Abstract
Rice bran (RB) is a promising food ingredient that can improve biological function. In this study, we investigated the effects of RB, both unfermented (RB30) and fermented (RBF30), with five different microorganisms on the neurobehavioral activity in zebrafish larvae. Analytical methods such as LC–UV and LC–MS were performed for the analysis of RB30 and RBF30 extracts. Interestingly, niacin content, which is known to improve brain functions such as cognition and emotion, was found to be higher in RBF30 than in RB30. Furthermore, niacin content was highly increased in the RBF30-exposed fish, compared to those in the control fish. Therefore, we profiled behavioral patterns and various neurochemistry in zebrafish larvae following supplementation with RBF30 as well as performed calcium imaging on Tg (huC:GAL4-VP16); (UAS:GCaMP7a) zebrafish larvae to determine the correlation of neural activity. RBF30 revealed greater stimulation of locomotor activity without negatively affecting decision-making behavior in zebrafish larvae, as compared to RB30 or niacin. Its behavioral activation is mainly linked with the elevations of neural activity and several neurochemicals such as serotonergic and dopaminergic systems that are implicated in the control of anxiety and stress. Taken together, these results suggest that RBF30 could be a food material that improves the behavioral health by modulating neural activity and brain neurochemistry.
1. Introduction
Rice bran (Oryza sativa L.), a crushed mixture obtained in rice milling, is known to have valuable nutrients and a bioactive component with health-related properties such as antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-reducing effects [1,2,3,4]. Because rice bran contains many nutrients and biologically active compounds, it is further processed using stabilization, fractionation, enzymatic treatment, or fermentation, to improve the biological activity and maintaining of the nutritional quality [5,6,7]. Fermentation using various microorganisms can increase the levels and availability of bioactive compounds in functional foods. For instance, fermentation of rice bran with Rhizopus oryzae leads to an increase in protein content and levels of vitamins and phenolic compounds, which contribute to various health benefits such as anti-inflammation, anti-tumor, and neuroprotection in animal models [8,9,10]. Moreover, rice bran, either alone or in a combination of fermentation with various microorganisms has been shown to prevent atopic dermatitis in rats (when fermented by Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Pichia deserticola), alleviate ulcerative colitis in mice (when fermented with fungi and lactic acid bacteria), provide neuroprotection in rats (when fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum), and delay and prevent brain aging in rats (no fermentation) [8,11,12,13]. However, the effects of fermented rice bran on the behavioral and neurochemical signaling that contribute to neural functions in animal models are not yet fully understood. Therefore, further study using various behavioral tasks, neural activity, and comprehensive neurochemistry in animal models are needed to determine the biological activity of fermented rice bran.
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a promising vertebrate for the screening of the central nervous system (CNS) with a high degree of genetic compatibility, and it also displays comprehensive neurochemistry similar to human beings [14,15]. The zebrafish’s organ formation and pharmacokinetic system are very similar to those of humans [16,17]. The use of zebrafish as an animal model has many practical advantages, such as those related to rapid fertilization and development, easy husbandry, small size, and high fecundity, as well as cost-effectiveness [18]. The recent emergence of high-throughput tracking of zebrafish larvae has improved the quality of behavioral studies, making the research more objective, repeatable, and efficient [19,20].
The purpose of this study was to determine the biological activity of rice bran fermentation extract (RBF30) on behaviors, neural activity, and comprehensive neurochemistry using a zebrafish larvae model. Therefore, we fermented rice bran with a combination of patented strains of microorganisms including L. buchneri RPG-L0001 [21], L. paracasei subsp. tolerans RPG-L0002 (in progress), L. harbinensis RPG-L0003 [22], S. fibuligera RPG-Y0001 [23], and P. kudriavzevii RPG-Y0002 to boost the biological activity. These strains have been shown to exhibit various biological functions, such as anti-inflammation, skin aging prevention, and anti-oxidation. We used a unique rice bran extract produced by fermentation with five microorganism strains: Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans, Lactobacillus harbinensis, Saccharomycopsis fibuligera, and Pichia kudriavzevii, after fractionation using ethanol solvent at 30% v/v of RBF. We performed three behavioral tasks such as locomotor test, light–dark transition test, and color preference test. In addition, we measured the neural activity using Tg lines (huC:GAL4-VP16); (UAS:GCaMP7a), and profiled a broad-spectrum neurochemistry including histaminergic, cholinergic, serotonergic, dopaminergic, and GABAergic systems in a zebrafish larvae model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation and Purification of RBF30
The rice bran used in this experiment was purchased from domestic rice paddy farmers, and the extract was produced using a hot water extractor (SHR-S400, Se-Han, and Chilgok-gun, Gyeongsanbguk-do, Republic of Korea). To inoculate L. buchneri RPG-L0001, tolerans RPG-L0002, and L. harbinensis RPG-L0003 were inoculated on Difco lactobacilli MRS broth (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C. For S. fibuligera RPG-Y0001 and P. kudriavzevii RPG-Y0002, we used Difco YM broth (BD Biosciences) and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C.
A schematic illustrating the purification of fermented rice bran is represented in Figure S1. The cultures were inoculated into a 10% rice bran extract at an OD600 of 0.02, and fermentation was conducted at 37 °C for 48 h. The fermentation broth was centrifuged and filtered to remove the cells and rice bran, and the supernatant was used. The fermentation broth was subjected to column chromatography using PB-600 resin (8 × 50 cm) and developed on the packed column. Ethanol concentrations ranging from 0 to 100%, (v/v) were fractionated into 500 mL using the stepwise method. The fraction obtained using 30% ethanol showed the best antioxidant activity and was selected for further experiments, as shown in Figure S2.
The fraction was concentrated using a 1 L round-bottomed flask with a vacuum concentrator (EYELA, NE1110, and Tokyo, Japan) at 70 °C. DW (100 mL) was added to the concentrated fermented rice bran, and the mixture was stirred to facilitate dissolution. When the solution was dissolved completely, 500 mL of ethanol was added to yield a powdered precipitate. The solution was stirred for 30 min and then vacuum-filtered. After filtration, the crystals were transferred to a 1 L flask, 500 mL of ethanol was added, and the mixture was allowed to form a slurry for 30 min. Next, the slurry was vacuum-filtered, then transferred to a 1 L flask, and 500 mL of ethanol was added. The mixture rested as a slurry for 30 min and was vacuum-filtered. The filtered mixture was placed in a dryer and dried overnight (for 12–16 h) at 45 °C. After drying, the solid was milled using a conventional mill.
2.2. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Analysis
RB30 and RBF30 were dissolved in 50% acetonitrile (ACN) and then filtered through a 0.2 μm polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane filter. RB30 and RBF30 were analyzed using an ACQUITY UPLC system (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) coupled to a photodiode array (PDA) detector, QDA detector for scanning UV spectrum, and full mass (MS) in rice bran extracts, respectively. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in water (eluent A) and 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in ACN (eluent B), obtained by isocratic elution (A:B = 10:90, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min and run time of 6 min. The injection volume was 5 μL. The UV spectrum at wavelengths from 210 to 500 nm, and full MS scan at m/z 50 to 500, were analyzed. The chromatographic separation was accomplished using BEH C18 and a Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) column (130 Å, 2.1 mm × 50 mm i.d., 1.7 μm; Waters) maintained at 40 °C. For quantification of niacin, multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode by electrospray positive ionization (ESI+) was used according to the ionic transition m/z 124.2 → 80.1. The water and ACN used as HPLC grade were obtained from J.T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA). All other chemicals and solvents were reagent grade or better.
2.3. Maintenance of Zebrafish
Zebrafish were maintained under standard conditions as previously described [24]. All experiments have adhered to the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978). All experimental protocols involving the zebrafish were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (7B-ZF1).
2.4. Behavioral Analysis of Zebrafish Larvae
At 5 days post-fertilization (dpf), larvae were transferred to a transparent 96-well plate (1 individual per well) with 100 μL of embryonic medium and allowed to acclimate at 28 °C for 30 min. Two neural stimulants such as pentylenetetrazole (PTZ; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and modafinil (MDF; USP Reference Standard, Rockville, MD, USA) were used as positive controls. All substances containing drugs and food materials such as RB30 and RBF30 were dissolved in embryonic medium, individually added to each well.
After treatment, behavioral movements were recorded for 60 min, and fish locomotion was quantified using the DanioVision and EthoVision 10 XT locomotion tracking software (Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands). For the light–dark response assay, the movement of larvae treated with PTZ, MDF, and RBF30 was recorded in four cycles of alternating 10 min light and dark periods for 80 min. The light–dark transition test is commonly used to measure anxiety-like behavior in rodents and zebrafish larvae [25,26].
The color preference test was performed to characterize the visual discrimination on the cognitive function, according to previously published protocols [27]. Briefly, zebrafish larvae were introduced plus (+) maze (ZENOMIC DESIGN, Daejeon, Korea) with four differently colored arms (red, yellow, blue, and white), with 20 mL of embryonic medium containing RBF30, PTZ, and MDF, respectively. The zone preference to each color was measured every 2 min for 30 min by a digital camera (HDR-CX130, Sony, Japan).
2.5. Assessments of Neural Activity in Zebrafish Larvae
To visualize neural activity in real time, calcium imaging experiments were performed on Tg (elavl3:GAL4-VP16); Tg (UAS:GCaMP7a) transgenic zebrafish (kindly provided by Dr. C.-H. Kim from Chungnam National University, Republic of Korea) [28,29]. The zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf were introduced in a transparent 12-well plate (n = 20 per group), and exposed to 5 mM PTZ, 1 mM MDF, and 1 mg/mL of RBF30 for 1 h. Larvae were mounted on low-melting agarose (Sigma-Aldrich), and the fluorescence image per second was captured for 3 min using a Lionheart FX Automated Microscope (Biotex, Winooski, VT, USA). The images were quantitatively analyzed for measuring fish neural activity using Gen5 software (BioTek). The calcium signal activity was normalized by comparing the ratio between increases in fluorescence level (△F) at a designated time/baseline fluorescence level (F0) peak, according to previous reports [29,30].
2.6. Measurement of Endogenous Neurochemicals in Zebrafish Larvae
To quantify endogenous neurochemicals in zebrafish larvae, we performed the highly sensitive targeted MRM analysis using LC–MS/MS, according to our previously reported method in zebrafish and mouse models [31]. Briefly, 50 pooled larvae (n = 7) at 5 dpf were exposed to 1000 μg/mL of RBF30-containing medium for 2 h. The larvae were washed three times with 0.1 M ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS); the supernatant was then carefully removed. Wet larvae were lysed by snap-freezing using liquid nitrogen, and 300 µL of DW was added, followed by ultrasonication (Vibra cell VCX-130, Sonics, Hartford, CT, USA) for 5 s on the ice. The homogenate from the larvae was normalized to the same quantity as the total protein content (μg/mg whole larvae) for each sample and precipitated by adding an equal amount of methanol containing 0.1% formic acid. The endogenous neurochemicals were extracted by vortexing for 5 min and centrifuging for 10 min at 21,130× g at 4 °C, and the final supernatants were kept at −20 °C until analysis.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Behaviors, neurochemical, and neural activity data were statistically analyzed by an unpaired t-test. The statistical significance was set at 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001 (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, and *** p ≤ 0.001). The multiple comparison of means was performed using Duncan’s new multiple range test.
3. Results
3.1. RBF30 Increased Locomotor Activity and Alleviated Anxiety-Like Behavior
We conducted a preliminary experiment to fractionate rice bran extracts using different concentrations of ethanol and assess the effects on zebrafish larvae behavior. The fraction obtained using 30% ethanol (RB30) was found to be the most effective in inducing behavioral activation in zebrafish larvae (Figure S2).
Further experiments were conducted using RB30 and RBF30, at a concentration of 1000 μg/mL. Both RB30 and RBF30 were found to increase movement and induce hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae during a 60 min period. In particular, RBF30 treatment resulted in an increase of 114%, whereas RB30 treatment resulted in an increase of 83%, as compared with the control group, indicating that RBF30 was more effective than RB30 (F(2, 51) = 20.6; p < 0.0001, Figure 1). Positive control drugs, such as PTZ, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor antagonist [32] and MDF, a selective dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine transporter inhibitor [33], also showed similar effects on fish locomotion (Figure S3). The study also determined that a concentration of 1000 μg/mL of RBF30 was the optimal dose for inducing behavioral activation without causing any morphological malformations.

Figure 1.
Behavioral effects of RB30 (1000 μg/mL) and RBF30 (1000 μg/mL) in zebrafish larvae. At 5 dpf, larvae demonstrated significantly elevated locomotor activity after RB30 and RBF30 treatments. (A,B) Locomotor activity is represented as total distance moved (percentage of control) during (A) a 60 min period and (B) as total distance moved per 10 min interval. Data are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (n = 18). Significance was set at * p ≤ 0.05, *** p ≤ 0.001 versus control and p ≤ 0.05 between RB30 and RBF30.
Furthermore, we performed a light and dark transition test in zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf that had been exposed to RBF30. This test is commonly used to determine the anxiety-related behavior, indicating hyper-locomotion, in response to light and dark transitions in rodent and zebrafish models [25,26]. The results showed that RBF30-supplemented larvae increased locomotor activity throughout the light and dark periods compared with the control group (Figure 2A). Additionally, the RBF30-treated group displayed reduced anxiety-like movements, resulting from a change from light to dark, compared to the control group (Figure 2B). Statistical significance was found in all dark-to-light phases, with p-values of 0.021 for the first phase (0–20 min), 0.011 for the second phase (20–40 min), 0.009 for the third phase (40–60 min), and 0.023 for the fourth phase (60–80 min). These findings suggest that RBF30 treatment can increase locomotor activity while reducing anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish larvae.


Figure 2.
Larval locomotor activity in alternating periods of light and dark after administration of RBF30 (1000 μg/mL). (A) Total distance moved under alternating light–dark cycles in each 2 min period. (B) Distance moved (percentage of control) of control and RBF30-treated larvae in each 10 min light–dark period. Data are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (n = 8). Significance was set at * p ≤ 0.05 and ** p ≤ 0.01 versus control.
Furthermore, while RBF30 and MDF treatments resulted in increased locomotion and alleviation of anxiety-like behavior, the PTZ treatment caused a reversal in locomotion under light–dark transition (Figure S4).
3.2. RBF30 Contains More Niacin Than RB30
To elucidate the difference in biological activities between the RB30 and RBF30 in zebrafish larvae, we used a PDA detector to scan the UV spectra of the two extracts. The UV spectral peaks of RBF30 were significantly higher than RB30 at 258.1 nm (Figure S5A). We further performed a full MS scan to identify the main components between the two extracts. The full MS scan (m/z 50 to 500) showed a single peak at [M + H]+ 124.1 at the same retention time as the UV spectra. The m/z 124.1 observed in RB30 and RBF30 was identified as protonated niacin, as previously reported (Figure S5B,C) [34,35]. Therefore, we applied the targeted MRM mode for the quantification of niacin in LC–MS/MS. We found that the niacin content in RBF30 (785 μg/g) was about 1.8 times higher than that in RB30 (418 μg/g).
In addition, we quantitatively analyzed niacin contents in the zebrafish larvae following exposure to RBF30. Our data revealed that the endogenous level of niacin was markedly higher (4-fold) in the RBF30-exposed group (0.47 ± 0.05 μM/single larva) than in the control group (0.12 ± 0.03 μM/single larva) in a zebrafish single larva (Figure 3A). These findings suggest that the RBF30-induced behavioral activation may be attributed to niacin absorption.

Figure 3.
Niacin contents and its behavioral effects in zebrafish larvae. (A) Niacin contents in control fish body and RBF30 (1000 μg/mL)-exposed fish body. (B) Comparison of behavioral effects of niacin (10 and 100 μM) and RBF30 (1000 μg/mL) in zebrafish larvae. During the first 10 min, niacin treatment resulted in increased locomotor activity; however, this effect was not maintained longer for the entire 60 min interval. The locomotor effects of RBF30 treatment on zebrafish larvae were maintained for 60 min. Data are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (n = 10). The lowercase alphabet letters in the graph are Duncan’s multiple range test.
Since the biological effects of niacin on larval behavior were not known, we introduced niacin to zebrafish larvae and compared fish locomotion with that induced by RBF30. The results indicated that niacin treatment dose-dependently increased locomotor activity during a 10 min period. However, it failed to maintain this hyperactivity for a period of 60 min as effectively as RBF30 treatment (Figure 3B). Overall, our results revealed that RBF30 contains a higher amount of niacin, which played a greater role in improving maintenance of hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae than RB30.
3.3. RBF30 Did Not Affect Innate Color Preference
Numerous studies have suggested that visual discrimination to the color can be a useful tool to characterize the drug response to the behavioral abnormality such as learning and memory function, and decision making following exposure to CNS drugs and neurotoxic agents [27,36]. Therefore, the innate color preference test was performed to better understand the neurobehavioral response to the dietary substance in zebrafish larvae. In the control group, normal fish exhibited an innate preference to the blue color, and avoidance to the yellow color (Figure 4A). These behavioral patterns were paralleled by RBF30- and MDF-treated groups (Figure 4B,C). However, PTZ treatment markedly disturbed these color preferences (Figure 4D). The p-value resulting from the two-way ANOVA analysis is presented in Table S1. These data indicate that RBF30 induces behavioral activation without affecting the decision making of zebrafish larvae.

Figure 4.
Color-preference patterns. Color preference (%) was calculated as the average number of larvae in each arms for 2 min for a total of 30 min of tracking. (A,B) Untreated control, (C,D) 5 mM PTZ, (E,F) 1 mM MDF, (G,H) 1000 μg/mL of RBF30 treatment (n = 40).
3.4. RBF30 Stimulate the Neural Activity
Recent imaging technology combined with stable expression of genetically encoded calcium indicators (GCaMPs) are powerful tools for brain activity mapping in in vivo [37]. To visualize the neuronal activity in RBF30-exposed zebrafish larvae, we crossed Tg (elavl3:GAL4-VP16) driver transgenic zebrafish with Tg (UAS:GCaMP7a). GAL4-VP16 protein is under control of the neuronal elavl3 promoter in Tg (elavl3:GAL4-VP16), and GCaMP7a is controlled by GAL4 upstream activation sequence (GAL4-UAS) in Tg (UAS:GCaMP7a) transgenic zebrafish. In the control group, we observed calcium transients at a frequency of two to four events per 3 min (Figure 5B). However, when the fish are supplemented with RBF30, fluorescence events were detected more frequently of four to seven on the tectum compared to the control group (Figure 5C). These data demonstrate that RBF30-induced behavioral activations are correlated with the upregulation of neuronal activity in zebrafish larvae.
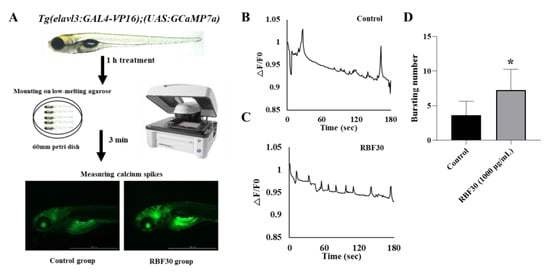
Figure 5.
Optical measurement of neuronal activity by RBF30 in zebrafish larvae. (A) Experimental setup. (B,C) Representative calcium traces (F/F0) of (B) control, (C) RBF30 treatment for 1 h. (D) Comparison of bursting numbers from control, and RBF30-treated larvae (n = 5). Significance was set at * p ≤ 0.05 versus control.
3.5. RBF30-Regulated Neurochemistry
We investigated whether the RBF30-induced hyperactivity with an alleviation of anxiety-like behavior resulted from the regulation of brain neurochemistry in zebrafish larvae. We profiled the comprehensive neurochemical systems such as histaminergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic, and serotonergic, mainly contributed to the fish behaviors such as motor activity, mood, and emotional response [38,39,40,41]. In the dopaminergic system, TYR was significantly downregulated by 73.0% (p < 0.001), whereas DA and NE were significantly upregulated by 123% (p < 0.001) and 139% (p < 0.005), respectively, in zebrafish larvae following exposure to RBF30 as compared to those in the control group. In the serotonergic system, RBF30 also significantly upregulated 5-HIAA and KYN by 123% (p < 0.001) and 139% (p < 0.005), respectively, compared to the control (Figure 6). These results suggest that RBF30-induced behavioral alteration might have pharmacological relevance to the regulations of serotonergic and dopaminergic neurochemicals in zebrafish larvae.

Figure 6.
Neurochemical effects of RBF30 treatment (1000 μg/mL) on the broad-spectrum neurochemistry in zebrafish larvae, as determined by LC–MS/MS. Quantification of endogenous neurochemicals including HA: histamine; HIS: histidine; ACHO: acetylcholine; BET: betaine; CHO: choline; SE: serine, PHE: phenylalanine; TYR, Tyrosine; DA: dopamine; NE: norepinephrine; 3-MT: 3-methoxytyramine; TRYP: tryptophan; 5-HTP: 5-hydroxytryptophan; 5-HIAA: 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; KYN: kynurenine. Endogenous levels of each neurochemical are represented as fold change relative to the control group. The data are expressed by means ± standard deviation of the mean value (n = 50 × 7). Significance was set at ** p ≤ 0.01 and *** p ≤ 0.001 versus the control group.
4. Discussion
Functional foods are defined as natural products or processed foods that contain biologically active compounds and provide health benefits for the prevention and treatment of various diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammation [42,43]. Rice bran, which is a by-product of rice processing, contains several nutrients and bioactive ingredients such as magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and pyridoxine) [44], which regulate physiological functions such as metabolism and homeostasis. Rice bran can be produced using different processes including stabilization, enzymatic treatment, and fermentation [7,45,46]. Food fermentation by microorganisms is a widely used processing technology that improves nutritional and therapeutic properties [47,48,49]. Several studies have investigated the health benefits of fermented rice bran which include anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, and lipid-lowering effects [8,11,12,13]. However, the neurological functions of fermented rice bran as a brain food were limitedly known in animals.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of food fermentation with various microorganisms [21,22,23,50] on brain functions, including behavioral activity, neural activity, and neurochemistry in zebrafish larvae after exposure to RBF30. We determined the no observed adverse effect concentration (NOAEC) of RBF30 in zebrafish larvae to be 1000 μg/mL. Our results showed that RFB30-exposed zebrafish exhibited increased locomotor activity compared to control and RB30-exposed fish (Figure 1). This hyperactivity was correlated with increased neural activity (Figure 4) in the Tg (huC:GAL4-VP16), (UAS:GCaMP7a) zebrafish larvae and was similar to the effects of CNS stimulants such as MDF and PTZ (Figure 5). Furthermore, RBF30 treatment significantly alleviated anxiety-like behavior (Figure 2). The color preferences of the zebrafish larvae were not affected by RBF30 exposure (Figure 4). On the other hand, PTZ caused confused preferences and hyperactivity, suggesting a different mechanism of action. These findings highlight the importance of understanding the mechanisms of action of drugs in behavioral studies.
Furthermore, niacin, one of the bioactive components found in rice bran, was identified as an active ingredient, which is responsible for the induction of hyperactivity in RBF30-supplemented zebrafish larvae (Figure S5). The endogenous niacin was found to be markedly elevated by 4-fold in the larval body, compared to control fish (Figure 3A). The main active ingredient of RBF30 was confirmed to be niacin and used to compare the behavioral effects of RBF30 and niacin. While niacin supplementation also increased locomotor activity in the first 10 min of exposure, it did not maintain hyperactivity for the entire 60 min period (Figure 3B). These findings suggest that the high levels of niacin resulting from RBF30 supplementation may be responsible for the sustained hyperactivity.
Niacin is a type of vitamin B3 that includes two vitamers, such as nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, that can act as a precursor to generate the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and its phosphate form, the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) in the body. These coenzymes are responsible for the redox regulation, but also play essential roles in energy metabolism, redox homeostasis, and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Given that niacin is involved with a variety of biological events in the body [51,52], its deficiency due to the blockage of the kynurenergic pathway in the TRYP metabolism has been implicated in neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia [53,54,55]. In addition, a low level of vitamin B3 was detected in the behavioral-defected PD symptoms in a combination of reduced DA level, which is responsible for motor function and mood. The pharmacological relationships between niacin and PD were found in several cases, depletion of niacin occurred as a reduced DA level in the striatal region, while niacin supplement leads to improvements of motor functions in PD patients [51,52,53,54,55,56,57].
In this study, we further explored the broad-spectrum neurochemistry including histaminergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic, and serotonergic systems to better understand the behavioral effects of RBF30 in zebrafish larvae. Interestingly, the results revealed that RBF30-caused behavioral profiles resulted from metabolic regulations of serotonergic and dopaminergic neurochemistry. In particular, DA and its metabolite NE were markedly elevated in RBF30-exposed zebrafish (Figure 6). The dopaminergic control is known to be associated with motor functions and anxiety behaviors [39,58,59], and the relationship between RBF30-induced hyperactivity and increased dopaminergic neurochemicals such as DA and NE suggests that this may be the underlying mechanism for the neurobehavioral action of RBF30 in the zebrafish larvae model.
The current study demonstrated that fermented rice bran extract, which was prepared using a combination of five microorganisms, has beneficial effects on the nervous system of zebrafish larvae. However, further studies are necessary to investigate the individual effects of microorganisms on the biological activity of rice bran fermentation extract. This approach can provide important information on how microorganisms contribute to the nutrient profile and biological activity of rice brain extract. Although our study did not provide a molecular mechanism for the observed behavioral alterations in the zebrafish larvae model, our results suggest that RBF30 has the potential to regulate brain neurochemistry, which was confirmed by LC–MS/MS-based metabolomics. Further investigation into neurochemical signaling, particularly the serotonergic and dopaminergic systems, may be necessary to interpret the pharmacological relevance between rice bran fermentation and behavior in the zebrafish model.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the biological effects of RBF30, a rice bran fermented by five patented microorganism strains on behaviors, neural activity, and comprehensive neurochemistry in zebrafish larvae. Various behavioral assays showed that RBF30 treatment increased locomotor activity and reduced anxiety-like behavior, with a normal decision-making pattern in zebrafish larvae. Furthermore, RBF30 treatment upregulated serotonergic and dopaminergic neurochemicals such as DA, NE, 5-HIAA, and KYN in zebrafish, thereby influencing behavioral profiles. Overall, RBF30 could potentially be used as a food supplement to improve brain function by modulating endogenous neurochemical levels.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9050479/s1, Figure S1: Schematic illustrating the purification of RBF30; Figure S2: Behavioral effects of ethanol (EtOH) fractions 0 to 100% (v/v) of various concentrations of RBF30 in 5 dpf zebrafish larvae; Figure S3: Larval locomotor activity in 5 dpf zebrafish larvae; Figure S4: Larval locomotor activity in alternating periods of light and dark after administration of MDF and PTZ; Figure S5: UV and MS spectrum; Table S1: Statistical analysis of color preference using two-way Anova (treatment versus color).
Author Contributions
J.S.C., S.S.K. and K.-S.H.: investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. H.K., J.Y.Y., B.L., D.-S.S. and B.P.: investigation and resources. M.A.B.: writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, supervision, and project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (grant No. 2020-10063396) and the Ministry of SMEs & Startups (S2666329), Republic of Korea. This work was also partially supported by a project of the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (SI2231-40), Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the NIH guide for the care and use of Laboratory Animals (No. 8023, revised in 1996), and this work was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (7B-ZF1).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data can be available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boonloh, K.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Kongyingyoes, B.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Thawornchinsombut, S.; Pannangpetch, P. Rice bran protein hydrolysates improve insulin resistance and decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in rats fed a high carbohydrate-high fat diet. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6313–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Bhanger, M.; Anwar, F. Antioxidant properties and components of some commercially available varieties of rice bran in Pakistan. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Yang, S.-B.; Hong, S.-G.; Lee, S.-A.; Hwang, S.-J.; Shin, K.-S.; Suh, H.-J.; Park, M.-H. A polysaccharide extracted from rice bran fermented with Lentinus edodes enhances natural killer cell activity and exhibits anticancer effects. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, A.; Kawakami, Y.; Kimura, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Nakagawa, K. α-tocopherol attenuates the triglyceride-and cholesterol-lowering effects of rice bran tocotrienol in rats fed a western diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5361–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, N.; Rodriguez-Alegria, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Lopez-Munguia, A. Enzymatic treatment of rice bran to improve processing. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinger, E.; Ziegler, V.; da Silva Catalan, A.A.; Krabbe, E.L.; Elias, M.C.; Xavier, E.G. Whole rice bran stabilization using a short chain organic acid mixture. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2015, 61, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alauddina, M.; Islama, J.; Shirakawaa, H.; Kosekib, T.; Ardiansyahc, K.M. Rice bran as a functional food: An overview of the conversion of rice bran into a superfood/functional food. In Superfood and Functional Food-An Overview of Their Processing and Utilization; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Baek, S.E.; Ingkasupart, P.; Park, H.J.; Kang, S.G. Effects of rice bran extracts fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum on neuroprotection and cognitive improvement in a rat model of ischemic brain Injury. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 2015, 21, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupski, L.; Cipolatti, E.; Rocha, M.D.; Oliveira, M.d.S.; Souza-Soares, L.d.A.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Solid-state fermentation for the enrichment and extraction of proteins and antioxidant compounds in rice bran by Rhizopus oryzae. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2012, 55, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yeo, D.; Hong, J.H. Effect of dihydroferulic acid obtained from fermented rice bran extract on neuroprotection and behavioral recovery in an ischemic rat model. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagl, S.; Asseburg, H.; Heinrich, M.; Sus, N.; Blumrich, E.-M.; Dringen, R.; Frank, J.; Eckert, G.P. Effects of long-term rice bran extract supplementation on survival, cognition and brain mitochondrial function in aged NMRI mice. Neuromol. Med. 2016, 18, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Koseki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Budijanto, S.; Oikawa, A.; Alauddin, M.; Goto, T.; Aso, H.; Komai, M.; Shirakawa, H. Dietary supplementation of fermented rice bran effectively alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, E.; Lee, C.H.; Da Hye Jeong, K.L.; Kim, T.-H.; Roh, S.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Rhee, M.H. Fermented rice bran prevents atopic dermatitis in DNCB-treated NC/Nga mice. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kan, H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Yang, J.Y.; Son, Y.; Shin, D.-S.; Lee, B.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Cho, S.-H. Neurochemical Effects of 4-(2Chloro-4-Fluorobenzyl)-3-(2-Thienyl)-1, 2, 4-Oxadiazol-5 (4H)-One in the Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Epileptic Seizure Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.; Mullins, M.C. Dissection of organs from the adult zebrafish. JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2010, 37, e1717. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.S.; Im, S.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-R.; Kim, G.R.; Chae, J.S.; Shin, D.-S.; Song, J.S.; Ahn, S.; Lee, B.H. Zebrafish as a screening model for testing the permeability of blood–brain barrier to small molecules. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C. The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A review. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish larvae as a behavioral model in neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegelenbosch, R.A.; Noldus, L.P.; Richardson, M.K.; Ahmad, F. Zebrafish embryos and larvae in behavioural assays. Behaviour 2012, 149, 1241–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H. Novel Lactobacillus Buchneri and Use Thereof. KR Patent KR101917497B1, 9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.H. Novel Lactobacillus Harbinensis and Use Thereof. KR Patent KR101889647B1, 20 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.H. Novel Saccharomycopsis Fibuligera and Use Thereof. KR Patent KR101876668B, 19 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; 2000; Available online: https://zfin.org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.html (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Ellis, L.D.; Seibert, J.; Soanes, K.H. Distinct models of induced hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae. Brain Res. 2012, 1449, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrant, A.E.; Schramm-Sapyta, N.L.; Kuhn, C.M. Use of the light/dark test for anxiety in adult and adolescent male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.; Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, T.-I.; Bae, Y.-K.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, C.-H. Innate color preference of zebrafish and its use in behavioral analyses. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Satou, C.; Higashijima, S.-I. V2a and V2b neurons are generated by the final divisions of pair-producing progenitors in the zebrafish spinal cord. Development 2008, 135, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, A.; Ohkura, M.; Abe, G.; Nakai, J.; Kawakami, K. Real-time visualization of neuronal activity during perception. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Long, Y.; Xie, J.; Ren, J.; Zhou, T.; Song, G.; Li, Q.; Cui, Z. Generation of GCaMP6s-Expressing Zebrafish to Monitor Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Calcium Signaling Elicited by Heat Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Song, J.S.; Bae, M.-A.; Ahn, S. UPLC-MS/MS-based profiling of 31 neurochemicals in the mouse brain after treatment with the antidepressant nefazodone. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrikanova, T.; Serruys, A.-S.K.; Buenafe, O.E.; Clinckers, R.; Smolders, I.; de Witte, P.A.; Crawford, A.D.; Esguerra, C.V. Validation of the zebrafish pentylenetetrazol seizure model: Locomotor versus electrographic responses to antiepileptic drugs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornell, F.; Valvassori, S.S.; Steckert, A.V.; Deroza, P.F.; Resende, W.R.; Varela, R.B.; Quevedo, J. Modafinil effects on behavior and oxidative damage parameters in brain of Wistar rats. Behav. Neurol. 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosniyana, A.; Hashifah, M.; Norin, S.S. The physico-chemical properties and nutritional composition of rice bran produced at different milling degrees of rice. J. Trop. Agric. Food Sci. 2007, 35, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncel, N.B.; Yılmaz, N.; Kocabıyık, H.; Uygur, A. The effect of infrared stabilized rice bran substitution on B vitamins, minerals and phytic acid content of pan breads: Part II. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Hwang, K.-S.; Yang, J.Y.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, G.R.; Kan, H.; Jung, M.H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Song, J.S.; Ahn, S. Neurochemical and behavioral analysis by acute exposure to bisphenol A in zebrafish larvae model. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerboom, J.; Chen, T.-W.; Wardill, T.J.; Tian, L.; Marvin, J.S.; Mutlu, S.; Calderón, N.C.; Esposti, F.; Borghuis, B.G.; Sun, X.R. Optimization of a GCaMP calcium indicator for neural activity imaging. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 13819–13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Sallinen, V.; Sundvik, M.; Kolehmainen, J.; Torkko, V.; Tiittula, A.; Moshnyakov, M.; Podlasz, P. Modulatory neurotransmitter systems and behavior: Towards zebrafish models of neurodegenerative diseases. Zebrafish 2006, 3, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacprzak, V.; Patel, N.A.; Riley, E.; Yu, L.; Yeh, J.-R.J.; Zhdanova, I.V. Dopaminergic control of anxiety in young and aged zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.; Li, Y.-W.; Chen, Q.-L.; Shen, Y.-J.; Liu, Z.-H. Tributyltin enhanced anxiety of adult male zebrafish through elevating cortisol level and disruption in serotonin, dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid neurotransmitter pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 111014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Takai, Y.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Persistent impact of amitriptyline on the behavior, brain neurotransmitter, and transcriptional profile of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, R.; Thomas, P.R. Opportunities in the Nutrition and Food Sciences: Research Challenges and the Next Generation of Investigators; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, M.; Anese, M. Re-thinking functional food development through a holistic approach. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 81, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, L. Rice processing: Beyond the farm gate. In Encyclopedia of Food Grains, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.-H.; Chang, H.-C. Rice bran fermentation using Lactiplantibacillus plantarum EM as a starter and the potential of the fermented rice bran as a functional food. Foods 2021, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.P.; Heuberger, A.L.; Weir, T.L.; Barnett, B.; Broeckling, C.D.; Prenni, J.E. Rice bran fermented with Saccharomyces boulardii generates novel metabolite profiles with bioactivity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheigh, H.S.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, C. Biochemical, microbiological, and nutritional aspects of kimchi (Korean fermented vegetable products). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1994, 34, 175–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.; Ferrão, J.; Fernandes, T. Nutritional guidelines and fermented food frameworks. Foods 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.S.; El Sheikha, A.F.; Hammami, R.; Kumar, A. Traditionally fermented pickles: How the microbial diversity associated with their nutritional and health benefits? J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H. Novel Pichia Kudriavzevii and Use Thereof. KR Patent KR101876669B1, 9 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, R.-S.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. NAD (H) and NADP (H) redox couples and cellular energy metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperi, V.; Sibilano, M.; Savini, I.; Catani, M.V. Niacin in the central nervous system: An update of biological aspects and clinical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T. Niacin metabolism and Parkinson’s disease. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2005, 10, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakade, C.; Chong, R.; Bradley, E.; Morgan, J.C. Low-dose niacin supplementation modulates GPR109A, niacin index and ameliorates Parkinson’s disease symptoms without side effects. Clin. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seamon, M.; Purohit, S.; Giri, B.; Baban, B.; Morgan, J.; Chong, R.; Wakade, C. Niacin for Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 11, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakade, C.; Chong, R. A novel treatment target for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 347, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, R.; Wakade, C.; Seamon, M.; Giri, B.; Morgan, J.; Purohit, S. Niacin Enhancement for Parkinson’s Disease: An Effectiveness Trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 667032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Sima, Y.; Zhong, Z.-m.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.-F.; Liu, C.-F. Parkinson’s disease-like motor and non-motor symptoms in rotenone-treated zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 2017, 58, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shontz, E.; Souders, C.; Schmidt, J.; Martyniuk, C. Domperidone upregulates dopamine receptor expression and stimulates locomotor activity in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, e12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).