Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Silage Preparation
2.2. Analyses of Fermentation Characteristics and Chemical Compositions
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR and Sequencing
2.4. Microbial Community Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Forage Oat Prior to Ensiling
3.2. Fermentation Parameters of Forage Oat Silage Treated without or with Additives
3.3. Bacterial Community Compositions
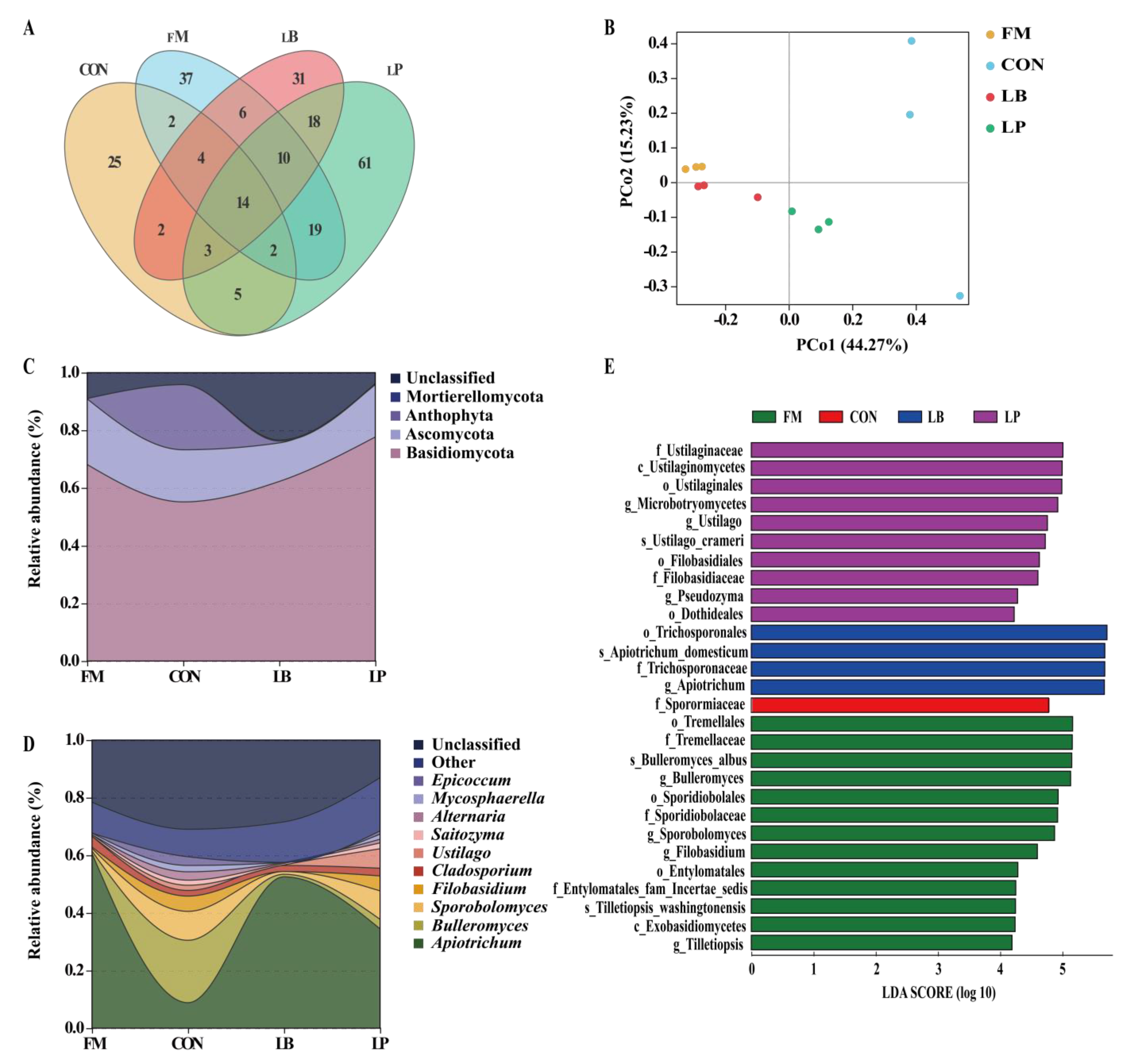
3.4. Fungal Community Compositions
3.5. Association between Microbial Community and Fermentation Features in Forage Oat Silage
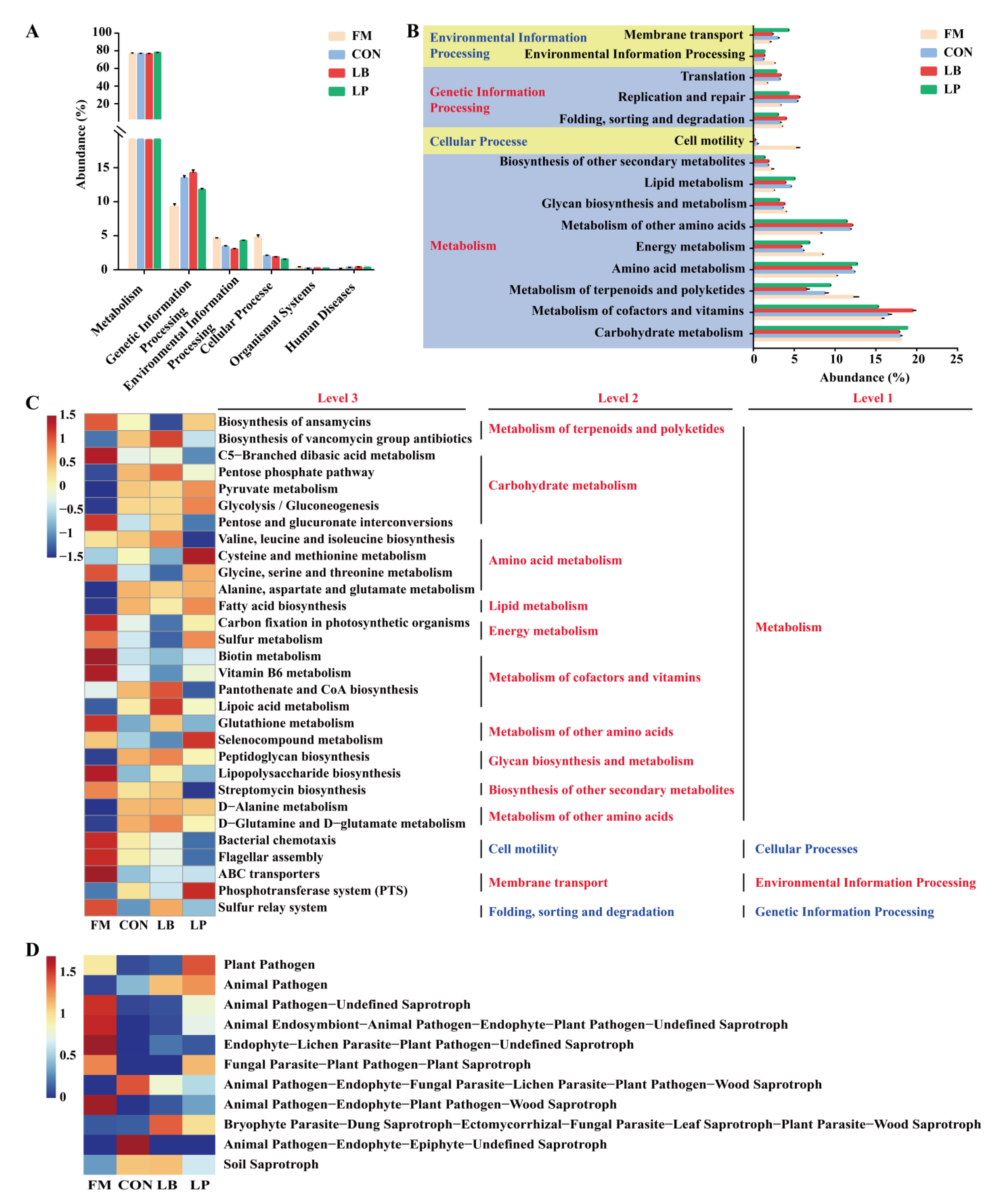
3.6. Predicted Functions of the Microbial Community in Forage Oat Silage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, F.; Jiang, D.; Lin, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Ni, K.; et al. Exploring the Effects of Different Bacteria Additives on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Community and In Vitro Gas Production of Forage Oat Silage. Animals 2022, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shen, H.; Hu, H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Kang, J.; Xing, A.; Wang, S.; et al. Yield and quality properties of silage maize and their influencing factors in China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Lin, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P. Exploring the bacterial community and fermentation characteristics during silage fermentation of abandoned fresh tea leaves. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Guo, J.S.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.X. The correlations and spatial characteristics of microbiome and silage quality by reusing of citrus waste in a family-scale bunker silo. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Kung, L., Jr. Effect of silage additives on ensiling. In Proceedings from the Silage: Field to Feedbunk North American Conference. Hershey, PA, USA, 11–13 February 1997. NRAES-99. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Sun, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J. Bioaugmentation of sweet sorghum ensiling with rumen fluid: Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition, microbial community, and enzymatic digestibility of silages. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, É.B.; Liu, X.; Mellinger, C.; Gressley, T.F.; Stypinski, J.D.; Moyer, N.A.; Kung, L., Jr. Effect of dry matter content on the microbial community and on the effectiveness of a microbial inoculant to improve the aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5024–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Ravindran, B.; Soundharrajan, I.; Awasthi, M.K.; Choi, K.C. Improved performance and microbial community dynamics in anaerobic fermentation of triticale silages at different stages. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.K.; Yang, H.X.; Wei, H.U.A.; Wang, Y.P.; Pang, H.L. Selection and characterisation of lactic acid bacteria isolated from different origins for ensiling Robinia pseudoacacia and Morus alba L. leaves. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowska, M.; Przemieniecki, S.W.; Purwin, C.; Lipiński, K.; Kurowski, T.P.; Karwowska, A. The effect of an additive containing three Lactobacillus species on the fermentation pattern and microbiological status of silage. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2020, 100, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.K.; Gu, Q.C.; Liang, M.Z.; Mu, S.L.; Zhou, B.; Huang, F.; Lin, B.; Zou, C.X. Analysis of the correlation between bacteria and fungi in sugarcane tops silage prior to and after aerobic exposure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Hosseini Salekdeh, G. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Huan, H.L.; Gu, H.R.; Xu, N.X.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C.L. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.R.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Saldinger, S.S. Bacterial dynamics of wheat silage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Yu, Z. Effect of temperature and fermentation time on fermentation characteristics and biogenic amine formation of oat silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Dong, D.; Shao, T. Effect of epiphytic microbiota from napiergrass and Sudan grass on fermentation characteristics and bacterial community in oat silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.T. An automated procedure for the determination of soluble carbohydrates in herbage. J. Sci. Food Agr. 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.V.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Jiang, S.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, H.; Qian, M.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Q. Changes in microbial community and methanogenesis during high-solid anaerobic digestion of ensiled corn stover. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Du, S.; Ge, G.; Wan, T.; Jia, Y. Microbial community and fermentation characteristics of native grass prepared without or with isolated lactic acid bacteria on the Mongolian Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, B.; Beeck, M.O.D.; Thijs, S.; Truyens, S.; Weyens, N.; Boerjan, W.; Vangronsveld, J. Performance of 16s rDNA primer pairs in the study of Rhizosphere and Endosphere bacterial microbiomes in metabarcoding studies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scibetta, S.; Schena, L.; Abdelfattah, A.; Pangallo, S.; Cacciola, S.O. Selection and experimental evaluation of universal primers to study the fungal microbiome of higher plants. Phytobiomes J. 2018, 2, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankenbrand, M.J.; Keller, A.; Wolf, M.; Schultz, J.; Forster, F. ITS2 database V: Twice as much. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 3030–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R.; Kolde, M.R. Package ‘Pheatmap’. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Revelle, W.; Revelle, M.W. Package ‘psych’. Compr. R Arch. Netw. 2015, 337, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Borreani, G.; Chion, A.R.; Colombini, S.; Odoardi, M.; Paoletti, R.; Tabacco, E. Fermentative profiles of field pea (Pisum sativum), faba bean (Vicia faba) and white lupin (Lupinus albus) silages as affected by wilting and inoculation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 151, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, E. Effects of plant species, stage of maturity and additive on the feeding value of whole-crop cereal silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Kaka, N.A.; Shao, T. Sequencing and microbiota transplantation to determine the role of microbiota on the fermentation type of oat silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco-Correa, J.; Li, Y. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of fungal pretreated Miscanthus sinensis harvested in two different seasons. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. Identification and characterization of Enterococcus species isolated from forage crops and their influence on silage fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage; Chalcombe Publications: Southampton, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, N.C.; Nascimento, C.F.; Nascimento, F.A.; De Resende, F.D.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Siqueira, G.R. Fermentation and aerobic stability of rehydrated corn grain silage treated with different doses of Lactobacillus buchneri or a combination of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4158–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, W.H.; Oh, Y.K.; Park, K.; Kwak, W.S. Long-term anaerobic conservation of fruit and vegetable discards without or with moisture adjustment after aerobic preservation with sodium metabisulfite. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Microorganisms that are critical for the fermentation quality of paper mulberry silage. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Kung, L., Jr. The effects of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 and Pediococcus pentosaceus R1094 on the fermentation of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Schmidt, R.J.; McDonell, E.E.; Klingerman, C.M.; Kung, L., Jr. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krooneman, J.; Faber, F.; Alderkamp, A.C.; Elferink, S.O.; Driehuis, F.; Cleenwerck, I.; Swings, J.; Gottschal, J.C.; Vancanneyt, M. Lactobacillus diolivorans sp. nov.; a 1, 2- propanediol- degrading bacterium isolated from aerobically stable maize silage. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.I.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; You, S.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y. Dynamics of the fermentation quality and microbiota in Ephedra sinica treated native grass silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Shao, T. Effects of freeze–thaw event on microbial community dynamics during red clover ensiling. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Cervantes, A.P.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: Effects of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Bolsen, K.K.; Brent, B.E.; Fung, D.Y.C. Epiphytic lactic acid bacteria succession during the pre-ensiling and ensiling periods of alfalfa and maize. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 73, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Ye, G.; Zhang, K. Diversity, function, and application of Clostridium in Chinese strong flavor baijiu ecosystem: A review. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Song, Z.; Zhang, M.; Nie, Y.; Xu, Y. The deletion of Schizosaccharomyces pombe decreased the production of flavor-related metabolites during traditional Baijiu fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, B.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Zong, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y. Dynamics of defatted rice bran in physicochemical characteristics, microbiota and metabolic functions during two-stage co-fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 362, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Abbas, M.; Meng, L.; Cai, H.; Peng, Z.; Li, Q.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Yan, L.; Zhao, X. Analysis of the fungal diversity and community structure in sichuan dark tea during pile–fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 706714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Jiang, Z.; Hao, L.; Li, W.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, C.; Lu, Z.; Jin, M.; et al. Variations of soybean meal and corn mixed substrates in physicochemical characteristics and microbiota during two-stage solid-state fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 688839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Joo, Y.; Park, J.; Tiezzi, F.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, E.; Castillo, M.S. Bacterial and fungal communities, fermentation, and aerobic stability of conventional hybrids and brown midrib hybrids ensiled at low moisture with or without a homo-and heterofermentative inoculant. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3057–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Liu, R.M.; Zhang, G.J.; Liu, W.; Xia, B.X.; Sun, Q. Dynamics of fungal community during silage fermentation of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum) produced in northern Vietnam. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D. Changes of fungal community and non-volatile metabolites during pile-fermentation of dark green tea. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Chang, W.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Yang, B.C.; Xu, M.R.; Lin, M.K.; Chen, H.J.; Cheng, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Phytochemicals levels and biological activities in Hibiscus sabdariffa L. were enhanced using microbial fermentation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 176, 114408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.L.; Niu, Q.H.; Ke, T.; Li, Y.X. Cryptococcus nanyangensis sp. nov.; a new Basidiomycetous yeast isolated from the gut of wood-boring larvae. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grazia, L.; Suzzi, G.; Romano, P. Isolation and identification of moulds in maize silage. Inf. Agrar. 1990, 46, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Park, E.J. Postharvest-induced microbiota remodeling increases fungal diversity in the phyllosphere mycobiota of broccoli florets. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Dong, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Shi, P.; Yan, J.; Zhuang, D.; Shao, T.; Wang, W.; Gu, M. Evaluating the fermentation quality and bacterial community of high-moisture whole-plant quinoa silage ensiled with different additives. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fresh Materials | Treatment | Distilled Water | LAB Additives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forage oat | CON | 10 mL/kg FM | 0 |
| LB | 10 mL/kg FM | L. buchneri (1 × 106 CFU/g) | |
| LP | 10 mL/kg FM | L. plantarum (1 × 106 CFU/g) |
| Item | Forage Oat |
|---|---|
| DM (%) | 426.92 ± 1.26 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 163.26 ± 0.36 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 124.64 ± 0.12 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 533.33 ± 1.57 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 340.51 ± 0.71 |
| LAB (lg10 CFU/g FM) | 4.57 ± 0.07 |
| Yeasts (lg10 CFU/g FM) | 4.67 ± 0.11 |
| Molds (lg10 CFU/g FM) | 4.13 ± 0.09 |
| Items | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | LB | LP | |
| DM (%) | 43.13 ± 0.05 a | 42.93 ± 0.35 a | 41.17 ± 0.47 b |
| WSC (% DM) | 25.66 ± 1.08 a | 17.50 ± 0.51 b | 14.33 ± 0.57 c |
| pH | 4.67 ± 0.13 a | 4.57 ± 0.03 a | 4.23 ± 0.08 b |
| NH3-N (% DM) | 6.13 ± 0.11 a | 5.96 ± 0.33 a | 4.39 ± 0.88 b |
| LA (% DM) | 4.47 ± 0.32 c | 5.51 ± 0.22 b | 7.49 ± 0.27 a |
| AA (% DM) | 1.74 ± 0.12 b | 2.48 ± 0.17 a | 1.22 ± 0.05 c |
| PA (% DM) | 0.09 ± 0.03 b | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | 0.05 ± 0.02 b |
| BA (% DM) | ND | ND | ND |
| Characteristic | FM | CON | LB | LP | Total No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of sequences | 112,652 ± 2668 c | 180,449 ± 2986 a | 170,449 ± 3186 ab | 17,429 ± 10,062 b | 1,853,774 |
| No. of ASV | 37 ± 1 ab | 51 ± 7 a | 46 ± 3 a | 27 ± 2 b | 486 |
| Chao1 index | 47.60 ± 2.11 ab | 57.65 ± 10.49 ab | 60.72 ± 9.19 a | 32.14 ± 6.06 b | |
| Shannon index | 1.18 ± 0.34 b | 2.12 ± 0.11 a | 1.46 ± 0.07 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 c | |
| Good’s coverage | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Characteristic | FM | CON | LB | LP | Total No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of sequences | 65,210 ± 1001 | 64,992 ± 2456 | 65,227 ± 1927 | 61,725 ± 362 | 771, 465 |
| No. of ASV | 51 ± 9 b | 36 ± 1 b | 43 ± 4 b | 69 ± 2 a | 602 |
| Chao1 index | 55.33 ± 7.80 a | 42.20 ± 2.04 b | 45.08 ± 5.05 b | 41.06 ± 2.24 b | |
| Shannon index | 3.26 ± 0.43 a | 2.43 ± 0.07 b | 2.28 ± 0.30 bc | 2.05 ± 0.14 c | |
| Good’s coverage | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xin, X.; Xu, L.; Du, S. Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation 2022, 8, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120707
Xiao Y, Sun L, Wang Z, Wang W, Xin X, Xu L, Du S. Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation. 2022; 8(12):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120707
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yanzi, Lin Sun, Zhijun Wang, Wei Wang, Xiaoping Xin, Lijun Xu, and Shuai Du. 2022. "Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri" Fermentation 8, no. 12: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120707
APA StyleXiao, Y., Sun, L., Wang, Z., Wang, W., Xin, X., Xu, L., & Du, S. (2022). Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation, 8(12), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120707









