Abstract
Strain preservation to maintain stable vitality and the recombinant enzyme activity plays a crucial role in industrial fermentation. A Pichia pastoris strain is routinely stored at −80 °C in a glycerol vial and activated on an antibiotic-containing YPD agar plate before being used for fermentation. Alternatively, the activated strain should be preserved in the agar slant at 2~4 °C (low-temperature storage) for a short period before use. To maximize the utilization of the low-temperature storage for fermentation, we evaluated this method by observing the capacity of both the vitality and the recombinant enzyme activity of the strain at different preservation durations. We found that engineered yeast could be preserved by low-temperature storage for at least 30 months without losing its vitality and biomass enzyme activity by the end of fermentation and could be directly used for the seed cultivation of fermentation, which is more time-saving than strain recovery from −80 °C in a glycerol vial. Moreover, the antibiotic added to the agar slant could be omitted if the heterologous gene was integrated into the host chromosome. Our approach may greatly elevate the production efficiency of the strain.
1. Introduction
Strain preservation is one of the key steps in industrial fermentation for the production of various high-value added products, including enzymes and other organic components. The stable vitality and production ability of the strain are required during the preservation period to guarantee production when the strain is used for fermentation. Pichia pastoris has advantages such as easy genetic handling, rapid growth, cost-effective mediums, and the ability to develop post-translational modifications, which has been widely utilized for the production of various high-value added products, including recombinant proteins [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. The engineered Pichia pastoris is routinely stored at −80 °C in a glycerol vial and activated on the YPD agar plate containing 4 mg/mL of G418 before it is used for fermentation [9,10]. The activated strain is subjected to series of seed cultivation(s) (in shaking flasks or seed tank) and high-cell-density fermentation till the end of the process [1]. Generally, ultra-low temperature storage (between −70 °C and −80 °C) guarantees the vitality and production ability of the preserved strains for as long as several years [11,12]. However, the manipulation on strain activation and amplification from the glycerol vial stored at an ultra-low temperature through the agar plate to shaking flask seed cultivation takes much time, which inevitably decreases the production efficiency in fermentation, especially in large-scale fermentation [11]. On the other hand, the low temperature storage (2~4 °C) in agar slant is an easy-to-use method and is often applied to the strain preservation of microorganisms for a short period [13,14]. However, how long the strain of P. pastoris can be preserved in the slant before it loses its viability and production capacity is unknown. Therefore, our primary goal was to examine this method in order to maximize the utilization of the low-temperature storage for the fermentation of the engineered yeast. If the capacity of this approach is thoroughly evaluated and extensively utilized, a combination of the two storage approaches should greatly elevate the production efficiency in the fermentation process. Taxol (generic name: Paclitaxel) is a well-known antitumor compound produced by yew trees at very low concentrations [15,16,17,18], causing a worldwide shortage of this important anticancer medicine. However, concentrations of its analogs, especially 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol (XDT), often have a much higher presence in the same plant [18,19]. XDT can be transformed into 10-deacetyltaxol (DT) by chemical or enzymatic removal of the C-7 xylosyl residue, and the intermediate (DT) can be further transformed into Taxol by acetylation at the C-10 position of DT [20,21]. In our previous study, we excavated and characterized a glycoside hydrolase (designated LXYL-P1-2) from the fungus Lentinula edodes, which could efficiently hydrolyze the xylosyl group from 7-β-xylosyl-taxanes, including XDT. This enzyme has been heterologously and intracellularly expressed by the engineered P. pastoris (designated GS115-3.5K-P1-2) [22,23]. The high-cell-density fermentation approach of this engineered yeast has been successfully established [11,12,13]. Additionally, the highly active mutants of the enzyme have been obtained by protein engineering strategy [24,25,26].
In this paper, we used the engineered P. pastoris GS115-3.5K-P1-2 as the model strain and evaluated the influence of the long-term low-temperature storage in the agar slant at 4 °C on the strain vitality and the enzyme activity of LXYL-P1-2. Our results indicated that the vitality and biomass enzyme activity of the preserved strain could be maintained within 30 months of the preservation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Media
The engineered strain GS115-3.5K-P1-2 was constructed in our laboratory by transforming the host strain P. pastoris GS115 (Mut+) with the recombinant plasmid pPIC3.5K-LXYL-P1-2 (intracellular expression, Figure S1) harboring the sequence encoding LXYL-P1-2 [22] and preserved at −80 °C prior to use. A yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD) medium containing (w/v) 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose, and 1.5% agar was used to prepare the agar slant and agar plate, respectively. A BMGY medium containing (per liter) 10 g of yeast extract, 20 g of peptone, 100 mm of potassium phosphate buffer pH 6, 13.4 g of yeast nitrogen base without amino acids, 400 μg of biotin, and 10 mL of glycerol was used for the cultivation in shaking flasks (purchased from Chonqing Synthware Glass Co., Chongqing, China).
2.2. Agar-Slant Preparation
The agar slant was prepared in a flat-topped glass tube with external diameter 15 mm × length 150 mm and sealed with a silicone tapered plug (12 mm diameter) (purchased from Chonqing Synthware Glass Co., Chongqing, China) containing 5 mL YPD agar medium and wrapped with a kraft paper in the outer layer. Alternatively, a glass tube with a screw cap could also be used.
2.3. Strain Preservation
The engineered strain stored at −80 °C in a glycerol vial was activated on the YPD agar plate containing 4 mg/mL of the antibiotic G418 by incubation at 30 °C for 3 days. The newly activated single colony was then streak-inoculated onto the antibiotic-free YPD agar slants and the antibiotic-containing (4 mg/mL G418) YPD agar slants, respectively, with the wire inoculating loop and continued cultivation for 3 days until the surface of the agar was fully covered by the lawn. Then, the slants were wrapped with kraft paper and preserved in a 4 °C fridge (Haier Group, Qingdao, China) for as long as 36 months. During long-term preservation, the samples were taken regularly to determine the strain vitality and the recombinant enzyme activity at different preservation time points.
2.4. Shaking Flask Cultivation
The preserved-strain lawns (~0.8 mm2) were picked up by the wire inoculating loop (loop inner diameter: 3 mm, purchased from Beijing Innochem Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) from the agar slants (antibiotic-free YPD agar slant and antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant) every 6 months for shaking flask cultivation, with the newly activated single colony of the strain from the ultra-low temperature refrigerator at −80 °C as the control. Samples taken from the three cultures were inoculated into the 500-mL shake flasks containing 100 mL BMGY medium, three biological repeats for each experiment (Figure 1). The flasks were incubated at 30 °C and 220 rpm for ~28 h (glycerol incubation phase), and then methanol was added every day to maintain 1% (v/v) for inducing gene expression (methanol induction phase). Meanwhile, the biomass and β-xylosidase activity were analyzed based on periodic sampling.

Figure 1.
Scheme for detecting the influence of long-term agar-slant preservation at 4 °C on the strain vitality and the recombinant enzyme activity of the engineered yeast.
2.5. Biomass Measurement and Enzyme Assay
The biomass measurement and enzyme assay methods were similar to those in our previous work [25]. Briefly, samples were taken during the time course of fermentation, and aliquots of 1 mL were washed three times with dH2O via centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 3 min, and the cell pellet was resuspended with dH2O in the same volume of culture broth. Biomass concentration was monitored by optical density at 600 nm (OD600nm) and by dry cell weight (DCW) measurements. Aliquots of the cell pellet were freeze-dried to a constant weight, and biomass was gravimetrically expressed as DCW (g/L).
The chromogenic substrate p-Nitrophenyl-β-D-xylopyranoside (PNP-Xyl, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used to monitor enzyme activity with spectrophotometry. This activity was then evaluated by calculating U/g (biomass enzyme activity). More specifically, absorbance was recorded at a wavelength of 405 nm (OD405nm) in a total volume of 60 μL, containing 10 μL of properly diluted fermentation broth and 50 μL of 5 mM PNP-Xyl in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 5.0. Reaction was performed at 50 °C for 20 min, and then it was terminated by adding 1 mL of saturated Na2B4O7 solution. One unit of activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 nM p-nitrophenol per minute.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All the experiments were carried out in triplicate and each presented value was the average of three independent experiments. Graphpad Prism 9.0 software (GraphPad Softwar, http://www.graphpad-prism.cn)was used to conduct ANOVA analysis on the data to determine the statistical difference; p < 0.05 was significant (*), p < 0.01 was extremely significant (**), and p > 0.05 was considered as no difference.
3. Results
3.1. Cell Growth Ability of the Engineered Yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 in the Slants Preserved at 4 °C
The cell growth ability of the engineered yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 after different preservation times (1, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 months, respectively) was shown in Figure 2. Both the cultures from the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant and the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant in the first four groups (1 month, 6 months, 12 months, 18 months) showed almost no difference in the biomass accumulation with the newly activated strain from the glycerol vial stored at −80 °C (control) during 250 h cultivation, which included the glycerol cultivation phase and the methanol induction phase (Figure 2a–d). In the 24 months group (Figure 2e, Table S1) and at 28 h time point (in the glycerol cultivation phase), the cultures from the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant and the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant reached 17.40 g/L and 17.67 g/L, respectively, decreased by 13.56% and 12.21% with that of the control (20.13 g/L), leading to the lagged glycerol cultivation phase till 52 h before methanol induction phase. However, during the whole phase of methanol induction, all three cultures exhibited the same level of biomass accumulation.
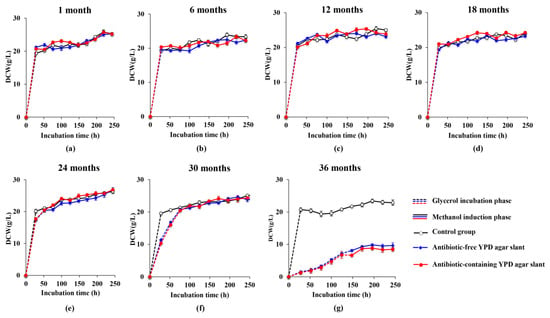
Figure 2.
Curves of growth abilities of the engineered yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 preserved in the YPD agar slants at 4 °C for different months (a–g). Dotted lines: glycerol incubation phase; Solid lines: methanol induction phase; Black hollow lines: the control group; Blue solid lines: the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant; Red solid lines: the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant.
The vitality of the two slant cultures was apparently lower than that of the control during the glycerol cultivation phase of the 30 months group (Figure 2f, Table S1), and the glycerol cultivation phase lasted for 76 h before the methanol induction phase. However, after 76 h, the two cultures showed almost no difference in biomass accumulation compared to the control. It means that, by extending the glycerol cultivation phase and shortening the methanol induction phase, the slant preserved at 4 °C for 30 months can still be used for the fermentation.
Unfortunately, the vitality of the two slant cultures preserved at 4 °C for 36 months (Figure 2g) extremely declined compared with that of the control, even extending the glycerol cultivation phase to 148 h. The biomass amount of the two cultures did not even surpass 10 g/L during the whole course of cultivation.
Thus, in terms of t=cell vitality, the engineered yeast strain in the YPD slant, regardless of the antibiotic, could be kept at 4 °C for up to 30 months before it is used for fermentation.
3.2. Biomass Enzyme Activity of the Engineered Yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 in the Slants Preserved at 4 °C
With respect to vitality, keeping the recombinant enzyme activity of the cells is equally important. We found that all three cultures showed similar trends in the biomass enzyme activity profiles (i.e., the biomass enzyme activities were almost linearly increased during the methanol induction phase), and at each time point, the biomass enzyme activities are also very similar in the first four preservation groups (1 month, 6 months, 12 months, 18 months) (Figure 3a–d). At the 24th month and 30th month (Figure 3e,f, Table S2), although the biomass enzyme activity profiles of the cultures from the antibiotic-free and antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant had no apparent change compared with that of the control, the delayed methanol induction in the two cultures resulted in the curves of the biomass enzyme activity drifted apparently to the right of the control (Figure 3e,f, Table S2). However, by the end of the fermentation, the biomass enzyme activities of the two cultures (i.e., the antibiotic-free and antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant) in these two groups (24th-month and 30th-month groups) were much similar to that of the control, both of them have caught up with that of the control at 220 h and 244 h of total cultivation, respectively (both corresponding to the 7th day of methanol induction), in which the glycerol cultivation phase was longer (i.e., lasted for 52 h and 76 h, respectively) but the methanol induction phase was shorter compared with those of the control (Figure 2e,f, Table S1, Figure 3e,f, Table S2). At the 36th month (Figure 3g), the biomass enzyme activities of the two cultures were drastically reduced compared with that of the control, which was consistent with the dramatic change in cell vitality (Figure 2g), indicating that after the 36 months of preservation, the strain had almost lost its enzyme production ability. These results demonstrated that the engineered yeast grown in the YPD slant could be kept at 4 °C for at least 30 months before it was used for fermentation. Additionally, the heterologous Lxyl-p1-2 gene on the chromosome of the host strain was quite stable and could not be easily lost during the preservation. Thus, the antibiotic (G418) added in the agar slant could be omitted.
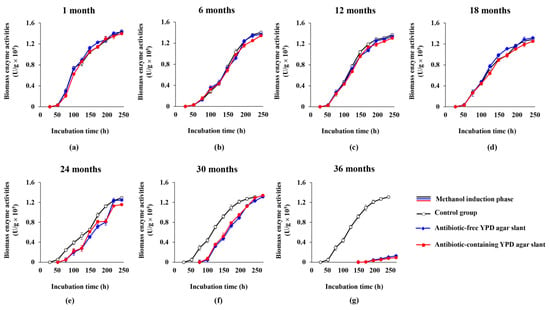
Figure 3.
Curves of biomass enzyme activities of the GS115-3.5K-P1-2 preserved in the YPD agar slants at 4 °C for different months (a–g). Black hollow lines: the control group; Blue solid lines: the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant; Red solid lines: the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant.
As for the recombinant yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2, the total cultivation commonly lasted for 220 h, which included 28 h of the glycerol cultivation phase, and 192 h of the methanol induction phase (8 days of induction) to finish the fermentation. Since then, the increasing speed of biomass enzyme activities started to slow down. Therefore, the biomass enzyme activities at 220 h (the 8th day of methanol induction) of each control group were regarded as relative standards. Toward the end of fermentation, the enzyme activities and the corresponding time point of the two cultures in the antibiotic-free and antibiotic-containing agar slants among the different preservation groups were compared, and the results were summarized in Figure 4. Within 24 months, the biomass enzyme activities of the cultures in the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant had no apparent difference compared with those of the control, while the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant showed a little decline on the enzyme activity but was still reasonable compared with the control. In the 24th month group, the biomass enzyme activities of the two cultures reached (for the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant) or approached (the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant) that of the control at 220 h (corresponding to the 7th day of methanol induction of each culture), coincided with the normal termination time of the fermentation. At the 30th month, the time point to achieve the equivalent level of the control for the two slant cultures was delayed from 24 h until 244 h (corresponding to the 7th day of methanol induction of each culture), nevertheless, it still saves time rather than strain resuscitation from −80 °C in a glycerol vial. These results indicate that the engineered strain can be kept in the agar slant at 4 °C for at least 30 months without apparently losing its biomass enzyme activity. Additionally, the antibiotic added in the solid medium can be omitted.

Figure 4.
Biomass enzyme activities toward the end of the fermentation and the corresponding time point of the two cultures in the agar slants among the different preservation groups. Black hollow column: the control group; Blue solid column: the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant; Red solid column: the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant. Data are presented as the mean ± SD; p > 0.05 was considered not significant (ns), p < 0.05 was significant (*), p < 0.01 was extremely significant (**). The blue mark of ANOVA analysis: the antibiotic-free YPD agar slant vs. the control group, the red mark of ANOVA analysis: the antibiotic-containing YPD agar slant vs. the control group.
4. Discussion
Effective storage can be defined as a viable state free of contamination or genetic drift of a microorganism, which allows easy storage without genotypic or phenotypic alterations to the original characteristics and properties [27]. Thus, the selection of a preservation method for recombinant strains represents an important procedure, ensuring not only that the viability will remain stable but also that the metabolic activity of interest should be preserved over time. There are several preservation methods, including cryopreservation [28], freeze-drying [29], liquid nitrogen cryopreservation [30,31], agar slant preservation [13,14], and mineral oil preservation, which is derived from agar slant preservation [32]. Cryopreservation and freeze-drying are the most frequently used in long-term storage with good microorganism recovery [33], while agar slant preservation is usually used for the short-term preservation of microbial strains.
Cryopreservation at −80 °C with glycerol as cryoprotectants is a well-defined method to preserve microorganisms and also has been recommended to preserve P. pastoris [28]. Alvarado-Fernández et al. evaluated the effect of glycerol and skim milk in cryopreservation at −80 °C on the cell viability and activity of a recombinant lysosomal enzyme produced in the P. pastoris GS115 strain. The results showed that cryopreservation with either glycerol or skim milk could maintain viability entirely after one year. In terms of activity, glycerol cryopreservation had a positive effect on the enzymatic activity over time, however, huge fluctuations and instability in the enzyme activity were displayed in cryopreservation with skim milk for one year [34]. Bryukhanov et al. estimated the survival rate of diverse species of obligate anaerobes after 3 years of storage in 25% glycerol (cryoprotective agent) at −70 °C. The results indicated that the spore-forming clostridia, most acetogenic bacteria, several sulfate-reducing bacteria, and even the methanogenic archaea can be stored for such a long time. Admittedly, this method could significantly increase the duration of storage while it required 2~6 times reinoculations into a freshly prepared nutrient media to achieve the initial specific growth rate [35].
The freeze-drying method is based on the removal of ice water by sublimation under vacuum conditions [36,37]. In general, the cell suspension of strain was frozen at ultra-low temperature (−80 °C) and subsequently lyophilized in a freeze-drying apparatus operating at −46 °C and 121 × 10−3 mbar pressure for 15 h; then, the sealed cryotubes could be stored at a low temperature (4 °C) before use [34]. Alvarado-Fernández et al. also reported that freeze-drying was an appropriate preservation method for the P. pastoris recombinant strain. The use of disaccharides or sorbitol in combination with skim milk is recommended in the freeze-drying process, which could keep strain viability for one year with survivals above 80%. Moreover, the use of disaccharides showed a positive effect on enzyme activity levels [34]. Yukie et al. investigated the survival rates of diverse species of microorganisms after freeze-drying (frozen at −60 °C, dried for 20 h) and 10-year preservation in a vacuum at 5 °C. The survival rates of five gram-positive bacteria were around 80% immediately after drying and did not decrease significantly during the 10-year storage period [38].
Cryopreservation has a lower cost compared to freeze-drying and does not need a large storage space, but it has high energy consumption, the transportation of microorganisms is difficult since it requires dry-ice packages during the shipping time, and it is dependent on the storage temperature [37]. On the other hand, freeze-drying is convenient for transport. However, it is expensive, depends on the availability of specific equipment, and may be a complex process to develop in a research laboratory [37]. Most notably, a common disadvantage of these two methods is that researchers may have to exert much effort to recover and reactivate the strain.
In this study, our results indicate that the engineered P. pastoris can be preserved in the agar slant at 2~4 °C for at least 30 months to keep its viability and production capacity, and during this period, the strain stored in the slant could be directly used for the seed cultivation of the fermentation, although the vitality recession was observed at the 30th month exhibited by the lagged glycerol cultivation phase, in which the biomass amount could still reach the requirement by properly extending the glycerol cultivation phase until 76 h. Additionally, the methanol induction phase could be shortened when the biomass accumulation reached the same level of the control (Figure 2f) with no effect on the total cultivation period for 250 h. Notably, the biomass enzyme activities of the 30th-month group achieved an almost identical level of the control at 244 h (Figure 3f, i.e., the 7th day of methanol induction). Despite the total cultivation being delayed for 24 h compared to the control, it was still worthwhile to save time and cost compared to the strain resuscitation from −80 °C in a glycerol vial.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the longest observation of the impact of the low temperature (4 °C) storage on the vitality and enzyme production ability of the engineered yeast strain. Since one slant can be used to prepare more seed cultures or can be repeatedly used for many times within 30 months of the preservation and the strain activation can be omitted, this approach is hopeful to save the cost in the fermentation process. It should be noted that ultra-low temperature storage (stored at −80 °C in a glycerol vial) is indispensable to preserving large amounts of the samples for long time, while this approach can be combined with low-temperature storage (preserving in the agar slant at 4 °C) for the engineered P. pastoris to sufficiently elevate the production efficiency in the fermentation process. Our approach also has a useful reference value for the engineered P. pastoris that produces other enzymes in industrial fermentation.
Additionally, the antibiotic (G418) added to the agar slant can be omitted if the heterologous gene is integrated into the host chromosome since the heterologous gene is much stable during preservation, which will further reduce the cost of fermentation. Typically, we observed that both the biomass amount and the biomass enzyme activity were significantly reduced at the 36th month (Figure 2g and Figure 3g), which might result from the pronounced decline on the vitality of large number of cells.
The drawback of the agar slant storage is that the moisture is slowly depleted from the solid medium [39], and moreover, the strain is not completely dormant, thus the strain is usually unable to keep the viability and production capacity in the slant for long time. In our study, agar-slant preservation’s strain viability and enzyme activity remained unchanged for 30 months, which may be attributed to the silicone tapered plug with good seal tightness, showing an excellent capacity for retaining moisture. It is noteworthy that the gradual loss of moisture in the agar slant has apparently impacted the preserved strain after 30 months of storage, and at the 36th month, this gradual dryness of the medium led to the significant decline in the strain viability and enzyme activity.
Whether or not the long-term agar-slant preservation can be applied to other yeast species, such as Sacharomyces cerevisae, another well-known host in industrial fermentation, requires further investigation. Finally, we proposed a workflow diagram of the procedure for the future preservation and fermentation of the recombinant yeasts, which is based on our results present in this work (Figure 5). If the recombinant gene is carried by an episomal plasmid, we suggest that the antibiotic should be added to the agar slant. If the low-temperature storage lasts for 30 months, we suggest that a pre-experiment should be done before the formal fermentation to ensure the vitality and production ability of the strain by comparing it with the newly activated single colony from the YPD plate on which the strain was inoculated from the ultra-low temperature storage.
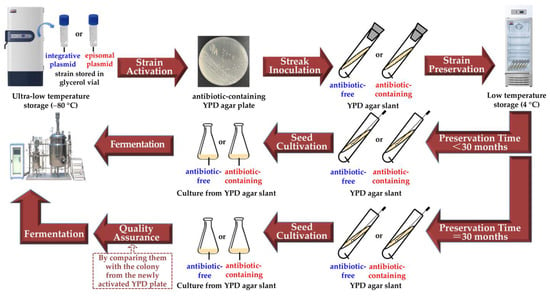
Figure 5.
Flowchart for the preservation and fermentation of recombinant yeasts.
5. Conclusions
In order to elevate the production efficiency of the engineered P. pastoris in the fermentation process, the low temperature storage (2~4 °C) in agar slant and the ultra-low temperature storage (between −70 °C and −80 °C) can be combined to preserve the engineered yeast. The engineered strain can be kept in the agar slant at 4 °C for at least 30 months without apparently losing its vitality and biomass enzyme activity. To the best of our knowledge, this is the longest observation of the impact of the low temperature storage on the vitality and the enzyme production ability of the engineered yeast strain. Additionally, if the heterologous gene, together with an antibiotic marker (for example, hph marker), is integrated into the host chromosome, the antibiotic added in the solid medium can be omitted. Our approach hopes to save costs and elevate the production efficiency in the fermentation process and also provides a useful reference for engineered P. pastoris expressing other enzymes in industrial fermentation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9020104/s1, Figure S1: Recombinant plasmid pPIC3.5K harboring Lxyl-p1-2. Table S1: Biomass enzyme activities of the engineered yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 of the 24th month and 30th month groups after cultivation for 250 h. Table S2: Cell growth abilities of the engineered yeast GS115-3.5K-P1-2 of the 24th month and 30th month groups after cultivation for 250 h.
Author Contributions
X.L. designed and conducted the experiments, collected data, created the graphs and wrote the manuscript; T.G., J.-J.C., T.-J.C. and J.-L.Y. helped to analyze the data; P.Z. conceived the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (No. CIFMS-2021-I2M-1-029), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2018YFA0901900), and the PUMC Disciplinary Development of Synthetic Biology (201920100801, China).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the currentstudy are available from the author X.L. on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Wen-Bo Yu and Wan-Cang Liu for their assistance in shaking flask cultivation and fermentation during their graduate study in our lab.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cregg, J.M.; Vedvick, T.S.; Raschke, W.C. Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Bio/Technology 1993, 11, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Yi, P.; Liu, J.; Yan, Q.J.; Jiang, Z.Q. High-level expression of an engineered β-mannanase (mRmMan5A) in Pichia pastoris for manno-oligosaccharide production using steam explosion pretreated palm kernel cake. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werten, M.W.; Eggink, G.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Wolf, F.A. Production of protein-based polymers in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.M.; Ning, C.; Yuan, M.X.; Fu, X.D.; Yang, S.X.; Wei, X.Y.; Xiao, M.S.; Mou, H.J.; Zhu, C.L. High-efficiency expression of a superior β-mannanase engineered by cooperative substitution method in Pichia pastoris and its application in preparation of prebiotic mannooligosaccharides. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Duan, X.P.; Wu, X.Y.; Gao, L.H.; Ye, M.; Zhou, Y.J. Recombination machinery engineering facilitates metabolic engineering of the industrial yeast Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 7791–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.J.; You, S.P.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Qi, W.; Su, R.X.; He, Z.M. Rational design of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type3 for improving testosterone production with an engineered Pichia pastoris. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.R.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, J.Y.; Xu, R.R.; Li, J.H.; Du, G.C.; Kang, Z. Biosynthesis of non-animal chondroitin sulfate from methanol using genetically engineered Pichia pastoris. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4365–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.R.; Xue, C.L.; Liu, W.Q.; Zuo, S.Q.; Wei, P.L.; Huang, L.; Lian, J.Z.; Xu, Z.N. High-level secretory production of leghemoglobin in Pichia pastoris through enhanced globin expression and heme biosynthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, R.; Karbalaei, M.; Soleimanpour, S.; Mosavat, A.; Rezaee, S.A.; Ghazvini, K.; Farsiani, H. Practical methods for expression of recombinant protein in the Pichia pastoris system. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- User Manual of Multi-Copy Pichia Expression Kit for the Isolation and Expression of Recombinant Proteins from Pichia Pastoris Strains Containing Multiple Copies of a Particular Gene; Cat.no.K1750-01., Manual part no.25-0170; Invitrogen TM: Waltham, MA, USA, 2010.
- Athmaram, T.N.; Singh, A.K.; Saraswat, S.; Srivastava, S.; Misra, P.; Kameswara Rao, M.; Gopalan, N.; Rao, P.V.L. A simple Pichia pastoris fermentation and downstream processing strategy for making recombinant pandemic Swine Origin Influenza a virus Hemagglutinin protein. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onions, A.H.S. Chapter IV preservation of fungi. Methods Microbiol. 1971, 4, 113–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.P. Preserving bacteria at low temperature involves inoculating purified bacteria into suitable solid slant culture medium, and performing culturing process, sealing cultured product using sealing film and refrigerating product. Chinese Patent CN106609244-A, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.P. Preservation of low temperature-bacterial slant culture involves storing pure bacterial inoculum in solid slant medium, culturing under preset conditions, sealing with parafilm, and storing at preset temperature. Chinese Patent CN105695332-A, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, F.; Pan, L.; Ottenbruch, M.; List, T.; Gaich, T. The chemistry of nonclassical taxane diterpene. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, L.Y.; Zhuang, W.B.; Zhang, F.J.; Shu, X.C.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Recent research progress in taxol biosynthetic pathway and acylation reactions mediated by Taxus acyltransferases. Molecules 2021, 26, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Sharma, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Madhusudanan, K.P. A process for the production of Taxol. EP Patent 090 5130 B1, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.J.; Wang, H.; Gong, T.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, T.J.; Yang, J.L.; Zhu, P. Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V. Semi-synthesis of paclitaxel from naturally occurring glycosidic precursors. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1997, 34, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Zhao, R.Y.; Chen, T.J.; Yu, W.B.; Wang, F.; Cheng, K.D.; Zhu, P. Cloning and characterization of the glycoside hydrolases that remove xylosyl groups from 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2013, 12, 2236–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.B.; Liang, X.; Zhu, P. High-cell-density fermentation and pilot-scale biocatalytic studies of an engineered yeast expressing the heterologous glycoside hydrolase of 7-β-xylosyltaxanes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Zhu, P. Pilot studies on scale-up biocatalysis of 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues by an engineered yeast. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Gong, T.; Wang, Q.H.; Liang, X.; Chen, J.J.; Zhu, P. Scaling-up fermentation of Pichia pastoris to demonstration-scale using new methanol-feeding strategy and increased air pressure instead of pure oxygen supplement. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Liang, X.; Li, H.X.; Chen, T.J.; Zhu, P. Improving the catalytic property of the glycoside hydrolase LXYL-P1-2 by directed evolution. Molecules 2017, 22, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Wen, Y.H.; Chen, T.J.; Liu, W.C.; Gong, T.; Yang, J.L.; Zhu, P. Combination mutation on the β-glycosidase specific to 7-β-xylosyltaxanes and increasing the mutated enzyme production by engineering the recombinant yeast. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Liang, X.; Chen, T.J.; Yang, J.L.; Zhu, P. Site-directed mutagenesis of a β-glycoside hydrolase from Lentinula edodes. Molecules 2019, 24, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, R.; Paoli, P.D. Collection and preservation of frozen microorganisms. In Methods in biobanking; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Cregg, J.M.; Higgins, D.R. Pichia Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blanquet, S.; Garrait, G.; Beyssac, E.; Perrier, C.; Denis, S.; H´ebrard, G.; Alric, M. Effects of cryoprotectants on the viability and activity of freeze dried recombinant yeasts as novel oral drug delivery systems assessed by an artificial digestive system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 61, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koštál, V.; Zahradníčková, H.; Šimek, P. Hyperprolinemic larvae of the drosophilid fly, Chymomyza costata, survive cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13041–13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isachenko, E.; Isachenko, V.; Rahimi, G.; Nawroth, F. Cryopreservation of human ovarian tissue by direct plunging into liquid nitrogen. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2003, 108, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.L. Survival, growth and pathogenicity of Gaeumannomyces graminis var. graminis with different methods of long-term storage. Mycologia 2005, 97, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, C. Cryopreservation of yeast cultures. In Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado-Fernández, A.M.; Rodríguez-López, E.A.; Espejo-Mojica, A.J.; Mosquera-Arévalo, A.R.; Alméciga-Díaz, C.J.; Trespalacios-Rangel, A.A. Effect of two preservation methods on the viability and enzyme production of a recombinant Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) strain. Cryobiology 2022, 105, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryukhanov, A.L.; Netrusov, A.I. Long-term storage of obligate anaerobic microorganisms in glycerol. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siberry, G.; Brahmadathan, K.N.; Pandian, R.; Lalitha, M.K.; Steinhoff, M.C.; John, T.J. Comparison of different culture media and storage temperatures for the long-term preservation of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the tropics. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.; Stacey, G. Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto-Shinohara, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Sukenobe, J.; Murakami, Y.; Kawamura, S.; Komatsu, Y. Survival rate of microbes after freeze-drying and long-term storage. Cryobiology 2000, 41, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homolka, L.; Lisá, L. Long-term maintenance of fungal cultures on perlite in cryovials—an alternative for agar slants. Folia Microbiol. 2008, 53, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).