Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Experimental Design and Setup
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Methane Production
| Treatment | CH4 (%) * | mL CH4/ g VS | mL CH4/g COD | mL CH4/ g wet sludge | mL CH4/ g feed # | mL H2S/ g VS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5% FS | 59.4 ± 0.3 | 422 ± 11 | 240 ± 6 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 92 ± 2.4 | 0.90 ± 0.04 |
| 2.5% FS | 58.8 ± 0.2 | 483 ± 6 | 274 ± 3 | 10.5 ± 0.1 | 105 ± 1.3 | 0.99 ± 0.00 |
| 3.5% FS | 58.9 ± 0.3 | 519 ± 5 | 295 ± 3 | 15.9 ± 0.1 | 113 ± 1.1 | 1.10 ± 0.03 |
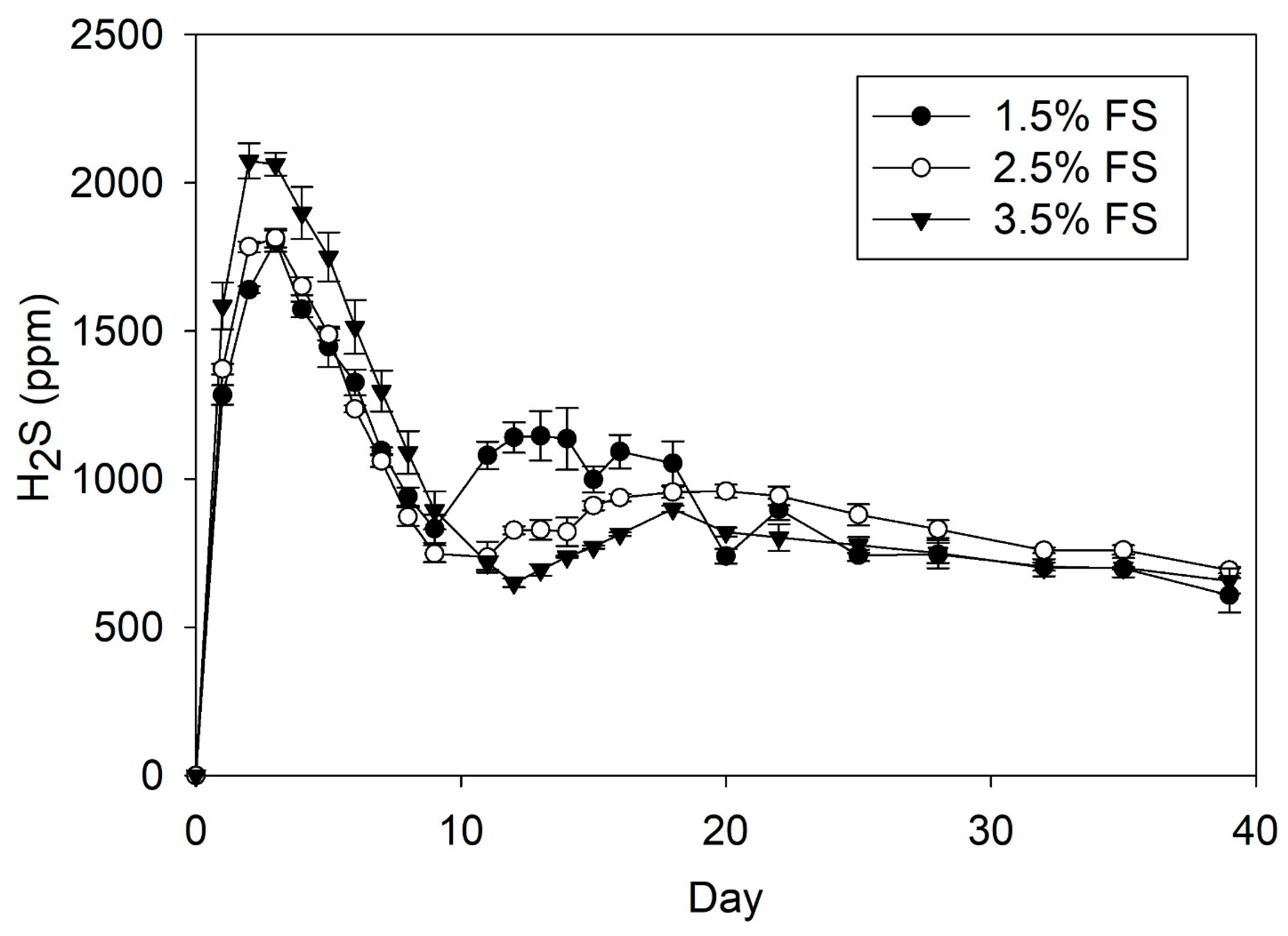
3.2. Hydrogen Sulfide Production
3.3. Volatile Fatty Acids
3.4. Solids and Organic Matter Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Badiola, M.; Basurko, O.C.; Piedrahita, R.; Hundley, P.; Mendiola, D. Energy Use in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS): A Review. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 81, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Lepine, C.; Witarsa, F.; Good, C. Anaerobic Digestion Challenges and Resource Recovery Opportunities from Land-Based Aquaculture Waste and Seafood Processing Byproducts: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrer, M.; Rishel, K.; Taylor, A.; Vinci, B.J.; Summerfelt, S.T. The Cost and Effectiveness of Solids Thickening Technologies for Treating Backwash and Recovering Nutrients from Intensive Aquaculture Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6630–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyan, N.; Tal, Y.; Gross, A. Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge from Intensive Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Review. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.M.; Apolinario, E.A.; Gross, A.; Sowers, K.R. Characterization of a Microbial Consortium That Converts Mariculture Fish Waste to Biomethane. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerström, A.; Seadi, T.A.; Rasi, S.; Briseid, T. The Role of Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas in the Circular Economy. In IEA Bioenergy Task 37; IEA Bioenergy: Cork, Ireland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moeller, L.; Zehnsdorf, A. Process Upsets in a Full-Scale Anaerobic Digestion Bioreactor: Over-Acidification and Foam Formation during Biogas Production. Energ. Sustain. Soc. 2016, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ye, J.; Zhang, P.; Xu, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Fang, W.; Wang, B.; Zeng, G. Hydrogen Sulfide Formation Control and Microbial Competition in Batch Anaerobic Digestion of Slaughterhouse Wastewater Sludge: Effect of Initial Sludge PH. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi-Borazjani, S.A.; Capela, I.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Over-Acidification Control Strategies for Enhanced Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Shirai, T.; Yamashiro, T.; Yasui, S.; Iwasaki, M.; Ihara, I.; Nishida, T.; Tangtaweewipat, S.; Umetsu, K. Valorizing Waste Iron Powder in Biogas Production: Hydrogen Sulfide Control and Process Performances. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 208, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farghali, M.; Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Ahmed, M.M.; Kotb, S.; Yamashiro, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Umetsu, K. Impacts of Iron Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Biogas Production: Hydrogen Sulfide Mitigation, Process Stability, and Prospective Challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier-Gordo, C.O.; Mancini, E.; Pedersen, P.B.; Angelidaki, I.; Fotidis, I.A. Saline Fish Wastewater in Biogas Plants—Biomethanation Toxicity and Safe Use. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, L.B.; Burns, R.T.; Bishop, G.; Sell, S.T.; Spajic, R. Using Biochemical Methane Potential Assays to Aid in Co-Substrate Selection for Co-Digestion. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2011, 27, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Miao, H.; Huang, Z.; Gao, S.; Ruan, W. In Situ Volatile Fatty Acids Influence Biogas Generation from Kitchen Wastes by Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amha, Y.M.; Anwar, M.Z.; Brower, A.; Jacobsen, C.S.; Stadler, L.B.; Webster, T.M.; Smith, A.L. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Processes: Applications of Molecular Tools. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehariya, S.; Patel, A.K.; Obulisamy, P.K.; Punniyakotti, E.; Wong, J.W.C. Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge for Methane Production: Current Status and Perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Assay Method for Anaerobic Digestion Research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Mustafa, A.M.; Sheng, K. Effects of Inoculum to Substrate Ratio and Co-Digestion with Bagasse on Biogas Production of Fish Waste. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Aziz, N.I.H.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Mohamed Ali, M.Y. Sustainable Biogas Production from Agrowaste and Effluents—A Promising Step for Small-Scale Industry Income. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.K.; Bureau, D.P.; Hua, K.; Drew, M.D.; Forster, I.; Were, K.; Hicks, B.; Vandenberg, G.W. Sustainability Issues Related to Feeding Salmonids: A Canadian Perspective. Rev. Aquacult. 2013, 5, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the Use of Insects in the Diet of Farmed Fish: Past and Future. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, D.; Franci, C. Biogas Production from Solid Wastes Removed from Fish Farm Effluents. Aquat. Living Resour. 1998, 11, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, K.I.; Letelier-Gordo, C.O.; Lund, I. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste in RAS: Effect of Reactor Type on the Biochemical Acidogenic Potential (BAP) and Assessment of the Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) by a Batch Assay. Aquac. Eng. 2015, 65, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, K. Process Performance of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge and Aquaculture Sludge. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 90, 102090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.P.L.; Joyce, A.; Wuertz, S.; Jijakli, M.H.; Gross, A.; Eding, E.H.; Bläser, I.; Reuter, M.; Keizer, L.C.P.; et al. Nutrient Mineralization and Organic Matter Reduction Performance of RAS-Based Sludge in Sequential UASB-EGSB Reactors. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 83, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.; Summerfelt, S. Solids Flushing, Mixing, and Water Velocity Profiles within Large (10 and 150 M3) Circular ‘Cornell-Type’ Dual-Drain Tanks. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AgSTAR. Managing Manure with Biogas Recovery Systems Improved Performance at Competitive Costs; EPA: Springfield, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Timmons, M.B.; Vinci, B.J. Recirculating Aquaculture, 5th ed.; Ithaca Publishing Company LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Belle, A.J.; Lansing, S.; Mulbry, W.; Weil, R.R. Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production during Co-Digestion of Forage Radish and Dairy Manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 80, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Qiao, W. Transformations and Impacts of Ammonia and Hydrogen Sulfide in Anaerobic Reactors. In Anaerobic Biotechnology: Environmental Protection and Resource Recovery; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015; pp. 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Shelford, T.J.; Gooch, C.A.; Lansing, S.A. Performance and Economic Results for Two Full-Scale Biotrickling Filters to Remove H2S from Dairy Manure-Derived Biogas. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2019, 35, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Shelford, T.; Felton, G.; Gooch, C.; Lansing, S. Evaluation of Hydrogen Sulfide Scrubbing Systems for Anaerobic Digesters on Two U.S. Dairy Farms. Energ. 2019, 12, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, I.; Fdz-Polanco, M. Microaerobic Control of Biogas Sulphide Content during Sewage Sludge Digestion by Using Biogas Production and Hydrogen Sulphide Concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanmehr, F.; Solon, K.; Maisonnave, V.; Daniel, O.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Gillot, S.; Buffiere, P. Sulfur Transformations during Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion and Intermediate Thermal Hydrolysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, R.; Eikebrokk, B. Mesophilic Anaerobic Treatment of Sludge from Salmon Smolt Hatching. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letelier-Gordo, C.O.; Aalto, S.L.; Suurnäkki, S.; Pedersen, P.B. Increased Sulfate Availability in Saline Water Promotes Hydrogen Sulfide Production in Fish Organic Waste. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 89, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, J.; Fonarev, N.; Berkowitz, B. Anaerobic Treatment of Intensive Fish Culture Effluents: Digestion of Fish Feed and Release of Volatile Fatty Acids. Aquaculture 1995, 133, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, L.; Yao, Y.; Sun, G.; Guo, X. Anaerobic digestion of swine manure using aqueous pyrolysis liquid as an additive. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruti, K.; Begum, S.; Ahuja, S.; Anupoju, G.R.; Juntupally, S.; Gandu, B.; Ahuja, D.K. Exploitation of Rapid Acidification Phenomena of Food Waste in Reducing the Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) of High Rate Anaerobic Digester without Conceding on Biogas Yield. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patni, N.K.; Jui, P.Y. Volatile Fatty Acids in Stored Dairy-Cattle Slurry. Agric. Wastes 1985, 13, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.R.; Landis, A.E.; Rittmann, B.E.; Young, M.N.; Parameswaran, P. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of food waste through biochemical methane potential assays at different substrate: Inoculum ratios. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Fish Sludge (FS) | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|
| Total solids (mg/L) | 35,700 ± 794 | 53,700 ± 587 |
| Volatile solids (mg/L) | 31,133 ± 1471 | 42,367 ± 936 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 54,875 ± 1151 | 64,650 ± 2406 |
| Total ammonia (mg/L) | 422 ± 2 | 1072 ± 16 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 2265 ± 33 | 2535 ± 64 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 750 ± 6 | 440 ± 6 |
| Total VFA (mg/L) | 6540 ± 232 | 36 ± 3 |
| pH | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 7.7 ± 0.0 |
| Treatment | Inoculum (mL) | Fish Sludge (mL) | Substrate TS (g) | Substrate VS (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculum Control | 75 | - | - | - |
| 1.5% FS | 75 | 122.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| 2.5% FS | 75 | 73.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| 3.5% FS | 75 | 52.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| Treatment | %TS Reduction | %VS Reduction | %COD Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5% FS | 44% | 30% | 57% |
| 2.5% FS | 42% | 27% | 62% |
| 3.5% FS | 50% | 29% | 69% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choudhury, A.; Lepine, C.; Good, C. Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations. Fermentation 2023, 9, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020094
Choudhury A, Lepine C, Good C. Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020094
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoudhury, Abhinav, Christine Lepine, and Christopher Good. 2023. "Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020094
APA StyleChoudhury, A., Lepine, C., & Good, C. (2023). Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations. Fermentation, 9(2), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020094






