Effects of Metal Chloride Salt Pretreatment and Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Poplar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Characterization of Raw and Pretreated Poplar
2.5. Determination of Activity and Content of Cellulase
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Different Metal Chloride Pretreatment on Chemical Composition and Glucose Yield
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Chemical Composition and Glucose Yield
3.3. Physical and Chemical Structure Characterization of the Raw and Pretreated Poplar
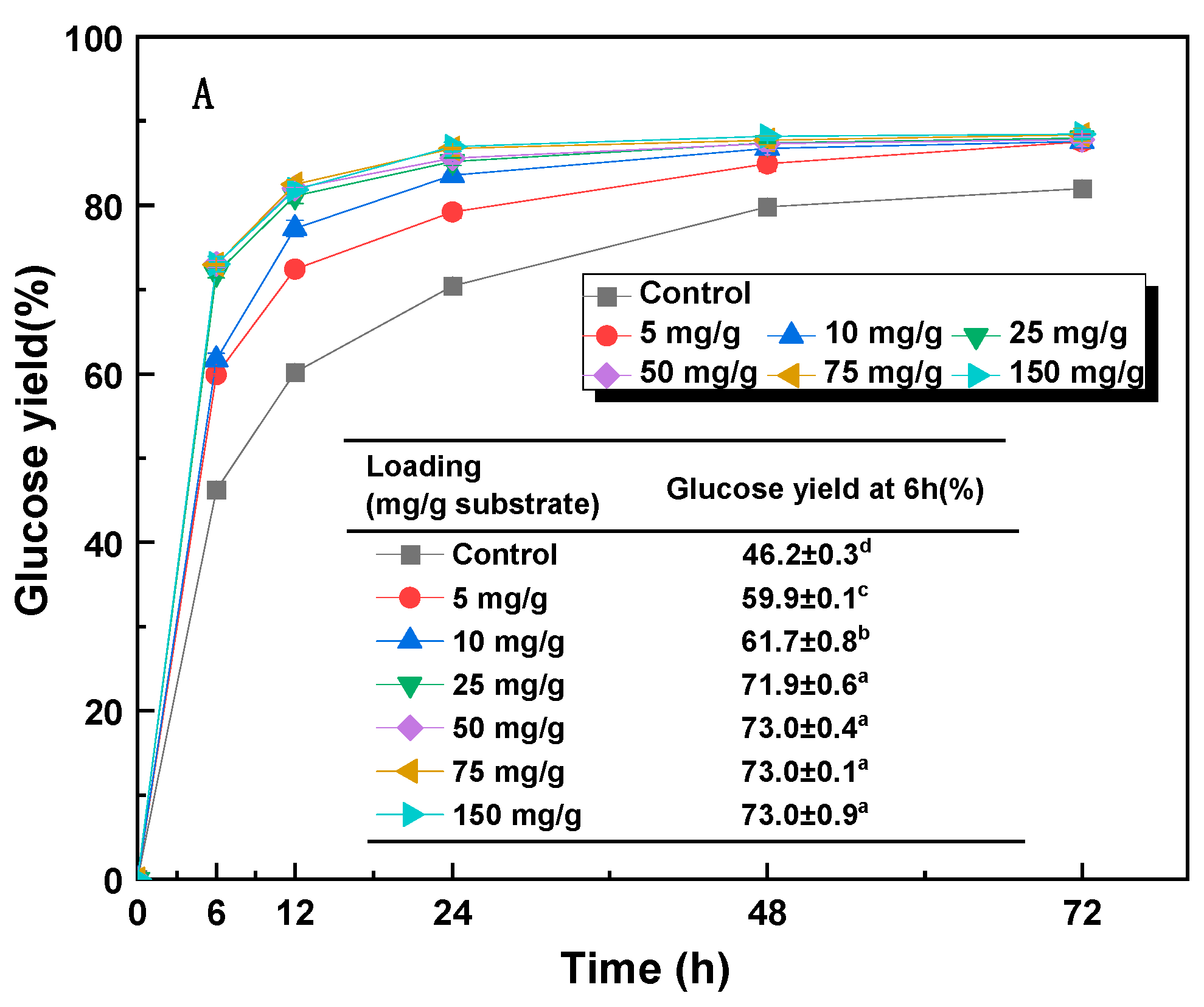
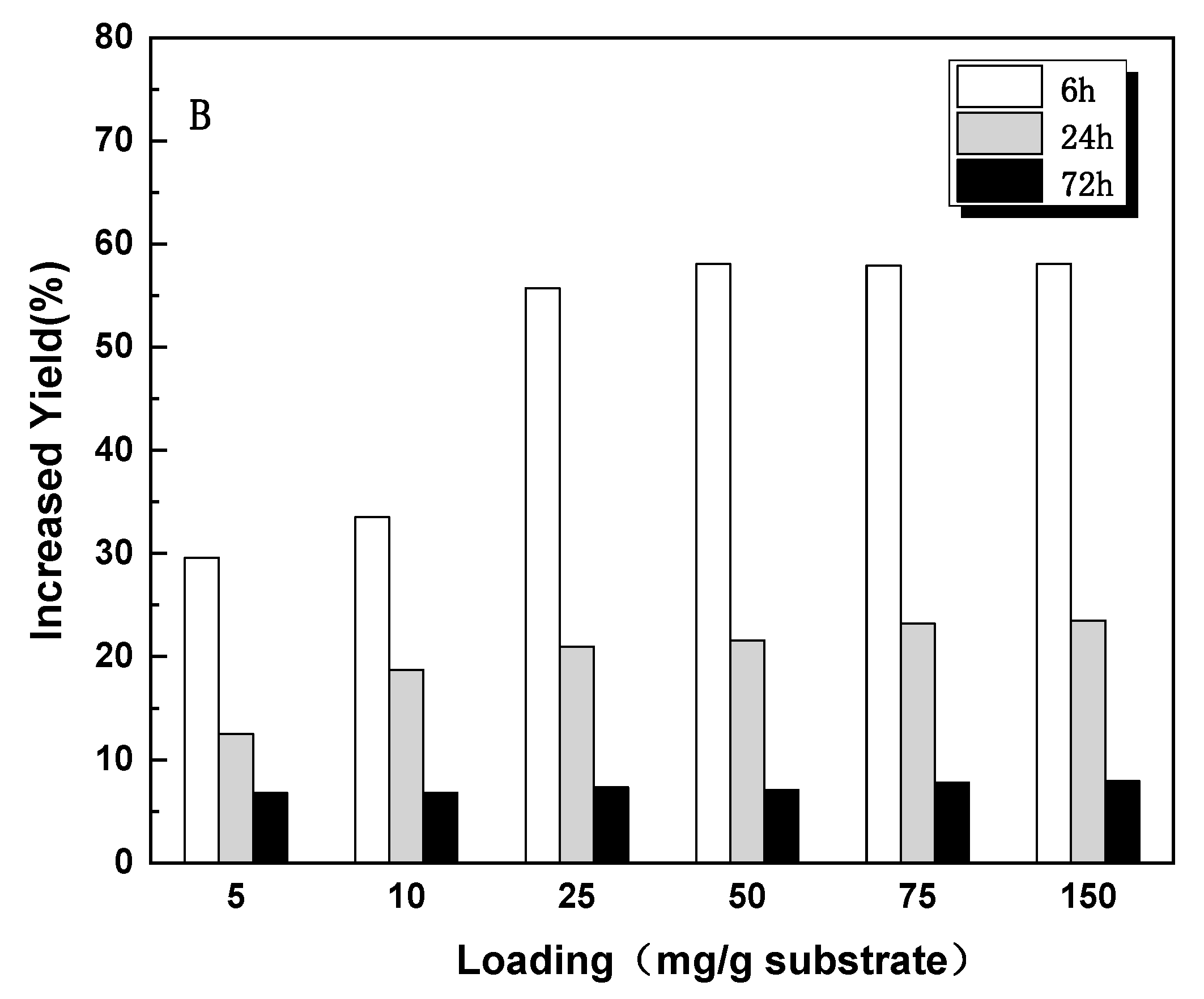
3.4. Effect of Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis
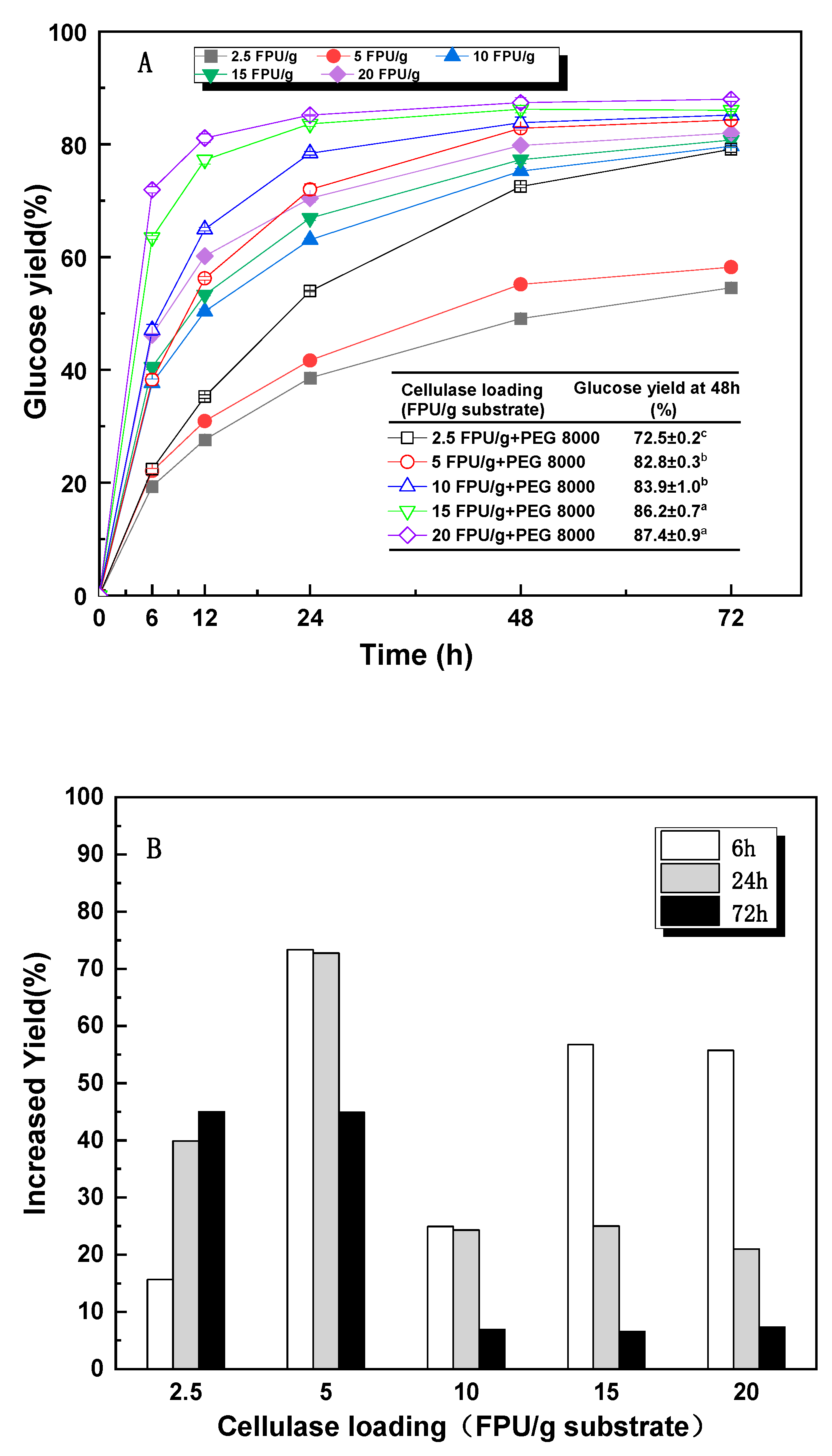
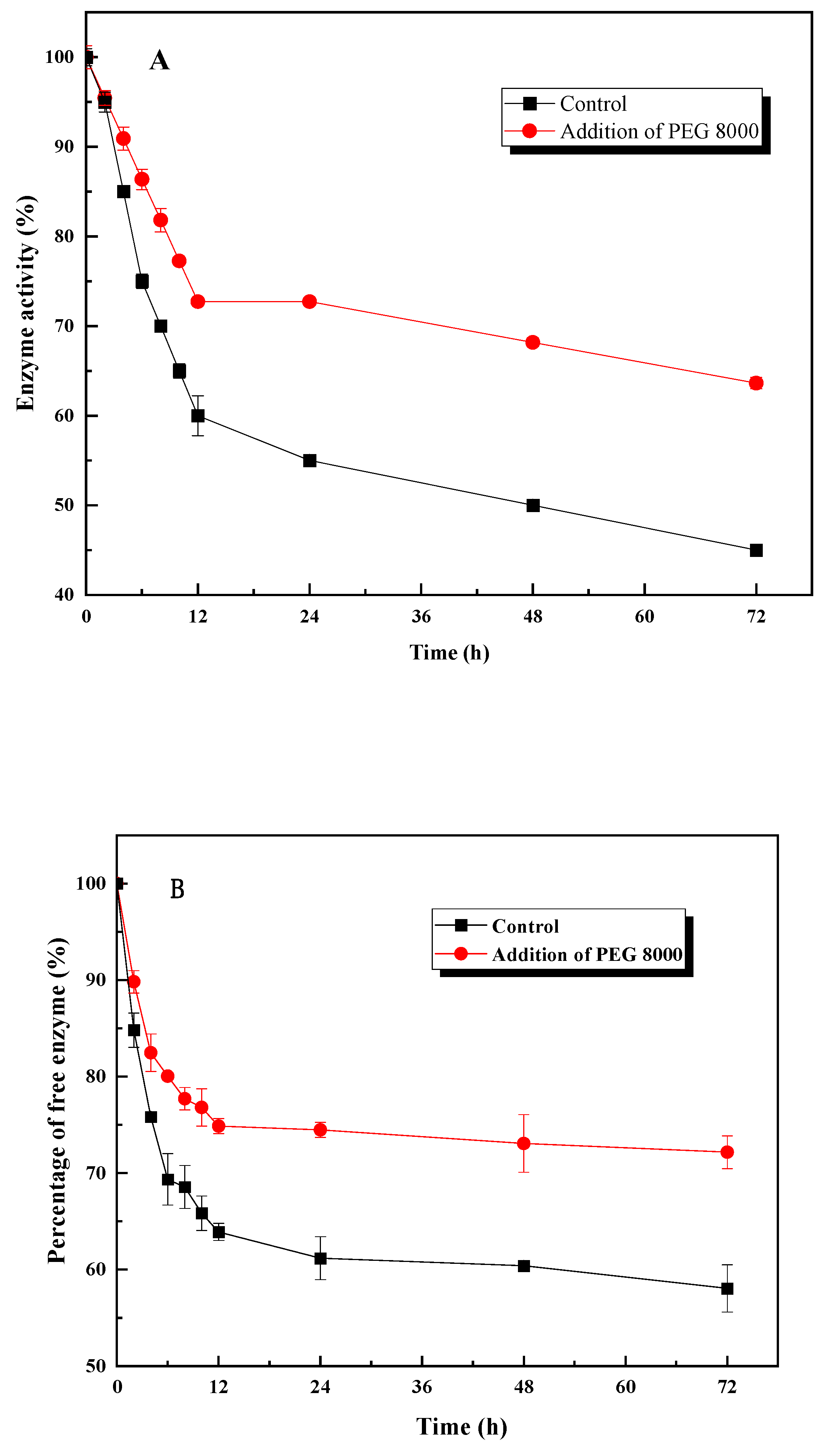
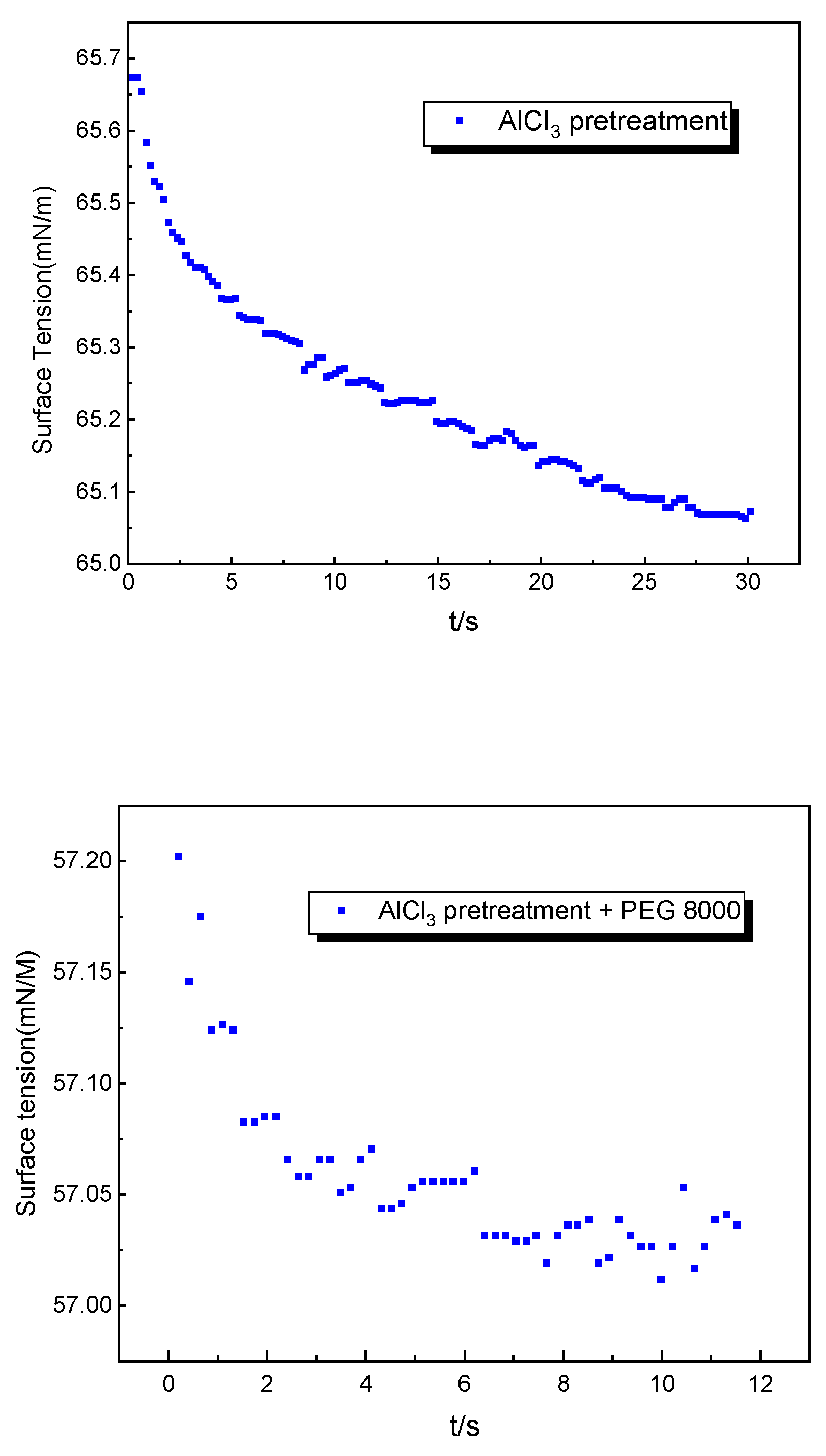
3.5. The Mechanism of PEG 8000 on Enzymatic Hydrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, X.; Sun, R. Recent advances in lignocellulose prior-fractionation for biomaterials, biochemicals, and bioenergy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanian, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Almasi, F.; Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H.; Nizami, A.-S.; Ok, Y.S.; Lam, S.S.; Tabatabaei, M. A critical review of the effects of pretreatment methods on the exergetic aspects of lignocellulosic biofuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 212, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogalakshmi, K.N.; Usman, T.M.M.; Kavitha, S.; Sachdeva, S.; Thakur, S.; Kumar, S.A.; Banu, J.R. Lignocellulosic Biorefinery Technologies: A Perception into Recent Advances in Biomass Fractionation, Biorefineries, Economic Hurdles and Market Outlook. Fermentation 2023, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Oryani, B.; Cho, J.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Sabbagh, F.; Hashemi, B.; Rupani, P.F.; Mohammadi, A.A. Different pretreatment technologies of lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production: An overview. Energy 2020, 199, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, R.; Parra-Cruz, R.A.; Pakalapati, H.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C.; Chen, W.H.; Tao, Y. Recent advances in the pretreatment of microalgal and lignocellulosic biomass: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Lv, Z.-W.; Rao, J.; Tian, R.; Sun, S.-N.; Peng, F. Effects of hydrothermal pretreatment on the dissolution and structural evolution of hemicelluloses and lignin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 281, 119050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woiciechowski, A.L.; Neto, C.J.D.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.; Sydney, A.C.N.; Letti, L.A.J.; Karp, S.G.; Torres, L.A.Z.; Soccol, C.R. Lignocellulosic biomass: Acid and alkaline pretreatments and their effects on biomass recalcitrance—Conventional processing and recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasic, K.; Knez, Z.; Leitgeb, M. Bioethanol Production by Enzymatic Hydrolysis from Different Lignocellulosic Sources. Molecules 2021, 26, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Li, N.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, F. Extracting high β-O-4 content lignin and by-producing substrate susceptible to enzymatic hydrolysis by a green flow through process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 453, 139730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimos, K.; Paschos, T.; Louloudi, A.; Kalogiannis, K.G.; Lappas, A.A.; Papayannakos, N.; Kekos, D.; Mamma, D. Effect of Various Pretreatment Methods on Bioethanol Production from Cotton Stalks. Fermentation 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Xie, J.; Qin, Y.L. Effects of NaOH-catalyzed organosolv pretreatment and surfactant on the sugar production from sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.G.; Meng, X.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. The critical role of lignin in lignocellulosic biomass conversion and recent pretreatment strategies: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Candido, J.P.; de Angelis, D.d.F.; Brienzo, M. Semi-Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation Improved by Lignin and Extractives Removal from Sugarcane Bagasse. Fermentation 2023, 9, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, P.L.; Wen, J.L.; Sun, R.C. Effects of aluminum chloride-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment on the structural characteristics of lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Chen, R.; Fu, S.Y. Preliminary exploration on pretreatment with metal chlorides and enzymatic hydrolysis of bagasse. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, N.; Liu, H.; Xie, J.; Lou, H.; Pan, X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, F. Changing the role of lignin in enzymatic hydrolysis for a sustainable and efficient sugar platform. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2023, 183, 113445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, S.S.; Balbino, T.R.; Alba, E.M.; Barbosa, F.G.; de Pier, F.T.; de Almeida, A.L.M.; Zilla, A.H.B.; Antunes, F.A.F.; Hilares, R.T.; Balagurusamy, N.; et al. Surfactants in biorefineries: Role, challenges & perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.-F.; Liu, K.-L.; Chen, F.-S.; Zhang, L.-F.; Guo, Z. Cationic Surfactant-assisted Microwave-NaOH Pretreatment for Enhancing Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Fermentable Sugar Yield from Peanut Shells. Bioresources 2014, 9, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ling, R.; Gong, M.; Wei, W. Enhancement of glucose production from sugarcane bagasse through an HCl-catalyzed ethylene glycol pretreatment and Tween 80. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, H.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. The hydrothermal-alkaline/oxygen two-step pretreatment combined with the addition of surfactants reduced the amount of cellulase for enzymatic hydrolysis of reed. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 308, 123324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Zeng, M.; Hu, Q.; Cai, C.; Lin, X.; Qiu, X.; Yang, D.; Pang, Y. Nonionic surfactants enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by reducing cellulase deactivation caused by shear force and air-liquid interface. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templaton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J. Investigation of alkaline hydrogen peroxide pretreatment and Tween 80 to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjesson, J.; Engqvist, M.; Sipos, B.; Tjerneld, F. Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) on enzymatic hydrolysis and adsorption of cellulase enzymes to pretreated lignocellulose. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamireddy, S.R.; Li, J.; Tucker, M.; Degenstein, J.; Ji, Y. Effects and Mechanism of Metal Chloride Salts on Pretreatment and Enzymatic Digestibility of Corn Stover. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guo, G.; Shen, D.; Tang, Y. Metal Salt-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment of Moso Bamboo to Improve Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Fermentation 2023, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, B.; Meng, L.; Yue, F.; Lan, W.; Sun, R.; Ren, J. Corncob Biorefinery for Platform Chemicals and Lignin Coproduction: Metal Chlorides as Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Xie, D.N.; Yang, Q.L.; Liu, Q.J.; Hou, Q.X.; Tao, Z.Y. Improving the Efficiency of Biomass Pretreatment and Enzymatic Saccharification Process by Metal Chlorides. Bioresources 2018, 13, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J. Statistical optimization of aqueous ammonia pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of corn cob powder for enhancing sugars production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 174, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huo, D.; Si, C.; Fang, G.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Improving enzymatic saccharification of eucalyptus with a pretreatment process using MgCl2. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; You, Y.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, L. Enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse by pretreatment combined green liquor and sulfite. Fuel 2017, 203, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, W.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Meng, X. Revealing the mechanism of surfactant-promoted enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, M.; Martin, J.F.G.; Bravo, V.; Sanchez, S. Ethanol Production from Olive Stones through Liquid Hot Water Pre-Treatment, Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Fermentation. Influence of Enzyme Loading, and Pre-Treatment Temperature and Time. Fermentation 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B.; Zhang, L.H.; Liu, D.H. Biomass recalcitrance. Part I: The chemical compositions and physical structures affecting the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining-Biofpr. 2012, 6, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, N.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Pretreatment of sweet sorghum straw and its enzymatic digestion: Insight into the structural changes and visualization of hydrolysis process. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Ling, R.; Jin, Y. Co-production of fermentable glucose, xylose equivalents, and HBS-lignin from sugarcane bagasse through a FeCl3-catalyzed EG/H2O pretreatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 165, 113440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, T. The effects of four different pretreatments on enzymatic hydrolysis of sweet sorghum bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4585–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Pei, H.; Zhang, J. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis and structural features of corn stover by FeCl3 pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5853–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Jin, H.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, H. Separation of surface sediments generated during the pre-hydrolysis via an efficient solvent dissolution and its physicochemical characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Li, W.; An, S.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Wu, M.; Wei, X. Ethylene glycol based acid pretreatment of corn stover for cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14140–14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S.; Shen, G.; Yuan, X.; Deng, Q.; Shen, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Efficient Corncob Biorefinery for Ethanol Initiated by a Novel Pretreatment of Densifying Lignocellulosic Biomass with Sulfuric Acid. Fermentation 2022, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-L.; Chen, X.-M.; Han, Y.-J.; Wang, X.-Q.; Potprommanee, L.; Ning, X.-A.; Liu, J.-Y.; Sun, J.; Peng, Y.-P.; Sun, S.-Y.; et al. Synergistic effects of surfactant-assisted ionic liquid pretreatment rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, R.; Woods, T.; Casey, W.; Cerrone, F.; Davis, R.; O’Connor, K.; Ruhal, R.; Babu, R. Surfactant-mediated hydrothermal pretreatment of Ryegrass followed by enzymatic saccharification for polyhydroxyalkanoate production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, R.; Tang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, X. Improve Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass by Modifying Lignin Structure via Sulfite Pretreatment and Using Lignin Blockers. Fermentation 2022, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpour, N.; Mousavi, S.M.; Shojaosadati, S.A. A novel surfactant-assisted ionic liquid pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Chen, X.; Wan, Y. Pretreatment of wheat straw by nonionic surfactant-assisted dilute acid for enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4875–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, R.; Kuttiraja, M.; Preeti, V.E.; Vani, S.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Binod, P. A novel surfactant-assisted ultrasound pretreatment of sugarcane tops for improved enzymatic release of sugars. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Qi, F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D. Non-ionic surfactants do not consistently improve the enzymatic hydrolysis of pure cellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Lan, T.Q.; Zhu, J.Y. Lignosulfonate and elevated pH can enhance enzymatic saccharification of lignocelluloses. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ramaswamy, S.; Xu, F. Synergy of hemicelluloses removal and bovine serum albumin blocking of lignin for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Yang, G.; Song, J.; Zheng, P.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, X.; Shuai, L. Understanding the promoting effect of non-catalytic protein on enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of lignocelluloses. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, N.; Chandraraj, K. Improved high solids loading enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of cotton microdust by surfactant addition and optimization of pretreatment. Process. Biochem. 2021, 106, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammad, A.; Adewale, P.; Kuttiraja, M.; Christopher, L.P. Enhancing enzyme-aided production of fermentable sugars from poplar pulp in the presence of non-ionic surfactants. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X. Evaluation of the action of Tween 20 non-ionic surfactant during enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose: Pretreatment, hydrolysis conditions and lignin structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, H.; Jiang, T.; Cai, C.; Li, X. Comparison of Hydrolysis Efficiency and Enzyme Adsorption of Three Different Cellulosic Materials in the Presence of Poly(ethylene Glycol). Bioenergy Res. 2013, 6, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Jiang, J. Stimulatory effects of rhamnolipid on corncob residues ethanol production via high-solids simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Fuel 2019, 257, 116091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
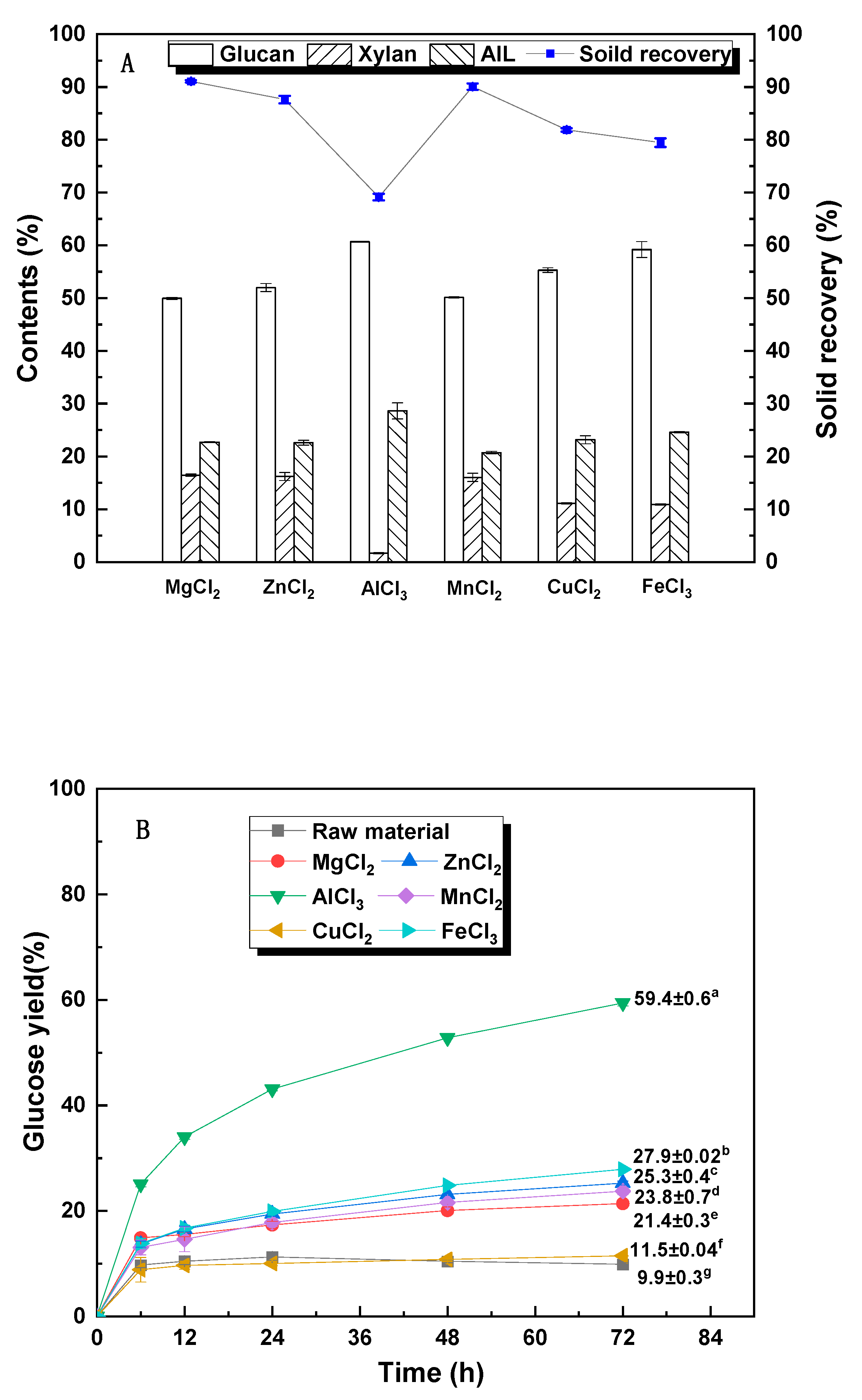
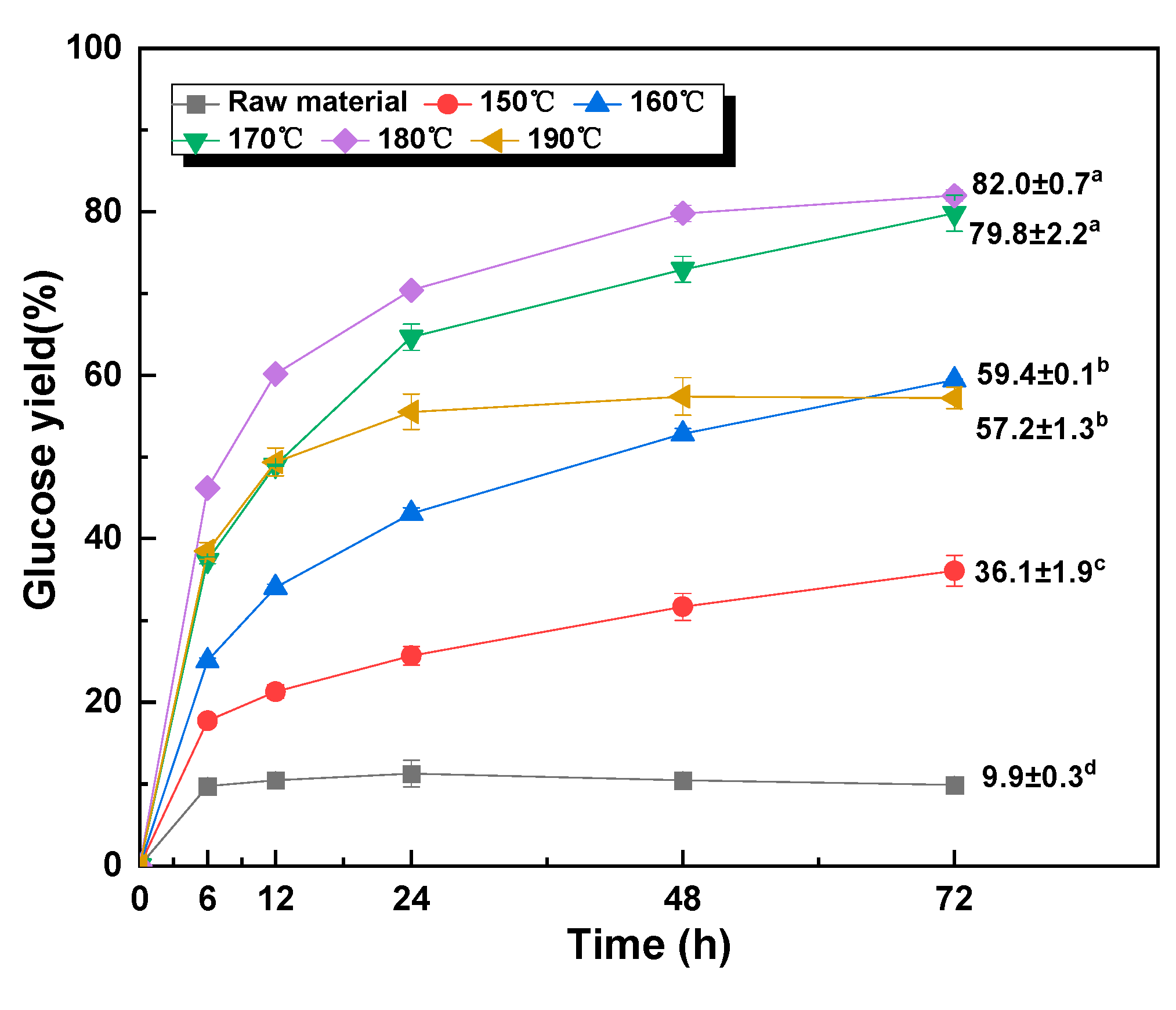
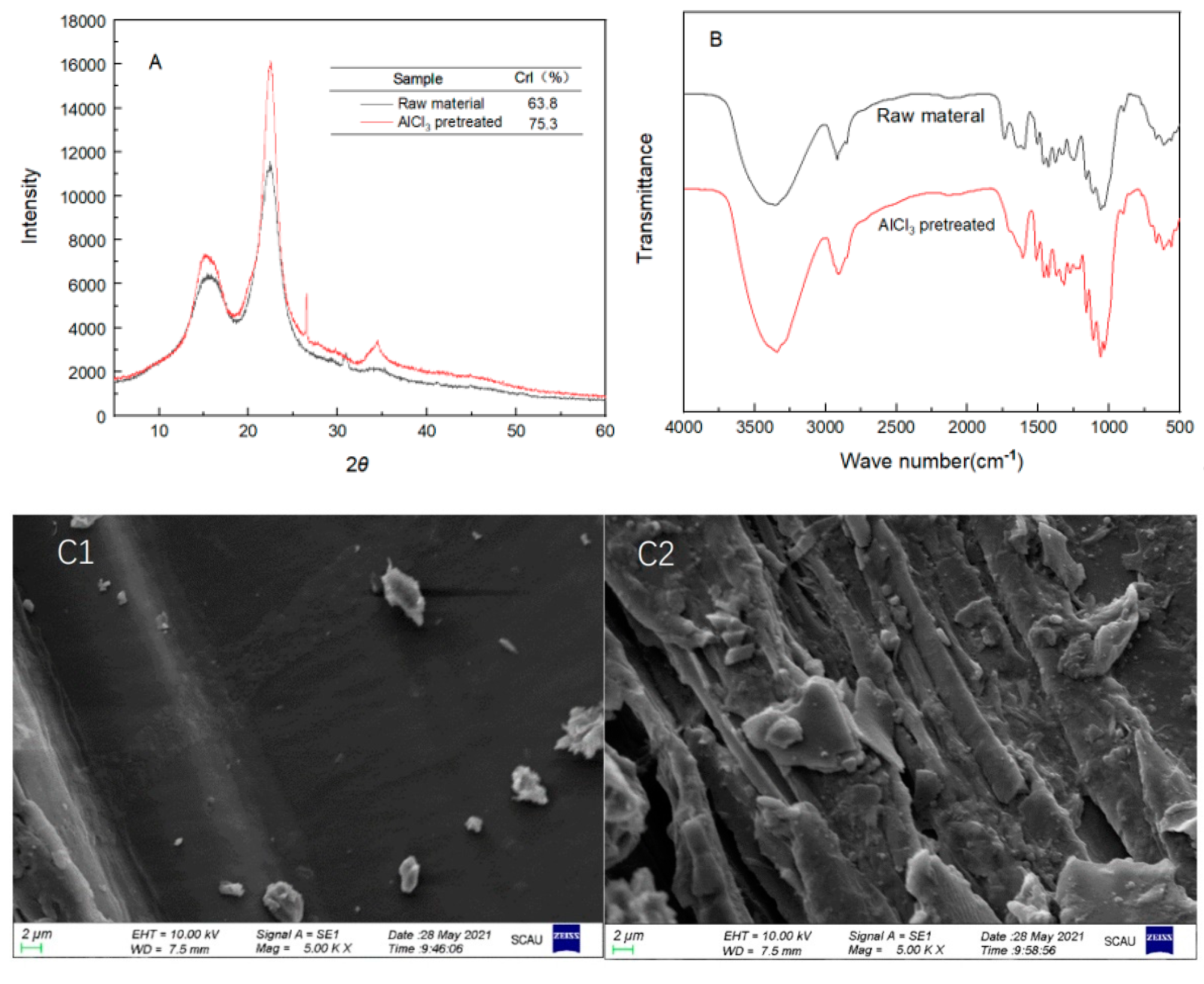
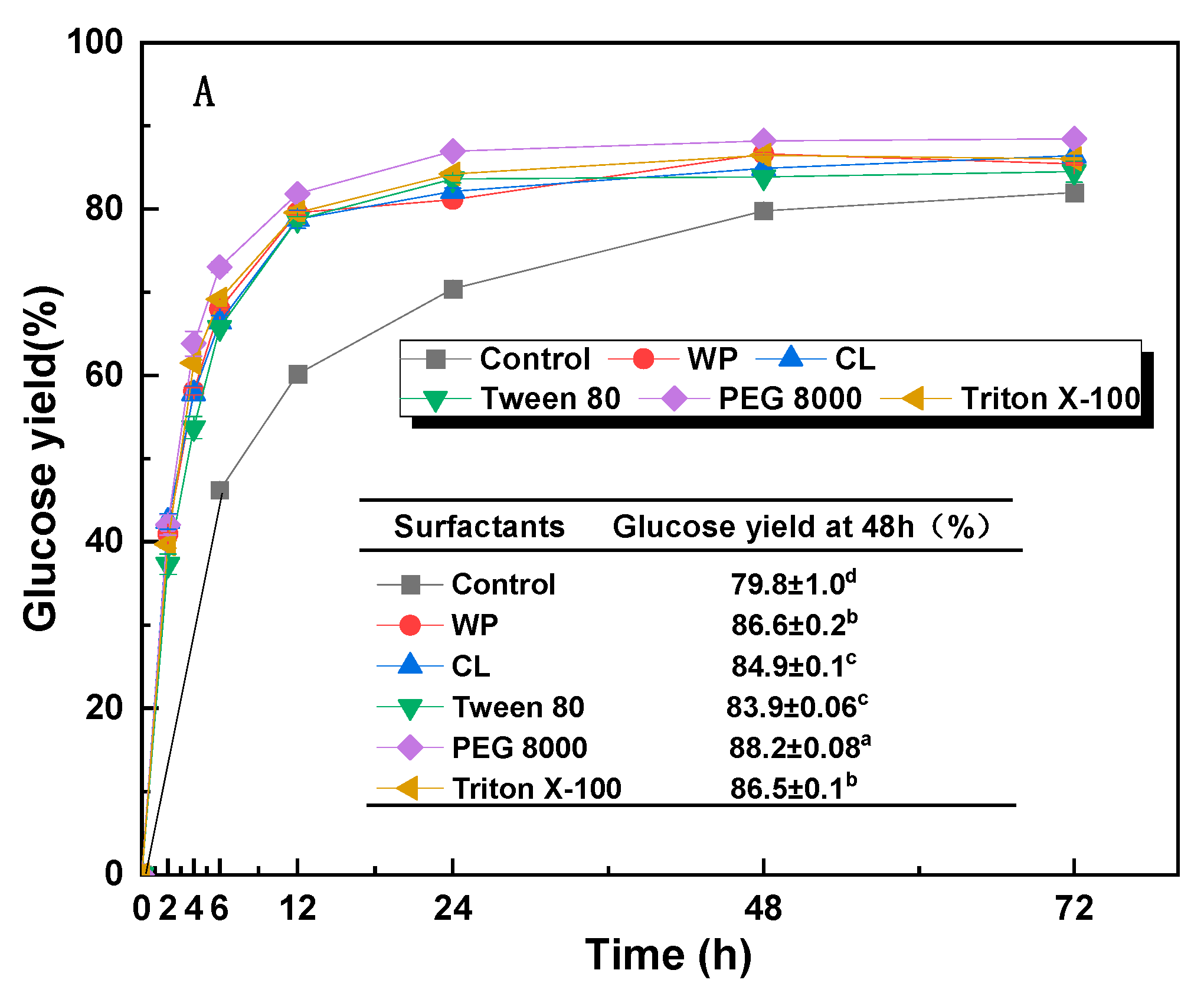

| Sample | Solid Recovery (%) | Contents (%) | Recovered Glucan (%) | Removed Xylan (%) | Removed AIL (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | AIL | |||||
| 150 °C | 76.3 ± 0.2 | 59.1 ± 0.05 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 25.0 ± 0.6 | 98.9 | 77.5 | 16.6 |
| 160 °C | 69.1 ± 0.6 | 62.0 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 28.3 ± 0.07 | 94.1 | 92.3 | 14.3 |
| 170 °C | 66.3 ± 1.0 | 64.2 ± 0.7 | -- | 30.4 ± 0.4 | 93.5 | 100 | 11.9 |
| 180 °C | 63.5 ± 0.5 | 63.7 ± 0.3 | -- | 32.0 ± 1.8 | 88.7 | 100 | 11.1 |
| 190 °C | 51.8 ± 1.2 | 42.2 ± 0.8 | -- | 39.6 ± 0.7 | 48.0 | 100 | 10.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Mai, S.; Fan, M.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H. Effects of Metal Chloride Salt Pretreatment and Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Poplar. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9121022
Zhao C, Mai S, Fan M, Xie J, Zhang H. Effects of Metal Chloride Salt Pretreatment and Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Poplar. Fermentation. 2023; 9(12):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9121022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chenbiao, Shenyi Mai, Meishan Fan, Jun Xie, and Hongdan Zhang. 2023. "Effects of Metal Chloride Salt Pretreatment and Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Poplar" Fermentation 9, no. 12: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9121022
APA StyleZhao, C., Mai, S., Fan, M., Xie, J., & Zhang, H. (2023). Effects of Metal Chloride Salt Pretreatment and Additives on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Poplar. Fermentation, 9(12), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9121022





