high K2SO4, as opposed to high nitrogen and phosphorus, enhanced chrysanthemum growth throughout the seedling growth stage (Table 2). Subsequent research validated our findings, showing that chrysanthemum growth rates for plant height, number of primary branches, number of secondary branches, and number of leaves were dramatically accelerated at 200 kg⸳ha−1 and 150 kg⸳ha−1 of nitrogen and potassium, respectively [23]. Although potassium is essential for the stability of chlorophyll production in a range of physiological and biochemical processes [8], it also plays an important role in cell division and cellular differentiation in the plant system, causing stunted development when deficient [23]. Hence, we hypothesize that the enhanced plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, and flower diameter at 450 kg⸳ha−1 potassium sulfate might be due to an increase in cellular differentiation in the chrysanthemum cultivar Boju.
4.2. Fertilization Effects on the Fresh and Dry Weight of Chrysanthemum
In addition to increasing crop growth, fertilizer application is crucial for preserving agricultural sustainability and increasing crop biomass [24,25]. As a measure of plant biomass accumulation, plant fresh and dry weight are significant indicators of growth vigor [25]. Nitrogen and potassium are significant factors in plant fresh and dry matter accumulation [23,26]. Similarly, the current study revealed that a combined application of 330 kg⸳ha−1 nitrogen and 169 kg⸳ha−1 potassium resulted in a considerably higher number of fresh and dry weights in chrysanthemum, but potassium fertilization had the greatest effect (Figure 2). These findings were also congruent with the findings of Shah et al. [27], who discovered that increasing potassium dosages resulted in an increase in the number of leaves in Zinnia elegans. Bulawa et al. [28] found that potassium doses had a favorable impact on the fresh and dry weights of T. divaricate flower buds, shoots, and roots. Furthermore, the greatest dry weight of the plant was obtained by applying 150 kg⸳ha−1 potassuim to the Chrysanthemum coronarium cultivar [23]. We propose that an increase in the fresh and dry weight of chrysanthemum plants may be a result of increased vegetative growth.
4.3. The Effect of Fertilizer Doses on Chlorophyll Content of Chrysanthemum
Optimal NPK availability is often linked to higher nitrogen absorption, which in turn enhances the turgidity of mesophyll cells and chloroplasts and the stability of chlorophyll, increasing the chlorophyll content in crops [8]. For instance, an optimal nitrogen treatment dose was observed to improve chlorophyll a and b, total chlorophyll content, and carotene concentration in Tagetes erecta genotypes [29]. Recent investigations in chrysanthemum also demonstrated that chlorophyll content was 1.13, 1.05, and 1.17 times higher than the control at 30, 60, and 90 days after planting with 100:150:100 kg NPK/ha/year treatments [8]. According to the results of some parts of this study, the chlorophyll content of the Boju cultivar increased in response to NPK treatment (Figure 4). Furthermore, low potassium, high potassium, and balanced fertilization substantially enhanced chlorophyll content at 60, 120, and 180 days after planting, respectively (Figure 4). Our present findings align with previous studies, which show that nitrogen and potassium are two of the main components of proteins, amino acids, and major ingredients of chlorophyll [23]; therefore, we hypothesize that elevated levels of these elements may contribute to an increased chlorophyll rate and, consequently, enhanced photosynthesis.
4.4. The Effect of NPK Treatment on the Defense Benefit System of Chrysanthemum
Previous studies on fertilizer’s effects on plants have concentrated on the impact they have on the accumulation of antioxidants and secondary metabolites, particularly with the aim of enhancing protection against oxidative stress. For example, organic fertilizer application greatly increases the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Mongal F1 tomatoes [30]. Furthermore, in sweet pepper, health-promoting bioactive components and antioxidant activity are enhanced by organic fertilizers [31]. However, plant protective antioxidant activities provided by fertilizer application for proper growth and development remain elusive. High precipitation and high evapotranspiration levels in arid and semi-arid regions restrict water passage through the soil profile and ultimately increase the soil’s capacity to leach salts and produce toxic ions like sodium and chlorine, which have a detrimental effect on plant growth and yield due to nutrient imbalances [32,33]. Indeed, plants possess an effective antioxidant system that controls the scavenging of reactive oxygen species. These innate defense systems typically generate enzymes that help repair the damage caused by free radicals and increase the plant’s ability to withstand disease; for instance, polyphenol oxidase (PPO), phenylalanine aminolase (PAL), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) act as defense-related enzymes, which play an important role in this regard [34,35]. In this work, plant defense-related enzymes (phenylalanine aminolase and peroxidase) were found in high amounts in response to HK, BF, and O+ (Figure 5). Although nitrogen, potassium, and organic fertilizers are important contributors to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties in plants [36], we hypothesize that these nutrients may also improve plant defense antioxidants such as POD and PAL mechanisms in the Boju chrysanthemum cultivar (Figure 5).
4.5. The Effect of Various Fertilizers on Antioxidant Levels in Chrysanthemum
Plant antioxidants may provide health benefits by counteracting reactive oxygen species (ROS) [37]. Flavonoids and chlorogenic acids have strong antioxidant properties and are among the physiologically active components of chrysanthemum tea [19]. Plant flavonoid compounds are naturally occurring antioxidants, and their ability to scavenge free radicals is considered to play an essential role in the prevention of many chronic diseases [37]. Chlorogenic acids, on the other hand, are esters formed between caffeic and quinic acids that are involved in mitigating oxidative stress [38]. Existing studies display that different levels of fertilization of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium affect the production of secondary metabolites in plants. As verified by Ibrahim et al. [37], the production of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in plants is negatively impacted by N supply. Additional research corroborated the idea that lettuce leaves with nitrogen treatments of 1200 mg⸳L–1 or more may have decreased mineral content and antioxidant capability [39]. These results, in accordance with our hypothesis, demonstrate that LN treatment with 300 kg⸳ha−1 of nitrogen content increased the levels of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid (Figure 6), in contrast to LK, BF, and LP nutrition, with 330 kg⸳ha−1 of nitrogen content. As demonstrated by earlier research, potassium sulfate enhances plant primary metabolites, which may have an impact on the formation of several antioxidant compounds. Similarly, foliar potassium sulphate on Bouhouli trees causes a substantial change in total phenolic and flavonoid content and elevated chlorogenic acid from 0.87 to 1.70 mg⸳g−1 DW compared to the control [26]. As confirmed in this study, HK treatment (N-P-K, 330-196-450 kg⸳ha−1) substantially increases the flavonoids and chlorogenic acid levels in chrysanthemum (Figure 6). Moreover, Yaldiz et al.’s [40] findings also revealed that potassium application raises the polyphenol flavonoid content of thistle milk (Silybum marianum) and is associated with an increase in antioxidant activity.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the current work presents additional experimental data on the comparison of eight treatments on a medicinal cultivar of Chrysanthemum morifolium. We discovered that, although the indicators under different fertilizer treatments differed, varied levels of high N, P, and K increased chrysanthemum growth and output. Moreover, the designated application amounts of N, P, and K of chrysanthemum set at N (330 kg⸳ha−1), P (196 kg⸳ha−1), and K (450 kg⸳ha−1) were suitable dosages for chrysanthemum. In general, the chrysanthemum crop response to fertilizer application improved antioxidant attributes. Thus, we draw the conclusion that high potassium and balanced fertilization dosages may be the most beneficial for chrysanthemum growth, flowering attributes, and functional indicators, and further research is needed in this area to elucidate and test the potency of the HK and BF dosages.
Author Contributions
K.J. and S.P.: conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft. J.G.: supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. Z.Y. and X.L.: data curation and formal analysis. L.X. and M.S.: investigation and visualization. D.L.: supervision, validation, and writing—review and editing. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded and supported by the Natural Science Research Major Project of Anhui Educational Committee (2022AH040127) and the Major Science and Technology Unveiling and Leading Project of Bozhou City in Anhui Province (bzzd2021004).
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Karik, Ü.; Tunçtürk, M. Production, Trade and Future Perspective of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in Turkey. Anadolu J. AARI 2019, 2, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Jafarikukhdan, A.; Hosseini, A.; Armand, R. The Application of Medicinal Plants in Traditional and Modern Medicine: A Review of Thymus Vulgaris. Int. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 6, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Zandi, P.; Cheng, Q. A Review of Chrysanthemum, the Eastern Queen in Traditional Chinese Medicine with Healing Power in Modern Pharmaceutical Sciences. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 13355–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Scotti, F.; Reich, E.; Kirchhof, R.; Booker, A.; Heinrich, M. Chrysanthemum Species Used as Food and Medicine: Understanding Quality Differences on the Global Market. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 148, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Luo, Y.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.L. Chemical Compositions of Chrysanthemum Teas and Their Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitra, G.S.; Seetharamu, G.K.; Kumar, R.; Munikrishnappa, P.M.; Shivanna, M. Effect of Different Levels of Macro Nutrients (NPK) and Mulching on Growth, Quality and Yield of Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora) cv. Marigold. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 88, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.; Bhatt, D.S.; Chawla, S.L.; Bhatt, S.T.; Priya, S.S. Effect of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Growth, Flowering and Yield of Cut Chrysanthemum cv. Thai Chen Queen. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2019, 7, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, U.; Choudhary, R.; Kumar, R.; Jat, R.; Nidhibahen, P.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Al-Dosary, M.A.; Al-Wasel, Y.A.; et al. Various Fertilization Managements Influence the Flowering Attributes, Yield Response, Biochemical Activity and Soil Nutrient Status of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.). Sustainabilty 2022, 14, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pareek, N.K.; Rathore, V.S.; Nangiya, V.; Yadava, N.D.; Yadav, R.S. Effect of Water and Nitrogen Levels on Yield Attributes, Water Productivity and Economics of Cluster Bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) in Hot Arid Region. Legume Res. 2020, 43, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, A.; Hirosawa, K.; Masumoto, H.; Daimon, H. Effects of Maize as a Catch Crop on Subsequent Garland Chrysanthemum and Green Soybean Production in Soil with Excess Nitrogen. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 273, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaxton, W.C.; Tran, H.T. Metabolic Adaptations of Phosphate-Starved Plants. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Khalid, M.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tang, D. Controlled-Release Compound Fertilizers Improve the Growth and Flowering of Potted Freesia hybrida. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G.; Ju, J.; Mao, W.; Zhao, H. Response of Rice Grain Yield and Soil Fertility to Fertilization Management under Three Rice-Based Cropping Systems in Reclaimed Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guan, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Fang, W.; Zhao, S. Effects of Inorganic, Organic and Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Growth, Rhizosphere Soil Microflora and Soil Function Sustainability in Chrysanthemum Monoculture. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.C.; Song, Y.; Xiao, P.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, P.; Xu, L. The Genus Chrysanthemum: Phylogeny, Biodiversity, Phytometabolites, and Chemodiversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krucker, M.; Hummel, R.L.; Cogger, C. Chrysanthemum Production in Composted and Noncomposted Organic Waste Substrates Fertilized with Nitrogen at Two Rates Using Surface and Subirrigation. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 45, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Shao, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, L. Characterization of Pigmentation and Cellulose Synthesis in Colored Cotton Fibers. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Guo, B.; Pan, Y.; Lv, C.; Shen, H.; Xu, R. Morpho-Anatomical and Physiological Responses to Waterlogging Stress in Different Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Genotypes. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 85, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Kang, D.; Khan, M.A.; Li, H.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Chrysanthemum Flowers Grown under Hydroponic and Soil-Based Systems: Yield and Transcriptome Analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Lei, Q.; Ren, T.; et al. Managing Irrigation and Fertilization for the Sustainable Cultivation of Greenhouse Vegetables. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.S.; Varu, D.K.; Barad, A.V.; Pathak, D.M. Performance of Varieties and Chemical Fertilizers on Growth and Flowering in Chrysanthemum. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 9, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Roggatz, U.; McDonald, A.J.S.; Stadenberg, I.; Schurr, U. Effects of Nitrogen Deprivation on Cell Division and Expansion in Leaves of Ricinus communis L. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, P.R.; Bhaskar, V.V.; Dorajeerao, A.V.D.; Subbaramamma, P. Effect of Graded Levels of Nitrogen and Potassium on Growth and Flower Yield of Annual Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum coronarium L.). Plant Arch. 2017, 17, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.J.; Xiao, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, J.Q. Effects of Different Fertilization Rates on Growth, Yield, Quality and Partial Factor Productivity of Tomato under Non-Pressure Gravity Irrigation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z.; Chen, X. Accumulation and Distribution Characteristics of Biomass and Nitrogen in Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia L.) under Different Fertilization Strategies. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaliche, B.; Ladhari, A.; Zarrelli, A.; Ben Mimoun, M. Impact of Foliar Potassium Fertilization on Biochemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Fig (Ficus carica L.). Sci. Hortic. 2019, 253, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.; Ali, A.; Shah, M.; Abid, K. Potassium Influence on Flowering and Morphology of Zinnia Elegans. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2014, 3, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa, B.; Sogoni, A.; Jimoh, M.O.; Laubscher, C.P. Potassium Application Enhanced Plant Growth, Mineral Composition, Proximate and Phytochemical Content in Trachyandra divaricata Kunth (Sandkool). Plants 2022, 11, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polara, N.D.; Gajipara, N.N.; Barad, A.V. Effect of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrition on Growth, Flowering, Flower Yield and Chlorophyll Content of Different Varieties of African Marigold (Tagetes erecta L.). J. Appl. Hortic. 2015, 17, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serme, A.; Dabire, C.; Koala, M.; Somda, M.K.; Traore, A.S. Influence of Organic and Mineral Fertilizers on the Antioxidants and Total Phenolic Compounds Level in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Var. Mongal F1. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2016, 4, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Papalia, T.; Mallamaci, C.; Carabetta, S.; Di Sanzo, R.; Russo, M. Effect of Organic Fertilizers on Selected Health Beneficial Bioactive Compounds and Aroma Profile of Red Topepo Sweet Pepper. Foods 2020, 9, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimani, N.; Arraouadi, S.; Hajlaoui, H. Biochemical and Physiological Behavior against Salt Stress Effect on Two Quinoa Accessions (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Int. J. Agric. Anim. Prod. 2022, 2, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudari, A.; Latique, S.; Mayane, A.; Colinet, G.; Oukarroum, A. Polyphosphate Fertilizer Impacts the Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity of Wheat Plants Grown under Salinity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, S.; Ansari, S.A.; Ansari, M.I.; Fujita, M. Abiotic Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güne, A.; Kordali, Ş.; Turan, M. Industrial Crops & Products Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Phenolic Contents of Some Species of the Asteraceae Family from Medicanal Plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Duan, N.; Rong, L.; Wu, Z.; Shen, Y. Effect of Different Doses of Nitrogen Fertilization on Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Brown Rice. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1071874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Rahmat, A.; Rahman, Z.A. Involvement of Nitrogen on Flavonoids, Glutathione, Anthocyanin, Ascorbic Acid and Antioxidant Activities of Malaysian Medicinal Plant Labisia pumila Blume (Kacip Fatimah). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Kitts, D.D. Role of Chlorogenic Acids in Controlling Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Conditions. Nutrients 2015, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, D.; Winkler, S.; Jones, R. Reduced Nitrogen Availability during Growth Improves Quality in Red Oak Lettuce Leaves by Minimizing Nitrate Content, and Increasing Antioxidant Capacity and Leaf Mineral Content. Agric. Sci. 2011, 2, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaldiz, G. Effects of Potassium Sulfate [K2SO4] on the Element Contents, Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Milk Thistle [Silybum Marianum]. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).