Analysis of Volatile Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics Contributing to Regional Style of Red Wines from Hexi Corridor Based on Sixteen Grape Varieties/Clones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grape Materials
2.2. Yeast Strains
2.3. Chemical Reagents
2.4. Winemaking Process
2.5. Volatile Compound Analysis
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.7. Identification of Characteristic Aroma
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
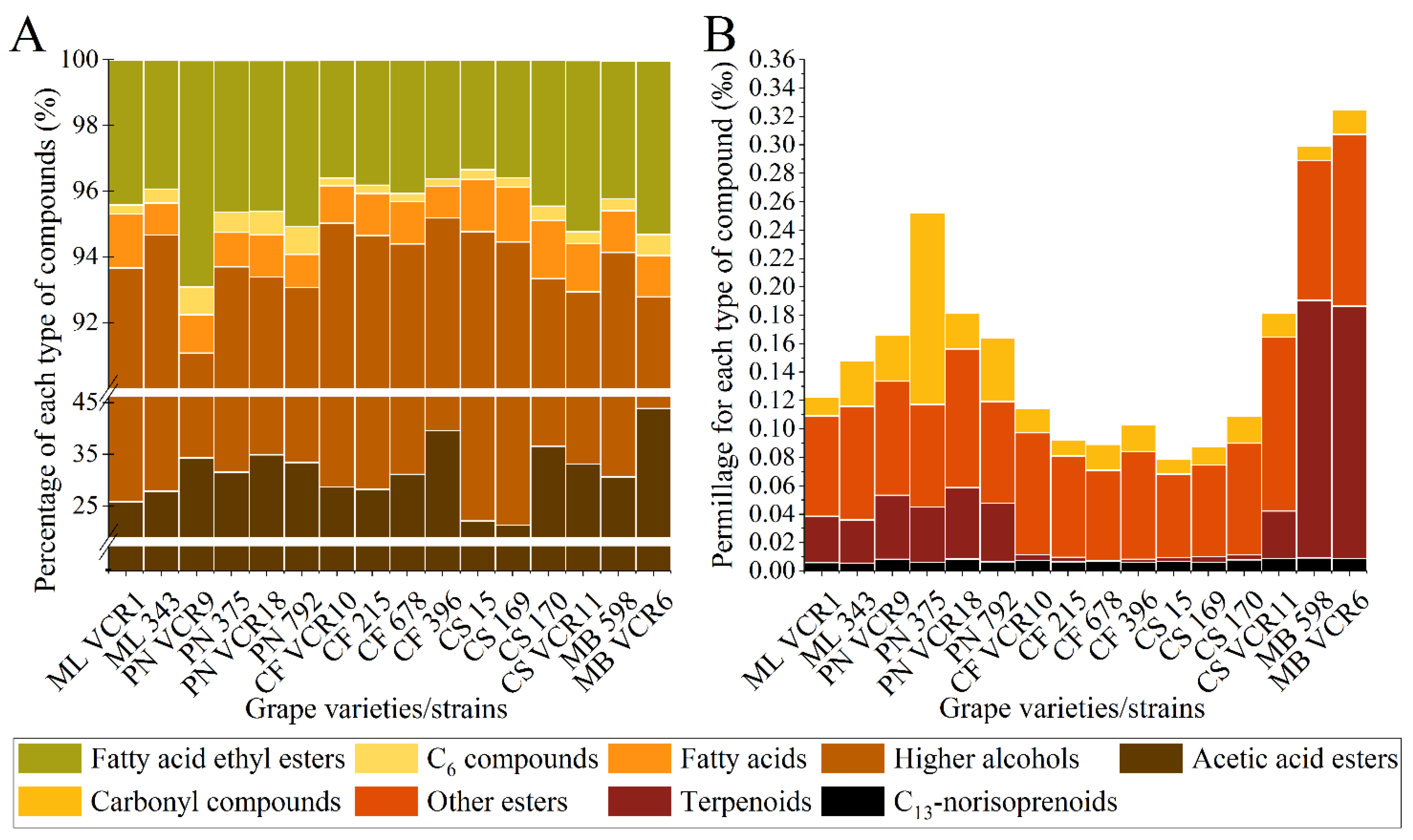
3.1. Volatile Component Analysis
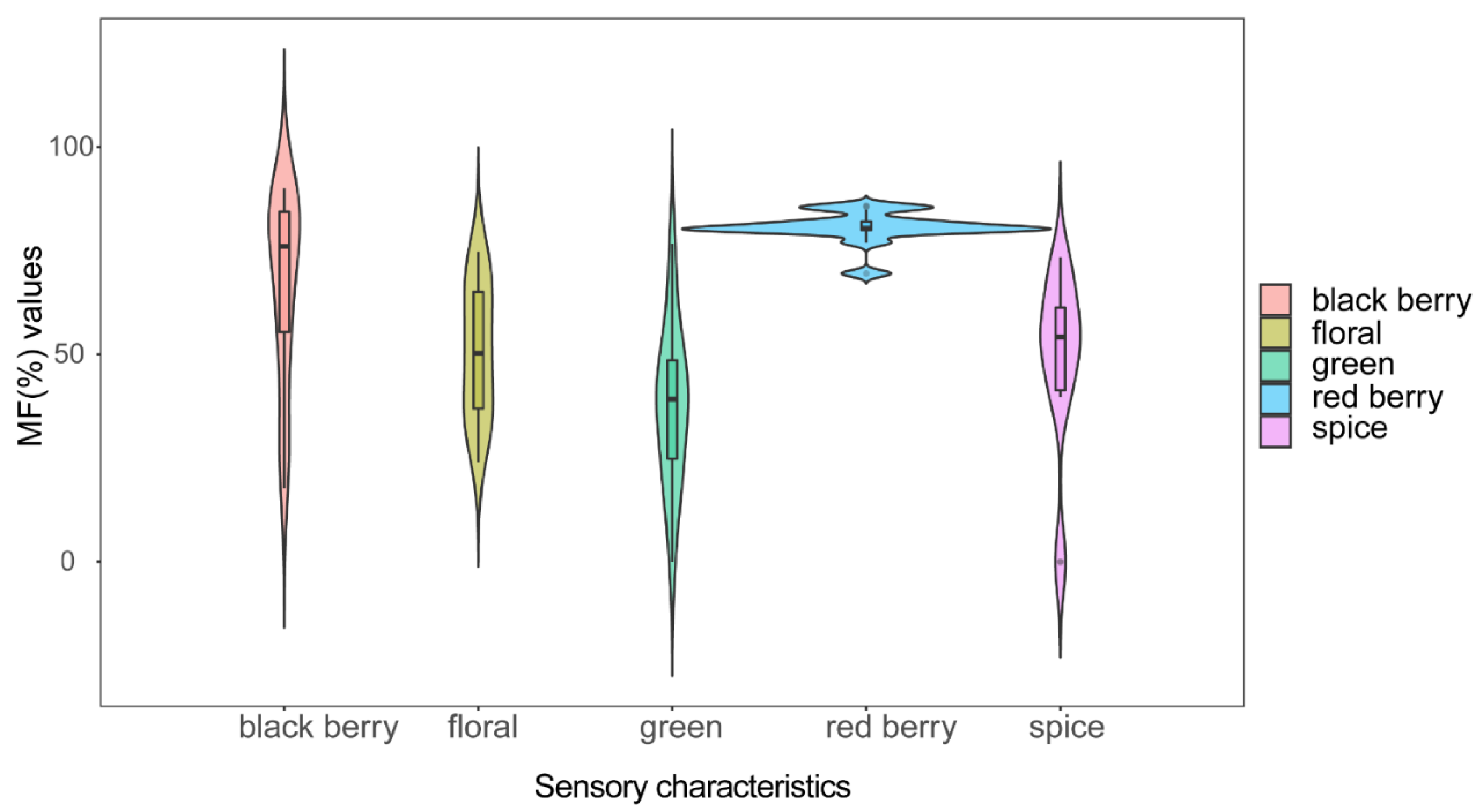
3.2. OAV-Based Characteristic Aroma Analysis
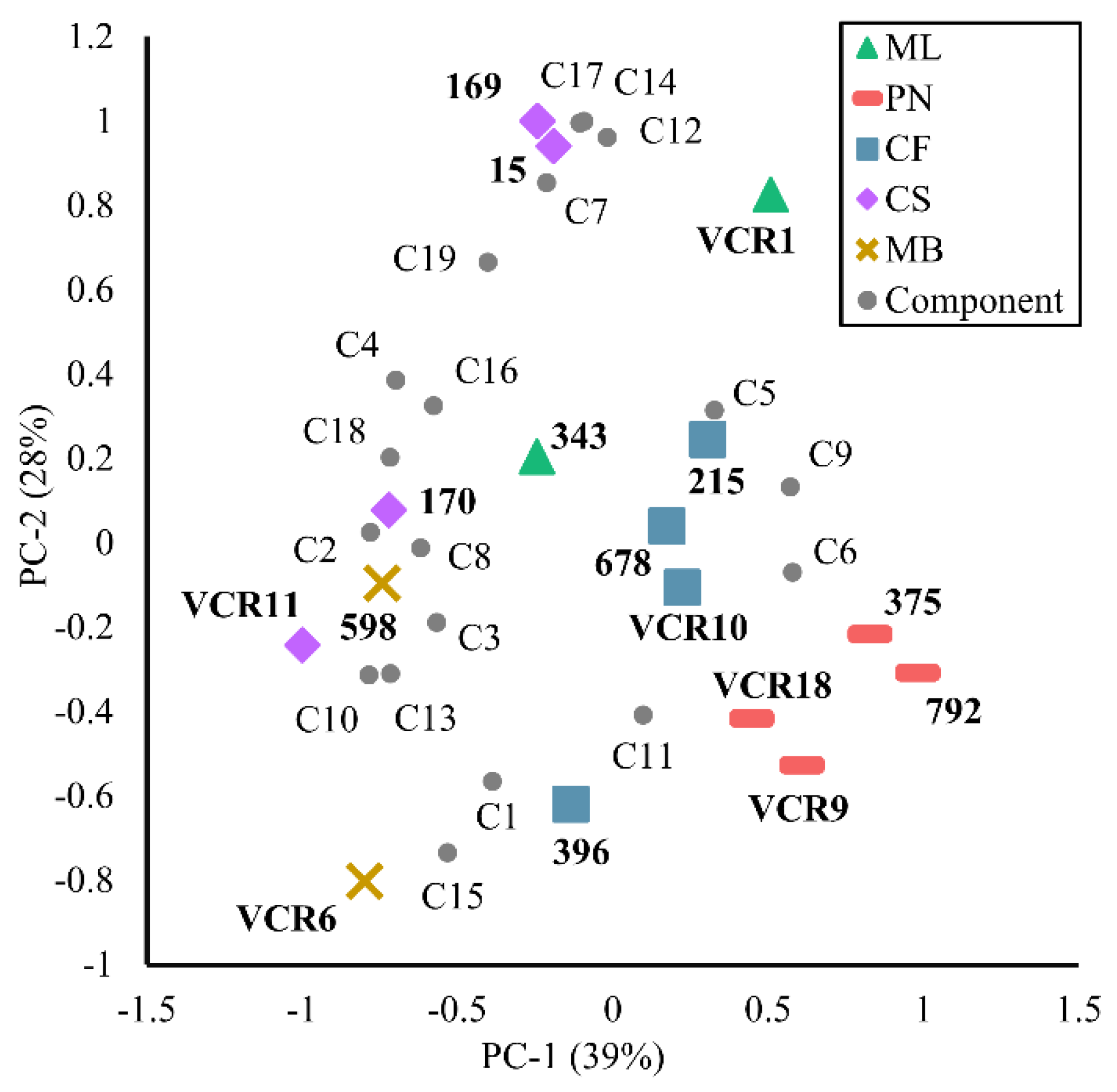
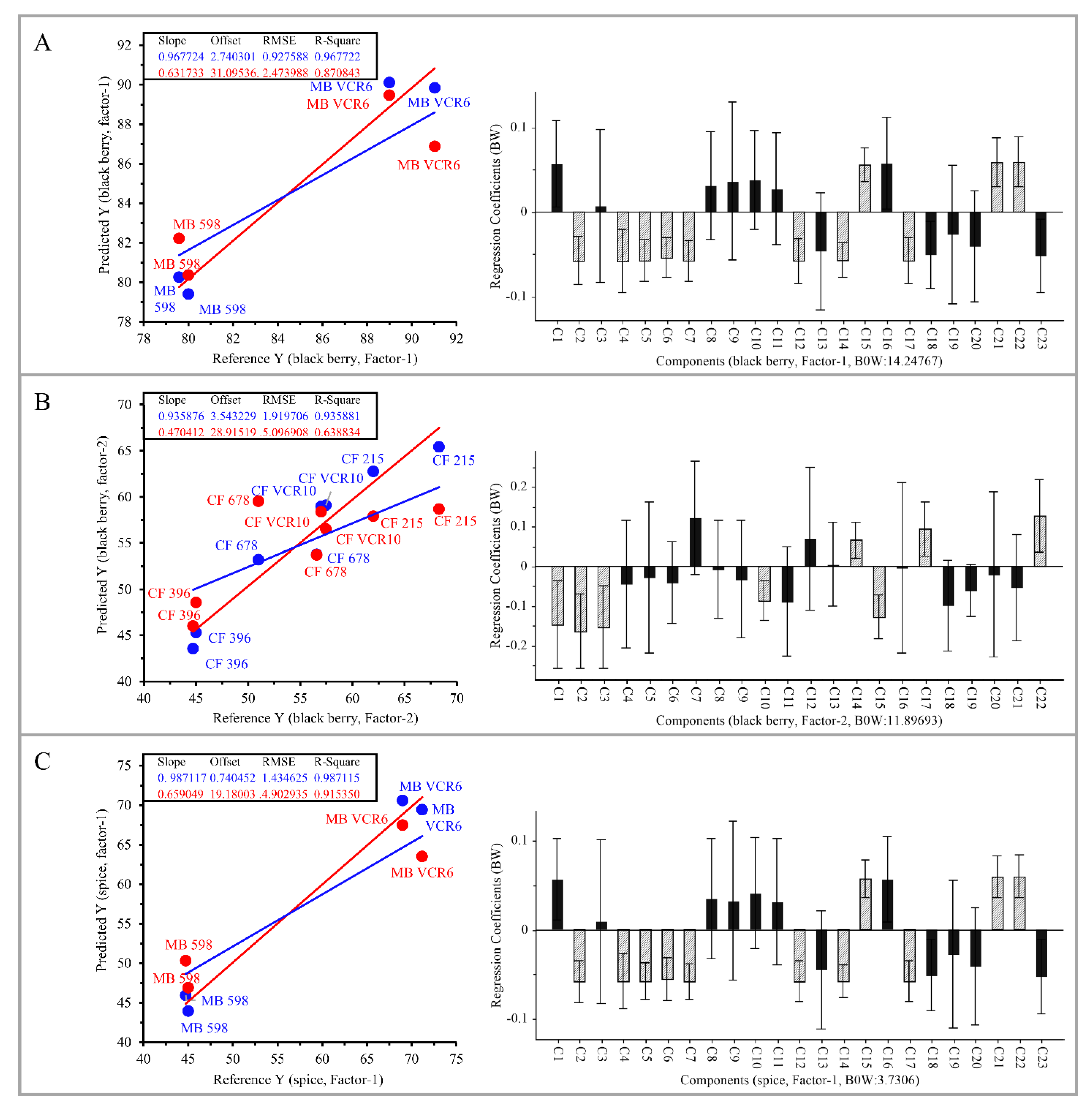
3.3. PLSR-Based Characteristic Aroma Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yang, B.; Li, N.-N.; Niu, J.-M.; Shi, X.; Han, S.-Y. Copigmentation evidence of phenolic compound: The effect of caffeic and rosmarinic acids addition on the chromatic quality and phenolic composition of Cabernet Sauvignon red wine from the Hexi Corridor region (China). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.-Q.; Jin, B.C.; Yu, X.Y. Effects of three morphometric features of roots on soil water flow behavior in three sites in China. Geoderma 2018, 320, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Hao, L.L.; Shi, X.; Niu, J.M.; Zhang, B. Development and application of a new QuEChERS method in UHPLC-QqQ-MS/MS to detect seven biogenic amines in Chinese wines. Foods 2019, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Thorngate, J.H.; Richardson, P.M.; Mills, D.A. Microbial biogeography of wine grapes is conditioned by cultivar, vintage, and climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 111, E139–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urvieta, R.; Buscema, F.; Bottini, R.; Coste, B.; Fontana, A. Phenolic and sensory profiles discriminate geographical indications for Malbec wines from different regions of Mendoza; Argentina. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Barreiro, C.; Rial-Otero, R.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Wine aroma compounds in grapes: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2015, 55, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Asta, C.; Cirlini, M.; Morini, E.; Galaverna, G. Brand-dependent volatile fingerprinting of Italian wines from Valpolicella. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7557–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.; Carew, A.; Sawyer, S.; Kemp, B.; Kerslake, F. A review on the aroma composition of Vitis vinifera L. Pinot noir wines: Origins and influencing factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ma, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, J.-M.; Li, L.-X.; Tang, K.; Xu, Y. Chemosensory characteristics of regional Vidal icewines from China and Canada. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Xi, Z.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Z. Comparison on aroma compounds in Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot wines from four wine grape-growing regions in China. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, L. Intensity prediction of typical aroma characters of cabernet sauvignon wine in Changli County (China). LWT 2010, 43, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Wen, H.-S.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zhang, A.; Yuan, C.-L. Geographical Origin Classification of Chinese Wines Based on Carbon and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Elemental Profiles. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-B.; Xiang, X.-F.; Qian, X.; Wang, J.-M.; Ling, M.-Q.; Zhu, B.-Q.; Liu, T.; Sun, L.-B.; Shi, Y.; Reynolds, A.G.; et al. Characterization and differentiation of key odor-active compounds of ‘Beibinghong’ icewine and dry wine by gas chromatography-olfactometry and aroma reconstitution. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Li, H. Sensory characters of Cabernet Sauvignon dry red wine from Changli County (China). Food Chem. 2009, 114, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolotti, L.; Mall, V.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds in a Commercial Rum and an Australian Red Wine by Means of a New Sensomics-Based Expert System (SEBES)—An Approach To Use Artificial Intelligence in Determining Food Odor Codes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4011–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueuermann, C.; Khakimov, B.; Engelsen, S.B.; Bremer, P.; Silcock, P. GC-MS Metabolite Profiling of Extreme Southern Pinot noir Wines: Effects of Vintage, Barrel Maturation, and Fermentation Dominate over Vineyard Site and Clone Selection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Q.; Duan, C.; Qu, W.; Wu, Y. Comparative Study of Aromatic Compounds in Young Red Wines from Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, and Cabernet Gernischet Varieties in China. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C248–C252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, D.; Barker, A.; Pearson, W.; Francis, I. Influence of inclusion of grapevine leaves, rachis and peduncles during fermentation on the flavour and volatile composition of Vitis vinifera cv. Shiraz wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. 2021, 27, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.; Parker, M.; Siebert, T.E.; Capone, D.L.; Francis, I. Terpenoids and their role in wine flavour: Recent advances. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2015, 21, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Carrau, F.; Versini, G.; Dellacassa, E. Terpene Compounds as Possible Precursors of 1,8-Cineole in Red Grapes and Wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1633–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, B.; Barbe, J.C.; Van Leeuwen, C.; Dubourdieu, D. Which impact for β-damascenone on red wines aroma? J. Agr. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4103–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, J.E.; Zanus, M.; Lazzarotto, M.; Zini, C.A. Quantitative analysis of headspace volatile compounds using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography and their contribution to the aroma of Chardonnay wine. Food Res. Int. 2014, 59, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C.; Kania-Zelada, I.; del Barrio-Galán, R.; Medel-Marabolí, M.; Gil, M.; Peña-Neira, Á. Study of the changes in volatile compounds, aroma and sensory attributes during the production process of sparkling wine by traditional method. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lerma, N.L.; Peinado, R.A.; Puig-Pujol, A.; Mauricio, J.C.G.; Moreno, J.; Garcia-Martinez, T. Influence of two yeast strains in free, bioimmobilized or immobilized with alginate forms on the aromatic profile of long aged sparkling wines. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristezza, M.; di Feo, L.; Tufariello, M.; Grieco, F.; Capozzi, V.; Spano, G.; Mita, G. Simultaneous inoculation of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria: Effects on fermentation dynamics and chemical composition of Negroamaro wine. LWT 2016, 66, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gómez, R.; Zalacain, A.; Pardo, F.; Alonso, G.; Salinas, M. Moscatel vine-shoot extracts as a grapevine biostimulant to enhance wine quality. Food Res. Int. 2017, 98, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Mu, J.; Gao, Z. Effects of spontaneous fermentation on the microorganisms diversity and volatile compounds during ‘Marselan’ from grape to wine. LWT 2020, 134, 110193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabani, M.; Ravera, M.J.; Wunderlin, D.A. Markers of typical red wine varieties from the Valley of Tulum (San Juan-Argentina) based on VOCs profile and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma—A review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Shen, X. Correlation analysis between aroma components and microbial communities in Wuliangye-flavor raw liquor based on HS-SPME/LLME-GC–MS and PLFA. Food Res. Int. 2020, 140, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Caldeira, M.; Câmara, J. Development of a dynamic headspace solid-phase microextraction procedure coupled to GC–qMSD for evaluation the chemical profile in alcoholic beverages. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 609, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setkova, L.; Risticevic, S.; Pawliszyn, J. Rapid headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic–time-of-flight mass spectrometric method for qualitative profiling of ice wine volatile fraction: II: Classification of Canadian and Czech ice wines using statistical evaluation of the data. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1147, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafkas, E.; Cabaroglu, T.; Selli, S.; Bozdoğan, A.; Kürkçüoğlu, M.; Paydaş, S.; Başer, K.H.C. Identification of volatile aroma compounds of strawberry wine using solid-phase microextraction techniques coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Flavour Frag. J. 2006, 21, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K. Green leaf volatiles: Hydroperoxide lyase pathway of oxylipin metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, A. The biogeneration of green odour by green leaves. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 1201–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Yang, N.; Linforth, R.; Sacchi, R.; Fisk, I. The role of phenolic compounds on olive oil aroma release. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, P.; Zhan, P.; Yan, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, F. Effects of β-glucosidase on the aroma characteristics of flat peach juice as assessed by descriptive sensory analysis and gas chromatography and compared by partial least squares regression. LWT 2017, 82, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, B.; Jimenez-Hierro, M.; Cantos-Villar, E.; Marrufo-Curtido, A.; Carbú, M.; Cuevas, F.; Moreno-Rojas, J.; González-Rodríguez, V.; Cantoral, J.; Ruiz-Moreno, M. The influence of yeast on chemical composition and sensory properties of dry white wines. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsonval, M.; Alexandre, H.; Grandvalet, C. Genetically engineered Oenococcus oeni strains to highlight the impact of estA2 and estA7 esterase genes on wine ester profile. Food Microbiol. 2016, 60, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dack, R.E.; Black, G.W.; Koutsidis, G.; Usher, S.J. The effect of Maillard reaction products and yeast strain on the synthesis of key higher alcohols and esters in beer fermentations. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variety | Clone | Abbreviate | Reducing Sugars (g/L) | Titratable Acidity (g Tartaric Acid/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merlot | 343 | ML | 257.38 | 7.02 | 3.60 |
| VCR1 | 230.20 | 6.27 | 3.91 | ||
| Pinot Noir | VCR9 | PN | 210.30 | 7.34 | 3.70 |
| 375 | 235.70 | 6.75 | 3.71 | ||
| VCR18 | 226.40 | 7.53 | 3.80 | ||
| 792 | 246.30 | 6.95 | 3.81 | ||
| Cabernet Franc | VCR10 | CF | 231.30 | 5.79 | 3.60 |
| 215 | 268.20 | 4.25 | 3.79 | ||
| 678 | 235.30 | 5.02 | 3.70 | ||
| 396 | 233.50 | 6.57 | 3.51 | ||
| Cabernet Sauvignon | 15 | CS | 229.40 | 7.33 | 3.61 |
| 169 | 248.90 | 7.72 | 3.60 | ||
| 170 | 222.70 | 7.72 | 3.60 | ||
| VCR11 | 238.70 | 8.87 | 3.50 | ||
| Malbec | 598 | MB | 245.70 | 8.87 | 3.71 |
| VCR6 | 228.00 | 8.50 | 3.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, X.; Du, Q.; Qu, R.; Ye, D.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Volatile Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics Contributing to Regional Style of Red Wines from Hexi Corridor Based on Sixteen Grape Varieties/Clones. Fermentation 2022, 8, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100501
Zang X, Du Q, Qu R, Ye D, Lu Y, Liu Y. Analysis of Volatile Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics Contributing to Regional Style of Red Wines from Hexi Corridor Based on Sixteen Grape Varieties/Clones. Fermentation. 2022; 8(10):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100501
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Xiaomin, Qing Du, Rui Qu, Dongqing Ye, Yao Lu, and Yanlin Liu. 2022. "Analysis of Volatile Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics Contributing to Regional Style of Red Wines from Hexi Corridor Based on Sixteen Grape Varieties/Clones" Fermentation 8, no. 10: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100501
APA StyleZang, X., Du, Q., Qu, R., Ye, D., Lu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). Analysis of Volatile Aroma Compounds and Sensory Characteristics Contributing to Regional Style of Red Wines from Hexi Corridor Based on Sixteen Grape Varieties/Clones. Fermentation, 8(10), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100501




