Abstract
Anaerobic co-digestion of sheep manure and potato waste was studied under batch and semi-continuous conditions. Biochemical methane potential tests were carried out for the different substrates before evaluating co-digestion at high-solid content. The reactors presented stable performance under mesophilic conditions, at an organic loading rate (OLR) of 3.5–4.0 kg VS/m3 and a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of approximately 20 days. Increasing the OLR of semi-continuous reactors decreased the methane yield and degradation efficiency of the digestion. Methane-specific production was in the range of 196 and 467 mL CH4/g vs. (sheep manure system and co-digestion, respectively). Based on the experimental data obtained, a techno-economic study was performed for wet and solid-state fermentation systems, with the first configuration presenting better results. The economic feasibility of the hypothetical plant was analyzed considering the variability in electricity and compost selling prices. The economic feasibility of the plant was determined with an electricity selling price of EUR 0.25/kWh, and assuming a centralized plant serving several farmers. Still, this price was considered excessive, given the current electricity market values.
1. Introduction
Anaerobic digestion is a well-established process for the treatment of organic wastes and the recovery of energy through biogas valorization. The process transforms organic compounds into methane-rich gas, which is easily transformed into electricity, helping to mitigate global warming [1]. A liquid slurry is also obtained from the digestion process, called digestate, which contains microbial biomass, metabolic compounds, complex organic structures, and material that is not degradable under anaerobic conditions. Mineralization is achieved by the removal of volatile solids and accumulation of mineral components; thus, digestate usually presents an inorganic content higher than that of the original substrate [2,3].
The benefits of anaerobic digestion are clear, but the economic feasibility of this type of treatment plant are not as clear. High installation and maintenance costs are among the main reasons for the low popularity of these plants in Spain. Livestock farms have to deal with strict regulations regarding the management of manure and prevention of nitrogen runoff. Digestion technology should be considered an important adjunct to aid in the prevention of environmental pollution, and the production of renewable energy. The reality is that the number of digestion plants treating manure in Spain is much lower than in other European countries, due to inadequate public incentives.
The digestion of manure has been extensively studied [4,5,6], with reports of synergistic effects associated with higher methane yields, and improved removal of volatile solids. Co-digestion of different substrates is a suitable way to increase the treatment capacity of existing plants, taking advantage of better process performance, and increased economic profitability. Additionally, the production of bioenergy from different wastes would not only address the environmental hazards associated with other waste treatment techniques, such as incineration plants and sanitary landfill sites, but also aid in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, while replacing the use of fossil fuels [7].
Manure is characterized by a high nitrogen content, leading to a low C/N ratio, which causes the accumulation of ammonia in anaerobic reactors. High ammonia levels can give rise to negative interactions with volatile fatty acids, adversely affecting the digester microflora [8]. In addition, the recalcitrant nature of some of the compounds present in manure makes it imperative to apply different strategies to enhance digestion, such as using pre-treatments and adding rich carbohydrate substrates to promote synergies and enhance microbial degradation [9].
Pre-treatments such as thermal hydrolysis, steam explosion, the addition of chemicals, and other processes to facilitate the access of microorganisms to the carbon source have been successfully evaluated [10,11,12,13]. However, applying pre-treatments is not always possible, due to the additional cost of some of these technologies, the high energy demand associated with their operation, and the intrinsic limitations related to the economy of scale [14,15].
Anaerobic digestion of different co-substrates has been studied under both wet and batch configurations. Wet digestion presents the evident disadvantage of lowering the efficiency of the reactor, due to the presence of an excessive amount of water. Thus, the logical strategy for improving reactor productivity would be to work at higher organic loading rates and solid content. Batch digestion tests performed by Abdelsalam et al. [16], studying the digestion of lettuce waste and cow manure at 20% total solid (TS) content, showed an increase in methane yield from 328 to 405.5 mL CH4/g VS. These batch assays were performed under mesophilic conditions, and kept for 45 days of operation, and did not reach a plateau at the end of the process.
In another study, Achinas et al. [17] evaluated the co-digestion of potato peels and cow manure. In this case, the authors performed batch tests (biochemical methane potential (BMP) tests) at a concentration of 10 g/L, and reported lower methane yields in the range of 193–211 mL CH4/g VS. These lower values may be explained by the different characteristics of substrates, but it was clear that much less digestion time was needed, only between 21 and 29 days to digest the whole material.
It is not easy to make comparisons between different experiments due to the varied substrate characteristics, experimental conditions, and activity of anaerobic microflora. However, it has been described that increasing the organic content of anaerobic digestion may adversely affect performance, due to diffusion limitations and accumulation of ammonia and acid intermediaries [18,19].
In a study carried out by Jansson and co-workers [20], it was reported that an increase in solid content from 14 to 20% TS resulted in significantly reduced performance regarding methane yield and the cumulative methane production rate, clearly evidencing difficulties in the development of the process. These authors treated food and paper industry wastes, and recommended the use of a lower substrate–inoculum ratio for BMP dry batch tests, but this led to a decrease in the organic feeding of the reactor and, thus, lower productivity.
This research aimed to evaluate the anaerobic co-digestion of sheep manure and waste materials derived from a potato chip processing factory under high solid concentration. The study is intended to highlight the benefits of this technology and increase social acceptance, which is crucial for integrating these systems into the production cycle, and increasing the degree of circularity of the economic model. Co-digestion was studied under batch and semi-continuous conditions at high organic loadings, and a technical analysis was performed to establish process feasibility without considering feed-in tariffs. The novelty of this work is in the technical analysis, performed using experimental digestion data obtained under high solid conditions. The study presented here reports on available configurations for reactor operation, extrapolating experimental performance to a hypothetical plant dealing with previously studied waste materials. Wet and dry digestion systems were evaluated in terms of biogas productivity, and economic feasibility was analyzed using a Monte Carlo simulation.
2. Materials and Methods
The sheep manure used in the experiments was from a livestock farm located in La Bañeza (León), a property of the livestock society Maragata de Vacuno S.C.L. The manure collected had an equal composition from lambs and an Assaf sheep breed dedicated to meat production. The mean TS content was 23.4 ± 0.7 (w/w), with a volatile solid (VS) content of 74.7 ± 1.4%. Potato waste was obtained from an agro-industrial facility, Aperitivos Gus S.L., dedicated to snack production, in Riego de la Vega (León). Two types of waste were collected: potato peels from the peeling processing stage, and fried chips that did not meet quality criteria. Potato waste had a TS content of 12.3 ± 0.3% (w/w), with a VS content of 86.5 ± 0.9%. Fried chips had a TS content of 85.8 ± 0.1%, with a VS content of 94.7 ± 0.2%.
The inoculum used for starting up the digester was obtained from the wastewater treatment plant of León. This digester worked under mesophilic conditions, with a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 26 days, treating a mixture of primary and waste-activated sludge. The inoculum had a TS content of 18.0 ± 1.0 g/L, with a VS content of 66.1 ± 0.2%.
2.1. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Tests
Digestion of the individual substrates was carried out using 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. Three replicates were used for each assay. Temperature was controlled by a water bath at 34 ± 1 °C. Magnetic stirrers were used for mixing. Gas volume was accumulated in bottle gasometers, and measurements were corrected to standard temperature and pressure (STP; 0 °C and 100 kPa). The batch reactors were filled with inoculum and substrate at a volatile solid (VS) ratio of 1:1 (inoculum:substrate (I:S)) using 5 to 10 g of substrate. Reactors containing inoculum were used as controls to measure the background gas production of the system, and this value was subtracted from those obtained from the digestion tests.
Cumulative biogas curves were fitted to the modified Gompertz function (Equation (1)), and the first-order rate decay model (Equation (2)) [21]. These models were selected based on the work of several authors regarding their better fit when evaluating easily degradable wastes, and fitting hydrolysis-limiting substrates or those containing inhibitory compounds [22,23,24]. OriginPro 8.0 software was used to fit the data to the equations and obtain model parameters.
Here, P(t) is cumulative biogas production (mL), Pmax is the maximum value of biogas produced (mL), Rmax is the maximum rate of biogas evolution (mL/d), λ is the time needed for adapting to the test conditions (d), and e is 2.71.
Here, P(t) is cumulative biogas production (mL), as in the previous equation. P0 was assumed to equal the final value of P(t) at the end of fermentation (mL), with a similar description to that of Pmax in the Gompertz model. The parameter k represents the exponential decay of substrate degradation.
The diauxic model (Equation (3)) proposed by Gomes et al. [24] was also evaluated for the gas data obtained from discarded fried chip samples. This model considers the summation of two phases following the modified Gompertz model.
2.2. Semi-Continuous Digestion Experiments
Semi-continuous experiments were performed using completely stirred reactors, with a working volume of 3 L operating at 34 ± 1 °C. The reactors had mechanical stirrers, and biogas was measured using a water displacement device with a wet-tip counter. The reactors were initially loaded with 3 L of inoculum, and evaluated at a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 50 days. The OLR was gradually increased until the desired point of the evaluation was reached, or an HRT between 20 and 33 days was achieved. The selection of the HRT for starting up these reactors was based on previous experience with digesting complex substrates [25,26].
The OLR applied to the co-digestion systems was increased to reach a value between 2.5 and 4.0 g VS/L d. The reactor was manually fed once a day, and liquid was withdrawn prior to feeding. The semi-continuous reactor treating sheep manure as a single substrate was denoted as R_manure. The co-digestion systems were denoted as R_m + peels and R_m + fries, referring to mixtures with potato peels and discarded chips, respectively. The mixture was prepared at a vs. ratio 3:1 (manure:co-substrate).
The reactor digesting manure was evaluated at an OLR of 2.5 g VS/L d. The system treating the mixture of manure and potato peels (R_m + peels) worked at an OLR of 2.5 and 3.5 g VS/L d, using two different reactors (see Figure 1). The system digesting the mixture of manure and discarded chips was tested at 3.5 and 4.0 g VS/L d. To perform this experimental phase, the reactor that previously treated sheep manure was fed with the mixture using discarded chips at 3.5 g VS/L d. The reactor that previously evaluated the mixture with potato peels was subsequently fed with the discarded chips mixture at 4.0 g VS/L d.

Figure 1.
Schematic representation of experimental methodology for evaluating semi-continuous reactors for digesting manure (R_manure) and mixtures with potato peels (R_m + peels) and chips (R_m + fries).
2.3. Analytical Techniques
Nitrogen concentration was measured using the Kjeldahl method. Lipid content was determined by Soxhlet extraction, using Velp Scientifica SER 148/3. Total solids, volatile solids, and total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) were measured in accordance with the American Public Health Association (APHA) [27]. These parameters were regularly monitored during the digestion process, by taking liquid samples from the reactor.
A Varian CP-3800 gas chromatograph was used to measure biogas composition. The chromatograph was equipped with a thermal conductivity detector. A HayeSep Q 80/100 (4 m long), followed by a molecular-sieve column (1 m long), were used to separate CH4, CO2, N2, H2, and O2. Helium was the carrier gas. Columns were operated at a pressure of 331 kPa, and a temperature of 50 °C.
Samples from the reactor liquor were regularly withdrawn to measure volatile fatty acids (VFAs). These acids were measured using the same chromatograph, equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID). A Nukol capillary GC column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm) from Supelco was used to measure VFAs. Helium was also used as the carrier gas. The injector and detector temperatures were 220 and 250 °C, respectively. The oven temperature was set at 150 °C for 3 min, and increased to 180 °C, with increments of 10 °C/min. The detection limit for VFA analysis was 5.0 mg/L. A mixture of standard volatile acids from Supelco (for the analysis of fatty acids C2 to C7) was used for calibration. Samples were previously centrifuged (10 min, 3500× g), and the supernatant was filtered through 0.45 μm cellulose filters. The total phosphorus content in the extract was quantified through spectrophotometry, using a Hitachi 2001 spectrophotometer after reduction of phosphomolybdate with ascorbic acid.
The determination of K, Na, Ca, and Mg was carried out using a PerkinElmer Optima 2000 DV inductively coupled plasma (ICP) atomic emission spectrometer. The analysis was performed by digesting 0.3 g of sample in 10 mL of nitric acid at 65% in a microwave oven at 100 °C for 5 min, and then at 190 °C for 30 min.
2.4. Technical Analysis of the Digestion Process
The technical analysis considered a hypothetical digestion plant treating sheep manure as a single substrate, and potato peels and discarded chips as co-substrates. The maximum solid content of the digestion system was 14% (TS, w/w), to adjust to the technical requirements of reactors with low to medium solid content. The HRT of the digester was between 30 and 20 days. Biogas was used as fuel in a combined heat and power unit (CHP). Digested material was either stored for further stabilization in a post-digestion tank and then dewatered, or composted.
Fresh manure production per animal was 1.3 kg/day [28]. The number of animals in the province of León was, on average, 39,500 in 2019 [29], considering in this census animals younger than 12 months, stallions, and breeding animals. Thus, livestock farms with an average size of 2000 animals each were assumed.
The manure produced was considered to come from different livestock farms located close to the potato processing plant. The digestion plant was also assumed to be in the vicinity of livestock farms, and served as a centralized treatment unit for 5 farms. The treatment plant was to be located at a maximum linear transport distance of 20 km, considering a tortuosity factor of 1.4, to keep in line with distance values recommended by Rajendran and Murthy [30].
The production capacity of the processing plant was 35,000 t/year of potatoes, and 15% of potato peel waste was assumed to be derived from potato processing [31]. The number of discarded chips was considered to be 1% of potato chip production. These chips have a moisture content of 0.02 kg/kg [32], and grease content of 35%.
Water is recirculated within the digestion plant from the dewatering stage of digestate to account for the set value for the digester feeding stream. The volume of the anaerobic reactor was calculated considering the mass flow of waste and headspace volume for accumulating biogas equivalent to 30% of the total reactor volume. The basic evaluation was carried out for a digestion plant (37 °C) comprising a waste reception area for storing manure, the reactor, and ancillary equipment. The biogas produced is assumed to accumulate in the head of the reactor. Removal of condensates and sulfide is necessary prior to using this gas in CHP units. The thermal demand of fermentation is met by the heat recovery system of the engine.
The solid content of the digestate stream was calculated considering that biogas is derived from VS, while inorganic material remains constant. Digestate is dewatered through the use of a rotary press attaining 25% solid content. Gas and energy production was estimated based on Equations (4)–(6), as described by González et al. [33] for biogas and electricity production:
where Biogas is expressed in m3/d (reported at standard temperature and pressure (STP), 0 °C and 100 kPa), Fv is the volumetric flow of the incoming stream (m3/d), VSinlet is the volatile solid content of the inlet stream (g/L), and SMP is the specific methane production (L CH4/kg) of the substrate. The composition of biogas is assumed to be 60%, and is represented in the equation as %CH4. Electricity production (kWh) was calculated using the lower heating value (LHV) of methane (35.8 MJ/m3) and an electrical efficiency (ƞE) of 34%, to take into consideration the small scale of the plant. The total efficiency of the CHP unit was 85% [34]. The heat demand to keep the digestion temperature in the mesophilic range was estimated by using an average temperature of the influent feeding stream of 6 °C in winter and 18 °C in summer.
Biogas = (Fv × VSinlet × SMP)/(1000 × %CH4)
Electricity = (Biogas × LHV × ηE)/3.6,
Thdig = m × cp × (Tdigester − Tslurry),
Here, Thdig is the energy demand for increasing the slurry temperature (Tslurry) to 37 °C (temperature of the mesophilic digester, Tdigester), and m is the mass flow of slurry, and the heat capacity of the slurry was assumed to be the same as that of water (cp, 4.18 kJ/kg K). The heat demand was increased by 8% in summer and 12% in winter, to account for thermal losses. The stream inlet temperature was assumed to be 10 °C in summer and 5 °C in winter.
The wet digestion configuration was evaluated considering a mixing tank for the addition of co-substrate, the digester operating under a mesophilic regimen, and a post-digestion unit for further stabilization of the digested slurry that did not require additional heating. It was assumed that 15% additional biogas was recovered from this final stabilization stage. The solid phase configuration was also analyzed, and compared with the wet digestion reactor. The estimation of reactor costs for the wet digestion configuration was based on plant cost data reported by Balussou et al. [35], and following the six-tenths rule, also followed by Aui et al. [36] for price estimation of plant components. Engine costs were estimated using the equation proposed by Oreggioni et al. [37]:
The net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) concepts were used in the economic analysis. NPV was calculated as the summation of cash flows, considering today’s currency. A discount rate (r) of 3% was assumed in the calculation:
where TCC is the total capital investment cost of the co-digestion plant, and CFt is the cash flow at time t, and calculated as the difference between revenues and expenditures. A plant construction period of 1.5 years was assumed. The straight-line depreciation method was used for the economic calculation, with a 15-year period and a salvage value of 5%. The average lifespan of the plant was 30 years. Money disbursement took place over 2 years, with 40% in the first year. Operating and labor costs were estimated at 3% of TCC. Engine maintenance costs (O&Mengines) were calculated using the equation of Oreggioni et al. [37], assuming a conversion of EUR 1 equivalent to GBP 0.877. Transport costs were assigned a price of EUR 0.18/t km
A Monte Carlo simulation was used to estimate NPV, under the assumptions of an electricity selling price of EUR 0.25/kWh (normal distribution, with standard deviation of EUR 0.05/kWh), and compost selling price of EUR 21/t (normal distribution, with standard deviation of EUR 2/t). A dataset consisting of 10,000 data points was randomly generated, and incorporated into the VPN and IRR calculations. The simulation iterates to create unique combinations of all parameters. An Excel spreadsheet was used to perform this analysis.
3. Results
Results regarding the chemical characteristics of the different materials are shown in Table 1. Sheep manure presents a high solid content, with a TS-to-VS proportion of 74.7%. This material is suitable for operating under a high solid content configuration, given the high value of volatiles. The two selected co-substrates also presented the same feature, with discarded chips having extremely low humidity. The ammonia content of the mixture could be balanced thanks to the wide difference in C/N ratio. Potato waste has a much lower amount of nitrogen; therefore, this parameter could be used to establish the limits for the different mixture proportions, if co-digestion is considered. The main interesting characteristic of using discarded chips as a co-substrate is the high lipid content associated with the cooking process. Table 1 shows the high lipid value measured for this material, indicating that a small addition of this co-substrate should be of great benefit for the digestion process. Regarding metal content, Na and K levels are of particular interest, due to the salinity that the remaining digestate may contain, and the effect on agricultural soils when the final disposal option selected is land application.

Table 1.
Characterization of substrates used in this study.
3.1. Results from Batch Digestion Tests
Batch digestion tests were performed for the individual substrates. Digestion of the materials proceeded at rates that were in line with their characteristic composition. Thus, sheep manure presented behavior that can be categorized as linear in its initial stage, which is indicative of hydrolysis limitations (see Figure 2). The first-order model for describing hydrolysis performance applies when the surface of the particulate substrate is the rate-limiting factor [38], and no other phenomena are implicit in the degradation process. Similarly, the performance of potato peels can be assumed to follow the same type of kinetics. Thus, the steep increase observed in the cumulative gas curve gives an indication of the ease of degradation. In a study by Achinas et al. [17], the result of the digestion of potato peels was 217.8 mL CH4/g VSadded. This value is just slightly higher than that obtained here (200 mL CH4/g VSadded), but denotes consistency in results.
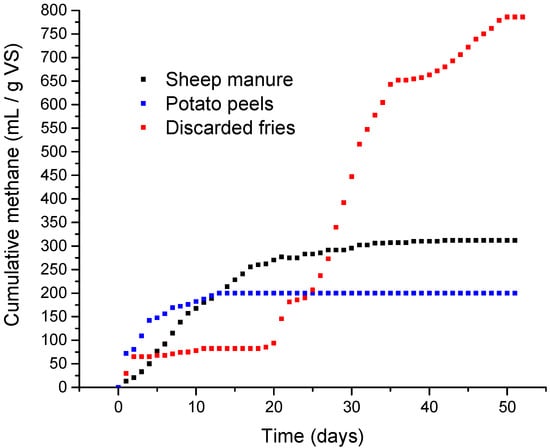
Figure 2.
Cumulative methane curves obtained from mesophilic batch tests (BMP tests). Substrates tested were sheep manure, potato peel waste, and discarded chips.
On the contrary, discarded chips, which are characterized by high lipid content, presented an initial pattern of gas ceasing after the first days of starting the process, and continuing thereafter at an extremely low rate, but on day 20 of the experiment, a clear increase in microbial activity took place. Thus, the existence of a lag phase in this particular digestion test suggests the better applicability of the modified Gompertz model [39] to account for the initial delay experienced.
Table 2 shows the results from data fitting to the exponential model and the modified Gompertz model. The samples of sheep manure and potato peels can both be adjusted to any of the models considered. The limitation experienced in the hydrolysis stage causes a lower slope in the cumulative gas curve of the sheep manure sample. Thus, these data show a better fit with this model than the exponential model (see Figure 2). In the case of potato peels, a better fit is obtained from the exponential model. There is no apparent delay in the production of biogas, and the inadequacy of the Gompertz model is noted by the negative value reported for the delay parameter (λ).

Table 2.
Parameters obtained from the exponential modified Gompertz model.
Figure 3 shows the results of fitted curves from the models and the graphs obtained from residual values of the fitted responses. In this case, residual values are greater for the exponential model when adjusting data obtained from the sheep manure and discarded chips. There was an extended phase of cumulative gas production in these two cases, when the sample underwent slow degradation. Although both models report reasonable fitting results for sheep manure data, the modified Gompertz model has a better adjustment for extreme values, that is, at the beginning of the test, and at the final stage.

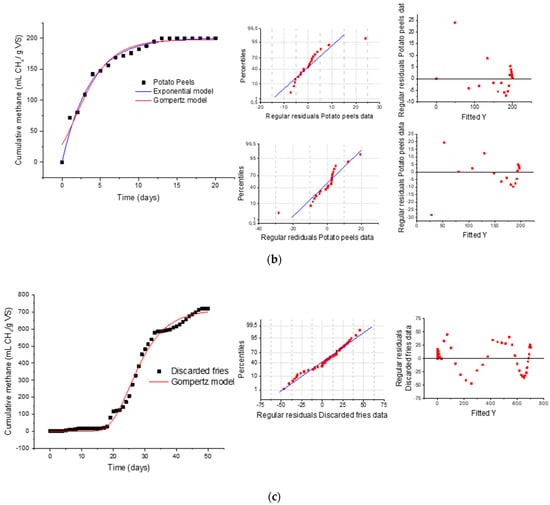
Figure 3.
Results obtained from adjusting exponential and modified Gompertz models to cumulative curves for methane. Data obtained from batch digestion of samples of (a) sheep manure, (b) potato peels, and (c) discarded chips.
The last sample analyzed was that of discarded chips. In this digestion, the gas evolution started with a small production of gas that ceased almost immediately after the start, presenting flat behavior. Around day 18 of the experiment, there was a steep increase in gas evolution associated with the end of the microbial adaptation to the substrate. The rapid evolution of biogas is clearly determined by the Rmax parameter, which is much higher than the values obtained for sheep manure and potato peel samples. This cumulative curve was adjusted exclusively to the modified Gompertz model. The fitted data were corrected by neglecting the initial evolution of biogas in this model.
The behavior of the sample of discarded chips regarding the evolution of biogas can also be interpreted as a two-phase evolution, in which the initial phase, once the acclimation stage is over, lasts 35 days, with the second phase subsequently taking place, with a lower gas evolution rate. This approximation was used by Gomes et al. [24], who proposed diauxic behavior for biogas evolution. The results of adjusting the BMP test data to their proposed model are presented in Figure 4. A better approximation was observed, where the two rates for biogas evolution could be estimated. Therefore, in the first stage, Rmax had a value of 49.7 ± 1.3 mL/d, and, after day 35, this value was reduced to 18.1 ± 0.29 mL/d, clearly evidencing differences in the degradation rate of substrate components.

Figure 4.
Representation of fitted curves for modified and diauxic Gompertz models proposed by Gomes et al. [24].
3.2. Results from Semi-Continuous Digestion Systems
The inoculum was first kept in reactors to adjust the conditions and the gas sealing system. On day 5, the reactor started at an HRT of 50 days, and a progressive increase in the incoming flow was set to adjust the OLR. The semi-continuous reactor treating sheep manure, denoted as R_manure, underwent a decrease in HRT associated with the higher OLR, until the desired value of 2.5 g VS/L d was reached. As observed in Figure 5, the average specific methane production was 264 ± 37 mL CH4/g VS. This value decreased progressively with increased feeding volume, as is clearly observed in the figure, to a final value of 196 ± 43 mL CH4/g VS. Other authors have also reported that the increase in organic loading is sometimes accompanied by lower specific gas production [3,40,41], as in the present case.

Figure 5.
Evolution of methane production obtained from reactor treating sheep manure as a single substrate.
Sánchez et al. [42] described a much lower rate of removal of volatile solids when the OLR was increased to 7 g VS/L d. Habagil et al. [43] reported variations in biogas yield associated with the organic load applied to the reactor, and the C/N ratio of the feeding mixture. Other authors indicated minor changes in biogas yield when the solid content of the feed was increased [44]. Ellacuriaga et al. [45] noted the need to increase reactor productivity by increasing organic loading. However, a balance should be found between the greater treatment capacity of the reactor, the degradation characteristics of the substrate, and the decrease in conversion capacity into biogas of the process.
Table 3 shows the average results of parameters measured for the feed, and values obtained from reactors at the end of digestion. Data were derived from measurements collected during the last 30 days of the experiment, once the desired retention time was reached. Even though no excessively high ammonia values were observed in the manure reactor, the methane yield obtained with an HRT of 30 days was much lower than that derived from batch experiments, by approximately 40%.

Table 3.
Results from semi-continuous reactors treating sheep manure and mixture of potato peel waste and discarded chips.
BMP tests provide the maximum amount of methane produced from a substrate, but do not allow any conclusion concerning digestion performance to be made. The stability of the process when working under continuous or semi-continuous conditions cannot be predicted using results from these tests. There are several dynamic conditions inside the reactor that influence the value of methane production finally obtained at a given OLR and HRT, and for the same reasons that methane yields obtained from batch tests are higher than those derived from semi-continuous operating reactors [46]. It is not easy to make direct comparisons with results reported by other authors, given the intrinsic differences associated with the experimental set-up and the characteristics of inoculum and substrate [47]. However, a study by Song et al. [48] reported a value of 219.7 mL CH4/g VSadded (from BMP tests) from the co-digestion of sheep and chicken manure. A similar value was obtained by Li et al. [49] under batch tests when using sheep manure as a single substrate (207 mL CH4/g VSadded), but a lower value for methane production (179 mL CH4/g VSadded) was obtained under continuous operation (OLR of 1 g VS/L d) when testing a mixture of sheep and cattle manure. Alvarez and Lidén [50] reported a methane production value of 120 mL CH4/g VSadded from a continuous reactor working at 25 °C and an HRT of 50 d (OLR of 1.2 g VS/L d).
The performance of co-digestion of sheep manure and potato peels was evaluated using two different reactors, initially operating as replicates (see Figure 6a). One of them evaluated the loading at 2.5 g VS/L d, whereas the other kept working with a progressive reduction of retention time to reach a loading of 3.5 g VS/L d. In this particular case, the increase in OLR did not translate into a decrease in specific methane production. The average specific yield was initially 213.3 ± 54.9 mL CH4/g VS when the HRT was 50 days. Increasing the OLR did not dramatically affect the methane yield. When the HRT was decreased to 30 days, the average value was 214.2 ± 33.3 mL CH4/g VS for the two reactors, and stayed about the same when the OLR was again increased to 3.5 g VS/L d. Therefore, the addition of the co-substrate stabilized the system.

Figure 6.
Evolution of specific methane production obtained from semi-continuous reactors treating (a) sheep manure and potato peel waste (R_m + peels) and (b) sheep manure and discarded chips (R_m + fries).
The change in degradability of the mixture by adding readily degradable peels allowed digestion of the feed with successful results, although there was less residence time inside the reactor. Changes in the C/N ratio of the feed has been shown to affect reactor performance due to the influence of ammonia, VFA interactions, and the solid content of the reactor [51]. In the present case, the components of potato peels were easily degraded, so full conversion was attained in a short time, as demonstrated by previously performed BMP tests. However, in the case of sheep manure, a longer time was needed. Decreased HRT caused an increase in organic loading, and, thus, a greater availability of easily degradable substrate, which was converted into biogas, possibly compensating for the incomplete conversion of manure, and leading to similar methane production value at lower HRT.
Figure 6b represents the evolution of methane production for reactors treating the mixture of manure and discarded chips (R_m + fries). The reactors used for this experiment were previously working with manure and the co-digestion mixture with potato peels. Thus, the mean values reported in Table 3 regarding the specific methane production correspond to data from the last HRT, to avoid the effect of feed change. The reactor treating sheep manure as a single substrate was then used to evaluate co-digestion with discarded chips at an OLR of 3.5 g VS/L d. This reactor experienced a perturbation in biogas production approximately 20 days later, after the feed was changed due to the higher load applied. Therefore, its evaluation period was prolonged to stabilize it for the new feed.
The co-digestion mixture containing discarded chips at an OLR at 4.0 g VS/L d was evaluated in the reactor that previously treated the mixture with potato peels, and, since microflora were acclimatized to tolerate a readily degradable substrate, no significant perturbations were observed with the change of feed. The increase in OLR was not reflected in greater biogas production. The value obtained from the higher loading reactor was lower, translating to lower substrate degradation. Figure 6b also shows the result of one-way ANOVA for the whole set of data, representing the average value for the whole period evaluated. The analysis reports differences for the dataset at the 0.05 significance level. Tukey’s test indicated differences between the means (prob 0.00182, alpha 0.05).
3.3. Technical Analysis of Mono-Digestion
A schematic description of the plant is presented in Figure 7 considering, in this case, a wet configuration for the digestion system. A digester treating sheep manure from a single farm with 2000 animals is assumed. One of the main factors affecting plant feasibility is the scale, along with the reactor configuration. The volume for the wet configuration, setting the 14% TS content in the feed as a limit, translates to a value of 124–186 m3 for an HRT of 20 to 30 days when dealing with manure produced by a single livestock farm. The case study analyzed here has several limitations regarding its applicability to results on an industrial scale derived from batch assays. Limitations are also associated with extrapolating this scenario to other countries, where the valorization of food processing waste presents greater benefits if used as animal feed. However, this academic approach is interesting with regard to the difficulties associated with scale and energy production.

Figure 7.
Schematic representation of digestion treatment plant using sheep manure as a single substrate. This plant is assumed to serve one single livestock farm with 2000 animals, working as a wet digestion system.
The average estimated biogas production would be 153 m3/d (6.4 m3/h), resulting in input power of 36.8 kW, if the same specific methane production obtained from continuous laboratory reactors is considered. This value is too low to be suitable for biogas valorization considering standard CHP units, as it has input values higher than 50 kW, while most applications have inputs greater than 100 kW [52,53].
Micro CHPs are also available, offering an electrical output of 20 kW (www.tedom.com; Výčapy, Czech Republic) (accessed on 10 September 2021) [54], but even the expected gas production in the present case is too low to be considered feasible for this option. For this small application, other energy solutions are now available, such as the Prometheus 5 (Metacon’s small CHP system) with a biogas consumption of 2.1 m3/h. This unit is capable of producing electricity (5 kW) and heat (7 kW), considering that reforming of the fuel leads to hydrogen production of 5 m3/h. This is done by means of a flameless steam multi-reformer and a PEM fuel cell (Helbio.com, Rio, Greece) [55]. In the present case, three small fuel cell units of this type could be installed, producing 3 mol H2/mol CH4 [55], leading to electrical power of 11.2 kW and thermal power of 15.6 kW, which is enough to meet the thermal demand of the digester (6.12 kW in summer conditions, and 7.5 kW in winter conditions).
If a post-digestion tank is considered to achieve a higher degree of stabilization and increase digestate agronomic quality, then the post-digestion system would have a volume of between 200 and 255 m3 for HRT of 40–55 days. The second digestion tank has a much greater volume, but even if thermal requirements are not set for this post-digestion stage, the size needed is excessive, which would mean high installation costs.
Liquid–solid separation and subsequent composting present greater benefits in this case, due to the much lower volume needed for storage and better handling of the composted organic material [56]. For this, 15–20 days of curing would be needed [57], but the addition of a structuring material would increase the material obtained as organic amendment, unless recovery of chips by screeners is performed. The mass of organic material mineralized during composting can be estimated by using a first-order decay model, proposed by Kulikowska and Bernat [58]. Thus, a reduction of 8.7 g/kg dry matter would be expected for a 20-day windrow composting process.
The mass flow of digestate submitted to composting would be 1.4 t/d. This value is doubled if a 1:1 ratio is used, by adding wood chips as a structuring agent. The final mass of composted material obtained if 90% of the wood chips are recovered by screeners would account for 0.89 t/d, calculated by considering the mineralization rate indicated above, and 55% humidity of the composted material. The proposed valorization option would require the farmer to find a way to dispose of 325 t/year of compost. Figure 7 shows the main characteristics estimated for the anaerobic reactor under wet configuration, with regard to volume and average biogas production.
If a solid phase digestion system is considered using garage-type reactors operated under batch conditions, then several reactors working in a staggered mode would be needed. Five units were considered for stabilization of the manure produced by a single plant. Each reactor would treat the material accumulated over 10 days, and a retention time of 50 days was established as enough to stabilize the substrate. The need for a structuring agent to allow leachate recirculation and favor digestion performance would lead to a significant increase in reactor volume. Thus, for this type of system, using a structuring ratio of 1:1 and a density of bed material of 0.6 kg/m3, the volume of the reactor would be close to that of the wet digestion system, with the additional disadvantage that five units are needed to treat the annual manure production. Figure 8 shows characteristics of the anaerobic reactor needed under solid phase configuration.
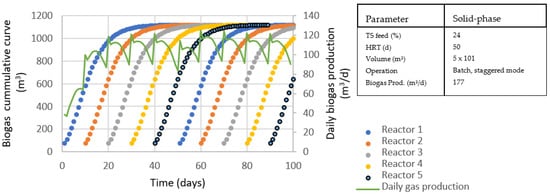
Figure 8.
Expected biogas flow of a solid-phase batch reactor operating under a staggering mode. A 20% decrease in biogas yield was assumed, with regard to that obtained from BMP tests. Data for a solid-phase plant of equivalent treatment capacity to that of wet digestion are also presented.
The average production of biogas, in this case, will be affected by the different stages, in which each reactor is operative. Figure 8 presents the expected evolution of gas, considering that no additional methane will be produced from wood chips if they are used as a structuring agent, and also assuming a decrease of 20% in the global biogas yield, compared to that obtained from BMP tests, to take into account the effect of working under solid-phase conditions. The daily methane production was then estimated to be 106.6 ± 9.6 m3/d (equivalent to daily production of 177 ± 16 m3/d). Under the considered assumptions, this value is higher than that obtained under wet configuration. However, as a disadvantage, the solid-phase reactor has a longer retention time, and the batch operation mode makes the system require more labor (due to loading and unloading operations). If working under solid-phase configuration causes a greater decrease in microbial performance than that initially assumed, to the disadvantage of higher volume and labor demand, an even lower methane production may be added. This negative effect was reported by Jansson et al. [20] when evaluating high solid content digestion, indicating a decrease in methane production of 78–123% by further increasing solid content from 14% TS to 16 and 20% TS.
3.4. Techno-Economic Analysis of the Co-Digestion Case: Manure and Potato Processing Factory Waste
The wet co-digestion configuration was analyzed in this scenario due to lower reactor volumes. A digestion plant designed to cover the manure production of five livestock farms was considered, to take advantage of scale costs and the greater efficiency of lean turbocharge CHP units. The daily manure production would account for 13,000 kg/d (see Figure 9). The total amount of discarded chips used as co-substrate and 2.84% of the peeling waste produced would be assumed to also be treated in this plant. The same co-digestion ratio of 3:1 (manure:co-substrate) was attained. Estimations were based on an HRT of 30 days.

Figure 9.
Main characteristics of co-digestion plant for treating a mixture of sheep manure and potato processing waste. Transport costs were estimated for both substrates.
Table 4 shows the results of the plant technical analysis and economic assessment considering plant depreciation, operating costs, and revenues listed in the table. NPV estimated using data reported here was negative (EUR-818,718) even though revenues from manure fees (EUR5/t), selling compost (EUR 21/t), and thermal energy were considered along with electricity revenues. Selling thermal energy is not an option for many digestion plants. In the present case, even under this assumption, the NPV obtained was negative. The use of a Monte Carlo simulation for estimating NPV under the assumption of an electricity selling price of EUR 0.25/kWh and the same compost selling price of EUR 21/t resulted in a mean NPV value of EUR 548,680 with an IRR of 6.08% (see Figure 9). However, it should be pointed out that the electricity selling price considered in this simulation was excessively high compared with the average current electricity price of EUR 0.188/kWh [59], which is already causing controversy over its effects on economic activity.

Table 4.
Techno-economic parameters of a co-digestion plant for treating a mixture of sheep manure and potato processing waste.
The analysis carried out for any of these cases, considering the single digestion of manure or co-digestion with potato processing residues, takes as a basic premise the possibility of collecting manure from animals. However, this may not be the case on many farms where sheep are extensively raised. Manure management, in that case, is not considered an environmental pollution problem. The results presented here assume that centralized manure treatment is the best option when energy production is the objective of the recovery scheme. The costs associated with this alternative are still high, making it difficult to implement on an industrial scale. A large reduction in equipment and installation costs is needed to make anaerobic digestion a feasible option for small- and medium-scale waste treatment systems.
4. Conclusions
The digestion process was improved by adding potato waste as a co-substrate when digesting sheep manure. The increase in organic loading and the availability of readily degradable substrate were the reasons for the better performance of the mixture. The experimental study of semi-continuous digestion systems indicated that decreased performance was obtained with increased organic loading. Specific methane production was lower for reactors treating sheep manure and its mixture with discarded chips when the hydraulic retention time was approximately 20 days. This effect was less notable for the mixture of manure and peels, due to the high degradability of potato peels, which are degraded at shorter retention times.
The technical analysis indicated that wet digestion systems can be expected to attain higher productivity, due to their capacity of operating at shorter retention times. Economic feasibility of the plant can barely be attained if the installation is capable of serving several livestock farms, and the available co-substrate is mainly composed of discarded chips, thus achieving higher biogas production. At an electricity selling price of EUR 0.13 /kWh, the profitability of the installation is null. An increase in the electricity price to EUR 0.25/kWh (standard deviation EUR 0.05/kWh, normal distribution) results in a mean NPV of EUR 548.680, with an IRR of 6.08%, but a substantial set of simulations reported negative values. The mean value was attained with a compost selling price of around EUR 21/t, and considering income from manure treatment fees. These assumptions may not be available for many treatment plants, making the process unfeasible. In addition, the electricity prices considered here may pose a risk to economic activities, which should not be underestimated.
New regulations should consider incentives specifically designed to improve the economic feasibility of small- and medium-scale treatment plants, which currently struggle with the disadvantage of high installation and operating costs, but may benefit from better social acceptance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.G. and X.G.; methodology, D.B.; validation, D.B., D.C.-P. and R.G.; formal analysis, X.G.; investigation, J.G.C.; resources, X.G.; data curation, X.G. and J.G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.G. and R.G.; writing—review and editing, D.C.-P.; visualization, D.C.-P.; supervision, X.G.; project administration, X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank EXPORINSA for data support and the availability of economic information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, Y.R.; Tsai, W.T. Valorization of Value-Added Resources from the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine-Raising Manure for Circular Economy in Taiwan. Fermentation 2020, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, X.; Cuetos, M.J.; García, A.I.; Morán, A. Evaluation of digestate stability from anaerobic process by thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 426, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Morán, A.; Otero, M.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry blood with OFMSW: FTIR and TG–DTG study of process stabilization. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quiroga, X.; Aboudi, K.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Romero-García, L.I. Enhancement of methane production in thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of exhausted sugar beet pulp and pig manure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, C. Treatment of cattle manure by anaerobic co-digestion with food waste and pig manure: Methane yield and synergistic effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Tang, X.; Zhao, K.; Balan, V.; Zhu, Q. Biogas Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Spent Mushroom Substrate with Different Livestock Manure. Energies 2021, 14, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lin, Y.Q. Analysis of Promotion Policies for the Valorization of Food Waste from Industrial Sources in Taiwan. Fermentation 2021, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Mohd Ghazi, T.I.; Omar, R. Anaerobic digestion technology in livestock manure treatment for biogas production: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Krooneman, J.; Euverink, G.J.W. Strategies to boost anaerobic digestion performance of cow manure: Laboratory achievements and their full-scale application potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 142940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Effect of mild-temperature thermo-alkaline pretreatment on the solubilization and anaerobic digestion of spent coffee grounds. Energies 2018, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrentino, R.; Merzari, F.; Fiori, L.; Andreottola, G. Biochemical methane potential tests to evaluate anaerobic digestion enhancement by thermal hydrolysis pretreatment. Bioenergy Res. 2019, 12, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi Aski, A.; Borghei, A.; Zenouzi, A.; Ashrafi, N.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Steam explosion pretreatment of sludge for pharmaceutical removal and heavy metal release to improve biodegradability and biogas production. Fermentation 2020, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şenol, H.; Açıkel, Ü.; Oda, V. Anaerobic digestion of sugar beet pulp after acid thermal and alkali thermal pretreatments. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 11, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cascallana, J.; Borge-Díez, D.; Gómez, X. Enhancing the efficiency of thermal hydrolysis process in wastewater treatment plants by the use of steam accumulation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 3403–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cascallana, J.; Gómez, X.; Martinez, E.J. Thermal Hydrolysis of Sewage Sludge: A Case Study of a WWTP in Burgos, Spain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.M.; Samer, M.; Amer, M.A.; Amer, B.M. Biogas production using dry fermentation technology through co-digestion of manure and agricultural wastes. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 8746–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Li, Y.; Achinas, V.; Euverink, G.J.W. Biogas potential from the anaerobic digestion of potato peels: Process performance and kinetics evaluation. Energies 2019, 12, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Liu, C. Influence of solids concentration on diffusion behavior in sewage sludge and its digestate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 152, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellacuriaga, M.; Cascallana, J.G.; González, R.; Gómez, X. High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance. Environments 2021, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, A.T.; Patinvoh, R.J.; Sárvári Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Dry anaerobic digestion of food and paper industry wastes at different solid contents. Fermentation 2019, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González, R.; Smith, R.; Blanco, D.; Fierro, J.; Gómez, X. Application of thermal analysis for evaluating the effect of glycerine addition on the digestion of swine manure. J. Thermal Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Martínez, E.J.; Fierro, J.; Otero, M. Feasibility of anaerobic co-digestion of poultry blood with maize residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulé, M.; Oechsner, H.; Jungbluth, T. Exponential model describing methane production kinetics in batch anaerobic digestion: A tool for evaluation of biochemical methane potential assays. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.S.; Strangfeld, M.; Meyer, M. Diauxie Studies in Biogas Production from Gelatin and Adaptation of the Modified Gompertz Model: Two-Phase Gompertz Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gomez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste (SHW) at laboratory scale: Influence of co-digestion with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion of slaughterhouse waste (SHW): Influence of heat and pressure pre-treatment in biogas yield. Waste Manage. 2010, 30, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environmental Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Melikoglu, M.; Menekse, Z.K. Forecasting Turkey’s cattle and sheep manure based biomethane potentials till 2026. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 132, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://agriculturaganaderia.jcyl.es/web/es/efectivos-ganaderos-2019.html (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Rajendran, K.; Murthy, G.S. Techno-economic and life cycle assessments of anaerobic digestion—A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepelev, I.; Galoburda, R. Industrial potato peel waste application in food production: A review. Res. Rural Dev. 2015, 1, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Pedreschi, F.; Moyano, P. Oil uptake and texture development in fried potato slices. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; González, J.; Rosas, J.G.; Smith, R.; Gómez, X. Biochar and energy production: Valorizing swine manure through coupling coupling co-digestion and pyrolysis. C 2020, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, A.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental impacts of generating electricity and heat from biogas produced by anaerobic digestion. Energy 2014, 70, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balussou, D.; Kleyböcker, A.; McKenna, R.; Möst, D.; Fichtner, W. An economic analysis of three operational co-digestion biogas plants in Germany. Waste Biomass Valori. 2012, 3, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aui, A.; Li, W.; Wright, M.M. Techno-economic and life cycle analysis of a farm-scale anaerobic digestion plant in Iowa. Waste Manage. 2019, 89, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreggioni, G.D.; Gowreesunker, B.L.; Tassou, S.A.; Bianchi, G.; Reilly, M.; Kirby, M.E.; Toop, T.A.; Theodorou, M.K. Potential for energy production from farm wastes using anaerobic digestion in the UK: An economic comparison of different size plants. Energies 2017, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vavilin, V.A.; Fernandez, B.; Palatsi, J.; Flotats, X. Hydrolysis kinetics in anaerobic degradation of particulate organic material: An overview. Waste Manage. 2008, 28, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Porhemmat, M.; Pramanik, B.K. Performance and kinetic model of a single-stage anaerobic digestion system operated at different successive operating stages for the treatment of food waste. Processes 2019, 7, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Wu, B.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions: Feasibility study. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowski, S.; Domański, J.; Weatherley, L. Anaerobic co-digestion of swine and poultry manure with municipal sewage sludge. Waste Manage. 2014, 34, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Herrmann, C.; Maja, W.; Borja, R. Effect of organic loading rate on the anaerobic digestion of swine waste with biochar addition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38455–38465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habagil, M.; Keucken, A.; Sárvári Horváth, I. Biogas production from food residues—the role of trace metals and co-digestion with primary sludge. Environments 2020, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Process performance of high-solids batch anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2652–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellacuriaga, M.; García-Cascallana, J.; Gómez, X. Biogas Production from Organic Wastes: Integrating Concepts of Circular Economy. Fuels 2021, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Hafner, S.D.; Weinrich, S.; Astals, S.; Holliger, C. Power and limitations of biochemical methane potential (BMP) tests. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; Seruga, A.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Urbanowska, A. Anaerobic digestion performance: Separate collected vs. mechanical segregated organic fractions of municipal solid waste as feedstock. Energies 2020, 13, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, D.; Fang, H.; Cao, X.; Liu, R.; Niu, Q.; Li, Y.Y. Revealing the correlation of biomethane generation, DOM fluorescence, and microbial community in the mesophilic co-digestion of chicken manure and sheep manure at different mixture ratio. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19411–19424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Achinas, S.; Zhao, J.; Geurkink, B.; Krooneman, J.; Euverink, G.J.W. Co-digestion of cow and sheep manure: Performance evaluation and relative microbial activity. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Lidén, G. Low temperature anaerobic digestion of mixtures of llama, cow and sheep manure for improved methane production. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Banji, A.A.; Rahman, S.; Sunoj, S.; Igathinathane, C. Impact of corn stover particle size and C/N ratio on reactor per-formance in solid-state anaerobic co-digestion with dairy manure. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2016/09/f33/CHP-Recip%20Engines.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.wolf-ps.de/fileadmin/WPS/Broschueren/WOLF_PS_CHP_solutions_with_added_value_EN.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.tedom.com/en/chp-units/biogas/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Available online: https://helbio.com/small-chp-systems/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Mucha, A.P.; Dragisa, S.; Dror, I.; Garuti, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Repinc, S.K.; Muňoz, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, S.; Stres, B.; Ust’ak, S.; et al. Re-use of digestate and recovery techniques. In Trace Elements in Anaerobic Biotechnologies; Fermoso, F.G., van Hullebusch, E., Collins, G., Roussel, J., Mucha, A.P., Esposito, G., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2019; p. 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drennan, M.F.; DiStefano, T.D. Characterization of the curing process from high-solids anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K. Waste Willow-Bark from Salicylate Extraction Successfully Reused as an Amendment for Sewage Sludge Composting. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.omie.es/es/market-results/daily/daily-market/daily-hourly-price (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Lovarelli, D.; Falcone, G.; Orsi, L.; Bacenetti, J. Agricultural small anaerobic digestion plants: Combining economic and environmental assessment. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).