Use of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Potential Functional Ingredient for the Production of Traditional Herzegovinian Product Ćupter
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Brewers’ Spent Grain
1.2. Must
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
Procedure for Preparation of Traditional and Ćupter with Added Industrial and Craft BSG
2.2. Nutritive and Chemical Analysis of Ćupter
2.2.1. pH Determination
2.2.2. Water Activity (Aw) Measurement
2.2.3. Moisture Determination
2.2.4. Ash Determination
2.2.5. Protein Determination
2.2.6. Fat Determination
2.2.7. Total Sugar Measurement
2.2.8. Energy Kcal
2.2.9. Chemical Analysis of White Grape Must
2.2.10. Preference Test Determination
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutritive Value
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. Water Activity and Moisture
3.1.3. Ash Determination
3.1.4. Protein
3.1.5. Energy
3.1.6. Fat
3.1.7. Total Sugars
3.2. Preference Test
Preference Test Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, P.J.; Jew, S. Functional food development: Concept to reality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.R., 3rd; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Dalal, D.; Riemersma, R.A.; Appel, L.J.; Guallar, E. Meta-analysis: High-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CBellisle, F.; Blundell, J.E.; Dye, L. Functional food science and behaviour and psychological functions. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, S173–S193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M.B. Concepts and strategy of functional food science: The European perspective. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1660S–1664S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G. Micronutrients and cancer: Time for action? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.; Wall, A.; Khaldi, N.; Kussmann, M. Artificial intelligence in functional food ingredient discovery and characterisation: A focus on bioactive plant and food peptides. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Dragone, G.; Roberto, I.C. Brewers’ spent grain: Generation, characteristics and potential applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.W.; Hardiman, K.; Atzler, J.J.; Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Valdeperez, D.; Münch, S.; Cattaneo, G.; O’Riordan, P.; Arendt, E. Rejuvenated brewer’s spent grain: The impact of two BSG-derived ingredients on techno-functional and nutritional characteristics of fibre-enriched pasta. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. Biotechnological potential of brewing industry by-products. In Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilisation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, W. Technology Brewing and Malting, 5th ed.; VLB Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karlović, A.; Jurić, A.; Ćorić, N.; Habschied, K.; Krstanović, V.; Mastanjević, K. By-products in the malting and brewing industries—Re-usage possibilities. Fermentation 2020, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ spent grain: A review with an emphasis on food and health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, M. Composition and nutrient value proposition of brewers spent grain. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.L.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; Piggott, C.O.; FitzGerald, R.J.; O’Brien, N.M. Brewers’ spent grain; Bioactivity of phenolic component, its role in animal nutrition and potential for incorporation in functional foods: A review. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.; Pereira, P.; Rijo, P.; Amaral, O.; Amaral, A.; Palma, L. Vitis vinera L. Pomace: Chemical and nutritional characterization: Caracterização química e nutricional do bagaço de Vitis vinera L. J. Biomed. Biopharm. Res. 2018, 15, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; l’Anson, K.J.; Treimo, J.; Faulds, C.B.; Brocklehurst, T.F.; Eijsink, V.G.; Waldron, K.W. Profiling brewers’ spent grain for composition and microbial ecology at the site of production. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermeño, M.; Connolly, A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Flynn, C.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E.; FitzGerald, R.J. Identification of bioactive peptides from brewers’ spent grain and contribution of Leu/Ile to bioactive potency. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, A.J.; Parker, M.L.; Faulks, R.; Husband, F.; Wilde, P.; Smith, A.C.; Faulds, C.B.; Waldron, K.W. A systematic micro-dissection of brewers’ spent grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ishizawa, H.; Inoue, D.; Toyama, T.; Yu, J.; Mori, K.; Ike, M.; Lee, T. Microalgal transformation of food processing byproducts into functional food ingredients. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, S.T.; Chen, W.N. Valorization of brewer’s spent grain using fungi solid-state fermentation to enhance nutritional value. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, S.T.; Lee JJ, L.; Chen, W.N. Evaluation of brewers’ spent grain as a novel media for yeast growth. AMB Express 2017, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaş, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Diaconeasa, Z. Volatile profile, fatty acids composition and total phenolics content of brewers’ spent grain by-product with potential use in the development of new functional foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smejtková, A.; Vaculík, P.; Přikryl, M.; Pastorek, Z. Rating of malt grist fineness with respect to the used grinding equipment. Res. Agric. Eng. 2016, 62, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurković, R. Geographical Distribution of the Vineyards and Wine Production in Rural Areas of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Folia Geogr. 2017, 59, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- AGENCY for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina. 2012. Available online: https://bhas.gov.ba/?option=com_content&view=article&id=46&lang=en (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Gülcü, M.; Demirci, A.Ş.; Güner, K.G. Siyah üzüm zengin besin içeriği ve sağlik açisindan önemi. Türkiye 2008, 10, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Betül, E. Solar Drying of Traditional Herzegovinian Fruit Sweet Cupter. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Tropical AgriSciences, Prague, Czech Republic, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cauvain, S.P. Bread and other bakery products. In The Stability and Shelf Life of Food; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.S.; Alzamora, S.M.; Chirife, J. Effects of water activity (aw) on microbial stability as a hurdle in food preservation. In Water Activity in Foods, 1st ed.; Gustavo, V., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbaș, M.; Ertugay, M.F.; Certel, M. Moisture adsorption behaviour of semolina and farina. J. Food Eng. 2005, 69, 191–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Zannini, E.; Sahin, A.W.; Arendt, E.K. Barley protein properties, extraction and applications, with a focus on brewers’ spent grain protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.L.; Marinac, L. The effect of mashing on malt endoproteolytic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, D.M.; Jacob, F.; Titze, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Fibre, protein and mineral fortification of wheat bread through milled and fermented brewer’s spent grain enrichment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, S.; Özboy, ö.; Cavidoğlu, I.; Köksel, H. Effects of brewer’s spent grain on the quality and dietary fibre content of cookies. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A.; Almiron-Roig, E. Chapter 11 human perceptions and preferences for fat-rich foods. In Fat Detection: Taste, Texture, and Post Ingestive Effects; Montmayeur, J.P., Le Coutre, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; p. 265. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53528/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Knezović, Z.; Mandić, A.; Perić, N.; Beljo, J.; Žulj Mihaljević, M. Morphological and genetic characterization of vine grape cultivars of Herzegovina. Croat. Rev. Econ. Bus. Soc. Stat. 2017, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Crofton, E.; Scannell, A.G.; Hannon, J.A.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Gallagher, E. Sensory properties and aromatic composition of baked snacks containing brewer’s spent grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combest, S.; Warren, C.; Patterson, M. Upcycling brewers’ spent grain: The development of muffins and biomarker response after consuming muffins for 8-weeks in healthy adults from randomized-controlled trial. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Barczewski, M.; Skórczewska, K.; Szulc, J.; Chmielnicki, B.; Korol, J.; Formela, K. Sustainable upcycling of brewers’ spent grain by thermo-mechanical treatment in twin-screw extruder. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
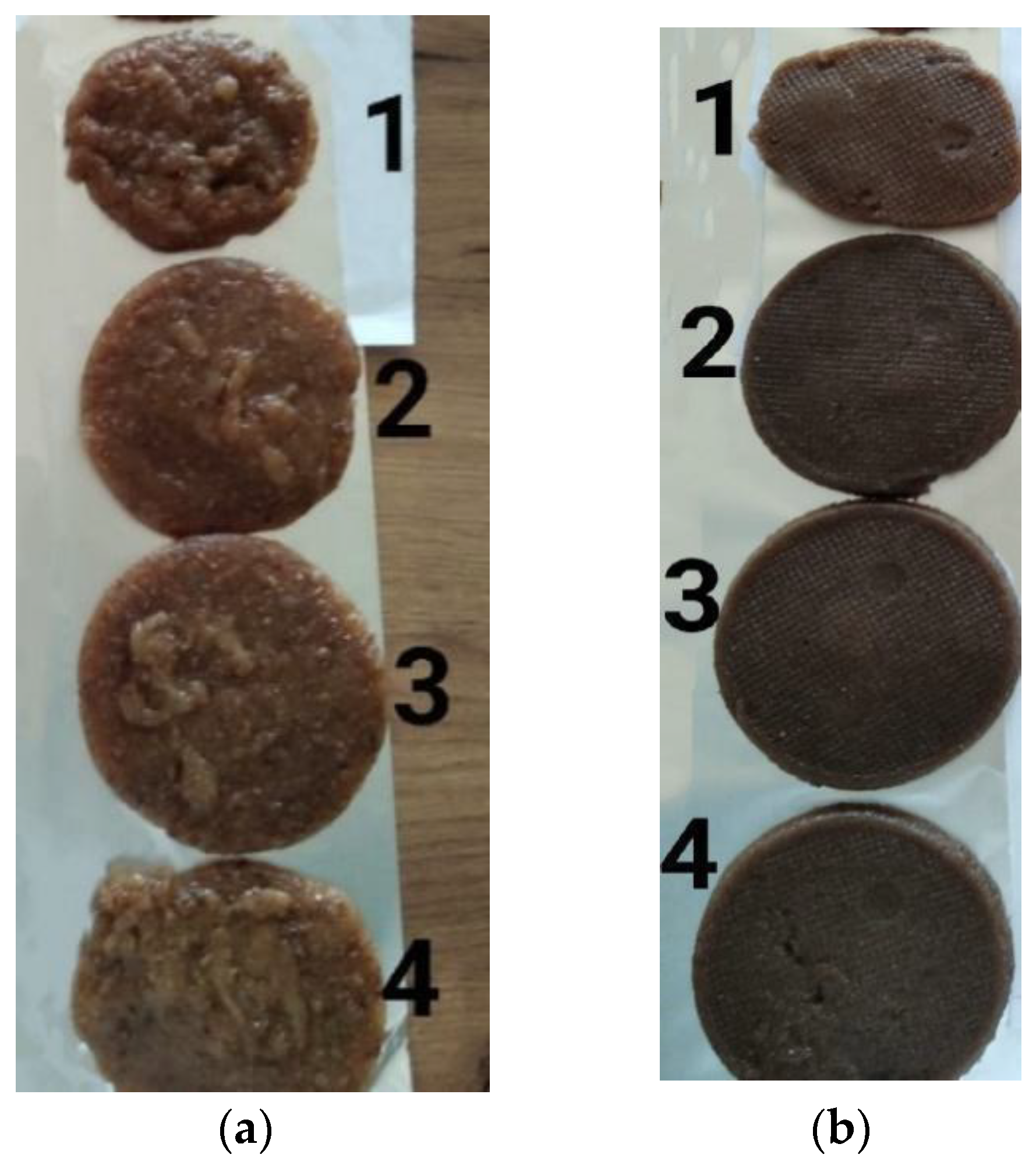
| Sample | Recipe for Ćupters |
|---|---|
| 1 | 180 mL of white grape must + 18 g of IBSG + 11.2 g of semolina |
| 2 | 180 mL of white grape must + 18 g of CBSG + 11.2 g of semolina |
| 3 | 180 mL of white grape must + 13.5 g of CBSG + 22.5 g of flour |
| 4 | 180 mL of white grape must + 13.5 g of IBSG + 22.5 g of flour |
| Gender | Age | Trained (Yes/No) | Student/Faculty Employee |
|---|---|---|---|
| M → 8.5% F → 91.5% | <20 → 0% 20–30 → 100% >30 → 0% | yes → 100% no → 0% | Student → 93.5% Faculty employee → 6.5% |
| Sample | pH | Water Activity (%) | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) | Total Sugars (%) | Energy kcal/kJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 3.56 ± 0.01 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 27.08 ± 0.54 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 52.25 ± 0.32 | 212.9/891.4 ± 0.87 |
| 1 | 4.11 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 24.02 ± 1.52 | 1.50 ± 0.39 | 6.13 ± 0.07 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | 51.07 ± 0.83 | 275.3/1152.6 ± 0.22 |
| 2 | 3.94 ± 0.005 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 21.92 ± 0.69 | 1.87 ± 0.37 | 5.95 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 37.43 ± 0.87 | 277.1/1160.2 ± 0.27 |
| 3 | 3.90 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 41.82 ± 1.68 | 1.41 ± 0.10 | 5.93 ± 0.12 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | 39.66 ± 0.72 | 200.1/837.8 ± 0.65 |
| 4 | 3.86 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 41.11 ± 1.41 | 1.42 ± 0.10 | 6.60 ± 0.17 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 40.37 ± 0.77 | 200.0/837.4 ± 1.15 |
| Sample | pH | Reducing Sugars (Glucose and Fructose) | Total Acids | Ethanol vol% | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White grape must | 3.58 ± 0.01 | 240 ± 0.01 | 3.7 ± 0.06 | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 0.66 ± 0.007 |
| Sample | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Fat (%) | Proteins (%) | Total Sugars (%) | Energy kcal/kJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBSG | 66.30 ± 0.75 | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 1.67 ± 0.14 | 13.03 ± 0.19 | 10.33 ± 0.32 | 186.9/782.6 ± 0.30 |
| IBSG | 72.75 ± 0.30 | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 2.97 ± 0.04 | 12.76 ± 0.19 | 5.04 ± 0.42 | 184.6/772.6 ± 0.25 |
| Sample | Color | Texture | Scent | Flavor | General Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.17 ± 1.69 | 3.05 ± 1.79 | 3.43 ± 1.73 | 3.45 ± 1.89 | 3.20 ± 1.61 |
| 2 | 2.90 ± 1.53 | 3.25 ± 1.76 | 3.60 ± 1.66 | 3.56 ± 1.82 | 3.13 ± 1.84 |
| 3 | 3.30 ± 1.77 | 3.15 ± 1.76 | 3.40 ± 1.82 | 3.83 ± 1.65 | 3.45 ± 1.75 |
| 4 | 3.47 ± 1.70 | 2.71 ± 1.60 | 3.45 ± 1.68 | 3.37 ± 1.91 | 3.20 ± 1.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lalić, A.; Karlović, A.; Marić, M. Use of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Potential Functional Ingredient for the Production of Traditional Herzegovinian Product Ćupter. Fermentation 2023, 9, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020123
Lalić A, Karlović A, Marić M. Use of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Potential Functional Ingredient for the Production of Traditional Herzegovinian Product Ćupter. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleLalić, Anita, Andrea Karlović, and Marina Marić. 2023. "Use of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Potential Functional Ingredient for the Production of Traditional Herzegovinian Product Ćupter" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020123
APA StyleLalić, A., Karlović, A., & Marić, M. (2023). Use of Brewers’ Spent Grains as a Potential Functional Ingredient for the Production of Traditional Herzegovinian Product Ćupter. Fermentation, 9(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020123







