Abstract
The global production of fossil-based plastics has reached critical levels, and their substitution with bio-based polymers is an urgent requirement. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) is a biopolymer that can be produced via microbial cultivation, but efficient microorganisms and low-cost substrates are required. Halomonas boliviensis LC1, a moderately halophilic bacterium, is an effective PHB producer, and hydrolysates of the residual stalks of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) can be considered a cheap source of sugars for microbial fermentation processes in quinoa-producing countries. In this study, H. boliviensis LC1 was adapted to a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks obtained via acid-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification. The adapted strain was cultivated in hydrolysates and synthetic media, each of them with two different initial concentrations of glucose. Cell growth, glucose consumption, and PHB formation during cultivation were assessed. The cultivation results showed an initial lag in microbial growth and glucose consumption in the quinoa hydrolysates compared to cultivation in synthetic medium, but after 33 h, the values were comparable for all media. Cultivation in hydrolysates with an initial glucose concentration of 15 g/L resulted in a higher glucose consumption rate (0.15 g/(L h) vs. 0.14 g/(L h)) and volumetric productivity of PHB (14.02 mg/(L h) vs. 10.89 mg/(L h)) than cultivation in hydrolysates with 20 g/L as the initial glucose concentration. During most of the cultivation time, the PHB yield on initial glucose was higher for cultivation in synthetic medium than in hydrolysates. The produced PHBs were characterized using advanced analytical techniques, such as high-performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). HPSEC revealed that the molecular weight of PHB produced in the cellulosic hydrolysate was lower than that of PHB produced in synthetic medium. TGA showed higher thermal stability for PHB produced in synthetic medium than for that produced in the hydrolysate. The results of the other characterization techniques displayed comparable features for both PHB samples. The presented results show the feasibility of producing PHB from quinoa stalks with H. boliviensis.
1. Introduction
The exponential growth of industry during the last century has turned plastics into an indispensable everyday resource. The current global production of plastics exceeds 390 million tons per year [1], and a large amount of used plastic ends up as waste. The weight of plastic waste generated in 2020, more than 580 million tons [2], is more than the weight of the human population on Earth. Most of the currently used plastics are polymers produced from fossil resources, mainly from the petrochemical industry [3]. The high demand for plastics is due to their physical and mechanical properties. These properties also make most plastics non-biodegradable and extremely difficult to remediate, which makes them a significant environmental problem [4,5].
Microbial biopolymers, which are produced by different microorganisms, could be used as an alternative to reduce the use of fossil-based plastics. Microbial biopolymers include biological macromolecules, such as polysaccharides, polyamides, and polyesters [6,7]. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), which are polyesters, are among the most widely studied microbial biopolymers [8].
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) is a PHA that has steadily attracted considerable attention in recent years. It is produced by certain bacteria, and it is used as a reserve material. PHB accumulates intracellularly and is used either as energy storage in excess of carbon or as a protective agent under stress conditions [9]. PHB is fully biodegradable, biocompatible, and thermoplastic, which makes it suitable for replacing fossil-based plastics in various valuable applications. It can be used in bone tissue engineering [10], surgical sutures [11], and other plastic-requiring applications [8].
The production of microbial biopolymers is a rather straightforward process, but the feasibility of large-scale cultivation using pure sugars as substrates is restricted by high production costs [12]. Therefore, the use of inexpensive raw materials, such as agricultural and agro-industrial residues, for cultivating biopolymer-producing microorganisms is desirable to make their production economically viable [13,14]. The identification of microorganisms able to efficiently produce biopolymers by growing on substrates based on lignocellulosic materials is crucial for this purpose. Halomonas boliviensis is an extremophilic bacterium that was isolated from the Bolivian Altiplano, a habitat with high salinity and UV radiation in which most other microorganisms cannot survive. H. boliviensis has been identified as an effective producer of PHB [15,16].
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa), with a global production of more than 175,000 ton per year [17], is an important crop in many countries, especially in the Andean region, where Peru and Bolivia are the top global producers. Quinoa stalks, along with seed coats, are major residues generated during quinoa harvest. Although the use of quinoa stalks for energy generation has been considered [18], no high-value-added application has so far been implemented.
Quinoa stalks have a high polysaccharide content that makes them a relevant source of fermentable sugars, which can be released via pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification and used in biorefining [19,20,21]. Pretreatment liquids [22] and enzymatic hydrolysates [23] of quinoa stalks have previously been shown to be suitable for producing biopolymers, namely exopolysaccharides, through cultivation of the halotolerant bacterium Bacillus atrophaeus. It is of high scientific interest to investigate whether quinoa stalk hydrolysates are an appropriate substrate for producing other biopolymers, for instance, PHB, using H. boliviensis.
In this study, PHB production through the cultivation of H. boliviensis in cellulosic hydrolysates from quinoa stalks is reported for the first time. Cultivation in synthetic media was performed as a reference. Thorough characterization of the PHB produced from hydrolysates and synthetic media was performed using advanced analytical techniques, such as 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, high-performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
Halomonas boliviensis LC1 (NCBI:txid1072583), a moderately halophilic bacterial strain isolated from the Bolivian Andes [16], was used. The strain was maintained on modified tryptic soy agar (TSA) medium containing (in % (w/v)) NaCl (5.0), agar (1.5), tryptone (1.5), and soy peptone (0.5). The pH of the medium was adjusted to 7.5 with a 2 M aqueous solution of NaOH.
2.2. Raw Material
Stalks of royal quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.), collected from the Bolivian Altiplano, were used as a raw material for producing cellulosic hydrolysates. The stalks were milled and sieved to a particle size between 1 and 1.7 mm and subjected to the extraction of saponins. Extraction was performed according to a protocol previously described by Carrasco et al. [20].
2.3. Preparation of the Cellulosic Hydrolysate
2.3.1. Sulfuric Acid-Catalyzed Hydrothermal Pretreatment
Pretreatment was carried out in a 1 L pressurized benchtop reactor (Parr Instrument Co., Moline, IL, USA). Fifty grams (dry weight, DW) of saponin-free quinoa stalks were placed in the reactor vessel and mixed with a solution of dilute sulfuric acid at a loading of 0.2 g H2SO4 per 100 g of dry biomass. The liquid-to-solid ratio (LSR) was 9:1, and the total loading of the reactor was 500 g of the mixture. The pretreatment reaction was performed at 200 °C for 5 min. At the end of the pretreatment, the resulting slurry was vacuum filtered, thoroughly washed with deionized water until neutral pH, and stored at 4 °C until further use. Two pretreatment batches were run.
2.3.2. Enzymatic Saccharification
Two saccharification batches were prepared. In each batch, 30 g (DW) of pretreated stalks were suspended in 50 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 5) at a 10% (w/w) solid content. The suspension was placed in an orbital incubator (INFORS HT Ecotron, Bottmingen, Switzerland) at 45 °C and 170 rpm for one hour. Then, the enzyme blend Cellic CTec2 (obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) was added at a load of 200 CMCase units/g biomass, as in previous related research [23], and the mixture was incubated for 72 h under the same conditions. At the end of the saccharification process, the slurry was separated via vacuum filtration. The cellulosic hydrolysates, i.e., the liquid recovered from both saccharification experiments, were combined and stored at 4 °C for compositional analysis and subsequent use as culture media.
2.4. Media
If not stated otherwise, all chemicals used for the media were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich. Before use, the pH of all media was adjusted to 7.5 using a 5 M aqueous solution of NaOH.
Two synthetic media were used: a modified TSB (Tryptic Soy Broth) medium (SM-TSB), which was used for normal bacterial growth, and SM-PHB medium, which was used for PHB production. The SM-TSB medium contained (% (w/v)): NaCl (5.0), tryptone (1.5), soy peptone (0.5), and glucose (2.0). The SM-PHB medium contained (% (w/v)): NaCl (5.0), monosodium glutamate (0.2), K2HPO4 (0.35), NH4Cl (0.4), MgSO4·7 H2O (0.0038), Fe2SO4·7 H2O (0.00167), and glucose (either 1.0 or 1.5). The synthetic media were sterilized via autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min, except for the solutions of MgSO4·7 H2O and Fe2SO4·7 H2O, which were filter-sterilized using 0.20 µm Acrodisc syringe filters (Pall, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), and then, added to the autoclaved SM-PHB medium after cooling.
Cellulosic hydrolysate (CH) medium, prepared via dilution of the hydrolysates with ultrapure water, was used in the adaptation (CH-TSB medium, Section 2.5) and in PHB production (CH-PHB medium, Section 2.6). The carbon source in the CH-TSB medium was glucose (20 g/L), either as reagent-grade synthetic glucose or as part of a cellulosic hydrolysate that was gradually added during the adaptation. In the final adaptation stage, the carbon source of CH-TSB was exclusively the glucose of the hydrolysate. The cH-PHB medium used for PHB production contained the same salts in the same concentrations as those in the SM-PHB medium. The carbon source in the CH-PHB medium was glucose (either 15 or 20 g/L) from the cellulosic hydrolysate. CH-TSB and CH-PHB media were filter-sterilized using 0.20 µm rapid-flow disposable filter units with polyethersulfone (PES) membranes (Thermo Scientific, Tijuana, Mexico).
2.5. Adaptation
An initial experiment was conducted to test the tolerance of H. boliviensis LC1 to increasing concentrations of CH (5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, and 15% (v/v)). All media were supplemented with the nutrients used in the SM-PHB medium, and glucose was added so that the initial concentration was always 20 g/L, and the C/N ratio was maintained at 16.5. Cultivation was performed with shaking at 35 °C. Determination of the optical density (OD) at 600 nm was used to assess microbial growth.
After the initial test of the tolerance, adaptation was initiated using CH-TSB medium with 7.5% (v/v) hydrolysate in shake flasks at 35 °C. When vigorous growth was observed (OD ≥ 5), a portion of the culture was taken and inoculated into the medium containing 10% (v/v) hydrolysate using a 1:10 (v/v) inoculum-to-medium ratio. The operation was repeated consecutively with media containing increasing concentrations of hydrolysate. As the share of hydrolysate in the medium increased, the addition of synthetic glucose decreased, so that the initial glucose concentration always remained at 20 g/L.
After cultivation in media with two successive hydrolysate concentrations, for instance, 7.5% (v/v) and 10% (v/v), a portion of the culture was withdrawn, plated on solid TSA medium (described in 2.1), and incubated at 35 °C for 24 h. Then, a preculture was developed from a single colony, and the adaptation process was resumed (Figure 1a). The increase in the hydrolysate concentration during the whole adaptation sequence is shown in Figure 1b. When vigorous growth was observed in CH-TSB medium containing 40% (v/v) hydrolysate, a portion of the culture was transferred into CH-PHB medium containing 40% (v/v) of the hydrolysate and cultivated at 35 °C for 24 h. A portion of the resulting culture was withdrawn, plated on TSA medium, and incubated at 35 °C for 24 h. Single colonies of the plated culture, hereafter referred to as the adapted strain, were used in further cultivation experiments.
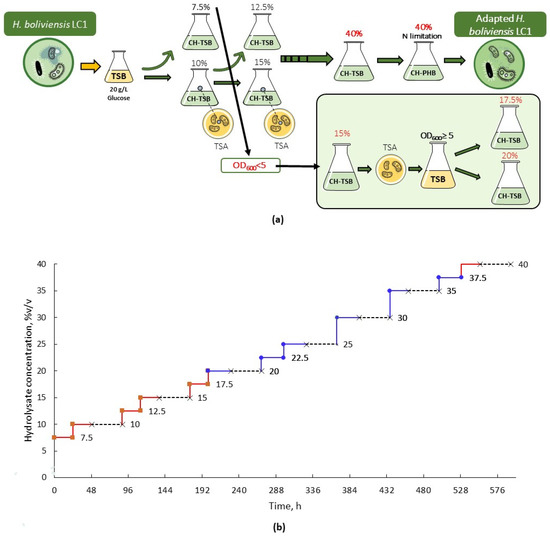
Figure 1.
Adaptation of H. boliviensis LC1 to cellulosic hydrolysates of quinoa stalks. (a) Overview of the adaptation operations. (b) Hydrolysate concentration (% (v/v)) during the adaptation process. The continuous lines show cultivation in CH-TSB medium. Red segments indicate cultivation periods of 24 h. Blue segments indicate cultivation periods longer than 24 h. The dotted lines represent periods of growth in solid medium and preculture development before a subsequent increase in hydrolysate concentration.
2.6. Bacterial Cultivation
The dynamics of bacterial growth and PHB formation were investigated in a first cultivation experiment. The cultivations were performed in 250 mL baffled flasks using 100 mL of either SM-PHB or CH-PHB medium. The glucose concentration in the SM-PHB medium was 15 g/L. The hydrolysate concentrations (17 and 33% (v/v)) in the CH-PHB media were within the range that the bacterial strain was adapted to (Section 2.5). This corresponded to glucose concentrations of 15 and 20 g/L. Pre-cultures of the adapted strain, inoculated from TSA agar plates, were grown at 35 °C and 200 rpm for 18 h in 1 L flasks with 250 mL of CH-TSB medium. The hydrolysate concentration in the preculture was 10% (v/v) to ensure vigorous pre-inoculum development. An OD600 of 5, corresponding to a bacterial biomass load of 1.7 g/L, was reached in the preculture, which was then inoculated into the cultivation medium at a 1:10 ratio. All the cultivations were performed in triplicate. Cultivation was carried out under the same conditions as previously described for 48 h. Microbial growth was monitored via OD measurements at 600 nm.
A second cultivation experiment, which aimed to produce enough PHB for a thorough characterization, was also performed. Two different cultivations were performed: one in SM-PHB, and one in CH-PHB. A preculture of the adapted bacterial strain was inoculated into SM-PHB and CH-PHB media, both with a glucose concentration of 10 g/L. The cultivation was performed at 35 °C and 200 rpm for 22 h.
2.7. Isolation, Purification, and Quantification of the PHB
Bacterial biomass was collected via centrifugation at 5000× g for 15 min at room temperature. Differential digestion of the non-PHB cellular materials was carried out by adding 5 mL of sodium hypochlorite (44 g/L active chlorine) to 5 mL of culture medium. Digestion was performed at 37 °C for 30 min, and the PHB was collected via centrifugation at 8000× g for 15 min. The PHB was thoroughly washed with ultrapure water to avoid the degrading effect of sodium hypochlorite, which could lead to a decrease in the molecular weight of the PHB. Finally, the PHB was freeze-dried and stored at 4 °C for further analysis.
PHB was quantified using the Law and Slepecky method [24], which is based on the acid hydrolysis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) to crotonic acid as described by Quillaguamán et al. [25]. Dry bacterial biomass was digested with 10 mL of 97% (v/v) H2SO4 at 100 °C for 1 h. The solution was cooled to room temperature and the absorbance was measured at 235 nm using H2SO4 as a blank. Pure H. boliviensis PHB was used as the calibration standard.
2.8. Analysis of the Hydrolysates and Cultivation Samples
Glucose in the hydrolysates was analyzed using a Thermo Scientific Ultimate 3000 HPLC system (Dionex Softron GmbH, Germering, Germany) equipped with a refractive index detector. An Aminex HPX-87H column (Bio-Rad Laboratories AB, Solna, Sweden) was used for separation. The content of acetic acid was determined via high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAEC) with conductivity detection (CD). A Dionex ICS-6000 system (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) equipped with a 4 × 250 mm separation column (Dionex AS15) and a 4 × 50 mm guard column (Dionex AG15) was used. Elution was performed with a flow rate of 1 mL/min and an isocratic gradient of 5% 200 mM NaOH for 23 min, and the temperature was kept at 30 °C. Prior to each injection, the system was washed with 200 mM NaOH for 4 min to remove contaminations, and then, it was allowed to equilibrate for 16 min. An ADRS 600 (4 mm) RFIC self-regenerating suppressor (Dionex) used in internal regeneration mode, with a current of 300 mA prior to the CD, was part of the system. The CD temperature was set to 35 °C.
To investigate the dynamics of bacterial growth and PHB formation, 1 mL culture samples were withdrawn every 3 h during the first 24 h, after 33 h, and at the end of the cultivation period at 48 h. OD measurements were performed at 600 nm using a UV-1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) for all the time points to monitor growth. Additionally, a 5 mL sample was collected for the determination of cell dry weight (CDW) after 9, 18, 24, 33, and 48 h. The PHB mass was deducted from the measured CDW. The samples were collected via centrifugation at 2500× g for 15 min, washed with ultrapure water, and dried at 75 °C for 24 h. Finally, the CDW was measured gravimetrically. Glucose in the cultivation samples was determined via HPLC using the same conditions described above for the hydrolysates.
2.9. Calculations
The glucose consumption rate was calculated by dividing the glucose consumption up to 24 h (in g/L) by 24, i.e., the number of hours up to that point. The PHB yield, in grams, of initial glucose (YIG) was calculated by dividing the PHB formed up to the 24 h time point (in g/L) by the initial glucose concentration (in g/L). Yield, in consumed glucose (YCG), was calculated by dividing the PHB formed up to 24 h (in g/L) by the glucose consumed up to that time point (in g/L). The volumetric productivity of PHB was calculated by dividing PHB formation up to the 33 h time point by the number of hours (33).
2.10. Characterization of PHB
2.10.1. High-Performance Size-Exclusion Chromatography (HPSEC)
The molecular weight distribution (MWD) of the PHBs was determined via high-performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC). The HPSEC system consisted of an HP 1100 high-pressure pump (Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and two T6000M (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) columns in series. PHB was detected via a refractive index and light scattering (LS) using detectors acquired from Malvern Panalytical. For LS, two-angle detection (at 90° and 7°) was used. The temperature in the autosampler, columns, and detectors was 30 °C. The mobile phase was CHCl3, which was eluted at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The samples for HPSEC were prepared by dissolving 3.5 mg of each PHB preparation in 1 mL chloroform and filtering the solutions through 0.20 μm filters before injection. The temperature was 30 °C. Each sample was injected three times, and the injection volume was 100 µL. The detectors were calibrated with polystyrene standards dissolved in CHCl3 at 3 mg/mL. The data were processed using OMISEC 11.37 software from Malvern Panalytical, which was also used for calculating the weight-average molecular weights (Mw) from the MWDs.
2.10.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
FTIR spectroscopy was performed to confirm the presence of specific PHB functional groups. Around 20 mg of each PHB sample was mixed with approximately 380 mg of potassium bromide (IR spectroscopy grade, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). An agate mortar was used to finely grind the mixture before taking measurements. The FTIR spectra were recorded under vacuum (4 mbar), using a Bruker IFS 66v/S spectrometer (Bruker Optik GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany), which was equipped with a diffuse reflectance 16-sample holder carousel accessory (Harrick Scientific Products, Pleasantville, NY, USA). Pure potassium bromide was used as a background, recorded in the same carousel round and using the same parameters. The FTIR spectra were collected via 128 scans at a resolution of 4 cm−1 in the region 400–5200 cm−1. The spectra were converted to data point tables using OPUS software (version 5.5, Bruker Optik GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany) and processed using the free, Matlab-based, open-source GUI available from the Vibrational Spectroscopy Core Facility (https://www.umu.se/en/research/infrastructure/visp/downloads/, accessed on 20 April, 2023). Baseline correction was performed via asymmetrical least squares (AsLS) fitting, where the parameters λ and p were set to 106 and 10−3, respectively. The total area of the spectra was normalized over a spectral range 470–1870 cm−1.
2.10.3. 1H nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
A total of 20 mg of each PHB sample was dissolved in 600 µL CDCl3 and transferred to 5 mm NMR tubes. 1H and 2D 1H-13C HSQC spectra were recorded at 298 K on a Bruker 600 MHz Avance III HD spectrometer (Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany) equipped with a BBO cryo-probe. The residual CHCl3 signal was used as an internal reference (d 1H 7.27 ppm and d 13C 77.2 ppm). 13C chemical shifts were taken from the HSQC spectrum, and thus, the carbonyl carbon was not included. The spectra were processed and visualized using TopSpin 3.6 (Bruker Biospin, Rheinstetten, Germany).
2.10.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The surface morphology of PHBs was observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at an accelerating voltage of 5 kV. The samples were dispersed onto carbon adhesive tape, mounted on an aluminum stub, and coated with a thin platinum layer (2 nm). Images were obtained at UCEM (Umeå Centre for Electron Microscopy, Umeå, Sweden) using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Carl Zeiss Merlin GmbH, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with an in-chamber (ETD) secondary electron detector.
2.10.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
Powder X-ray diffraction was performed using a Bruker AXS D8 Advance diffractometer with a Våntec-1 detector, using CuKα radiation and a Ni-filter on the detector side, operated in 2θ mode. The PHB sample produced with SM-PHB medium was mounted on a standard plastic sample holder, and the sample produced from CH-PHB medium was mounted on a Si single-crystal low-background sample holder and set to rotation mode during data collection. Continuous scans were applied within a 2θ angle range of 10–70 degrees. The data collection time for each sample was at least 5 h.
2.10.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermogravimetric analysis of the two investigated PHB preparations was performed using a TGA Q5000IR analyzer (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). Calibration using the 5-point method based on Curie point standard calibration materials was applied. Around ten milligrams of each PHB sample was loaded into a platinum pan and heated to 920 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The heating rate was 10 °C/min. The obtained TGA and DTG (negative time derivate of the mass loss) curves were used for analyzing the decomposition characteristics of the PHB samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adaptation of H. boliviensis LC1 to Cellulosic Hydrolysate
Quinoa stalks are highly available in the Andean region, where quinoa farming plays a major role in local agriculture. Therefore, quinoa stalks are substrates of interest for biorefinery processes. The saccharification of quinoa stalks produces sugars that can be used for producing biopolymers via microbial fermentation. In this study, a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks was chosen as the substrate for the cultivation of the halophilic bacterial strain H. boliviensis LC1 to produce poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). The hydrolysate was prepared via sulfuric-acid-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment followed by enzymatic saccharification using the approach previously developed by Carrasco et al. [20]. The hydrolysate contained glucose (60 g/L), acetic acid (3.6 g/L), and traces of xylose.
The tolerance of the halophilic strain H. boliviensis LC1 to cellulosic hydrolysates was tested in an initial screening using CH-TSB media with hydrolysate concentrations between 5 and 15% (v/v). In the CH-TSB media containing up to 7.5% (v/v) of the hydrolysate, no visible growth limitations were detected, but at 10% (v/v) hydrolysate, the bacterial viability was already affected, and the growth was completely abolished in media with hydrolysate concentrations above 10% (v/v). The lack of growth might be attributed to toxic effects exerted by acetic acid, a known microbial inhibitor [26] that was present in the cellulosic hydrolysate.
To overcome inhibition, H. boliviensis LC1 was adapted to quinoa hydrolysates. The goal was to reach good growth in cellulosic hydrolysates diluted to 30–40% (v/v) of their initial concentration, which correlates to 18–24 g/L of glucose. This would mean that no commercial glucose has to be added to the cultivation media. Based on the results of the initial screening, an adaptation strategy, where CH-TSB medium with 7.5% and 10% (v/v) hydrolysate serve as the starting points, was generated. Successive passes and repeated-batch cultivations in media with increasing hydrolysate concentrations were applied. To ensure cell viability, after reaching certain milestones, the culture samples were plated, and the next adaptation round could continue from that isolate (Figure 1a).
In the early adaptation steps, the bacterium quickly adapted to the increasing hydrolysate content, and relatively good cell growth was achieved rather early in the cultivation. However, from 15% (v/v), the lag phase was prolonged, and it took around 30 h to reach an optical density that allowed for a successful transfer to a medium with higher hydrolysate content (Figure 1b). The repeated-batch cultivation process continued until the bacterium had been adapted to a 40% (v/v) hydrolysate medium. At that point, the bacterium was considered adapted because it was able to grow in media with hydrolysate concentrations that inhibited growth before the adaptation. The good growth (OD600 ≥ 5) observed in the medium containing 40% (v/v) indicates that the chosen adaptation strategy was effective for H. boliviensis LC1. The differences between the growth of the adapted isolate and that of the non-adapted strain during their cultivation in the 40% (v/v) hydrolysate under the same conditions are displayed in Figure 2. Adaptation to higher hydrolysate concentrations was not attempted because this would have no practical implications for producing PHB using H. boliviensis LC1 [25]. The adapted isolate was used in consecutive experiments. Similar adaptation strategies have been reported before for other microorganisms, such as Zymonomas mobilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae [27]. No other studies on adapting H. boliviensis to cellulosic hydrolysates have so far been reported.
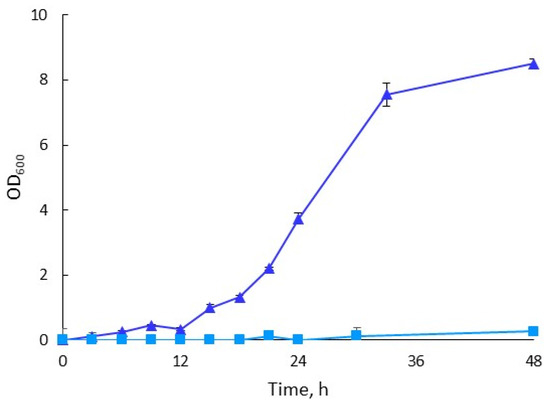
Figure 2.
Growth of adapted (triangles) and non-adapted (squares) H. boliviensis LC1 during cultivation in a 40% (v/v) hydrolysate.
3.2. Cultivation of the Adapted H. boliviensis LC1 in Synthetic Media and Cellulosic Hydrolysates
3.2.1. Comparison of Bacterial Growth and PHB Formation in Synthetic- and Hydrolysate-Based Media
The dynamics of bacterial growth and PHB formation were investigated in small-scale cultivations in a synthetic medium (SM-PHB) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate-based medium (CH-PHB). Both media had an initial glucose concentration of 15 g/L. Comparisons of glucose consumption and cell density revealed shorter lag phases for SM-PHB than for CH-PHB (Figure 3a). At 24 h, around 60% of the initial glucose had been consumed in the SM-PHB medium, whereas only 27% of the initial glucose had been consumed at that point in the hydrolysate. In the synthetic medium, growth was observed from the very beginning, whereas in the hydrolysate, it took around 12 h for growth to become evident (Figure 3a). The highest OD600 value in the synthetic medium was reached at 33 h, while in the hydrolysate, it was reached after 48 h. It is apparent that even if the adapted strain can grow in the hydrolysate, it requires some time to acclimatate to the inhibitors before it starts growing. The microbial growth achieved in the synthetic medium was lower than previously reported values for non-adapted H. boliviensis LC1 under the same conditions [28]. This might be related to alterations in the metabolic activity of the bacterial strain during the adaptation process.
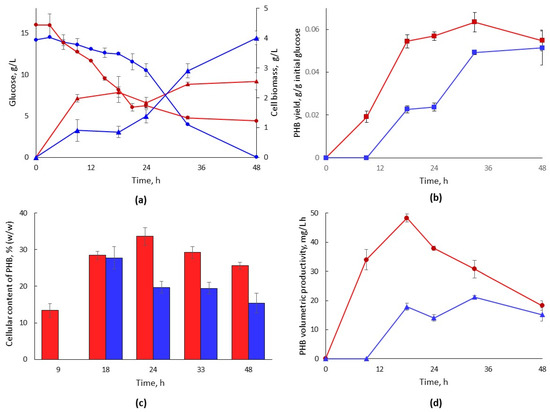
Figure 3.
Growth and PHB production during cultivation of adapted H. boliviensis LC1 in a synthetic medium and in a hydrolysate. (a) Cell growth (triangles) and glucose consumption (circles) during cultivation; (b) PHB yield on initial glucose (YIG) at different time points; (c) PHB content in cell biomass; (d) volumetric productivity of PHB. The growth is based on CDW measurements and correction for PHB mass. Red color is used for synthetic medium and blue color for hydrolysate-based medium. The graphs show means of triplicate experiments. The error bars show the standard deviation.
Spectrophotometric measurement of crotonic acid was the chosen method of monitoring the PHB production capacity of the adapted strain, because it has previously been shown to provide accurate quantification of PHB production by different bacteria [29]. The PHB yield on initial glucose (YIG) was higher for the synthetic medium than for the hydrolysate-based medium along different time points of the cultivation (Figure 3b). In the SM-PHB, PHB formation was detected after 9 h of cultivation, whereas in the hydrolysate, PHB quantification was possible only after 18 h. This agrees well with the prolonged lag phase observed for the hydrolysate (Figure 3a). PHB formation in the SM-PHB medium remained higher than in the hydrolysate during most of the cultivation time.
For SM-PHB medium, PHB accumulation reached a maximum at 33 h of cultivation, and then, it started to decrease (Figure 3b). A similar decrease was previously reported for H. boliviensis in synthetic medium [30], and it can be attributed to PHB consumption by the microorganism. In the hydrolysate-based medium, PHB accumulation continued to increase during the cultivation. After 48 h in CH-PHB, YIG became comparable with the yield in synthetic medium. This disagrees with a previous report on H. boliviensis LC1 cultivated in hydrolysates of wheat bran and potato waste [31]. In that report, the cultivation displayed comparable growth dynamics to those in the current study, except that PHB accumulation dropped after around 20 h.
The PHB content in the bacterial biomass at 18 h was around 30% of the total cell dry weight (CDW) for both the synthetic medium and the hydrolysate (Figure 3c), while the cell biomass was higher for the synthetic medium than for the hydrolysate (Figure 3a). For the cultivation in the synthetic medium, the highest PHB percentage in the cells was observed at 24 h, whereas for the hydrolysate, the maximum was observed for samples taken at 18 h. The volumetric productivity over time was always higher in the synthetic media (Figure 3d).
3.2.2. Bacterial Growth and PHB Formation in Hydrolysate-Based Media with Different Glucose Concentrations
The effect of different glucose concentrations on bacterial growth and PHB formation was evaluated in cultivations in hydrolysate-based media with 15 g/L (CH-PHB-15) and 20 g/L (CH-PHB-20) glucose. The glucose consumption rate was slightly higher for the cultivations with the lower initial glucose concentrations (CH-PHB-15) (Table 1). Overall glucose consumption after 48 h was 100% in CH-PHB-15, while in the more concentrated hydrolysate (CH-PHB-20) some glucose remained unused, and the overall consumption was 93% of the initial concentration. Higher bacterial growth was observed in CH-PHB-20 than in CH-PHB-15, which is a consequence of the different initial glucose concentrations in the media.

Table 1.
PHB production parameters and glucose consumption rate in cultivations of H. boliviensis LC1 in hydrolysates with initial glucose concentrations of 15 g/L (CH-PHB-15) and 20 g/L (CH-PHB-20). Mean of triplicate experiments. The standard deviations are shown in parentheses. Cell biomass is based on cell dry weight after deducting PHB mass.
PHB yield on consumed glucose (YCG) (calculated at 24 h, the time point at which the PHB cellular content was the highest for the synthetic medium (Figure 3c)) was higher for CH-PHB-15 medium than for CH-PHB-20 medium (Table 1). In any case, the achieved yield was lower than the maximum PHB yield from glucose reported for H. boliviensis (0.12 g/g) [25] and the theoretical yield reported for Escherichia coli (0.48 g/g) [32]. The volumetric productivity of PHB was also higher for cultivations with low initial glucose concentration.
3.2.3. PHB Production and Isolation for Characterization
Larger-scale cultivations using a hydrolysate-based medium and a synthetic medium were performed, with the aim of producing a sufficient amount of PHB for thorough characterization. The concentration of glucose in both media was set at 10 g/L, considering that the small-scale experiments described above (Section 3.2.2) revealed that cultivations of the adapted strain in hydrolysates with low glucose concentration are effective for consuming the available glucose, and for achieving high PHB yield and volumetric productivity (Table 1). The produced PHB was recovered from the bacterial biomass, isolated, and freeze-dried. The refined PHB samples were then characterized by different advanced techniques that have previously been used for the characterization of PHB produced by other bacteria [33,34,35,36].
3.3. PHB Characterization
3.3.1. High-Performance Size-Exclusion Chromatography (HPSEC)
HPSEC was used for determining the average molecular weight (Mw) of the produced PHB. Identifying the Mw of biopolymers is important for determining their suitability for industrial applications.
The MDW of the PHB samples revealed that the molecular weight average of the PHB produced via cultivation in a synthetic medium (Mw = 1560 ± 6 kg/mol) was two times higher than that of the sample produced in the hydrolysate (690 ± 2 kg/mol) (Figure 4). The Mws of the PHB produced in this study are well above 50 kg/mol, which is the minimum value required for most PHB uses [33], but still below 3000 kg/mol, which is the lower limit to be considered an ultra-high-molecular-weight PHB [34]. There are not many reports on the Mw of PHB produced in hydrolysates. One of the few published studies, which was on PHB production by Cupriavidus necator in hydrolysates of alligator weed [35], reported a Mw of 185 kg/mol, which is considerably lower than the values reported in the present work.
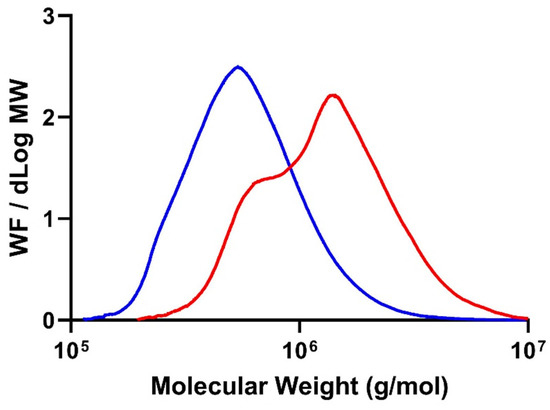
Figure 4.
MWD of the PHB produced via cultivation of H. boliviensis LC1 in glucose-based synthetic medium (red line) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (blue line).
3.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
The FTIR spectra of the two PHB samples (one PHB preparation produced via bacterial cultivation in synthetic media and one produced via cultivation in a cellulosic hydrolysate) are shown in Figure 5. The assignment and interpretation of the bands were based on [37].
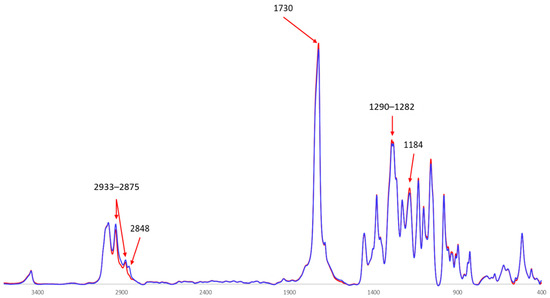
Figure 5.
Normalized FTIR spectra of the PHB produced by cultivating H. boliviensis LC1 in a glucose-based synthetic medium (red line) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (blue line).
The FTIR spectra of both samples exhibited a sharp, distinctive peak at 1730 cm−1 (Figure 5). This signal corresponds to the carbonyl bond stretching vibration of the ester group, which is characteristic of polyhydroxyalkanoates and other polyesters. The peak was slightly more intense for the PHB produced in the synthetic medium than for that produced in the cellulosic hydrolysate. The intensity differences in the carbonyl bond signal in PHB have previously been correlated with crystallinity features. In a study on the characterization of different PHB samples produced by Paraburkholderia xenovorans, strong signals at 1720 cm−1 were associated with higher-order crystalline formations, while weaker signals were related to samples with a higher proportion of amorphous structures [36]. However, the crystallinity pattern revealed by the X-ray diffractograms in this study was similar for both PHB samples (Section 3.3.5).
The peaks corresponding to the asymmetric C-H stretching vibration of methyl and methylene groups (at 2933 and 2875 cm−1) were visible for both samples. Similar peaks have previously been reported for spectra of PHB produced by other organisms, such as P. xenovorans LB400 [36,38]. In the current study, the intensity of these peaks was higher for the PHB produced in the cellulosic hydrolysate than for that produced in the synthetic medium. Furthermore, the peak at 2848 cm−1, which can be attributed to symmetric CH2 stretching vibrations, was visible only for the spectrum of the PHB produced in the hydrolysate. This discrepancy can be related to differences in crystallinity [39].
The spectra of both samples also displayed other peaks that are typically reported for PHB. These include peaks at 1454 and 1381 cm−1, attributed to aliphatic methylene and methyl groups, respectively [40,41], as well as bands around 1290, 1282, 1184, and 1132 cm−1, which are typical features of vibrations of the -C-O, -C-C-O, and C-O-C bonds in esters [41,42].
The peaks at 1282 and 1184 cm−1 were more intense for the PHB produced in the synthetic medium than for that produced in the cellulosic hydrolysate. This variation can be attributed to small differences in the physical state of both polymers [43], as the PHB produced from the hydrolysate was slightly more amorphous than that from the synthetic medium. In general, the FTIR spectra of both PHB samples displayed a rather comparable pattern with no major differences in the detected peaks or in signal intensity, regardless of the substrate used. Comparable FTIR spectra were reported for C. necator and Bacillus megaterium [44].
3.3.3. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
1H NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for determining the structure of polymers, and in this work, it was used to verify the structure of the produced PHB. Both PHB samples had similar spectra, displaying three clearly defined signals that are typical of PHB homopolymers [45]. Peaks at chemical shifts (δ) of 5.26, 2.61, 2.48, and 1.28 ppm were detected for both samples (Figure 6). The multiplet at δ = 5.26 ppm corresponds to the methine (–CH) group, while the doublet of doublet peaks at δ = 2.61/2.48 ppm and the doublet at 1.28 ppm correspond, respectively, to the methylene (–CH2) and methyl (–CH3) groups. Since these signals have been found before in PHB standards [43], and they are identical for both of our samples, it can be confirmed that the biopolymer synthesized by H. boliviensis LC1 in both the synthetic medium and the cellulosic hydrolysate is a PHB. This conclusion is further corroborated by the 13C chemical shifts derived from the 1H-13C HSQC spectra, where the shift values were found to be 67.6 ppm (-CH), 40.8 ppm (-CH2), and 19.8 ppm (-CH3). Comparable 1H and 13C chemical shifts have also been reported for PHB produced by B. megaterium and C. necator [44].
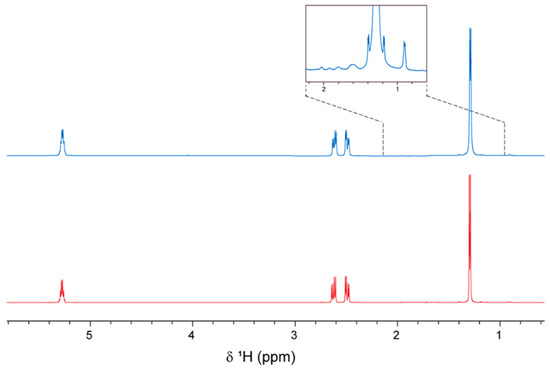
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectra of the PHB produced by cultivating H. boliviensis LC1 in a glucose-based synthetic medium (red line) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (blue line). The insert in the top spectrum shows a magnification of the δ = 0.6–2.2 ppm area.
1H NMR indicated the presence of pure PHB in both samples, especially that produced in a synthetic medium (Figure 6). The PHB produced via cultivation in a cellulosic hydrolysate contained some minor impurities, which can be detected if the spectra are zoomed in. Magnification of the chemical shift area between δ = 0.6 and 2.2 ppm shows a relatively small peak at δ = 0.9 ppm and some weaker peaks at δ = 1.6 and 2.1 ppm for the PHB produced in the hydrolysate. A signal at δ = 0.9 ppm in the 1H NMR spectrum of PHB from C. necator has previously been attributed to impurities [33], and the peak at 1.6 ppm most likely originates from trace amounts of H2O in the solvent [46,47]. The weak signal at 2.1 ppm might also be attributed to impurities, and they were not visible in the spectrum of the PHB produced in the synthetic medium.
3.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
SEM imaging revealed that both PHB samples displayed comparable morphological features consisting of granules with mostly elliptical (or slightly spherical) shapes, and a rather unsmooth surface (Figure 7), similar to those granules obtained from recombinant E. coli and B. megaterium [48]. No porosity was evident from the granular features. Despite the similarity in shape, the PHB granules produced via cultivation in a synthetic medium had a slightly higher average diameter of (0.6–0.7 µm) than those produced via cultivation in the cellulosic hydrolysate (< 0.5 µm). Furthermore, it is important to highlight that the PHB granules from the synthetic medium were rather discrete and well-defined (Figure 7-top), while those from the hydrolysate medium tended to bind to each other and rendered the particle shape more indistinguishable (Figure 7-bottom). This morphological disparity between the samples agrees with results obtained from other analyses, as NMR revealed impurities in the sample from the hydrolysate but not in that from the synthetic medium, as SEC revealed a larger molecular weight of the sample from the synthetic medium, and as TGA revealed slightly more thermal stability of the sample from the synthetic medium (see Section 3.3.6).
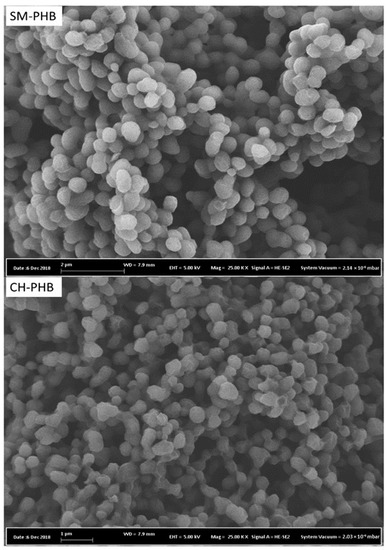
Figure 7.
SEM images of the PHB produced via cultivation of adapted H. boliviensis LC1 in glucose-based synthetic medium (SM-PHB) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (CH-PHB). Magnification: 25,000×.
3.3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction is commonly used to assess the amorphous and crystalline nature of biopolymers [49]. The XRD patterns of the PHB samples are shown in Figure 8. Both materials exhibited a good match with the structure reported by Yokouchi et al. [50] (powder diffraction file number 00-068-1411). The diffractograms displayed five intense peaks, where the two at 13.5° and 16.9° are sharp and come from the planes (0 2 0) and (1 0 1), indicating greater repeatability in those directions. The peak at around 22° is an overlap arising from slightly broadened reflections in the planes (0 2 1), (1 0 1), and (1 1 1) appearing as one. The blunt peak with a shoulder on its left side is likely to stem from less repetition in these directions. The PHB produced via cultivation in synthetic medium displayed a stronger peak at 26.8° and some additional peaks around 36°, 40°, 54°, 56°, and 67°. These peaks belong to the displaced rutile (TiO2) from the sample holder, together with a non-crystalline contribution with a maximum of around 20°. At 26.8°, a rutile peak coincided with the PHB (0 4 0) reflection, giving the appearance of a large peak at this position. The low attenuation of X-rays in the sample led to penetration and the generation of signals from the sample holder, with a slight displacement towards higher angles because of the height difference between the sample and the holder. The amount of PHB sample produced from cellulosic hydrolysate that was available for XRD required the use of a low-background Si holder to obtain the diffractograms. This sample holder did not produce as much background as the standard holder did. Considering this, the crystalline characteristics of the two samples were very similar. Rather similar diffractograms have been reported for PHB produced by B. megaterium, C. necator [44], and P. xenovorans [36].
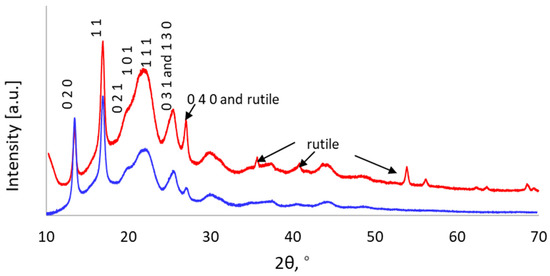
Figure 8.
X-ray diffraction pattern of PHB produced by cultivating H. boliviensis LC1 in glucose-based synthetic medium (red line) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (blue line). Main peaks are annotated with corresponding Miller indices.
3.3.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA analysis of the PHB preparations revealed that both samples had good thermal stability up to around 200 °C (Figure 9). For both samples, distinct weight loss was observed between 200 and 310 °C. After that, no major volatilization was observed, and some material remained as a residue. More residual material was observed for the PHB from cultivation in the synthetic medium (10.3% (w/w)) than for that from the hydrolysate (7.1% (w/w)).
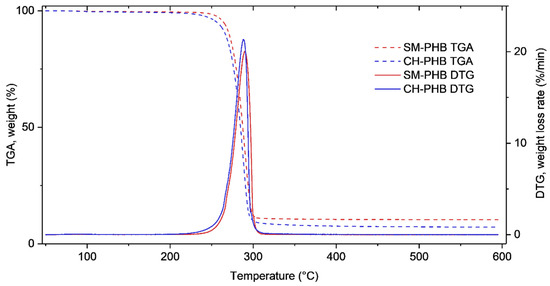
Figure 9.
Thermogravimetric (TGA) and derivative thermogravimetric (DTG) curves resulting from the analysis of PHB produced by cultivating H. boliviensis LC1 in a glucose-based synthetic medium (red lines) and in a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks (blue lines).
For the PHB produced in the hydrolysate, the weight loss started at around 180 °C and the maximum was reached at 288 °C (Figure 9). For the PHB from the synthetic medium, the weight loss started later, at around at 210 °C, than for the sample from the hydrolysate, but the maximum weight loss rate was reached at approximately the same temperature, around 290 °C. The thermal degradation was very sharp for both samples. These values are within the average range reported earlier for different for PHBs, which generally display a maximum weight loss rate at temperatures between 225 and 295 °C [51,52,53]. The PHB produced in the synthetic medium presented slightly higher thermal stability than the sample produced in the cellulosic hydrolysate. The slightly lower thermal stability of the sample produced in the hydrolysate might be linked to the presence of acetic acid in the production medium, or with its relatively lower molecular weight (see Section 3.3.1). It has been reported that using acetic acid in PHB isolation can affect thermal stability by inducing some decomposition of PHB into crotonic acid [54]. Previous studies have shown that the thermal stability of PHAs is directly correlated with their molecular weight [52]. However, the difference in thermal stability between the PHB preparations in the present study was not as striking as the difference in their average molecular weights. Both samples showed similar thermostability compared with PHB from C. necator [44].
4. Conclusions
The moderately halophilic bacterium H. boliviensis LC1 was adapted to a cellulosic hydrolysate of quinoa stalks, and the capacity of the adapted strain to produce PHB in cellulosic hydrolysates was demonstrated. Cultivation of the adapted strain revealed different dynamics in a glucose-based synthetic medium and in cellulosic hydrolysates, but the produced PHB exhibited rather comparable properties.
Characterization using advanced techniques revealed that the PHB samples produced from glucose-based synthetic media and cellulosic hydrolysate displayed similarities regarding FTIR and NMR spectra, and some other general features. Some differences in molecular weight, thermal stability, particle size, and crystallinity were revealed via HPSEC, SEM, XRD, and TGA. Although these differences could limit its applicability to an extent, the produced PHB is expected to be suitable for different biomaterial uses, which will be addressed in a further investigation. The results of this study demonstrate the feasibility of using quinoa stalks to produce PHB with adapted H. boliviensis strains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.M., C.C. and L.J.J.; methodology: C.M., C.C., L.J.J., L.R.-S. and J.Q.; formal analysis: D.A.M., K.M., O.S., A.G., M.H., M.C. and M.B.; investigation: D.A.M., K.M. and J.L.; resources: C.M., C.C. and L.J.J.; writing—original draft preparation: D.A.M. and C.M.; writing—review and editing: C.M., C.C., L.J.J. and L.R.-S.; visualization: D.A.M. and C.M.; supervision: C.M., C.C. and L.J.J.; project administration: C.M., C.C. and L.J.J.; funding acquisition: C.M., C.C. and L.J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida contribution No. 54100087), the Swedish Research Council (2016-05822), the Bio4Energy research environment (www.bio4energy.se, accessed on 20 April 2023), and Sparebankstiftelsen Hedmark (https://sparebankstiftelsenhedmark.no, accessed on 20 April 2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
Stefan Stagge is thanked for his support with HPLC and HPAEC. Cheng Choo Lee from the Umeå Centre for Electron Microscopy and National Microscopy Infrastructure (UCEM-NMI) is acknowledged for providing the SEM images and helping with their interpretation. The core facilities and technical platforms at the Chemical Biological Center (KBC) of Umeå University and of the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU) are gratefully acknowledged for the support they provided. The Biopolymer Analytical Platform assisted with HPSEC. The Vibrational Spectroscopy Core Facility performed the FTIR analysis. The Swedish NMR Centre at Umeå University analyzed the NMR spectra.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Statista. Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Benson, N.U.; Bassey, D.E.; Palanisami, T. COVID pollution: Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on global plastic waste footprint. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.; Rothman, R. Life cycle assessment of bio-based and fossil-based plastic: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: Frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.; Patra, B.R.; Patel, R.; Bakos, J.; Dalai, A.K. Innovations in applications and prospects of bioplastics and biopolymers: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dake, M. Biodegradable polymers: Renewable nature, life cycle, and applications. Microbial Factories: Biodiversity, Biopolymers. Bioact. Mol. 2016, 2, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial biopolymers: From pathogenesis to advanced materials. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meereboer, K.W.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Review of recent advances in the biodegradability of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastics and their composites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5519–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Santos, M.; Koskimäki, J.J.; Silveira, L.P.; de Souza, E.M.; Jendrossek, D.; Pirttilä, A.M. The protective role of PHB and its degradation products against stress situations in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadalipour, M.; Behzad, T.; Karbasi, S. Optimization and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate/lignin electro-spun scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, M.B.; Vikhoreva, G.A.; Mokhova, O.N.; Bonartseva, G.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Core–Sheath Surgical Sutures Modified with Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2007, 43, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.A.M.; Serafim, L.S.; Lemos, P.C.; Ramos, A.M. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by mixed microbial cultures. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2003, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.H.; Mustafa, S.; Man, Y.B.C. Microbial polysaccharides and their modification approaches: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Soto, L.; Byrne, E.; van Niel, E.W.J.; Sayed, M.; Carrasco, C.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Hydrogen and polyhydroxybutyrate production from wheat straw hydrolysate using Caldicellulosiruptor species and Ralstonia eutropha in a coupled process. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.N.; Srivastava, S.; Khare, S.K.; Prakash, V. Extremophiles: An Overview of Microorganism from Extreme Environment. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Hatti-kaul, R.; Mattiasson, B.; Alvarez, M.T.; Delgado, O. Halomonas boliviensis sp. nov., an alkalitolerant, moderate halophile isolated from soil around a Bolivian hypersaline lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Crops and Livestock Products. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Filik, G. Biodegradability of quinoa stalks: The potential of quinoa stalks as a forage source or as biomass for energy production. Fuel 2020, 266, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Cuno, D.; Carlqvist, K. SO 2 -catalysed steam pretreatment of quinoa stalks. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 90, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Jönsson, L.J.; Martín, C. Hydrothermal pretreatment of water-extracted and aqueous ethanol-extracted quinoa stalks for enzymatic saccharification of cellulose. Energies 2021, 14, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.; Carrasco, C.; Jönsson, L.J.; Romero-Soto, L.; Chambi, D.; Oliva-Taravilla, A. Biorefining of quinoa residues for production of advanced biofuels and biopolymers. In Proceedings of the 30th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition Proceedings, online, 9–12 May 2022; pp. 1126–1130, ISSN 2282-5819. [Google Scholar]
- Chambi, D.; Romero-Soto, L.; Villca, R.; Orozco-Gutiérrez, F.; Vega-Baudrit, J.; Quillaguamán, J.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Martín, C.; Carrasco, C. Exopolysaccharides Production by Cultivating a Bacterial Isolate from the Hypersaline Environment of Salar de Uyuni (Bolivia) in Pretreatment Liquids of Steam-Exploded Quinoa Stalks and Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Curupaú Sawdust. Fermentation 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambi, D.; Lundqvist, J.; Nygren, E.; Romero-Soto, L.; Marin, K.; Gorzsás, A.; Hedenström, M.; Carlborg, M.; Broström, M.; Sundman, O.; et al. Production of Exopolysaccharides by Cultivation of Halotolerant Bacillus atrophaeus BU4 in Glucose- and Xylose-Based Synthetic Media and in Hydrolysates of Quinoa Stalks. Fermentation 2022, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.H.; Slepecky, R.A. Assay of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. J. Bacteriol. 1961, 82, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Doan-Van, T.; Guzmán, H.; Guzmán, D.; Martín, J.; Everest, A.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Halomonas boliviensis in fed-batch culture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 78, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, L.J.; Martín, C. Pretreatment of lignocellulose: Formation of inhibitory by-products and strategies for minimizing their effects. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrommati, M.; Daskalaki, A.; Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Adaptive laboratory evolution principles and applications in industrial biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Terceros, P.; Tito, E.; Torrico, S.; Carballo, S.; Van-Thuoc, D.; Quillaguaman, J. Production of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) by Halomonas boliviensis in an air-lift reactor. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquel, N.; Lo, C.W.; Wei, Y.H.; Wu, H.S.; Wang, S.S. Isolation and purification of bacterial poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Muñoz, M.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Optimizing conditions for poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) production by Halomonas boliviensis LC1 in batch culture with sucrose as carbon source. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Thuoc, D.; Quillaguamán, J.; Mamo, G.; Mattiasson, B. Utilization of agricultural residues for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Halomonas boliviensis LC1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, M.; Xian, M.; Zhao, G. Comparison of glucose, acetate and ethanol as carbon resource for production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and other Acetyl-CoA derivatives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramvash, A.; Moazzeni Zavareh, F.; Gholami Banadkuki, N. Comparison of different solvents for extraction of polyhydroxybutyrate from Cupriavidus necator. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaya, L.; Millán, M.; Peña, C.; Jendrossek, D.; Espín, G.; Tinoco-Valencia, R.; Guzmán, J.; Pfeiffer, D.; Segura, D. Inactivation of an intracellular poly-3-hydroxybutyrate depolymerase of Azotobacter vinelandii allows to obtain a polymer of uniform high molecular mass. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2693–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. Preparation, statistical optimization and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) fermented by Cupriavidus necator utilizing various hydrolysates of alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) as a sole carbon source. Biotechnol. Prog. 2020, 36, e2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanhueza, C.; Diaz-Rodriguez, P.; Villegas, P.; González, A.; Seeger, M.; Suárez-González, J.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Acevedo, F. Influence of the carbon source on the properties of poly-(3)-hydroxybutyrate produced by Paraburkholderia xenovorans LB400 and its electrospun fibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, D. FT-infrared and FT-Raman spectroscopy in biomedical research. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2001, 36, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Prabhu, K.; Shah, L.; Radha, P. Biologically and environmentally benign approach for PHB-silver nanocomposite synthesis and its characterization. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.S.; Razghandi, K.; Aggarwal, N.; Michler, G.H.; Groth, T. Nanofibers from blends of polyvinyl alcohol and polyhydroxy butyrate as potential scaffold material for tissue engineering of skin. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.; Woldesenbet, F. Production of biodegradable plastic by polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) accumulating bacteria using low cost agricultural waste material. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Nair, A.; Annamalai, K.; Kamala Kannan, S.; Kuppusamy, S. Characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoates produced by Bacillus subtilis isolated from soil samples. Malaya J. Biosci. 2014, 1, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Drusilla Wendy, Y.B.; Nor Fauziah, M.Z.; Siti Baidurah, Y.; Tong, W.Y.; Lee, C.K. Production and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Burkholderia cepacia BPT1213 using waste glycerol as carbon source. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 41, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansiz, K.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; McNaughton, D. Quantitative determination of the biodegradable polymer poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain by use of mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariative statistics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Dikshit, P.K.; Moholkar, V.S. Production, ultrasonic extraction, and characterization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) using Bacillus megaterium and Cupriavidus necator. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohini, D.; Phadnis, S.; Rawal, S.K. Synthesis and characterization of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate from Bacillus thuringiensis R1. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zi, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Hu, N. Psychrotrophic Pseudomonas mandelii CBS-1 produces high levels of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate. Springerplus 2013, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahishi, L.H.; Tripathi, G.; Rawal, S.K. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthesis by recombinant Escherichia coli harbouring Streptomyces aureofaciens PHB biosynthesis genes: Effect of various carbon and nitrogen sources. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; K Johnson, D. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokouchi, M.; Chatani, Y.; Tadokoro, H.; Teranishi, K.; Tani, H. Structural studies of polyesters: 5. Molecular and crystal structures of optically active and racemic poly (β-hydroxybutyrate). Polymer 1973, 14, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbukarasu, P.; Sauvageau, D.; Elias, A. Tuning the properties of polyhydroxybutyrate films using acetic acid via solvent casting. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Michely, L.; Moradkhani, G.; Akbari, V.; Cochez, M.; Vagner, C.; Renard, E.; Saeb, M.R.; Langlois, V. Thermal stability and flammability behavior of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) based composites. Materials 2019, 12, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galego, N.; Rozsa, C. Thermal decomposition of some poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates). Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).