Abstract
The residue remaining after the water extraction of soapberry pericarp from a biotechnology plant was used to produce a series of biochar products at pyrolytic temperatures (i.e., 400, 500, 600, 700 and 800 °C) for 20 min plant was used to produce a series of biochar products. The effects of the carbonization temperature on the pore and chemical properties were investigated by using N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The pore properties of the resulting biochar products significantly increased as the carbonization temperature increased from 700 to 800 °C. The biochar prepared at 800 °C yielded the maximal BET surface area of 277 m2/g and total pore volume of 0.153 cm3/g, showing that the percentages of micropores and mesopores were 78% and 22%, respectively. Based on the findings of the EDS and the FTIR, the resulting biochar product may be more hydrophilic because it is rich in functional oxygen-containing groups on the surface. These results suggest that soapberry pericarp can be reused as an excellent precursor for preparing micro-mesoporous biochar products in severe carbonization conditions.
1. Introduction
Biochar is a carbon-rich material which can be produced from a variety of lignocellulosic residues in a closed system under limited or no oxygen (or air). Due to its chemical and physical characteristics, biochar can be used as a product itself or as an ingredient within a mixed product for multiple objectives, including soil improvement, waste management, energy (or fuel) production, water pollution, and mitigation of climate change [1]. For example, biochar has been commonly used as a soil enhancer, thus making soils more fertile and also sequestering carbon in soils for a long time without greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions [2]. Concerning its porous structure and surface characterization, biochar has high adsorption potential for the removal of pollutants from water streams [3,4,5,6,7]. In recent years, there is an increasing interest in exploiting biochar as an excellent carbon material for environmental applications, or reusing different lignocellulosic feedstocks for producing biochar with high pore properties (e.g., specific surface area), which includes wood [8], oil palm shell [9], maize straw [10], cocoa pod husk [11], rice husk [12] and so on.
Soapberry (Sapindus mukorossi), also called soapnut, is a deciduous plant in the family Sapindaceae, which is commonly planted in tropical and sub-tropical Asian regions (including Taiwan) for its folk values [13]. The fruit is famous for the natural surfactants (i.e., saponins) present in its pericarp. Apart from its traditional use in detergents and shampoo for hair, skin and clothing, the pharmacological and biological actions of this plant have been recently exploited in the fields of medicine [14,15] and herbicides [16,17]. Because of the chemical characteristics of its saponins, it has been used in food applications as a natural preservative and emulsifier [18]. In order to extract the saponins from soapberry pericarp, the commonly used methods were to use the aqueous extraction solvent with the proper solid/liquid ratio at a mild temperature [14]. Furthermore, the residual biomass after the extraction of soapberry pericarps was thus generated without further utilization, causing problems of waste management and environmental pollution. In this regard, reusing the residual soapberry pericarp as a precursor in the production of carbon materials could be a promising route.
Similar to other lignocellulosic biomasses, the main components of soapberry pericarp are composed of cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose. However, there is limited literature on the use of soapberry pericarp for biochar production [19,20]. Zhang et al. [19] performed the oxidative torrefaction of three nutshells (including soapberry pericarp) at 250 and 300 °C for the production of biochar, which has potential for reuse as a solid fuel and for carbon storage. Velusamy et al. [20] prepared biochar from soapberry pericarp at 450 °C for about 2 h under a heating rate of 3 °C/min. The resulting biochar material (specific surface area = 2.2 m2/g) was tested to determine its adsorption performance of antibiotic ciprofloxacin (one of emerging contaminants) in aqueous solution.
In view of the few studies on the preparation of biochar from soapberry pericarp in the literature, the aim of this work was to produce soapberry-based biochar products at severe carbonization temperatures (i.e., 400–800 °C), because this process parameter has the greatest influence on their physical structures [21,22]. The pore and chemical characteristics of the resulting biochar products were characterized as a function of carbonization temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this work, the residual soapberry pericarp as a starting feedstock for biochar production was obtained from a local biotechnology factory (Tainan city, Taiwan), which adopted the mild water system for extracting saponins from soapberry pericarp. The biomass sample first had its moisture removed under sunlight and was then dried by an air-circulation oven. The dry sample was shredded by a knifer and further sieved to a size in the range of mesh no. 80 (opening = 0.18 mm) and 40 (opening = 0.40 mm). The sample was subsequently used for the thermochemical analyses and the carbonization experiments.
2.2. Thermochemical Properties of Soapberry Pericarp
The characteristics of biomass feedstock greatly influence the performance of a thermochemical conversion system [23]. In this work, the thermochemical properties of soapberry pericarp included proximate analysis, ultimate analysis, calorific value, inorganic element analysis and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The operations and procedures for these thermochemical analyses have been reported previously [24,25].
2.3. Carbonization Experiments
In order to enhance the pore properties of the resulting biochar, the preparation of biochar from soapberry pericarp (about 5 g for each experiment) was carried out at higher carbonization temperatures (400–800 °C by an interval of 100 °C) for 20 min under the nitrogen gas flow (500 cm3/min). Another carbonization experiment was performed at the highest temperature (i.e., 800 °C) for 80 min to evaluate the effect of residence time on the pore properties preliminarily. The operations of carbonization experiments and procedures at 10 °C/min for producing biochar products can refer to the previous studies [26,27]. Herein, the yield of the resulting biochar was obtained by the ratio of its weight to the weight of soapberry pericarp fed.
2.4. Analysis of Resulting Biochar Properties
The pore properties of the resulting biochar, including surface area, pore volume and pore size distribution, were determined by an accelerated surface area and porosimetry instrument (ASAP 2020; Micromeritics Co., Norcross, GA, USA), which was based on nitrogen (N2) adsorption–desorption isotherms at −196 °C [28]. Prior to the measurement, the biochar sample was degassed at 250 °C in a vacuum for 3 h. The N2 isotherms were measured over a relative pressure (P/Po) range between 10−5 and 0.999. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and micropore volume (and micropore surface area) were determined by using the BET equation and t-plot analysis, respectively [29]. On the other hand, the elemental distributions and functional groups of the resulting biochar products with high pore properties were observed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) (7021-H; HORIBA Co., Kyoto, Japan) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) (FT/IR-4600; JASCO Co., Tokyo, Japan), respectively. The biochar sample preparation and analytical conditions have been stated in the previous study [11].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermochemical Characteristics of Soapberry Pericarp
Table 1 showed the main thermochemical properties of the dried soapberry pericarp (SP), including proximate analysis, ultimate analysis and calorific value. The data in Table 1 were very close to those in the literature [19]. For instance, the carbon content and calorific value in Table 1 were 52.96 wt% and 21.75 MJ/kg, respectively, in comparison with 53.24 wt% and 20.93 MJ/kg [19]. By contrast, the dried SP has a relatively lower ash content (2.28 wt%) than those of other biomass residues in the range from 1.41 to 20.26% (dry basis) [30]. The calorific value (i.e., 20.96 MJ/kg) was in accordance with its high contents of carbon (C, 52.96 wt%) and hydrogen (H, 7.29 wt%). It should be noted that the contents of nitrogen (N, 1.48 wt%) and sulfur (S, 0.36 wt%) for the dried biomass were obviously higher than those for other biomass husks [30], thus posing significant emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur oxides (SOx) while it is burned without an installed control system. The main inorganic elements in the biomass sample (as listed in Table 2) are calcium (Ca), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg) and iron (Fe), which could be present in the forms of oxides and/or carbonates [30]. Furthermore, the contents of inorganic elements (i.e., Si, Al, Na, Cu, P and Ti) were not determined by the inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) because they were lower than their method detection levels (Table 2). Based on the data in Table 2, the total amounts (1.73 wt%) of inorganic elements by their oxides (i.e., CaO, K2O, MgO and Fe2O3) were close to the low ash content (2.28 wt%) in Table 1.

Table 1.
Thermochemical properties of soapberry pericarp (SP).

Table 2.
Contents of inorganic elements of soapberry pericarp (SP).
The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and derivative thermogravimetry (DTG) curves of the dried SP (about 0.2 g) were obtained at four different heating rates (i.e., 5, 10, 15 and 20 °C/min) under the nitrogen flow (50 cm3/min), as depicted in Figure 1. Obviously, these curves revealed similar thermal behaviors according to the residual weight percentages as a function of temperature. Using the TGA curve at 10 °C/min as an example, the initial weight decline occurred in the range from 100 to 200 °C, which should be attributed to the losses of attached matters (e.g., moisture) and light volatiles due to the incipient decompositions of liable organic matters. Subsequently, significant mass loss was observed at the temperature range of 200 to 400 °C, which corresponded well to the decompositions of organic constituents such as hemicellulose and cellulose [18]. When the temperature was raised to above 400 ℃, the continued mass loss was caused by the volatilization of complex lignocellulosic fractions (e.g., lignin) and inorganic carbonates/oxides. These data were consistent with those in the literature [31]. From the TGA curves (Figure 1), it was suggested that the dried SP could be an excellent precursor for producing biochar at higher carbonization temperatures. In this regard, this work adopted carbonization conditions in the range from 400 to 800 °C at the heating rate of 10 °C/min for producing biochar products with high pore properties.
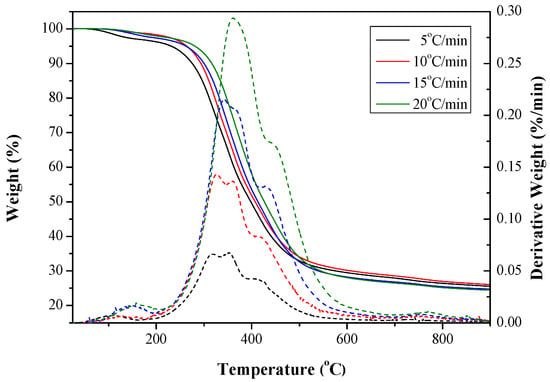
Figure 1.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, solid line)/derivative thermogravimetry (DTG, dotted line) curves of soapberry pericarp (SP) at various heating rates (5–20 °C/min).
3.2. Pore Properties of Resulting Biochar
The pore properties of porous materials commonly refer to specific surface area, pore volume, pore size and pore size distribution, which are closely related to their applications. In order to compare with the data clearly, the resulting products were coded by the “SP-BC-temperature” to mean the preparation of biochar (BC) from soapberry pericarp (SP) at different carbonization temperatures. The average yields of the resulting products prepared in duplicate at 400, 500, 600, 700 and 800 °C were 34.5, 26.5, 26.7, 23.7 and 21.0 wt%, respectively. At higher carbonization temperatures, the charring will cause the gradual mass decline by the formation of pyrolyzed gases such as carbon monoxide (CO). At this time, the chemical structure will be transformed from amorphous char to composite char with turbostratic crystallites [21]. Therefore, it was shown that the pore properties of biochar products would be enhanced with increasing temperature due to the development of porosity. The formations of micropores and mesopores were attributed to the fused ring structures of the aromatic carbon matrix.
Table 3 summarized the pore properties of the SP-BC products, which were prepared at 400–800 °C (an interval of 100 °C) for 20 min. Obviously, the BET surface areas of the resulting biochar products significantly rose from 0.3 to 277.1 m2/g when the carbonization temperature increased from 400 to 800 °C, especially for the temperature in the range of 700 to 800 °C. As mentioned above, the carbonization at high temperature will lead to the formation of nanopores in the resulting turbostratic char, thus enhancing its pore properties significantly [21]. In order to test the effect of residence time on the pore properties of the resulting biochar, another carbonization experiment was performed at 800 °C for 80 min, showing a slight decline in the BET surface area from 277.1 to 240.8 m2/g. This finding can be attributed to the severe carbonization reaction, leading to the structural breakdown of the resulting biochar and a reduction in its surface area [21,22,32]. On the other hand, the SP-BC-800 product was prepared in duplicate to assure its high pore properties consistently, showing that the BET surface area was about 300 ± 30 m2/g. As listed in Table 3, other pore properties such as single point surface area and total pore volume also indicated an increasing trend. As summarized above, the temperature should be the most important process parameter for determining the pore properties of the biochar products as more pores were generated in severe carbonization conditions. The findings were consistent with those reported by the other feedstocks such as cocoa pod husk [11], rice husk [12], goat manure [21], biogas digestate [33] and dairy manure [34]. The maximal BET surface area of about 300 m2/g can be obtained by using these feedstocks in the biochar production when the carbonization temperature reached 800 or 900 °C. In addition, the average pore diameter was obtained from the data on the BET surface area and the total pore volume assuming the pore is of cylindrical and uniform geometry, showing that the pore diameter of the SP-BC-800 product was close to the boundary limit (2.0 nm) between micropores and mesopores. In this regard, both the microporous and mesoporous structures could be presented in the optimal biochar SP-BC-800.

Table 3.
Pore properties of SP-BC products.
Figure 2 showed the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of all resulting SP-BC products at −196 °C. Herein, the isotherms of the SP-BC-400 and SP-BC-500 products were not depicted in Figure 2 because of their relatively low adsorption/desorption amounts. From the isotherm shape, the SP-BC-800 product obviously exhibited the characteristics of Type I. Based on the definition by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) [28], carbon material with the Type I isotherm could be highly microporous because it has a high potential for adsorption at very low relative pressure (P/P0) (˂0.1) by micropore filling. However, typical microporous materials often contain pores over a wide range of sizes, including micropores (˂2 nm) and mesopores (2–50 nm). When the values of P/P0 increased from 0.1 to 1.0, the curves in Figure 2 indicated a low slope of the plateau, which was attributed to the multilayer adsorption on the pore surface of the resulting biochar products. Based on the capillary condensation of N2 at a relative pressure of about 1.0, all pores were thus filled by liquid N2, suggesting that total pore volume can be estimated by converting the saturated adsorption amount into liquid N2 volume using its liquid density (i.e., 0.808 g/cm3). It was also seen that the resulting SP-BC-800 product also exhibited a hysteresis loop with the Type IV isotherms [29], which showed the existence of a micro-mesoporous composite structure from the Type I and Type IV isotherms. Furthermore, this can be observed in its pore size distribution (Figure 3), which can be consistently linked to its pore properties, as listed in Table 3.
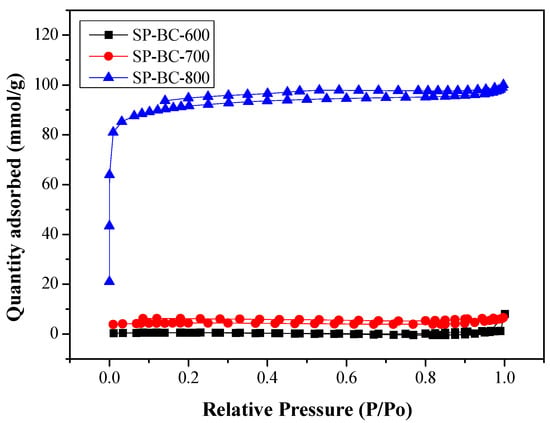
Figure 2.
N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of SP-BC products prepared at different carbonization temperatures.
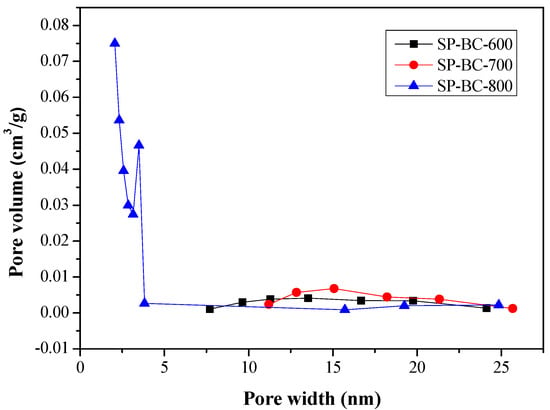
Figure 3.
Pore size distribution curves of SP-BC products prepared at different carbonization temperatures.
3.3. Chemical Characteristics of Resulting Biochar
In this work, the changes in the elemental distributions on the surface of the biochar products were analyzed by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Figure 4 illustrated the EDS spectra of the resulting biochar products (i.e., SP-BC-600 and SP-BC-800) prepared at different temperatures (i.e., 600 and 800 °C). It clearly showed that the main elements on the surface of the biochar products included carbon and oxygen. In addition, the carbon contents of the biochar products slightly increased from 76.7 wt% to 80.2 wt% as the temperature increased from 600 °C to 800 °C. The high content of oxygen in the biochar should be indicative of the functional oxygen-containing groups on the surface such as carbonyl (C=O-). Furthermore, the presence of magnesium (Mg), potassium (K) and calcium (Ca) was observed in the biochar products, which could be associated with the forms of carbonates or oxides. It can be seen that the metal elements in the biochar products should be derived from the precursor SP, as listed in Table 2.
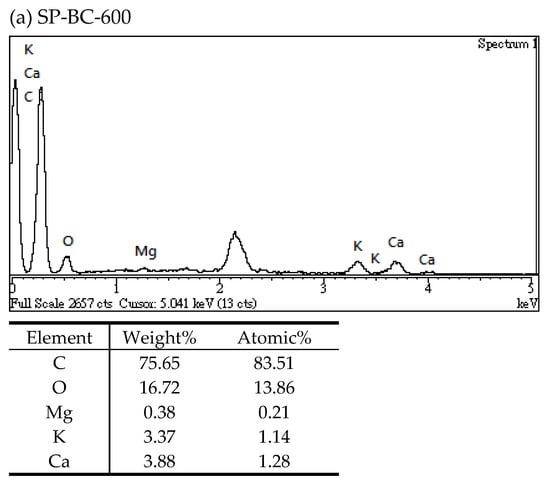
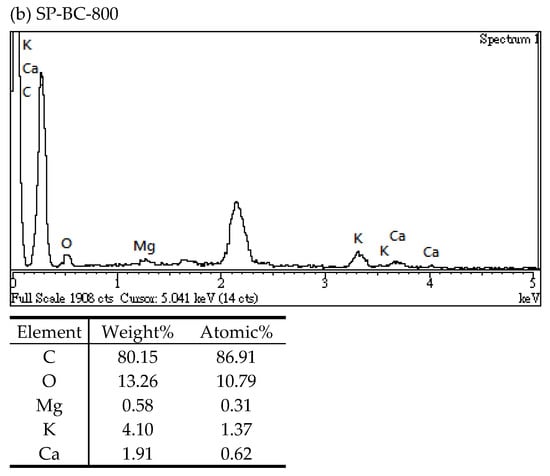
Figure 4.
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectra of (a) SP-BC product (SP-BC-600) and (b) SP-BC product (SP-BC-800).
The Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of the biochar product with the highest pore properties (i.e., SP-BC-800) was recorded in the range of 400–4000 cm−1, as shown in Figure 5. Clearly, there were four significant absorption peaks at about 3440, 1640, 1385 and 1115 cm−1, which could be associated with functional oxygen-containing groups [35,36]. For example, the absorption peak at 3450 cm−1 in the biochar product could be assigned to the stretching vibration of hydroxyl group (O-H). In addition, the sharp peaks at about 1640, 1385 and 1115 cm−1 may be attributed to the carbonyl (C=O-), O-H bending (phenolic) and symmetric C-O stretching, respectively [36]. From the findings of the EDS (Figure 4) and the FTIR (Figure 5), the SP-BS-800 biochar product may be hydrophilic because its surface is rich in oxygen.
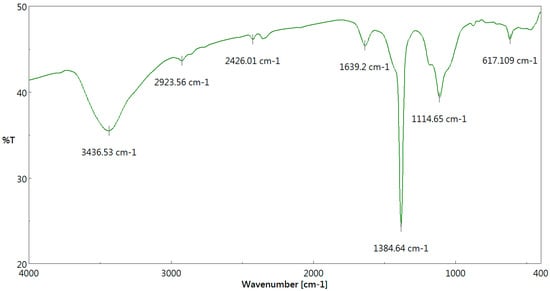
Figure 5.
FTIR spectrum of the resulting biochar (SP-BC-800).
4. Conclusions
The preparation of porous biochar from soapberry pericarp has been carried out by a carbonization process at 400–800 °C for 20 min. Under the conditions examined, the process had a biochar yield of at least 20%. The pore properties of the resulting biochar products indicated an increasing trend when the carbonization temperature increased from 400 to 800 °C, especially for the temperature in the range of 700 to 800 °C. The biochar with a BET surface area of about 300 m2/g was produced at 800 °C for 20 min. According to the data on N2 isotherms and pore size distribution, the existence of micro-mesoporous composite structure in the optimal biochar was shown. From the findings of the EDS and the FTIR, the biochar product may be hydrophilic because its surface is rich in oxygen. These results suggest that soapberry pericarp can be reused as an excellent precursor for preparing micro-mesoporous biochar products in severe carbonization conditions. It would be helpful to study the adsorptive removal of cationic pollutants from the aqueous solution using the resulting biochar material with high pore properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.-T.T.; methodology, C.-H.T.; validation, T.-J.J. and H.-L.C.; formal analysis, T.-J.J. and H.-L.C.; data curation, Y.-Q.L.; writing-original draft preparation, W.-T.T.; writing-review and editing, W.-T.T.; visualization, Y.-Q.L.; supervision, W.-T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Sincere appreciation was expressed to acknowledge the National Pingtung University of Science and Technology for their assistances in the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for environmental management: An introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management, 2nd ed.; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- BIOCHAR (International Biochar initiative). Available online: https://biochar-international.org/biochar/ (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Biochar as an adsorbent for inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus removal from water: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26297–26309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Nguyen, T.A.H.; Rudolph, V.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Huang, L. Characterization of hard- and softwood biochars pyrolyzed at high temperature. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Lam, S.S.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Liew, R.K.; Ma, N.L.; Osman, M.S.; Wong, C.C. Self-purging microwave pyrolysis: An innovative approach to convert oil palm shell into carbon-rich biochar for methylene blue adsorption. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zou, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Song, S. Surface characterization of maize-straw derived biochar and their sorption mechanism for Pb2+ and methylene blue. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lin, Y.Q.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, W.S.; Chang, Y.T. Enhancing the pore properties and adsorption performance of cocoa pod husk (CPH)-derived biochars via post-acid treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lin, Y.Q.; Huang, H.J. Valorization of rice husk for the production of porous biochar materials. Fermentation 2021, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.H.; Malik, S.; Garain, A.; Mandal, S.; Saha, B. Extraction of natural surfactant saponin from soapnut (Sapindus mukorossi) and its utilization in the remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated water. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2017, 54, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lu, M.K.; Liao, C.H. Aqueous extract of Sapindus mukorossi induced cell death of A549 cells and exhibited antitumor property In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, G.C.; Liu, J.M.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.L.; Zhang, D.G.; Jia, L.M. Metabolomics analysis of the soapberry (Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn.) pericarp during fruit development and ripening based on UHPLC-HRMS. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddaya, T.; Boughdad, A.; Sibille, E.; Chaimbault, P.; Zaid, A.; Amechouq, A. Biological activity of Sapindus mukorossi Gaerten (Sapindaceae) aqueous extract against Thysanoplusia orichalcea (Lepidoptera- Noctuidae). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.J.; Sun, J.; Tang, F. Laboratory and field evaluation of the phytotoxic activity of Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn pulp extract and identification of a phytotoxic substance. Molecules 2021, 26, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.J.; Sorensen, P.M. Characterization of saponin foam from Saponaria officinalis for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ho, S.H.; Chen, W.H.; Fu, Y.; Chang, J.S.; Bi, X. Oxidative torrefaction of biomass nutshells: Evaluations of energy efficiency as well as biochar transportation and storage. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, K.; Periyasamy, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Jayaraj, T.; Krishnasamy, R.; Sindhu, J.; Sneka, D.; Subhashini, B.; Vo, D.V.N. Analysis on the removal of emerging contaminant from aqueous solution using biochar derived from soap nut seeds. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chia, C.H.; Downie, A.; Munroe, P. Characteristics of biochar: Physical and structural properties. In Biochar for Environmental Management, 2nd ed.; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, P. Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.T.; Huang, P.C. Characterization of acid-leaching cocoa pod husk (CPH) and its resulting activated carbon. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2018, 8, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lin, Y.Q.; Tsai, C.H.; Chung, M.H.; Chu, M.H.; Huang, H.J.; Jao, Y.H.; Yeh, S.I. Conversion of water caltrop husk into biochar by torrefaction. Energy 2020, 195, 116967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touray, N.; Tsai, W.T.; Chen, H.R.; Liu, S.C. Thermochemical and pore properties of goat-manure-derived biochars prepared from different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 109, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Huang, C.N.; Chen, H.R.; Cheng, H.Y. Pyrolytic conversion of horse manure into biochar and its thermochemical and physical properties. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2015, 6, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.B. Surface Area and Porosity Determinations by Phyisorption: Measurement and Theory; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, B.M.; Baxter, L.L.; Miles, T.R., Jr.; Miles, T.R. Combustion properties of biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 54, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosek, O.; Johnston, C.T. Thermal analysis for biochar characterisation. In Biochar: A Guide to Analytical Methods; Singh, B., Camps-Arbestain, M., Lehmann, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Mukome, F.N.D.; Parikh, S.J. Chemical, physical, and surface characterization of biochar. In Biochar: Production, Characterization, and Applications; Ok, Y.S., Uchimiya, S.M., Chang, S.X., Bolan, N., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 67–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.Y.; Tsai, W.T.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, Y.Q.; Chang, Y.M. Characterization of biochar prepared from biogas digestate. Waste Manag. 2017, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.Q. Characterization of biochars produced from dairy manure at high pyrolysis temperatures. Agronomy 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantrell, K.B.; Hunt, P.G.; Uchimiya, M.; Novak, J.M.; Ro, K.S. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.T. Biochar analysis by Fourier-transform infra-red spectroscopy. In Biochar: A Guide to Analytical Methods; Singh, B., Camps-Arbestain, M., Lehmann, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).