Screening and Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes by Bacillus paranthracis Strain MHDS3, a Potential Probiotic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and DNA Extraction
2.2. Enzyme Screening
2.2.1. Amylase
2.2.2. Cellulase
2.2.3. Pectinase
2.3. Optimizations of Different Parameters for Increased Enzyme Yield
2.3.1. pH
2.3.2. Incubation Period
2.3.3. Temperature
2.3.4. Carbon and Nitrogen Sources
2.3.5. Effect of NaCl
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Enzyme Production
2.4.1. Amylase Production and Activity Assay
2.4.2. Cellulase Production and Activity Assay
2.4.3. Pectinase Production and Activity Assay
2.5. Identification of Genes Involved in Amylase, Pectinase and Cellulase Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Primary Screening of Each Enzyme
3.2. Quantitative Screening
3.2.1. Amylase Production and Characterization
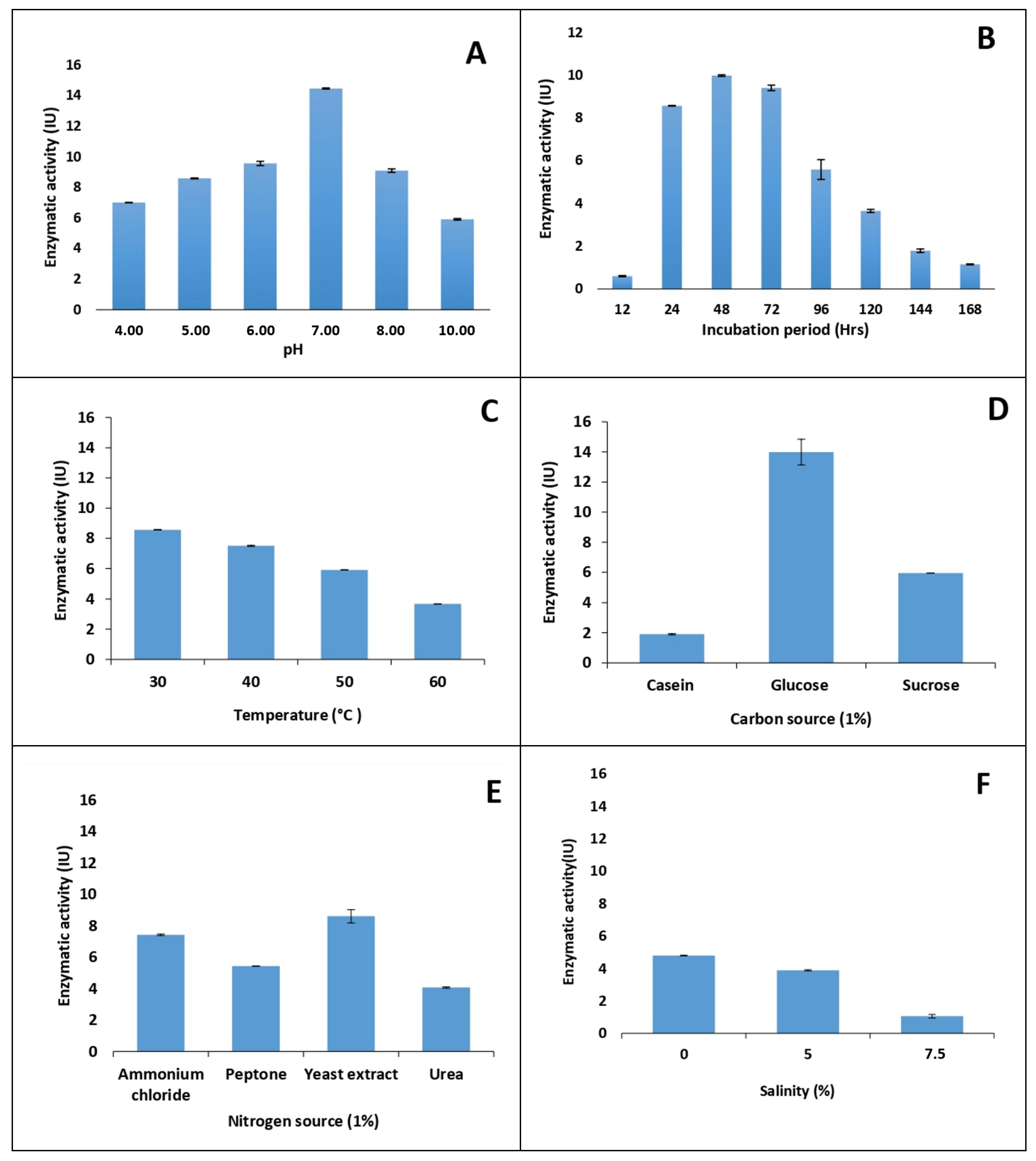
Effect of pH
Effect of Incubation Period
Effect of Temperature
Effect of Carbon and Nitrogen Sources
3.2.2. Cellulase Production and Characterization
Effect of pH on Cellulase Production
Effect of the Incubation Period
Effect of Temperature on Cellulase Production
Effect of Carbon and Nitrogen Source
Effect of Salinity on Cellulase Production
3.2.3. Pectinase Production and Characterization
Effect of pH
Effect of Incubation Period
Effect of Temperature
Effect of Carbon Source and Nitrogen Source
Effect of Salinity on Pectinase production
Pectinase, Cellulose, and Amylase Genes Identified from B. paranthracis MHSD3
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNS | 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid |
| CAZyme | Carbohydrate-active enzymes |
| PGAP | Prokaryotic Genome Annotation pipeline |
| CMC | Carboxymethyl cellulose |
| IU | International unit for enzyme |
References
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo-Useros, N.; Nova, E.; González-Zancada, N.; Díaz, L.E.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Marcos, A. Microbiota and lifestyle: Aspecial focus on diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.; Bird, A. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, S.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. Toxins and mobile antimicrobial resistance genes in Bacillus probiotics constitute a potential risk for One Health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, N.; Jassal, B.; Kumar, R. Probiotics in health and disease. Int. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2018, 7, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechagia, M.; Basoulis, D.; Konstantopoulou, S.; Dimitriadi, D.; Gyftopoulou, K.; Skarmoutsou, N.; Fakiri, E.M. Health benefits of probiotics: A Review. ISRN Nutr. 2013, 2013, 481651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Kollmann, T.; Patole, S. Probiotics to prevent early-life infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.-T.; Wu, J.M.; Wu, W.-T.; Liu, X.T.; Ye, T.T.; Chen, X.R.; Zeng, X.-A.; Manzoor, M.F.; Wang, L.H. Advances in the Study of Probiotics for Immunomodulation and Intervention in Food Allergy. Molecules 2023, 28, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indira, M.; Venkateswarulu, T.C.; Abraham-Peele, K.; Nazneen, B.M.; Krupanidhi, S. Bioactive molecules of probiotic bacteria and their mechanism of action: A review. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, S.J.; Rautonen, N.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Henrikson, A.C.; Steele, P. Developing effective probiotic products: Bioavailability and other factors. In Designing Functional Foods; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 230–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.R.; Naik, S.; Vakil, B. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepper, J.D.; Irwin, G.; Kang, K.; Dagenais, K.; Lemon, T.; Shinouskis, A.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R. Probiotics in gut-bone signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1033, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strozzi, G.P.; Mogna, L. Quantification of folic acid in human feces after administration of Bifidobacterium probiotic Strains. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S179–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathi, T.; Bhargavi, R.; Priyanka, P.R.; Niranjan, N.R.; Pavitra, P.V. Screening of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria and production of amylase and its partial purification. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewski, A.; Kordowska-Wiater, M. Probiotic and potentially probiotic yeasts—Characteristics and food application. Foods 2021, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, V.; van de Steeg, E.; van Bilsen, J.; Meijerink, M. Mechanisms and immunomodulatory properties of pre- and probiotics. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Margolles, A.; Sánchez, B. How do Bifidobacteria counteract environmental challenges? Mechanisms involved and physiological consequences. Genes Nutr. 2011, 6, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapatzi, G.; Filidou, E.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Spathakis, M.; Gaitanidou, M.; Arvanitidis, K.; Drygiannakis, I.; Valatas, V.; Kotzampassi, K.; Manolopoulos, V.; et al. The probiotic strains Bifidοbacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces boulardii regulate wound healing and chemokine responses in human intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: A Summary of the evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Muzaffar, K.; Jan, R.; Ahmad-Bhat, N.; Gani, A.; Shagoo, A.M. Commercially available probiotics and prebiotics used in human and animal nutrition. In Advances in Probiotics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornplang, P.; Piyadeatsoontorn, S. Probiotic isolates from unconventional sources: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Probiotic characteristics of Bacillus coagulans and associated implications for human health and diseases. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.M.; Serra, C.R.; La Ragione, R.M.; Woodward, M.J.; Henriques, A.O. Screening for Bacillus Isolates in the broiler gastrointestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisashvili, V.; Kachlishvili, E.; Chikindas, A.O. Recent advances in the physiology of spore formation for Bacillus probiotic production. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus as potential probiotics: Status, concerns, and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanya, M.; Yamauchi, K.E. Histological alterations of intestinal villi in chickens fed dried Bacillus subtilis var. natto. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002, 133, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diale, M.O.; Kayitesi, E.; Serepa-Dlamini, M.H. Genome in silico and in vitro analysis of the probiotic properties of a bacterial endophyte, Bacillus Paranthracis Strain MHSD3. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 672149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, M.; Mittal, A.; Mehta, P.K. Microbial enzymes: Industrial progress in 21st century. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, S.; Serepa-Dlamini, M.H. First report of bacterial endophytes from the leaves of Pellaea calomelanos in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2018, 114, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankin, H.; Anagnostakis, S.L. The use of solid media for detection of enzyme production by Fungi. Mycologia 1975, 67, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hur, S.H.; Hong, J.H. Purification and characterization of an alkaline cellulase from a newly isolated alkalophilic Bacillus sp. HSH-810. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, A.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Abraham, A.S.; Mathew, A.K.; Pandey, A. Production of Pectinase from Bacillus sonorensis MPTD1. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elhalem, B.T.; El-Sawy, M.; Gamal, M.R.; Abou-Taleb, K.A. Production of amylases from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens under submerged fermentation using some agro-industrial by-products. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simair, A.A.; Qureshi, A.S.; Khushk, I.; Ali, C.H.; Lashari, A.; Bhutto, M.A.; Mangrio, G.S.; Lu, C. Production and partial characterization of α-Amylase enzyme from Bacillus sp. BCC 01-50 and potential applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9173040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temsaah, H.; Azmy, A.; Raslan, M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Hozayen, W. Isolation and characterization of thermophilic enzymes producing microorganisms for potential therapeutic and industrial use. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 12, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Roy, N. Screening, purification and characterization of cellulase from cellulase producing bacteria in molasses. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ge, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Yin, Y. dbCAN3: Automated carbohydrate-active enzyme and substrate annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W115–W1212023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, H. Influence of probiotics on dietary protein digestion and utilization in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 20, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msarah, M.J.; Ibrahim, I.; Hamid, A.A.; Aqma, W.S. Optimisation and production of alpha amylase from thermophilic Bacillus spp. and its application in food waste biodegradation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Tang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Probiotic potential and amylolytic properties of lactic Acid Bacteria isolated from Chinese fermented cereal foods. Food Control. 2020, 111, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaziz, A.M.; Karam, E.A.; Ghanem, M.M.; Moharam, M.E.; Kansoh, A.L. Production of a novel α-Amylase by Bacillus atrophaeus NRC1 isolated from honey: Purification and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakaz, M.A.; Hussien, M.O.; Ibrahim, H.M. Isolation, extraction, purification, and molecular characterization for thermostable α-Amylase from locally isolated Bacillus Species in Sudan. Biochem. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6670380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.; Talukdar, S.A.; Mohsina, K.; Sarker, P.K.; Sayem, S.A. Production and partial characterization of extracellular amylase enzyme from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens P-001. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, P.A.; De Biase, D.; Liran, O.; Scheler, O.; Mira, N.P.; Cetecioglu, Z.; Fernández, E.N.; Bover-Cid, S.; Hall, R.; Sauer, M.; et al. Understanding how microorganisms respond to acid pH is central to their control and successful exploitation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 556140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raul, D.; Biswas, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kumar Das, S.; Gupta, S. Production and partial purification of alpha amylase from Bacillus subtillis (MTCC 121) using solid state fermentation. Biochem. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 568141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, S.N.; Jiru, T.M.; Indracanti, M. Screening and characterization of thermostable amylase-producing Bacteria isolated from soil samples of Afdera, Afar region, and molecular detection of amylase-coding gene. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 5592885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, C. Proteins. In Essentials of Food Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroosi, M.; Borujeni, F.B.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Babavalian, H.; Hassanshahian, M. Halophilic amylase production and purification from Haloarcula Sp. Strain D61. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 7382–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, P.E.; Mba, E.U.; Ezekiel-Hart, H. Screening, isolation and characterization of amylase producing bacteria and optimization for production of amylase. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2022, 4, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto, H.; Trivedi, U.; Patel, K. Alpha amylase production by Bacillus cereus MTCC 1305 using solid-state fermentation. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 44, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Gomaa, A.M.; Ibrahim, I.H.; Al-Talhi, H.A. Solid fermentation of wheat bran for hydrolytic enzymes production and saccharification content by a local isolate Bacillus megatherium. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukder, A.; Mobashshera, T.A.; Ahmed, I.U.; Islam, N.N. Bacteriological and EcfX- Gene specific PCR based identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Chittagong industrial area and characterization of its extracellular amylase. Jahangirnagar Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 7, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, F.S.; Renu, A. Efficacy of amylase for wastewater treatment from Sp. SP2 isolated from Stagnant Water Penic. J. Environ. Biol. 2018, 39, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, H.; Uyar, F.; Tolan, V.; Baysal, Z. Optimization and enhanced production of α-amylase and protease by a newly isolated Bacillus licheniformis ZB-05 under solid-state fermentation. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 63, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Mitra, D.; Roy, S.N.; Sinha, C.; Pal, P. Characterization and optimization of amylase producing bacteria isolated from solid waste. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 04, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusro, A.; Aarti, C. Molecular identification of newly isolated Bacillus strains from poultry farm and optimization of process parameters for enhanced production of extracellular amylase using OFAT method. Res. J. Microbiol. 2015, 10, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Khanal, A.; Bajracharya, M.R.; Timalsina, A.; Bishwokarma, A.; Basnet, A. Production, purification and optimisation of amylase by submerged fermentation using Bacillus subtilis. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladejana, O.M.; Oyedeji, O.; Omoboye, O.; Bakare, M. Production, purification and characterization of thermostable alpha amylase from Bacillus subtilis Y25 isolated from decaying yam (Dioscorea Rotundata) Tuber. Not. Sci. Biol. 2020, 12, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushk, I. Environmental friendly production of amylase from Aspergillus niger EFRL-FC-024 using corn waste as carbon source. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2021, 22, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanaa, T.N.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Alyahya, S.A. Solid state fermentation of amylase production from Bacillus subtilis D19 using agro-residues. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Luz, J.A.; Ribeiro, D.D.S.; Teixeira, J.M.; Silva, T.M.; Leão, D.J.; Franco, M.; Gualberto, S.A.; de Freitas, J.S. α-Amylase production obtained from Aspergillus niger ATCC 1004 by solid state fermentation using croton linearifolius residues as substrate. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e510101119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.; Gummadi, S.N. α-Amylase and cellulase production by novel halotolerant Bacillus Sp. PM06 isolated from sugarcane pressmud. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwitha, K.; Kumar, P.; Pindi, K.; Rani, A.S. Screening and isolation of cold-adapted cellulolytic bacteria from extreme habitats—Production and optimization of culture conditions. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 18, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Sarkar, P.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Suzauddula, M. Optimization of fermentation condition for cellulase enzyme production from Bacillus sp. Malays. J. Halal Res. 2019, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. Solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellapandi, P.; Jani, H.M. Production of endoglucanase by the native strains of Streptomyces isolates in submerged fermentation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, S.; Ayele, A. Pectinase from microorganisms and its industrial applications. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 1881305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyonzima, F.N. Detergent-compatible bacterial cellulases. J. Basic Microbiol. 2018, 59, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrudula, S.; Murugammal, R. Production of cellulase by Aspergillus niger under submerged and solid state fermentation using coir waste as a substrate. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Vucurovic, D.; Bajic, B.; Dodic, S.; Vlajkov, V.; Jevtic-Mucibabic, R. Optimization of the simultaneous production of cellulase and xylanase by submerged and solid-state fermentation of wheat chaff. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2020, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K. Optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulase production by Bacillus subtilis CY5 and Bacillus circulans TP3 isolated from fish gut. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2007, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Demain, A.L. Metabolic regulation and overproduction of primary metabolites. Microb. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 283–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.; Datta, A.; Gupta, B.L.; Gupta, S. Optimization of cellulase production from bacteria isolated from soil. ISRN Biotechnol. 2013, 2013, 985685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diasa, P.V.; Ramosa, K.O.; Padilhab, I.Q.; Araújob, D.A.; Santosa, S.F.; Silvaa, F.L. Optimization of cellulase production by Bacillus Sp. isolated from sugarcane cultivated soil. Chem. Eng. 2014, 38, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu, S.; Ghosh, P.K.; Aditya, G.; Maiti, T.K. Optimization and strain improvement by mutation for enhanced cellulase production by Bacillus sp. (MTCC10046) isolated from cow dung. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2014, 26, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairnar, Y.; Joshi, J.; Mujapara, A.; Jhadav, A.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, G.; Patil, P.; Trivedi, S.; Gupta, N.; Boraste, A.; et al. Study of pectinase production in submerged fermentation using different strains of Aspergillus niger. Indian J. Med. Res. 2009, 1, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, R.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Gupta, R. Screening of bacterial strains for polygalacturonase activity: Its production by Bacillus sphaericus(MTCC 7542). Enzym. Res. 2010, 2010, 306785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumer, O.J.; Abate, D. Comparative studies of pectinase production by Bacillus subtilis strain Btk 27 in submerged and solid-state fermentations. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1514795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Garg, N. Production, purification of pectinase from Bacillus sp. MBRL576 isolate and its application in extraction of juice. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 648–652. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, H.A.; Azzaz, H.H. Microbial pectinases and ruminant nutrition. Res. J. Microbiol. 2011, 6, 246–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berutu, C.A.M.; Fahrurrozi, F.; Meryandini, A. Pectinase production and clarification treatments of apple (Malus domestica) juice. Ann. Bogor. 2017, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.C.; Morata de Ambrosini, V.I. Cold-Active acid pectinolytic system from psychrotolerant Bacillus: Color extraction from red grape skin. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2023, 64, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, P.; Lilge, L.; Hausmann, R.; Henkel, M. Modeling and exploiting microbial temperature response. Processes 2020, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, O.; Dursun, A.Y. Exo-pectinase production by Bacillus pumilus using different agricultural wastes and optimizing of medium components using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9911–9920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.; Weloosamy, H.; Sheh-Hong, L. Potential use of nylon scouring pad cubes attachment method for pectinase production by Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Singh, A.K.; Mukherjee, G. Isolation and characterization of alkaline pectinase productive Bacillus tropicus from fruit and vegetable waste dump soil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2021, 64, e21200319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anab-Atulomah, C.; Nwachukwu, E. Optimization of pectinase and protease produced from Bacillus subtilis isolated from market waste. South Asian J. Res. Microbiol. 2021, 8, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Dayanand, A. Production of pectinase from deseeded sunflower head by Aspergillus niger in submerged and solid-state conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2054–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kaur, H.P.; Prasad, T.B.; Bharti, E. Production and optimization of pectinase by Bacillus sp. isolated from vegetable waste soil. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 6, 4185–4190. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.J.; Gupta, V.K. Production of pectinolytic enzymes pectinase and pectin iyase by Bacillus subtilis SAV-21 in solid state fermentation. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.N.; Abd El Rahman, H.M. Optimizing the production of pectinase of orange peel waste by Penicillium chrysogum MF318506 using response surface methodology in submerged fermentation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 11, e3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Siddique, N.N.; Aman, A.; Nawaz, M.A.; Baloch, A.H.; Qader, S.A.U. Morphological and molecular based identification of pectinase producing Bacillus licheniformis from rotten vegetable. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Pan, Y.; Long, X.; Tan, F.; Zhao, X. Enzyme producing activity of probiotics and preparation of compound enzyme. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 9140281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilova, I.; Sharipova, M. The practical potential of bacilli and their enzymes for industrial production. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, M.R.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Rancurel, C.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: Towards improved functional annotations of -amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2006, 19, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, P.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Cai, C.; Gu, J.; Lü, X. Metagenomic mining pectinolytic microbes and enzymes from an apple pomace-adapted compost microbial community. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.C.; Freund, H.L.; Kasanjian, J.; Berlemont, R. Function, distribution, and annotation of characterized cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases from CAZy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, U.; Sohail, M.; Ghanemi, A. Cellulases: From bioactivity to a variety of industrial applications. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.R.; Moravej, H.; Tabandeh, F.; Zaghari, M.; Shivazad, M. Screening of lactic acid bacteria toward their selection as a source of chicken probiotic. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Substrate | Amylase | Cellulase | Pectinase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon source | 1% Glucose Corn steep Starch Galactose Sucrose | 1% Dextrose Mannitol Starch Sucrose | 1% Glucose Sucrose Casein |
| Nitrogen source | 0.5% Peptone Beef extract Yeast extract Ammonium chloride | 1% Peptone Yeast extract Urea Ammonium sulfate | 1% Urea Ammonium chloride Peptone Yeast extract |
| Gene ID/Contig Number | Enzyme Activity | Family Group |
|---|---|---|
| Genes encoding pectinolytic enzymes | ||
| contig_4_56 | Endo-polygalacturonase (EC 3.2.1.15) | GH28 |
| contig_1_502 contig_3_223 | Rhamnogalacturonase (EC 3.2.1.171), Xylogalacturonan hydrolase (EC 3.2.1.174), Polygalacturonase (EC3.2.1.15) | GH28 |
| contig_1_362 | α-L-rhamnosidase (EC 3.2.1.40) | GH78 |
| contig_4_458 | α-L-fucosidase (EC 3.2.1.51) | GH95 |
| contig_12_94 | Feruloyl esterase (EC 3.1.1.73) | CE1 |
| contig_5_162 | Binding to galactose, lactose, polygalacturonic acid, and LacNAc | CBM32 |
| Amylase genes | ||
| contig_22_33 contig_4_56 | α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) | GH13 CBM34 |
| contig_2_420 | α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1), maltogenic amylase (EC 3.2.1.133), maltotetraose-forming α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.60), isoamylase (EC 3.2.1.68), maltohexaose-producing α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.98) | GH13 |
| contig_10_170 | Pullulanase (EC 3.2.1.41) | GH13_14 |
| contig_16_5 | Cyclomaltodextrinase (EC 3.2.1.54), glucan 1,4-alpha-maltohydrolase (EC 3.2.1.133), neopullulanase (EC 3.2.1.135) | GH13_20 |
| contig_11_75 | alpha,alpha-phosphotrehalase (EC 3.2.1.93) | GH13_29 |
| contig_16_6 | Glucan 1,6-a-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.70) | GH13_31 |
| contig_7_217 | Modules from the CBM41 family bind to the α-glucans amylose, amylopectin, pullulan, and oligosaccharide fragments derived from these polysaccharides | CBM41 |
| contig_10_4 | 1,4-a-Glucan branching enzyme (EC 2.4.1.18) | GH13_9 CBM48 |
| Contig 5_298 | α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) | GH26 |
| Cellulase genes | ||
| contig_4_56 | Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4) | GH18 |
| contig_3_402 | Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4) | GH5_11 |
| contig_13_89 | cellulose synthase (EC 2.4.1.12) | GT2 |
| contig_12_98 | beta-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21) | GH1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tshisikhawe, M.L.; Diale, M.O.; Abrahams, A.M.; Serepa-Dlamini, M.H. Screening and Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes by Bacillus paranthracis Strain MHDS3, a Potential Probiotic. Fermentation 2023, 9, 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9110938
Tshisikhawe ML, Diale MO, Abrahams AM, Serepa-Dlamini MH. Screening and Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes by Bacillus paranthracis Strain MHDS3, a Potential Probiotic. Fermentation. 2023; 9(11):938. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9110938
Chicago/Turabian StyleTshisikhawe, Musundwa Locardia, Mamonokane Olga Diale, Adrian Mark Abrahams, and Mahloro Hope Serepa-Dlamini. 2023. "Screening and Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes by Bacillus paranthracis Strain MHDS3, a Potential Probiotic" Fermentation 9, no. 11: 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9110938
APA StyleTshisikhawe, M. L., Diale, M. O., Abrahams, A. M., & Serepa-Dlamini, M. H. (2023). Screening and Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes by Bacillus paranthracis Strain MHDS3, a Potential Probiotic. Fermentation, 9(11), 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9110938





