Abstract
In this study, an algal–bacterial symbiotic consortium was integrated with the sediment microbial fuel cell (SMFC) to construct an algal–bacterial cathode SMFC (AC-SMFC) for excess sewage sludge treatment and electricity generation. A bacterial cathode SMFC (BC-SMFC) and a static settling system (SS-system) were used as controls. Electrochemical analysis confirmed that the algal–bacterial biofilm on the cathode improved electricity production. The maximum power density of AC-SMFC was 75.21 mW/m2, which was 65.70% higher than that of the BC-SMFC (45.39 mW/m2). After 60 days of treatment, AC-SMFC achieved much higher removal efficiencies of the total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) (59.60%), suspended solids (SS) (62.42%), and volatile suspended solids (VSS) (71.44%) in the sediment, compared to BC-SMFC and the SS-system, exhibiting an effective degradation of the organic matter in the sediment sludge. Moreover, the lower concentration of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) in the overlying water of AC-SMFC demonstrated that the algae on the cathode could inhibit the accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus released from the sediments. The three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy revealed that the tryptophan protein and aromatic protein in the loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (LB-EPS) of the sediment sludge in the AC-SMFC were significantly decreased. Additionally, the abundance of functional microbiota in the AC-SMFC increased, such as Trichococcus, Alphaproteobacteria, and Clostridia, which contributed to electricity generation and sludge degradation. The combined application of microalgae and the SMFC provided a promising approach for excess sludge reduction and energy recovery.
1. Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid improvement of sewage treatment capacity, the amount of sludge has also increased significantly. The composition of urban sewage sludge is complex, containing a large number of pathogenic microorganisms, parasites, heavy metals, and carcinogens. If improperly disposed, it will cause serious secondary pollution to the water and soil.
The amount of sludge produced each year in various countries is constantly increasing, making it difficult to manage and dispose of excess sludge. The traditional activated sludge process has been widely used to treat various urban and industrial wastewater. Traditional treatment technologies (incineration and landfill) are not sustainable. Sludge reduction can be accomplished by using oxidants to oxidize the excess organic matter and microorganisms in the sludge. Adding 0.133 g Cl2 per gram of mixed liquid suspended solids (MLSS) can achieve 65% sludge reduction [1]. A combined sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process with the ClO2 technology significantly reduced sludge production by up to 58% [2]. A combination of ultrasonic and alkaline was also an effective method for sludge reduction [3]. Furthermore, separating the energy coupling between the decomposition and synthesis metabolism of microorganisms in sludge, inhibiting the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and using decoupling metabolism aimed to reduce sludge [4].
Sediment microbial fuel cell (SMFC) is a technology that utilizes the life activities of microorganisms to convert chemical energy into electrical energy. With addition of graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) into the SMFC, the sludge reduction rate could be increased to 3 and 2.2 times that of the ordinary SMFC [5]. The SMFC could be introduced into a secondary settling tank to complete sludge reduction in situ. In the reported research, installing inclined plate anodes to enlarge the surface area of the electrodes is a useful approach to improve the effectiveness of sludge disintegration [6], achieving higher power density, lower internal resistance, and higher sludge reduction, compared with normal SMFCs. The lack of electron acceptors remains a significant barrier limiting the efficiency of electricity generation and sludge reduction in the research progress of SMFCs for excess sludge treatment. It is of great necessity to develop novel SMFCs that can efficiently treat excess sludge while improving the electricity generation performance; therefore, it has become a research hotspot.
The oxygen reduction rate of SMFCs can be increased by adding a catalyst to the cathode; however, this is not the ideal option due to the high expense and potential environmental pollution problems [7,8]. Using microorganisms as catalysts to enhance electrochemical reduction on the cathode surface is a feasible method [9]. It makes sense to combine microalgae photosynthesis with SMFCs in order to improve the electrochemical performance with lower energy use [10]. As reported by Wang D B et al. [11], an algae-assisted cathode in the SMFC could increase the dissolved oxygen concentration and oxygen reduction rate, with an output power density of 21 mW/m2. SMFCs with excess activated sludge as sediment could simultaneously achieve electricity recovery and sludge reduction. However, large amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus might be released from the sedimental sludge into the overlying water which should be further treated before discharge, thus increasing the treatment cost of the excess sludge. It is worth noting that microalgae could effectively utilize nitrogen and phosphorus during their growth and metabolism. Therefore, applying an algae-assisted cathode into SMFCs with excess sludge as sediment might be effective for simultaneous electricity recovery enhancement and removal of the nitrogen and phosphorus in the overlying water. Additionally, the improvement of the electrochemical performance could facilitate the treatment efficiency of the sedimental sludge. However, the research concerning the SMFC with an algae-assisted cathode for sludge treatment is rarely reported.
Therefore, this study introduced algal–bacterial consortia into the SMFC to construct an algal–bacterial cathode sediment microbial fuel cell (AC-SMFC) for the effective treatment of excess sludge and electricity recovery. The AC-SMFC system could reduce sludge while improving power generation performance. At the same time, the symbiotic biofilm of bacteria and algae could remove the nitrogen and phosphorus released from the sediment, inhibiting nutrient accumulation in the overlying water. A bacterial cathode sediment microbial fuel cell (BC-SMFC) and static settling system (SS-system) were operated as controls. The electrochemical performance, sludge treatment efficiency, transformation of nitrogen and phosphorus, changes of the sludge properties, and bacterial community of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were investigated. Our study will be helpful to develop effective technologies for excessive sludge reduction and energy recovery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of SMFCs
The SMFCs in this study were built using the rotating cathode MFC disclosed in a previous study [12], which was comparable to rotating biological contactors (RBC) utilized in wastewater treatment. The rotating cathode was comprised of 10 pieces of round graphite felts (diameter 9.0 cm) which were connected in series on a horizontal graphite rod and partially immersed in the wastewater. The graphite rod that was attached to a motor device by a stainless steel connector. A piece of graphite felt was placed at the bottom of a rectangular plexiglass chamber (30 [L] × 10 [H] × 10 [W] cm3, with a working volume of 2 L) to be used as the anode. During the experiment, half of the cathode was immersed in the overlying water, with a 3 cm gap between the top of the anode and the bottom of the cathode. No membrane was placed between cathode and anode. The anode and cathode were connected through copper wires and resistance. The graphite felts were washed in 1 M HCl and 1 M NaOH for 24 h, respectively, before being rinsed with deionized (DI) water to eliminate any trace metals or biomass contamination.
2.2. Operating Conditions
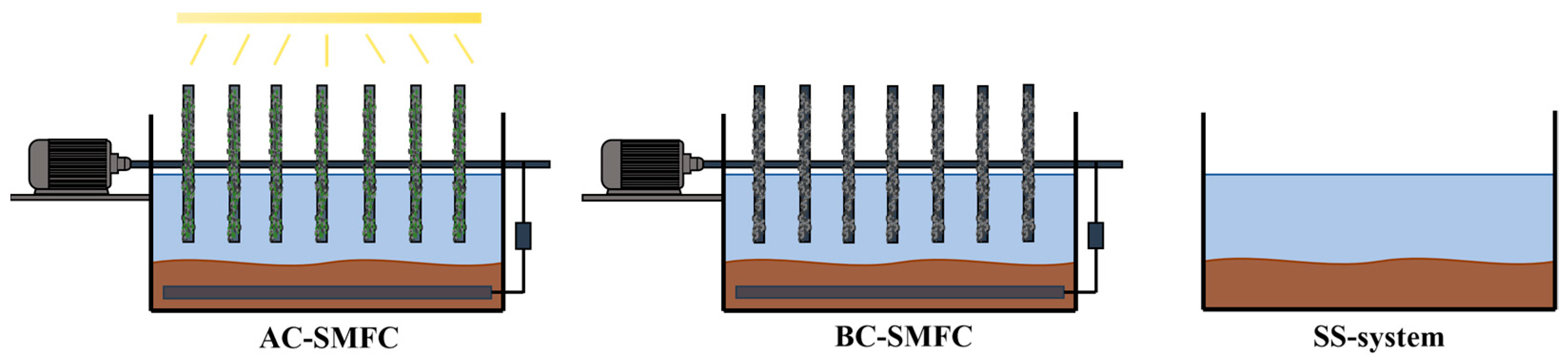
In this research, three experimental systems were constructed: algal–bacterial cathode SMFC (AC-SMFC), bacterial cathode SMFC (BC-SMFC), and static settling system (SS-system). The three systems were operated in parallel as sequencing batch reactors (Figure 1). During the experiment, the external resistances (Rex) of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC were both 10 Ω. The cathodes of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC were rotated at a constant speed of 2.8 rpm. The distinctions between the microorganisms in the biofilm were what made AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC different from one another. The cathode of AC-SMFC was a biofilm of algal–bacterial symbiosis, while the cathode of BC-SMFC was a bacterial biofilm. The algae used in this research was C. vulgaris, and the bacteria came from the activated sludge. The SS-system simulated the degradation of excess sludge under natural conditions.
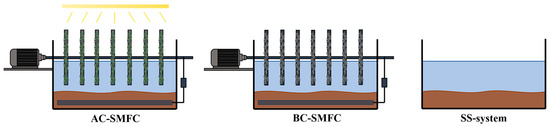
Figure 1.
Construction of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.
The overlying water was the effluent of the secondary sedimentation tank. Sediment excess sludge used in this research was collected from Yindingzhuang Wastewater Treatment Plant of Hebei. The excess sludge had total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) concentrations of 22,820 mg/L, suspended solids (SS) concentrations of 31.35 g/L, and volatile suspended solids (VSS) concentrations of 18.38 g/L. The three systems ran continuously for 60 days, using deionized (DI) water to replenish the surface of the overlying water lost during the operation.
2.3. Electrochemical and Chemical Analysis Methods
The output voltage of the SMFCs was recorded every 5 min using a paperless recorder (VX5302R, Pangu, China). By adjusting the external resistance from 5000 Ω to 10 Ω and allowing the circuit to stabilize for 15 min at each resistance, polarization curves were measured. Then, the current (I) was calculated from the measured voltages (U) and external resistance (R) according to Ohm’s law: I = U/R. The power density P (mW/m2) was determined using the equation P = UI/SAn, where SAn is the area of the anode. Using the polarization slope approach, internal resistances were calculated based on the slope of the polarization curves [13]. Cyclic voltammograms (CV) were performed by the electrochemical workstation (CHI660D, Chenhua, China) in a three-electrode mode (cathode: working electrode, Ag/AgCl: reference electrode, anode: counter electrode). The reference electrode was placed in the cathode compartments during the measurements [14].
TCOD concentration was measured using a TOC/TN analyzer (TOC-V, Shimadzu, Japan). Measurements of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), SS, and VSS were determined by the standard methods [15]. The extraction of loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS) and tightly bound EPS (TB-EPS) from the sediment was performed using a modified heat extraction method described by Yin et al. [16]. The concentrations of protein (PN) and polysaccharides (PS) in the EPS samples were measured using the Lowry method [17] and the sulfuric-acid–anthrone colorimetric method [18], respectively. Additionally, three-dimensional EEM (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy of EPS was measured using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (F-7000, Hitachi, Japan) to characterize the fluorescence properties of the EPS samples.
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
Through regular sampling from the sediment and anode, high-throughput sequencing analysis was carried out to determine the dominant microbial community types in different periods. To amplify the bacterium, the universal primers 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) were employed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Performance of SMFCs
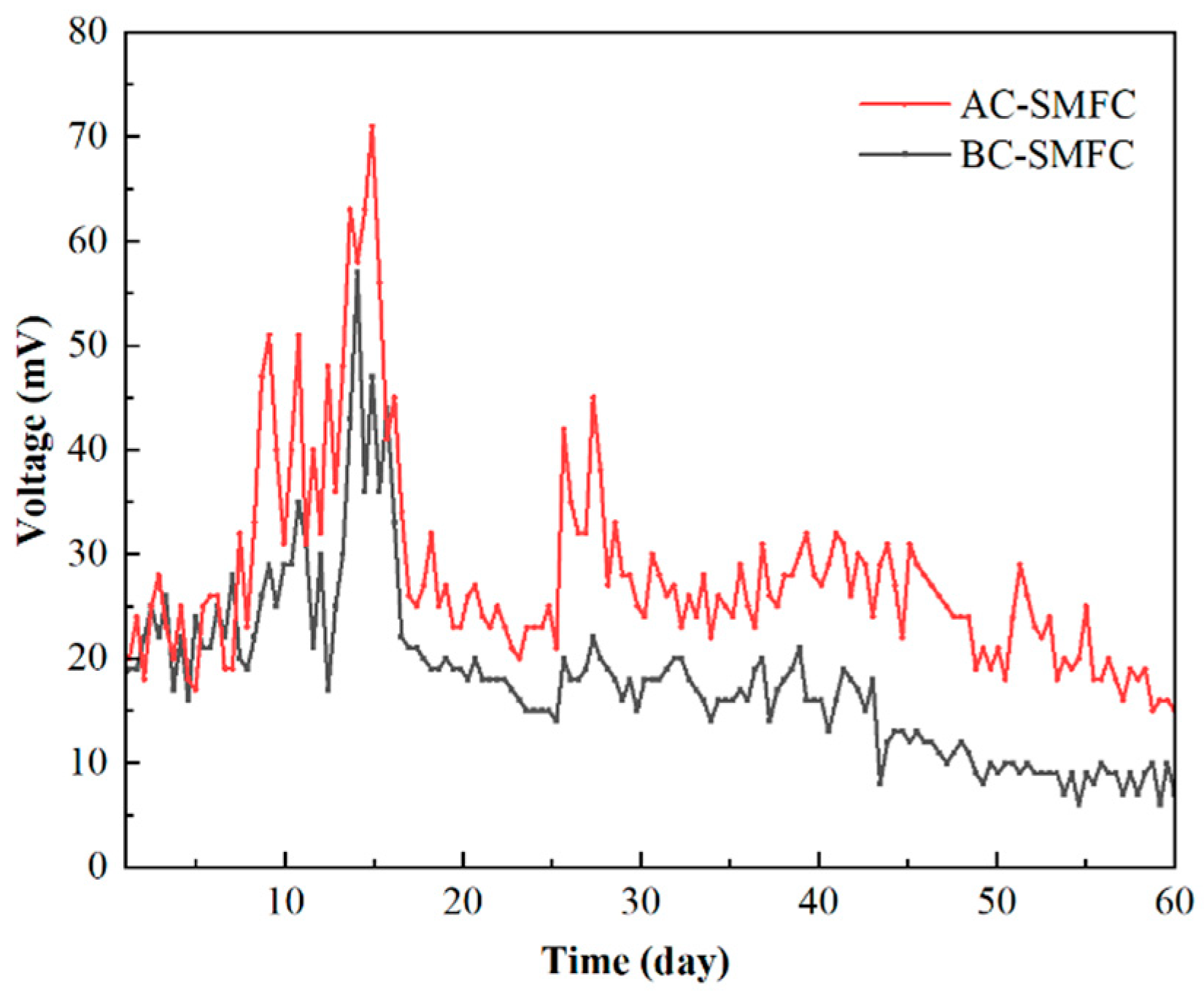
The variation of the voltage output of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC during the 60 days is shown in Figure 2. The initial voltage fluctuations of the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC were significant, with an overall upward trend. The voltage began to stabilize in its output on the 14th day of operation. In the later stage of system operation, the voltage of the two systems began to slowly decrease. This phenomenon indicates that during the system operation stage, the microbial population enriched and oxidized some easily biodegradable organic matter in the sediment. As the content of easily biodegradable organic matter decreased, the voltage then slowly decreased, and the microorganisms began to degrade large molecules of organic matter. During the 60 days, the average voltage outputs of the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC were 27.8 ± 9.7mV and 17.9 ± 8.1 mV, respectively.
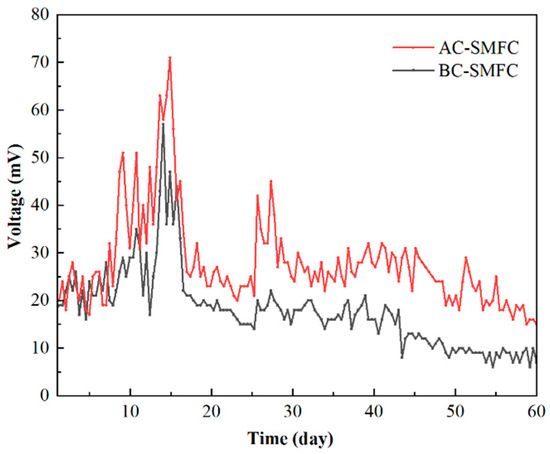
Figure 2.
The voltage output of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC.
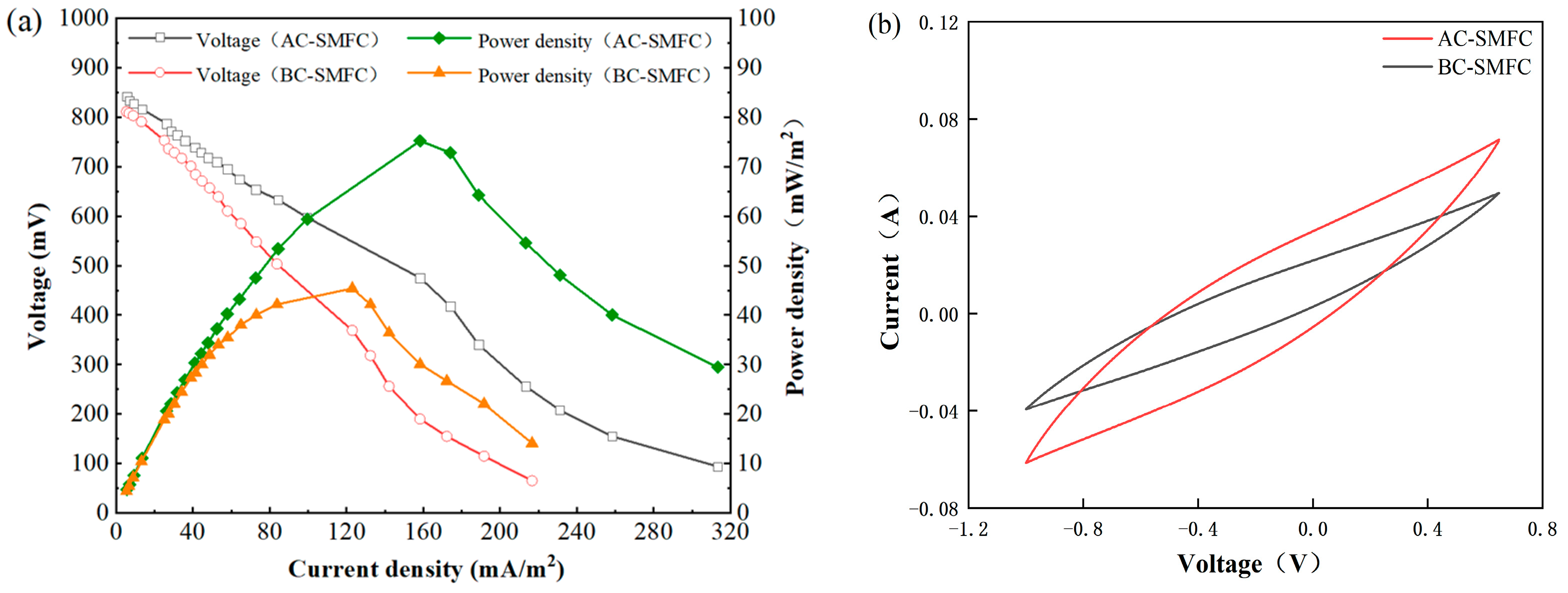
At the end of the operation period, the power and polarization curves of the SMFC were determined (Figure 3a). As the external resistance changed, the current density continuously increased, and the power density also increased accordingly. When the current density increased to 158.33 mA/m2, the power density of the AC-SMFC reached its maximum value of 75.21 mW/m2. When the current density increased to 123.00 mA/m2, the power density of the BC-SMFC reached its maximum value of 45.39 mW/m2. Subsequently, the power density decreased with the increase in current density, which was caused by the polarization effect inside the battery [19]. The maximum power density of the AC-SMFC was 65.70% higher than that of the BC-SMFC. Algae biomass contains a lot of carbon and other resources that electrogenic bacteria can use to generate electricity [11].
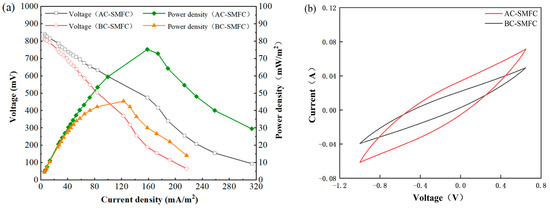
Figure 3.
Power density curve, polarization (a), and cyclic voltammetry curves (b) of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC.
Internal resistance was estimated from the slope of the plot of voltage versus current. The rotating cathode can increase the oxygen availability of the cathode, so AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC could both decrease internal resistance, compared to the reported SMFC with the stationary cathode. The internal resistances of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC were 86 Ω and 128 Ω, respectively, which were much lower than the reported SMFCs [11,13,20]. Furthermore, when compared to the BC-SMFC, the internal resistance of the AC-SMFC was reduced by 32.81%, owing to C. vulgaris increasing oxygen availability on the cathode and promoting the oxygen reduction processes. The above results demonstrated that the algae on the cathode could improve electricity generation and decrease internal resistance.
CVs were extensively used to examine the redox properties of species in SMFCs. The integral area of the scanning curve represented the discharge capacity of the system. As shown in Figure 3b, the capacitance of the AC-SMFC increased by 108.26%, compared to the BC-SMFC. The results showed that the algae-assisted cathode was important in the catalytic behavior of the oxygen reduction reaction, which was commensurate with the power generation.
3.2. Organic Matter Removal Efficiency in the Sediment of the SMFCs
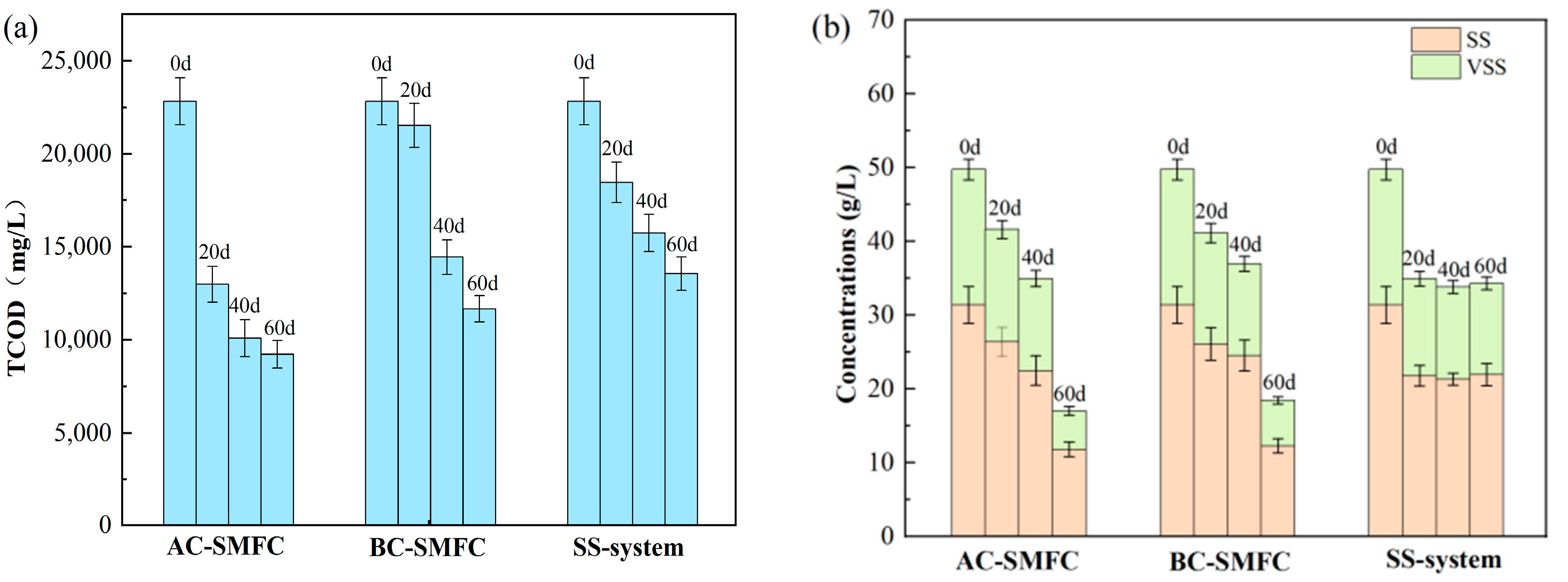
The concentrations of TCOD, SS, and VSS of the sediment sludge in the three systems were analyzed to investigate the removal efficiency of organic matter. The variations of TCOD, SS, and VSS in the sediment of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system are illustrated in Figure 4. The TCOD content of the initial excess sludge before treatment was 22,820 mg/L. During the treatment, the organic matter in the excess sludge was partly used for anaerobic digestion and electricity generation. The microorganisms obtained the energy they required through the metabolic process and thus generated electricity. After 60 days of treatment, the removal efficiency of the TCOD in the sediments of AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system reached 59.60%, 48.90%, and 40.64%, respectively (Figure 4a). The AC-SMFC exhibited higher removal efficiency of TCOD in the sediment, which was mainly because the AC-SMFC could effectively capture oxygen and this improved the operational efficiency of the system by treating excess sludge through the symbiotic interactions between the bacteria and algae.
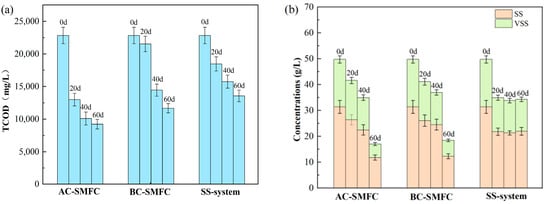
Figure 4.
Variations of TCOD (a) and VSS (b) in the sediment of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.
The excess sludge was composed of organic matter and inorganic matter. The removal rate of VSS could reflect the sludge reduction effect of the SMFCs [21]. The SS removal efficiencies in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system reached 62.42%, 60.86%, and 30.11% after the treatment, respectively, and the VSS removal efficiencies reached 71.44%, 66.48%, and 32.59%, respectively (Figure 4b). Compared to the SS-system, both the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC had better performance in the degradation of organic matters in the sediment, which was mainly because the electricity generation in the SMFCs could enhance the sediment reduction [22]. AC-SMFC exhibited a higher sludge reduction rate than BC-SMFC, most likely because the microalgae on the cathode produced oxygen as electron acceptors.
3.3. Variation of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations in SMFCs
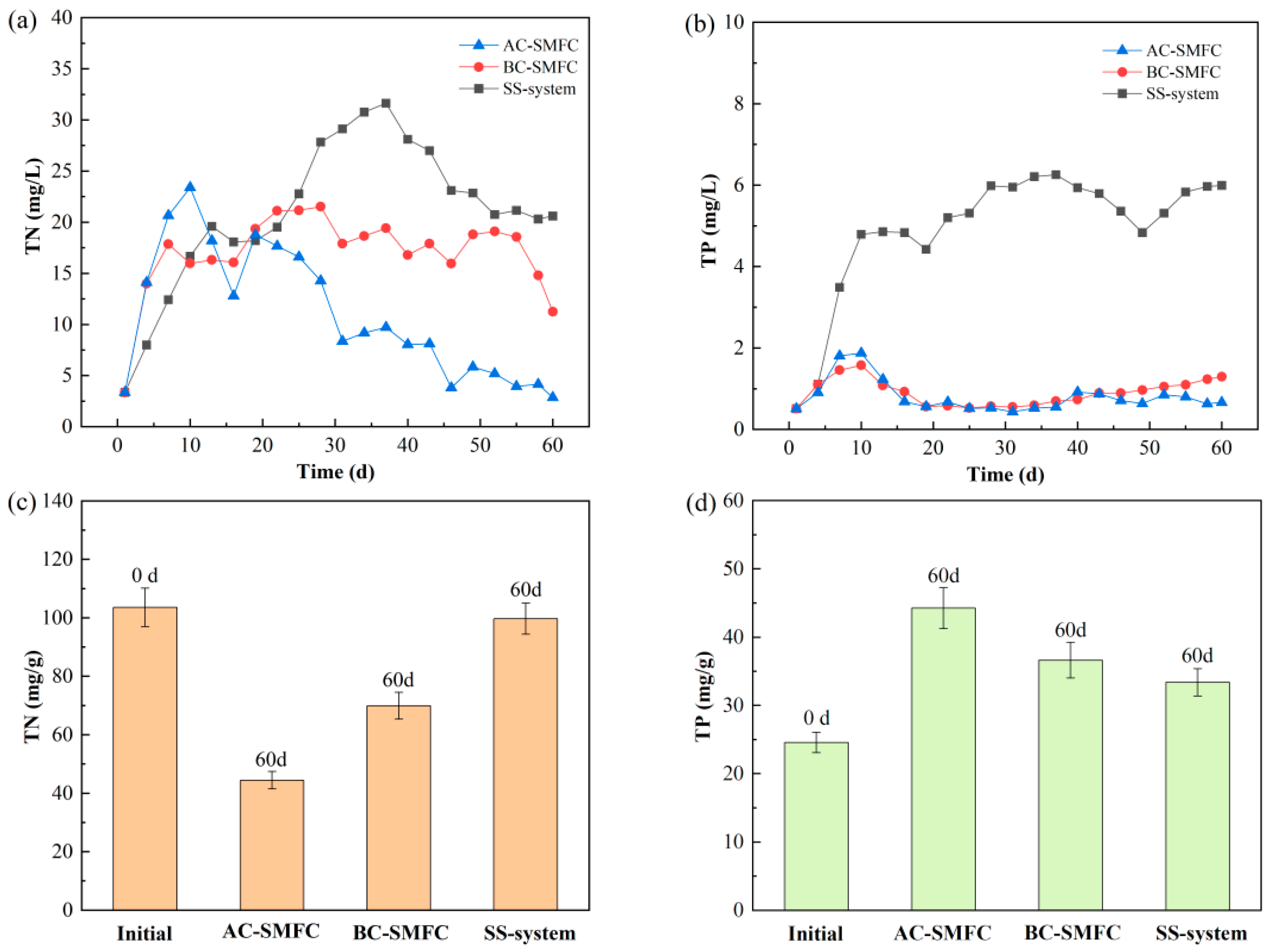
Figure 5 presents the variation in the concentrations of TN and TP in the overlying water and the sediment in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system. During the initial stage, with the release of sediment, the TN concentration in the three systems gradually increased, and AC-SMFC had the highest growth rate (Figure 5a). The concentration of TN in the overlying water of AC-SMFC rapidly decreased after the 20th day. After 60 days of treatment, the concentration of TN in the overlying water in the AC-SMFC decreased to 2.85 mg/L, which was lower than that of the BC-SMFC and SS-system. The removal efficiency of TN in the overlying water by algal–bacterial biofilms was better than that of bacterial biofilms [23]. The variation in TN removal performance in the sediment of the three systems is depicted in Figure 5c. After the experimental operation, the removal rates of TN in the excess sludge of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 57.10%, 32.48%, and 3.70%, respectively. The AC-SMFC had the best removal effect of TN in the excess sludge. In the process of nitrogen removal, there are two main nitrate removal routes: one is denitrification in the anode area, and the other is aerobic denitrification near the cathode [24]. The presence of algae microorganisms had a good promoting effect on the removal of nitrogen in the sediment and overlying water.
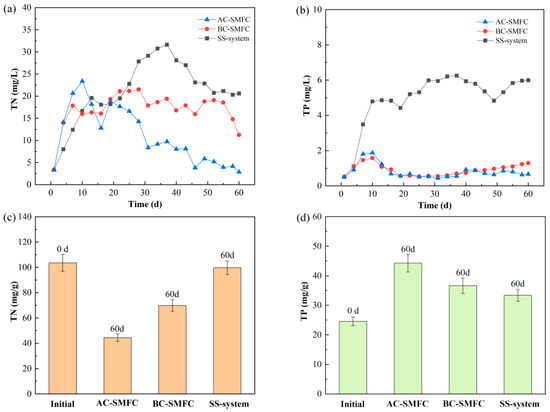
Figure 5.
Nitrogen and phosphorus of the overlying water (a,b) and sediment (c,d) in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.
After the experimental operation, the concentration of TP in the AC-SMFC was 0.66 mg/L, lower than that in the BC-SMFC and SS-system. This was mainly due to the existence of the microalgae biofilm on the cathode of the AC-SMFC, which could utilize the phosphorus to synthesize biomass through photosynthesis under light conditions, enhancing the removal of phosphorus from the liquid media [25]. The continuous increase in TP concentration in the overlying water of the SS-system during the period of 0–30 days might be attributed to the release of phosphorus from the sediment under anaerobic conditions due to the absence of turbulence [26]. After the 30th day, the TP contents in the overlying water and sediment of the SS-system were in dynamic equilibrium, and the sediment exhibited alternating release and absorption of phosphorus, inducing the fluctuations in TP concentration in the overlying water [27]. As shown in Figure 5d, initially, the TP content of the excess sludge was 24.59 mg/g. After 60 days of treatment, the TP contents of the excess sludge in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 44.25 mg/g, 35.43 mg/g, and 26.78 mg/g, respectively. The phosphorus in the sediment diffuses significantly into the overlying water due to two factors: firstly, the low dissolved oxygen in the water facilitates diffusion, and secondly, the electricity generation performance of the SMFC inhibits the release of phosphorus in excess sludge [28], resulting in a lower TP content in the SS-system than the SMFCs. Moreover, the algae on the cathode could absorb and utilize phosphorus, resulting in a decrease in phosphorus in the overlying water.
3.4. Characterization of the EPS of the Sediment Sludge
3.4.1. Content and Composition of the EPS
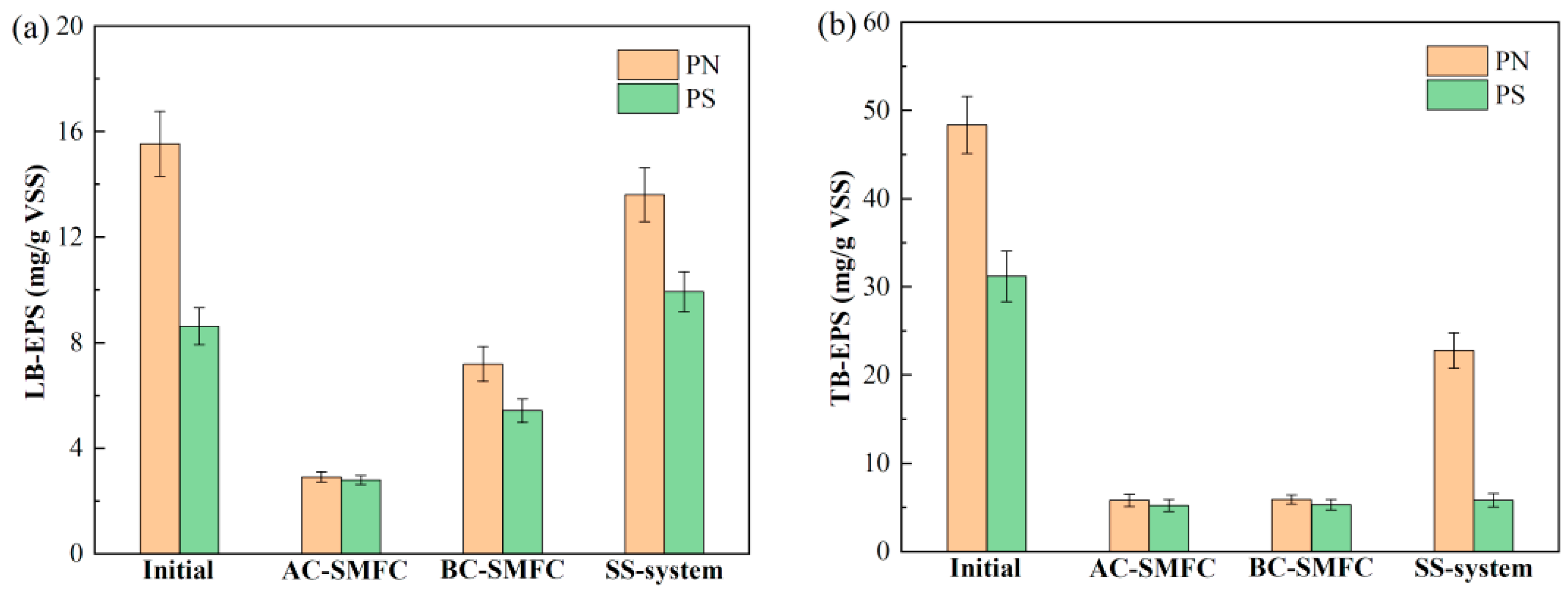
EPS refers to natural organic compounds produced by microorganisms for self-protection and mutual adhesion. These compounds are mostly made up of proteins (PN) and polysaccharides (PS), with trace amounts of lipids, DNA, and humic acids. Among them, PN and PS are the main products of sludge hydrolysis and are also easily utilized by electricity-producing microorganisms [22]. It is possible to categorize EPS into two groups based on the degree of tight binding: loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS) and tightly bound EPS (TB-EPS). This study mainly analyzed the PN and PS content in EPS, and used the sum of PN and PS concentrations as the concentration of EPS [29]. The contents of PN and PS of LB-EPS and TB-EPS are revealed in Figure 6.
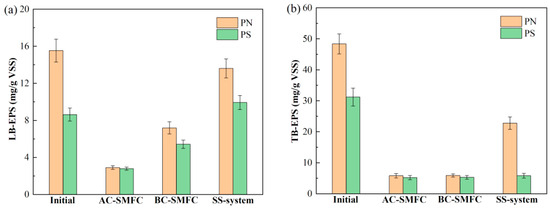
Figure 6.
Contents of LB-EPS (a) and TB-EPS (b) of the sediment sludge in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.
From Figure 6a, it could be seen that the initial concentration of LB-EPS was 24.15 mg/g VSS. There were significant differences in the changes of LB-EPS among the three systems after 60 days of treatment, and the LB-EPS content in the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC continued to decrease. After the treatment, the concentrations of LB-EPS in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 5.70 mg/g VSS, 12.61 mg/g VSS, and 23.54 mg/g VSS, respectively, achieving 76.40%, 47.78%, and 2.53% removal efficiencies, respectively. The removal rates of TB-EPS in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 86.13%, 85.93%, and 30.30% (Figure 6b), respectively. The AC-SMFC exhibited an increase in oxygen reduction rate due to the presence of algal–bacterial cathodes, resulting in high electrical output and the degradation of EPS, simultaneously. The PN and PS contents in LB-EPS and TB-EPS decreased the most.
3.4.2. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectra of the EPS
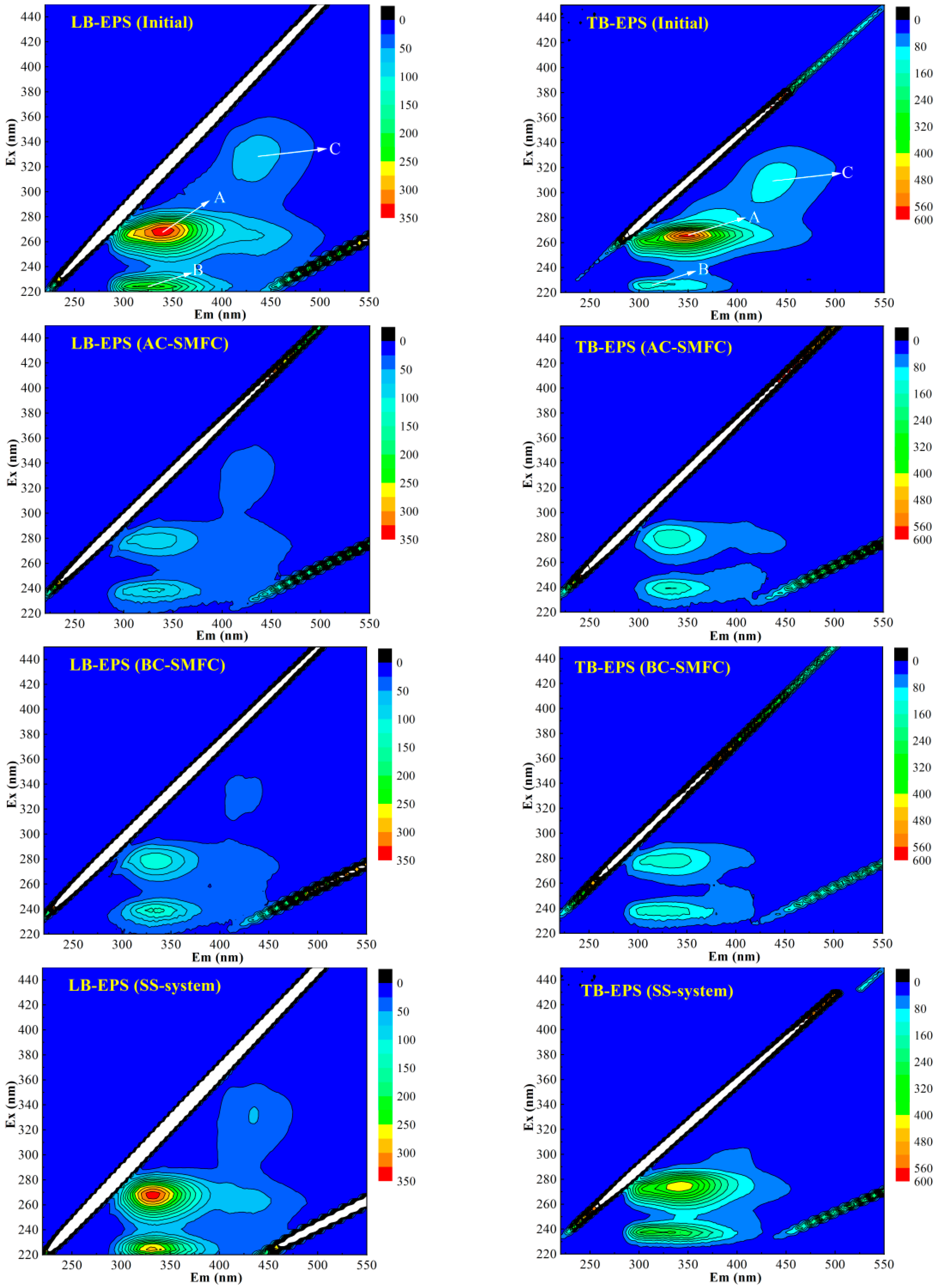
Based on the three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy analysis conducted on the LB-EPS and TB-EPS of the sludge in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system, the study aimed to clarify the protein types and content changes of EPS during the treatment of excess sludge. Figure 7 presents the three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of LB-EPS and TB-EPS, while Table 1 provides information on the fluorescence peak positions and intensities of LB-EPS and TB-EPS. Peak A and B, located at the excitation/emission wavelengths (Ex/Em) of 265–270 nm/328–349 nm and 224 nm/322–329 nm, respectively, represented tryptophan protein-like substances and aromatic protein-like substances, respectively. Peak C (Ex/Em: 305–346 nm/408–457 nm) was identified as humic acid substances, as previously recognized by He et al. and Liu et al. [17,30]. By analyzing the fluorescence peaks and intensities, the study aimed to gain insights into the changes in protein types and content within the EPS of the sediment sludge during the treatment process in the three systems.
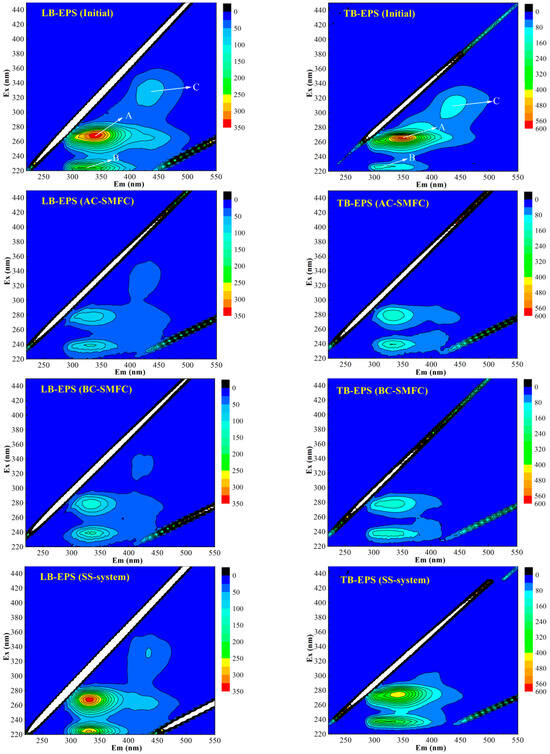
Figure 7.
The 3D-EEM fluorescence spectra of the LB-EPS and TB-EPS extracted from the initial and treated sediment in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.

Table 1.
Fluorescence spectral parameters of LB-EPS and TB-EPS extracted from the initial and treated sediment in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system.
The peak intensity of tryptophan protein-like substances in LB-EPS of the sludge in the three systems all decreased after the 60-day treatment. The fluorescence peak intensity of tryptophan protein-like substances in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system decreased by 73.90%, 65.20%, and 2.90%, respectively. The aromatic protein-like substances intensity of the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC decreased by 56.10% and 44.40%, respectively (Table 1). The fluorescence peak intensity of tryptophan protein-like substances in TB-EPS of the sludge in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system decreased by 73.40%, 75.70%, and 24.10% (Table 1), respectively. However, the fluorescence peak intensity of aromatic protein-like substances had an upward trend.
Peak A demonstrated a blue shift in all three systems (AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system), which might be attributed to a decrease in the quantities of aromatic rings, conjugate bonds, or specific functional groups such as carbonyls, hydroxyl groups, or amines [30]. Furthermore, in all three systems, there was a red shift in peak B, which may be attributed to an increase in different functional groups such as carbonyls, hydroxyl groups, or amines [17]. These shifts in fluorescence peaks confirmed the chemical composition changes of the fluorophores in the EPS during the treatment process. These findings indicate that the treatment process, particularly in the AC-SMFC system, influenced the chemical composition of LB-EPS and TB-EPS, potentially leading to the degradation or transformation of specific functional groups within the EPS.
3.5. Bacterial Community Structure Analysis
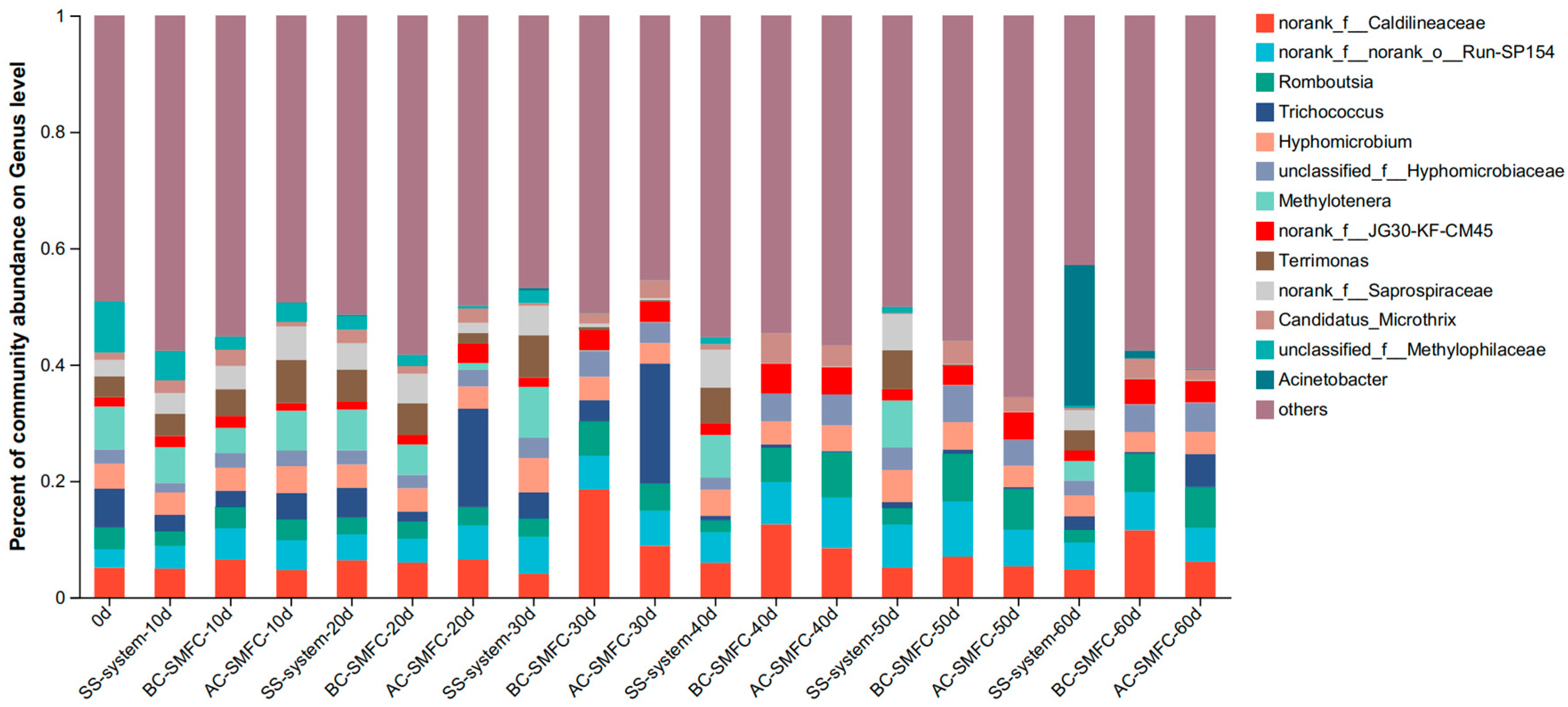
The electrode microbial populations were studied using high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. Microbial community analysis samples were collected from the sediment of the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system. As shown in Figure 8, at the level of genus, the abundance levels of Hyphomicrobium in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 3.70%, 3.40%, and 3.50%, respectively. Hyphomicrobium had the function of aerobic denitrification when dissolved oxygen was sufficient [31]. The TN removal rate of excess sludge in AC-SMFC was the highest among the three systems. Due to the increase in dissolved oxygen at the sludge–water interface caused by the cathode rotation, the anaerobic environment in the sediment was destroyed. The high abundance of Hyphomicrobium could enable the AC-SMFC to complete aerobic denitrification and achieve the removal of TN in the remaining sludge. Trichococcus and Terrimonas were common denitrification bacteria. The abundance levels of Trichococcus in the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system were 5.70%, 0.20%, and 2.30%, respectively. Trichococcus could degrade organic substances, such as glucose, and was closely related to the accumulation of lactic acid and acetic acid [32]. After the treatment, the TCOD and EPS contents in the excess sludge of the AC-SMFC were the lowest, and the high abundance of Trichococcus was conducive to the degradation of organic matter in the remaining sludge.
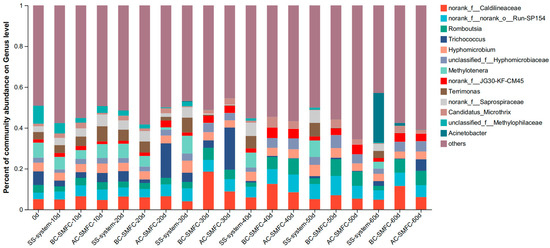
Figure 8.
Community analysis of sediment bacteria from the AC-SMFC, BC-SMFC, and SS-system at the level of genus.
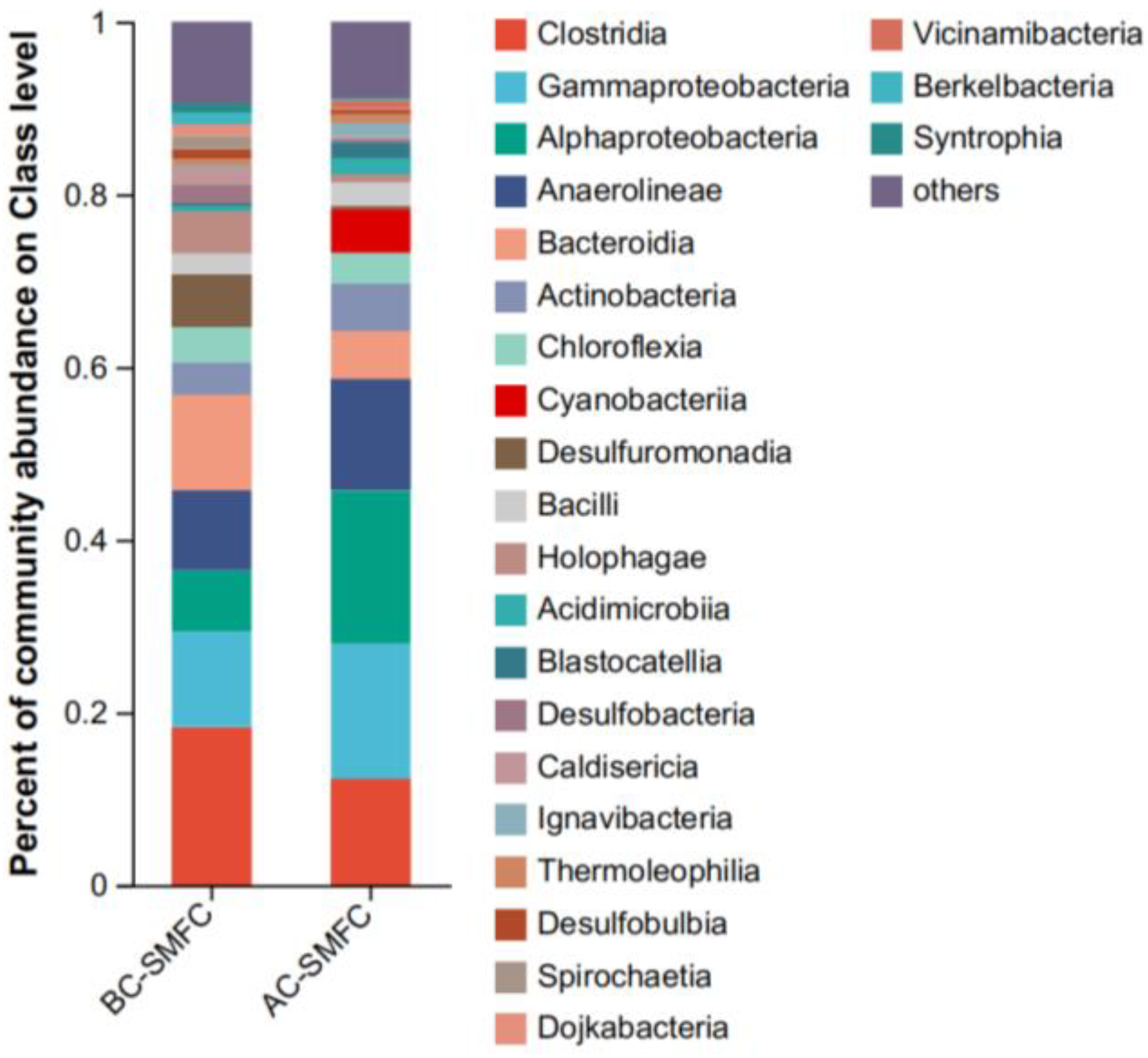
In order to better analyze the differences in electricity production performance between the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC, a community analysis of the anode microbiota in the two systems was conducted at the class level (Figure 9). Alphaproteobacteria was α-proteobacteria, with abundances of 17.71% and 7.09% in the anodes of the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC, respectively. Gammaproteobacteria was γ-proteobacteria, with abundances of 15.64% and 11.07% in the anodes of the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC, respectively. In the Firmicutes, electricity-producing bacteria were distributed in the class Clostridia and Bacilli. The abundance of Actinobacteria in the anodes of AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC was 17.71% and 7.09%, respectively. Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, Clostridia, Bacilli, and Actinobacteria are all common electricity-producing bacteria [33], and the abundance of the bacterial communities in the anode of the AC-SMFC was higher than that of the anode of the BC-SMFC. This corresponds to the higher electricity-producing performance of the AC-SMFC mentioned above, indicating that the type and abundance of the bacterial community will affect the operational efficiency of the system.
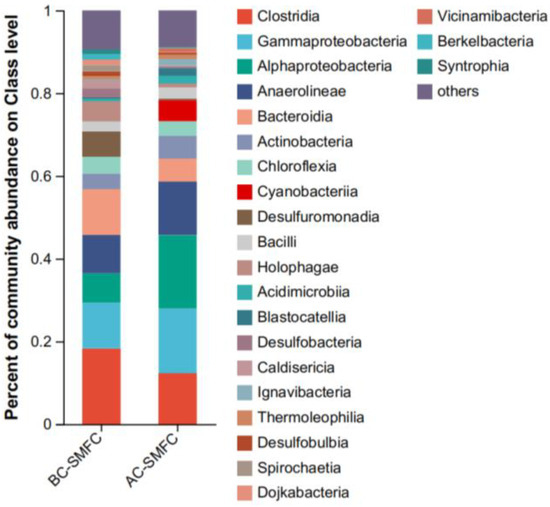
Figure 9.
Community analysis of anodic bacteria in the AC-SMFC and BC-SMFC at the class level.
4. Conclusions
Introducing the symbiotic technology of bacteria and algae into SMFCs, an algal–bacterial cathode SMFC (AC-SMFC) was constructed, which could achieve excess sludge reduction and electrical energy recovery. The maximum power density of AC-SMFC was 75.21 mW/m2, which was 65.70% higher than that of the BC-SMFC. The TCOD removal efficiency of AC-SMFC was 59.60%, which was 10.70% and 18.96% higher than the BC-SMFC and SS-system, respectively. The algae on the cathode of the AC-SMFC could effectively utilize the TN and TP, inhibiting nutrient accumulation in the overlying water. Additionally, the tryptophan protein and aromatic protein in the LB-EPS of the sediment sludge in the AC-SMFC were significantly decreased. High-throughput sequencing of microbial communities indicated that the algae in the AC-SMFC increased the abundance of functional microbiota (Trichococcus, Alphaproteobacteria, and Clostridia) which contributed to electricity generation and sludge degradation. The AC-SMFC with the algae-assisted cathode could achieve efficient electricity generation, excess sludge reduction, and removal of nitrogen and phosphorus in the overlying water. This study provided a viable approach for excess sludge reduction and energy recovery with less discharge of nutrients. Moreover, using the algae to remove the nutrients released during the excess sludge treatment could simultaneously achieve algae cultivation for biomass energy production, which might be a prospective resourcalization technology for excess sludge treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C. and H.L.; methodology, L.C.; software, H.Z.; validation, H.Z., Y.L. and C.Z.; formal analysis, L.L. (Ling Liu) and L.S.; investigation, Y.L. and L.S.; resources, L.C. and L.L. (Lipin Li); data curation, L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C.; writing—review and editing, H.L., L.S. and L.L. (Lipin Li); visualization, C.Z.; supervision, L.L. (Ling Liu); project administration, L.S.; funding acquisition, H.L. and L.L. (Lipin Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (Grant No. HC202242), the Interdisciplinary Research Program of Natural Science of Hebei University (Grant No. DXK202106), the Key R&D Project of Hebei Province (Grant No. 21373601D), and the Hebei Province Science Foundation for Youths (Grant No. D2021201003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not currently publicly available due to privacy and trademark.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saby, S.; Djafer, M.; Chen, G.-H. Feasibility of using a chlorination step to reduce excess sludge in activated sludge process. Water Res. 2002, 36, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sui, J.; Shen, H.; Liang, S.; He, X.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, Y. Reduction of excess sludge production in sequencing batch reactor through incorporation of chlorine dioxide oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Xi, B.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Duan, J. Excess sludge reduction using pilot-scale lysis-cryptic growth system integrated ultrasonic/alkaline disintegration and hydrolysis/acidogenesis pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 116, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, C.; Quiroga, J.M.; Coello, M.D. Comparison of four chemical uncouplers for excess sludge reduction. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Da, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Cui, H. Enhancing the electricity generation and sludge reduction of sludge microbial fuel cell with graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Feng, Y. Integrating sludge microbial fuel cell with inclined plate settling and membrane filtration for electricity generation, efficient sludge reduction and high wastewater quality. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Wang, L.; Waseem, H.; Song, B.; Djellabi, R.; Pan, G. Turning harmful algal biomass to electricity by microbial fuel cell: A sustainable approach for waste management. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-H.; Narindri, B.; Chu, H.; Whang, L.-M. Recent advancement on biological technologies and strategies for resource recovery from swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wei, J.; Liang, P.; Huang, X. Microbial community analysis in biocathode microbial fuel cells packed with different materials. Amb. Express 2012, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqsud, M.A. Bioelectricity generation and remediation of sulfide contaminated tidal flat sediment. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-B.; Song, T.-S.; Guo, T.; Zeng, Q.; Xie, J. Electricity generation from sediment microbial fuel cells with algae-assisted cathodes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 13224–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shao, H.; Angenent, L.T. Increased power production from a sediment microbial fuel cell with a rotating cathode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3252–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zou, L.; Ge, X.; Zhao, Y.; Si, Z.; Wang, Y. Chlorella vulgaris on the cathode promoted the performance of sediment microbial fuel cells for electrogenesis and pollutant removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhong, S.; Zhuang, L. Electrocatalytic activity of anodic biofilm responses to pH changes in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattaapha, W.; Greenberg, A.E.; Clesceri, L.S.; Eaton, A.D.; Eaton, D.L.; Rice, W.; Greenberg, A.S.; Rice, E.W.; Connors, J.; Jenkis, D. Standards methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Health Lab. Sci. 1985, 4, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Meng, F.; Chen, G.-H. Spectroscopic characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from a mixed culture dominated by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Water Res. 2015, 68, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Gao, S.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Yu, J. Elevated salinity deteriorated enhanced biological phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor performing simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Evolution and functional analysis of extracellular polymeric substances during the granulation of aerobic sludge used to treat p-chloroaniline wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touch, N.; Hibino, T.; Nagatsu, Y.; Tachiuchi, K. Characteristics of electricity generation and biodegradation in tidal river sludge-used microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethu, B.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Electricity generation through a photo sediment microbial fuel cell using algae at the cathode. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3269–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, F.; Grimaud, J.; Hurst, J.; He, Z. Long-term investigation of microbial fuel cells treating primary sludge or digested sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M. Sludge decrement and electricity generation of sludge microbial fuel cell enhanced by zero valent iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Noori, J.S.; Angelidaki, I. Simultaneous organic carbon, nutrients removal and energy production in a photomicrobial fuel cell (PFC). Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4340–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, L.; Yu, H.; Yi, X.; Wei, C. Simultaneous phenol removal, nitrification and denitrification using microbial fuel cell technology. Water Res. 2015, 76, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-m. Combination of Microbial Fuel Cells with Microalgae Cultivation for Bioelectricity Generation and Domestic Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 34, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, W.; Cao, Z.; Ji, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, Z. Microalgae simultaneously promote antibiotic removal and antibiotic resistance genes/bacteria attenuation in algal-bacterial granular sludge system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zou, J.; Liu, M. Research On the Characteristics of Sediment and the Release Law of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollutants in Landscape Lake. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2186, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, N.; Wang, G.; Yan, Y. Realignment of phosphorus in lake sediment induced by sediment microbial fuel cells (SMFC). Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Gao, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, P.; Wang, D. Malodorous volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) formation after dewatering of wastewater sludge: Correlation with the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y. Impact of Al-based coagulants on the formation of aerobic granules: Comparison between poly aluminum chloride (PAC) and aluminum sulfate (AS). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarek, A.; Rodziewicz, J.; Janczukowicz, W.; Dulski, T.; Ciesielski, S.; Thornton, A. Denitrification aided by waste beer in anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (AnSBBR). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Feng, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons stimulate acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis during anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrevaya, X.C.; Sacco, N.; Mauas, P.J.D.; Corton, E. Archaea-based microbial fuel cell operating at high ionic strength conditions. Extremophiles 2011, 15, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).