Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase Addition on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Bacteria Composition of Low Water-Soluble Carbohydrates Oat Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Preparation and Treatments
2.2. Chemical Composition and Fermentation Composition
2.3. Microbial Sequencing
2.4. Aerobic Stability
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Oat before Ensiling
3.2. Nutrient Composition of Oat during Different Treatments and Periods of Ensiling
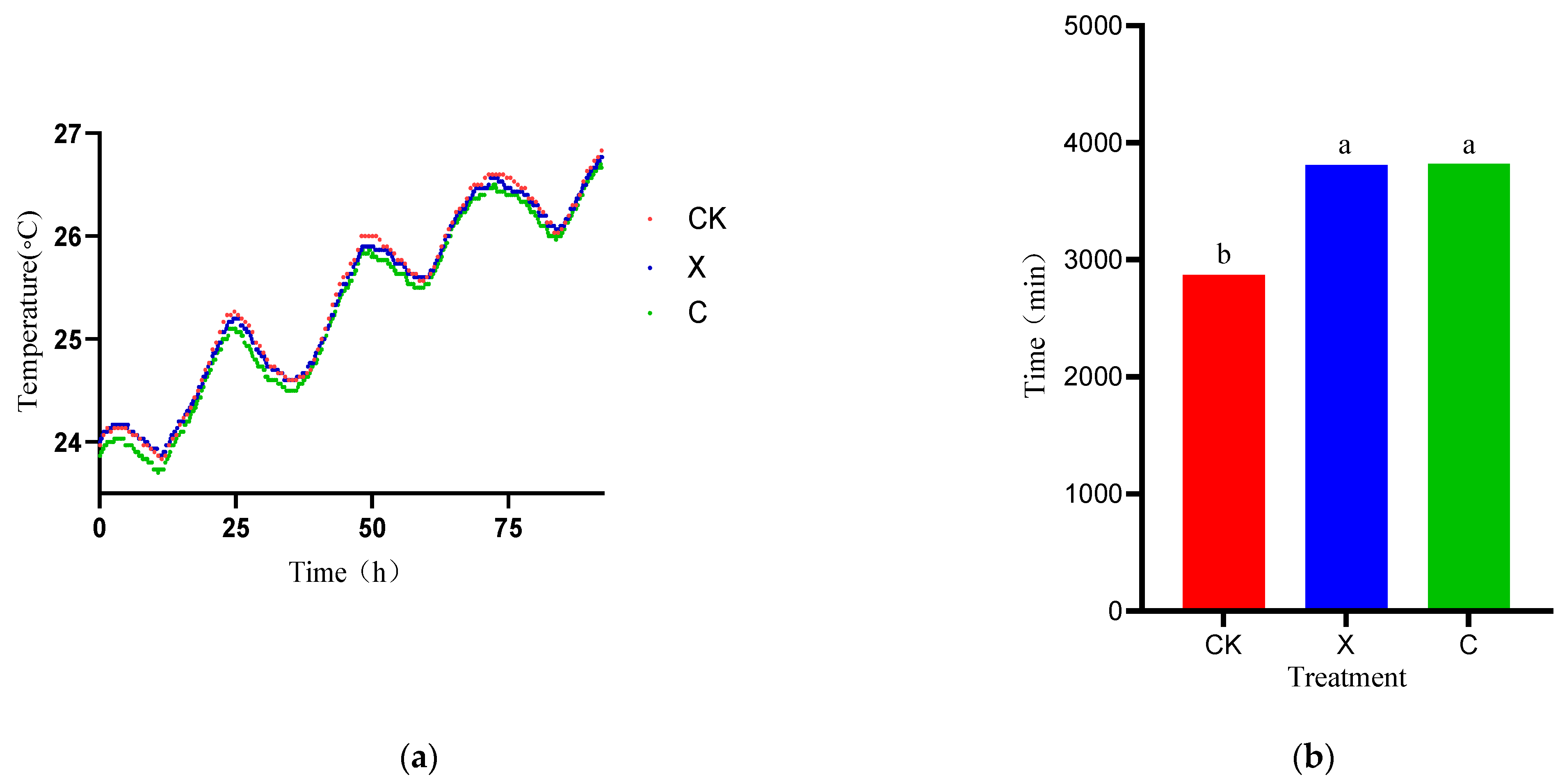
3.3. Dynamics of Temperature Fermentation Quality of Oat during Different Treatments and Periods of Ensiling
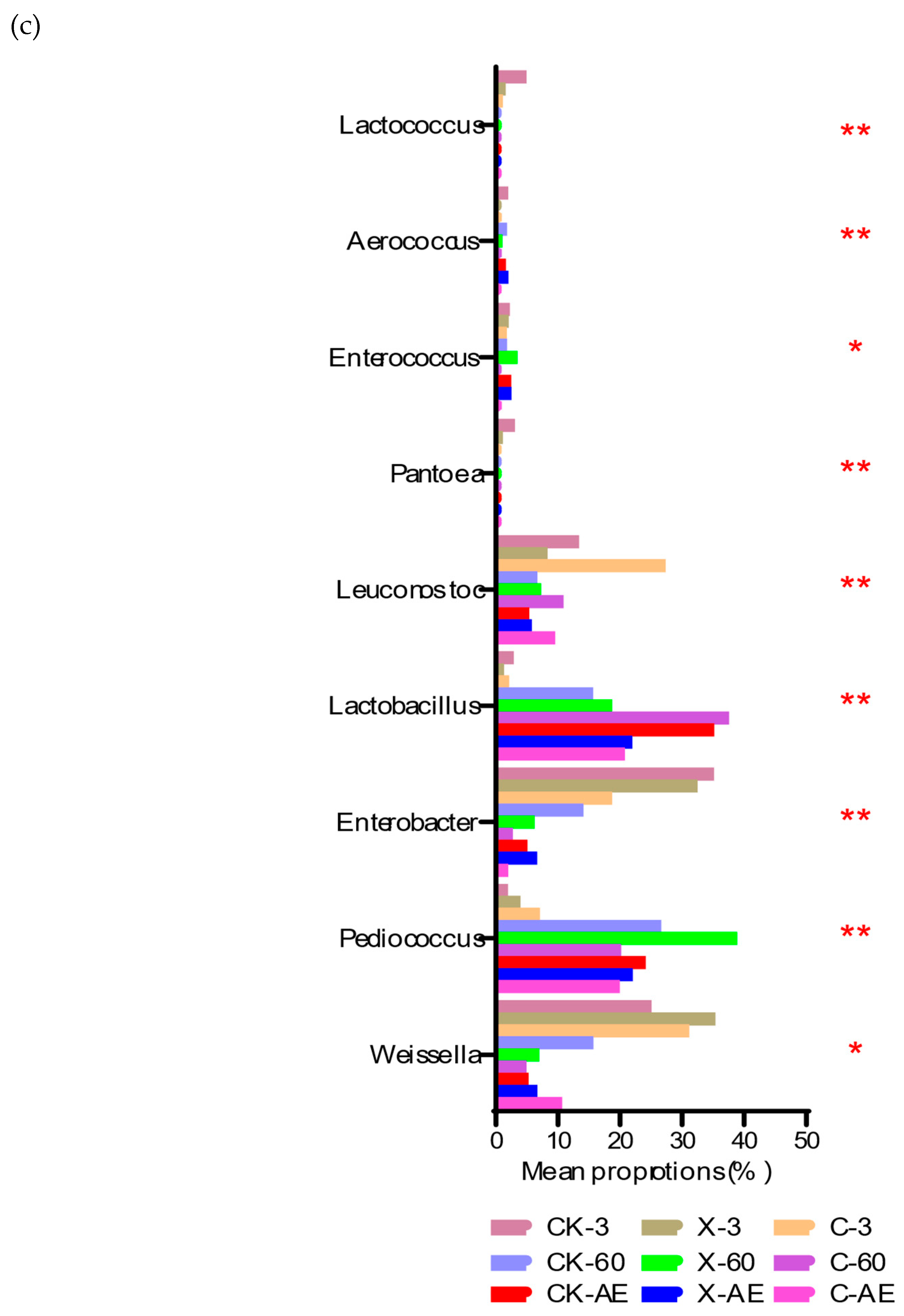
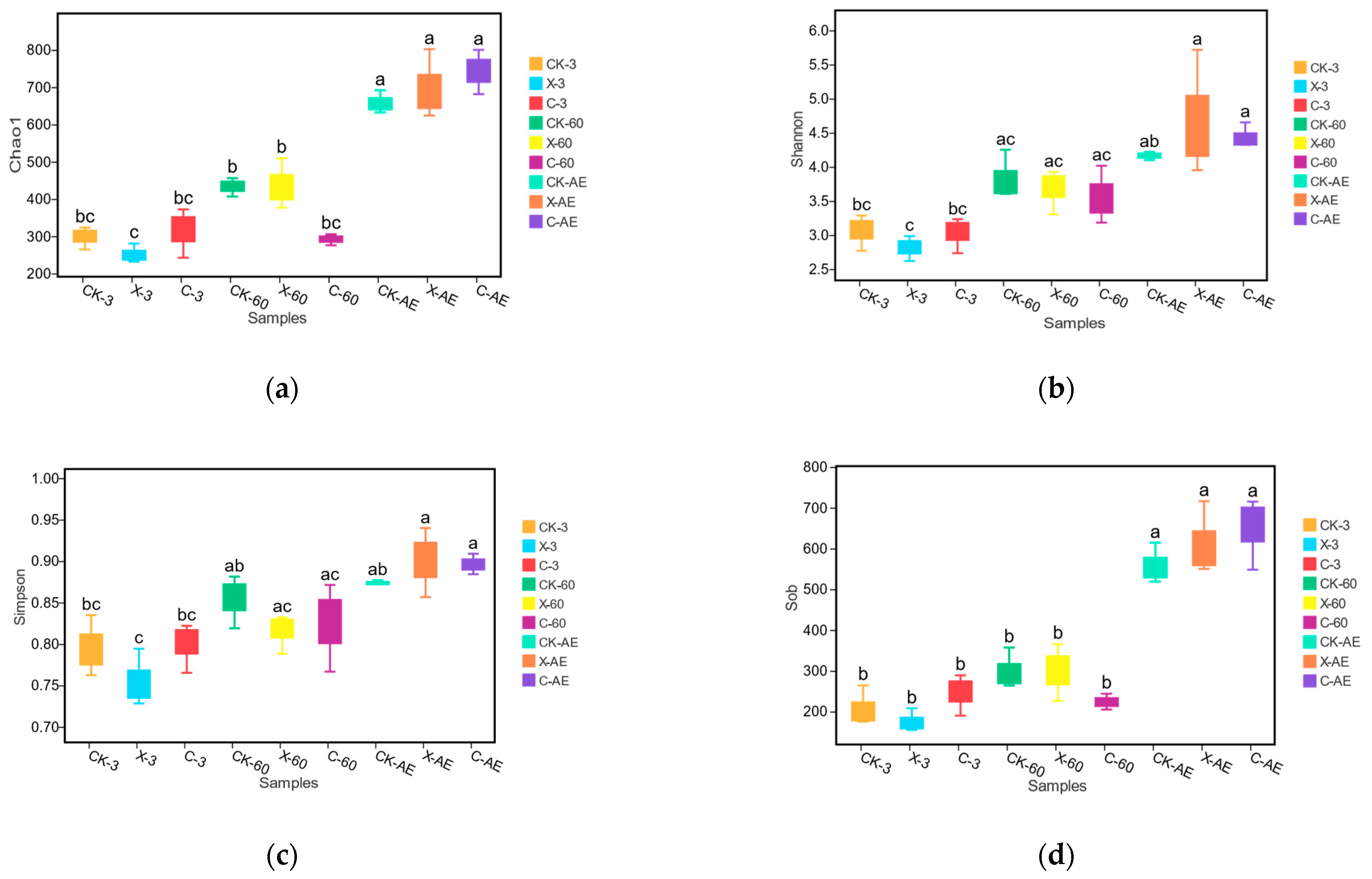
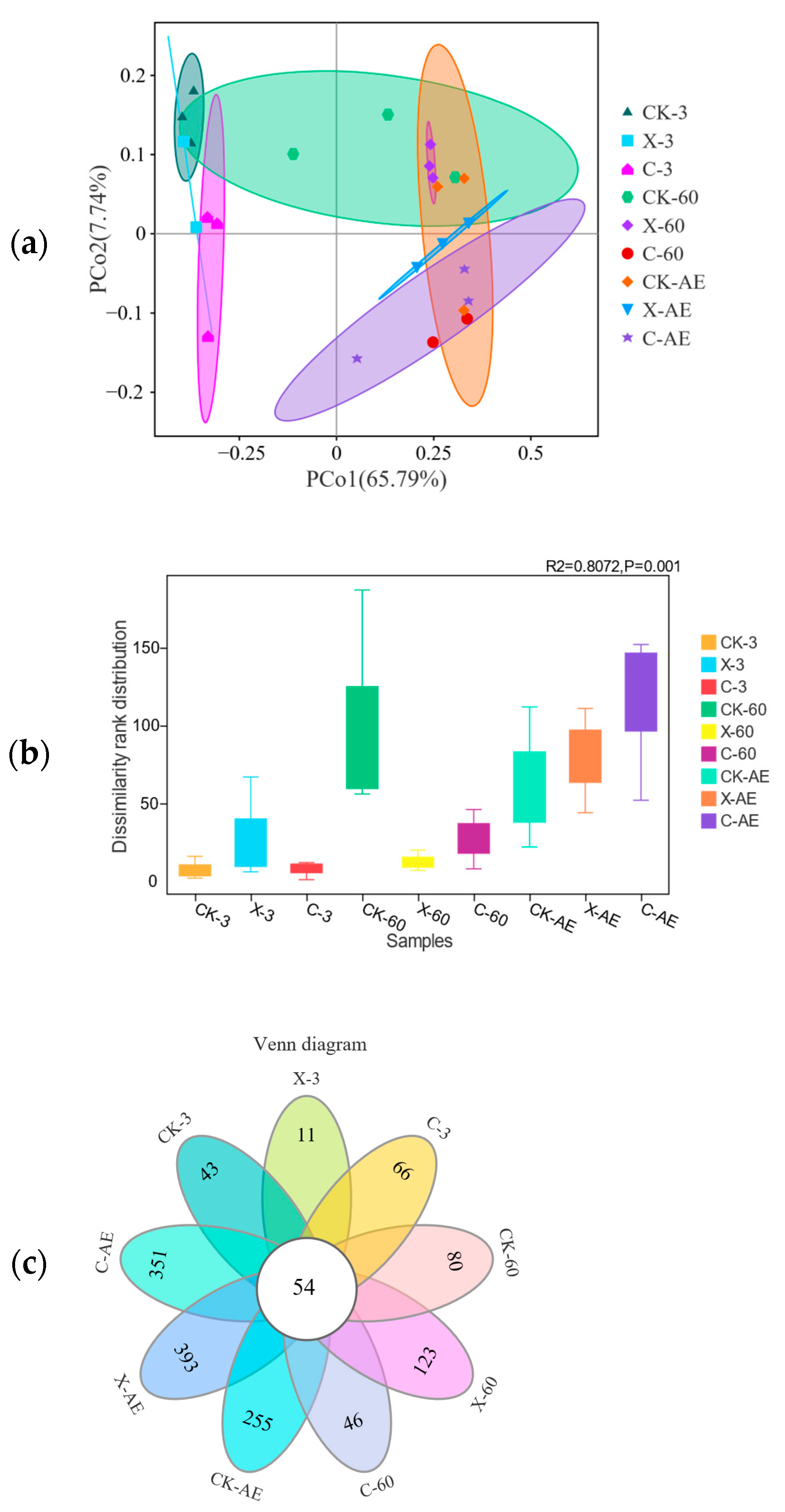
3.4. Microbial Community of Oat Silage during Different Treatments and Periods of Ensiling
4. Discussion
4.1. Material Characteristics and Silage Quality
4.2. Microbial Community in Silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Himmel, M.E.; Ding, S.-Y.; Johnson, D.K.; Adney, W.S.; Nimlos, M.R.; Brady, J.W.; Foust, T.D. Biomass Recalcitrance: Engineering Plants and Enzymes for Biofuels Production. Science 2007, 315, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytioja, J.; Hilden, K.; Yuzon, J.; Hatakka, A.; de Vries, R.P.; Makela, M.R. Plant-polysaccharide-degrading enzymes from Basidiomycetes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 614–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, P. General background on microbial xylanolytic enzymes. In Microbial Xylanolytic Enzymes; Bajpai, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Kanpur, India, 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.H.; Takiya, C.S.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Jesus, E.F.d.; Zanferari, F.; Rennó, F.P. Effects of dietary fibrolytic enzymes on chewing time, ruminal fermentation, and performance of mid-lactating dairy cows. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 221, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-C.; Guevara-Oquendo, V.H.; Refat, B.; Yu, P. Effects of Exogenous Fibrolytic Enzyme Derived from Trichoderma reesei on Rumen Degradation Characteristics and Degradability of Low-Tannin Whole Plant Faba Bean Silage in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy 2022, 3, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wang, W.K.; Wu, Q.C.; Yang, H.J. The release and catabolism of ferulic acid in plant cell wall by rumen microbes: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenja, K.; Qendrim, Z. A review on the potentials of using feeds rich in water-soluble carbohydrates to enhance rumen health and sustainability of dairy cattle production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Dong, D.; Shao, T. Effect of epiphytic microbiota from napiergrass and Sudan grass on fermentation characteristics and bacterial community in oat silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.C.; Silvello, M.A.; Goldbeck, R. Cellulase and oxidative enzymes: New approaches, challenges and perspectives on cellulose degradation for bioethanol production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizeli, M.L.; Rizzatti, A.C.; Monti, R.; Terenzi, H.F.; Jorge, J.A.; Amorim, D.S. Xylanases from fungi: Properties and industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Effects of Cellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality, Chemical Composition, and Microbial Community of Mixed Silage of Whole-Plant Corn and Peanut Vines. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, F.; Alborino, V.; Dini, I.; Balestrieri, A.; Marra, R.; Davino, R.; Di Francia, A.; Masucci, F.; Serrapica, F.; Vinale, F. In Vitro Application of Exogenous Fibrolytic Enzymes from Trichoderma Spp. to Improve Feed Utilization by Ruminants. Agriculture 2022, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Industrial applications of xylanases. In Microbial Xylanolytic Enzymes; Academic Press: Kidlington, UK, 2022; pp. 149–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of Cellulase, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Sucrose on Fermentation Parameters, Chemical Composition, and Bacterial Community of Hybrid Pennisetum Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Xie, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Cellulase interacts with Lactobacillus plantarum to affect chemical composition, bacterial communities, and aerobic stability in mixed silage of high-moisture amaranth and rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewpila, C.; Thip-uten, S.; Cherdthong, A.; Khota, W. Impact of Cellulase and Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculant to Modify Ensiling Characteristics and In Vitro Digestibility of Sweet Corn Stover and Cassava Pulp Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.T.; Mann, S.P.; Charley, R.C.; Parfitt, D. Formulation for Treating Silage Containing β-1,4-Xylanase and β-1,3-Xylosidase but Essentially Free of β-1,4-Glucanase and β-1,4-Cellobiohydrolase, and One or More Lactic Acid-Producing Bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 1996, 83, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of lactobacillus spp. from An inoculant and of weissella and leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.; Mugabe, W.; Shao, T. Characterization of Enterococcus faecalis JF85 and Enterococcus faecium Y83 isolated from Tibetan yak (Bos grunniens) for ensiling Pennisetum sinese. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.V.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, C.M.; Artuso-Ponte, V.; Stein, H.H. Effects of isoquinoline alkaloids on apparent ileal digestibility of amino acids, crude protein, starch, and acid hydrolyzed ether extract and apparent total tract digestibility of energy and crude protein by growing and finishing pigs fed corn-soybean meal diets. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 299, 115623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprys-Caruk, M.; Choinska, R.; Dekowska, A.; Piasecka-Jozwiak, K. Silage quality and biogas production from Spartina pectinata L. fermented with a novel xylan-degrading strain of Lactobacillus buchneri M B/00077. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, L.J.; Kung, L. Effects of combining Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 with various lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 159, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, T.; Du, Z.; Dong, X.; Xin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Kang, B.; Jiang, D.; et al. Assessment on the Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Mixed Silage of Faba Bean With Forage Wheat or Oat. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 875819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.H. Theoretical Carbohydrates Requirement for Alfalfa Silage Production. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.M. The Biochemistry of Silage. Exp. Agric. 1982, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zong, C.; Dong, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, T. Effects of cellulolytic lactic acid bacteria on the lignocellulose degradation, sugar profile and lactic acid fermentation of high-moisture alfalfa ensiled in low-temperature seasons. Cellulose 2020, 27, 7955–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.Z.M.; Buendía-Rodríguez, G.; Elghandour, M.M.M.; Berasain, M.A.M.; Jiménez, F.J.P.; Pliego, A.B.; Chagoyán, J.C.V.; Cerrillo, M.A.; Rodríguez, M.A. Effects of cellulase and xylanase enzymes mixed with increasing doses of Salix babylonica extract on in vitro rumen gas production kinetics of a mixture of corn silage with concentrate. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jia, S.; Yang, F.; et al. Impacts of Low Temperature and Ensiling Period on the Bacterial Community of Oat Silage by SMRT. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Risu, N.; Gentu, G.; Jia, Y.; Cai, Y. Dynamic changes and characterization of the protein and carbohydrate fractions of native grass grown in Inner Mongolia during ensiling and the aerobic stage. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, F.; Rao, D.; Shen, P.; Fang, S.; Wu, B. Prolonged drought regulates the silage quality of maize (Zea mays L.): Alterations in fermentation microecology. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1075407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.E.; Foster, J.L.; McCuistion, K.C.; Redmon, L.A.; Jessup, R.W. Nutritive value, fermentation characteristics, and in situ disappearance kinetics of sorghum silage treated with inoculants. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7120–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, M.; de Morais, J.P.G.; Capucho, E.; Garcia, T.M.; Pedrini, C.A.; Gandra, J.R.; Valle, T.A.D. Fibrolytic Enzymes Increase Fermentation Losses and Reduce Fiber Content of Sorghum Silage. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Lv, R.; Zhou, H.; Tang, J. Effects of Citric Acid and Lactobacillus plantarum on Silage Quality and Bacterial Diversity of King Grass Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, S.; You, M.; Xiao, B.; Li, P.; Cai, Y. Effect of a low temperature tolerant lactic acid bacteria inoculant on the fermentation quality and bacterial community of oat round bale silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 269, 114669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Kaka, N.A.; Shao, T. Sequencing and microbiota transplantation to determine the role of microbiota on the fermentation type of oat silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Shao, T. Effects of Freeze-Thaw Event on Microbial Community Dynamics During Red Clover Ensiling. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoyan, W.; Charles, A.; Zhaojing, Y.; Jiaokun, L.; Yuandong, L.; Li, S.; Runlan, Y.; Xueling, W.; Xuewen, X.; Shiyong, T.; et al. Evaluation of fungal community assembly and function during food waste composting with Aneurinibacillus sp. LD3 inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.; Yang, H.E.; Redman, A.A.; Chevaux, E.; Drouin, P.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Effects of a mixture of Lentilactobacillus hilgardii, Lentilactobacillus buchneri, Pediococcus pentosaceus and fibrolytic enzymes on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and performance of growing beef cattle. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureenok, S.; Langsoumechai, S.; Pitiwittayakul, N.; Yuangklang, C.; Vasupen, K.; Saenmahayak, B.; Schonewille, J.T. Effects of fibrolytic enzymes and lactic acid bacteria on fermentation quality andin vitrodigestibility of Napier grass silage. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, B.; Marcia, F.; Zitong, D.; Lin, H.; Wencan, K.; Musen, W.; Dongmei, X.; Ziqian, L.; Yixin, Z.; Lin, A.; et al. Effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis on fermentation, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts of whole-plant corn silage. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, M.; Pan, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C.; Xue, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis or Lentilactobacillus buchneri on aerobic stability, and the microbial community in aerobic exposure of whole plant corn silage. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1177031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

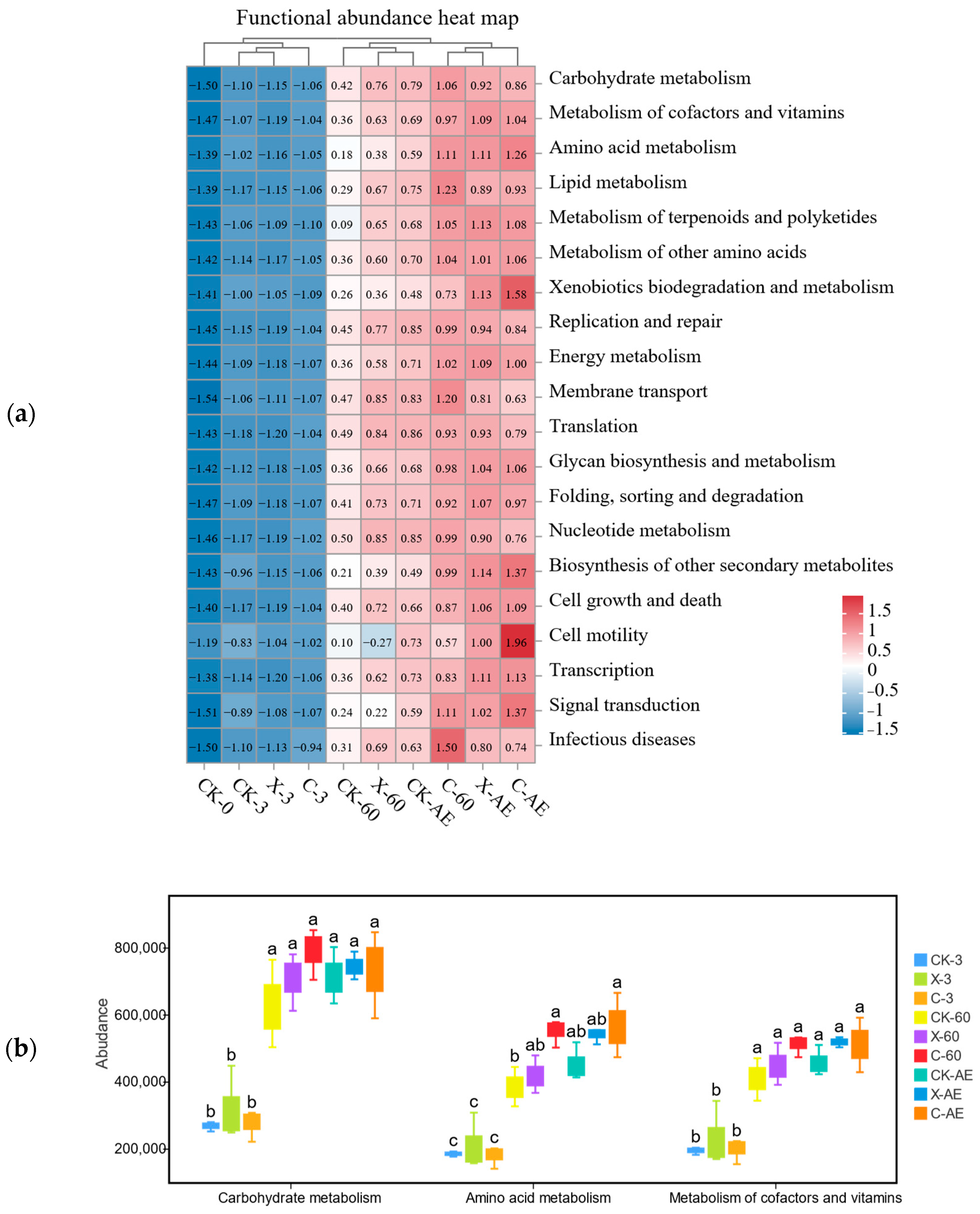

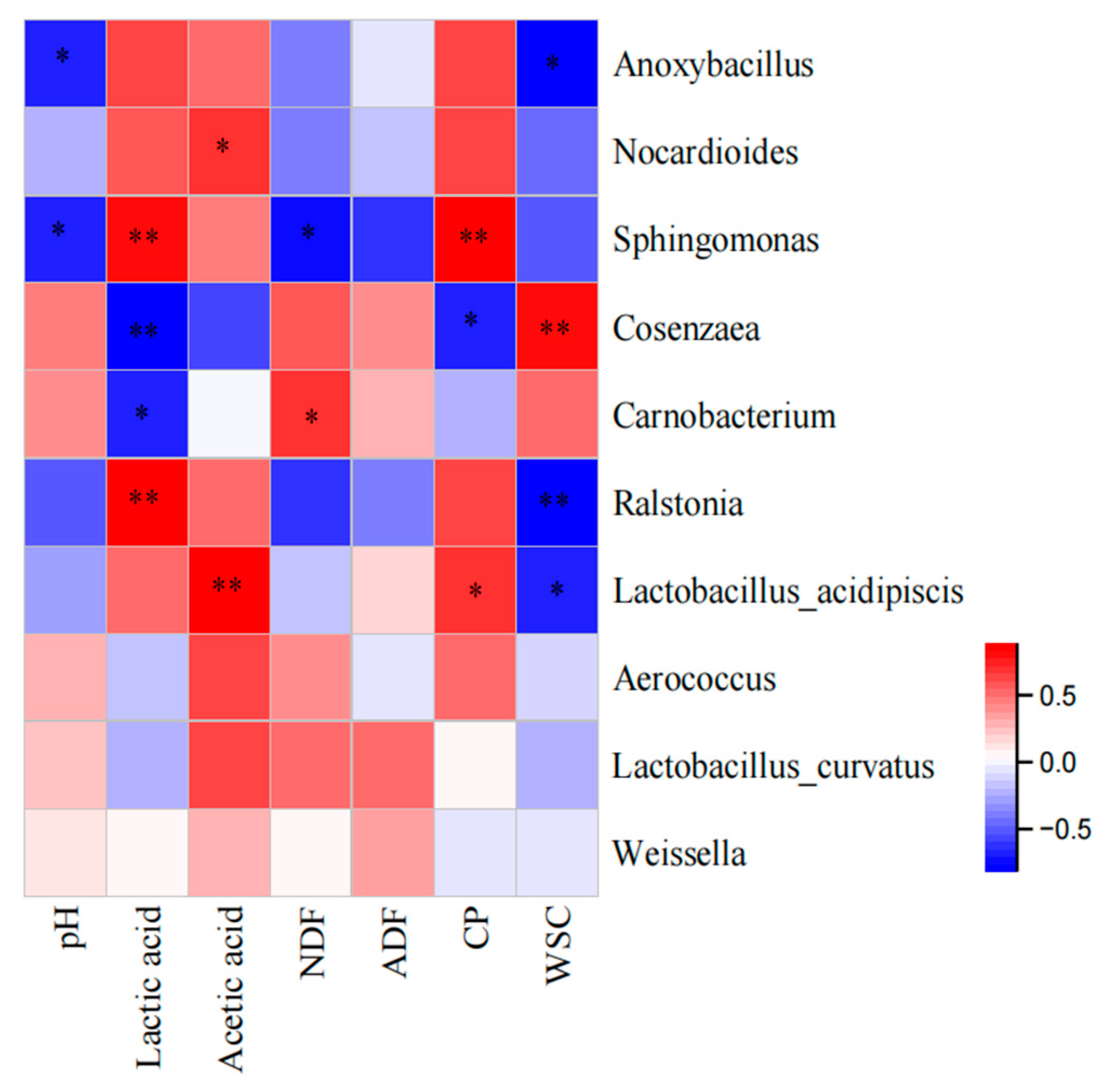
| Items | Oat Silage | SEM |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.41 | 0.014 |
| DM (g/kg FW) | 290.24 | 0.218 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 663.04 | 0.455 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 378.19 | 0.325 |
| ADL (g/kg DM) | 56.80 | 0.149 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 123.47 | 0.068 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 62.13 | 0.087 |
| Ash (g/kg DM) | 62.19 | 0.056 |
| EE (g/kg DM) | 15.50 | 0.145 |
| LAB (lg CFU/g) | 1.51 | 0.006 |
| Yeast (lg CFU/g) | 2.01 | 0.038 |
| Items 1 | Treatment 2 | Ensilage Period 3 | Mean 4 | SEM 5 | Signifificance 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 60 | AE | T | D | T × D | ||||
| CK | 297.05 bA | 307.77 aA | 295.75 b | 300.19 A | 0.620 | ||||
| DM (g/kg FW) | X | 287.02 bB | 297.25 aB | 296.43 a | 293.57 B | 0.120 | ns | ns | ns |
| C | 295.11 A | 294.12 B | 292.62 | 293.95 B | 0.609 | ||||
| CK | 638.54 aA | 607.34 cA | 627.40 bA | 624.43 A | 0.172 | ||||
| NDF (g/kg DM) | X | 626.70 aB | 568.63 bB | 576.15 bB | 590.49 B | 0.870 | ** | ** | ** |
| C | 602.49 aC | 550.77 bB | 545.79 bB | 566.35 C | 0.429 | ||||
| CK | 329.44 bB | 346.58 aA | 357.01 aA | 344.34 A | 0.329 | ||||
| ADF (g/kg DM) | X | 344.90 aA | 321.35 bB | 305.30 bB | 323.85 B | 0.301 | ** | ** | ** |
| C | 339.31 aB | 308.22 bB | 315.48 bB | 321.00 B | 0.514 | ||||
| CK | 46.53 | 42.95 | 49.89 A | 46.46 | 0.297 | ||||
| ADL (g/kg DM) | X | 50.46 a | 45.72 b | 36.95 cB | 44.38 | 0.329 | ns | ns | * |
| C | 51.64 a | 50.66 a | 44.85 bA | 49.05 | 0.086 | ||||
| CK | 309.10 aA | 260.76 bA | 270.39 bA | 280.08 A | 0.379 | ||||
| Hemicellulose (g/kg DM) | X | 281.80 aB | 247.28 bB | 240.85 bB | 266.64 B | 0.834 | ** | ** | ns |
| C | 263.18 aB | 242.56 bB | 230.31 bB | 245.35 C | 0.690 | ||||
| CK | 282.91 b | 303.63 aA | 307.11 aA | 297.88 A | 0.397 | ||||
| Cellulose (g/kg DM) | X | 294.44 a | 275.63 bB | 268.35 bB | 279.47 B | 0.435 | ns | ** | ** |
| C | 287.67 a | 257.56 bB | 276.97 bB | 274.07 B | 0.504 | ||||
| CK | 133.87 bA | 143.04 a | 143.65 a | 140.23 | 0.011 | ||||
| CP (g/kg DM) | X | 124.51 bB | 144.68 a | 145.19 a | 138.25 | 0.012 | ns | ** | ** |
| C | 134.35 bA | 142.72 a | 142.10 a | 139.87 | 0.012 | ||||
| CK | 31.52 a | 17.89 bB | 16.19 cb | 21.87 | 0.054 | ||||
| WSC (g/kg DM) | X | 30.80 a | 21.90 bA | 16.66 c | 23.12 | 0.097 | ns | ** | ** |
| C | 33.08 a | 16.58 bB | 17.09 b | 22.25 | 0.075 | ||||
| CK | 18.26 b | 27.23 a | 23.85 b | 23.11 | 0.129 | ||||
| EE (g/kg DM) | X | 17.98 b | 28.02 a | 24.48 b | 23.49 | 0.143 | ** | ns | ns |
| C | 19.95 b | 27.76 a | 21.81 b | 23.17 | 0.159 | ||||
| Items | Treatment 1 | Ensilage Period 2 | Mean 3 | SEM 4 | Signifificance 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 60 | AE | T | D | T × D | ||||
| CK | 4.97 a | 4.63 Ab | 4.91 Aa | 4.84 A | 0.058 | ||||
| pH | X | 4.85 a | 4.46 Bb | 4.65 Bb | 4.65 B | 0.095 | ** | ** | ns |
| C | 4.94 a | 4.39 Bc | 4.59 Bb | 4.64 B | 0.043 | ||||
| CK | 7.02 B | 24.36 aC | 22.32 bC | 17.90 B | 0.397 | ||||
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | X | 8.80 bA | 31.90 aB | 32.08 aB | 24.26 A | 0.320 | ** | ** | ** |
| C | 9.05 cA | 35.98 bA | 40.25 aA | 28.43 A | 0.325 | ||||
| CK | 1.29 bA | 1.43 aA | 1.53 aA | 1.42 | 0.028 | ||||
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | X | 0.88 bB | 1.36 aB | 1.41 aB | 1.22 | 0.050 | ** | ** | ** |
| C | 0.88 bB | 1.22 aB | 1.35 aB | 1.15 | 0.021 | ||||
| CK | 2.92 | 3.19 | 3.35 | 3.15 | 0.320 | ||||
| Propionic acid (g/kg DM) | X | 2.60 | 2.51 | 2.60 | 2.57 | 0.037 | ** | ns | ns |
| C | 2.49 | 2.48 | 2.46 | 2.48 | 0.097 | ||||
| CK | 2.92 | 3.19 | 3.35 | 3.15 | 0.320 | ||||
| Butyric acid (g/kg DM) | X | 2.60 | 2.51 | 2.60 | 2.57 | 0.037 | ns | ** | ns |
| C | 2.49 | 2.48 | 2.46 | 2.48 | 0.097 | ||||
| CK | 19.04 Bc | 39.45 Bb | 43.75 Ca | 34.08 B | 0.397 | ||||
| NH3-N (g/kg DM) | X | 21.70 Ac | 47.25 Ab | 51.97 Ba | 40.31 A | 0.766 | ** | ** | ** |
| C | 23.23 Ac | 51.08 Ab | 56.14 Aa | 43.48 A | 0.528 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Si, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Du, S.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase Addition on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Bacteria Composition of Low Water-Soluble Carbohydrates Oat Silage. Fermentation 2023, 9, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070638
Liu W, Si Q, Sun L, Wang Z, Liu M, Du S, Ge G, Jia Y. Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase Addition on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Bacteria Composition of Low Water-Soluble Carbohydrates Oat Silage. Fermentation. 2023; 9(7):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070638
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, Qiang Si, Lin Sun, Zhijun Wang, Mingjian Liu, Shuai Du, Gentu Ge, and Yushan Jia. 2023. "Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase Addition on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Bacteria Composition of Low Water-Soluble Carbohydrates Oat Silage" Fermentation 9, no. 7: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070638
APA StyleLiu, W., Si, Q., Sun, L., Wang, Z., Liu, M., Du, S., Ge, G., & Jia, Y. (2023). Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase Addition on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Bacteria Composition of Low Water-Soluble Carbohydrates Oat Silage. Fermentation, 9(7), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070638








