Analyses of Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Cerasus humilis Orchards with Different Planting Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity
2.4. DNA Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing and Raw Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Planting Years on Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Effects of Different Planting Years on Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activity
3.3. Effects of Planting Years on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Characteristics
3.3.1. Alpha Diversity and PCoA Analyses
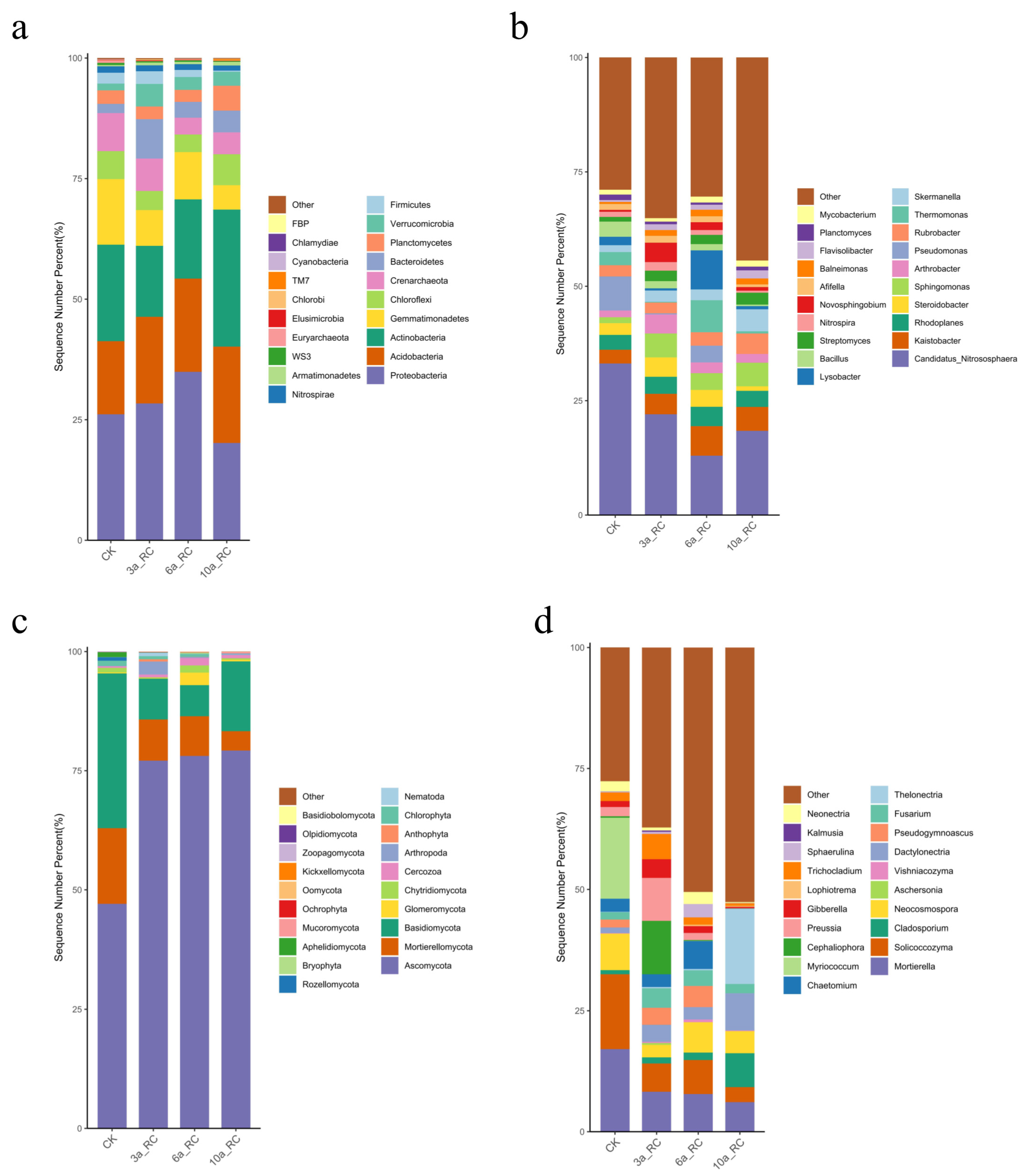
3.3.2. Microbial Community Composition and Structure
3.4. Correlation between Rhizosphere Microorganisms and Soil Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Planting Year on the Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activity of Rhizosphere Soil in C. humilis
4.2. Impact of Planting Year on the Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community in C. humilis
4.3. Impact of Planting Year on the Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Fungal Community in C. humilis
4.4. Correlation between Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Community Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.F.; Huang, F.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Sun, L.N.; Song, X.S. Establishment of a high-frequency regeneration system in Cerasus humilis, an important economic shrub. J. For. Res. 2016, 21, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yue, J.H.; Xia, W.X.; Li, T.T.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Fu, X.Y. Exploring the beneficial effects and mechanisms of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok fruit for calcium supplementation and promotion. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Bi, Y.L.; Du, S.Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Christie, P. Response of ecological stoichiometry and stoichiometric homeostasis in the plant-litter-soil system to re-vegetation type in arid mining subsidence areas. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 184, 104298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Jia, L.T.; Du, J.J.; Zhang, J.C.; Mu, X.P.; Ding, W. Improvement of soil quality by Chinese dwarf cherry cultivation in the Loess Plateau steep hill region. Acta Pratacul. Sin. 2017, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.W.; Jiang, Y.H.; Weng, B.Q.; Lin, W.X. Variations of rhizosphere bacterial communities in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) continuous crop soil by high-throughput pyrosequencing approach. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Bi, Y.L.; Du, S.Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C. Effects of re-vegetation type and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculation on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass in coal mining subsidence areas of Northern China. Catena 2019, 177, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Liu, L.; Xue, L.P.; Sun, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, P. Effects of Cerasus humilis on Soil Fractal Characteristics and Erodibility on Sloping Cropland in Loess Hilly and Gully Region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nihorimbere, V.; Ongena, M.; Smargiassi, M.; Thonart, P. Beneficial effect of the rhizosphere microbial community for plant growth and health. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2011, 15, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.F.; Chaparro, J.M.; Reardon, K.F.; Zhang, R.F.; Shen, Q.R.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere interactions: Root exudates, microbes, and microbial communities. Botany 2014, 92, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Netherway, T.; Hildebrand, F.; Pritsch, K.; Drenkhan, R.; Loit, K.; Anslan, S.; Bork, P.; Tedersoo, L. Plant nutrient-acquisition strategies drive topsoil microbiome structure and function. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.H.; Pan, Y.S.; Xiang, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Fu, W.B.; Hao, G.F.; Geng, Z.C.; Chen, S.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Han, D.F. Assembly of rhizosphere microbial communities in Artemisia annua: Recruitment of plant growth-promoting microorganisms and inter-kingdom interactions between bacteria and fungi. Plant Soil 2022, 470, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Akinola, S.A.; Babalola, O.O. The fungal and archaeal community within plant rhizosphere: A review on their contribution to crop safety. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Jia, T.H.; Qi, T.Y.; Li, S.S.; Degen, A.A.; Han, J.; Bai, Y.F.; Zhang, T.; Qi, S.; Huang, M.; et al. Root exudates enhanced rhizobacteria complexity and microbial carbon metabolism of toxic plants. iScience 2022, 25, 105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Wang, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Rhizosphere bacteriome structure and functions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.M.; da Silva, T.F.; Vollu, R.E.; Blank, A.F.; Ding, G.C.; Seldin, L.; Smalla, K. Plant age and genotype affect the bacterial community composition in the tuber rhizosphere of field-grown sweet potato plants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Tang, Y.J.; Bao, J.S.; Wang, H.K.; Peng, F.R.; Chen, M.Y.; Tan, P.P. Pecan plantation age influences the structures, ecological networks, and functions of soil microbial communities. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3294–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.L.; Xiao, L.; Guo, C.; Christie, P. Revegetation type drives rhizosphere arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil organic carbon fractions in the mining subsidence area of northwest China. Catena 2020, 195, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.S.; Meng, T.T.; Zhu, N.; Li, X.; Leng, F.F.; Wang, Y.G. Composition, function and driving factors of microbial communities in rhizosphere soil and root endophyte of Codonopsis pilosula in different years. Rhizosphere 2023, 27, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghdad, J.; Tohid, G.; Labelle, E.R. Soil physio-chemical and biological indicators to evaluate the restoration of compacted soil following reforestation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.G.; Guo, F.X.; Chen, Y.; Bai, G.; Guo, A.F. Astragalus-cultivated soil was a suitable bed soil for nurturing Angelica sinensis seedlings from the rhizosphere microbiome perspective. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.N.; Li, Q.; Yan, J.H.; Liu, C.; Zhong, J.X. Vegetation restoration facilitates belowground microbial network complexity and recalcitrant soil organic carbon storage in southwest China karst region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, A.; Yang, H.; Müller, W.E.G. Impact of rocky desertification control on soil bacterial community in karst graben basin, southwestern china. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yao, T.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Yuan, L.H. Screening, identification and characteristics of endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in Cerasus humilis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 30, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.Q.; Dong, J.Q.; Nie, Y.D.; Chang, C.; Yin, Q.; Lv, M.J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.H. Alfalfa Plant Age (3 to 8 Years) Affects Soil Physicochemical Properties and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Saline–Alkaline Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, E.J.B.N.; Vasconcellos, R.L.F.; Bini, D.; Miyauchi, M.Y.H.; Santos, C.A.D.; Alves, P.R.L.; Paula, A.M.D.; Nakatani, A.S.; Pereira, J.D.M.; Nogueira, M.A. Soil health: Looking for suitable indicators. What should be considered to assess the effects of use and management on soil health? Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.D.; Deng, Y.; Zou, K.; Zhang, S.F.; Duan, Z.C.; Wu, X.H.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.H.; Liu, X.D.; Liang, Y.L. Dynamic variation of Paris polyphylla root-associated microbiome assembly with planting years. Planta 2023, 257, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagnoni, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Mocali, S.; Arenella, M.; Nannipieri, P.; Renella, G. Availability of different nitrogen forms changes the microbial communities and enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of maize lines with different nitrogen use efficiency. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, C.; Almagro, M.; Amaducci, S. Carbon sequestration potential in perennial bioenergy crops: The importance of organic matter inputs and its physical protection. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 8, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledo, A.; Smith, P.; Zerihun, A.; Whitaker, J.; Vicente-Vicente, J.L.; Qin, Z.; McNamara, N.P.; Zinn, Y.L.; Llorente, M.; Liebig, M.; et al. Changes in soil organic carbon under perennial crops. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4158–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, G.; Ren, Z.P. Changes in soil nutrient and enzyme activities under different vegetations in the Loess Plateau area, Northwest China. Catena 2012, 92, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.Y.; Lv, Y.P.; Sun, Y.D.; Chen, X.P.; Li, Y. Assessment of Soil Enzyme Activities in Plant Root Zone of Saline Soil Reclaimed by Drip Irrigation with Saline Groundwater. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, P.G.; Miller, A.J.; Hirsch, P.R. Are root exudates more important than other sources of rhizodeposits in structuring rhizosphere bacterial communities? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.N.; Wu, Z.L.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.Y.; Zeng, Q.Y.; Qi, Y.W. Rhizosphere bacterial community characteristics over different years of sugarcane ratooning in consecutive monoculture. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4943150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Liu, D. Effects of revegetation on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activities, and nutrient cycling on the Loess Plateau in China. Restor. Ecol. 2013, 21, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.M.; Sun, H.Y.; An, S.S. The restoration age of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation impacts soil microbial biomass and microbial community structure in the Loess Plateau. Catena 2018, 165, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.D.; He, Y.S.; Zhou, W.X.; Ai, L.Q.; Liu, H.H.; Chen, L.; Xie, Y. Effects of continuous crop of Codonopsis tangshen on rhizospheric soil bacterial community as determined by pyrosequencing. Diversity 2021, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhang, C.; Ying, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Vaisman, H.S.; Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Shi, R. Long-term continuous mono-cropping of Macadamia integrifolia greatly affects soil physicochemical properties, rhizospheric bacterial diversity, and metabolite contents. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 952092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Chai, D.; Gu, Y.F.; Zhao, K.; Yu, X.M.; Shui, Z.B.; Liu, H.J.; et al. The crop obstacle of garlic was associated with changes in soil physicochemical properties, enzymatic activities and bacterial and fungal communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828196. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, B.; He, Y.; Luo, Z.B.; Peng, H.W.; Cai, H.Q.; Zhu, Y.N.; Bin, J.; Ding, M.J. Response of rhizosphere soil physicochemical properties and microbial community structure to continuous cultivation of tobacco. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.T.; Liu, J.X.; Jiang, W.Y.; Ji, P.S.; Li, Y.G. Metabolomics and microbiomics reveal impacts of rhizosphere metabolites on alfalfa continuous crop. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 833968. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Yang, J.; Liao, B.S.; Li, X.W.; Chen, S.L. High-throughput sequencing technology reveals that continuous crop of American ginseng results in changes in the microbial community in arable soil. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.Y.; Liu, A.; Hou, Q.W.; Zhao, Q.S.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.J. Diversity patterns of soil microbial communities in the Sophora flavescens rhizosphere in response to continuous monocrop. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.F.; Chen, F.L.; Xiang, D. Effects of consecutive monoculture of sweet potato on soil bacterial community as determined by pyrosequencing. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Z.; Penton, C.R.; Lv, N.; Xue, C.; Yuan, X.F.; Ruan, Y.Z.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.R. Banana Fusarium wilt disease incidence is influenced by shifts of soil microbial communities under different monoculture spans. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Han, M.K.; Xu, J.J.; Ma, Z. Correction to: Effects of continuous cropping of sweet potatoes on the bacterial community structure in rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Liu, J.; Hoover, T.R. Phylogenetic distribution, ultrastructure, and function of bacterial flagellar sheaths. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.H.; Liu, L.X.; Wang, L.; Dong, G.Z.; Liu, Y.G. Effects of different seasons on bacterial community structure in rose rhizosphere soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, X.M.; Yuan, H.F.; Lv, G.H. Differed growth stage dynamics of root-associated bacterial and fungal community structure associated with halophytic plant Lycium ruthenicum. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.B.; Wang, X.W.; Yan, J.W.; Luo, L.X. Characterizing the Intra-Vineyard Variation of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar]
- Purahong, W.; Wubet, T.; Lentendu, G.; Schloter, M.; Pecyna, M.J.; Kapturska, D.; Hofrichter, M.; Krüger, D.; Buscot, F. Life in leaf litter: Novel insights into community dynamics of bacteria and fungi during litter decomposition. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4059–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voříšková, J.; Baldrian, P. Fungal community on decomposing leaf litter undergoes rapid successional changes. ISME J. 2023, 7, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Li, Z.W.; Arafat, Y.; Lin, W.X. Studies on fungal communities and functional guilds shift in tea continuous cropping soils by high-throughput sequencing. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Ding, C.J.; Zhang, W.X.; Wei, Y.W.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zhu, W.X. Community characteristics of soil ectomycorrhizal fungi under different forests in the sandy areas of Northeastern China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.D.; Zhu, S.X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.Q.; Sheng, L.Y.; Mao, H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter rhizosphere fungal community characteristics of Acorus calamus to improve cr resistance. PeerJ. 2023, 11, e15681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.L.; Zhang, E.; Wu, J.M.; Ma, D.H.; Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Wang, B. Effects of Different Modified Materials on Soil Fungal Community Structure in Saline-Alkali Soil. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2024, 45, 3562–3570. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.G.; Sui, X.; Li, M.S. Effects of forest age on soil fungal community in a northern temperate ecosystem. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.J.; Liu, W.B.; Zhu, C.; Luo, G.; Kong, Y.L.; Ling, N.; Wang, M.; Dai, J.Y.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. Bacterial rather than fungal community composition is associated with microbial activities and nutrient-use efficiencies in a paddy soil with short-term organic amendments. Plant Soil 2018, 424, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jeelani, N.; Xia, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Luo, Y.Q.; Cheng, X.L.; An, S.Q. Soil fungal communities vary with invasion by the exotic Spartina alternifolia Loisel. in coastal salt marshes of eastern China. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.K.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Z.G.; Qin, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, W.X. Comparative metagenomic analysis of rhizosphere microbial community composition and functional potentials under Rehmannia glutinosa consecutive monoculture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, P.P.; Chen, L.; Jie, X.L.; Hu, D.S.; Feng, B.; Yue, K.; et al. Rare fungus, Mortierella capitata, promotes crop growth by stimulating primary metabolisms related genes and reshaping rhizosphere bacterial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, M.; Godoy, L.; Gebauer, M.; Catrileo, D.; Albornoz, F. Screening for indole-3-acetic acid synthesis and 1-aminocyclopropane-carboxylate deaminase activity in soil yeasts from Chile uncovers Solicoccozyma aeria as an effective plant growth promoter. Plant Soil 2024, 496, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.N.; Zhang, J.C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Pan, L.J.; Chen, N.; Wang, T.; Jing, Y.; Chi, X.Y.; Du, B.H. Long-term continuously monocropped peanut significantly disturbed the balance of soil fungal communities. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraz, U.; Erhunmwunse, A.S.; Dubeux, J.C., Jr.; Mackowiak, C.; Liao, H.L.; Wang, X.B. Soil fungal community structure and function response to rhizoma perennial peanut cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.W.; Wang, S.X.; Li, K.; Qiao, J.; Guo, Y.S.; Liu, Z.D.; Guo, X.W. Responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to the long-term monoculture of grapevine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 7035–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.L.; Wu, Y.Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, W.L.; Lyu, L.; Li, W.L. Long-term cultivation drives dynamic changes in the rhizosphere microbial community of blueberry. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 962759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obalum, S.E.; Chibuike, G.U.; Peth, S.; Ouyang, Y. Soil organic matter as sole indicator of soil degradation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Index | CK | 3a_RC | 6a_RC | 10a_RC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.47 ± 0.33 a | 8.03 ± 0.33 b | 7.73 ± 0.09 c | 7.43 ± 0.03 d |
| Available N (mg/kg) | 58.03 ± 1.86 c | 93.96 ± 1.46 b | 119.74 ± 1.46 a | 61.10 ± 1.07 c |
| Available P (mg/kg) | 9.70 ± 0.34 bc | 8.96 ± 0.37 c | 10.30 ± 0.82 ab | 16.89 ± 0.39 a |
| Available K (mg/kg) | 79.08 ± 2.34 d | 180.761 ± 3.64 c | 194.82 ± 2.43 b | 271.02 ± 2.22 a |
| Total N (g/kg) | 0.87 ± 0.06 d | 1.37 ± 0.06 b | 1.73 ± 0.10 a | 1.10 ± 0.06 c |
| Total P (g/kg) | 0.49 ± 0.01 d | 0.67 ± 0.01 c | 0.83 ± 0.02 b | 1.25 ± 0.01 a |
| Total K (g/kg) | 13.06 ± 0.38 d | 18.85 ± 0.30 c | 24.73 ± 0.91 b | 29.22 ± 0.13 a |
| Organic matter (g/kg) | 10.96 ± 0.54 c | 13.02 ± 0.89 c | 22.41 ± 0.64 b | 25.56 ± 0.15 a |
| Soil Enzyme Activity | CK | 3a_RC | 6a_RC | 10a_RC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline phosphatase activity (mg/(g·d)) | 0.75 ± 0.03 d | 1.07 ± 0.05 b | 1.47 ± 0.01 a | 0.96 ± 0.01 c |
| Urease activity (mg/(g·d)) | 0.67 ± 0.01 c | 0.93 ± 0.02 b | 1.06 ± 0.00 a | 0.95 ± 0.03 b |
| Sucrase activity (mg/(g·d)) | 18.10 ± 0.61 d | 23.55 ± 1.58 c | 56.49 ± 0.31 a | 44.55 ± 0.77 b |
| Catalase activity (mg/(g·20 min)) | 3.81 ± 0.03 d | 4.01 ± 0.07 c | 5.83 ± 0.10 a | 5.02 ± 0.03 b |
| Planting Years | Ace | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | CK | 1712.23 c | 1715.71 c | 9.579 b | 0.997 a | 0.99 a |
| 3a_RC | 2577.76 a | 2491.80 a | 10.045 a | 0.997 a | 0.99 a | |
| 6a_RC | 2162.85 b | 2178.74 b | 9.732 b | 0.996 a | 0.99 a | |
| 10a_RC | 2491.80 a | 2491.03 a | 10.127 a | 0.998 a | 0.99 a | |
| Fungi | CK | 548.10 a | 543.23 a | 5.632 b | 0.926 b | 0.99 a |
| 3a_RC | 493.58 b | 496.13 b | 6.226 a | 0.965 a | 0.99 a | |
| 6a_RC | 564.16 a | 563.21 a | 6.425 a | 0.969 a | 0.99 a | |
| 10a_RC | 568.78 a | 570.27 a | 6.438 a | 0.969 a | 0.99 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, H.; Ding, J.; Mou, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P. Analyses of Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Cerasus humilis Orchards with Different Planting Years. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101102
Mu X, Wang J, Qin H, Ding J, Mou X, Liu S, Wang L, Zhang S, Zhang J, Wang P. Analyses of Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Cerasus humilis Orchards with Different Planting Years. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(10):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101102
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xiaopeng, Jing Wang, Hao Qin, Jingqian Ding, Xiaoyan Mou, Shan Liu, Li Wang, Shuai Zhang, Jiancheng Zhang, and Pengfei Wang. 2024. "Analyses of Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Cerasus humilis Orchards with Different Planting Years" Horticulturae 10, no. 10: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101102
APA StyleMu, X., Wang, J., Qin, H., Ding, J., Mou, X., Liu, S., Wang, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, J., & Wang, P. (2024). Analyses of Rhizosphere Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure in Cerasus humilis Orchards with Different Planting Years. Horticulturae, 10(10), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101102





