Abstract
Antibiotics have been used to maintain the overall health of poultry by increasing production efficiency, promoting growth, and improving intestinal function for more than 50 years. However, they have a number of side effects, such as antibiotic resistance, gut dysbiosis, destruction of beneficial bacteria, and the potential to spread diseases to humans. In order to address the aforementioned issues, a lot of effort is put into the development of antibiotic alternatives. One of them is the use of probiotics that can be added to the feed in order to increase poultry performance and avoid the aforementioned problems. Probiotics are live microorganisms consumed as feed additives or supplements. They function in the poultry gastrointestinal tract to benefit the host. Probiotics improve growth performance, bone health, meat and eggshell quality. The addition of probiotics to the diet also positively affects the immune response, intestinal microflora, and disease resistance. Careful selection of probiotic strains is of utmost importance. This review focuses on the significance of probiotics as a potential antibiotic-free alternative and the way in which they can be used as supplements in poultry feed for boosting production and safeguarding health.
1. Introduction
Over the past seventy years, the improvement of feed consumption and genetic selection have been the primary areas of poultry research [1]. The control of a variety of microbial infectious diseases caused by Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Yersinia, Bacillus, Clostridium, Mycobacterium, Enterococcus, Klebsiella and Proteus species has been less thoroughly investigated [2]. The immune system of broilers is not fully developed during the first few weeks and therefore it is more susceptible to bacterial infection [3]. Furthermore, it can take up to eight weeks for the gut microbiota to develop and stabilize. The longer the time necessary to reach bacterial homeostasis, the greater the risk of bacterial infection [1]. Poultry are kept in closed facilities to minimize the risk of bacterial infection [4]. In many cases, farmers continue to supplement feed with antibiotics [5]. In the past decades, in traditional commercial poultry production, antibiotics have been one of the most frequently used additives to improve feed conversion, growth rate, and bird health, thereby increasing profitability and productivity [6,7]. Poultry constitute the largest global population of food animals [8]. Antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria (microbes) in any poultry system, leaving behind some resistance genes that can be passed on to other bacteria [9]. Antibiotic resistance results from the ability of these resistant bacteria to spread from one host to another, either directly or indirectly [10]. Antibiotics exert negative effects on human and animal welfare when used excessively at subtherapeutic levels or continuously for an extended period of time [11]. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria can develop in a variety of ways, including a decreased permeability of bacterial cell membranes, changes in the antibiotic binding sites and enzyme production. It can also be acquired from other bacterial species present in the environment [12]. Numerous bacteria have developed antibiotic resistance as a result of inappropriate antibiotic use [13]. Oxacillin and tetracycline resistance has been found in Staphylococci directly linked to poultry farms. Some species of Staphylococcus commonly infecting poultry and causing staphylococcosis, pododermatitis, and septicemia have developed resistance to β-lactam antibiotics [14]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from Ghanaian poultry were resistant to cephalosporins, carbapenems, penicillin, quinolones, monobactam, and aminoglycosides [15]. In Nigeria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed resistance to β-lactams, tetracycline, nitrofurantoin, tobramycin, and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim [16]. In a similar way, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, ceftriaxone, meropenem, and colistin resistance was found in Pakistani poultry [17]. Furthermore, Escherichia coli has increased its resistance to the majority of poultry-specific medications, such as tetracycline [18]. Different Salmonella species have been found to be resistant to ampicillin, tetracycline, trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, and sulfamethazole [19]. In the same way, it has been reported that Campylobacter jejuni and Escherichia coli were resistant to erythromycin and tetracycline [1,20]. On the other hand, the involvement of antibiotic growth promoters in the emergence of multi-drug-resistant microorganisms has raised concerns for global public health. The development of antibiotic-resistant microbial populations in animal populations led to the potential transfer of antibiotic-resistant genes from animals to humans [21]. Therefore, many European countries forbade the use of antibiotics in poultry feed in 2006 [22]. Similarly, the US Food and Drug Administration issued Veterinary Feed Directives in 2015. They recommended the limited application of antibiotics only for animal treatment [23]. In Sweden, antimicrobial medications for growth promotion and prophylaxis were banned in 1986 and 1988, respectively [1]. South Korea was the first country in Asia to forbid the use of antibiotic growth promoters in animal feed in July 2011 [22]. The restriction of antibiotic use in feed raises the demand for alternatives to avoid a sharp decline in animal productivity and economic losses. In the past two decades, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, phytobiotics, enzymes, essential oils, and fatty acids have gained widespread popularity among poultry nutritionists. Among them, probiotics have been shown to improve immune function, gut morphology and physiology. This, in turn, increases poultry performance and well-being. Feed supplements known as probiotics contain live beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Streptococci, yeast such as Candida and Saccharomyces, and fungi like Aspergillus awamori, A. niger, and A. oryza, all of which have the potential to maintain the balance of intestinal microflora, and stimulate the immune system [24]. Some well-known probiotics of bacterial origin include Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Streptococci, and Bacillus subtilis, which show antimicrobial activity against some pathogenic species, such as Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella typhimurium [25]. This review describes the ways in which probiotics boost growth and health and discusses the benefits of including them as feed supplements in poultry diet.
2. Probiotics and Growth Performance
The pathogen most prevalent in the intestines of chickens, particularly broilers, is Salmonella. Therefore, probiotics have been potential candidates for growth promoters in the majority of commercial poultry diets since the withdrawal of antibiotic growth enhancers in poultry nutrition. Antibiotic growth promoters act by blocking the production and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokine-degrading intermediates in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in the disturbed gut microbiota [26]. Probiotics, on the other hand, alter the gut environment and strengthen its barrier function through the immune system stimulation, as presented in Table 1 [27]. A total of 280 females of Japanese quails were fed with a mixture of without rapeseed meal, non-fermented post-extraction rapeseed meal (5%, 10%, 15%), and a fermented one (5%, 10%, 15%). The data analysis revealed that the addition of 10% fermented rapeseed meal had the most beneficial effects as such egg quality traits as egg weight, specific gravity, yolk index and color, and albumen pH [28]. In broilers, probiotic non-pathogenic bacteria compete with the pathogenic ones for nutrients in the gut. They also colonize the intestines, preventing pathogenic bacteria from inhabitation and stimulating the secretion of digestive enzymes (e.g., β-galactosidase, α amylase), thus facilitating the absorption of nutrients, and enhancing broiler growth performance [29]. An increased average dietary feed consumption and conversion result in an improved body weight gain, which in turn affects production performance, even though probiotics do not always significantly influence feed consumption and feed conversion. All of the above-mentioned processes depend on several factors, including strain selection and application, time concentration, as well as the absorption of dietary probiotics [30]. An increased average dietary feed consumption and an enhanced feed conversion efficiency are closely attributed to an improvement in body weight gain, which in turn complements production performance [31]. The application of dietary supplementation of probiotics improves body weight gain and feed conversion, even though probiotics do not always significantly enhance feed consumption [32]. The body weight gain, average daily diet consumption, feed conversion efficiency, and production performance of the poultry birds are influenced by several potential factors including strains selection, application, time concentration, and absorption of dietary supplementation of probiotics [33].

Table 1.
Summary of the beneficial probiotics on poultry performance.
Wang et al. [45] immunized hatched chicks with a strain of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LT-113, and found that it protected against Salmonella typhimurium by limiting gastrointestinal invasion and inhibiting tight junction gene expression in intestinal cells. In the control group, Salmonella infection compromised the intestinal mucosal barrier. On the other hand, Olnood et al. [46] revealed that the oral administration of Lactobacillus johnsonii decreased Salmonella and Clostridium perfringens invasion in the gastrointestinal system. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the combination of xylanase and a multistrain probiotic enhanced dietary energy absorption in the intestine and its preservation in the liver [47]. Energy changes may result from improved nutrient digestibility and feed conversion rate. Probiotics increased synthesis of short-chain fatty acids, stimulated the immune system and metabolism [48,49].
Short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) metabolites produced during microbial carbohydrate fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract impact leukocytes and endothelial cells by stimulating G-protein-coupled receptors and inhibiting histone deacetylase. SCFAs increase the level of IgA produced by B immune cells, impede the NF-κB transcription factors and reduce the production of proinflammatory cytokines [50,51]. Dietary supplementation of poultry with Bacillus licheniformis, a facultative anaerobic bacterium, enhances the gastrointestinal tract absorption rate and surface area. It also stimulates the growth and multiplication of probiotic bacteria such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Aspergillus awamori, as shown in Figure 1 [52].
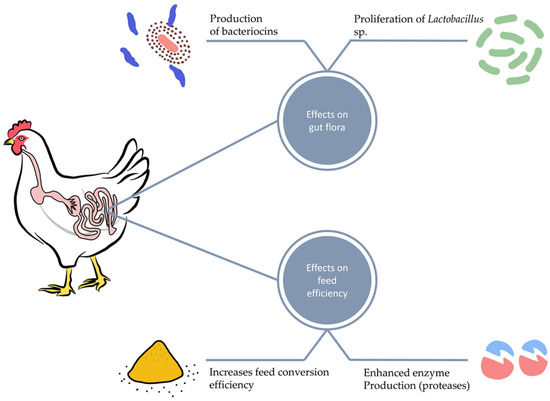
Figure 1.
Effect of probiotics on growth performance, gut macroflora and feed efficiency.
3. Probiotics and Intestinal Morphology
Poultry health status and improved growth efficiency are strongly correlated with the gut condition and intestinal microflora. The intestines play a very important role in the digestive tract of birds as they harbor a diverse community of beneficial microbes, which degrade complex nutrient compounds into simpler molecules that are more easily assimilated and metabolized [53,54]. The structural organization and adherence properties of the gastrointestinal epithelial cells are crucial for nutrient absorption and the protection of the bird’s body from pathogenic microbes that could infiltrate the bloodstream [55]. The most important parameters associated with the higher nutritional absorption resulting from larger surface area available for nutrient assimilation are those related to intestinal morphology, i.e., increased villus height, a lower crypt depth, and the higher villus height to crypt depth ratio [56]. Sound gastrointestinal microbiota is the prime requirement for avoiding microorganism infections in the gastrointestinal tract of birds. This is achieved by preventing microorganism colonization through pathogenic bacteria antagonism, inhibition of adhesion sites in the gut and impediment to bacterial exercises [57]. Similarly, another marker of gastrointestinal health status is the amount of gastric mucosa, which produces mucin and prevents pathogenic organisms from adhering to mucosal surfaces [58]. Even though the intestinal microflora is relatively stable, it is still affected by numerous environmental factors (feed composition, hygienic standards, physical stress, etc.) and overall health condition of the animal. However, the key element with the greatest impact on intestinal microflora is diet. Probiotics are commonly used for intestinal flora regulation [59] and improvement of gastrointestinal histomorphology; however, the potential effects may slightly differ from one strain to another [60]. Dietary supplementation of broilers with Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus reuteri significantly affected barrier activity and reduced colonization by certain opportunistic or pathogenic microorganisms [61].
Zheng et al. [36] exposed broilers to Salmonella enteritidis (SE) and found a significant decline in goblet cell membranes at 7 days post-infection (DPI), as well as a reduction in villus height and villus-crypt ratio in the small intestine. In contrast, birds fed dietary supplementation of Bacillus coagulans had a relatively low crypt depth, a greater villus-crypt ratio, and a larger number of goblet cells in the jejunum at 7 and 17 days post-infection. Gastrointestinal mucous cells synthesize mucin-2, a constituent of mucus, which facilitates the enhancement of barrier activity in Salmonella enteritidis-infected birds. Supplementation with a Bacillus licheniformis-fermented product at 1.25 and 5 g/kg improved cecal morphology and increased the survival rate of broilers and conserve a stable number of goblet cells in the ileum as well as in the caecum under Eimeria tenella challenge. A 1.25 g/kg dose reduced lesions scores in the cecum, while that of 5 g/kg decreased the oocyst-count index. Furthermore, surfactin C isolated from Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products inhibited Eimeria oocyst sporulation and disrupted sporozoite morphology [62].
4. Probiotics and Immune Response
The chicken requires a strong immune system for optimal performance. The immune system comprises lymphoid organs located in the different parts of the body. In addition to highly specialized lymphoid structures like Meckel’s diverticulum, the bursa of Fabricius, cecal tonsils, and Peyer’s patches, which are connected to the gastrointestinal lumen, numerous lymphoid cells can be found in the epithelial mucous membrane (intraepithelial lymphocytes) [63,64]. Enteric neurons and gut immune cells communicate with each other in order to coordinate their actions against stressors [65]. Among the neuroendocrine compounds produced by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and sympathetic-adrenal medullary axes are corticosterone and catecholamines, which have the potential to influence immune regulation and phagocyte activity in a variety of immune cells [55]. Physical restrictions such as a low gastric pH and rapid transit in the small intestine play a crucial role in preventing pathogens from colonizing the gastrointestinal tract and causing inflammation [58]. In addition, pathogens must overcome the physical barriers imposed by the epithelium and intestinal microflora as well as the response of the host defense system in order to ultimately cause infection [66]. Cristofori et al. [67] showed that some non-pathogenic gut microbiota altered physiological cellular responses and the ability of an organism to fight infections by interacting with the host defense system and epithelium. Other potential advantages of probiotics are based on their significant impact on the intestinal environment. Epithelial and dendritic cells that constitute sentinel cells in the mucosa are found in lymphoid tissue connected to the intestinal tract. The binding of probiotic microbe-associated molecular patterns to Toll-like receptors on sentinel cells triggers NF-kB and MAP kinase pathways [67]. This activation does not only exert cytoprotective effects but also increases or inhibits the expression of genes controlling the inflammatory process by stimulating, signaling, and interpreting antimicrobial factors [68]. Additional advantages include enhanced epithelial barrier function, bacterial adhesion to the intestinal epithelium, and inhibition of microbial adhesion [58]. Probiotics are considered potential alternatives to antibiotics for improving immune health and growth performance in broilers. Cheng et al. [69] reported that dietary supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis enhanced T-cell immunity without impairing bird growth. It also directly impacted chemokine expression of genes and enhanced the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the mucosal surface, which had a profound effect on the immune system. Probiotics also influence immune function by affecting B-lymphocytes. Two bioactive secondary metabolites produced by probiotic bacteria, short-chain fatty acids, and bacteriocins, prevent infectious agents from growing and surviving [70]. Notably, several Lactobacillus strains producing lactic acid were found to be able to lower the pH level of their surroundings. Lie et al. [34] observed that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens initially reduced the stress caused by the immune response in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broiler chickens and increased plasma lysozyme activity and WBC count in 192-day-old males. Consequently, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens was able to restore impaired immune status and growth performance [71]. Yitbarek et al. [72] fed a mix of probiotics obtained from various strains of Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Lactobacillus casei and prebiotics (yeast-derived carbohydrates) to 300-day-old Lohman pullets. In this case, synbiotics enhanced the immune system and maintained homeostasis through an IL-10-specific response. Synbiotic supplementation resulted in the increased concentrations of IL-6, interferon-γ (IFN), and IL-4 in the ileum.
Hetab et al. [73] demonstrated that the production of antibodies against the Newcastle disease virus in layers was significantly enhanced by probiotic bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium). Therefore, broiler chickens supplemented with B. subtilis showed higher levels of antibodies against Newcastle disease, infectious bronchitis, and bursal disease [74].
5. Mode of Action Probiotics
5.1. Probiotics and Competitive Exclusion
Bacteria attempt to eradicate pathogens harmful to the gastrointestinal tract due to their natural competitiveness, which is called bacterial intervention, competitive exclusion (CE), or bacterial belligerence [71]. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics exhibit the property of competitive exclusion. The Nurmi concept, which later evolved into the competitive exclusion concept, is based on the introduction of gastrointestinal flora into young chickens in order to induce bacterial resistance to pathogenic microbes [75]. These microbes colonize cell attachment sites or mucosal surfaces and disrupt microbiome composition in the gut causing intestinal infections. On the other hand, probiotics are capable of adhering to the inner mucosal layer, greatly increasing the amount of time during which they may remain in the gastrointestinal tract [2,55]. Therefore, probiotic bacteria occupy more space in this tract, thus eliminating pathogens through competition. Consequently, birds are able to consume more nutrients. Competitive exclusion is usually considered to occur in the caeca and intestines of birds [76]. Supplementation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (BAP) for 35 days (20 g/kg) significantly improved the growth of broiler chickens due to the facilitated food digestion, nutrient absorption and availability in a healthy digestive system [77]. A form of competitive exclusion, i.e., the oral administration of spores, primarily from the genus Bacillus, may support and enhance host defense against infectious diseases. The potential molecular biological mechanisms of probiotic action and competitive pathogen elimination are presented in Figure 2 [44].
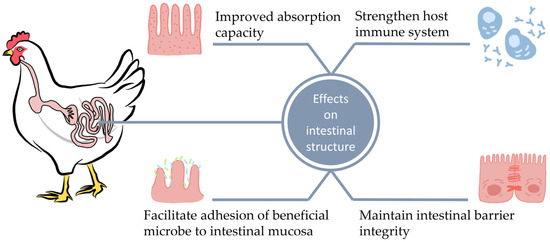
Figure 2.
Effects of probiotics on intestinal health and immune function.
5.2. Probiotics and Organic Acid (Acidity and pH)
Organic acids or acidifiers are naturally occurring compounds with acidic properties that could be defined as weak carboxylic acids (R-COOH) such as acetic, propionic, lactic, formic, fumaric, and sorbic acids. It has been stated that the inclusion of organic acids improved growth performance, feed efficiency, and the digestibility of nutrients [78]. Additionally, organic acids may play a role in both suppressing the colonization of pathogenic bacteria and triggering the immune system [79]. These enhancements could be made through lowering the pH of the GIT, increasing the utilization of nutrients in diets, suppressing the growth and proliferation of pathogens, and increasing the immune responsiveness of poultry [80].
From the scientific evidence, it is hypothesized that probiotics and organic acids may work together to enhance beneficial bacteria in the GIT and protect against pathogenic bacteria. Previously it has been reported that feeding broiler chickens a diet high in organic acids and probiotics had a number of promising effects on growth performance, energy and protein utilization, and gut microflora [81]. It has the ability to penetrate the cellular cytoplasm. In addition to inhibiting bacterial cell enzymes such as decarboxylase and catalases, the acid disintegrates within the cell cytoplasm [82]. In order to increase the production and distribution of organic acids (such as lactic acid and acetic acids) in the intestinal tract of monogastric animals, bacterial probiotics such as propionic acid and fumaric acid can be added to their diet, lowering the pH of the gastrointestinal tract. This may improve the intestinal microbial environment for some native microorganisms and mitigate the invasion of pathogenic microbes [83]. Furthermore, probiotic strains are capable of competitive exclusion, thus preventing the evolution of pathogenic bacteria.
Some probiotic strains have a remarkable capacity to endure hostile environments in their hosts. They are able to pass through the digestive tract and survive under extremely acidic conditions, such as gastric acid and bile [84]. This is quite difficult since the pH in the stomach of many animals ranges from 1.5 to 3.0. Furthermore, bile salts and several digestive and intestinal enzymes significantly contribute to the disruption of microbiota balance [85]. Nevertheless, it has been demonstrated that spores can sprout properly and survive all the way through the gastrointestinal tract being attached to feed particles, which play a protective role. Re-sporulation is the most common way for bacteria to stay alive during their transit in the animal body and diet seems to influence spore sprouting and propagation, since it contains the nutrients necessary for their survival [86]. Propionic acid and fumaric acid supplementation lowers the pH of the local gut environment and prevents the growth of certain pathogens like Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Clostridium perfringens, enhancing nutrient absorption and immunity, ultimately leading to improved physical and productive performance in different poultry species [87].
5.3. Probiotics and Gut Microbiota
Probiotics have a significant impact on the composition and function of the gut microbiome by competing with other microbes for nutrient content, binding to sites and receptors on the intestinal mucosa, and producing antimicrobial agents to inhibit the growth of other microbes [71]. Potential mechanisms for the antagonistic activity of probiotics include the lowering of gut pH, modulation of the immune system, and production of organic acid [51]. Probiotics can also significantly improve intestinal barrier integrity, maintain immunogenicity and affect microbial signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells [88].
A variety of tools are used to investigate the effects of probiotics on gut microbiota function, variation, and composition, including culture-dependent methods, metagenomic sequencing, and in vivo assays. However, in vivo probiotic administration is the most effective and efficient technique for obtaining precise results [89]. Several studies have shown that probiotics, especially lactic acid bacteria, can effectively prevent Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli 078:K80 infections in poultry [90].
Furthermore, the enforcement of the diet with probiotics has been reported to strengthen the composition of the gut microbiota by limiting pathogen proliferation and increasing the number of beneficial microorganisms. Abdel-Moneim et al. [91] found that in ovo inoculation with Bacillus bifidum, Bacillus animalis, Bifidobacterium longum, and Bifidobacterium infantis improved ileal bacterial composition by enhancing the intestinal colonization with bacterial species such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while decreasing the total amount of coliforms bacteria. Abou-Kassam et al. [92] also observed that the potential addition of Bacillus toyonesis and Bacillus bifidum to the diet impeded the growth of fungi and coliforms and decreased the number of E. coli and coliforms in the caecum, whereas Anas Abdelqader et al. [93] reported that dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis reduced the abundance of Clostridium and cecal coliforms, while preventing the multiplication of coliforms in the diet.
5.4. Application and Validation of Probiotics Secondary Metabolites
Probiotics are live microorganisms that benefit the health of their hosts when applied in sufficient quantities [94]. Numerous reports have addressed their use in poultry farming and human health. A number of microbes, particularly fungi and bacteria, possess probiotic properties; however, Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, and Bacillus sp. are the most frequently used ones as presented in Table 2 [95]. The significance of Bacillus-derived probiotics to industry depends on several factors, including their high safety level, quick growth rate, short fermentation time, and capacity to secrete proteins into extracellular medium [96]. Different Bacillus species, such as Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus claussi, are utilized as probiotics in poultry diets.

Table 2.
An overview of the use of bacteria beneficial in poultry farming.
Bacillus-derived peptides have been demonstrated to possess antifungal, antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, antiviral, anti-amoebic, and anti-mycoplasmic properties [110]. It has been shown that Bacillus subtilis, one of the most significant aerobic bacteria, exerts positive effects on poultry diets by limiting the spread of aerobic pathogens and increasing the efficiency of diet protein. Extracellular digestive enzymes produced by Bacillus subtilis may enhance the immune response and function and the development of the gastrointestinal tract [111], increasing internal egg quality and decreasing the cholesterol content of egg yolks [112].
Cheng et al. [113] reported that 4 days of Bacillus subtilis-fermented products containing the highest concentration of surfactin showed the greatest antimicrobial activity against pathogens like Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella typhimurium. In broilers infected with Clostridium perfringens, dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis-fermented products containing surfactin significantly affected gastrointestinal tract morphology and healed ulcerated lesions. Bacillus subtilis treatment could boost broiler growth and productivity. It also improved bone quality, gastrointestinal structure, and function. Cheng et al. [114] found that surfactin isolated from Bacillus subtilis-fermented products was a prospective antibiotic and antibacterial agent substitute, which exerted significant antibacterial effects against Brachyspira hyodysenteriae by altering its morphological characteristics and preventing bacterial growth. Additionally, it reached maximum activity against Clostridium perfringens. Surfactin derived from the fermented products of Bacillus licheniformis inhibited in vitro growth of Clostridium perfringens in a dose-dependent manner. Broilers challenged with the above-mentioned bacterium showed significant improvements in body weight and average daily weight gain when supplemented with Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products (2 g/kg). They also benefited from reduced necrotic lesions and improved intestinal tract morphology [69]. Moreover, surfactin derived from Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products was more effective against Clostridium perfringens than that obtained from the Bacillus subtilis-fermented products.
In a similar way, Lactobacillus-based probiotics increased the number of goblet cells in the duodenum and jejunum of broilers. By decreasing goblet cell proliferation and differentiation and regulating mucin mRNA expression, probiotics are said to increase the number of goblet cells [115]. Broilers fed probiotics containing Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium thermophilum and Enterococcus faecium had increased villus height and a lower crypt depth [44].
Additionally, dietary supplementation of broilers with Bacillus coagulans [36], Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus salivarius, propionic bacterium acidopropionic [42], mixture of Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae [116] and Pediococcus acidilactici [117] improved villus length and the ratio of villus height to crypt depth, suggesting that probiotics may increase nutrient absorption. On the other hand, acetic and benzoic acids lowered lesion scores in broiler chickens challenged with the different Eimeria species [118,119]. The former had also anticoccidial properties against Eimeria tenella. Oocysts were adversely impacted by lowering the pH levels of the caeca, ultimately resulting in lower lesion scores [119].
One of the organic acids, lactic acid, produced by the bacteria fermenting feed carbohydrates lowers the pH of the local environment and prevents the growth of certain pathogens like Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Clostridium perfringens [87]. Finally, blends of acetic, butyric, and lactic acids increased feed conversion ratio and weight gain in 7-day-old broilers exposed to Clostridium perfringens [120], whereas Lactobacillus johnsonii-based probiotics improved intestinal development and microbiota balance in birds challenged with Clostridium perfringens [121].
In broiler chicken, dietary supplementation of Enterococcus faecium PNC01 improved ileal villus height and crypt depth and decreased the comparative length of the cecum at day 21 and enhanced the relative length of the jejunum and ileum at day 42. Additionally, Enterococcus faecium-supplemented diets enhanced the relative abundance of Firmicutes and Lactobacillus and decreased the relative abundance of Bacteroides in the cecal microflora [122]. Svetoch et al. [123] conducted a research study on bacteriocin producer Enterococcus faecium that peptide class IIa bacteriocin E50-52 have minimal inhibitory concentration against Clostridium jejuni, Yersinia specie, Salmonella specie, and Escherichia coli ranged from 0.025 to 32 μg/mL. In the therapeutic broilers trail, oral supplementation with E50-52 decreased Clostridium jejuni as well as Salmonella enteritidis by more than 100,000 times in the caeca, and systemic Salmonella enteritidis was reduced in both liver and spleen.
Volzing et al. [124] demonstrated that recombinant Lactococcus lactis that produce and secreted heterogenous antimicrobial peptides A3APO and Alyteserin showed maximum inhibitory activity against pathogenic bacteria Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Volzing et al. observed that A3APO and Alyteserin containing recombinant Lactococcus lactis inhibited the growth of the pathogenic bacteria Escherichia coli and Salmonella by up to 20-fold while sustaining the host’s viability. Yang et al. [125] documented that, immunized chickens with recombinant invasive Lactobacillus plantarum against coccidiosis induced greater levels of specific antibodies in the serum and the secretory IgA (SIgA) was increased in the intestinal washes. Furthermore, a higher proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were detected in the peripheral blood. These results demonstrate that recombinant Lactobacillus palantarum effectively activated immune responses against E. tenella infection. Therefore, it should be emphasized that probiotic supplements aid in combating pathogens, enhancing nutrient absorption and immunity, ultimately leading to improved physical and productive performance in different poultry species.
6. Conclusions
Probiotics improve gut health by promoting the activity of digestive enzymes, which increase nutrient digestibility and growth performance in poultry. This suggests that they can be used as growth promoters. Additionally, probiotics protect the host from pathogens by regulating immunomodulatory response and utilizing a competitive exclusion strategy to prevent the colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by pathogenic microorganisms. However, the full elucidation of probiotic effects at a molecular level and the interactions between probiotics, pathogens, and epithelial cells needs further investigation. This review points to the involvement of metagenomic, metabolomic, and proteomic research and analysis in determining the biological effect of probiotics. Therefore, the revelation of previously unknown facts will enable the thorough understanding of the role of probiotics in the growth and health of poultry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-H.C.; methodology, R.A., Y.-H.Y., F.S.-H.H., A.D. and H.-C.H.; data curation, R.A. and Y.-H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A. and Y.-H.Y.; writing—review and editing, I.A. and Y.-H.C.; visualization, R.A. and Y.-H.Y.; supervision, Y.-H.C.; project administration, R.A., Y.-H.Y. and Y.-H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, grant number 108-2321-B-197-001.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Daniel Zabroski, Department of Ruminant Science, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Poland, who polish the English of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neveling, D.P.; Dicks, L.M. Probiotics: An antibiotic replacement strategy for healthy broilers and productive rearing. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyare, C.; Boamah, V.E.; Zumbi, C.N.; Osei, F.B. Antibiotic use in poultry production and its effects on bacterial resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance—A Global Threat; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Neveling, D.P.; van Emmenes, L.; Ahire, J.; Pieterse, E.; Smith, C.; Dicks, L. Effect of a multi-species probiotic on the colonisation of Salmonella in broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurson, G.C.; Urriola, P.E.; van de Ligt, J.L. Can we effectively manage parasites, prions, and pathogens in the global feed industry to achieve One Health? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, Y.; Létourneau-Montminy, M.-P.; Gaucher, M.-L.; Chorfi, Y.; Suresh, G.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Côté, C.; Ramirez, A.A.; Godbout, S. Use of antibiotics in broiler production: Global impacts and alternatives. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, U.; Kim, W.; Oh, S.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to antibiotics for maximizing growth performance and feed efficiency in poultry: A review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, J.M.; Rothrock Jr, M.J.; Fluharty, F.L.; Callaway, T.R. The successional changes in the gut microbiome of pasture-raised chickens fed soy-containing and soy-free diets. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żbikowska, K.; Michalczuk, M.; Dolka, B. The use of bacteriophages in the poultry industry. Animals 2020, 10, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, E.; Kaur, P. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: Relationships between resistance determinants of antibiotic producers, environmental bacteria, and clinical pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, Z.; Ding, T. Quorum-sensing regulation of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Huang, J.; Shah, J.M.; Ali, I.; Rahman, S.U.; Wang, L. Characterization and resistant determinants linked to mobile elements of ESBL-producing and mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli recovered from the chicken origin. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Kerorsa, G.B.; Marami, L.M.; Kandi, V. Epidemiology, pathogenicity, animal infections, antibiotic resistance, public health significance, and economic impact of staphylococcus aureus: A comprehensive review. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2020, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hayford, O. Isolation and Characterisation of Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Clinical, Environmental and Poultry Litter Sources in Ashanti Region of Ghana. Master’s Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aniokette, U.; Iroha, C.; Ajah, M.; Nwakaeze, A. Occurrence of multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria from poultry and poultry products sold in Abakaliki. Int. J. Aric. Sci. Food Technol. 2016, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Galav, V.; Agrawal, M.; Faridi, F.; Kumar, B. Multi-drug resistance pattern of bacterial flora obtained from necropsy samples of poultry. J. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 5, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, C.; Guerin, M.T.; Brash, M.L.; Slavic, D.; Boerlin, P.; Susta, L. Antimicrobial resistance in fecal Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica isolates: A two-year prospective study of small poultry flocks in Ontario, Canada. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, X.; Niu, Q.; Yang, B. Prevalence, serotype, antibiotic susceptibility, and genotype of Salmonella in eggs from poultry farms and marketplaces in Yangling, Shaanxi province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Yao, F.; Bilal, H.; Rahman, S.U.; Zeng, M.; Ali, I.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Jiao, X. Synergistic Activity of Tetrandrine and Colistin against mcr-1-Harboring Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingmongkolchai, S.; Panbangred, W. Bacillus probiotics: An alternative to antibiotics for livestock production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, J.; Khan, S.; Su, J.Q.; Hesham, A.E.-L.; Ditta, A.; Nawab, J.; Ali, A. Antibiotics in poultry manure and their associated health issues: A systematic review. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.U.; Wang, G. An updated review on probiotics as an alternative of antibiotics in poultry. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Khidr, R.E.; Paswan, V.K.; Ibrahim, N.S.; El-Ghoul, A.A.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Gabr, S.A.; Mesalam, N.M.; Elbaz, A.M. Nutritional manipulation to combat heat stress in poultry—A comprehensive review. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 98, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, M.M.; Mazzotti, L.; Silvi, S.; Scalise, A.; Orpianesi, C.; Cresci, A.; Verdenelli, M.C. Antimicrobial activity of SYNBIO® probiotic formulation in pathogens isolated from chronic ulcerative lesions: In Vitro studies. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedokun, S.A.; Olojede, O.C. Optimizing gastrointestinal integrity in poultry: The role of nutrients and feed additives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 5, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaifah, H. Benefits of probiotics and/or prebiotics for antibiotic-reduced poultry. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengerska, K.; Czech, A.; Knaga, S.; Drabik, K.; Próchniak, T.; Bagrowski, R.; Gryta, A.; Batkowska, J. The Quality of Eggs Derived from Japanese Quail Fed with the Fermented and Non-Fermented Rapeseed Meal. Foods 2022, 11, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, A.A.; Yalçın, S.; Latorre, J.D.; Basiouni, S.; Attia, Y.A.; Abd El-Wahab, A.; Visscher, C.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Huber, C.; Hafez, H.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and phytogenic substances for optimizing gut health in poultry. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.; Duong, T.; Askelson, T.; Dersjant-Li, Y.; Gibbs, K.; Awati, A.; Lee, J. Effects of direct fed-microorganisms and enzyme blend co-administration on growth performance in broilers fed diets with or without antibiotics. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, C.; Carmona, J.F. Nutrition and climatic environment. In Nutrition of the Rabbit; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, E. Weight gain by gut microbiota manipulation in productive animals. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.; Askelson, T.; Dersjant-Li, Y.; Gibbs, K.; Awati, A.; Duong, T.; Lee, J. Effect of Direct-Fed Microorganisms and enzyme blend co-administration on broilers fed US commercial-type, diets with or without agp. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 28, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens supplementation alleviates immunological stress in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers at early age. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanko, M.S.; Gorlov, I.F.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Makarenko, M.S.; Usatov, A.V.; Bren, A.B.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Tutelyan, A.V.; Komarova, Z.B.; Mosolova, N.I. Bacillus probiotic supplementations improve laying performance, egg quality, hatching of laying hens, and sperm quality of roosters. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, W.; Shao, Y.; Gong, X.; Wu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of dietary Bacillus coagulans supplementation on growth performance and immune responses of broiler chickens challenged by Salmonella enteritidis. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pender, C.M.; Kim, S.; Potter, T.D.; Ritzi, M.M.; Young, M.; Dalloul, R.A. In ovo supplementation of probiotics and its effects on performance and immune-related gene expression in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, C.; Acuti, G.; Manuali, E.; Proietti, P.C.; Pavone, S.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Moscati, L.; Onofri, A.; Lorenzetti, C.; Franciosini, M.P. Effects of two different probiotics on microflora, morphology, and morphometry of gut in organic laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2528–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Wen, C.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Y. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality and muscular antioxidant capacity and mineral contents in broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3699–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulski, D.; Jankowski, J.; Mikulska, M.; Demey, V. Effects of dietary probiotic (Pediococcus acidilactici) supplementation on productive performance, egg quality, and body composition in laying hens fed diets varying in energy density. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountzouris, K.; Tsitrsikos, P.; Palamidi, I.; Arvaniti, A.; Mohnl, M.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fegeros, K. Effects of probiotic inclusion levels in broiler nutrition on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, plasma immunoglobulins, and cecal microflora composition. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.A.; Babot, J.D.; Lorenzo-Pisarello, M.J.; Apella, M.C.; Chaia, A.P. Feed supplementation with avian Propionibacterium acidipropionici contributes to mucosa development in early stages of rearing broiler chickens. Benef. Microbes. 2016, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanein, S.M.; Soliman, N.K. Effect of probiotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) adding to diets on intestinal microflora and performance of Hy-Line layers hens. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Alagawany, M.; El-Hack, A.; Mohamed, E.; Farag, M.R.; Sachan, S.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K. The use of probiotics as eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in poultry nutrition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10611–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Q.; Feng, J.; Zhao, X. Lactobacillus plantarum restores intestinal permeability disrupted by Salmonella infection in newly-hatched chicks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olnood, C.G.; Beski, S.S.; Choct, M.; Iji, P.A. Use of Lactobacillus johnsonii in broilers challenged with Salmonella sofia. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, G.R.; Persia, M.E. Influence of a direct-fed microbial and xylanase enzyme on the dietary energy uptake efficiency and performance of broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Raza, A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Li, L. Nutrient sensing mechanism of short-chain fatty acids in mastitis control. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 170, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Rahman, Z.U. Efficacy of protein, symbiotic and probiotic supplementation on production performance and egg quality characteristics in molted layers. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Li, C.; Kuang, M.; Shah, A.U.; Shafiq, M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Abdalmegeed, D.; Li, L.; Wang, G. Nrf2 Activation and NF-Kb & caspase/bax signaling inhibition by sodium butyrate alleviates LPS-induced cell injury in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 148, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, D.S.; Zeng, D.; Khalique, A.; Rajput, S.S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Ni, X. Pretreatment with probiotics ameliorate gut health and necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens, a substitute to antibiotics. AMB Express 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.M.; Davares, A.K.; Andreevna, S.L.; Vladimirovich, E.A.; Carime, B.Z.; Marouf, R.; Khelifi, I. The use of probiotics in animal feeding for safe production and as potential alternatives to antibiotics. Vet. World 2021, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H. The effect of microbiome modulation on the intestinal health of poultry. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Yu, Y.-H.; Hsiao, F.S.-H.; Su, C.-H.; Liu, H.-C.; Tobin, I.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Y.-H. Influence of Heat Stress on Poultry Growth Performance, Intestinal Inflammation, and Immune Function and Potential Mitigation by Probiotics. Animals 2022, 12, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (direct-fed microbials) in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, growth and laying performance, and gut health: A systematic review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalique, A.; Zeng, D.; Shoaib, M.; Wang, H.; Qing, X.; Rajput, D.S.; Pan, K.; Ni, X. Probiotics mitigating subclinical necrotic enteritis (SNE) as potential alternatives to antibiotics in poultry. AMB Express 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, H.; Payros, D.; Pinton, P.; Theodorou, V.; Mercier-Bonin, M.; Oswald, I.P. Impact of mycotoxins on the intestine: Are mucus and microbiota new targets? J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2017, 20, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezirtzoglou, E.E.V. Intestinal cytochromes P450 regulating the intestinal microbiota and its probiotic profile. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhidarian, B.; Roldos, L.; Iskandar, M.M.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Kubow, S. Probiotic supplementation and micronutrient status in healthy subjects: A systematic review of clinical trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.M.; Fries-Craft, K.A.; Bobeck, E.A. Composition and inclusion of probiotics in broiler diets alter intestinal permeability and spleen immune cell profiles without negatively affecting performance. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skz383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-M.; Chen, W.-J.; Hua, K.-F.; Liu, J.-R.; Cheng, Y.-H. Effectiveness of Bacillus licheniformis-Fermented Products and Their Derived Antimicrobial Lipopeptides in Controlling Coccidiosis in Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochi, T.; Jansen, C.A.; Toyomizu, M.; Eden, W. The well-developed mucosal immune systems of birds and mammals allow for similar approaches of mucosal vaccination in both types of animals. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostagno, M.H. Effects of heat stress on the gut health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykin, H.; Rolls, A. The neuroimmune response during stress: A physiological perspective. Immunity 2021, 54, 1933–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Pepin, D.M.; Tropini, C. Cause or effect? The spatial organization of pathogens and the gut microbiota in disease. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: A door to the body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Guan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Xiao, Y. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens TL downregulates the ileal expression of genes involved in immune responses in broiler chickens to improve growth performance. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Horng, Y.-B.; Dybus, A.; Yu, Y.-H. Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products improve growth performance and intestinal gut morphology in broilers under Clostridium perfringens challenge. Poult. Sci. J. 2021, 58, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquier, V.; Nelson, A.; Jlali, M.; Rhayat, L.; Brinch, K.; Devillard, E. Bacillus subtilis 29784 induces a shift in broiler gut microbiome toward butyrate-producing bacteria and improves intestinal histomorphology and animal performance. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Qattan, S.Y.; Batiha, G.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Abdel-Moneim, A.M.E.; Alagawany, M. Probiotics in poultry feed: A comprehensive review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yitbarek, A.; Echeverry, H.; Munyaka, P.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J. Innate immune response of pullets fed diets supplemented with prebiotics and synbiotics. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatab, M.; Elsayed, M.; Ibrahim, N. Effect of some biological supplementation on productive performance, physiological and immunological response of layer chicks. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, M.; Khalaji, S.; Hedayati, M.; Pirany, N. Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis and bacitracin methylene disalicylate on growth performance, digestibility, blood metabolites, immunity, and intestinal microbiota after intramuscular inoculation with Escherichia coli in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajagai, Y.S.; Klieve, A.V.; Dart, P.J.; Bryden, W.L. Probiotics in Animal Nutrition: Production, Impact and Regulation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zaefarian, F.; Abdollahi, M.; Ravindran, V. Particle size and feed form in broiler diets: Impact on gastrointestinal tract development and gut health. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2016, 72, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Hrnčár, C.; Gašparovič, M.; Weis, J.; Arpášová, H.; Pistová, V.; Fik, M.; Bujko, J. Effect of three-strain probiotic on productive performance and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Sci. Pap. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 49, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ebeid, T.; Al-Homidan, I.; Fathi, M.; Al-Jamaan, R.; Mostafa, M.; Abou-Emera, O.; El-Razik, M.A.; Alkhalaf, A. Impact of probiotics and/or organic acids supplementation on growth performance, microbiota, antioxidative status, and immune response of broilers. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittoe, D.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kiess, A.S. Organic acids and potential for modifying the avian gastrointestinal tract and reducing pathogens and disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, A.; Parreira, V.R.; Goodridge, L.; Farber, J.M. Current and future perspectives on the role of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in controlling pathogenic Cronobacter spp. in infants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 755083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Hajkhodadadi, I.; Farahani, A.K. Intestinal microbial ecology, immune response, stress indicators, and gut morphology of male broiler chickens fed low-phosphorus diets supplemented with phytase, butyric acid, or Saccharomyces boulardii. Livest. Sci. 2020, 234, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Koh, C.B. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.D.; Head, D.A.; Devine, D.A. Dental plaque as a biofilm and a microbial community—Implications for treatment. J. Oral Biosci. 2015, 57, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Abdalla, A.K.; AlKalbani, N.S.; Baig, M.A.; Turner, M.S.; Liu, S.-Q.; Shah, N.P. Invited review: Characterization of new probiotics from dairy and nondairy products—Insights into acid tolerance, bile metabolism and tolerance, and adhesion capability. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8363–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Choct, M. The foregut and its manipulation via feeding practices in the chicken. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3188–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.A.; Sylte, M.J.; Looft, T. In-feed bacitracin methylene disalicylate modulates the turkey microbiota and metabolome in a dose-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.T.; Everaert, N.; Bindelle, J. Review on the effects of potential prebiotics on controlling intestinal enteropathogens Salmonella and Escherichia coli in pig production. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Akteruzzaman, M.; Islam, S.S.; Das, B.C.; Siddique, M.P.; Kabir, S.L. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus-based probiotics on the growth performance, gut morphology, intestinal microbiota and immune response in low biosecurity broiler chickens. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2021, 14, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foligne, B.; Nutten, S.; Grangette, C.; Dennin, V.; Goudercourt, D.; Poiret, S.; Dewulf, J.; Brassart, D.; Mercenier, A.; Pot, B. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2007, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanasawaeng, N.J.P.S.W.; Chansiripornchai, N. Efficacy of competitive exclusion to reduce Salmonella in broiler chickens. Thai. J. Vet. Med. 2019, 49, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- El-Moneim, A.E.-M.E.A.; El-Wardany, I.; Abu-Taleb, A.M.; Wakwak, M.M.; Ebeid, T.A.; Saleh, A.A. Assessment of in ovo administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium longum on performance, ileal histomorphometry, blood hematological, and biochemical parameters of broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Kassem, D.; Elsadek, M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.; Mahgoub, S.; Elaraby, G.; Taha, A.; Elshafie, M.; Alkhawtani, D.; Abd El-Hack, M.; Ashour, E. Growth, carcass characteristics, meat quality, and microbial aspects of growing quail fed diets enriched with two different types of probiotics (Bacillus toyonensis and Bifidobacterium bifidum). Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelqader, A.; Abuajamieh, M.; Hayajneh, F.; Al-Fataftah, A.-R. Probiotic bacteria maintain normal growth mechanisms of heat stressed broiler chickens. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 92, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Reimer, R.A.; Reid, G.; Verbeke, K.; Scott, K.P.; Holscher, H.D.; Azad, M.B.; Delzenne, N.M. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, D. Bacillus subtilis: A universal cell factory for industry, agriculture, biomaterials and medicine. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Niu, M.; Yu, X.; Bao, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, X. Horizontally Acquired Polysaccharide-Synthetic Gene Cluster From Weissella cibaria Boosts the Probiotic Property of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, V.A.; Moradi, S.; Harsini, S.G.; Rahimi, M. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and natural antibacterials on growth performance and Salmonella colonization in broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella enteritidis. Livest. Sci. 2020, 233, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Ashida, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Iwatani, S.; Yamamoto, N. Dietary Bacillus subtilis C-3102 supplementation enhances the exclusion of Salmonella enterica from chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2021, 58, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, C.; Shuju, Z.; Yang, Z.; Celi, P.; Ding, X.; Bai, S.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, X.; Xu, S. Differential analysis of gut microbiota and the effect of dietary Enterococcus faecium supplementation in broiler breeders with high or low laying performance. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.G.; Song, A.A.; Kim, E.B.; Yoon, S.-H.; Bok, J.-D.; Cho, C.-S.; Kil, D.Y.; Kang, S.-K.; Choi, Y.-J. Improved antimicrobial activity of Pediococcus acidilactici against Salmonella Gallinarum by UV mutagenesis and genome shuffling. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5353–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, H.; Di Cerbo, A.; Zulfiqar, F.; Sabia, C.; Nawaz, A.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Aqeel, M.; Ghazanfar, S. Probiotic Characterization and Population Diversity Analysis of Gut-Associated Pediococcus acidilactici for Its Potential Use in the Dairy Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha Filho, R.A.C.; Díaz, S.J.A.; Fernando, F.S.; Chang, Y.-F.; Andreatti Filho, R.L.; Junior, A.B. Immunomodulatory activity and control of Salmonella Enteritidis colonization in the intestinal tract of chickens by Lactobacillus based probiotic. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 167, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, A.; Chang, W.; Zheng, A.; Chen, Z.; Cai, H.; Liu, G. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the growth performance, immune response, and intestinal barrier function of broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli O157. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards-Rios, P. Understanding the Chicken Intestinal Microbiome: Towards a Rational Approach to Feed-Based Interventions. Doctoral Dissertation, The University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, G.; Shao, D.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wu, T.; Ji, C.; Shi, S. Dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis promotes growth performance of broilers by altering the dominant microbial community. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.; Zaki, R.; Negm, E.; Mahmoud, M.; Cheng, H. Effects of dietary supplementation of a probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) on bone mass and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerqin, C.; Rhayat, L.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Gharib-Naseri, K.; Kheravii, S.; Devillard, E.; Crowley, T.; Wu, S.-B. Probiotic Bacillus subtilis 29,784 improved weight gain and enhanced gut health status of broilers under necrotic enteritis condition. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neijat, M.; Shirley, R.; Barton, J.; Thiery, P.; Welsher, A.; Kiarie, E. Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis DSM29784 on hen performance, egg quality indices, and apparent retention of dietary components in laying hens from 19 to 48 weeks of age. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5622–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghari, M.; Sarani, P.; Hajati, H. Comparison of two probiotic preparations on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, nutrient digestibility and cytokine gene expression in broiler chickens. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2020, 48, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Yang, R.; Khalid, A.; Wang, Z. Probiotic Feeding Effect of Bacillus Subtilis on Broilers Chicks’ Microflora, TLRs and Interleukin Gene Expression; Research Square, Anhui Agricultural University: Hefei, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.R. Effect of Probiotics Instead of Antibiotics as Growth Promoters in Broiler Production; Department of Animal Production and Management, Sher-e-bangla Agricultural: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Han, J.C.; Chang, C.W.; Hsiao, F.S.H.; Yu, Y.H. Optimization of surfactin production from Bacillus subtilis in fermentation and its effects on Clostridium perfringens-induced necrotic enteritis and growth performance in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Horng, Y.-B.; Chen, W.-J.; Hua, K.-F.; Dybus, A.; Hsiao, F.-H.; Yu, Y.-H. Development and validation the efficacy of Bacillus-based fermented products as an antibiotics alternative in domestic animals. Acta Sci. Pol. Zootech. 2021, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangnumsawang, Y.; Zentek, J.; Goodarzi Boroojeni, F. Development and functional properties of intestinal mucus layer in poultry. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Long, S.; Mahfuz, S.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Piao, X. Effects of probiotics as antibiotics substitutes on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, intestinal morphology, and barrier function of broilers. Animals 2019, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, V.; Foroozandeh, A.; Toghyani, M.; Dastar, B.; Koochaksaraie, R.R. Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici, mannan-oligosaccharide, butyric acid and their combination on growth performance and intestinal health in young broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella Typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.; Kiess, A.; Adhikari, R.; Jha, R. An approach to alternative strategies to control avian coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristimunha, P.; Rosa, A.; Boemo, L.; Garcez, D.; Rosa, D.; Londero, A.; Scher, A.; Forgiarini, J. A blend of benzoic acid and essential oil compounds as an alternative to antibiotic growth promoters in broiler diets. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2016, 25, 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.; Menten, J.F.M.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Napty, G.; Longo, F.; Vittori, J.; Lourenço, M.; Santin, E. Organic acid blend in diets of broiler chickens challenged with Clostridium perfringens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2015, 24, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Ni, X.; Liu, L.; Lai, J.; Khalique, A.; Pan, K.; Jing, B. Preventing subclinical necrotic enteritis through Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 by ameliorating lipid metabolism and intestinal microflora in broiler chickens. AMB Express 2017, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Lei, J.; Ito, K.; Zhang, B. Enterococcus faecium PNC01 isolated from the intestinal mucosa of chicken as an alternative for antibiotics to reduce feed conversion rate in broiler chickens. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetoch, E.A.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Perelygin, V.V.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Borzenkov, V.N.; Levchuk, V.P.; Svetoch, O.E.; Kovalev, Y.N.; Stepanshin, Y.G. Diverse antimicrobial killing by Enterococcus faecium E 50-52 bacteriocin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volzing, K.; Borrero, J.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Kaznessis, Y.N. Antimicrobial peptides targeting Gram-negative pathogens, produced and delivered by lactic acid bacteria. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H.-B.; Yang, W.-T.; Shi, C.-W.; Cao, X.; Yang, G.-L. Recombinant invasive Lactobacillus plantarum expressing the Eimeria tenella fusion gene TA4 and AMA1 induces protection against coccidiosis in chickens. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109161. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).