Abstract
Bitter gourd has picked up noteworthy consideration for its pharmacological benefits. However, the impact of amino acids (AAs) dosage on growth, yield, and antioxidants is uncertain. In this study, we investigated the effects of foliar spraying bitter gourd with 100, 200, and 300 mg/L dosages of tryptophan (Trp), glutamine (Gln), and phenylalanine (Phe). The results revealed that Trp, at a dosage of 300 mg/L, produced the most substantial increase in plant length, followed by 300 mg/L Phe. Additionally, the highest values of the fresh dry weight of the plants, fresh weight of the first fruit, fruit number per plant, fresh weight of the fruits per plant, and total fruit output per hectare were seen at 300 mg/L of Trp, followed by 300 mg/L of Gln. Phe at 300 mg/L yielded the highest levels of total phenolics and total flavonoids, coupled with strong scavenging activity against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl. These outcomes show the potential of Trp and Gln foliar sprays to enhance bitter gourd growth, yield, and certain antioxidant compounds. These findings carry substantial implications for the enhancement of bitter gourd cultivation and quality. By revealing AA’s potential for improving bitter gourd, our research contributes to bolstering the agricultural sustainability of this remarkable crop.
1. Introduction
Bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) is a tropical vine, known variously as bitter apple, bitter melon, or balsam pear, renowned for its dual significance as both a culinary delicacy and a potent medicinal plant. Its rich history spans traditional cuisines and healing practices in India, China, and Southeast Asia, where it has earned recognition for its diverse health benefits and nutritional value [1]. Abundant in bioactive compounds distributed throughout its roots, leaves, vines, and fruits; bitter gourd stands as a reservoir of medicinally valuable constituents. These compounds, replete with health-promoting attributes, include antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties [2,3]. Notably, bitter gourd seeds have demonstrated efficacy in addressing conditions such as ulcers, liver and spleen disorders, high cholesterol, and wound healing [4]. Given this remarkable profile, the cultivation of bitter gourd has garnered significant interest from both farmers and consumers alike, driven by the desire to optimize its growth, yield, and overall quality.
The desire to maximize bitter gourd’s growth, yield, and overall quality has led to the consideration of various strategies. Among these, amino acids (AAs) have emerged as promising candidates, given their pivotal roles in plant metabolism, physiology, and stress responses [5]. AAs, as essential organic compounds, play integral roles in diverse biological functions, including hormone synthesis, enzymatic reactions, and nutrient transport [6]. They serve as crucial precursors to hormone synthesis, act as signaling molecules in physiological pathways, and regulate processes such as nitrogen fixation, root development, antioxidant metabolism, and nutrient uptake efficiency [6,7,8].
Although earlier research has emphasized the beneficial effects of AAs on conventional growth parameters, such as plant height, biomass, leaf area, and yield in various crops, such as ‘Washington’ navel orange (Citrus sinensis) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) [9,10], there exists a significant research gap. This gap pertains to the less-explored aspects of AAs’ influence, particularly concerning quality parameters. This involves assessing the extent to which AAs affect not only plant growth but also key quality attributes, including antioxidant activity, phenolic components, and flavonoids.
Phenolic components hold a significant place among the bioactive compounds contributing to the health-promoting attributes of bitter gourd. These phenolic compounds, recognized as key secondary metabolites in plants, are esteemed for their potent antioxidant properties and their potential to counteract oxidative stress-related ailments [11,12]. Additionally, bitter gourd is known to contain appreciable quantities of phenolic components including gallic acid, gentisic acid, chlorogenic acid, tannic acid, and tannins, all of which bear pharmacological significance [13,14]. Furthermore, it is rich in flavonoids, such as catechin and epicatechin, which is a class of bioactive compounds associated with various health benefits [15,16].
In light of these considerations, our study focuses on exploring the effects of foliar spray treatments with three specific AAs: Tryptophan (Trp); glutamine (Gln); and phenylalanine (Phe). The selection of these AAs is underpinned by their established roles in fundamental plant processes, their potential to enhance growth, their role as precursors of many secondary metabolites, and their contribution to stress tolerance [17]. Trp serves as the foundation for the production of auxin, phytoalexins, alkaloids, and indole glucosinolates [18]. Gln plays a pivotal role in the metabolism of AAs in plants. It is classified as a proteinogenic AA and serves as an N transporter and NH3 carrier. Its roles encompass the synthesis of numerous molecules, functioning as sources of both energy and carbon, along with nitrogen backbones. This multifaceted functionality supports cellular homeostasis and the accumulation of biomass [19]. As noted by Croteau et al. [20], among these AAs, Phe, recognized as a pivotal component in plant growth and development, serves as a foundational component for an array of compounds. These include phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, lignin, tannins, and salicylate, which collectively play indispensable roles in fostering plant growth, supporting reproduction, and fortifying the plant’s resilience against both abiotic and biotic stresses [21]. Notably, the utilization of these compounds resulted in a substantial rise in the levels of these constituents compared to plants that were not subjected to the foliar spray treatment.
The influence of foliar applications of Trp, Gln, and Phe on bitter gourd’s growth, yield, and antioxidant activity has not been extensively explored. To bridge this knowledge gap, we conducted an extensive field experiment spanning two consecutive seasons. This comprehensive approach allowed us to evaluate the influence of these AAs on diverse growth parameters, including plant height, fruit length, fresh and dry plant weight, fruit yield, and branch numbers. Additionally, we explored their potential effects on antioxidant activity, total phenolic content (TPC), and total flavonoid content (TFC) in bitter gourd plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites
The study was performed at the Investigational Farm located in the Horticulture Department, Faculty of Agriculture at Moshtohor (30.3527° N longitude, 31.229° E latitude), Benha University, Egypt. The research spanned two consecutive seasons, 2020 and 2021. The experimental site had a subtropical desert climate (classification: BWh) with a humidity of 53.07% and an average annual precipitation of 2.03 mm (6.37 rainy days annually). The annual high temperature was 29.3 °C, and the annual low temperature was 16.2 °C.
2.2. Soil Analysis
The physicochemical analysis of the investigational soil used in the testing was achieved at the Laboratories of the Chemistry Department, Faculty of Agriculture at Moshtohor, Benha University. The analysis of soil texture, pH, organic carbon, and total nitrogen followed the procedures outlined by Jackson [22], as detailed below. The hydrometer method determined the soil texture, while pH was measured potentiometrically in the supernatant suspension of a 1:2.5 soil–water mixture using a pH meter. Organic carbon levels were assessed through the Walkley and Black [23] wet oxidation method, and total nitrogen content was determined using the Kjeldahl method, following the guidelines provided by Dieckow et al. [24]. To extract the available potassium (K), NH4 OAc (pH 7.0) was utilized, and the extract underwent analysis for available K using a flame analyzer at 589 nm. The extraction of available phosphorus (P) involved the use of a sodium bicarbonate solution at a pH of 8.5, following the procedure outlined by Olsen [25].
Table 1 and Table 2 present the results obtained from the soil analysis performed according to these methods.

Table 1.
Mechanical analysis of the experimental farm soil.

Table 2.
The soil’s chemical analysis at the experimental farm.
2.3. Experimental Design
Field trials were carried out utilizing a randomized complete block design, with each experimental condition replicated three times. The seeds used in the experiment were soaked in water for two days and then sown in clay loam soils in mid-April in both seasons and harvested in mid-November in both seasons. The experiment included 30 plots, with each experimental unit containing three plants. The area of each plot was 6.66 m2 and each plant occupied an area of 1.5 m2. In accordance with the findings of previous studies, and in adherence to the recommendations of the Ministry of Agriculture in Egypt [26], the plants of all treatments were fertilized with chemical nutrients at the rates of 190 N, 75 P, and 238 K (kg/h). This was achieved using ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate, and calcium superphosphate. The experiment consisted of foliar spraying of AAs, Trp, Gln, and Phe on the plants; these compounds were purchased from the Cairo chem Company, El Saraya Building, Semouha, Alexandria, Egypt. The spraying process was conducted using three different doses: 100, 200, and 300 mg/L, with a 15-day interval between each application. The doses chosen (100, 200, and 300 mg/L) reflect a range that has been shown to influence plant growth and development in previous studies [20,27,28]. These doses were selected to encompass a spectrum of potential effects and to evaluate potential dose–response relationships. As a comparative reference, a control group was included, which involved foliar spraying with water. In all treatment groups, including the control group with water, Tween 20 was included as a surfactant. This was done to ensure uniformity in the application process and avoid any unintended influence on the experimental results. Subsequently, the effects of all treatments were evaluated and compared.
2.4. Data Verified
2.4.1. Vegetative Parameters
For the vegetative indicators data, we measured the following indicators in four plant samples:
1: Plant length (cm), 2: number of branches/plants, 3: fresh weight of herb per plant (g), and 4: dry weight of herb per plant (g).
2.4.2. Fruit Indicators
For the fruit-growing data, the following parameters were measured:
1: Fresh weight of first fruit (g), 2: length of first fruit (cm), 3: diameter of first fruit (cm), 4: number of fruits/plants, 5: fresh weight of fruits/plant (g), and 6: total fruit harvest (ton/ha).
2.4.3. Chemical Composition
Preparation of the Fruit Extract for the Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC), Total Flavonoid Content (TFC), and Radical–Scavenging Activity by 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH)
The bitter gourd fruits were initially cleaned and chopped into small pieces. Afterward, they were subjected to a 24 h drying process at 60 °C in an oven. Following drying, the fruits were mechanically ground into a powder and subsequently underwent a two-day extraction using 80% ethanol in a Soxhlet extractor. The resulting extracts were then filtered through a Buchner funnel and concentrated in a dark environment under vacuum conditions, employing a rotary vacuum evaporator (N-N series, EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) at 40 °C [29].
Estimation of the Overall Phenolic and Flavonoid Content
To assess the total phenol concentration in the ethanolic extracts, we utilized a UV spectrophotometer (SM1600 UV-vis Spectrophotometers, Azzota, Claymont, DE, USA) and followed a colorimetric oxidation/reduction technique outlined by Yawadio et al. [30]. The Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was employed as the oxidizing agent. In brief, we mixed 2.5 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent with 2 mL of Na2CO3 (75 g/L) and added this mixture to 0.5 mL of the diluted extract (10 mg in 10 mL of solvent). After incubating the samples for 5 min at 50 °C and allowing them to cool, a control sample using 0.5 mL of distilled water was prepared. The absorbance was measured at 760 nm, and the TPC was quantified in terms of gallic acid equivalent (GAE).
The determination of TFC followed the procedure outlined by Ordonez et al. [31]. In summary, 1.5 mL of an ethanolic solution containing 20 g/L of AlCl3 were combined with 0.5 mL of the extract solution (fruit extract) (10 mg in 10 mL solvent). After one hour, the absorbance at 420 nm was measured at room temperature, with the yellow coloration indicating the presence of flavonoids. The TFC was quantified in terms of quercetin equivalent (QE).
DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) Radical-Scavenging Activity
The DPPH approach is a broadly exploited assay for evaluating the antioxidant effects of natural products. DPPH is a constant free radical that reacts with electron donors, resulting in the reduction of the purple-tinted blend to yellow-colored DPPH-H. The degree of discoloration is measured spectrophotometrically, and the percentage of inhibition is calculated. The electron-contribution capability of the acquired extracts was scanned by whitening of the purple-dyed blend of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl.
Following the approach of Hatano et al. [32] the electron-donating capacity of the obtained extracts was assessed through the decolorization of a DPPH purple solution. To 3 mL of a 0.1 mM DPPH solution dissolved in ethanol, 100 µL of each extract (0.1 mg extract/10 mL solvent) were added (fruit extract). After incubating for 30 min at room temperature, the absorbance was compared to a standard at 517 nm. The percentage of antioxidant activity for the free radical DPPH was determined using the following formula:
Antioxidant activity (inhibition)% = [A(control) − A(sample))/A(control)] × 100
Here, A control represents the absorbance of the control reaction (100 µL methanol with 3 mL DPPH), and A sample indicates the absorbance in the plant extract.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
As per the methodologies outlined in studies conducted by Kuntic et al. and Lin et al. [33,34], the identification of phenolic compounds was carried out utilizing an HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) system, specifically, the Agilent 1260 series (Agilent Technologies, GmbH, Boblingen, Germany). This HPLC system was equipped with an autosampler (L-2200), a quaternary pump (L-2130), a degasser (G 1322 A), and a diode array detector (L-2455). The chromatographic column employed was an Eclipse C18 with dimensions of 4.6 mm (diameter) × 250 mm (length) and a particle size of 5 µm. The flow rate was set at 0.9 mL/min.
The mobile-phase composition consisted of H₂O (A) and 0.05% CF3COOH in CH3CN (B). A gradient elution method was applied, involving specific changes in the mobile-phase composition at designated time intervals to facilitate the separation of individual sample components. In the initial 5 min, the mobile phase comprised 80% solvent A and 20% solvent B. Subsequently, between 5 and 8 min, the composition transitioned to 60% solvent A and 40% solvent B, and this ratio was maintained between 8 and 12 min. Afterward, between 12 and 16 min, the mobile phase returned to its initial conditions of 82% solvent A and 18% solvent B, which were maintained from 16 to 20 min.
A 5 μL injection volume was utilized, and the chromatograms were acquired at a wavelength of 280 nm. All analyses were conducted in triplicate. The identification of phenolic compounds within the plant extracts was achieved by comparing their retention times to those of pure standards. The results were reported in terms of the concentration of phenolic compounds expressed as μg/mL.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The mean values of all collected data from the investigated factors were analyzed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) as factorial investigates within a complete randomized block design. The significance level is (p ≤ 0.05). To compare the distinctions among the mean values of the several treatments, Duncan’s multiple range test [35] was applied, following the methodology outlined by Snedecor and Cochran [36]. The statistical analysis was done via the MSTAT-C 2.1 software package.
3. Results
3.1. Vegetative Parameters
The data recorded on vegetative traits (plant length, number of branches, and both fresh and dry weights) of the bitter gourd plant as influenced by 100, 200, and 300 mg/L of Trp, Gln, and Phe in both seasons are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Impact of Trp, Gln, and Phe foliar spraying on vegetative growth characteristics of bitter gourd plants during both seasons.
The data reveals a significant increase in plant length during both seasons when Trp was applied at a concentration of 300 mg/L, as well as with 300 mg/L Phe and 300 mg/L Gln, in comparison to the control group. Notably, the application of Trp at 300 mg/L resulted in the highest plant lengths (343 cm in the first season and 323 cm in the second season), surpassing the results of 300 mg/L Phe (322 and 310 cm) and the control (195 and 205 cm), in that order. On the other hand, the number of branches significantly increased with the application of 300 mg/L Gln and 300 mg/L Trp compared to the control (p ≤ 0.05). Specifically, when sprayed with 300 mg/L Gln, the plants exhibited the highest number of branches (23 in the first season and 22.3 in the second season), surpassing the results of Trp at 300 mg/L (21.3 and 18.3 cm) and the control (10.3 cm in both seasons) (Table 3).
Furthermore, all treatments involving AAs had a positive impact on the fresh and dry weights of the herb per plant in both seasons. Notably, the application of Trp at a dosage of 300 mg/L resulted in the highest fresh weight (717 and 717 g/plant) and dry weight (217 and 233 g/plant) during the first and second seasons, respectively. Similarly, the use of 300 mg/L Gln yielded the highest fresh weight (650 and 517 g/plant) and dry weight (177 and 170 g/plant) during the first and second seasons, respectively, p ≤ 0.05, Table 3.
3.2. Fruit-Growth Parameters
3.2.1. Fresh Weight of the First Fruit
The results presented in Table 4 demonstrate that foliar application of Trp and Gln at a dose of 300 mg/L resulted in a significant increase in the fresh weight of the first fruit compared to the untreated plants. Specifically, the application of Trp at 300 mg/L led to a weight increase of 154.5 and 160.2 g in the first and second seasons, respectively. Similarly, the use of Gln at the same dose led to a weight increase of 140.6 g in the first season and 150.8 g in the second season. These values represent the utmost weight increases observed among all treatments, in comparison to the control group, which had fruit weights of 112 and 123.7 g in the first and second seasons, respectively (p ≤ 0.05).

Table 4.
Effect of spraying Trp, Gln, and Phe on fruit-growth characters of bitter gourd plants during 2020 and 2021 seasons.
3.2.2. Length of the First Fruit
The results presented in Table 4 indicate a significant increase in the length of the first fruit (cm) during both seasons when Trp was applied at 300 mg/L, along with Gln and Phe at the same dosage, in comparison to the control group. Notably, the most substantial increase in length was observed with the application of Trp at 300 mg/L, resulting in lengths of 15 cm in the first season and 15.6 cm in the second season. This surpassed the lengths observed with 300 mg/L Phe (14.2 cm and 15.1 cm) and the control (11.3 cm and 11.9 cm) in both seasons.
3.2.3. Diameter of the First Fruit
For the diameter of the first fruit (cm), the application of Gln at 300 mg/L and 200 ppm, as well as Phe at 300 mg/L, resulted in the largest fruit diameters compared to the control. The highest diameter was achieved with the application of 300 mg/L Gln, measuring 7.14 cm in the first season and 7.24 cm in the second season. This outperformed the diameters achieved with 300 mg/L Phe (6.87 cm and 6.74 cm) and the control treatment (6.14 cm and 6.36 cm) in both seasons (see Table 4).
3.2.4. Number of Fruits/Plants
The results presented in Table 5 show a noteworthy increase in the number of fruits per plant due to the application of Trp at 300 mg/L and Gln at 300 mg/L in comparison to the control. The highest fruit yield was observed in plants treated with 300 mg/L Trp yielding 5.67 fruits in the first season and 6.67 fruits in the second season. This was followed by plants treated with 300 mg/L Gln, which produced 5.0 fruits and 5.33 fruits per plant in the first and second seasons, respectively. These findings affirm the positive impact of Trp and Gln on enhancing the fruit yield of bitter gourd plants.

Table 5.
Effect of spraying Trp, Gln, and Phe on fruit numbers, fresh weight, and total yield of gourd plants during the 2020 and 2021 seasons.
3.2.5. Fresh Weights of the Fruits/Plant (g)
The data in Table 5 reveals that the application of Trp and Gln at a dose of 300 mg/L significantly increased the fresh weight of fruit per plant (g) compared to the control. Notably, Trp at 300 mg/L resulted in the utmost weight gain, measuring 876.20 g in the first season and 1068.27 g in the second season. This was followed by Gln at 300 mg/L, with an average of 703.84 g in the first season and 804.37 g in the second season, compared to the control’s 372.86 g in the first season and 535.50 g in the second season.
3.2.6. Total Fruit Yield
The data presented in Table 5 shows that the fruit yield per hectare (ton) significantly increased with the application of Trp and Gln at 300 mg/L when compared to the control. Specifically, Trp at 300 mg/L resulted in the highest yield, with 5.85 tons per hectare in the first season and 7.13 tons per hectare in the second season. This was followed by Gln at 300 mg/L, yielding 4.82 tons per hectare in the first season and 5.39 tons per hectare in the second season. In contrast, the control had a lower yield of 2.49 tons per hectare in the first season and 3.57 tons per hectare in the second season.
3.3. Chemical Composition
3.3.1. TPC, TFC, and Antioxidant Effects
Table 6 presents the data on the TPC of bitter gourd extract, revealing a significant increase when treated with Phe and Gln in comparison to the control in both seasons. The highest TPC was observed in plants sprayed with Phe at concentrations of 300, 200, and 100 mg/L, followed by Gln at 300 mg/L. These findings suggest that these AAs have the potential to enhance the production of phenolic compounds in bitter gourd. Conversely, plants treated with Trp at 100 mg/L exhibited the lowest TPC, measuring 11.17 and 11.23 mg/g GAE in both seasons, respectively.

Table 6.
Effect of spraying Trp, glutamine, and Phe on TFC; TPC and antioxidant activity of bitter gourd plants during 2020 and 2021 seasons.
This indicates that these AAs have the potential to enhance the biosynthesis of polyphenols in bitter gourd. Upon analyzing the data presented in Table 6, it becomes apparent that the bitter gourd extract exhibited the highest TFC in plants treated with a dose of 300 mg/L of Phe in both seasons, with a content of 316 mg/10 g QE in the first season and 324 mg/ 10 g QE in the second season. In contrast, the lowest TFC was observed in plants treated with a concentration of Trp at 200 mg/L, with a value of 102 and 102 mg/ 10 g QE in both seasons. respectively. Notably, the control treatment displayed a consistent TFC of 99 mg/10 g QE in both seasons.
The ethanol (EtOH) extracts of Mamordica charantia exhibited strong scavenging activity against DPPH radicals, as presented in Table 6. Our results indicate that samples with low TPC tend to exhibit reduced antioxidant activity. Specifically, the antioxidant activity of the Mamordica charantia fruit extracts, as measured by DPPH scavenging, was 18.5 and 19.6% in the untreated plant in both seasons, respectively. The plants treated with 300 mg/L Phe showed the highest activity, with a percentage of 59%, while the lowest activity was observed in plants sprayed with 200 mg/L Trp, registering percentages of 29.9% and 30.9% in the first and second seasons, respectively. These findings underscore the potential of Phe for enhancing the antioxidant properties of bitter gourd.
3.3.2. Identification of Antioxidant Components by HPLC
The chemical constituents of the fruit extract were analyzed, and the results are depicted in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. In the control group, the fruit extract was found to contain a total of seven phenolic compounds and seven flavonoid compounds. Among the phenolic compounds, catechol, syringenic, and cinnamic were present in the highest quantities, while pyrogallol and ferulic were present in the lowest quantities.
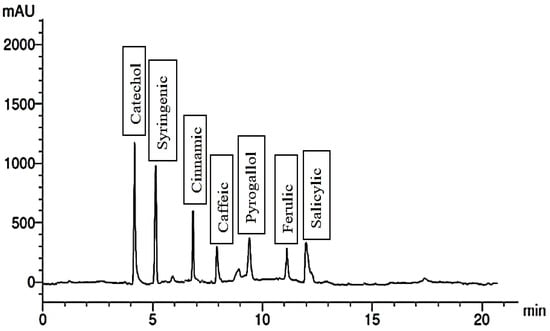
Figure 1.
Phenolic compounds of the control group.
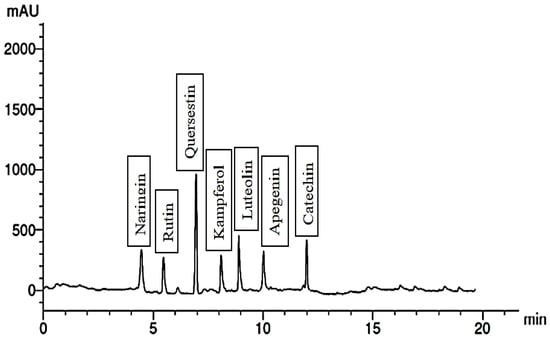
Figure 2.
Flavonoid compounds of the control group.
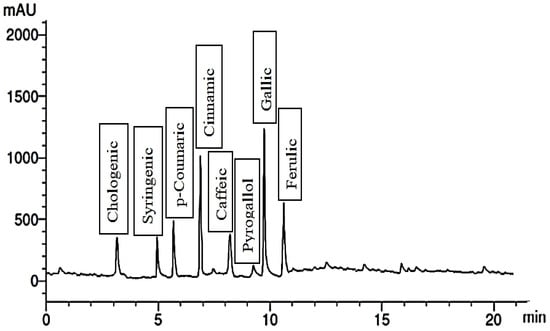
Figure 3.
Phenolic compounds of plants treated with 300 mg/L Trp.
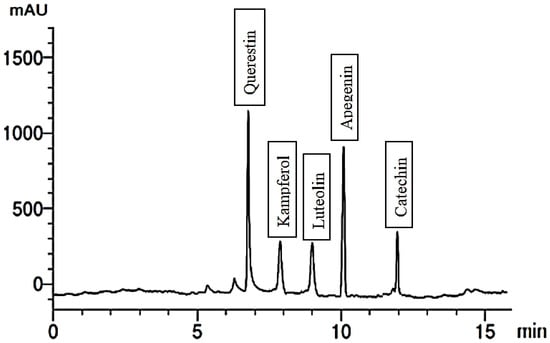
Figure 4.
Flavonoid compounds of plants treated with 300 mg/L Trp.
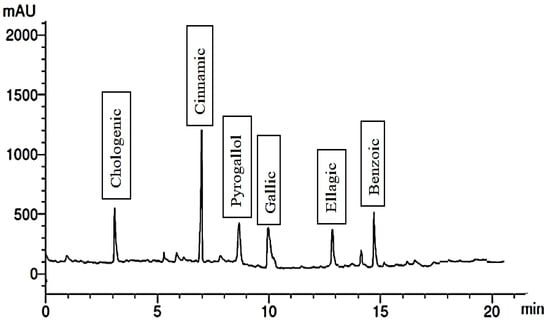
Figure 5.
Phenolic compounds extract of 300 mg/L Glu.
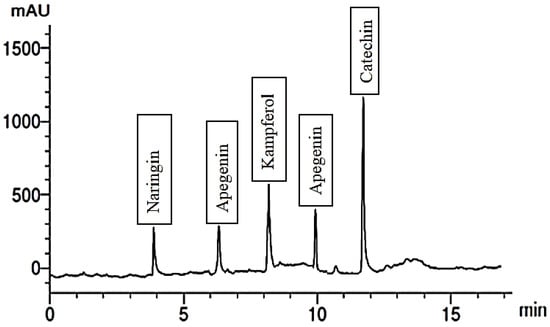
Figure 6.
Flavonoid compounds extract of 300 mg/L Glu.
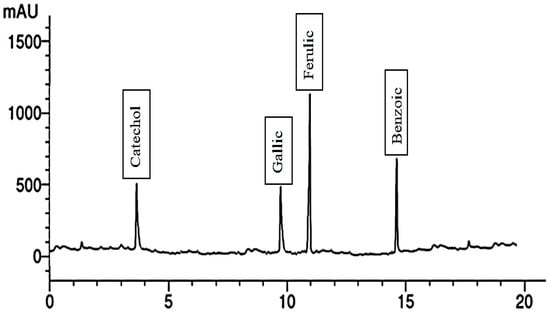
Figure 7.
Phenolic compounds of extract of plants treated with 300 mg/L Phe.
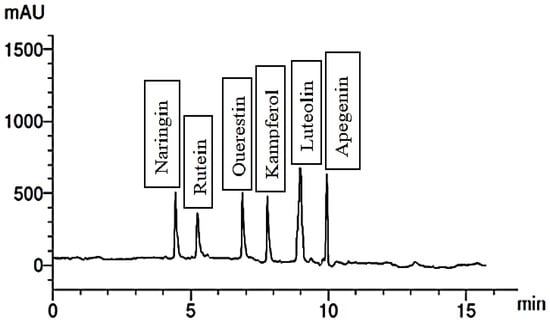
Figure 8.
Flavonoid compounds of extract of the group treated with 300 mg/L Phe.
Remarkably, the application of a 300 mg/L concentration of Trp to the plants resulted in significant changes in the chemical composition of the fruit extract. The extract contained eight phenolic compounds and five flavonoid compounds, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Gallic and cinnamic were the phenolic compounds present in the highest quantities, while pyrogallol had the lowest quantity. Additionally, the flavonoid compound quersestin showed increased quantities compared to the control. These findings suggest that treatment with Trp could enhance the quantities of specific phenolic and flavonoid compounds in the bitter gourd fruit extract, potentially contributing to its health benefits.
When the plants were treated with 300 mg/L of Gln, the fruit extract exhibited the presence of six phenolic compounds, with cinnamic being the most abundant and ellagic the least. Additionally, it contained five flavonoid compounds, including catechin and kaempferol, illustrated in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Conversely, treating the plants with 200 mg/L of Phe led to the identification of four phenolic compounds, namely ferulic, benzoic, catechol, and gallic. The extract also contained six flavonoid compounds, with apigenin being the most abundant and rutin the least abundant. These outcomes are detailed in Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. It is evident that foliar application of AAs holds the potential to enhance the levels of TPC, while also influencing the synthesis of diverse phenolic acids.
4. Discussion
Increasing the production of bioactive compounds in bitter gourd holds significant implications for enhancing its medicinal and nutraceutical properties. A potential approach to achieve this is by utilizing the potential of AAs, which are recognized for their role in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, including phenolic components and flavonoids, in various plant species.
In this study, the application of all AA treatments resulted in a significant enhancement of growth, yield, and antioxidant activity compared to the untreated plants, as indicated by our findings. Notably, the most pronounced impact on plant height was observed when Trp was applied at concentrations of 300 mg/L, followed by Gln at 300 mg/L. This positive influence of AAs aligns with similar observations documented in numerous plant species [37,38,39].
Trp serves as a key precursor to the plant hormone auxin, indole acetic acid. The application of Trp at suitable concentrations can distinctly impact plant growth due to the slow and gradual release of indole acetic acid from L-Trp [40]. Trp plays various roles in plants, including acting as an osmolyte, regulating ion transport, modulating stomatal opening, and contributing to defense mechanisms [41]. Furthermore, plant roots can absorb Trp-derived auxins generated by rhizosphere microorganisms and transport them to the shoot, initiating physiological reactions [42].
It is essential to acknowledge that the effect of AAs on plant growth might vary depending on factors such as the plant species, the dosage and time of application, and different climatic circumstances [43,44]. Nevertheless, the consistently positive outcomes observed across various studies suggest the potential of AAs as regulators of plant growth, warranting further research to comprehensively unravel their mechanisms of action and practical applications in agriculture. Spraying Trp, Gln, and Phe has been observed to have a stimulatory effect on vegetative growth in various plants, especially at high doses.
Gln plays an indispensable and multifaceted role in plant physiology and actively participates in numerous metabolic processes, especially those related to nitrogen assimilation [45,46]. In addition, Gln, along with arginine and asparagine, serves as one of the key AAs involved in a wide array of biochemical and metabolic reactions within plant systems. These reactions encompass tasks such as detoxification of toxins, neutralization of H+ ions generated in ammonium-fed plants, and conferring remarkable stress tolerance [47,48,49]. The outcomes of our study further underscore the pivotal role of Gln in promoting plant growth and development. This is evident in the significant increases observed in the fresh weight and first fruit diameter in bitter gourd plants sprayed with Gln at 300 followed by Trp 300 mg/L when compared to the control group.
Furthermore, the stimulating effects observed in our study, particularly at high concentrations, align with the stimulatory outcomes of foliar applications of Trp, Gln, and Phe on fruit-growth characteristics. This pattern of positive influence at higher concentrations corresponds with earlier findings in various plant species, such as Hibiscus sabdariffa [50], Silybum marianum [51], and Lupines termis [52], which supports our findings. The coherence between these prior studies and our results provides robust support for our findings.
The results of the present study revealed that the highest concentrations of TPC were achieved with elevated levels of both Phe 300 mg/L and Gln 300 mg/L. Phenolic compounds are recognized for their antioxidative characteristics and have been linked to a range of health advantages, including their ability to combat diseases related to oxidative stress. The observed increase in TPC suggests that the foliar application of Phe and Gln can contribute to enhancing the nutritional and health-promoting properties of bitter gourd. These findings are consistent with previous studies, such as the work conducted by Amira et al. [47], which also underscore the effectiveness of certain amino acids in promoting the synthesis of phenolic compounds. The outcomes of our study demonstrated that the application of all the employed AAs resulted in TFC compared to the unsprayed plants. Notably, Phe at a concentration of 300 mg/L displayed the highest levels of total flavonoids. This finding is consistent with a prior study by Klimek et al., which identified Phe as the most effective AA for enhancing total flavonoid synthesis, which is in alignment with our own results [53]. Previous research has also reported the stimulatory impact of Phe on plant growth and the production of secondary metabolite [49], further supporting our findings. This suggests that Phe treatment at a specific concentration can positively influence flavonoid production in bitter gourd plants, followed by Glu treatment. These compounds play significant roles in various aspects of plant biology, including growth, development, and defense mechanisms against both biotic and abiotic stressors [21]. Our results are consistent with earlier research that has documented the promotive impact of Phe on both plant growth and secondary metabolite production [51]. The stimulatory influence of Phe on flavonoid biosynthesis, like in Ocimum tenuiflorum and Mentha piperita plants, has been documented by studies conducted by Jacob and Thomas [54] and Roy et al. [55]. Among the flavonoid compounds, quersestin was present in the highest quantity, while rutin was found in the lowest amount. These results align with a previous study by Alper and Cennet [56], highlighting the interplay between specific plant varieties and the application of AAs through spraying in modulating phenol synthesis [43].
Studies have consistently shown that the application of AAs through foliar spraying at various concentrations can have a notable and favorable impact on the overall quantity of phenols, essential oil content, and their composition in different plant species. For instance, in the case of Ocimum basilicum plants, previous research has demonstrated that foliar spraying with AAs led to an increase in phenol content and the essential oil yield, along with modifications in their composition [27]. In another study by Farhan et al. [28] the application of Phe through foliar spraying at a concentration of 150 mg/L on Anethum graveolens L. resulted in a notable enhancement in herb-oil yield and increased TFC compared to untreated plants. Similarly, Poorghadir et al. [57], found that foliar spraying with Phe at a concentration of 1.5 g/L had the highest efficacy in augmenting the essential oil content, particularly carvacrol and gamma-terpinene, in Satureja hortensis plants. Remarkably, the application of these compounds significantly elevated the levels of these constituents compared to untreated plants. These studies collectively underline the positive influence of AAs on phenol content, essential oil yield, and composition, offering valuable insights for improving the phytochemical profile of various plant species.
Interestingly, our results show variations in the quantities of different compounds based on the AA treatments. Notably, the application of Phe at 300 mg/L led to significant alterations in the chemical composition of the extract, resulting in increased quantities of certain phenolic and flavonoid compounds. This suggests that the foliar application of AAs can effectively modulate the synthesis of specific compounds in bitter gourd, potentially contributing to its health-promoting attributes. The implications of our findings hold significance for both agricultural practices and human health. The ability to enhance the TPC, TFC, and antioxidant properties of bitter gourd through foliar spray treatments with AAs offers promising prospects for sustainable agriculture. These treatments have the potential to improve crop yield and quality, thereby contributing to the overall productivity of bitter gourd cultivation. Furthermore, the enriched chemical composition of bitter gourd can enhance its nutritional value and health-promoting properties, further emphasizing the importance of the present study.
5. Conclusions
The present study sheds light on the potential impact of AA foliar applications on the growth, yield, and antioxidant properties of the bitter gourd plant. Recognized for its pharmacological benefits, bitter gourd has shown promise for further enhancement through strategic AAs use. Key findings highlight that Trp at 300 mg/L had the most substantial effect on increasing plant length, with Phe at the same concentration yielding notable results. Additionally, remarkable improvements in various yield parameters, including fresh and dry plant weights, fresh weight of the first fruit, fruit number per plant, fresh weight of fruits per plant, and total fruit yield per hectare, were observed with Trp at 300 mg/L and Gln at 300 mg/L, emphasizing their practical significance for yield enhancement. Furthermore, Phe, at a dosage of 300 mg/L, exhibited the highest levels of TPC and TFC, along with potent scavenging activity against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl, underscoring its potential as an inducer of antioxidant compounds. These outcomes reveal the promising potential of Trp, Gln, and Phe foliar sprays to optimize bitter gourd growth, yield, and the concentration of specific antioxidant compounds. The practical implications of our research are noteworthy, offering a strategic approach for enhancing bitter gourd cultivation. This has far-reaching implications for sustainable agricultural practices and contributes to the agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors by elevating both the nutritional and medicinal attributes of this remarkable crop.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek) and N.S.; methodology, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek) and N.S.; software, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek) and N.S.; validation, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohssen Elbagory), M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), N.A., I.M., A.E.-D.O. and N.S.; formal analysis, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M. and N.S.; investigation, M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M., A.E.-D.O. and N.S.; resources, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek) and N.S.; data curation, L.E.-K., M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek) and N.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M. and A.E.-D.O.; writing—review and editing, M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M. and A.E.-D.O.; visualization, M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M. and A.E.-D.O.; supervision, M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek), I.M. and A.E.-D.O.; project administration, L.E.-K. and M.E. (Mohamed Elsadek); funding acquisition, M.E. (Mohssen Elbagory). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University through the Larg Groups Project under grant number: RGP2/164/44.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
All of the authors are grateful for the support provided by the Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Egypt, and the Soils, Water, and Environment Research Institute (SWERI), Agriculture Research Center (ARC), Egypt. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the Larg Groups Project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Behera, T.K.; Staub, J.; Behera, S.; Simon, P.W. Bitter gourd and human health. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, B.; Jini, D. Antidiabetic effects of Momordica charantia (bitter melon) and its medicinal potency. Asian Pacific J. Trop. Dis. 2013, 3, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Polito, L. Momordica charantia, a nutraceutical approach for inflammatory related diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, D. Medicinal Plants of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh; Daya Publishing House: Delhi, India, 2008; ISBN 10: 8170355672. [Google Scholar]
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino Acid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Fan, X.; Shen, Q.; Smith, S.J. Amino acids and nitrate as signals for the regulation of nitrogen acquisition. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, T.M.; Nunes Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L.; Braun, H.P. Amino Acid Catabolism in Plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillitteri, L.J.; Bertling, I.; Khuong, T.; Chao, C.T.; Lovatt, C.J. Foliar-applied tryptophan increases total yield and fruit size of navel orange and clementine mandarin. Acta Hortic. 2010, 884, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.B. Foliar application of amino acids modulates growth and biochemical parameters in wheat under drought stress conditions. Plants Physiol. Mol. Biol. 2019, 25, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant phenolics: Extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhanhani, A.R.H.; Kaur, N.; Ahmed, Z.F.R. Antioxidant phytochemicals and antibacterial activities of sidr (Ziziphus spp.) leaf extracts. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1353, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, D.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Jeon, J.; Park, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.U. Identification and characterization of phenylpropanoid biosynthetic genes and their accumulation in bitter melon (Momordica charantia). Molecules 2018, 23, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathry, K.S.; John, J.A. A comprehensive review on bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) as a gold mine of functional bioactive components for therapeutic foods. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2022, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Xie, J.H.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, Y. Ethanol modified supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of flavonoids from Momordica charantia L. and its antioxidant activity. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Parks, S.; Roach, P. An optimised aqueous extract of phenolic compounds from bitter melon with high antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Qin, J.; Hong, T.; Nguyen, N.; Liu, D.; Gan, H.; Ding, S.; Luo, Z.-B. Phenylalanine as a nitrogen source induces root growth and nitrogen-use efficiency in Populus × canescens. Tree Physiol. 2017, 38, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, J.; Serrani-Yarce, J.C.; Chen, F.; Baxter, D.; Venables, B.J.; Dixon, R.A. Role of bifunctional ammonia-lyase in grass cell wall biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, B.J.; Stine, Z.E.; Dang, C.V. From Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croteau, R.; Kutchan, T.M.; Lewis, N.G. Natural Products (Secondary Metabolites). In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants; Buchanan, B., Gruissem, W., Joneas, R., Eds.; American Society of Plant Biologists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 1250–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, M.; El-Azaz, J.; de la Torre, F.; Cañas, R.; Avila, C.; Cánovas, F. Biosynthesis and metabolic fate of phenylalanine in conifers. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Pentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1973; pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of The Degtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckow, J.; Mielniczuk, J.; Knicker, H.; Bayer, C.; Dick, D.P.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Comparison of carbon and nitrogen determination methods for samples of a Paleudult subjected to no-till cropping systems. Sci. Agric. 2007, 64, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Method of Soil Analysis. Chemical and Biological Properties; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeneys, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar-ul-hye, M.; Naeem, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, M.J.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Brtnicky, M.; Kintl, A.; Hussain, M.S.; El-esawi, M.A. Effect of Cadmium-Tolerant Rhizobacteria on Growth Attributes and Chlorophyll Contents of Bitter Gourd under Cadmium Toxicity. Plants 2020, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reham, M.S.; Khattab, M.E.; Ahmed, S.S.; Kandil, M.A.M. Influence of foliar spray with phenylalanine and nickel on growth, yield quality and chemical composition of genoveser basil plant. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, T.; Sachet, K.; Al-Mohammad, M.H.S.; Abbass, J.A. Effect of Biofertilizer and Spraying Phenylalanine on Mineral Content and Antioxidant Compounds of Dill. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2021, 15, 5540–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.S.; Abdel-Alim, M.; Said, H.E.M.; Foda, M.F. Phenolic Profiles, Antihyperglycemic, Anti-Diabetic, and Antioxidant Properties of Egyptian Sonchus oleraceus Leaves Extract: An In Vivo Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawadio Nsimba, R.; Kikuzaki, H.; Konishi, Y. Antioxidant activity of various extracts and fractions of Chenopodium quinoa and Amaranthus spp. seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, A.A.; Gomez, J.D.; Vattuone, M.A. Antioxidant activities of Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz extracts. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Kagawa, H.; Yasuhara, T.; Okuda, T. Two new flavonoids and other constituents in licorice root: Their relative astringency and radical scavenging effects. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntic, V.; Pejic, N.; Ivkovic, B. Isocratic RP-HPLC method for rutin determinationin solid oral dosage forms. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 718–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lin, J. Composition of Polyphenols in fresh Tea Leaves and Associations of their Oxygen Radical Absorbing Capacity with Antiproliferative Actions in Fibroblast Cells. J. Agri. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedecor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods, 8th ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Zefzafy, M.; Shahhat, I.M.; Yousef, R.S.; Elsharkawy, E.R. Influence of foliar application with amino acids and citric acid on physiological and phytochemical responses of Artemisia abrotanum produced by in vitro culture. Biosci. Biotech. Res. Commun. 2016, 9, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kareem, A.A.; El-Shamy, H.A.; Dawh, A.K.; Gwiefel, S.G. Milk thistle growth, productivity and chemical constituents as affected by foliar application of phenylalanine and tryptophan. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2017, 44, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozlo, Y.A.; Souri, M.K.; Delshad, M. Effects of foliar application of glycine and glutamine amino acids on growth and quality of sweet basil. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2019, 33, 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Zahir, A.Z.; Malik, M.A.; Arshad, M. Improving crop yield by the application of an auxin precursor L-TRP. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2000, 3, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, M.M.; Faham, S.Y.; Alva, A.K. Role of Foliar Application of Nicotinic Acid and Tryptophan on Onion Plants Response to Salinity Stress. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 68, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, E.; Iglesias, D.; Manuel, T.; Rainer, B. Tryptophan-dependent production of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasevičienė, Z.; Aloyzas, V.; Aurelija, P. Impact of Foliar Application of Amino Acids on Total Phenols, Phenolic Acids Content of Different Mints Varieties under the Field Condition. Plants 2021, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velička, A.; Tarasevičienė, Ž.; Hallmann, E.K.-D. Impact of Foliar Application of Amino Acids on Essential Oil Content, Odor Profile, and Flavonoid Content of Different Mint Varieties in Field Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.; Gharib, F.; El-Awadia, M.; Rashad, E.S. Physiological response of onion plants to foliar application of putrescine and glutamine. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, K.; Aminah, A.; Zuhair, A. Evaluation of bitter melon (Momordica charantia) extract administration in the antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of plasma and liver in male rat. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.P.; Gao, Z.K.; Li, J.T.; Xu, G.H.; Wang, M. Effects of extraneous glutamic acid on nitrate contents and quality of Chinese chive. Acta Hortic. 2010, 856, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feduraev, P.; Skrypnik, L.; Riabova, A.; Pungin, A.; Tokupova, E.; Maslennikov, P.; Chupakhina, G. Phenylalanine and Tyrosine as Exogenous Precursors of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Secondary Metabolism through PAL-Associated Pathways. Plants 2020, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendy, A.S.; Nosir, W.S. Improving productivity and chemical constituents of Roselle plant (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as affected by phenylalanine, L-tryptophan and peptone acids foliar application. Middle East J. Agric. 2016, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, A.M.; Abd-ElShafy, E.; Abu-Khudir, R.; Gaafar, R.M. Influence of gamma radiation and phenylalanine on secondary metabolites in callus cultures of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L.). J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, Y.A.; El-Naem, A.; Gamal, F.; Mahmoud, M.A. Effect of tryptophan and ascorbic acid on yield and some chemical constituents of lupine (Lupines termis L.) plants. Egypt. J. Agron. 2020, 42, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Klimek-Szczykutowicz, M.; Dziurka, M.; Blažević, I.; Đulović, A.; Miazga-Karska, M.; Klimek, K.; Ekiert, H.; Szopa, A. Precursor-Boosted Production of Metabolites in Nasturtium officinale Microshoots Grown in Plantform Bioreactors, and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Biomass Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Thomas, J. Flavonoids from cell suspension culture of Ocimum tenuiflorum and its enhancement using response surface methodology. Drug Inven. Today 2019, 11, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.; Mallick, B.; Samanta, D. Augmentation of antioxidative potential of in vitro propagated Mentha piperita L. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 58, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Alper, M.; Özay, C. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Composition of Ethanol Extracts of Momordica charantia and Datura stramonium. J. Agric. Nat. 2022, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorghadir, M.; Torkashvand, A.M.; Mirjalili, S.A.; Moradi, P. Interactions of amino acids (proline and phenylalanine) and biostimulants (salicylic acid and chitosan) on the growth and essential oil components of savory (Satureja hortensis L.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).