Abstract
Lignocellulosic biomass and agro-industrial residues are a source of fermentable sugars; however, pretreatments are needed to overcome biomass recalcitrance. This study evaluated the effect of sugarcane bagasse hydrolysis and fermentation in response to dilute acid pretreatment. In natura bagasse, extractive-free bagasse, partially delignified bagasse, and bagasse with added butylated hydroxytoluene antioxidant were pretreated with diluted acid and investigated in semi-simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (S-SSF). The effect of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) resulted in lower yields of inhibitors in the liquid fraction of the acid pretreatment (0.01 g L−1 of furfural, 0.01 g L−1 of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, and 0.68 g L−1 of acetic acid). Partially delignified material and material with BHT resulted in biomass with low hemicellulose and lignin contents, indicating that BHT influenced lignin removal. Extractives removal showed benefits for the acid pretreatment, decreasing the dioxane-soluble material, and a higher yield of glucose and ethanol via S-SSF for the partially delignified material. Enzymatic saccharification of partially delignified material showed 87% of cellulose conversion (24 h with 15 FPU/g), and after 48 h of S-SSF (25 FPU/g), residual 7.06 g L−1 of glucose and production of 15.17 g L−1 of ethanol were observed. The low content of extractives, lignin, and dioxane soluble material resulted in better cellulose accessibility and ethanol yield. Chemical compounds can help remove lignin from biomass favoring ethanol production by S-SSF.
1. Introduction
Excessive consumption of fossil fuels has led to an increase in the use of oil reserves, increasing greenhouse gas emissions and worsening environmental concerns. Changes in the environment have motivated researchers to explore alternative fuels based on sustainable biological resources [1]. Lignocellulosic materials are among the most abundant biomasses generated in the world. They contain carbohydrates that can be converted into ethanol defined as second-generation ethanol (2G ethanol) [2]. Among the various lignocellulosic residues used in the 2G ethanol production and commercial added-value compounds, sugarcane bagasse is a viable option. Using sugarcane bagasse generated in the sugar and alcohol industry can increase the production of 2G ethanol without needing to increase the cultivated area and to compete for physical space (arable land) with food crops [3].
Brazil is the largest sugarcane producer responsible for almost double of the amount produced by the second country (India, with 376 million tons) [4]. For each ton of sugarcane processed, 140 kg of dry bagasse and 140 kg of dry straw are generated. For every 8.4 million hectares of sugarcane cultivated, approximately 80 million tons of bagasse and 80 million tons of straw are produced. A large amount of residue from the sugar and ethanol industries was incinerated to produce steam for electric power generation. Integrated into the biorefinery process, the available sugarcane bagasse can be used in the production of bioproducts and biofuels, such as cellulosic ethanol [5,6]. Between 149 and 192 L of cellulosic ethanol per ton of bagasse can be produced, varying according to differences in pretreatments, enzymatic saccharification, and fermentation [1].
In 2G ethanol production, due to the highly recalcitrant nature of the biomass, pretreatments are required to remove/modify the hemicellulose/lignin. The pretreatment exposes cellulose to enzymatic action [7,8] solubilizing fermentable sugars [5] to the fermentation step. In acid pretreatments associated with high temperatures and pressures, sugar degradation products are formed, such as furfural, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), and acetic acid, resulting from the degradation of pentoses and hexoses, respectively [2]. These degradation products are inhibitors of the fermentation process, interfering with microorganism growth and ethanol production [9]. Sugar degradation products react with lignin fragments solubilized in acid pretreatment by polycondensation and/or polymerization, producing pseudo-lignin. This molecule consists of carbonyl, carboxylic, aromatic, and aliphatic structures that significantly inhibit the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Due to hydrophobic interactions, cellulases are irreversibly bound to droplets of pseudo-lignin, resulting in loss of enzyme activity and, consequently, requiring higher enzymatic loads [10]. Thereby, pseudo-lignin can influence enzymatic saccharification or Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF).
Enzymatic saccharification can be performed separately from the fermentation stage or simultaneously. Following two steps in ideal conditions leads to benefits, such as recycling cells after fermentation, but the capital cost is higher because two-unit steps are necessary, and the efficiency of the process can be limited by inhibiting enzymatic activity in the final product, especially when there is a high content of total solids. On the other hand, in the SSF process, enzymes and fermenting microorganisms work together, and glucose is fermented as it is produced. This procedure is carried out in a single reactor, but one of the steps does not occur in its optimum condition [11].
The pretreatment benefits the removal of lignin and consequently the saccharification of cellulose. However, the efficiency of chemical additives in removing lignin may vary according to the origin of the biomass used (nature of the lignin), type of pretreatment, and severity of conditions applied [12]. The addition of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) in the pretreatment can reduce the reaction rates of lignin monomers (degradation, modification, and/or condensation). Radical reactions associated with the effects of BHT for acidolysis conducted in dioxane-water were reported for the technical study of lignin composition. The action of BHT can scavenge electrophilic free radicals, which would increase aromatic nuclei at the position of the C-6 ring [13]. The BHT is an antioxidant used in the field of food, recognized as a cheap product.
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the cellulosic ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse by S-SSF, influenced by lignin and extractive content. A short pre-hydrolysis was conducted before SSF, with optimum conditions for each one. The sugarcane bagasse was subjected to dilute acid pretreatment (20% H2SO4 m/m at 121 °C for 30 min) in four different configuration. In natura biomass (1), a by-product of the ethanol and sugar industries; extractive-free biomass (2), obtained by washing with ethanol and water; partially delignified biomass (3), through the action of sodium chlorite and acetic acid treatment (70 °C for 5 h); and in natura biomass pretreated with BHT (4), a phenolic antioxidant widely used in foods to delay the auto-oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which is cheap and easy to use.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
Sugarcane bagasse was kindly donated by São João Plant (Araras-SP). The biomass was oven-dried at 55 °C for 24 h, and ground in a knife mill to reduce the particle size. The milled material was selected using a 20-mesh (screen/mesh opening: 0.85 mm) sieve knife mill. The sieved material was used in the study, called milled in natura biomass (IN).
2.2. Biomass Preparation
Approximately 10 g of the in natura sugarcane bagasse was subjected to the removal of extractives in the soxhlet apparatus. The biomass was packed in filter paper envelopes and the extraction took place for 8 h, consecutively using ethanol and water, obtaining extractive-free biomass. In natura biomass was subjected to the partial delignification process, using 10 g of bagasse in Schott flasks in 400 mL of ultrapure water, together with 3.76 g of sodium chlorite and 1.26 mL of glacial acetic acid. The glass flasks were sealed with a Teflon cap and heated in a water bath at 70 °C for 5 h. Three additional doses of sodium chlorite and acetic acid were added after 2, 3, and 4 h of reaction. After 5 h of reaction, biomass was filtered on filter paper and the liquid fraction was discarded. The solid fraction was washed with 1.5 L of water heated to 70 °C and 4 L of water at 25 °C. Partially delignified biomass (DL) was oven-dried at 55 °C for 24 h. Biomasses (in natura, extractive-free, and partially delignified) were stored in plastic bottles for future analysis [14].
2.3. Dilute Acid Pretreatment
The three biomass samples produced (in natura, extractive-free, and partially delignified) were subjected to dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment. First, 5 g of samples were soaked in 20% (m/m) H2SO4 (m/m, acid mass/bagasse mass equivalent to 2% acid mass/reaction volume), solid-to-liquid ratio 1:10. The reaction time was 30 min in an autoclave at 121 °C/1 atm. The fourth test was carried out with IN biomass, under the same conditions, adding butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), 20% m/m (2% m/v) in the reaction medium. BHT was applied at a low dosage, similar to acid concentration in the dilute acid pretreatment.
After natural cooling, the reaction medium was filtered using filter paper. The liquid fraction was stored for sugar and degradation products quantification by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The solid fraction was washed with distilled water until reaching neutral pH. The pretreated biomasses (in natura, extractive-free, partially delignified, and with BHT addition to acid pretreatment) were then oven-dried at 55 °C for 24 h and stored for future procedures.
2.4. Chemical Characterization
The untreated and pretreated sugarcane biomasses were subjected to chemical composition to determine the cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents. To achieve this, 300 mg of the biomass was conditioned in glass flasks coupled with 3 mL of 72% sulfuric acid and heated at 30 °C for 1 h. The reaction was periodical mixing with a glass rod and after adding 84 mL of distilled water, the material was autoclaved at 121 °C for 1 h. The biomass was filtered using porous plate crucibles previously dried at 105 °C and tared. The resulting hydrolysate was used to determine the soluble lignin (UV-VIS 215 and 280 nm) and sugars by HPLC. The crucibles containing the remaining biomass residue were dried in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h to determine the insoluble lignin [15].
2.5. Dioxane Compounds Solubilization
Pretreated biomass (1 g) was used to determine pseudo-lignin and similar chemical compound content. The sample was washed using a solution of 1.4 p-dioxane:water (9:1) for 8 h in a soxhlet. The pseudo-lignin was recovered by solvent evaporation [16]. Pseudo-lignin extracted samples were examined in Infrared (FTIR) attenuated total reflectance (ATR), using a FTIR-VERTEX 70/BRUKER spectrophotometer.
2.6. Microorganism and Culture Media
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (PE-2) was obtained from the stock culture of São Paulo State University (Unesp), Rio Claro, SP, Brazil. It was maintained in solid medium YEPD with agar: yeast extract (10 g L−1); peptone (20 g L−1); dextrose (20 g L−1); Agar (18 g L−1); chloramphenicol (5 ppm). The cultures were maintained in mineral oil and preserved at −4 °C, with regular transfer to new media. For cell culture multiplication, oil-preserved culture was added to 50 mL previously sterilized (121 °C for 15 min) of YEPD liquid medium in Erlenmeyer flasks and incubated at 30 °C, 130 rpm for 72 h in a shaker table. The culture suspension was used in the fermentation medium [9].
2.7. Enzymatic Saccharification
Untreated sugarcane bagasse and bagasse pretreated with acid were subjected to enzymatic saccharification with an enzyme load of 15 FPU/g of material (Cellic CTec 2—Novozymes). Approximately 0.1 g of biomass was added to a 5 mL solution of 0.05 mol L−1 sodium citrate buffer, pH 4.8, at 50 °C for 24 h [17]. Agitation was provided at 120 rpm in an incubator. The reaction was interrupted in boiling water for 5 min and then centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 15 min, obtaining liquid and solid fraction separation. The hydrolysate was evaluated by HPLC for sugar determination, and the values obtained were used to calculate the enzymatic digestibility of sugarcane bagasse (anhydroglucose released in relation to the glucan/cellulose content) from the cellulose content. Equation (1) was used to obtain the glucose yields as follows:
where glucose is the concentration of glucose released during enzymatic saccharification (g L−1); biomass is the dry biomass concentration at the beginning of the enzymatic saccharification (g L−1); f is the cellulose fraction in dry biomass (g 100 g−1); and 1.11 is the conversion factor of cellulose to glucose equivalents.
Cellulose conversion (%) = 100 × glucose concentration/(1.11 × f × mass biomass)
2.8. Semi-Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (S-SSF)
The four pretreated biomasses were subjected to S-SSF (Figure 1). YEP medium was prepared with yeast extract, peptone, and chloramphenicol (in the same concentrations mentioned in Section 2.6) in volumetric flasks, and the desired volume was completed with sodium citrate buffer (50 mmol L−1, pH 4.8) and then autoclaved at 121 °C for 15 min. Around 3 g of acid-pretreated sugarcane bagasse (in natura, extractive-free, partially delignified, and with BHT addition to acid pretreatment) was placed in fermenters containing 60 mL of sodium citrate buffer solution (solid-to-liquid ratio 0.5:10). The mixture was incubated at 50 °C with 25 FPU/g substrate (Cellic® CTec 2—Novozymes) under constant agitation of 120 rpm for 6 h. This pre-saccharification step under optimal conditions for enzymatic activity was performed to provide fermentable sugars to microorganisms at the time of inoculation. After cooling the reactors to 30 °C in a water bath, 10% v/v of fermenting yeasts (S. cerevisiae) were inoculated. The equivalent cell suspension was 1.4 × 109 cells mL−1 or 35 g L−1 in dry weight (105 °C/24 h, until constant weight). After subtle manual stirring to homogenize the medium, an aliquot of 100 µL was removed for counting viable microorganisms in the Neubauer chamber using erythrosine as a differential dye [9]. The fermenters were immediately shaken and incubated at 30 °C starting the fermentation time count (time 0).
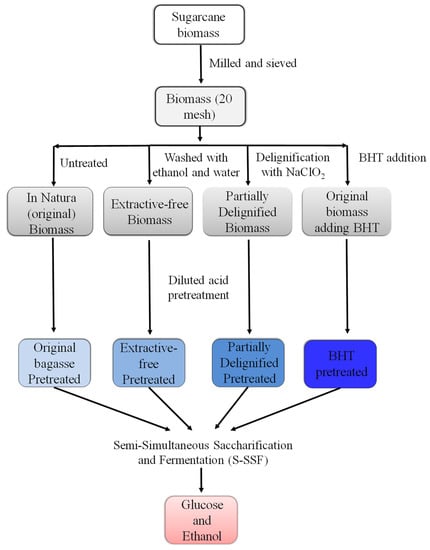
Figure 1.
Flowchart of Semi-Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (S-SSF). BHT—butylated hydroxytoluene.
The fermentation was carried out for 48 h, and every 12 h, aliquots were collected to count viable cells (survival percentage > 95%) and quantified sugars and ethanol in the liquid fraction by HPLC. The samples were centrifuged, and the supernatant was filtered by polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (PVDF 0.22 μm—Millipore) and stored in a freezer (−5 °C) for subsequent analysis. During fermentation analyzes, the pH of the medium was verified, with a variation of 4.8 (time 0) to 4.5 (12, 24, 36, and 48 h). As a preliminary measure, a Handheld RHB-90 optical refractometer was used to determine the sugar concentration in BRIX units (soluble solids content determined from the refraction index of the light passed through the sample) [18].
2.9. Ethanol, Sugars, and Acetic Acid Quantification
Pentoses, hexoses, ethanol, and acetic acid in the liquid fraction of the dilute acid pretreatment, chemical characterization, and S-SSF were quantified by HPLC Shimadzu HPLC, with Aminex column (Bio-Rad) HPX-87 H, mobile phase 50 mmol L−1 H2SO4, the flow of 0.6 mL min−1, 65 °C, and RID detector. HMF and furfural from dilute acid pretreatment were quantified in column C18 (NST) 150 mm × 4.6 mm × 0.5 μm, mobile phase water:acetonitrile (8:1) with 1% acetic acid, the flow of 0.8 mL min−1, oven 35 °C, UV-VIS detector, isocratic method.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrolysate from Acid Pretreatment (Liquid Fraction)
Bagasse acid pretreatment resulted in the highest glucose concentrations in the liquid fraction (3.35 g L−1) and the lowest glucose concentrations in partially delignified bagasse (0.74 g L−1). Xylose concentrations varied between 23.35 g L−1 and 21.18 g L−1 in the BHT and partially delignified biomasses, respectively. Pretreated bagasse presented 1.35 g L−1 of HMF in the hydrolysate, a concentration higher than that observed in the other pretreatments (0.4 g L−1 in extractive-free and 0.01 in BHT and partially delignified). Furfural concentration was between 0.1 g L−1 in partially delignified acid pretreatment and 0.01 g L−1 in BHT acid pretreatment, while acetic acid was observed in concentrations between 4.09 g L−1 (in natura pretreatment) and 0.68 g L−1 (BHT pretreatment). Bagasse in natura showed the highest concentrations of inhibitors (HMF and acetic acid) after acid pretreatment, while the experiments with BHT showed the lowest concentrations of inhibitors evaluated among the treatments (Table 1).

Table 1.
Monosaccharides and degradation products released in the hydrolysate (g L−1) from the dilute acid pretreatment (20% m/m H2SO4, 121 °C/30 min, solid-to-liquid ratio 1:10).
Pretreatments of sugarcane bagasse in a dilute acid medium (1% m/v sulfuric acid at 190 °C for 10 min and solid-to-liquid ratio 1:10) resulted in 3.09 g L−1 of glucose; 9.33 g L−1 of xylose; 0.02 g L−1 of HMF; 0.1 g L−1 of furfural; and 2.98 g L−1 of acetic acid in hydrolysate [19]. Glucose values observed in this study are close to those reported in the cited literature (3.09 g L−1): however, xylose values obtained were more than double the values presented in the literature. This difference may be a result of the sulfuric acid load and the pretreatment time applied to biomass, which can also interfere with the formation of inhibitors.
Bagasse was pretreated with 1% acid (v/v) for 60 min/121 °C with solid-to-liquid ratio 1:15 m/v [20]. The hydrolysate showed lower glucose and xylose content (1.7 g L−1 of glucose; 7.12 g L−1 of xylose) but a higher amount of furfural and acetic acid (0.11 g L−1 of furfural and 1.56 g L−1 of acetic acid) compared to the present study. In the present study, glucose concentrations are close to those found in the literature, while high xylose values can be attributed to the difference in biomass heterogeneity and recalcitrance (resistance to pretreatment). Moreover, the lower amounts of furfural were probably due to the shorter exposure time of the biomass in the pretreatment and also the lower solid:liquid proportion. Increasing the solid:liquid proportion showed a higher concentration of xylose and consequently the furfural and HMF concentration [21]. A long-exposure sugarcane bagasse pretreatment (150 min reaction time) with 1% sulfuric acid at 121 °C (20% solids loading) was applied. Increasing the solid:liquid proportion is positive for xylose release; however, it needs to increase the reaction time mainly if the acid concentration is reduced.
3.2. Chemical Characterization
Pretreatment with dilute acid changed the chemical composition of the biomass (raw material) with the partial removal of hemicellulose. The acid pretreatment caused cellulose and lignin percentage increase due to hemicellulose solubilization. Pretreatment with BHT and delignification resulted in a decrease in the lignin percentage. Component removal indicated that the dilute acid treatment removed large amounts of hemicellulose (between 71% and 81%), while BHT and sodium chlorite removed lignin from biomass (41% and 60%, respectively). However, sodium chlorite removed one-third more lignin than BHT (g 100 g−1 based on raw material) (Table 2). These results show a positive action of BHT in the removal of lignin compared to in natura (original) pretreatment and extractive-free pretreatment, indicating that this compound has a potential effect on the lignin fraction of the biomass.

Table 2.
Effect of lignin and extractives removal in the chemical composition of pretreated sugarcane bagasse (20% m/m H2SO4, 121 °C/30 min, solid-to-liquid ratio 1:10).
Sugarcane bagasse pretreated with dilute sulfuric acid (1%, v/v H2SO4, at 121 °C for 30 min) showed cellulose increase by 14% (percentual points—pp), hemicellulose decrease by 22% (pp), and lignin increase by 11% (pp) [22]. Higher yields of hemicellulose removal can be obtained with higher acid loads in the reaction medium, which is observed in the hemicellulose content of the pretreated bagasse in this study. Cellulose and lignin values are close to those found in the literature.
As reported in the literature, the chemical composition of sugarcane bagasse in natura average was 42% cellulose, 27.7% hemicellulose, and 20% lignin [23]. This average was calculated/reported considering 21 samples of sugarcane bagasse, showing the variability in the chemical composition. Cellulose ranged from 35% to 47.3%, hemicellulose 22.9 to 27.7%, and lignin 14.1% to 30.6%. A variation in the chemical composition have been reported for lignocellulosic materials [24,25,26]. After dilute acid pretreatment (10% H2SO4 m/v, at 120 °C for 10 min), 59% cellulose, 15% hemicellulose, and 22% lignin were observed. However, pretreated biomass subjected to delignification in an alkaline medium (1.5% NaOH m/v, at 100 °C for 1 h, solid-to-liquid ratio 0.5:10 m/v) and after chemical characterization revealed a composition of 83% cellulose, 5% hemicellulose, and 7% lignin [27]. Alkaline pretreatment removes lignin (with carbohydrate solubilization) increasing the porosity and surface area. However, combined with acid pretreatment, it generates cellulose-rich material. As observed in this study, lower levels of hemicellulose in the acid-pretreated biomass corresponded to the longer reaction time pretreatment.
The literature shows a great reduction in hemicellulose content that occurred when combining acid and alkaline pretreatments. Sugarcane bagasse with a chemical composition of 38% cellulose, 27% hemicellulose, and 17% lignin, after pretreatment (2% v/v sulfuric acid at 121 °C for 30 min and 20% m/v of residual biomass immersed in a 4% m/m sodium hydroxide solution at 121 °C for 30 min) resulted in values of 65% cellulose, 11% hemicellulose and 8% lignin [28]. A combination of acid pretreatment with delignification techniques can generate cellulose-rich biomass. However, mild conditions should be used to minimize the formation of inhibitors.
Pretreatment parameters not only cause biomass deconstruction but also contribute to the reorganization of lignin, which can vary according to the severity of the pretreatment. The breakdown of the cellulose–hemicellulose–lignin complex during the acid pretreatment increases the surface area of the cellulose. The main constituents of biomass agree with the data observed in the literature. However, the chemical composition of the bagasse can vary according to the cultivated genotype, location of the harvest, year of planting, and environmental parameters, such as rainfall index [3].
3.3. Material Solubilization in Dioxane
Dioxane was applied aiming to solubilize material adsorbed on the lignocellulosic fiber structure. This adsorbed material could be from lignin derivatives that were solubilized in an acid medium and further condensed and precipitated. The adsorbed material can also be from degradation products that condense and precipitate. The hypothesis was that a pretreatment or procedure could influence this soluble material in dioxane, leading to an increase or decrease avoiding compound formation or condensation/precipitation.
The highest levels of dioxane compound solubilization (comprising pseudo-lignin and chemically similar structures) were observed in bagasse in natura (original) pretreated with 10.99%, followed by BHT pretreated with 8.59%, extractive-free pretreated with 5.91%, and partially delignified biomass pretreated with 1.14%, as observed in Figure 2. Acid pretreatment was reported to increase the percentage of lignin in the sugarcane bagasse and straw (in the range of 49–54% and 76–128%, respectively, based on the whole biomass), primarily due to hemicellulose removal [29].
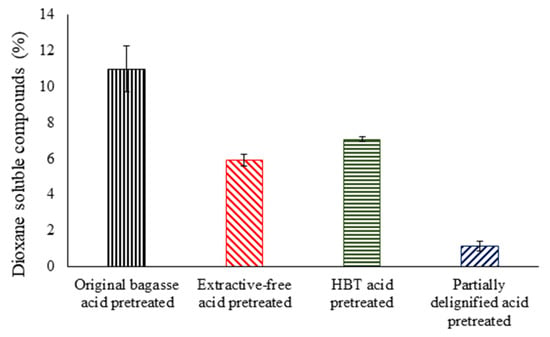
Figure 2.
Material solubilization in dioxane from sugarcane bagasse pretreated with dilute sulfuric acid (20%, m/m).
High acid concentration/temperature in acid pretreatment can result in higher yields of sugar degradation products that can form pseudo-lignin. The presence of structures containing lignin fragments that have precipitated on the fibers can be removed by the action of organic solvents. Even using solvent, organosolv pretreatments conducted with 6 types of chemical compounds (antioxidants and surfactants) revealed an increase in the content of dioxane extractable material in the pretreated biomass (pseudo-lignin and aggregates). Although some antioxidants had a positive effect on the removal of lignin from the biomass, there was an increase simultaneously in material adsorbed on the surface of the biomass, which can be extracted by dioxane [12]. Removal of lignin in the pretreatment does not imply the inhibition of the formation and adsorption of pseudo-lignin (and similar compounds) in the fibers of the biomass.
Sugarcane straw submitted to hydrothermal pretreatment (high-severity conditions, e.g., high acid concentration/temperature) showed loss of hydrolysable sugars, the formation of inhibitors, and pseudo-lignin. Pretreatment at 220 °C/15 min increases lignin concentration by approximately 18% (compared to the initial biomass) [30]. With concentrations above 2% (v/v) of sulfuric acid, biomass hydrolysis was observed, decreasing the glucose and xylose yields in the slurry but with a continuous increase in the levels of acetic acid and furfural in the liquid fraction [20]. Conditions of high severity increase the generation of furfural from xylan, contributing to the pseudo-lignin formation [29]. However, in a dilute acid medium, pseudo-lignin can be formed from the degradation of carbohydrates without the contribution of lignin, especially in conditions of high severity [3].
The original pretreated bagasse showed higher levels of material solubilization in dioxane compared to other pretreatments applied. This may be due to the extractives present in the biomass, which can react with HMF, furfural, and lignin derivatives under acid conditions. This extractive contribution is evident when comparing original material pretreated with extractive-free pretreated. BHT influenced the removal of lignin (Table 2), and condensation of monomers with sugar degradation products and subsequent precipitation on the fiber can occur at lower rates (BHT pretreated). It is likely that the higher mass recovery in the pretreatment with BHT could be related to the material soluble in the dioxane, which was 5.91 g/100 g higher in relation to the partially delignified pretreated biomass (Table 2). Dioxane-soluble material and lignin solubilization could be related to the action mechanism of BHT and sodium chlorite, respectively. BHT as an antioxidant can prevent condensation/precipitation of sugar degradation products. The sodium chlorite is a selective chemical for lignin removal applied at a lab scale for study purposes.
3.4. Dioxane Extracted Material—FTIR Analysis
The FTIR was applied aiming to distinguish dioxane-extracted material from the different sample preparation. The sample preparation could influence the acid pretreatment in the type of precipitated material. A wideband, observed in the region of 1710 cm−1, corresponds to the carbonyl groups bond C=O (conjugated aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and ester groups). The band in the region of 1600 and 1510 cm−1 is attributed to C=O stretching, corresponding to the lignin aromatic ring (skeletal vibration). Bands at 1460 cm−1 and 1410 cm−1 represent the C–H deformation and aromatic skeletal vibrations (combined with deformation C–H in plane), respectively. The band at 1300 cm−1 is attributed to the S ring and G ring condensed (G ring substituted at position 5) C–C, C–O, C=O stretch, G condensed > G etherified, secondary OH aromatic C–H in-plane deformation, typical for G units and primary OH. The band at 1230 cm−1 corresponds to the C=O stretch, which can be attributed to the G ring. HMF, alcohols and carboxylic acids can contribute to bands at 1163 cm−1 and 1020 cm−1, corresponding to C–O stretching. The S unit can be identified at 865 cm−1 that represents C–H out-of-plane at positions 2 and 6 (Figure 3) [10,31,32].
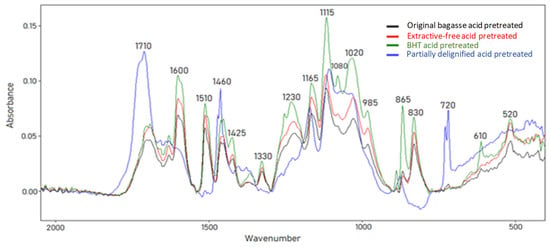
Figure 3.
FTIR-ATR spectra of dioxane extracted compounds formed in sugarcane bagasse during dilute acid pretreatment at 121 °C for 30 min.
The spectrum referring to partially delignified pretreated biomass showed a high-intensity band in the region of 1710 cm−1. This band can indicate C=O stretching in carbonyl and carboxylic, with a stronger band than in other biomass spectra. Furthermore, in partially delignified pretreated biomass, there are no bands in the region between 1600, 1510 corresponding in part to C=C stretching in the aromatic ring and 830 cm−1 corresponding to the –CH3 hydroxymethyl group (C–H out of plane vibration in lignin). Compounds such as furans, alcohols, ethers, or carboxylic acids can be suggested by the bands at 1165 cm−1 and 1020 cm−1, which were attributed to C–O stretching. This band appears in higher intensity in BHT pretreated material.
Based on FTIR analyses, material solubilization in dioxane mainly comprised hydroxyl, carbonyl, and aromatic structures. The characteristic of the aromatic ring (as the one in the lignin structure) was observed in all the solubilized materials in dioxane, except for the partially delignified material. The lower lignin content in partially delignified biomass probably prevented its contribution as precipitated material under the fiber after the dilute acid pretreatment. Similar behavior was observed for all the bands related to the lignin structure, suggesting different compositions of the precipitated material.
3.5. Semi-Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (S-SSF)
At this stage, enzymatic saccharification and fermentation take place simultaneously. As cellulase enzymes hydrolyze cellulose into glucose, S. cerevisiae uses sugar monomers for cell maintenance and growth as it produces ethanol in the medium. At the beginning of the experiment and every 12 h, aliquots were collected for the evaluation of BRIX, glucose content, and ethanol content in the solution. The starting BRIX concentration (T0) was 2.8% for all biomasses. In the first 12 h of fermentation, all treated materials showed an increase in the sugar release (based on BRIX), resulting from enzymatic saccharification, ranging from 5.7% (original bagasse pretreated) to 8.8% (BHT acid-pretreated). From 12 to 24 h only partially delignified pretreated acid had an increase in the amount of BRIX, indicating that the enzymatic conversion still occurred at a higher yield than the consumption of sugars by fermenting microorganisms, reaching 7.2% BRIX. From 24 to 36 h, all treated materials showed a reduction in their BRIX number, until reaching lower levels in the sugar BRIX after 48 h, between 1.95% and (BHT acid-pretreated) and 2.8% (partially delignified pretreated acid) (Figure 4).
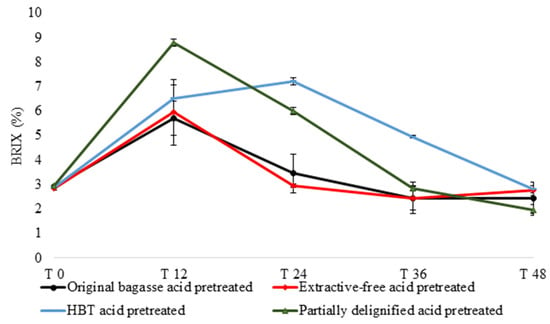
Figure 4.
BRIX variation during S-SSF using sugarcane bagasse from different pretreatments. T 0—initial time; T 12—12 h reaction; T 24—24 h reaction; T 36—36 h reaction; T 48—48 h reaction.
The enzymatic hydrolysis performed at 50 °C started 6 h before the inoculation of the microorganisms. At the time of adding the yeast (T0), 18.4 g L−1 of glucose was observed in the original pretreated bagasse hydrolysate. Extractive-free bagasse pretreated with acid showed glucose of 20.46 g L−1 at T0 and a concentration of 4.35 g L−1 after 48 h. Extractive-free pretreated and BHT pretreated biomasses had values close to the original pretreated bagasse, showing stability in glucose content between T12 and T24. This indicates a balance in enzymatic saccharification and uptake by yeast. However, partially delignified pretreated acid biomass showed 26.77 g L−1 (Figure 5).
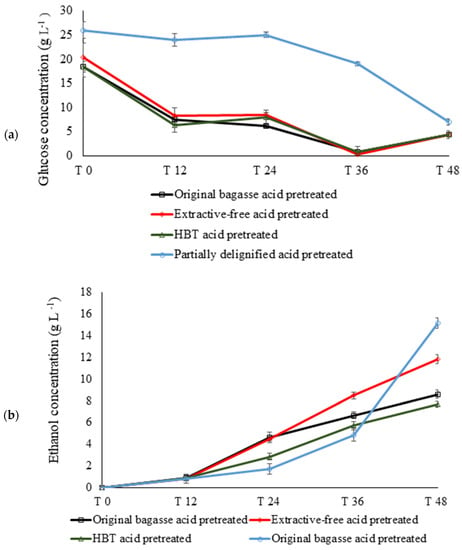
Figure 5.
Glucose (a) and ethanol (b) concentrations of sugarcane bagasse after 48 h of S-SSF (g L−1). T—initial time; T 12—12 h reaction; T 24—24 h reaction; T 36—36 h reaction; T 48—48 h reaction; BHT—butylated hydroxytoluene.
For glucose yield comparison after dilute acid pretreatment, another enzymatic saccharification of biomass was carried out in parallel, applying 15 FPU/g of cellulase enzymes in incubation at 50 °C for 24 h. The cellulose into glucose conversion was 54.14% for original pretreated bagasse, 69.66% for extractive-free pretreated acid, 75.92% for BHT pretreated acid, and 87% for partially delignified pretreated acid. This result suggested that the pretreated extractive-free material, BHT pretreated, and pretreated partially delignified acid shows low recalcitrance to enzymatic saccharification in comparison to the original pretreated bagasse. The S-SSF process was performed with a pre-saccharification of 6 h, using 25 FPU/g (Cellic® CTec 2—Novozymes, 60 FPU/mL) to provide fermentable sugars for S. cerevisiae.
After the first 12 h of fermentation (T12), values of 0.8 g L−1 and 0.9 g L−1 of ethanol for all biomasses were observed, indicating that yeasts converted sugars homogeneously in the first experimental stage due to the availability of glucose (Figure 5). Partially delignified pretreated acid material showed approximately twice as much ethanol compared to BHT pretreated after 24 h of S-SSF. On the other hand, there was an increase in yeast cell mass during the 48 h of fermentation (25% from T0 to T48), which in part can be one of the consequences to impair ethanol productivity. At the end of the experiment (T 48 h), the ethanol curve rose, indicating that ethanol production in the next few hours would be increased.
A previous study carried out with sugarcane bagasse in acid pretreatment submitted to S-SSF (solid-to-liquid ratio 0.5:10, with 15 FPU/g of cellulases and 7.5 IU/g of β-glucosidase) at 30 °C and 150 rpm (fermenting microorganism Pichia stipitis) resulted in glucose accumulation only in the first 6 h (4 g L−1) [22]. After 18 h of fermentation, glucose concentration was close to zero, indicating that the yeast was metabolically active throughout the fermentation. The maximum ethanol produced occurred after 24 h fermentation with 3.70 g L−1 and ethanol yield of 0.10 g ethanol/g available fermentable sugars (ethanol productivity of 0.15 g L−1/h, theoretical ethanol yield 20%) [22]. Different yeast species have different metabolic rates for converting glucose into ethanol.
Combined acid and alkaline pretreatment (0.5% m/v H2SO4 at 140 °C for 10 min and 1% m/v NaOH at 90 °C for 60 min) was applied to the sugarcane bagasse for ethanol production, resulting in biomass with 11% lignin [33]. After 48 h of pre-saccharification, S-SSF of this biomass with Saccharomyces cerevisiae resulted in 43 g L−1 of ethanol and 81% ethanol yield with an enzymatic loading of 15 FPU/g. In enzymatic loading of 10 FPU/g, the ethanol concentration was 43 g L−1 and the ethanol yield was 80%. Similar results in ethanol yield were observed with delignified biomass with Na2CO3 (81%) and NaClO (78%), both biomasses with a lignin content of approximately 11%. However, applying the pre-saccharification of the biomass containing 14% lignin (using a 1% NaOH treatment at 80 °C for 60 min), an ethanol yield of 64% was observed. Delignification of biomass in addition to reducing the formation of pseudo-lignin also helps in enzymatic saccharification, increasing levels of conversion and subsequent fermentation, as lignin is a limiting factor in the saccharification of biomass.
The lignin content was identified as a limiting parameter in the production of second-generation ethanol (2G), negatively correlated with digestibility and conversion of biomass. The increase in the yield of 2G ethanol can be obtained by decreasing the lignin content of the biomass [3]. Some chemical components are applied in enzymatic saccharification to potentiate enzymatic activity. The BHT action during the pretreatment improved lignin removal, with better enzymatic saccharification yield. However, it did not present desired levels in enzymatic saccharification and fermentation.
The removal of extractives from biomass minimizes pseudo-lignin and analogous molecule formation, which is harmful to enzymatic activity, benefiting the conversion of glucose into ethanol (extractive-free acid-pretreated). For a large scale, each ton of sugarcane acid-pretreated bagasse can produce 337 kg of cellulose, 232.5 kg of hemicellulose, and 193.59 L of ethanol (Figure 6). The mass balance predicting production of lignocellulosic components and ethanol can form a base for further studies in an economic evaluation of the process [34].
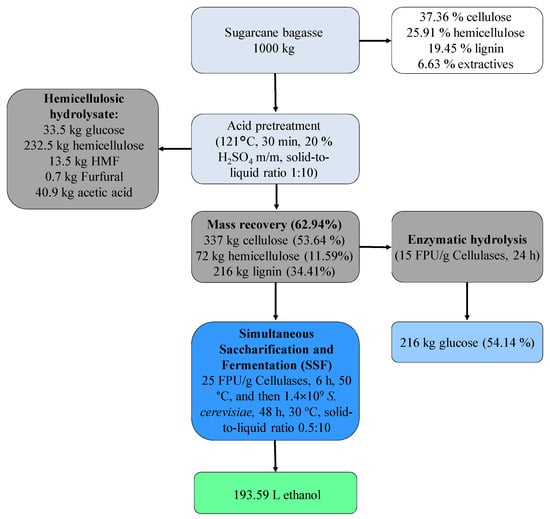
Figure 6.
Industrial-scale enzymatic saccharification and ethanol production via S-SSF of extractive-free acid-pretreated bagasse.
4. Conclusions
The antioxidant additive in the pretreatment (BHT) showed evidence of lower sugar degradation production formation, with levels similar to the partially delignified biomass. The chemical characterization of the pretreated bagasse indicated that BHT had a potential effect on lignin removal from the biomass. BHT represents a cheap antioxidant in the food industry and an easy-to-apply alternative for pretreatment. Extractive-free acid-pretreated and partially delignified acid-pretreated biomasses showed better enzymatic digestion after 24 h, indicating that extractives may have partially hindered the process, probably by condensation with inhibitors and lignin monomers. S-SSF from partially delignified acid-pretreated bagasse showed higher enzymatic digestion at T0 of saccharification, while the other biomass showed a similar profile but at lower levels. The ascending line and the availability of sugars after 48 h suggest increasing bioethanol production in the following moments. Understanding the action of antioxidant chemical compounds in pretreatment can enable processes to produce sugars from biomass.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.A.S. and M.B.; methodology, A.A.S., M.B., J.P.C. and D.d.F.d.A.; software, A.A.S.; formal analysis, A.A.S. and J.P.C.; investigation, A.A.S. and J.P.C.; resources, M.B. and D.d.F.d.A.; data curation, A.A.S. and J.P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.A.S., J.P.C., D.d.F.d.A. and M.B.; visualization, A.A.S., J.P.C., D.d.F.d.A. and M.B.; supervision, M.B.; project administration, M.B.; funding acquisition, M.B. and D.d.F.d.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq process number: 423730/2021-5; 303239/2021-2) and São Paulo Research Foundation (process number 2017/22401-8).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bezerra, T.L.; Ragauskas, A.J. Review A review of sugarcane bagasse for second-generation bioethanol and biopower production. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2016, 10, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.; Barros, M.V.; Sydney, A.C.N.; Piekarski, C.M.; de Francisco, A.C.; Vandenberghe, L.P.D.S.; Sydney, E.B. Sustainability of sugarcane lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment for the production of bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Tyhoda, L.; Brienzo, M. Sugarcane biomass conversion influenced by lignin. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2020, 14, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations—FAO. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#rankings/countries_by_commodity (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Melati, R.B.; Shimizu, F.L.; Oliveira, G.; Pagnocca, F.C.; de Souza, W.; Sant’Anna, C.; Brienzo, M. Key Factors Affecting the Recalcitrance and Conversion Process of Biomass. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, D.M.; Perez, A.; Garcia, J.C.; Colodette, J.L.; Lopez, F.; Díaz, M.J. Ethanol-soda pulping of sugarcane bagasse and straw. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2014, 48, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Salazar-Bryam, A.M.; Contiero, J.; Sant’Anna, C.; Brienzo, M. Pseudo-lignin content decreased with hemicellulose and lignin removal, improving cellulose accessibility, and enzymatic digestibility. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 14, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, F.L.; de Azevedo, G.O.; Coelho, L.F.; Pagnocca, F.C.; Brienzo, M. Minimum lignin and xylan removal to improve cellulose accessibility. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 13, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, J.P.; Claro, E.M.T.; de Paula, C.B.C.; Shimizu, F.L.; Leite, D.A.N.D.O.; Brienzo, M.; Angelis, D.D.F.D. Detoxification of sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate with different adsorbents to improve the fermentative process. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Jung, S.; Ragauskas, A. Pseudo-lignin formation and its impact on enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 117, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, P.V.; Pitarelo, A.P.; Ramos, L.P. Production of cellulosic ethanol from sugarcane bagasse by steam explosion: Effect of extractives content, acid catalysis and different fermentation technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 208, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Masarin, F.; Brienzo, M. Lignin removal and cellulose digestibility improved by adding antioxidants and surfactants to organosolv pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 15, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, M.; Bush, T.; Spark, A.; Bose, S.K.; Francis, R.C. An accurate and non-labor intensive method for the determination of syringyl to guaiacyl ratio in lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5834–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienzo, M.; Tyhoda, L.; Benjamin, Y.; Görgens, J. Relationship between physicochemical properties and enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse varieties for bioethanol production. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 16550:2018; Sugarcane Bagasse—Chemical Characterization. Brazilian National Standards Organization: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2018.
- Hu, F.; Jung, S.; Ragauskas, A. Impact of pseudolignin versus dilute acid-pretreated lignin on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienzo, M.; Fikizolo, S.; Benjamin, Y.; Tyhoda, L.; Görgens, J. Influence of pretreatment severity on structural changes, lignin content and enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse samples. Renew Energy 2017, 104, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpen, J.Y. Comparison of Sugar Content in Bottled 100% Fruit Juice versus Extracted Juice of Fresh Fruit. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.J.D.M.; Martin, C.; Soares, I.B.; Maior, A.M.S.; Baudel, H.M.; de Abreu, C.A.M. Dilute mixed-acid pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P.; Asthana, R.K.; Singh, S.P. Biohydrogen production from sugarcane bagasse by integrating dark- and photo-fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.H.D.S.; Rabelo, S.C.; da Costa, A.C. Effects of the pretreatment method on high solids enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation of the cellulosic fraction of sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritrakul, N.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Keawsompong, S. Evaluation of dilute acid pretreatment for bioethanol fermentation from sugarcane bagasse pith. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2017, 51, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienzo, M.; Carvalho, A.F.A.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Oliva Neto, P. Sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose properties, extraction technologies and xylooligosaccharides production. In Food Waste: Practices, Management and Challenges; Riley, G.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 155–188. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, B.S.; Schmatz, A.A.; de Freitas, C.; Masarin, F.; Brienzo, M. Fruit and Restaurant Waste Polysaccharides Recycling Producing Xylooligosaccharides. Recycling 2023, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.S.; de Freitas, C.; Contiero, J.; Brienzo, M. Enzymatic Production of Xylooligosaccharides from Xylan Solubilized from Food and Agroindustrial Waste. Bioenerg. Res. 2022, 15, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiyanzu, I.; Brienzo, M.; García-Aparicio, M.P.; Görgens, J.F. Application of endo-β-1,4,D-mannanase and cellulase for the release of mannooligosaccharides from steam-pretreated spent coffee ground. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 3538–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miléo, P.C.; Oliveira, M.F.; Luz, S.M.; Rocha, G.J.M.; Gonçalves, A.R. Thermal and chemical characterization of sugarcane bagasse cellulose/lignin-reinforced composites. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.D.A.; Dantas, P.V.F.; Padilha, C.E.D.A.; dos Santos, E.S.; de Macedo, G.R. Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse: Use of different fermentation strategies to enhance an environmental-friendly process. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, D.M.; Sevastyanova, O.; Penna, L.S.; da Silva, B.P.; Lindström, M.E.; Colodette, J.L. Assessment of chemical transformations in eucalyptus, sugarcane bagasse and straw during hydrothermal, dilute acid, and alkaline pretreatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 73, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.; Souza, R.B.; Pratto, B.; dos Santos-Rocha, M.S.; Cruz, A.J. Effect of severity factor on the hydrothermal pretreatment of sugarcane straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Trimukhe, K.; Pandare, K.; Bastawade, K.; Gokhale, D.; Varma, A. Lignin–carbohydrate complexes from sugarcane bagasse: Preparation, purification, and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Jia, Z.; Guo, C.; Luo, B.; Wang, S.; Min, D. How Pseudo-lignin Is Generated during Dilute Sulfuric Acid Pretreatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10116–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Tan, L.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Nishimura, H.; Takei, S.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Kida, K. Bioethanol from sugarcane bagasse: Focused on optimum of lignin content and reduction of enzyme addition. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.P.; Schmatz, A.A.; de Freita, L.A.; Mutton, M.J.R.; Brienzo, M. Solubilization of hemicellulose and fermentable sugars from bagasse, stalks, and leaves of sweet sorghum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).